Abstract
Background/Objectives: Timely and effective clinical management of leishmaniasis depends on a deep understanding of parasite biology and drug resistance mechanisms. Phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC) enzymes are critical for parasite survival and immune evasion and possibly influence treatment outcomes. This study aimed to characterize the PI-PLC gene family in the Leishmania infantum and Leishmania major genomes, with a focus on their expression profiles in antimony-susceptible and -resistant strains to uncover their diagnostic and prognostic relevance. Methods: This study conducted a comprehensive genome-wide screening to identify PI-PLC genes in L. infantum and L. major, followed by detailed analyses of their gene structures, conserved motifs, chromosomal localization, and phylogenetic relationships. To explore potential roles in drug resistance and clinical prognosis, RNA-seq data from antimony-resistant and -susceptible L. infantum strains were analyzed for differential gene expression. Results: Twenty-two PI-PLC genes were identified in each species, displaying conserved catalytic domains and diverse biochemical characteristics. Phylogenetic and chromosomal analyses revealed gene clustering and distribution patterns. Importantly, expression profiling highlighted several PI-PLC genes with differential regulation in resistant strains, suggesting a role in treatment response and potential as molecular markers. Conclusions: Our findings suggest that PI-PLC genes may be associated with drug susceptibility in L. infantum, warranting further functional investigation to validate their role as potential molecular markers.
1. Introduction
Leishmaniasis is an infectious disease caused by the obligate intracellular parasite Leishmania protozoan, transmitted by the bite of its vector, infected sandflies (Phlebotomus or Lutzomyia spp.) [1]. Globally, approximately 12 million people are estimated to be affected, while an estimated 350 million people are reported to be at risk of infection [2,3]. Although the clinical manifestations caused by the parasite can appear in various forms, they typically encompass a broad spectrum, ranging from skin lesions (cutaneous form) that often result in disfigurement and heal with scarring if left untreated, to potentially fatal visceral involvement (visceral form). The proliferation of Leishmania parasites within immune cells, including neutrophils, monocytes, and macrophages, and the subsequent initiation of the immune response against these parasites, constitute the underlying causes of the clinical symptoms observed in the disease [4].
Leishmania major and Leishmania infantum are two common species that frequently cause disease in humans and can lead to significant health complications. Cutaneous infections are commonly associated with species such as L. tropica and L. major, while visceral manifestations typically involve species like L. donovani and L. infantum. Studies have suggested that variations in gene expression regulation may be responsible for the clinical differences observed between Leishmania species [5,6]. Due to the absence of an effective vaccine and the resistance of the parasite to current medications, an enhanced understanding of Leishmania cell biology is crucial to developing effective treatments. In this context, a deeper exploration of the molecular structures of these species holds vital importance for devising future therapeutic and preventive strategies.
One of the most important processes in the intracellular proliferation of parasites is membrane biogenesis [7]. The production and homeostasis of membranes constitute a complex metabolic network that also involves phospholipid modification and recycling. Phospholipids are degraded by phospholipases, which are classified into four groups A, B, C, and D based on the enzymes’ activities in hydrolyzing specific ester bonds [8]. The enzyme phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC) plays a vital role in the survival, proliferation, and disease development of many parasitic pathogens, including Leishmania. PI-PLC is known to facilitate parasite invasion into host cells, modulate the host cell immune response, and increase the virulence of the pathogen [8,9,10]. Therefore, investigating the role of the PI-PLC enzyme in Leishmania species and performing genome-wide characterization of its gene family could offer significant insights into the biology and virulence of these parasites. Furthermore, the inhibition or targeting of this enzyme could be considered as a potential therapeutic strategy to prevent parasite invasion into host cells and alter the disease’s course.
