Assessment of the Diagnostic Accuracy of Artificial Intelligence Software in Identifying Common Periodontal and Restorative Dental Conditions (Marginal Bone Loss, Periapical Lesion, Crown, Restoration, Dental Caries) in Intraoral Periapical Radiographs
Abstract
1. Introduction
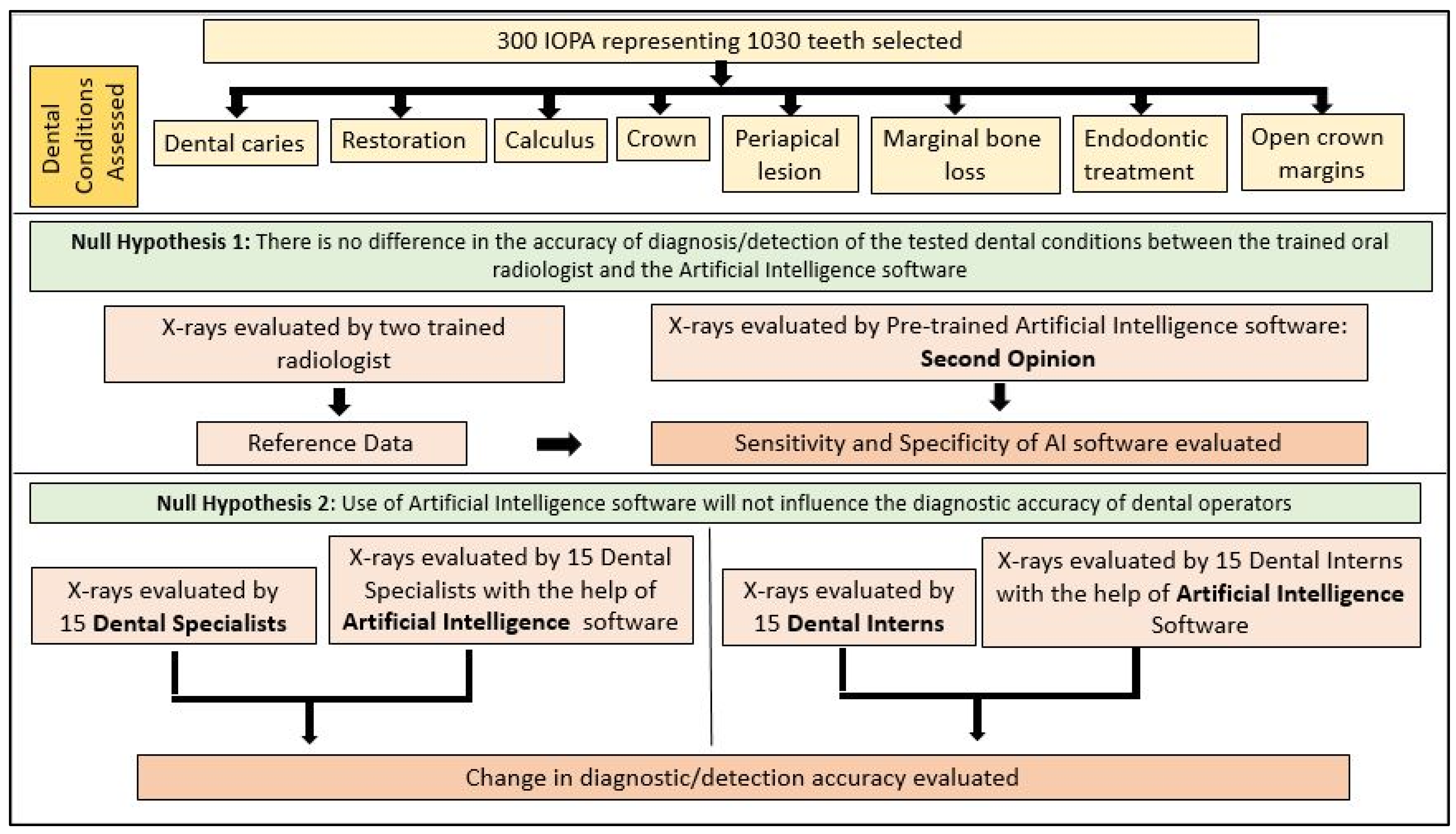
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Image Dataset Preparation
2.2. AI Software Architecture
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. AI in the Detection of Caries
4.2. AI in the Detection of Bone Loss
4.3. AI in the Detection of Periapical Lesions
4.4. AI in Detecting Open Crown Margins and Calculus
4.5. AI in the Detection of Dental Treatments (Crowns, Restorations, and Endodontic Treatments)
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eggmann, F.; Blatz, M.B. Recent Advances in Intraoral Scanners. J. Dent. Res. 2024, 103, 1349–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, H.; Fellows, C.; An, H. Digital Technologies for Restorative Dentistry. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2022, 66, 567–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Riet, T.C.T.; Chin Jen Sem, K.T.H.; Ho, J.T.F.; Spijker, R.; Kober, J.; de Lange, J. Robot technology in dentistry, part one of a systematic review: Literature characteristics. Dent. Mater. 2021, 37, 1217–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.; Durlik, I.; Łobodzińska, A.; Dorobczyński, L.; Jasionowski, R. AI in Context: Harnessing Domain Knowledge for Smarter Machine Learning. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 11612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Ji, X.; Rainey, C.; Zhang, J.; Lu, W. Integrating Machine Learning with Human Knowledge. iScience 2020, 23, 101656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundberg, L.; Holmström, J. Fusing Domain Knowledge with Machine Learning: A Public Sector Perspective. J. Strateg. Inf. Syst. 2024, 33, 101848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozan, N.M.; Kotsyubynska, Y.Z.; Zelenchuk, G.M. Using the artificial neural networks for identification unknown person. IOSR J. Dent. Med. Sci. 2017, 1, 107–113. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, J.A.; Krois, J.; Schwendicke, F. Demystifying artificial intelligence and deep learning in dentistry. Braz. Oral Res. 2021, 35, e094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellman, R. Artificial Intelligence: Can Computers Think? Thomson Course Technology; Boyd & Fraser: Boston, MA, USA, 1978; 146p. [Google Scholar]
- Kalota, F. A Primer on Generative Artificial Intelligence. Educ. Sci. 2024, 14, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, S.; Krois, J.; Cantu, A.G.; Arsiwala, L.T.; Schwendicke, F. Artificial intelligence for caries detection: Randomized trial. J. Dent. 2021, 115, 103849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantu, A.G.; Gehrung, S.; Krois, J.; Chaurasia, A.; Rossi, J.G.; Gaudin, R.; Elhennawy, K.; Schwendicke, F. Detecting caries lesions of different radiographic extension on bitewings using deep learning. J. Dent. 2020, 100, 103425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwendicke, F.; Cejudo Grano de Oro, J.; Garcia Cantu, A.; Meyer-Lueckel, H.; Chaurasia, A.; Krois, J. Artificial