Matrix Metalloproteinases 1 and 3 in Ovarian Cancer: Diagnostic and Prognostic Potential of Genetic Variants and Expression Profiling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Framework
2.2. Sample Size Calculation
2.3. Molecular and Immunohistochemical Profiling
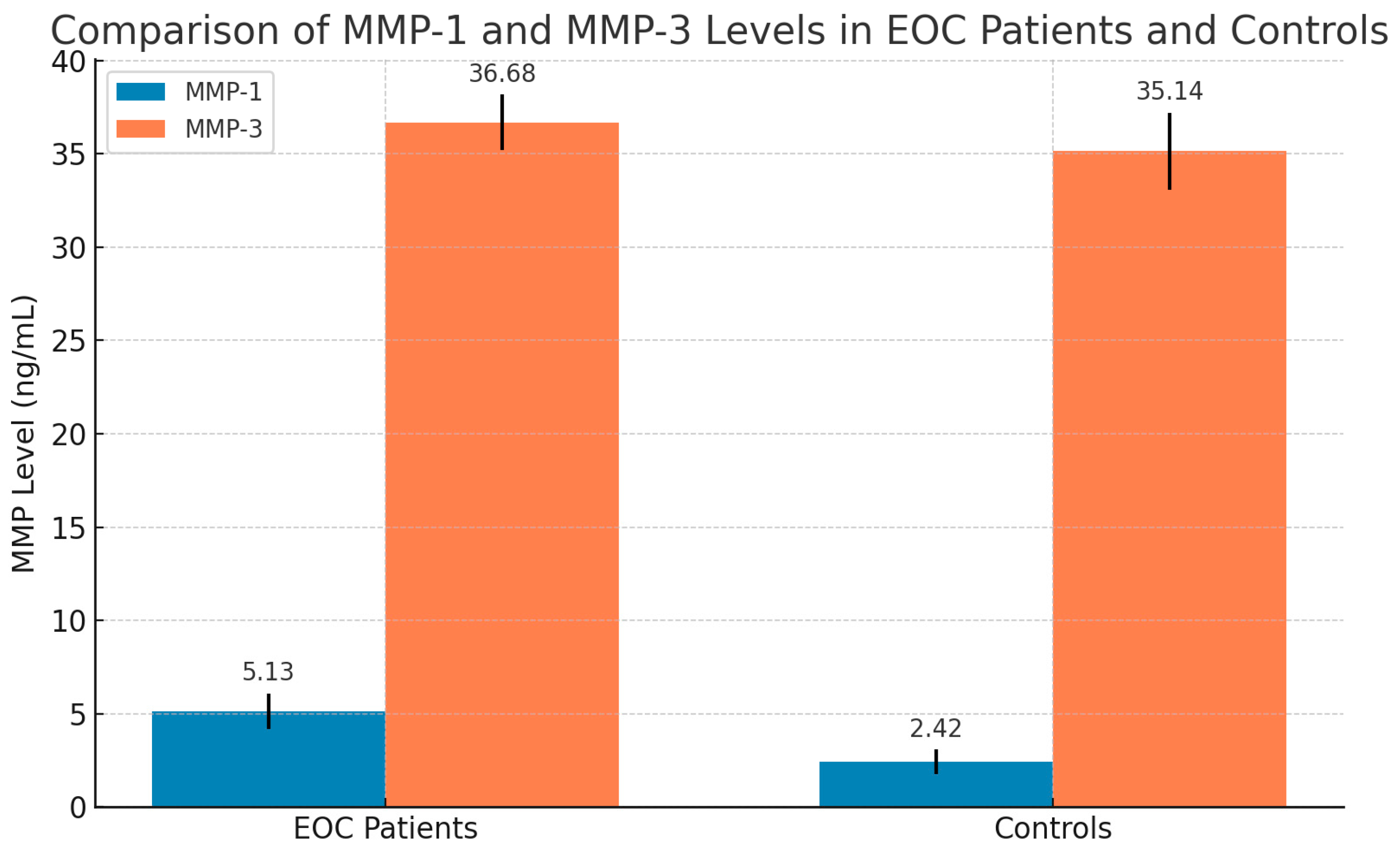
2.3.1. Quantification of MMPs-1,3 Within Ovarian Tissue