L. major was the first species to have its genome sequenced and has been the model for subsequent genome studies of other Leishmania species [11]. In 2007, the whole genome sequence of L. infantum was sequenced [12]. Although the genome sequences of these parasites are available, the genes involved in various metabolic pathways have not been investigated in detail. In this study, we conducted a comparative study to bioinformatically identify and analyze the PI-PLC gene family in the L. major and L. infantum genomes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification of PI-PLC Gene Family Members in the L. infantum and L. major Genomes
In this study, genome-wide identification of PI-PLC genes in L. infantum and L. major parasites was carried out using bioinformatic tools. The genomes of L. infantum JPCM5 (assembly ASM287v2) and L. major Friedlin strain (assembly ASM272v2) and the PI-PLC sequences of L. infantum and L. major were downloaded from the NCBI (National Center for Biotechnology Information). The L. infantum JPCM5 strain genome was used for analysis because it represents the reference genome for this species and offers high-quality, extensively annotated genomic data, which facilitates reliable comparative and functional genomics [13]. Hidden Markov Model (HMM) profiles for PLC-X (PF00388), PLC-Y (PF00387), and PLC-C2 (PF00168) were retrieved from the Pfam database (http://pfam.xfam.org/ [accessed on 8 May 2024]) and used to identify genes using HMMER Version 3.0 (http://hmmer.janelia.org/ [accessed on 3 July 2024]) with default parameters (E-value < e−20). The NCBI CDD (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/cdd/ [accessed on 3 July 2024]) database was used to validate all candidate proteins. The InterPro and Pfam databases were employed to confirm sequence verification. Biochemical properties such as isoelectric point (pI), molecular weight (MW), and protein size were identified using the online ExPASy tool (https://web.expasy.org/compute_pi/ [accessed on 15 July 2024]). The subcellular distribution of proteins were predicted using CELLO Version 2.5 (http://cello.life.nctu.edu.tw/ [accessed on 23 July 2024]).
2.2. Chromosome Locations and Synteny Analysis
For chromosomal localization of the LiPLCs and LmPLCs, the start and end points of the genes were retrieved from NCBI. Genetic maps were drawn using the online tool MapGene2Chrom Version 2 (http://mg2c.iask.in/mg2c_v2.1/index_cn.html [accessed on 25 July 2024]).
2.3. Conserved Motif and Gene Structure Analysis
The TBtools software Version 1.12 was used to visualize the L. infantum and L. major LiPLCs and LmPLCs gene structures [14]. The online software MEME Suite Version 5.5.5 (https://meme-suite.org/meme/tools/meme [accessed on 25 July 2024]) was used to perform motif prediction analysis of the L. infantum and L. major PI-PLCs [15].
2.4. Gene Expression Profiling and Functional Analysis
The identified LiPI-PLC genes were used for detecting the gene expression data from RNA-seq data available in the SRA database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra [accessed on 30 July 2024]) under project number PRJNA348689 [16]. RNA-seq data from resistant (SRR5574933 and SRR5575024) and susceptible (SRR5575022, SRR5575025, SRR5575026) L. infantum lines to potassium antimonyl tartrate (SbIII) were used for expression analysis. The clean reads were aligned to the L. infantum JPCM5 reference genome by using the HISAT2 algorithm. DESeq2 was utilized to identify differentially expressed genes, with genes having an adjusted p-value < 0.05 and fold-change > 1.5 considered as differentially expressed. Gene Ontology enrichment analysis was conducted using AmiGO Version 2 (http://amigo.geneontology.org/ [accessed on 30 July 2024]) [17].
3. Results
3.1. The Bioinformatic Identification of PI-PLCs in L. infantum and L. major
In this study, the HMM tool Version 3 was used to screen the conserved domains PLC-C, PLC-X, and PLC-Y in the genomes of L. infantum and L. major. A total of 22 PI-PLC gene family members were identified in L. infantum and L. major, individually. The basic physicochemical properties and gene characteristics are presented in Table 1 for L. infantum and Table 2 for L. major. The analyses revealed that PI-PLC family members contained at least one domain in Leishmania species, with the PLC-C domain being the most abundant. The coding sequence (CDS) lengths of the 22 LiPLC genes ranged from 738 bp (XP_001467341.1) to 7029 bp (XP_001462688.1), and the CDS lengths of the 22 LmPLC genes ranged from 804 (XP_001685053.1) to 6726 (XP_003721595.1). Both LiPI-PLC and LmPI-PLC genes consisted of only one exon without introns (Supplementary Figures S1 and S2).

