Abstract
Rare genetic diseases are often caused by structural variants (SVs), such as insertions, deletions, duplications, inversions, and complex rearrangements. However, due to the technical limitations of short-read sequencing, these variants remain underdiagnosed. Long-read sequencing technologies, including Oxford Nanopore and Pacific Biosciences high-fidelity (HiFi), have recently advanced to the point that they can accurately find SVs throughout the genome, including in previously unreachable areas like repetitive sequences and segmental duplications. This study underscores the transformative role of long-read sequencing in diagnosing rare diseases, emphasizing the bioinformatics tools designed for detecting and interpreting structural variants (SVs). Comprehensive methods are reviewed, including methylation profiling, RNA-seq, phasing analysis, and long-read sequencing. The effectiveness and applications of well-known tools like Sniffles2, SVIM, and cuteSV are also assessed. Case studies illustrate how this technique has revealed new pathogenic pathways and solved cases that were previously undetected. Along with outlining potential future paths like telomere-to-telomere assemblies and pan-genome integration, we also address existing issues, including cost, clinical validation, and computational complexity. For uncommon genetic illnesses, long-read sequencing has the potential to completely change the molecular diagnostic picture as it approaches clinical adoption.
1. Introduction
Rare genetic disorders are uncommon but collectively affect around 300 million people worldwide. These conditions are typically long-lasting, progressive, and potentially life-threatening, with many patients facing an extended and often years-long search for a definitive diagnosis []. The genetic variability that characterizes uncommon diseases is one of the most significant barriers to obtaining fast and accurate diagnoses. Despite significant advancements in next-generation sequencing (NGS)—particularly whole-exome and whole-genome sequencing—that have greatly improved the detection of single-nucleotide variations (SNVs) and small insertions or deletions (indels), many cases remain unsolved [,]. This demonstrates that some disease-causing variations may be beyond the detection capability of current short-read sequencing tools [].
These hard-to-detect variants consist of SVs, a diverse group of genomic changes including translocations, inversions, deletions, duplications, insertions, and more intricate rearrangements, usually spanning 50 base pairs (bp) or more []. Through coding sequence disruption, gene dosage changes, or regulatory element perturbations, SVs can significantly impact genome function. Emerging evidence indicates that SVs account for a significant proportion of pathogenic variants in undiagnosed rare genetic diseases []. However, detecting SVs remains a formidable challenge, especially when they are located within repetitive or low-complexity genome regions, which are poorly resolved by short-read sequencing [].
Conventional methods for detecting SVs, including chromosomal microarrays, karyotyping, and targeted PCR-based assays, offer inadequate resolution and efficiency required for comprehensive genome-wide analysis []. Although short-read sequencing is effective, it has basic limitations in detecting large or complex structural variants due to its use of reads limited to 150 to 300 base pairs. Undetected or mischaracterized structural changes can lead to missed diagnoses and a poor knowledge of the genetic basis of rare diseases [,].
Long-read sequencing has emerged as a potent and transformational technique for detecting and analyzing structural variations. PacBio and Oxford Nanopore (ONT) sequencing methods yield long reads ranging from several kilobases to more than a megabase, allowing for a more contiguous and thorough genome overview. These methods allow for more precise and reliable detection of SVs, especially in genomic regions that short-read methods cannot access []. Long-read sequencing technology has advanced the detection of complex structural variations, boosted the accuracy of allele phasing, and uncovered genetic variations that were previously missed in patients with rare disorders [].
This review underscores the value of long-read sequencing in identifying structural variations and advancing the diagnosis of rare genetic diseases. Long-read technologies deepen our insight into genomic variation by exposing regions that were previously hidden or not well understood, thus supporting the progress of precision diagnostics. We review current methods, advancements in emerging technologies, clinical integration, and the future outlook for incorporating long-read sequencing into mainstream diagnostic workflows.
2. Technological Landscape
Long-read sequencing technologies have significantly increased the ability of genomics research and clinical diagnostics to investigate previously poorly characterized genomic regions. PacBio HiFi sequencing and ONT have risen as the leading platforms, presenting unique strengths and compromises across read length, accuracy, throughput, and cost [,].
2.1. PacBio HiFi Sequencing
PacBio’s HiFi sequencing uses circular consensus sequencing (CCS), which involves repeatedly sequencing individual DNA molecules to obtain a precise consensus read. HiFi reads generally range from 10 to 25 kilobases (kb) and achieve base-level accuracy exceeding 99.9% (Q30–Q40). Owing to its high fidelity, HiFi sequencing is especially valuable for accurate structural variant detection, comprehensive haplotype phasing, and the differentiation of closely homologous sequences, such as pseudogenes and repetitive elements within the genome [,].
PacBio platforms, notably the Sequel IIe system, have significantly enhanced throughput while reducing the cost per sample. Despite this, PacBio sequencing is still very expensive per genome and has somewhat shorter read lengths than ONT. Nonetheless, its high accuracy makes it the ideal choice for clinical-grade applications such as the detection of uncommon genetic disorders, where variant calling precision is critical [].
2.2. Oxford Nanopore Sequencing
Oxford Nanopore Technologies provides a completely different way to sequencing by detecting nucleotide sequences as single DNA or RNA molecules pass through a protein nanopore implanted in a synthetic membrane. This methodology enables the generation of ultra-long reads, with lengths surpassing 1 megabase (Mb), thereby offering unparalleled resolution of large or complex structural variants and repetitive genomic regions [].
ONT platforms span from portable, low-throughput devices like the MinION to high-throughput systems like the PromethION, meeting a diverse variety of scientific and clinical requirements []. Although ONT read accuracy has traditionally lagged behind that of PacBio, recent advancements in basecalling algorithms (such as Bonito and Dorado) and improvements in sequencing chemistry (notably Q20+ chemistry) have elevated accuracy beyond 99%, enhancing its competitiveness for clinical applications []. ONT’s scalability, minimal capital investment, and rapid real-time sequencing capabilities make it particularly appealing for point-of-care diagnostics and field-based studies [].
