Non-Invasive Screening for Early Cognitive Impairment in Elderly Hyperuricaemic Men Using Transcranial Colour-Coded Duplex Sonography
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Equipment and Patient Positioning
2.3. TCCD Examination Procedure
2.4. Measurement Reproducibility
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics and Serum Uric Acid Levels
3.2. TCCD Findings: Structural and Haemodynamic Differences
3.3. Diagnostic Accuracy of TCCD Parameters for MCI
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MCI | mild cognitive impairment |
| HUA | hyperuricaemia |
| TCCD | transcranial colour-coded duplex |
| PSV | peak systolic velocity |
| EDV | end-diastolic velocity |
| MCA | middle cerebral artery |
| PCA | posterior cerebral artery |
| RI | resistive index |
| PI | pulsatility index |
| TVW | third ventricle width |
| MoCA | Montreal Cognitive Assessment |
| ICC | intraclass correlation coefficient |
| SPSS | Statistical Package for the Social Sciences |
| ROC | receiver operating characteristic |
| AUC | area under the ROC curve |
| BMI | body mass index |
| PRF | pulse repetition frequency |
References
- Chen, C.; Li, X.; Lv, Y.; Yin, Z.; Zhao, F.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Ji, S.; Zhou, J.; Wei, Y.; et al. High Blood Uric Acid Is Associated with Reduced Risks of Mild Cognitive Impairment Among Older Adults in China: A 9-Year Prospective Cohort Study. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 747686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Wang, J.; Fan, D.-Y.; Luo, T.; Li, Y.; Tu, Y.-F.; Shen, Y.-Y.; Zeng, G.-H.; Chen, D.-W.; Wang, Y.-R.; et al. The Association of Serum Uric Acid with Cognitive Impairment and ATN Biomarkers. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 943380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, H.; Sun, J.; Zhang, T.; Hui, Y.; Li, J.; Zhao, X.; Chen, S.; Liu, W.; Li, X.; Zhao, P.; et al. Associations of Serum Uric Acid Variability with Neuroimaging Metrics and Cognitive Decline: A Population-Based Cohort Study. BMC Med. 2024, 22, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijailovic, N.R.; Vesic, K.; Borovcanin, M.M. The Influence of Serum Uric Acid on the Brain and Cognitive Dysfunction. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 828476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tang, L.; Hu, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y. Uric Acid Is Associated with Cognitive Impairment in the Elderly Patients Receiving Maintenance Hemodialysis-A Two-Center Study. Brain Behav. 2020, 10, e01542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Lu, X.; Qiu, Y.; Teng, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, X.; Tang, H.; Xiang, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, B.; et al. Association between Uric Acid and Cognitive Dysfunction: A Cross-Sectional Study with Newly Diagnosed, Drug-Naïve with Bipolar Disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 2023, 327, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-J.; Huang, Y.-H.; Lin, Y.-Y.; Li, M.-M.; Chen, Y.-F.; Cai, R.-W. The Association of Uric Acid with Leukoaraiosis. J. Int. Med. Res. 2017, 45, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Shen, J.; Yang, J.; Chen, X.; Li, W.; Wang, J.; Xu, X.; Xu, X.; Liu, Z.; et al. Association of Plasma Uric Acid Levels with Cognitive Function among Non-Hyperuricemia Adults: A Prospective Study. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Tian, S.; Han, J.; Lin, H.; Guo, D.; Wang, J.; An, K.; Wang, S. U-Shaped Association Between Serum Uric Acid Levels and Cognitive Functions in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2019, 69, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jin, R.; Wu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Jin, X.; Han, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Guo, X.; Tao, L. Moderate Increase of Serum Uric Acid within a Normal Range Is Associated with Improved Cognitive Function in a Non-Normotensive Population: A Nationally Representative Cohort Study. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 944341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortner, M.; Hauser, C.; Schmaderer, C.; Muggenthaler, C.; Hapfelmeier, A.; Sorg, C.; Diehl-Schmid, J.; Kurz, A.; Förstl, H.; Ikenberg, B.; et al. Decreased Vascular Pulsatility in Alzheimer’s Disease Dementia Measured by Transcranial Color-Coded Duplex Sonography. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2019, 15, 3487–3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favaretto, S.; Walter, U.; Baracchini, C.; Cagnin, A. Transcranial Sonography in Neurodegenerative Diseases with Cognitive Decline. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 61, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malojcic, B.; Giannakopoulos, P.; Sorond, F.A.; Azevedo, E.; Diomedi, M.; Oblak, J.P.; Carraro, N.; Boban, M.; Olah, L.; Schreiber, S.J.; et al. Ultrasound and Dynamic Functional Imaging in Vascular Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease. BMC Med. 2017, 15, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corte, F.D.; Pifferi, S.; Capuano, L.; Magnoni, S.; Conte, V.; Ortolano, F.; Stocchetti, N. Accuracy of Transcranial Color-Coded Duplex Sonography in Predicting Clinical Vasospasm and Delayed Cerebral Ischemia in Patients with Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Crit. Care 2014, 18, P462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambeck, J.; Strecker, C.; Niesen, W.-D.; Bardutzky, J. Exclusive Color-Coded Duplex Sonography of Extracranial Vessels Reliably Confirms Brain Death: A Prospective Study. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 992511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viscogliosi, C.; Belleville, S.; Desrosiers, J.; Caron, C.D.; Ska, B.; BRAD Group. Participation after a Stroke: Changes over Time as a Function of Cognitive Deficits. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2011, 52, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasreddine, Z.S.; Phillips, N.A.; Bédirian, V.; Charbonneau, S.; Whitehead, V.; Collin, I.; Cummings, J.L.; Chertkow, H. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: A Brief Screening Tool for Mild Cognitive Impairment. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2005, 53, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespo-Cuevas, A.M.; Canento, T.; Hernández-Perez, M.; Cáceres, C.; González, A.; Ispierto, L.; Mataró, M.; Vilas, D.; Planas-Ballvé, A.; Martin, L.; et al. The Barcelona-Asymptomatic Intracranial Atherosclerosis (AsIA) Study: Subclinical Cervico-Cerebral Stenosis and Middle Cerebral Artery Pulsatility Index as Predictors of Long-Term Incident Cognitive Impairment. Atherosclerosis 2020, 312, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frid, P.E.; Schreiber, S.J.; Pade, O.; Doepp, F.; Valdueza, J. The Posterior Cerebral Artery and Its Main