Table 1.
Basic physicochemical properties and gene characteristics of L. infantum PI-PLC genes.

Table 2.
Basic physicochemical properties and gene characteristics of L. major PI-PLC genes.
We also performed the physicochemical characterization of all PI-PLC protein sequences. The protein lengths for the LiPI-PLCs ranged from 245 amino acids (aa) (XP_001467341.1) to 2342 aa (XP_001462688.1), while the LmPI-PLC proteins ranged from 267 aa (XP_001685053.1) to 2241 aa (XP_003721595.1). The highest molecular weight for the LiPI-PLCs was 251.464 kDa, and for the LmPI-PLCs it was 241.67 kDa. The average molecular weights were 101.102 kDa for L. infantum and 107.364 kDa for L. major. The isoelectric point (pI) for the LiPI-PLCs ranged from 4.40 (XP_001464332.1) to 9.46 (XP_001464095.2) with a median of 7.32, while for the LmPI-PLCs, the pI ranged from 4.40 (XP_001687745.1) to 9.41 (XP_001681820.1) with a median of 7.28. Subcellular localization predictions, based on in silico analysis using CELLO, suggest that the proteins are primarily located in the nucleus, plasma membrane, and cytoplasm; however, these localizations have not been experimentally validated.
3.2. Phylogenetic and Conserved Motif Analysis of the LiPI-PLC and LmPI-PLC Proteins
In order to accurately depict the evolutionary relationships of the LiPI-PLC and LmPI-PLC proteins, we conducted phylogenetic analyses. Since there were not enough sequences in other species, we performed analyses within species and between L. infantum and L. major. Based on protein sequences, the LiPI-PLC gene family was classified into five groups, with Group IV consisting of the highest number of proteins, while Group V had only one representative (Figure 1). In L. major, a total of 22 LmPI-PLCs were classified into six groups, with Group III containing the highest number of proteins (Figure 2).
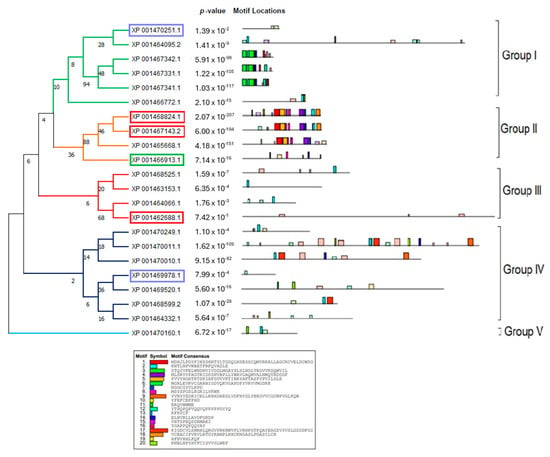
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic analysis of the LiPI-PLC gene family in L. infantum. The tree was constructed using protein sequences of the PI-PLC gene family, highlighting classification into five groups.
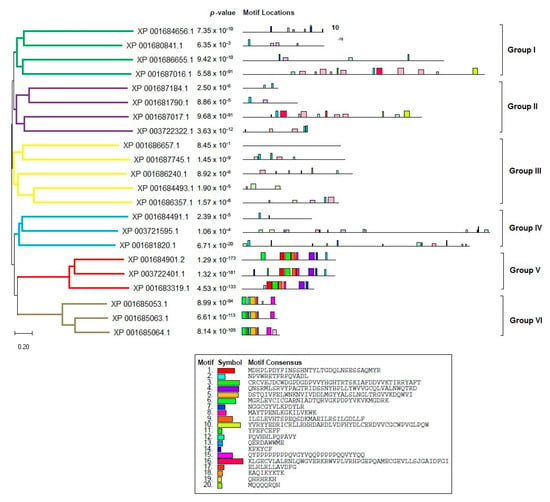
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic analysis of the LmPI-PLC gene family in L. major. The tree illustrates six distinct groups based on protein sequences.