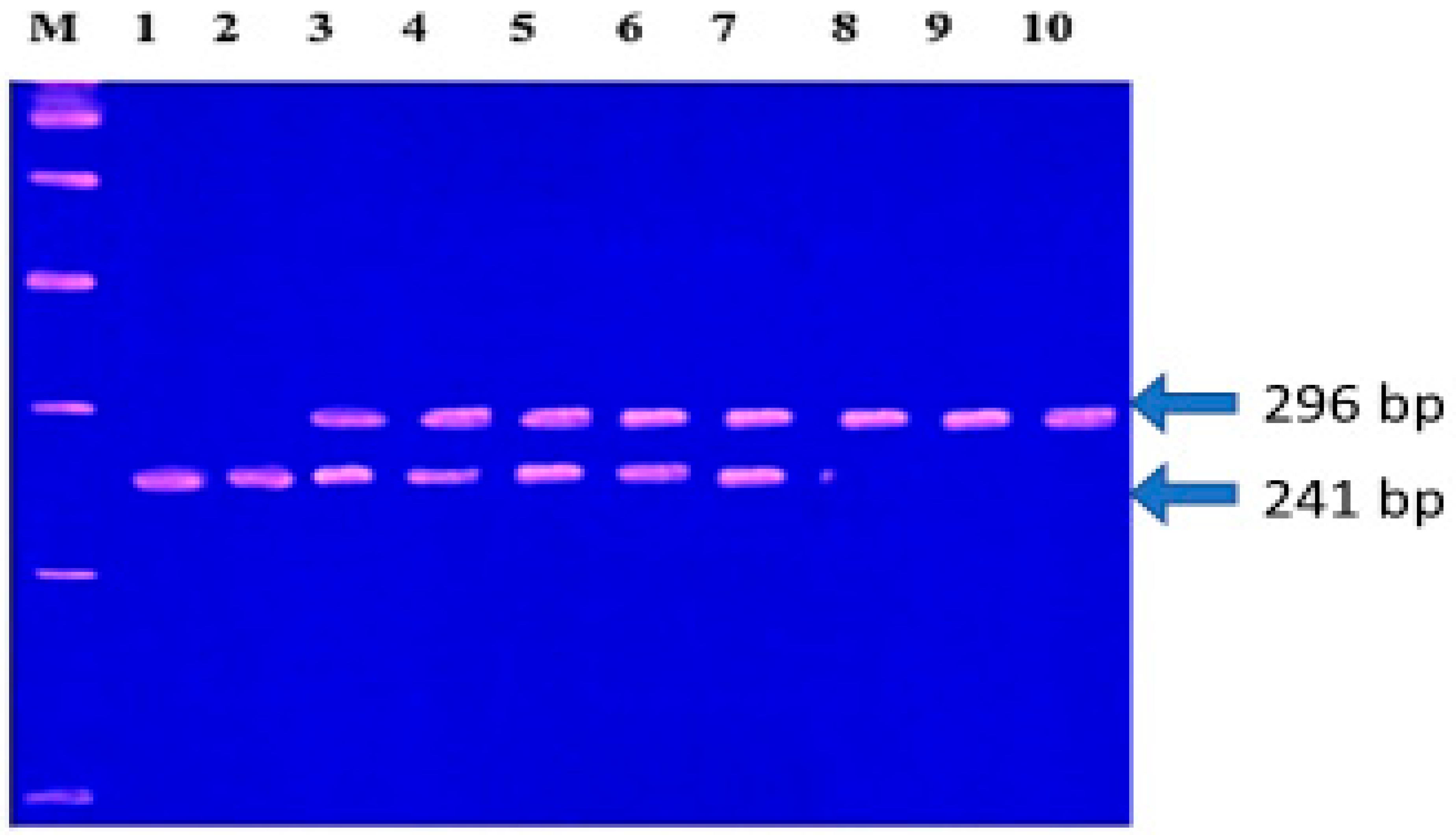
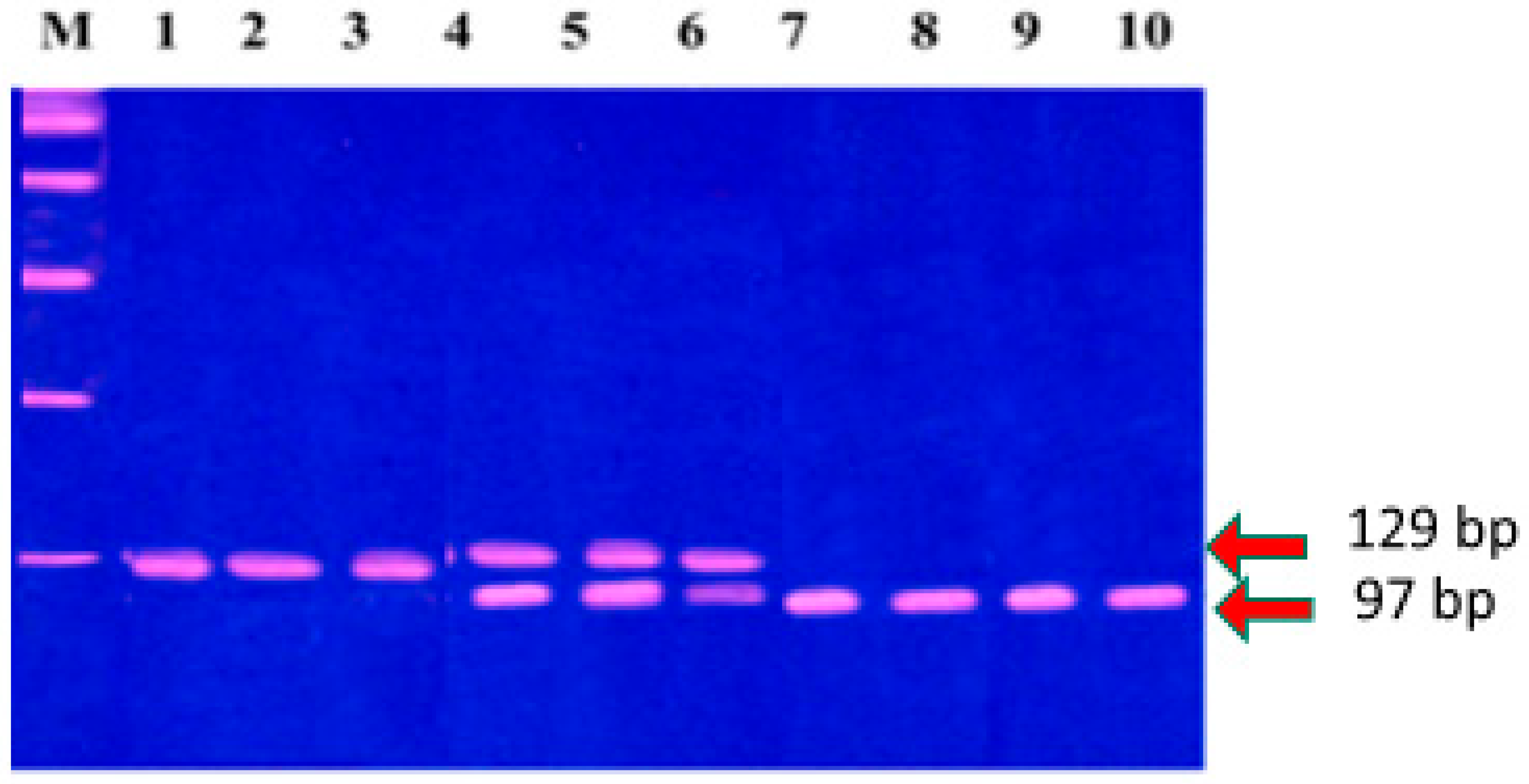
2.3.2. DNA Extraction and Genotyping
2.3.3. Selection Criteria for MMP-1 (-1607, 1G/2G) and MMP-3 (-1171, 5A/6A) Polymorphisms and Genotyping
Selection Criteria for Polymorphisms
- MMP-1 SNP Primers:
- Forward primer: 5′-TGACTTTTAAAACATAGTCTATGTTCA-3′.