Cortical Branches Identified with Noninvasive Transcranial Color-Coded Duplex Sonography. Ultrasound Int. Open 2015, 1, E53–E57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsivgoulis, G.; Sharma, V.K.; Hoover, S.L.; Lao, A.Y.; Ardelt, A.A.; Malkoff, M.D.; Alexandrov, A.V. Applications and Advantages of Power Motion-Mode Doppler in Acute Posterior Circulation Cerebral Ischemia. Stroke 2008, 39, 1197–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, P.; Roushdy, T.; Fathy, M.; Hamid, E.; Ibrahim, Y.A.; El-Belkimy, M.; Abdulghani, M.O.; Shalash, A. The Clinical and Neuroimaging Differences between Vascular Parkinsonism and Parkinson’s Disease: A Case-Control Study. BMC Neurol. 2024, 24, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staszewski, J.; Dȩbiec, A.; Skrobowska, E.; Stȩpień, A. Cerebral Vasoreactivity Changes over Time in Patients with Different Clinical Manifestations of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 727832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, D.T.; Fülesdi, B.; Kozma, B.; Páll, D.; Szatmári, S.; Hupuczi, P. Assessment of Cerebral Hemodynamic Changes During Roll-Over Test in Healthy Pregnant Women and Those with Mild and Severe Preeclampsia. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tana, C.; Ticinesi, A.; Prati, B.; Nouvenne, A.; Meschi, T. Uric Acid and Cognitive Function in Older Individuals. Nutrients 2018, 10, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrage, E.N.; Coblentz, T.; Prabhu, S.S.; Childers, R.; Bryner, R.W.; Lewis, S.E.; DeVallance, E.; Kelley, E.E.; Chantler, P.D. Xanthine Oxidase Mediates Chronic Stress-Induced Cerebrovascular Dysfunction and Cognitive Impairment. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2023, 43, 905–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicero, A.F.G.; Desideri, G.; Grossi, G.; Urso, R.; Rosticci, M.; D’Addato, S.; Borghi, C.; Brisighella Heart Study Group. Serum Uric Acid and Impaired Cognitive Function in a Cohort of Healthy Young Elderly: Data from the Brisighella Study. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2015, 10, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozova, I.; Zorkina, Y.; Berdalin, A.; Ikonnikova, A.; Emelyanova, M.; Fedoseeva, E.; Antonova, O.; Gryadunov, D.; Andryushchenko, A.; Ushakova, V.; et al. Dynamics of Cognitive Impairment in MCI Patients over a Three-Year Period: The Informative Role of Blood Biomarkers, Neuroimaging, and Genetic Factors. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Arendonk, J.; Neitzel, J.; Steketee, R.M.E.; van Assema, D.M.E.; Vrooman, H.A.; Segbers, M.; Ikram, M.A.; Vernooij, M.W. Diabetes and Hypertension Are Related to Amyloid-Beta Burden in the Population-Based Rotterdam Study. Brain 2022, 146, awac354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, F.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L. Serum Uric Acid and High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein as Predictors of Cognitive Impairment in Patients with Cerebral Infarction. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2020, 49, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latourte, A.; Soumaré, A.; Bardin, T.; Perez-Ruiz, F.; Debette, S.; Richette, P. Uric Acid and Incident Dementia over 12 Years of Follow-up: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchino, A.; Ito, S.; Kurita, H.; Tanaka, M. Duplicated Middle Cerebral Artery Arising from the Origin of the Hyperplastic Anterior Choroidal Artery That Mimicked Aneurysm on Routine MR Angiography. Neuroradiol. J. 2016, 29, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
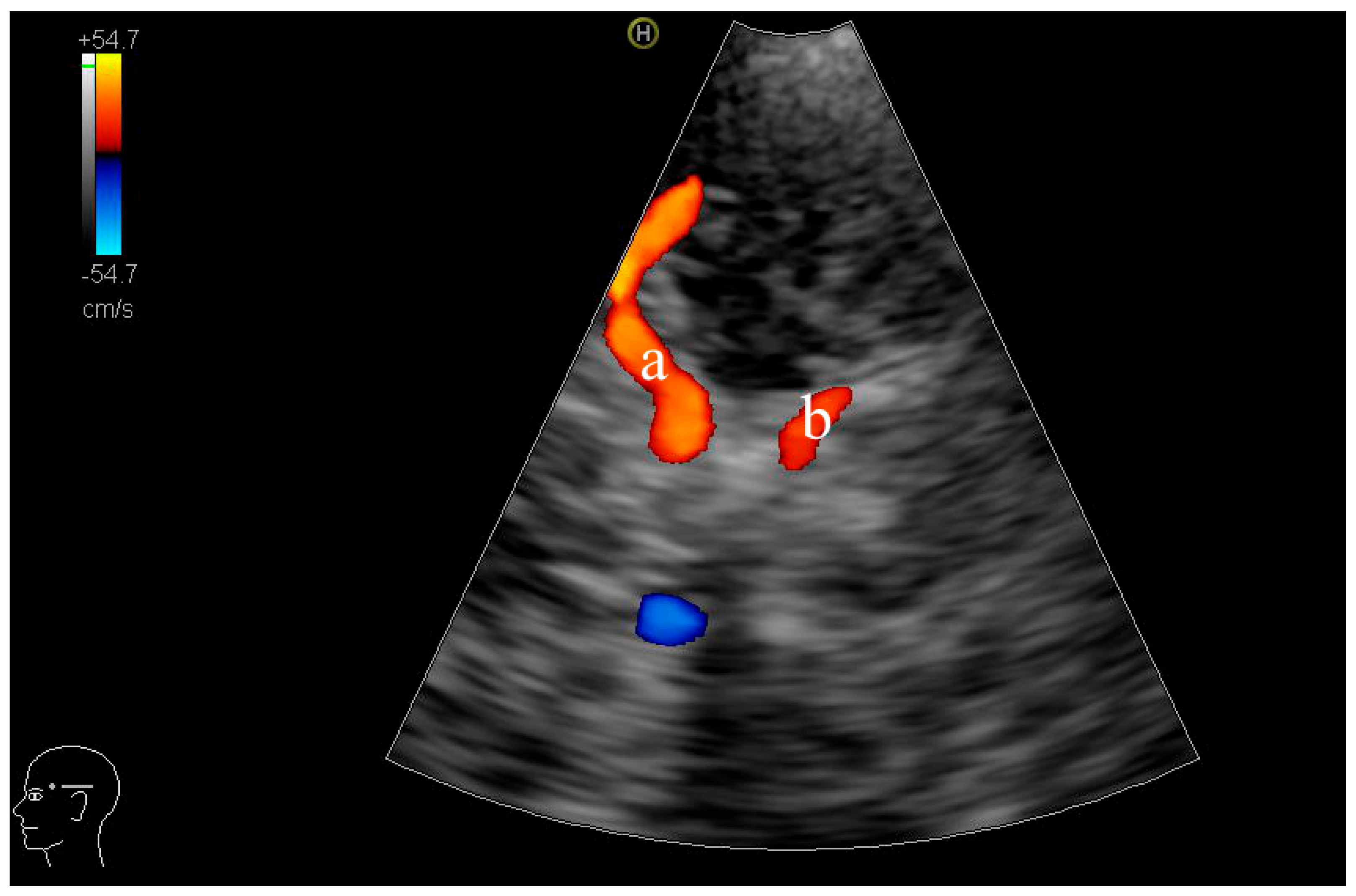
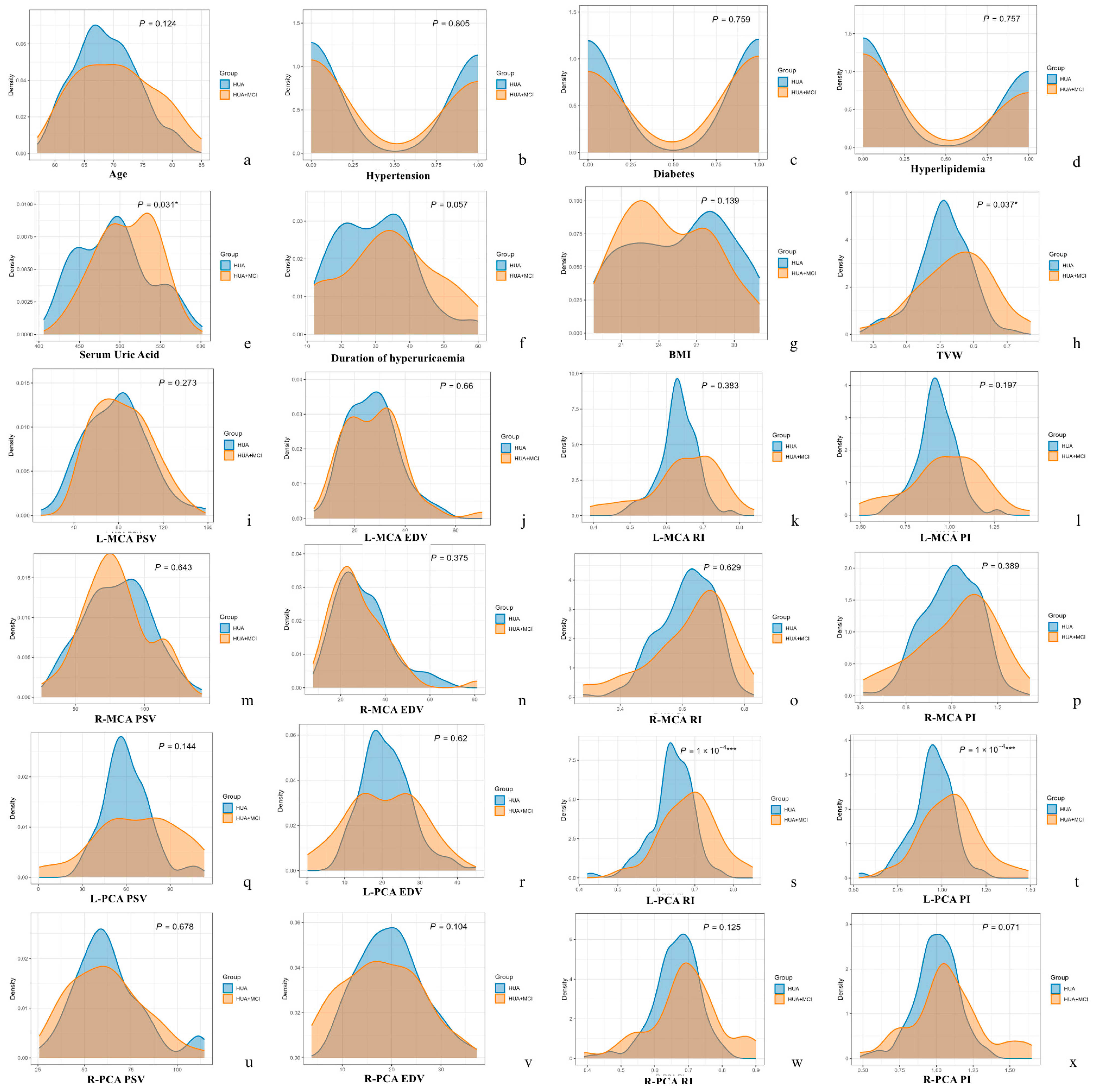
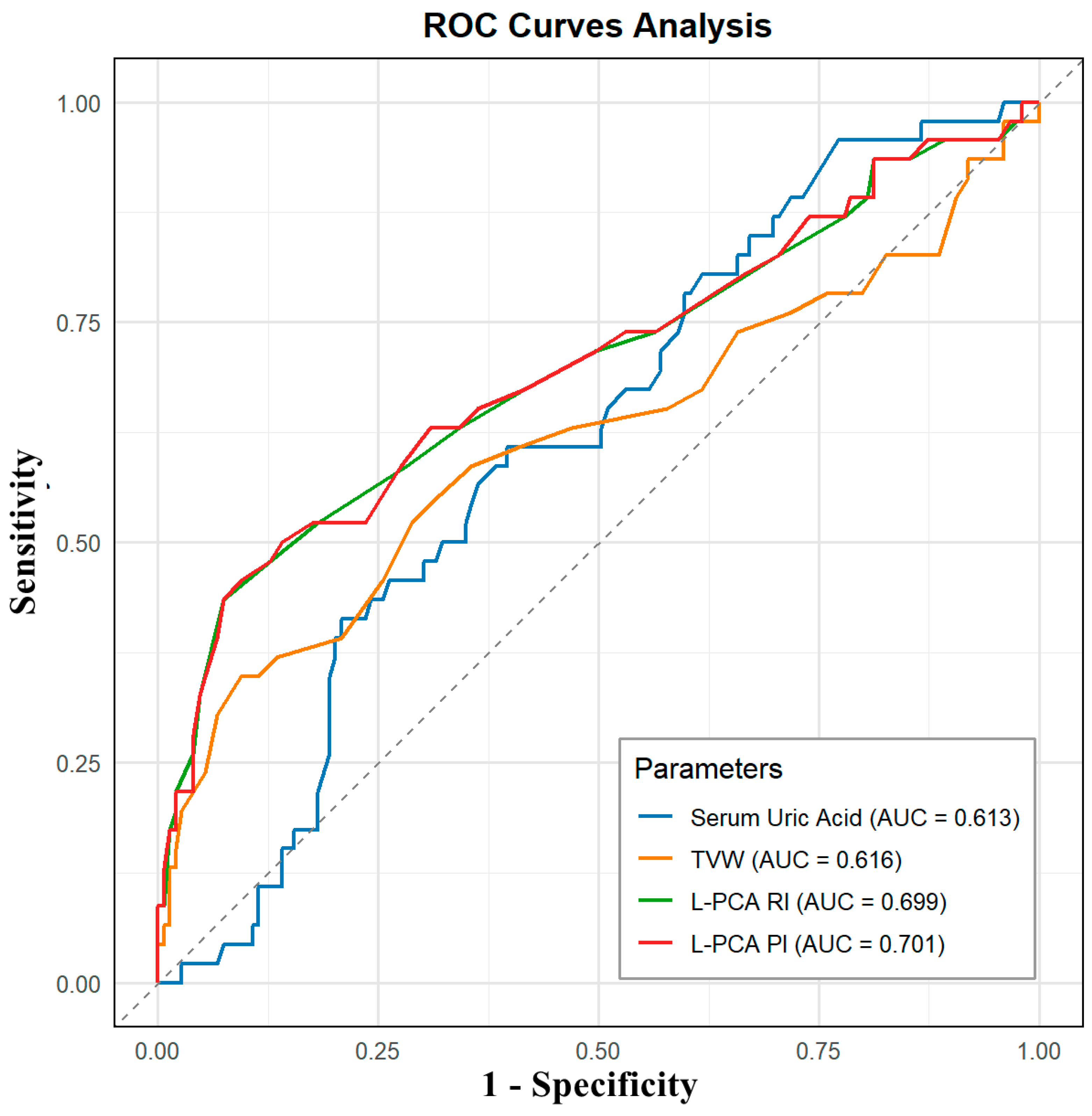
| Parameters | HUA Group (n = 149) | HUA + MCI Group (n = 46) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year, X ± SD) | 68.70 ± 5.29 | 70.37 ± 6.62 | 0.124 |
| Serum uric acid (μmol/L, X ± SD) | 492.93 ± 44.01 | 508.48 ± 36.25 | 0.031 * |
| Hypertension Duration (month, X ± SD) | 30.04 ± 11.19 | 33.87 ± 13.77 | 0.057 |
| Hypertension (n, %) | 70, 47.0 | 20, 43.5 | 0.805 |
| Diabetes (n, %) | 75, 50.3 | 25, 54.3 | 0.759 |
| Hyperlipidaemia (n, %) | 61, 40.9 | 17, 37.0 | 0.757 |
| BMI (X, X ± SD) | 25.7 ± 3.9 | 24.7 ± 3.5 | 0.139 |
| Parameters | HUA Group | HUA + MCI Group | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TVW (cm) | 0.51 ± 0.08 | 0.55 ± 0.11 | 0.037 * | |
| Left MCA | PSV (cm/s) | 78.06 ± 27.70 | 83.08 ± 25.05 | 0.273 |
| EDV (cm/s) | 27.03 ± 10.16 | 27.81 ± 11.79 | 0.660 | |
| RI | 0.63 ± 0.05 | 0.65 ± 0.10 | 0.383 | |
| PI | 0.93 ± 0.11 | 0.97 ± 0.21 | 0.197 | |