The concatenated motif structures of the PI-PLC protein sequences we identified in Leishmania species were also analyzed using MEME Suite (Supplementary Figure S3). In particular, the comparative motif profiles of the LmXP_001685053.1 and LiXP_001467331.1 proteins show that these two proteins are highly similar and are likely orthologous genes. Sequence alignment revealed 87% identity among these genes, suggesting they may have arisen from recent gene duplication events.
The phylogenetic tree of PI-PLC genes based on protein sequences from L. infantum and L. major is shown in Figure 3. In the phylogenetic tree, PI-PLC family proteins were grouped into eight subfamilies. LiPI-PLC XP001470160.1 and LmPI-PLC XP001686657.1 were clustered separately. Group I had the highest number of PI-PLC family members.
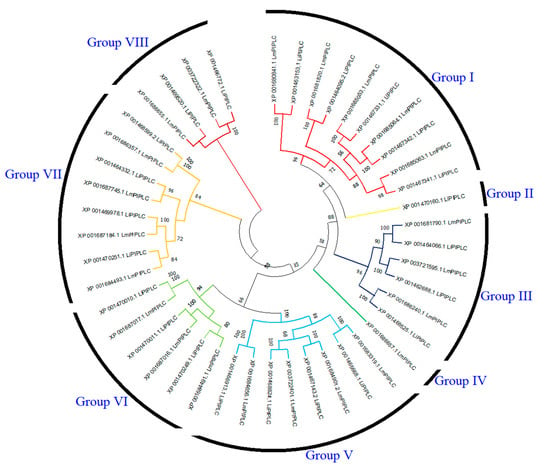
Figure 3.
Comparative phylogenetic tree of PI-PLC proteins in L. infantum and L. major. PI-PLC proteins were grouped into eight subfamilies based on sequence homology and evolutionary divergence. Different colors represent different subfamilies.
3.3. Chromosome Distribution, Gene Structure, and Synteny Analysis of the LiPI-PLC and LmPI-PLC Genes
The chromosomal localization was conducted using MG2C. According to the gene locus data, 22 LiPI-PLC and LmPI-PLC genes were mapped to 12 chromosomes (Chr01, Chr06, Chr13, Chr14, Chr22, Chr28, Chr29, Chr30, Chr31, Chr34, Chr35, and Chr36). Chr36 had the highest number of genes in both species (Supplementary Figures S4 and S5). To understand the evolutionary relationships of the LiPI-PLC and LmPI-PLC genes, syntenic analysis was performed between them. The results showed that the LiPI-PLC and LmPI-PLC genes were closely related.
3.4. Expression Pattern of the Genes
The transcriptomic profiles showed PI-PLC expression in L. infantum. The analysis revealed that PI-PLC genes were expressed at higher levels in susceptible lines of L. infantum (Figure 4). Out of the 22 LiPI-PLC transcripts, four of them were significantly expressed. All the transcripts, XP_001468599.2 (1.65-fold), XP_001469978.1 (2.01-fold), XP_001469520.1 (2.13-fold), and XP_001470011.1 (2.36-fold), were upregulated in the SbIII-susceptible L. infantum.
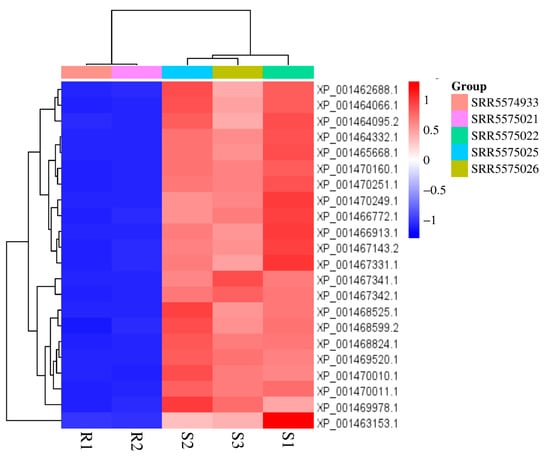
Figure 4.