2.3. Fundamental Differences Between PacBio and ONT Sequencing
The PacBio HiFi sequencing method uses circular consensus sequencing (CCS), which reads DNA molecules several times to produce extremely accurate consensus reads that are usually 10–25 kb long and have a base accuracy of greater than 99.9%. In contrast, ONT sequences single DNA or RNA molecules as they pass through a nanopore, producing ultra-long reads often exceeding 1 megabase []. Despite ONT’s historical inferiority to PacBio in accuracy, current developments in chemistry and basecalling algorithms have raised accuracy to more than 99%. For applications needing high precision, such as clinical diagnostics, PacBio’s platform is recommended despite being more expensive and producing shorter reads. ONT is ideally suited to field-based or point-of-care applications and the detection of complicated structural variants because it provides increased scalability, mobility, and quick real-time sequencing [].
2.4. Comparative Summary
PacBio HiFi and ONT platforms offer beneficial techniques for discovering structural variants in rare genetic conditions. PacBio’s exceptional accuracy is particularly suited to clinical use, whereas ONT’s adaptability and extended read lengths facilitate the analysis of intricate genomic rearrangements []. Progressive advances in sequencing technologies have led to an increase in the use of hybrid techniques that leverage each platform’s complementary strengths to improve diagnostic precision and yield []. Table 1 summarizes the key features of PacBio HiFi and ONT sequencing platforms.

Table 1.
Key features of PacBio HiFi and ONT sequencing platforms, comparing read length, accuracy, throughput, and costs. Also highlighted are each platform’s unique strengths, such as HiFi’s exceptional accuracy and ONT’s ultra-long reads and portability.
2.5. Benchmarking Performance for Structural Variant Detection
Benchmarking studies have allowed researchers to assess the performance of long-read sequencing technologies in SV identification and rare illness diagnosis [,]. Comparative evaluations have consistently demonstrated that PacBio HiFi sequencing and ONT possess distinct strengths, with both platforms achieving substantial performance improvements in recent years driven by advances in chemistry, basecalling algorithms, and computational methodologies [].
In the context of variant calling accuracy, the PrecisionFDA Truth Challenge V2 provided a comprehensive evaluation of SV detection performance across sequencing technologies []. PacBio HiFi consistently delivered top performance in structural variant detection, attaining F1 scores greater than 95%. This high level of precision stems from HiFi reads’ exceptional base-level accuracy (Q30–Q40), which minimizes false positives and enables the confident detection of variants in both unique and repetitive genomic regions []. Conversely, ONT displayed higher recall rates for specific classes of SVs, particularly larger or more complex rearrangements; however, early iterations of the technology were limited by higher base error rates, leading to less precision. However, recent advancements, such as the use of Q20+ chemistry and updated basecalling models like Dorado, have decreased the performance difference. ONT’s current sequencing generates SV calling F1 scores ranging from 85 to 90%, depending on the genomic context and variant type [,].
Read mapping and genome assembly metrics further highlight the complementary advantages of these platforms. According to a study, PacBio HiFi provides extraordinarily high alignment accuracy (>99.8%) and consistent coverage, even in low-complexity regions that are prone to mismapping with conventional technologies []. These qualities make it ideal for clinical diagnostics, where reducing false-positive variant calls is critical. ONT’s capability to generate long reads allows for the resolution of large structural variants and repetitive regions that are generally inaccessible using short-read sequencing []. This advantage allows ONT to resolve large structural variants and repetitive sequences that are typically inaccessible with shorter read lengths.
Clinical studies further underscore the diagnostic impact of long-read sequencing. Following extensive short-read sequencing without a diagnosis, PacBio HiFi whole-genome sequencing increased diagnostic yield by 10–15% in uncommon illness populations []. These cases frequently encompassed cryptic structural variants, phasing-dependent compound heterozygous mutations, or repetitive expansions that eluded detection by conventional methodologies []. Similarly, ONT sequencing has been instrumental in uncovering large insertions, tandem repeat expansions, and intricate rearrangements, especially in neurodevelopmental and neurological diseases. ONT sequencing has facilitated the discovery of pathogenic variants in patients with undiagnosed epileptic encephalopathy, muscular dystrophies, and intellectual disabilities that were not detected by chromosomal microarrays and short-read genome sequencing [].
PacBio HiFi presently incurs higher per-sample sequencing costs, covering both library preparation and sequencing reagents []. Conversely, ONT provides pricing alternatives that are more flexible and scalable. Whole-genome sequencing with ONT can be significantly more cost-effective, depending on the platform (e.g., MinION vs. PromethION) and the throughput approach used, making it an appealing choice for high-throughput research or clinical screening applications [].
Collectively, these benchmarking studies lay the groundwork for selecting an effective long-read sequencing technology depending on the specific needs of a study or clinical use case []. ONT offers unparalleled read lengths, cost-effectiveness, and scalability, making it ideal for exploratory research and the investigation of large or complex genomic rearrangements. In contrast, PacBio HiFi provides remarkable precision, making it especially well-suited to clinical diagnostics. As technology continues to advance, hybrid methods that combine the precision of HiFi sequencing with the long-read capabilities of ONT are anticipated to play a key role in the discovery of structural variants []. Table 2 compares PacBio HiFi and ONT (Q20+/R10.4.1) sequencing platforms across key metrics for structural variant analysis.

Table 2.
Comparison of PacBio HiFi and ONT (Q20+/R10.4.1) sequencing platforms across key metrics for structural variant analysis, including accuracy, assembly quality, cost, and diagnostic effectiveness. It highlights each platform’s strengths in SV detection and their impact on rare disease diagnosis.
3. Structural Variant Detection
SVs are genomic modifications that affect vast regions of DNA, often 50 bp or more. They cover a wide spectrum of variation types, including deletions, duplications, insertions, inversions, translocations, and more complex rearrangements []. SVs can disrupt gene coding sequences, change gene dosage, relocate regulatory elements, and modify chromatin architecture, all of which can have a significant impact on gene expression and phenotype. SVs are increasingly recognized as significant contributors to the genomic architecture of uncommon illnesses, cancer, and neurodevelopmental disorders [,].
Several repeating elements, such as Alu repeats and retrotransposons, are among the many SVs found in every human genome. Although improved datasets have improved the ability of analytical methods to filter and interpret these variants, difficulties still exist because of the size and complexity of the SVs that are present.