- Reverse primer: 5′-TCTTGGATTGATTTGAGATAAGTCATAGC-3′.
- MMP-3 SNP Primers:
- Sense primer: 5′-GGTTCTCCATTCCTTTGATGGGGGGAAAGA-3′.
- Antisense primer: 5′-CTTCCTGGAATTCACATCACTGCCACCACT-3′.
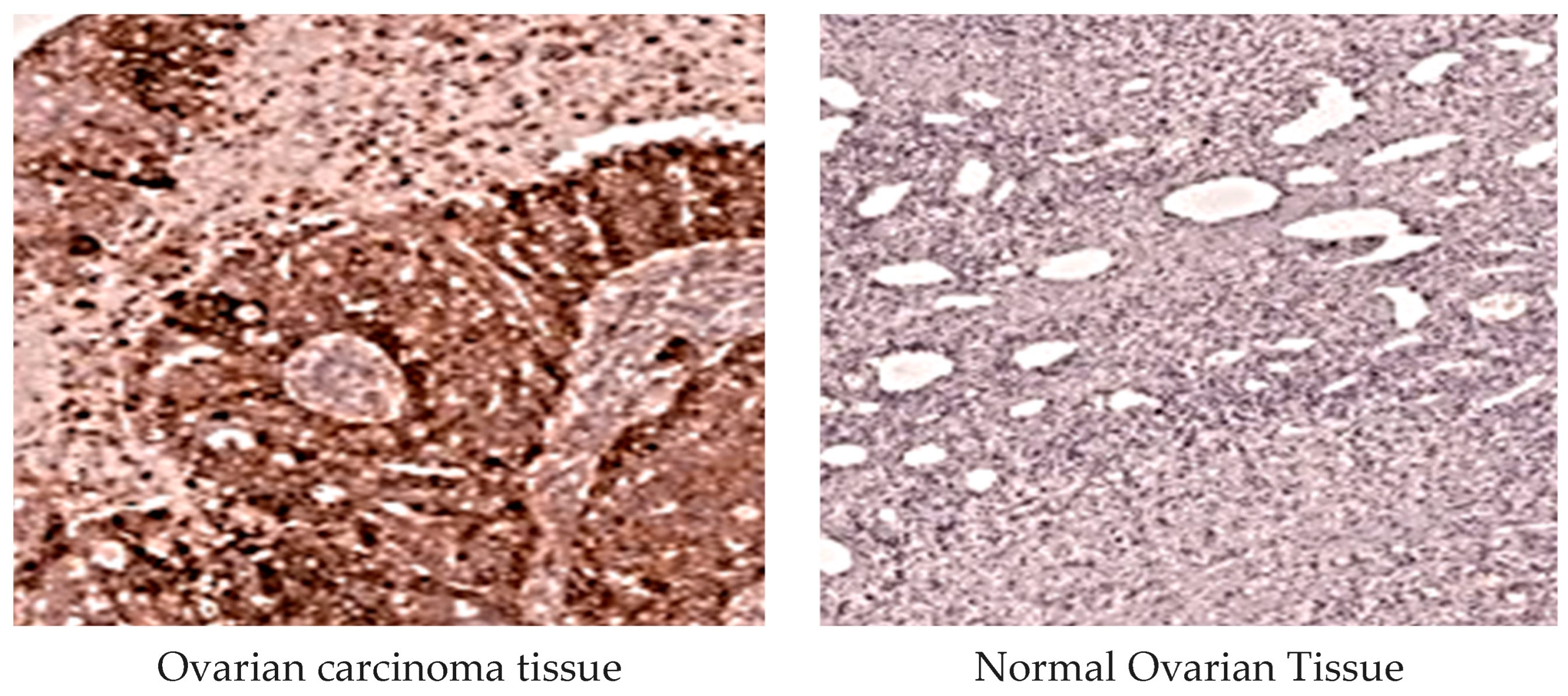
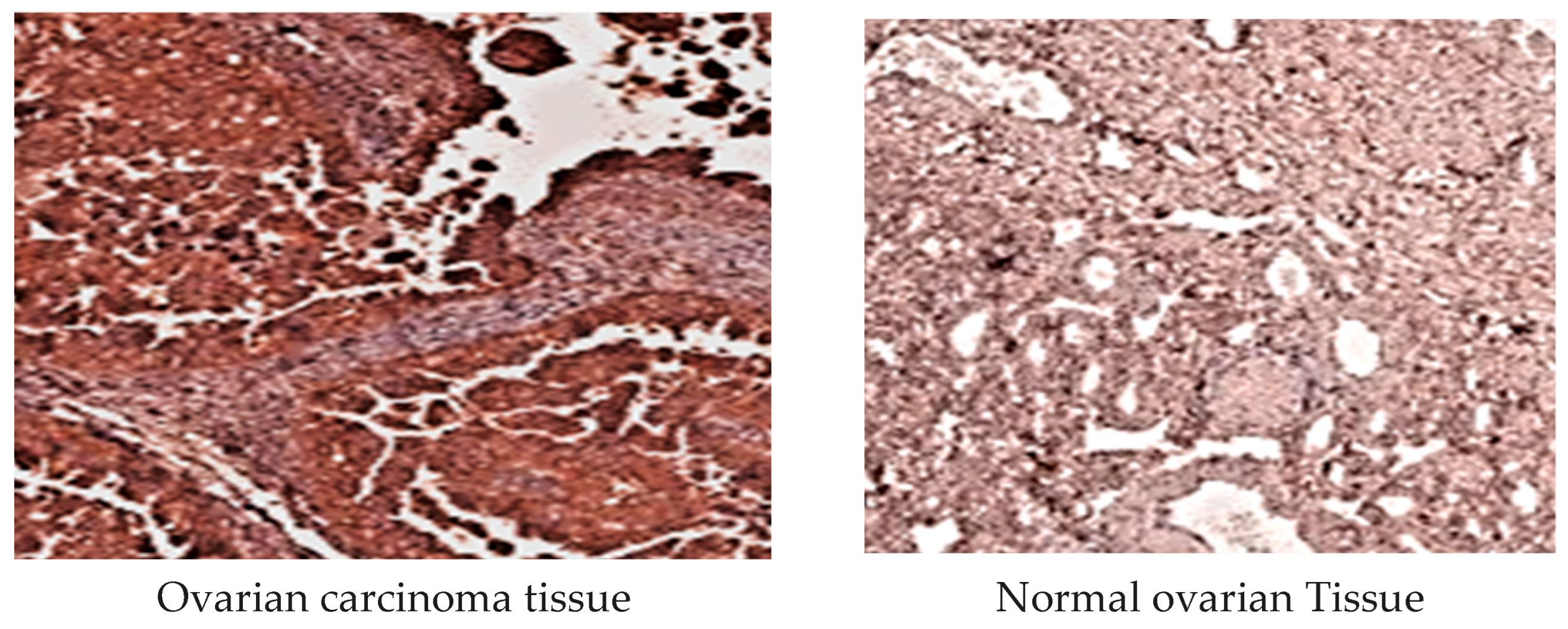
2.3.4. MMP-1 Immunohistochemical Analysis
2.3.5. MMP-3 Immunohistochemical Examination
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Ethical Approval and Informed Consent
3. Results
Diagnostic Value of MMP-1 and MMP-3 Alleles
4. Discussion
- -
- Population-specific focus: Unlike most previous studies, which were conducted in Asian or Caucasian populations, our study is among the first to investigate MMP-1 (-1607 1G/2G) and MMP-3 (-1171 5A/6A) polymorphisms specifically in Egyptian women with EOC, highlighting potential ethnicity-specific risk factors.
- -
- Combined analysis of genotype and protein expression: In addition to genotyping, we performed an immunohistochemical analysis of MMP-1 and MMP-3 protein levels, demonstrating a correlation between certain genotypes (2G/2G and 6A/6A) and elevated protein expression in EOC tissues, particularly in late-stage disease. This integrative approach provides a more functional and prognostically relevant perspective than previous genetic-only studies.
- -
- Diagnostic and prognostic value: Our ROC analysis revealed that MMPs -1,3 protein levels exhibited higher sensitivity and specificity compared to CEA, suggesting their superior potential as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for EOC.
Limitations and Recommendations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Howlader, N.; Noone, A.M.; Krapcho, M.; Miller, D.; Brest, A.; Yu, M.; Ruhl, J.; Tatalovich, Z.; Mariotto, A.; Lewis, D.R.; et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2017; National Cancer Institute: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2019. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2017/ (accessed on 1 November 2020).