Heatmap of PI-PLC gene expression profiles in susceptible and resistant L. infantum lines. The heatmap illustrates the differential expression of the PI-PLC genes based on RNA-seq data.
3.5. Gene Ontology
In the Gene Ontology (GO) and KEGG analysis of the PI-PLC genes, only biological process (BP) and molecular function (MF) information were accessible. We identified 13 items under BP and 25 items under MF. The most enriched BP items included signal transduction, signaling, and regulation of membrane potential. Under MF, potassium channel activity, hydrolase activity acting on ester bonds, and potassium ion transmembrane transporter activity were significantly enriched (Figure 5).
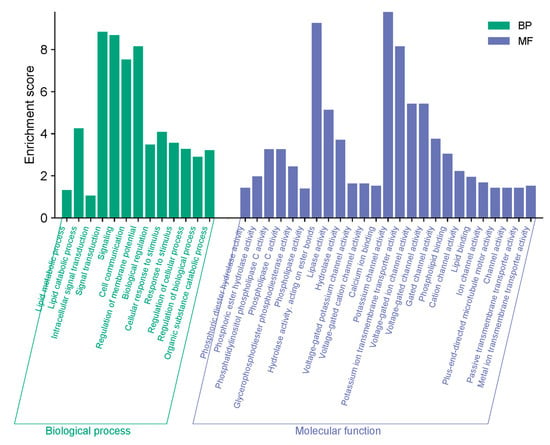
Figure 5.
Predicted gene ontology analysis of the PI-PLC genes in L. infantum and L. major. The GO enrichment analysis identifies the most significant biological processes and molecular functions associated with the PI-PLC genes.
4. Discussion
Leishmaniasis is a major global health concern caused by protozoan parasites of the genus Leishmania. Present in over 100 countries, it manifests in various clinical forms, most notably cutaneous and visceral leishmaniasis. Despite the existence of treatment options, increasing drug resistance continues to drive the search for novel therapeutic strategies [18].
Phospholipases are known to modulate host immune responses by generating lipid mediators that either promote inflammation or suppress immune functions. For example, deletion of the phospholipase C gene in Toxoplasma gondii reduced parasite replication and virulence in mice [19], while inhibition of phospholipase A2 in Plasmodium falciparum led to diminished parasite growth and increased susceptibility to antimalarials [20]. These examples underscore the therapeutic potential of targeting phospholipase genes.
In this study, we performed a genome-wide characterization of the PI-PLC gene family in L. infantum and L. major. To our knowledge, this is the first detailed genomic investigation of PI-PLCs in Leishmania species. We identified 22 genes containing PI-PLC-X, PI-PLC-Y, and C2 domains. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that LiPI-PLC and LmPI-PLC members clustered into five and six distinct groups, respectively. All but two proteins (LiXP_001470160.1 and LmXP_001686657.1) formed species-specific clusters, indicating high conservation.
To provide preliminary insights into the potential functions of the Leishmania PLC proteins identified in this study, we inferred their subcellular localization and key physicochemical features. In the context of Leishmania biology, subcellular localization is a critical factor. Membrane-associated or secreted PLCs may participate in host–parasite interactions, signaling cascades, or immune evasion mechanisms [21,22]. Therefore, predicting the localization of PLC proteins based on their physicochemical characteristics facilitates the development of testable hypotheses regarding their roles in parasite virulence and survival. These predictions form the foundation for future functional studies, including experimental validation through proteomics or localization assays. The biochemical properties and chromosomal localization of clustered PI-PLC proteins were nearly identical across both species, suggesting functional conservation and evolutionary stability. However, the two divergent genes, LiXP_001470160.1 and LmXP_001686657.1, differed significantly in sequence characteristics, localization, and potentially, function. Notably, LiXP_001470160.1 was localized to the plasma membrane, while its L. major counterpart was nuclear, implying that these genes may play species-specific roles in host–parasite interactions.