Despite their clinical relevance, accurately detecting structural variants remains a major challenge within the field of genomics. Short-read sequencing, which typically produces reads of 150 to 300 base pairs, is inherently limited in its ability to detect structural variations []. Short reads, for example, frequently do not cover the entire length of larger variants, making precise breakpoint resolution difficult. Second, relying on reference genome alignment hinders accurate mapping in repetitive, low-complexity, structurally polymorphic regions, which are particularly rich in structural variants. Third, many structural variants, particularly insertions and complex rearrangements, may be absent or underrepresented in the reference genome, resulting in their omission or inaccurate identification [].
Long-read sequencing, however, detects SVs significantly more frequently. Long-read sequencing can detect up to 20,000–30,000 SVs per genome, according to recent research. This is up to three–six times more sensitive than short-read sequencing, and even ten times more for insertions and complicated rearrangements in repetitive regions like retrotransposons and Alu elements [].
Long-read sequencing technologies from PacBio and Oxford Nanopore have substantially enhanced structural variant detection capabilities by producing reads that span from several kilobases up to megabase lengths [,]. Long reads enable direct coverage of structural variant breakpoints, improving both the accuracy and comprehensiveness of variant detection. Additionally, this sequencing approach supports de novo assembly and precise haplotype phasing, which are essential for resolving compound heterozygosity and complex allelic variants in rare genetic disorders. Furthermore, by collecting previously inaccessible genomic regions, long-read approaches lessen reliance on reference-based alignment, revealing unique or complex SVs that short-read sequencing would not discover [].
To harness the power of long-read sequencing for SV detection, a number of specialized computational tools have been developed. Sniffles2, SVIM, PBSV, and cuteSV are among the most commonly utilized. These tools are specifically developed to deal with the unique aspects of long-read data, such as increased error rates and varying read lengths [,].
Sniffles2, the successor to the widely used Sniffles program, allows for fast and sensitive SV calling over a wide range of variation types and is compatible with several systems, including PacBio HiFi and ONT []. The structural variant identification method (SVIM) is optimized for ONT data and employs a probabilistic model to identify SVs with great sensitivity, particularly in repeated regions. PacBio developed PBSV for HiFi readings, which provides great precision in clinical environments where accuracy is crucial [,]. A prominent example of modern structural variant detection tools, cuteSV offers robust compatibility with Oxford Nanopore and PacBio data []. Its rising prominence in genomics research is due to its efficient performance, scalability, and user-friendly interface, making it well-suited to large-scale variant analysis.
However, these tools also exhibit certain limitations. Due to alignment ambiguities, Sniffles2, despite its excellent sensitivity, may produce false positives in repeating sections. When SVIM detects minor insertions and deletions, its precision may be diminished []. Despite being tailored for PacBio HiFi data, PBSV is not very useful for ONT datasets. Similarly, compared to assembly-based methods, cuteSV’s computational efficiency comes at the expense of a marginally reduced sensitivity for intricate rearrangements. Addressing these restrictions is crucial when evaluating SV calls in research or clinical settings [].
Collectively, these tools facilitate the effective utilization of long-read sequencing data by researchers and clinicians for accurate and comprehensive SV detection []. Continued advances in computational approaches and sequencing technologies will make routine resolution of complicated genomic rearrangements feasible, bringing us closer to a thorough understanding of the genetic causes of rare diseases [].
4. Applications in Rare Disease Diagnostics
Rare genetic disorders, which collectively affect millions worldwide, often involve complex genomic alterations that evade detection by conventional sequencing techniques []. While short-read exome and genome sequencing have revolutionized the diagnostic landscape over the past decade, they still leave a substantial proportion of cases—often 40–60%—without a molecular diagnosis. Many of these unsolved cases are now believed to result from SVs, repeat expansions, and other non-coding or complex mutations that fall beyond the technical reach of short-read platforms []. Long-read sequencing technologies are increasingly being applied to fill this diagnostic gap, with growing success in uncovering elusive genetic variants that are causally linked to rare diseases [].
Long-read sequencing excels at resolving pathogenic repeat expansions, a class of genetic variations associated with a broad spectrum of neurological and neuromuscular disorders []. Short tandem repeat (STR) expansions, often occurring in intronic or untranslated regions, are the genetic basis of conditions such as Friedreich’s ataxia, myotonic dystrophy, fragile X syndrome, and several types of spinocerebellar ataxia []. While long-read platforms can directly sequence through enlarged alleles and precisely quantify repeat size and motif structure, traditional short-read sequencing usually falls short in characterizing the complete length and structure of these repeats. For example, Oxford Nanopore sequencing has been successfully used to detect pathogenic GAA expansions in the FXN gene in Friedreich’s ataxia, while PacBio HiFi sequencing has shown high concordance with gold-standard methods in sizing CTG repeats in myotonic dystrophy type 1 [].
Beyond the identification of repeat expansions, long-read sequencing approaches have uncovered a wide spectrum of structural variants that have historically evaded detection by conventional short-read whole-exome (WES) and whole-genome sequencing (WGS) technologies []. A notable investigation by the Rare Genomes Project underscored the value of PacBio HiFi sequencing in individuals with rare disorders who had previously received comprehensive genetic testing without definitive diagnoses []. HiFi sequencing has detected pathogenic insertions, inversions, and complex structural rearrangements across several cases. Examples include a tandem duplication that interfered with a gene essential to neurodevelopment and a deep intronic insertion that produced a unique splicing site that led to abnormal gene expression [].
Similarly, ONT has been used to detect mosaic chromosomal rearrangements and mobile element insertions responsible for phenotypes such as epileptic encephalopathy, hemophilia A, and congenital malformations []. In comparison to conventional exome and genome sequencing techniques, comparative studies demonstrate the complementary nature of long-read sequencing. While WES remains cost-effective and efficient for detecting small coding variants, it misses noncoding regions and has limited utility in SV detection. Large insertion detection, complex structural variant resolution, and phasing issues still plague short-read whole-genome sequencing, despite its improved coverage. Alternatively, long-read whole-genome sequencing delivers a more comprehensive and precise analysis of the genome, enabling improved identification of compound heterozygosity, repeat instability, and structural variants [,].