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almutairi, S.; Kalloush, H.M.; Manoon, N.A.; Bardaweel, S.K. Matrix Metalloproteinases Inhibitors in Cancer Treatment: An Updated Review (2013–2023). Molecules 2023, 28, 5567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Qian, J.; Zhu, F.; Wu, F.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, H. The prognostic values of matrix metalloproteinase in ovarian cancer. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 0300060519825983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.C.; Chanock, S.J. Current status of genome-wide association studies in cancer. Hum. Genet. 2011, 130, 59–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Alem, L.; Curry, T. Ovarian cancer: Involvement of the matrix metalloproteinases. Reproduction 2015, 150, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, M.; Udi, Y.; Solomonov, I.; Sagi, I. Next-generation matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors—Novel strategies bring new prospects. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2017, 1864, 1927–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berchuck, A.; Iversen, E.S.; Luo, J.; Clarke, J.P.; Horne, H.; Levine, D.A.; Boyd, J.; Alonso, M.A.; Secord, A.A.; Bernardini, M.Q.; et al. Microarray analysis of early-stage serous ovarian cancers shows profiles predictive of favorable outcomes. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 2448–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kicman, A.; Niczyporuk, M.; Kulesza, M.; Clarke, J.P.; Horne, H.; Levine, D.A.; Boyd, J.; Alonso, M.A.; Secord, A.A.; Bernardini, M.Q.; et al. Utility of Matrix Metalloproteinases in the Diagnosis, Monitoring, and Prognosis of Ovarian Cancer Patients. Cancer Manag. Res. 2022, 14, 3359–3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, M.; Malik, A.; Basit, M.A.; Naseer, M.I.; Manan, A.; Pushparaj, P.N.; Abuzenadah, A.M.; Al-Qahtani, M.H.; Kamal, M.A.; Gan, S.H.; et al. Evaluation of matrix metalloproteinases, cytokines, and their potential role in the development of ovarian cancer. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Będkowska, G.E.; Piskór, B.; Gacuta, E.; Jakubowicz-Gil, J.; Gancarczyk, K.; Woźniak, A.; Dmoszyńska, A.; Rolinski, J.; Błasiak, J.; Szemraj, J.; et al. Diagnostic power of selected cytokines, MMPs, and TIMPs in ovarian cancer patients—ROC analysis. Anticancer Res. 2019, 39, 2575–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Ma, X.; Wang, F.; Zhou, B.; Guan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, L.; et al. A Matrix Metalloproteinase-1 Polymorphism, MMP1-1607 (1G>2G), Is Associated with Increased Cancer Risk: A Meta-Analysis Including 21,327 Patients. Dis. Markers 2018, 2018, 7565834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, P.; Li, J.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Fu, Q.; Wu, J.; Chen, Z.; Wu, D.; Zhang, Y.; et al. PSCA rs2294008 polymorphism with increased risk of cancer. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.M.; Sun, W.F. Association between matrix metalloproteinases polymorphisms and ovarian cancer risk: A meta-analysis and systematic review. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, W.; Kim, J.W.; Park, N.H.; Song, Y.S.; Kang, S.B.; Lee, H.P. Matrix metalloproteinase-1 promoter polymorphism and epithelial ovarian cancer: Does ethnicity matter? J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2007, 33, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenham, R.M.; Calingaert, B.; Ali, S.; Berchuck, A.; Schildkraut, J.M. Matrix metalloproteinase-1 gene promoter polymorphism and risk of ovarian cancer. J. Soc. Gynecol. Investig. 2003, 10, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Jin, X.; Kang, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, B.; Yang, S.; Lou, G.; et al. Polymorphisms in the promoter regions of the matrix metalloproteinases-1, -3, -7, and -9 and the risk of epithelial ovarian cancer in China. Gynecol. Oncol. 2006, 101, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.W.; Ahn, S.E.; Rengaraj, D.; Jung, H.J.; Yoon, B.I.; Kim, J.H.; Han, J.Y. Matrix metalloproteinase 3 is a stromal marker for chicken ovarian cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2011, 2, 1047–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.; Zhao, W.; Wu, L.; Liu, W.; Wang, Q.; Yu, Y.; He, Z.; Liu, J.; et al. Molecular regulation of ovarian cancer cell invasion. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 11359–11366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, V.W.; Ruiz, B.; Killen, J.L.; Coté, T.R.; Wu, X.C.; Correa, C.N.; Ries, L.A.; Edwards, B.K. Pathology and classification of ovarian tumors. Cancer 2003, 97, 2631–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cawkwell, L.Q. Direct multiplex amplification of DNA from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue sections. J. Clin. Pathol. Mol. Pathol. 2000, 53, 51–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Spitz, M.R.; Lei, L.; Mills, G.B.; Wu, X. A single nucleotide polymorphism in the matrix metalloproteinase-1 promoter enhances lung cancer susceptibility. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 7825–7829. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gnasso, A.; Motti, C.; Irace, C.; Mattioli, P.L.; Pujia, A.; Cortese, C.; Bernardini, S.; Federici, G.; Scipione, L.; De Franceschi, M.S.; et al. Genetic variation in human stromelysin gene promoter and common carotid geometry in healthy male subjects. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2000, 20, 1600–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, S.; Chen, X.; Wang, K.; Jiang, J.; Lu, Y.; Yang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, X.; Li, L.; Zhou, C.; et al. Tumor microenvironment in ovarian cancer peritoneal metastasis. Cancer Cell Int. 2023, 23, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, S.; Ghosh, N.; Saha, D.; Saha, B.; Roy, S.; Chakraborty, J.; Roy, A.; Roychoudhury, S.; Roychoudhury, S. Matrix metalloproteinase-1 [MMP-1] promoter polymorphisms are well linked with lower stomach tumor formation in the eastern Indian population. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Kong, B. Analysis of the association of matrix metalloproteinase-1 gene promoter [rs1799750] polymorphism and risk of ovarian cancer. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2015, 25, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulukuri, S.M.; Rao, J.S. Matrix metalloproteinase-1 promotes prostate tumor growth and metastasis. Int. J. Oncol. 2008, 32, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [PubMed Central]
- Six, L.; Grimm, C.; Leodolter, S.; Tempfer, C.; Sliutz, G.; Speiser, P.; Reinthaller, A.; Zeillinger, R.; Hefler, L.A. A polymorphism in the matrix metalloproteinase-1 gene promoter is associated with the prognosis of patients with ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2006, 100, 506–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Q. Relationship between matrix metalloproteinases and the occurrence and development of ovarian cancer. Br. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2017, 50, e6104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackawy, A.; Megahed, O. Significance of matrix metalloproteinase-1 and -3 gene polymorphisms and their expression in normal and neoplastic endometrium. Meta Gene. 2017, 14, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Tsai, P.H.; Kandaswami, C.C.; Lee, P.P.; Huang, C.J.; Hwang, J.J.; Lee, M.T.; Lin, Y.C.; Chen, C.L.; Shen, C.N.; et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 cooperates with transcription factor Snail to induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Sci. 2011, 102, 815–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egeblad, M.; Werb, Z. New functions for the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabło, C.A.; Matejczyk, M.; Rosochacki, S. Matrix metalloproteinases [MMPs], the main extracellular matrix [ECM] enzymes in collagen degradation, as a target for anticancer drugs. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Kasberg, W.C.; Celo, A.; Liang, X.; Fang, X.; Marjanovic, M.; Toth, M.; Fridman, R. Post-translational modification of the membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase [MT1-MMP] cytoplasmic tail impacts ovarian cancer multicellular aggregate dynamics. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 13111–13121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klymenko, Y.; Kim, O.; Loughran, E.; Yang, J.; Lombard, R.; Morris, R.; Lai, T.; Stack, M.S. Cadherin composition and multicellular aggregate invasion in organotypic models of epithelial ovarian cancer intraperitoneal metastasis. Oncogene 2018, 37, 3382–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Carey, P.; Low, E.; Harper, E.; Stack, M.S. Metalloproteinases in Ovarian Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radisky, D.C.; Levy, D.D.; Littlepage, L.E.; Liu, H.; Nelson, C.M.; Fata, J.E.; Leake, D.; Godden, E.L.; Albertson, D.G.; Nieto, M.A.; et al. Rac1b and reactive oxygen species mediate MMP-3-induced EMT and genomic instability. Nature. 2005, 436, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, A.; Kitajima, Y.; Sumi, K.; Sato, K.; Hagiwara, A.; Koga, Y.; Miyazaki, K. Snail and SIP1 increase cancer invasion by upregulating the MMP family in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Br. J. Cancer. 2004, 90, 1265–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, P.; Rothe, M.; Florin, A.; Wellmann, A.; Wernert, N. Invasive properties of serous human epithelial ovarian tumors are related to Ets-1, MMP-1, and MMP-9 expression. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2001, 8, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hantke, B.; Harbeck, N.; Schmalfeldt, B.; Kuhn, W.; Schmitt, M.; Luther, T.; Schwarzler, P.; Schindlbeck, C.; Janicke, F.; Hofler, H.; et al. Clinical relevance of matrix metalloproteinase-13 determined with a new highly specific and sensitive ELISA in ascitic fluid of advanced ovarian carcinoma patients. Biol. Chem. 2003, 384, 1247–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadlmann, S.; Pollheimer, J.; Moser, P.L.; Raggi, A.; Amberger, A.; Margreiter, R.; Offner, F.A. Cytokine-regulated expression of collagenase-2 [MMP-8] is involved in the progression of ovarian cancer. Eur. J. Cancer. 