In particular, the high level of similarity between the motif profiles of LmXP_001685053.1 and Li XP_001467331.1 suggests that they may be orthologous genes. The presence of similar motif clusters in the N-terminal regions of both proteins indicates functionally conserved catalytic regions. In particular, the presence of motif sequences in the same positions supports the evolutionary derivation of these genes from a common ancestor. This indicates the functional importance of the PI-PLC family and also reveals the conserved structure of the genes across species. This highlights the evolutionary stability of the PI-PLC gene family in Leishmania species and suggests that these genes may play critical roles in host–pathogen interactions.
In the light of motif and sequence similarity analyses, it was evaluated that XP_001685053.1 and LiXP_001467331.1 genes, apart from interspecies orthologs, may have been formed by genomic duplication events in the past and may have been preserved in multi-copy regions, especially on chromosome 31. It is known that chromosome 31 is frequently supernumerary in Leishmania genomes and hosts many virulence factors. Therefore, the functional role as well as the evolutionary origin of this gene pair is worth investigating in further studies.
Given that PI-PLC proteins are known to be involved in signal transduction, immune modulation, and membrane remodeling, their conserved nature suggests a possible role in parasite survival and virulence. Interestingly, although the PI-PLC gene family is structurally conserved between L. major and L. infantum, the distinct clinical manifestations of these species suggest that species-specific regulation and localization of the PI-PLCs may contribute to pathogenic differences. These variations could influence clinical outcomes such as disease progression and treatment response, highlighting a potential role for PI-PLC genes in clinical prognosis and phenotype-based diagnosis [23,24].
Furthermore, previous studies have shown that gene expression profiles are strongly linked to antimony resistance in Leishmania. Resistant strains often display upregulation of stress response and resistance-related genes and downregulation of genes such as mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 (MAPK1) and aquaglyceroporin (AQP), both of which are implicated in drug uptake and efflux mechanisms [25,26,27].
Both L. major and L. infantum were found to possess 22 PI-PLC family members, indicating a high level of conservation in gene count between the two species. This conservation suggests that the PI-PLC repertoire may be essential for core biological processes in Leishmania spp. Despite having the same number of PI-PLC genes, subtle sequence variations or divergence in regulatory elements may lead to species-specific expression profiles and functional adaptations.
When compared to the known PI-PLC families in other eukaryotes, the Leishmania PI-PLCs exhibit partial structural similarity, such as the presence of conserved catalytic X and Y domains. However, the typical regulatory domains found in mammalian PLC families are largely absent or highly divergent. This suggests that these parasite enzymes may not fit neatly into classical PI-PLC families [28,29]. We propose that Leishmania PI-PLC family members may constitute a divergent and functionally specialized set of proteins adapted to parasitic life.
The genes LmXP_001685053.1 and LiXP_001467331.1, members of the PI-PLC family, are notable for their highly conserved motif structures and similar expression profiles. Such genes represent promising candidates as potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets for both diagnosis and treatment. Their conserved features suggest potential utility in RNA-based diagnostics, development of specific inhibitors, resistance prediction, and patient management strategies. However, further validation through in vitro and in vivo studies—such as gene knockout/knockdown experiments and pharmacological inhibition assays—will be essential to confirm their functional relevance.
5. Conclusions
In our study, we observed that the PI-PLC gene family was significantly upregulated in antimony-susceptible L. infantum strains compared to resistant strains. This suggests that PI-PLC genes may be downregulated as part of an adaptive resistance mechanism, potentially affecting antimony uptake or immune evasion strategies. These results underscore the potential clinical relevance of PI-PLC genes not only as molecular markers for predicting drug susceptibility but also as targets for precision therapy.