| Right MCA | PSV (cm/s) | 80.50 ± 23.88 | 78.65 ± 23.01 | 0.643 |
| EDV (cm/s) | 29.94 ± 12.17 | 28.08 ± 13.10 | 0.375 | |
| RI | 0.61 ± 0.09 | 0.62 ± 0.13 | 0.629 | |
| PI | 0.89 ± 0.18 | 0.93 ± 0.26 | 0.389 | |
| Left PCA | PSV (cm/s) | 60.45 ± 15.90 | 66.99 ± 28.59 | 0.144 |
| EDV (cm/s) | 21.18 ± 6.61 | 20.42 ± 9.70 | 0.620 | |
| RI | 0.64 ± 0.06 | 0.69 ± 0.07 | 0.0001 *** | |
| PI | 0.95 ± 0.12 | 1.05 ± 0.17 | 0.0001 *** | |
| Right PCA | PSV (cm/s) | 63.19 ± 18.66 | 61.85 ± 19.75 | 0.678 |
| EDV (cm/s) | 19.73 ± 6.41 | 17.87 ± 7.74 | 0.104 | |
| RI | 0.66 ± 0.07 | 0.69 ± 0.07 | 0.125 | |
| PI | 1.00 ± 0.15 | 1.07 ± 0.25 | 0.071 | |
| Parameter | AUC | Sensitivity | Specificity | Threshold |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serum Uric Acid | 0.613 | 60.87% | 60.40% | 500.500 |
| TVW | 0.616 | 34.78% | 90.60% | 0.605 |
| L-PCA RI | 0.699 | 43.48% | 92.62% | 0.705 |
| L-PCA PI | 0.701 | 45.65% | 90.60% | 1.075 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Z.; Ye, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Tan, K.; Li, S.; Su, S. Non-Invasive Screening for Early Cognitive Impairment in Elderly Hyperuricaemic Men Using Transcranial Colour-Coded Duplex Sonography. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1519. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15121519
Xu Z, Ye J, Wang H, Chen J, Tan K, Li S, Su S. Non-Invasive Screening for Early Cognitive Impairment in Elderly Hyperuricaemic Men Using Transcranial Colour-Coded Duplex Sonography. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(12):1519. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15121519
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Zhirong, Jiayi Ye, Han Wang, Jiemin Chen, Kailing Tan, Shilin Li, and Shanshan Su. 2025. "Non-Invasive Screening for Early Cognitive Impairment in Elderly Hyperuricaemic Men Using Transcranial Colour-Coded Duplex Sonography" Diagnostics 15, no. 12: 1519. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15121519
APA StyleXu, Z., Ye, J., Wang, H., Chen, J., Tan, K., Li, S., & Su, S. (2025). Non-Invasive Screening for Early Cognitive Impairment in Elderly Hyperuricaemic Men Using Transcranial Colour-Coded Duplex Sonography. Diagnostics, 15(12), 1519. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15121519