2003, 39, 2499–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Covic, L.; Sevigny, L.M.; Kaneider, N.C.; Lazar, J.B.; Kim, I.; Kuliopulos, A. Targeting a metalloprotease-PAR1 signaling system with cell-penetrating producing inhibits angiogenesis, ascites, and progression of ovarian cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 2746–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, A.; Tressel, S.L.; Kaimal, R.; Covic, L.; Kuliopulos, A. Identification of a metalloprotease-chemokine signaling system in the ovarian cancer microenvironment: Implications for antiangiogenic therapy. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 5880–5890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.Q.; Fisher, J.; Fishman, D.A. MMP-1-PAR1 axis mediates LPA-induced epithelial ovarian cancer [EOC] invasion. Gynecol. Oncol. 2011, 120, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Jia, J.; Liu, D.; Wang, M.; Wang, Z.; Wang, G.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, C.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Matrix metalloproteinase expressions play an important role in the prediction of ovarian cancer outcomes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabulut, S.; Aksit, E.; Tas, F.; Serilmez, M.; Duranyildiz, D.; Yasasever, V. Is there any diagnostic value of serum protease-activated receptor-1 [PAR1] levels on determining epithelial ovarian carcinoma? Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 4323–4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziebarth, J.D.; Bhattacharya, A.; Chen, A.; Cui, Y. PolymiRTS Database 2.0: Linking polymorphisms in microRNA target sites with human diseases and complex traits. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, S.; Eriksson, P.; Hamsten, A.; Kurkinen, M.; Humphries, S.E.; Henney, A.M. Progression of coronary atherosclerosis is associated with a common genetic variant of the human stromelysin-1 promoter which results in reduced gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 13055–13060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondi, M.L.; Turri, O.; Leviti, S.; Bernini, M.; Meregalli, S.; Scorza, R. MMP1 and MMP3 Polymorphisms in Promoter Regions and Cancer. Clin. Chem. 2000, 46, 2023–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghilardi, G.; Biondi, M.L.; Caputo, M.; Leviti, S.; DeMonti, M.; Guagnellini, E.; Scorza, R. A single nucleotide polymorphism in the matrix metalloproteinase-3 promoter enhances breast cancer susceptibility. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 3820–3823. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Freimark, B.D.; Feeser, W.S.; Rosenfeld, S.A. Multiple sites of the propeptide region of human stromelysin-1 are required for maintaining a latent form of the enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 26982–26987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul Aziz, M.; Jafrin, S.; Abdul Barek, M.; Siddiqua, T.F.; Paul, S.K.; Sultana, T. MMP-3 -1171 5A/6A promoter polymorphism and cancer susceptibility: An updated meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis. Future Oncol. 2023, 19, 1495–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szyllo, K.; Smolarz, B.; Romanowicz-Makowska, H.; Makowski, B.; Kulig, A.; Samulak, D.; Wilczyński, J. The promoter polymorphism of the matrix metalloproteinase 3 (MMP-3) gene in women with ovarian cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 21, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Ovarian Carcinoma Stages | Frequency [n%] |
|---|---|
| Stage I | n = 30, 30% |
| Stage II | n = 43, 43% |
| Stage III | n = 15, 15% |
| Stage IV | n = 12, 12% |
| Histological subtype | |
| SC | n = 45, 45% |
| MC | n = 15, 15% |
| EC | n = 27, 27% |
| CC | n = 13, 13% |
| Stages | Mean ± S.D of MMP-1 (ng/mL) | Mean ± S.D of MMP-3 (ng/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| Stage I [n = 30] | 4.71 ± 0.73 | 36.18 ± 1.14 |
| Stage II [n = 43] | 6.06 ± 0.96 | 37.12 ± 1.35 |
| Stage III [n = 15] | 6.2 ± 0.90 | 37.56 ± 1.04 |
| Stage IV [n = 12] | 6.61 ± 0.82 | 37.7 ± 0.86 |
| F-test, p-value | F = 21.14, p = 0.000 | F = 7.23, p = 0.000 |
| Histological subtype | Mean ± S.D of MMP-1 (ng/mL) | Mean ± S.D of MMP-3 (ng/mL) |
| SC, n = 45 | 5.6 ± 1.0 | 36.83 ± 1.63 |
| MC, n = 15 | 5.38 ± 1.09 | 36.24 ± 1.55 |
| EC, n = 27 | 5.8 ± 0.92 | 37.23 ± 1.33 |
| CC, n = 13 | 5.5 ± 0.99 | 36.8 ± 1.5 |
| F-test, p-value | F = 0.749, p = 0.520 | F = 1.355, p = 0.261 |
| Tumor Stages | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MMPs Genotype Patients = 100 | Stage 1, n = 30 n% | Stage 2, n = 43 n% | Stage3, n = 15 n% | Stage 4, n = 12 n% | ||||
| MMP-3 [5A/6A] | ||||||||
| 5A/5A | 7 | 23% | 9 | 21% | 3 | 20% | 2 | 17% |
| 5A/6A | 17 | 57% | 19 | 44% | 7 | 47% | 4 | 33% |
| 6A/6A | 6 | 20% | 15 | 35% | 5 | 33% | 6 | 50% |
| χ2 | 20.97 | |||||||
| p | 0.002 | |||||||
| 5A allele | 31 | 52% | 37 | 43% | 13 | 43.3% | 8 | 33% |
| 6A allele | 29 | 48% | 49 | 57% | 17 | 56.7% | 16 | 67% |
| χ2 | 7.33 | |||||||