Overall, our findings indicate that the PI-PLC gene family may influence key clinical outcomes in leishmaniasis, including disease progression, treatment efficacy, and resistance development. Thus, PI-PLC genes may serve as valuable molecular biomarkers in clinical settings for both diagnostic and prognostic purposes, as well as targets for novel antileishmanial therapies.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/diagnostics15111433/s1, Figure S1: Gene structure analysis of the L. infantum PI-PLC genes; Figure S2: L. major gene structure; Figure S3: Conserved motifs identified in the PI-PLC proteins from L. infantum and L. major using combined MEME analysis; Figure S4: Chromosomal distribution of the PI-PLC genes in L. infantum; Figure S5: Chromosomal distribution of the PI-PLC genes in L. major.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.S. and S.S.O.; methodology, S.S. and T.G.-T.; software, T.G.-T.; validation, S.S., S.S.O. and T.G.-T.; formal analysis, S.S.; investigation, S.S. and T.G.-T.; resources, S.S.O.; data curation, S.S. and S.S.O.; writing—original draft preparation, S.S. and S.S.O.; writing—review and editing, S.S. and T.G.-T.; visualization, T.G.-T.; supervision, T.G.-T.; and project administration, S.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Most of the data generated or analyzed are included in the article. The remaining datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| PI-PLC | phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase |
| NCBI | National Center for Biotechnology Information |
| HMM | Hidden Markov Model |
| pI | isoelectric point |
| MW | molecular weight |
| SRA | sequence read archive |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| BP | biological process |
| MF | molecular function |
| MAPK1 | mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 |
| AQP | aquaglyceroporin |
References
- Torres-Guerrero, E.; Quintanilla-Cedillo, M.R.; Ruiz-Esmenjaud, J.; Arenas, R. Leishmaniasis: A review. F1000Research 2017, 6, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reithinger, R.; Dujardin, J.C.; Louzir, H.; Pirmez, C.; Alexander, B.; Brooker, S. Cutaneous leishmaniasis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2007, 7, 581–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, F.; Sanchez, M.R. New and re-emerging cutaneous infectious diseases in Latin America and other geographic areas. Dermatol. Clin. 2003, 21, 655–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomiotto-Pellissier, F.; Bortoleti, B.T.D.S.; Assolini, J.P.; Gonçalves, M.D.; Carloto, A.C.M.; Miranda-Sapla, M.M.; Conchon-Costa, I.; Bordignon, J.; Pavanelli, W.R. Macrophage Polarization in Leishmaniasis: Broadening Horizons. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulusan Bağcı, Ö.; Sadıqova, A.; Caner, A. Comparative Gene Expression Profiles of Leishmania major and Leishmania infantum Promastigotesa. Turk. Parazitol. Derg. 2021, 45, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, H.W.; Berman, J.D.; Davies, C.R.; Saravia, N.G. Advances in leishmaniasis. Lancet 2005, 366, 1561–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, D.M.; Oghumu, S.; Gupta, G.; McGwire, B.S.; Drew, M.E.; Satoskar, A.R. Mechanisms of cellular invasion by intracellular parasites. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 1245–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flammersfeld, A.; Lang, C.; Flieger, A.; Pradel, G. Phospholipases during membrane dynamics in malaria parasites. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 308, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burda, P.C.; Ramaprasad, A.; Bielfeld, S.; Pietsch, E.; Woitalla, A.; Söhnchen, C.; Singh, M.N.; Strauss, J.; Sait, A.; Collinson, L.M.; et al. Global analysis of putative phospholipases in Plasmodium falciparum reveals an essential role of the phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C in parasite maturation. mBio 2023, 14, e0141323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, V.P.; Galizzi, M.; Salto, M.L.; Docampo, R.; Moreno, S.N. Developmental expression of a Trypanosoma cruzi phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C in amastigotes and stimulation of host phosphoinositide hydrolysis. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 4206–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivens, A.C.; Peacock, C.S.; Worthey, E.A.; Murphy, L.; Aggarwal, G.; Berriman, M.; Sisk, E.; Rajandream, M.