Incorporating long-read sequencing as a second-tier test to several diagnostic pipelines has resulted in a notable improvement in diagnostic yield, usually between 10% and 20%, particularly for patients whose findings from conventional testing were negative []. As sequencing costs decrease and analytical methods improve, long-read technologies are anticipated to be increasingly adoption in clinical genomics. These techniques contribute to more precise diagnoses and improved genotype–phenotype correlations through enhanced insight into disease mechanisms and more effective identification of pathogenic variants, thereby supporting more informed clinical decision-making for patients with rare genetic disorders []. Table 3 summarizes representative examples of rare disease groups where long-read sequencing has enabled the detection of pathogenic structural variants, including repeat expansions, deep intronic insertions, and complex rearrangements.

Table 3.
Applications of long-read sequencing technologies in rare disease diagnostics by variant type and disease group.
5. Challenges and Limitations
Although there are currently several barriers preventing long-read sequencing from being widely used in clinical and research settings, it has the potential to completely transform the diagnosis of rare diseases. These limitations encompass various sectors, including financial, computational, and regulatory areas, each of which poses specific challenges to routine implementation [].
The most notable obstacles are accessibility and expense. On a per-sample basis, long-read sequencing is still far more expensive than short-read sequencing, despite recent dramatic cost reductions. Whole-genome long-read sequencing remains costly (USD 500 to USD 1500) per sample, depending on the platform and throughput [,]. Additional expenses may be incurred for data processing, instrument operation, and library preparation. This cost remains prohibitive for many healthcare systems, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. Furthermore, not all laboratories have access to long-read sequencing systems such as Oxford Nanopore PromethION or PacBio Sequel IIe, which limits their viability for use in smaller or resource-constrained labs [].
Beyond the cost of sequencing, a significant bottleneck is posed by computational and bioinformatics challenges. Large and intricate, long-read datasets necessitate a strong infrastructure for processing, storing, and analyzing data. There is no general gold-standard pipeline, although new structural variant calling tools like Sniffles2, SVIM, PBSV, and cuteSV are tailored for long-read data. Performance can vary depending on platform, variant class, and genome context. Furthermore, long-read data, especially from ONT, can still contain residual base-level errors that complicate small variant calling or interpretation in coding regions. The integration of multiple variant types (e.g., SNPs, SVs, repeat expansions) into a single unified analysis remains technically demanding and often requires expertise that is not readily available in all clinical laboratories [,].
A third major challenge lies in the absence of standardized protocols, validation frameworks, and effective clinical integration. Regulatory agencies have started to recognize the benefits of long-read technologies; however, clinical implementation guidelines are still under development. The wide range of variant types and the rapid evolution of sequencing platforms present significant challenges in thoroughly establishing analytical validity, reproducibility, and clinical relevance when validating assays for diagnostic use []. In addition, there is a pressing demand for benchmarking datasets, standardized reference materials, and best practice protocols for the detection and interpretation of SVs. The lack of standardized protocols complicates the comparison of results between laboratories and hinders adherence to regulatory and accreditation standards [].
Larger SVs, particularly those in noncoding areas, are challenging to report in a clinical setting because the majority of reporting recommendations, including ACMG standards, are currently made for single nucleotide variations (SNVs) and small indels []. Improvements to these frameworks will be necessary to integrate long-read SV data, such as more precise classification criteria for the pathogenicity of SVs and functional validation techniques for complicated and noncoding SVs. To establish strong guidelines for SV interpretation and reporting, cooperation between sequencing consortia, clinical geneticists, and regulatory agencies is essential [].
Interpreting structural variations clinically is another difficult challenge. While structural variant detection techniques have improved, accurately determining pathogenicity continues to be a significant challenge, especially for complex or noncoding variants. Variants of unknown significance (VUS) account for a large number of discovered SVs, and interpretation is further constrained by the absence of extensive demographic and disease-specific databases []. Efforts such as the Genome in a Bottle Consortium and initiatives to expand SV annotations in gnomAD are steps in the right direction, but broader adoption of long-read data in clinical variant databases is still needed [].
Long-read sequencing technologies have a lot to offer in the diagnosis of rare diseases, but they will need to overcome obstacles in the areas of cost, computational complexity, clinical interpretation, and analytical standardization before they can be fully integrated into clinical genomics. For long-read sequencing to fully realize its potential in precision medicine, these challenges must be addressed by cooperative benchmarking, infrastructure investment, and regulatory framework development []. Figure 1 summarizes the strengths and limitations of short-read and long-read sequencing technologies in the context of structural variant detection and rare disease diagnostics.
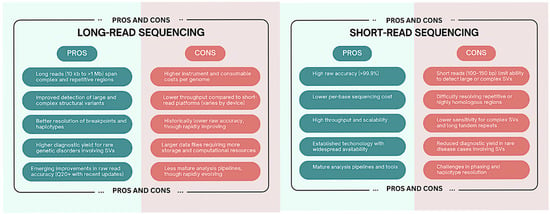
Figure 1.
This figure compares the strengths and limitations of short-read and long-read sequencing technologies in the context of structural variant detection and rare disease diagnostics.
6. Future Directions
The landscape of rare disease research is set to undergo significant transformation with the ongoing advancements in long-read sequencing technologies and their expanding integration into routine genomics and clinical diagnostic workflows. Ongoing advancements are expected to enhance the scope, accuracy, and accessibility of structural variant detection at both individual and population scales, while addressing current limitations [].
An effective approach involves the application of hybrid sequencing techniques, which leverage the long-range continuity provided by long-read platforms in conjunction with the high base-level accuracy characteristic of short-read sequencing []. This combined strategy has already proven beneficial in decreasing overall costs and improving both the sensitivity and phasing accuracy of variant detection. Hybrid assemblies provide a more thorough and nuanced view of individual genomes by enabling minor variation and SV detection in research and diagnostic pipelines [].
For instance, complex genomic rearrangements, insertion–deletion events, and cases of compound heterozygosity, often missed when using either sequencing method in isolation, can be reliably resolved with high confidence by integrating Illumina short reads with PacBio HiFi or ONT long reads [].