| p | 0.061 | |||||||
| MMP-1 [1G/2G] | ||||||||
| 1G/1G | 9 | 30% | 12 | 28% | 4 | 27% | 2 | 17% |
| 1G/2G | 16 | 53% | 21 | 49% | 6 | 40% | 4 | 33% |
| 2G/2G | 5 | 17% | 10 | 23% | 5 | 33% | 6 | 50% |
| χ2 | 29.067 | |||||||
| p | 0.000 | |||||||
| 1G allele | 34 | 57% | 45 | 52% | 14 | 47% | 8 | 33% |
| 2G allele | 26 | 43% | 41 | 48% | 16 | 53% | 16 | 67% |
| χ2 | 12.83 | |||||||
| p | 0.005 | |||||||
| Carcinoma 100 | Controls 60 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MMP Genotypes | Histological Subtypes | |||||
| All patients n% | SC = 45 n% | MC = 15 n% | EC = 27 n% | CC = 13 n% | n% | |
| MMP-3 [5A/6A] | ||||||
| 5A/5A | 32 32% | 17 38% | 3 20% | 8 30% | 4 31% | 39 65% |
| 5A/6A | 46 46% | 23 51% | 4 27% | 13 48% | 6 46% | 15 25% |
| 6A/6A | 22 22% | 5 11% | 8 53% | 6 22% | 3 23% | 6 10% |
| χ2 | 16.26 * | 11.826 ** | ||||
| p | 0.000 | 0.066 | ||||
| 5A allele carrier | 110 55% | 57 63% | 10 33% | 29 54% | 14 59% | 93 77.5% |
| 6A allele | 90 45% | 33 37% | 20 67% | 25 46% | 12 46% | 27 22.5% |
| χ2 | 16.370 * | 18.266 ** | ||||
| p | 0.000 | 0.04 | ||||
| OR [95% CI] | 0.355 [0.213–0.593] * | 2.0 [1.387–22.883] ** | ||||
| MMP-1 [1G/2G] | ||||||
| 1G/1G | 25 25% | 14 31% | 2 13% | 7 26% | 21 5.4% | 42 70% |
| 1G/2G | 52 52% | 22 49% | 10 67% | 14 52% | 64 6.1% | 14 23% |
| 2G/2G | 23 23% | 9 20% | 3 20% | 6 22% | 53 8.5% | 4 7% |
| χ2 | 31.539 * | 4.36 | ||||
| p | 0.000 | 0.620 | ||||
| 1G allele | 102 51% | 50 55% | 14 47% | 28 52% | 10 38.5% | 98 81.6% |
| 2G allele | 98 49% | 40 45% | 16 53% | 26 48% | 16 61.5% | 22 18.4% |
| χ2 | 30.1 * | 2.62 ** | ||||
| p | 0.000 | 0.453 | ||||
| OR [95% CI] | 0.23 [0.136–0.401] * | 2.673 [1.786–4.0] | ||||
| Parameters | MMP-1 [ng/mL] | MMP-3 [ng/mL] | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1G/1G | 1G/2G | 2G/2G | ANOVA [F-Value] p-Value | 5A/5A | 5A/6A | 6A/6A | ANOVA p-Value | |
| Controls [n = 60] | [n = 42] | [n = 14] | [n = 4] | F = 29.36 | n = 39 | n = 15 | n = 6 | F = 9.33 |
| 2.12 ± 0.49 | 3.05 ± 0.5 | 3.42 ± 0.15 | p = 0.000 | 34.8 ± 2.3 | 35.3 ± 1.37 | 36.7 ± 0.60 | p = 0.01 | |
| All patients [n = 100] | [n = 27] | [n = 47] | [n = 26] | F = 90.25 | n = 21 | n = 47 | n = 32 | F = 9.32 |
| 4.35 ± 0.60 | 5.7 ± 0.64 | 6.50 ± 0.53 | p = 0.000 | 36.1 ± 1.50 | 36.59 ± 1.60 | 37.6 ± 0.80 | p = 0.000 | |
| Stage I [n = 30] | n = 9 | n = 16 | n = 5 | F = 6.02 | n = 7 | n = 17 | n = 6 | F = 6.84 |
| 4.37 ± 0.57 | 4.67 ± 0.47 | 5.5 ± 0.34 | p = 0.007 | 35.4 ± 1.11 | 36.7 ± 1.2 | 37.7 ± 1.23 | p = 0.004 | |
| Stage II [n = 43] | n = 12 | n = 21 | n = 10 | F = 40.7 | n = 9 | n = 19 | n = 15 | F = 8.29 |
| 4.88 ± 0.78 | 6.29 ± 0.44 | 6.98 ± 0.48 | p = 0.000 | 35.8 ± 1.94 | 36.08 ± 1.70 | 37.95 ± 0.63 | p = 0.001 | |
| Stage III [n = 15] | n = 4 | n = 6 | n = 5 | F = 13.28 | n = 3 | n = 7 | n = 5 | F = 5.716 |
| 5.17 ± 0.48 | 6.06 ± 0.64 | 7.16 ± 0.56 | p = 0.001 | 36.04 ± 0.35 | 37.01 ± 0.63 | 37.73 ± 0.86 | p = 0.018 | |
| Stage IV [n = 12] | n = 2 | n = 4 | n = 6 | F = 7.07 | n = 2 | n = 4 | n = 6 | F = 59.23 |
| 5.56 ± 0.31 | 6.23 ± 0.43 | 7.22 ± 0.71 | p = 0.014 | 36.3 ± 0.07 | 36.81 ± 0.22 | 37.9 ± 0.22 | p = 0.000 | |
| AUC | SE | p-Value | CI | Sensitivity | Specificity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MMP-3 | 0.816 | 0.034 | 0.000 | 0.749–0.883 | 80.0% | 75.3% |
| MMP-1 | 0.956 | 0.15 | 0.000 | 0.926–0.986 | 94.0% | 90.0% |
| CEA | 0.64 | 0.062 | 0.032 | 0.52–0.76 | 55.6% | 61.6% |
| AUC | SE | p-Value | CI | Sensitivity | Specificity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MMP-3 | 0.797 | 0.043 | 0.000 | 0.713–0.80 | 77.8% | 70.0% |
| MMP-1 | 0.806 | 0.43 | 0.000 | 0.721–0.890 | 74.1% | 72.6% |
| CEA | 0.703 | 0.059 | 0.002 | 0.588–0.819 | 62.3% | 70.8% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mackawy, A.M.H.; Alharbi, H.O.; Almatroudi, A.; Alwanian, W.M.; Allemailem, K.S. Matrix Metalloproteinases 1 and 3 in Ovarian Cancer: Diagnostic and Prognostic Potential of Genetic Variants and Expression Profiling. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1521. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15121521
Mackawy AMH, Alharbi HO, Almatroudi A, Alwanian WM, Allemailem KS. Matrix Metalloproteinases 1 and 3 in Ovarian Cancer: Diagnostic and Prognostic Potential of Genetic Variants and Expression Profiling. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(12):1521. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15121521
Chicago/Turabian StyleMackawy, Amal Mohamad Husein, Hajed Obaid Alharbi, Ahmad Almatroudi, Wanian M. Alwanian, and Khaled S. Allemailem. 2025. "Matrix Metalloproteinases 1 and 3 in Ovarian Cancer: Diagnostic and Prognostic Potential of Genetic Variants and Expression Profiling" Diagnostics 15, no. 12: 1521. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15121521
APA StyleMackawy, A. M. H., Alharbi, H. O., Almatroudi, A., Alwanian, W. M., & Allemailem, K. S. (2025). Matrix Metalloproteinases 1 and 3 in Ovarian Cancer: Diagnostic and Prognostic Potential of Genetic Variants and Expression Profiling. Diagnostics, 15(12), 1521. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15121521