-A.; Adlem, E.; Aert, R.; et al. The genome of the kinetoplastid parasite, Leishmania major. Science 2005, 309, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peacock, C.S.; Seeger, K.; Harris, D.; Murphy, L.; Ruiz, J.C.; Quail, M.A.; Peters, N.; Adlem, E.; Tivey, A.; Aslett, M.; et al. Comparative genomic analysis of three Leishmania species that cause diverse human disease. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, E.; González-de la Fuente, S.; Solana, J.C.; Tabera, L.; Carrasco-Ramiro, F.; Aguado, B.; Requena, J.M. Leishmania infantum (JPCM5) Transcriptome, Gene Models and Resources for an Active Curation of Gene Annotations. Genes 2023, 14, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.H.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Boden, M.; Buske, F.A.; Frith, M.; Grant, C.E.; Clementi, L.; Ren, J.; Li, W.W.; Noble, W.S. MEME SUITE: Tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W202–W208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, J.M.; Gonçalves, L.O.; Liarte, D.B.; Lima, D.A.; Guimarães, F.G.; Resende, D.d.M.; Santi, A.M.M.; de Oliveira, L.M.; Velloso, J.P.L.; Delfino, R.G.; et al. Comparative transcriptomic analysis of antimony resistant and susceptible Leishmania infantum lines. Parasit. Vectors 2020, 13, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbon, S.; Ireland, A.; Mungall, C.J.; Shu, S.; Marshall, B.; Lewis, S.; the AmiGO Hub; Web Presence Working Group. AmiGO: Online access to ontology and annotation data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 288–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashford, R.W. The leishmaniases as emerging and reemerging zoonoses. Int. J. Parasitol. 2000, 30, 1269–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.K.; Heckendorn, J.; Martorelli Di Genova, B.; Koch, L.L.; Rooney, P.J.; Morrissette, N.; Lebrun, M.; Knoll, L.J. A Toxoplasma gondii patatin-like phospholipase contributes to host cell invasion. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zidovetzki, R.; Sherman, I.W.; O’Brien, L. Inhibition of Plasmodium falciparum phospholipase A2 by chloroquine, quinine, and arteether. J. Parasitol. 1993, 79, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConville, M.J.; Mullin, K.A.; Ilgoutz, S.C.; Teasdale, R.D. Secretory pathway of trypanosomatid parasites. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2002, 66, 122–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppens, I.; Joiner, K.A. Host but not parasite cholesterol controls Toxoplasma cell entry by modulating organelle discharge. Mol. Biol. Cell 2003, 14, 3804–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis-Cunha, J.L.; Valdivia, H.O.; Bartholomeu, D.C. Gene and Chromosomal Copy Number Variations as an Adaptive Mechanism Towards a Parasitic Lifestyle in Trypanosomatids. Curr. Genom. 2018, 19, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patino, L.H.; Muskus, C.; Ramírez, J.D. Transcriptional responses of Leishmania (Leishmania) amazonensis in the presence of trivalent sodium stibogluconate. Parasit. Vectors 2019, 12, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashutosh; Garg, M.; Sundar, S.; Duncan, R.; Nakhasi, H.L.; Goyal, N. Downregulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 of Leishmania donovani field isolates is associated with antimony resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maharjan, M.; Singh, S.; Chatterjee, M.; Madhubala, R. Role of aquaglyceroporin (AQP1) gene and drug uptake in antimony-resistant clinical isolates of Leishmania donovani. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2008, 79, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, M.; Goyal, N. MAPK1 of Leishmania donovani modulates antimony susceptibility by downregulating P-glycoprotein efflux pumps. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 3853–3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebecchi, M.J.; Pentyala, S.N. Structure, function, and control of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C. Physiol. Rev. 2000, 80, 1291–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadamur, G.; Ross, E.M. Mammalian phospholipase C. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2013, 75, 127–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).