The use of targeted capture and enrichment technologies to improve long-read sequencing efficiency is also gaining attention. Selective sequencing of therapeutically relevant regions can be achieved using methods including hybridization-based capture, adaptive sampling (on ONT platforms), and Cas9-mediated enrichment []. In diagnostic applications where whole-genome sequencing may not be required, these techniques are particularly helpful since they enrich for target loci, increasing coverage depth, decreasing data complexity, and lowering sequencing costs [].
Another groundbreaking advancement is the implementation of graph-based reference genomes, which move beyond the limitations imposed by a single linear reference. Conventional genome alignment maps sequencing reads to a standardized reference genome, a method that frequently fails to capture highly variable regions and genetic variation across populations []. Graph genomes improve read alignment, minimize reference bias, and increase the accuracy of variant detection, especially for structural variants and population-specific alleles, by incorporating multiple haplotypes and structural arrangements into a single comprehensive framework [].
Rare diseases can be influenced by population-specific variants. With the increasing availability of long-read sequencing data, employing graph-based reference genomes will enhance both the accuracy and inclusivity of genomic analyses across diverse ancestral groups [].
The creation of population-scale SV databases, which are essential for distinguishing between benign and pathogenic variations, is occurring concurrently with these technical advancements []. High-resolution catalogs of SVs across diverse populations are being generated through initiatives such as the Human Pangenome Reference Consortium, alongside ongoing efforts to integrate long-read SV calls into comprehensive resources like gnomAD. These databases will greatly increase the precision and effectiveness of variant interpretation by offering allele frequency data, enhancing the annotation of noncoding SVs, and lowering the number of variations of ambiguous relevance in clinical workflows []. In the long term, the role of structural variants in complex traits, variation penetrance, and genotype–phenotype correlations will be more thoroughly understood [].
In the near term, long-read sequencing will likely continue to augment existing short-read approaches rather than entirely supplant them. Clinical labs are anticipated to use long-read technology as a first-line diagnostic assay for genetically undetected patients, rather than merely as a secondary tool, as sequencing costs continue to drop, throughput rises, and automated bioinformatics pipelines become more reliable [].
In the short future, though, long-read sequencing is probably going to continue to supplement existing short-read methods rather than completely replace them. When routine testing yields equivocal results but there is a high diagnostic suspicion of a genetic condition, its usage may be prioritized. In these situations, long-read platforms are particularly well-suited to phasing variations without parental samples, resolving complex structural variants, and detecting complex genomic rearrangements, exon inversions, or retrotransposed insertions that short-read technologies cannot detect. Targeted application in such challenging contexts represents a pragmatic integration strategy; however, widespread adoption remains limited due to escalating costs and heightened infrastructure demands.
Clinical norms and expectations are changing as early adopters have already started to show the benefits of long-read sequencing in detecting diagnostic variations that traditional approaches miss. To fully exploit the clinical relevance of long-read data, integration with clinical decision support systems, electronic health records, and regulatory frameworks will be necessary [].
Ultimately, the convergence of long-read sequencing, advanced informatics, and collaborative data sharing promises a future in which comprehensive SV detection is routine, enabling more accurate diagnoses, earlier interventions, and more precise therapeutic strategies for individuals with rare genetic disorders [].
7. Conclusions
The introduction of long-read sequencing has enhanced genomics, providing high resolution for detecting SVs. Platforms such as PacBio HiFi and ONT allow precise detection of insertions, deletions, inversions, repeat expansions, and complex rearrangements related to an array of rare genetic disorders []. Its therapeutic value lies in solving unexplained cases, uncovering novel disease processes, and improving genotype–phenotype understanding. By characterizing pathogenic repeat expansions and revealing noncoding SVs, long-read sequencing advances diagnosis and offers hope to affected families [].
However, wider clinical integration requires reducing costs, improving bioinformatics, establishing reliable pipelines, and standardizing interpretations. Developing graph-based reference genomes, hybrid sequencing approaches, and extensive population-scale SV databases will be essential for promoting widespread adoption []. As technology advances and challenges to adoption are overcome, its incorporation into mainstream clinical practice holds enormous promise for providing more accurate, rapid, and thorough diagnoses to patients around the world.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.M. and S.S.; methodology, P.C. and A.P.; validation, A.Z., D.M. and G.K.; investigation, N.K. and I.A.; data curation, E.D.; writing—original draft preparation, E.M. and P.C.; writing—review and editing, A.P., A.Z., D.M., G.K., N.K., I.A., E.D., A.T.T., P.D. and S.S.; visualization, A.P.; supervision, A.T.T. and P.D.; project administration, S.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Lee, C.E.; Singleton, K.S.; Wallin, M.; Faundez, V. Rare Genetic Diseases: Nature’s Experiments on Human Development. iScience 2020, 23, 101123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.; Lee, D.; Hwang, A.; Kim, T.; Ryu, H.Y.; Choi, J. Rare disease genomics and precision medicine. Genom. Inf. 2024, 22, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuler, B.A.; Nelson, E.T.; Koziura, M.; Cogan, J.D.; Hamid, R.; Phillips, J.A., 3rd. Lessons learned: Next-generation sequencing applied to undiagnosed genetic diseases. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e154942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Del Gaudio, D.; Santani, A.; Scott, S.A. Applications of genome sequencing as a single platform for clinical constitutional genetic testing. Genet. Med. Open 2024, 2, 101840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Roberts, R.; Mercer, T.R.; Xu, J.; Sedlazeck, F.J.; Tong, W. Towards accurate and reliable resolution of structural variants for clinical diagnosis. Genome Biol. 2022, 23, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellingford, J.M.; Ahn, J.W.; Bagnall, R.D.; Baralle, D.; Barton, S.; Campbell, C.; Downes, K.; Ellard, S.; Duff-Farrier, C.; FitzPatrick, D.R.; et al. Recommendations for clinical interpretation of variants found in non-coding regions of the genome. Genome Med. 2022, 14, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinosa, E.; Bautista, R.; Larrosa, R.; Plata, O. Advancements in long-read genome sequencing technologies and algorithms. Genomics 2024, 116, 110842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jobanputra, V.; Andrews, P.; Felice, V.; Abhyankar, A.; Kozon, L.; Robinson, D.; London, F.; Hakker, I.; Wrzeszczynski, K.; Ronemus, M. Detection of Copy Number Variants by Short Multiply Aggregated Sequence Homologies. J. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 22, 1476–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choo, Z.N.; Behr, J.M.; Deshpande, A.; Hadi, K.; Yao, X.; Tian, H.; Takai, K.; Zakusilo, G.; Rosiene, J.; Da Cruz Paula, A.; et al. Most large structural variants in cancer genomes can be detected without long reads. Nat. Genet. 2023, 55, 2139–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oehler, J.B.; Wright, H.; Stark, Z.; Mallett, A.J.; Schmitz, U. The application of long-read sequencing in clinical settings. Hum. Genom. 2023, 17, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satam, H.; Joshi, K.; Mangrolia, U.; Waghoo, S.; Zaidi, G.; Rawool, S.; Thakare, R.P.; Banday, S.; Mishra, A.K.; Das, G.; et al. Next-Generation Sequencing Technology: Current Trends and Advancements. Biology 2023, 12, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logsdon, G.A.; Vollger, M.R.; Eichler, E.E. Long-read human genome sequencing and its applications. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2020, 21, 597–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Keskus, A.G.; Wagner, J.; Izydorczyk, M.B.; Timp, W.; Sedlazeck, F.J.; Klein, A.P.; Zook, J.M.; Kolmogorov, M.; Schatz, M.C. Unraveling the hidden complexity of cancer through long-read sequencing. Genome Res. 2025, 35, 599–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; He, J.; Li, M.; Peng, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Deng, F. Unlocking the Potential of Metagenomics with the PacBio High-Fidelity Sequencing Technology. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, D.; Zhang, S.; Ren, P.; Liang, F.; Sun, Z.; Meng, G.; Tan, Y.; Li, X.; Lai, Q.; Han, L.; et al. Comparison of the two up-to-date sequencing technologies for genome assembly: HiFi reads of Pacific Biosciences Sequel II system and ultralong reads of Oxford Nanopore. Gigascience 2020, 9, giaa123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Bollas, A.; Wang, Y.; Au, K.F. Nanopore sequencing technology, bioinformatics and applications. Nat. Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 1348–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto-Serrano, A.; Li, W.; Panah, F.M.; Hui, Y.; Atienza, P.; Fomenkov, A.; Roberts, R.J.; Deptula, P.; Krych, L. Matching excellence: Oxford Nanopore Technologies’ rise to parity with Pacific Biosciences in genome reconstruction of non-model bacterium with high G+C content. Microb. Genom. 2024, 10, 001316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Li, H.; Jiang, M.; Hou, H.; Gao, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, F.; Wang, J.; Peng, K.; Liu, Y.X. Nanopore sequencing: Flourishing in its teenage years. J. Genet. Genom. 2024, 51, 1361–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ermini, L.; Driguez, P. The Application of Long-Read Sequencing to Cancer. Cancers 2024, 16, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, N.D.; Wagner, J.; McDaniel, J.; Stephens, S.H.; Westreich, S.T.; Prasanna, A.G.; Johanson, E.; Boja, E.; Maier, E.J.; Serang, O.; et al. PrecisionFDA Truth Challenge V2: Calling variants from short and long reads in difficult-to-map regions. Cell Genom. 2022, 2, 100129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivucci, G.; Iovino, E.; Innella, G.; Turchetti, D.; Pippucci, T.; Magini, P. Long read sequencing on its way to the routine diagnostics of genetic diseases. Front. Genet. 2024, 15, 1374860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, S.K.; Yilmaz, K.C.; Acar, A. Benchmarking long-read structural variant calling tools and combinations for detecting somatic variants in cancer genomes. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 8707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udaondo, Z.; Sittikankaew, K.; Uengwetwanit, T.; Wongsurawat, T.; Sonthirod, C.; Jenjaroenpun, P.; Pootakham, W.; Karoonuthaisiri, N.; Nookaew, I. Comparative Analysis of PacBio and Oxford Nanopore Sequencing Technologies for Transcriptomic Landscape Identification of Penaeus monodon. Life 2021, 11, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.; Liu, Y.H.; Zhou, X.M. VolcanoSV enables accurate and robust structural variant calling in diploid genomes from single-molecule long read sequencing. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, G.E.; Dabernig-Heinz, J.; Lipp, M.; Cabal, A.; Simantzik, J.; Kohl, M.; Scheiber, M.; Lichtenegger, S.; Ehricht, R.; Leitner, E.; et al. Real-Time Nanopore Q20+ Sequencing Enables Extremely Fast and Accurate Core Genome MLST Typing and Democratizes Access to High-Resolution Bacterial Pathogen Surveillance. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2023, 61, e0163122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prodanov, T.; Bansal, V. Sensitive alignment using paralogous sequence variants improves long-read mapping and variant calling in segmental duplications. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, e114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conlin, L.K.; Aref-Eshghi, E.; McEldrew, D.A.; Luo, M.; Rajagopalan, R. Long-read sequencing for molecular diagnostics in constitutional genetic disorders. Hum. Mutat. 2022, 43, 1531–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisfeldt, J.; Ek, M.; Nordenskjold, M.; Lindstrand, A. Toward clinical long-read genome sequencing for rare diseases. Nat. Genet. 2025, 57, 1334–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damian, A.; Nunez-Moreno, G.; Jubin, C.; Tamayo, A.; de Alba, M.R.; Villaverde, C.; Fund, C.; Delepine, M.; Leduc, A.; Deleuze, J.F.; et al. Long-read genome sequencing identifies cryptic structural variants in congenital aniridia cases. Hum. Genom. 2023, 17, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplun, L.; Krautz-Peterson, G.; Neerman, N.; Schindler, Y.; Dehan, E.; Huettner, C.S.; Baumgartner, B.K.; Stanley, C.; Kaplun, A. ONT in Clinical Diagnostics of Repeat Expansion Disorders: Detection and Reporting Challenges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronner, I.F.; Dawson, E.; Park, N.; Piepenburg, O.; Quail, M.A. Evaluation of controls, quality control assays, and protocol optimisations for PacBio HiFi sequencing on diverse and challenging samples. Front. Genet. 2024, 15, 1505839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurgul, A.; Jasielczuk, I.; Szmatola, T.; Sawicki, S.; Semik-Gurgul, E.; Dlugosz, B.; Bugno-Poniewierska, M. Application of Nanopore Sequencing for High Throughput Genotyping in Horses. Animals 2023, 13, 2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amarasinghe, S.L.; Su, S.; Dong, X.; Zappia, L.; Ritchie, M.E.; Gouil, Q. Opportunities and challenges in long-read sequencing data analysis. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, S.S.; Urban, A.E.; Mills, R.E. Structural variation in the sequencing era. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2020, 21, 171–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, A.J.; Chiang, C.; Hall, I.M. Structural variants are a major source of gene expression differences in humans and often affect multiple nearby genes. Genome Res. 2021, 31, 2249–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Haene, E.; Vergult, S. Interpreting the impact of noncoding structural variation in neurodevelopmental disorders. Genet. Med. 2021, 23, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spies, N.; Weng, Z.; Bishara, A.; McDaniel, J.; Catoe, D.; Zook, J.M.; Salit, M.; West, R.B.; Batzoglou, S.; Sidow, A. Genome-wide reconstruction of complex structural variants using read clouds. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 915–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romagnoli, S.; Bartalucci, N.; Vannucchi, A.M. Resolving complex structural variants via nanopore sequencing. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1213917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Coster, W.; Van Broeckhoven, C. Newest Methods for Detecting Structural Variations. Trends Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tvedte, E.S.; Gasser, M.; Sparklin, B.C.; Michalski, J.; Hjelmen, C.E.; Johnston, J.S.; Zhao, X.; Bromley, R.; Tallon, L.J.; Sadzewicz, L.; et al. Comparison of long-read sequencing technologies in interrogating bacteria and fly genomes. G3 (Bethesda) 2021, 11, jkab083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolka, M.; Paulin, L.F.; Grochowski, C.M.; Horner, D.W.; Mahmoud, M.; Behera, S.; Kalef-Ezra, E.; Gandhi, M.; Hong, K.; Pehlivan, D.; et al. Detection of mosaic and population-level structural variants with Sniffles2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024, 42, 1571–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sindi, S.S.; Onal, S.; Peng, L.C.; Wu, H.T.; Raphael, B.J. An integrative probabilistic model for identification of structural variation in sequencing data. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, R22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tafazoli, A.; Hemmati, M.; Rafigh, M.; Alimardani, M.; Khaghani, F.; Korostynski, M.; Karnes, J.H. Leveraging long-read sequencing technologies for pharmacogenomic testing: Applications, analytical strategies, challenges, and future perspectives. Front. Genet. 2025, 16, 1435416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Xie, Z.; Li, M. Comprehensive and deep evaluation of structural variation detection pipelines with third-generation sequencing data. Genome Biol. 2024, 25, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meleshko, D.; Yang, R.; Maharjan, S.; Danko, D.C.; Korobeynikov, A.; Hajirasouliha, I. Blackbird: Structural variant detection using synthetic and low-coverage long-reads. bioRxiv 2024, 5, vbaf151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, S.; Wang, A.; Au, K.F. A comparative evaluation of hybrid error correction methods for error-prone long reads. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, R.; Hu, H.; Jiang, Z.; Cao, S.; Wang, G.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, T. SVHunter: Long-read-based structural variation detection through the transformer model. Brief. Bioinform. 2025, 26, bbaf203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommariva, E.; Bellin, M.; Di Resta, C. Advance in Genomics of Rare Genetic Diseases. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nisar, H.; Wajid, B.; Shahid, S.; Anwar, F.; Wajid, I.; Khatoon, A.; Sattar, M.U.; Sadaf, S. Whole-genome sequencing as a first-tier diagnostic framework for rare genetic diseases. Exp. Biol. Med. 2021, 246, 2610–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitsava, G.; Hawley, M.; Auriga, L.; de Dios, I.; Ko, A.; Marmolejos, S.; Almalvez, M.; Chen, I.; Scozzaro, K.; Zhao, J.; et al. Genome sequencing reveals the impact of non-canonical exon inclusions in rare genetic disease. medRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojcik, M.H.; Lemire, G.; Berger, E.; Zaki, M.S.; Wissmann, M.; Win, W.; White, S.M.; Weisburd, B.; Wieczorek, D.; Waddell, L.B.; et al. Genome Sequencing for Diagnosing Rare Diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 1985–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudaks, L.I.; Stevanovski, I.; Yeow, D.; Reis, A.L.M.; Chintalaphani, S.R.; Cheong, P.L.; Gamaarachchi, H.; Worgan, L.; Ahmad, K.; Hayes, M.; et al. Targeted Long-Read Sequencing as a Single Assay Improves the Diagnosis of Spastic-Ataxia Disorders. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2025, 12, 832–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doss, R.M.; Lopez-Ignacio, S.; Dischler, A.; Hiatt, L.; Dashnow, H.; Breuss, M.W.; Dias, C.M. Mosaicism in Short Tandem Repeat Disorders: A Clinical Perspective. Genes 2025, 16, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplun, L.; Krautz-Peterson, G.; Neerman, N.; Stanley, C.; Hussey, S.; Folwick, M.; McGarry, A.; Weiss, S.; Kaplun, A. ONT long-read WGS for variant discovery and orthogonal confirmation of short read WGS derived genetic variants in clinical genetic testing. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1145285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsuhashi, S.; Matsumoto, N. Long-read sequencing for rare human genetic diseases. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 65, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, C.T.; Marques-Bonet, T.; Sharp, A.J.; Mefford, H.C. The genetics of microdeletion and microduplication syndromes: An update. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2014, 15, 215–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lelieveld, S.H.; Spielmann, M.; Mundlos, S.; Veltman, J.A.; Gilissen, C. Comparison of Exome and Genome Sequencing Technologies for the Complete Capture of Protein-Coding Regions. Hum. Mutat. 2015, 36, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantere, T.; Kersten, S.; Hoischen, A. Long-Read Sequencing Emerging in Medical Genetics. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, R.; Brennan, N.F.; Trachana, K.; Katsandres, S.; Bodamer, O.; Belmont, J.; Veenstra, D.L.; Peng, S. A meta-analysis of diagnostic yield and clinical utility of genome and exome sequencing in pediatric rare and undiagnosed genetic diseases. Genet. Med. 2025, 27, 101398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianconi, I.; Aschbacher, R.; Pagani, E. Current Uses and Future Perspectives of Genomic Technologies in Clinical Microbiology. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovaka, S.; Ou, S.; Jenike, K.M.; Schatz, M.C. Approaching complete genomes, transcriptomes and epi-omes with accurate long-read sequencing. Nat. Methods 2023, 20, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, S.V.; Goodwin, S.; McCombie, W.R. Leveraging the power of long reads for targeted sequencing. Genome Res. 2024, 34, 1701–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarano, C.; Veneruso, I.; De Simone, R.R.; Di Bonito, G.; Secondino, A.; D’Argenio, V. The Third-Generation Sequencing Challenge: Novel Insights for the Omic Sciences. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastrorosa, F.K.; Miller, D.E.; Eichler, E.E. Applications of long-read sequencing to Mendelian genetics. Genome Med. 2023, 15, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, S.; Handler, H.P.; Victorsen, A.; Flaten, Z.; Ellison, A.; Knutson, T.P.; Munro, S.A.; Martinez, R.J.; Billington, C.J.; Laffin, J.J.; et al. Validation of a comprehensive long-read sequencing platform for broad clinical genetic diagnosis. Front. Genet. 2025, 16, 1499456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, S.M.; Prybutok, V. Balancing Privacy and Progress: A Review of Privacy Challenges, Systemic Oversight, and Patient Perceptions in AI-Driven Healthcare. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin-Tse, C.A.; Jobanputra, V.; Perry, D.L.; Bick, D.; Taft, R.J.; Venner, E.; Gibbs, R.A.; Young, T.; Barnett, S.; Belmont, J.W.; et al. Best practices for the interpretation and reporting of clinical whole genome sequencing. NPJ Genom. Med. 2022, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharo, A.G.; Hu, Z.; Sunyaev, S.R.; Brenner, S.E. StrVCTVRE: A supervised learning method to predict the pathogenicity of human genome structural variants. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2022, 109, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zawar, A.; Manoj, G.; Nair, P.P.; Deshpande, P.; Suravajhala, R.; Suravajhala, P. Variants of uncertain significance: At the crux of diagnostic odyssey. Gene 2025, 962, 149587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karczewski, K.J.; Weisburd, B.; Thomas, B.; Solomonson, M.; Ruderfer, D.M.; Kavanagh, D.; Hamamsy, T.; Lek, M.; Samocha, K.E.; Cummings, B.B.; et al. The ExAC browser: Displaying reference data information from over 60,000 exomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D840–D845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawood, M.; Heavner, B.; Wheeler, M.M.; Ungar, R.A.; LoTempio, J.; Wiel, L.; Berger, S.; Bernstein, J.A.; Chong, J.X.; Delot, E.C.; et al. GREGoR: Accelerating Genomics for Rare Diseases. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.14338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henglin, M.; Ghareghani, M.; Harvey, W.T.; Porubsky, D.; Koren, S.; Eichler, E.E.; Ebert, P.; Marschall, T. Graphasing: Phasing diploid genome assembly graphs with single-cell strand sequencing. Genome Biol. 2024, 25, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Showpnil, I.A.; Gonzalez, M.E.H.; Ramadesikan, S.; Marhabaie, M.; Daley, A.; Dublin-Ryan, L.; Pastore, M.T.; Gurusamy, U.; Hunter, J.M.; Stone, B.S.; et al. Long-read genome sequencing resolves complex genomic rearrangements in rare genetic syndromes. NPJ Genom. Med. 2024, 9, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hook, P.W.; Timp, W. Beyond assembly: The increasing flexibility of single-molecule sequencing technology. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2023, 24, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, X.M.; Yeung, M.H.Y.; Wong, A.N.N.; Tsang, H.F.; Yu, A.C.S.; Yim, A.K.Y.; Wong, S.C.C. Targeted Sequencing Approach and Its Clinical Applications for the Molecular Diagnosis of Human Diseases. Cells 2023, 12, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.C.; Solomon, B.; Mun, T.; Iyer, S.; Langmead, B. Reference flow: Reducing reference bias using multiple population genomes. Genome Biol. 2021, 22, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billingsley, K.J.; Meredith, M.; Daida, K.; Jerez, P.A.; Negi, S.; Malik, L.; Genner, R.M.; Moller, A.; Zheng, X.; Gibson, S.B.; et al. Long-read sequencing of hundreds of diverse brains provides insight into the impact of structural variation on gene expression and DNA methylation. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, R.M.; Ali, B.R.; Al-Jasmi, F.; Sinnott, R.O.; Al Dhaheri, N.; Mohamad, M.S. A review of genetic variant databases and machine learning tools for predicting the pathogenicity of breast cancer. Brief. Bioinform. 2023, 25, bbad479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafson, J.A.; Gibson, S.B.; Damaraju, N.; Zalusky, M.P.G.; Hoekzema, K.; Twesigomwe, D.; Yang, L.; Snead, A.A.; Richmond, P.A.; De Coster, W.; et al. High-coverage nanopore sequencing of samples from the 1000 Genomes Project to build a comprehensive catalog of human genetic variation. Genome Res. 2024, 34, 2061–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, M.; Emerson, J.J.; Macdonald, S.J.; Long, A.D. Structural variants exhibit widespread allelic heterogeneity and shape variation in complex traits. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brlek, P.; Bulic, L.; Bracic, M.; Projic, P.; Skaro, V.; Shah, N.; Shah, P.; Primorac, D. Implementing Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS) in Clinical Practice: Advantages, Challenges, and Future Perspectives. Cells 2024, 13, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negi, S.; Stenton, S.L.; Berger, S.I.; Canigiula, P.; McNulty, B.; Violich, I.; Gardner, J.; Hillaker, T.; O’Rourke, S.M.; O’Leary, M.C.; et al. Advancing long-read nanopore genome assembly and accurate variant calling for rare disease detection. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2025, 112, 428–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).