Intelligence for Caries Detection: Value of Data and Information. J. Dent. Res. 2022, 101, 1350–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prados-Privado, M.; García Villalón, J.; Martínez-Martínez, C.H.; Ivorra, C.; Prados-Frutos, J.C. Dental Caries Diagnosis and Detection Using Neural Networks: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maganur, P.C.; Vishwanathaiah, S.; Mashyakhy, M.; Abumelha, A.S.; Robaian, A.; Almohareb, T.; Almutairi, B.; Alzahrani, K.M.; Binalrimal, S.; Marwah, N.; et al. Development of Artificial Intelligence Models for Tooth Numbering and Detection: A Systematic Review. Int. Dent. J. 2024, 74, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwanathaiah, S.; Fageeh, H.N.; Khanagar, S.B.; Maganur, P.C. Artificial Intelligence Its Uses and Application in Pediatric Dentistry: A Review. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannes, T.; Akhilanand, C.; Joachim, K.; Shankeeth, V.; Anahita, H.; Saeed Reza, M.; Mohammad, B.; Hossein, M.R. Evaluation of AI Model for Cephalometric Landmark Classification (TG Dental). J. Med. Syst. 2023, 47, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bağ, İ.; Bilgir, E.; Bayrakdar, İ.Ş.; Baydar, O.; Atak, F.M.; Çelik, Ö.; Orhan, K. An artificial intelligence study: Automatic description of anatomic landmarks on panoramic radiographs in the pediatric population. BMC Oral Health 2023, 23, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, K.; Lyu, P.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Wu, J.; Lee, C.H. A deep learning approach to automatic teeth detection and numbering based on object detection in dental periapical films. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, T.; Lee, C.T.; Chen, L.; Jiang, X.; Shams, S. A comprehensive artificial intelligence framework for dental diagnosis and charting. BMC Oral Health 2022, 22, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfanti-Gris, M.; Garcia-Cañas, A.; Alonso-Calvo, R.; Salido Rodriguez-Manzaneque, M.P.; Pradies Ramiro, G. Evaluation of an Artificial Intelligence web-based software to detect and classify dental structures and treatments in panoramic radiographs. J. Dent. 2022, 126, 104301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Jo, E.; Kim, H.J.; Cha, I.H.; Jung, Y.S.; Nam, W.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, Y.H.; Oh, T.G.; et al. Deep Learning for Automated Detection of Cyst and Tumors of the Jaw in Panoramic Radiographs. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, H.J. Classification of dental implant systems using cloud-based deep learning algorithm: An experimental study. J. Yeungnam Med. Sci. 2023, 40, S29–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.; Schwendicke, F.; Krois, J.; Huh, J.K.; Lee, J.H. Identification of Dental Implant Systems Using a Large-Scale Multicenter Data Set. J. Dent. Res. 2023, 102, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, G.H.; Kwak, E.J.; Song, J.M.; Park, H.R.; Jung, Y.H.; Cho, B.H.; Hui, P.; Hwang, J.J. Automatic mandibular canal detection using a deep convolutional neural network. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinthia, P.; Deepika, V.; Sarmika, R. Anatomical Deep Learning Analysis for Automated Detection of Dental Caries: A Novel Approach. In Proceedings of the 2024 Ninth International Conference on Science Technology Engineering and Mathematics (ICONSTEM), Chennai, India, 4–5 April 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Lee, H.S.; Song, I.S.; Jung, K.H. DeNTNet: Deep neural transfer network for the detection of periodontal bone loss using panoramic dental radiographs. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krois, J.; Ekert, T.; Meinhold, L.; Golla, T.; Kharbot, B.; Wittemeier, A.; Dörfer, C.; Schwendicke, F. Deep learning for the radiographic detection of periodontal bone loss. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Wu, Y.F.; Aung, L.M.; Lin, J.C.; Ngo, S.T.; Su, J.N.; Lin, Y.M.; Chang, W.J. Automatic recognition of teeth and periodontal bone loss measurement in digital radiographs using deep-learning artificial intelligence. J. Dent. Sci. 2023, 18, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Issa, J.; Jaber, M.; Rifai, I.; Mozdziak, P.; Kempisty, B.; Dyszkiewicz-Konwińska, M. Diagnostic Test Accuracy of Artificial Intelligence in Detecting Periapical Periodontitis on Two-Dimensional Radiographs: A Retrospective Study and Literature Review. Medicina 2023, 59, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İçöz, D.; Terzioğlu, H.; Özel, M.A.; Karakurt, R. Evaluation of an artificial intelligence system for the diagnosis of apical periodontitis on digital panoramic images. Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 2023, 26, 1085–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwendicke, F.; Singh, T.; Lee, J.H.; Gaudin, R.; Chaurasia, A.; Wiegand, T.; Uribe, S.; Krois, J. Artificial intelligence in dental research: Checklist for authors, reviewers, readers. J. Dent. 2021, 107, 103610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossuyt, P.M.; Reitsma, J.B.; Bruns, D.E.; Gatsonis, C.A.; Glasziou, P.P.; Irwig, L.; Lijmer, J.G.; Moher, D.; Rennie, D.; De Vet, H.C.W.; et al. STARD 2015: An updated list of essential items for reporting diagnostic accuracy studies. BMJ 2015, 351, h5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mongan, J.; Moy, L.; Kahn, C.E. Checklist for Artificial Intelligence in Medical Imaging (CLAIM): A guide for authors and reviewers. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2020, 2, e200029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.hellopearl.com/products/second-opinion (accessed on 30 July 2024).
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, D.H.; Jeong, S.N.; Choi, S.H. Detection and diagnosis of dental caries using a deep learning-based convolutional neural network algorithm. J. Dent. 2018, 77, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, M.; Faria, M.; Giraldi, G.; Bastos, L.; Oliveira, L.; Conci, A. Classification of Approximal Caries in Bitewing Radiographs Using Convolutional Neural Networks. Sensors 2021, 21, 5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.T.; Kabir, T.; Nelson, J.; Sheng, S.; Meng, H.W.; Van Dyke, T.E.; Walji, M.F.; Jiang, X.; Shams, S. Use of the deep learning approach to measure alveolar bone level. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2022, 49, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
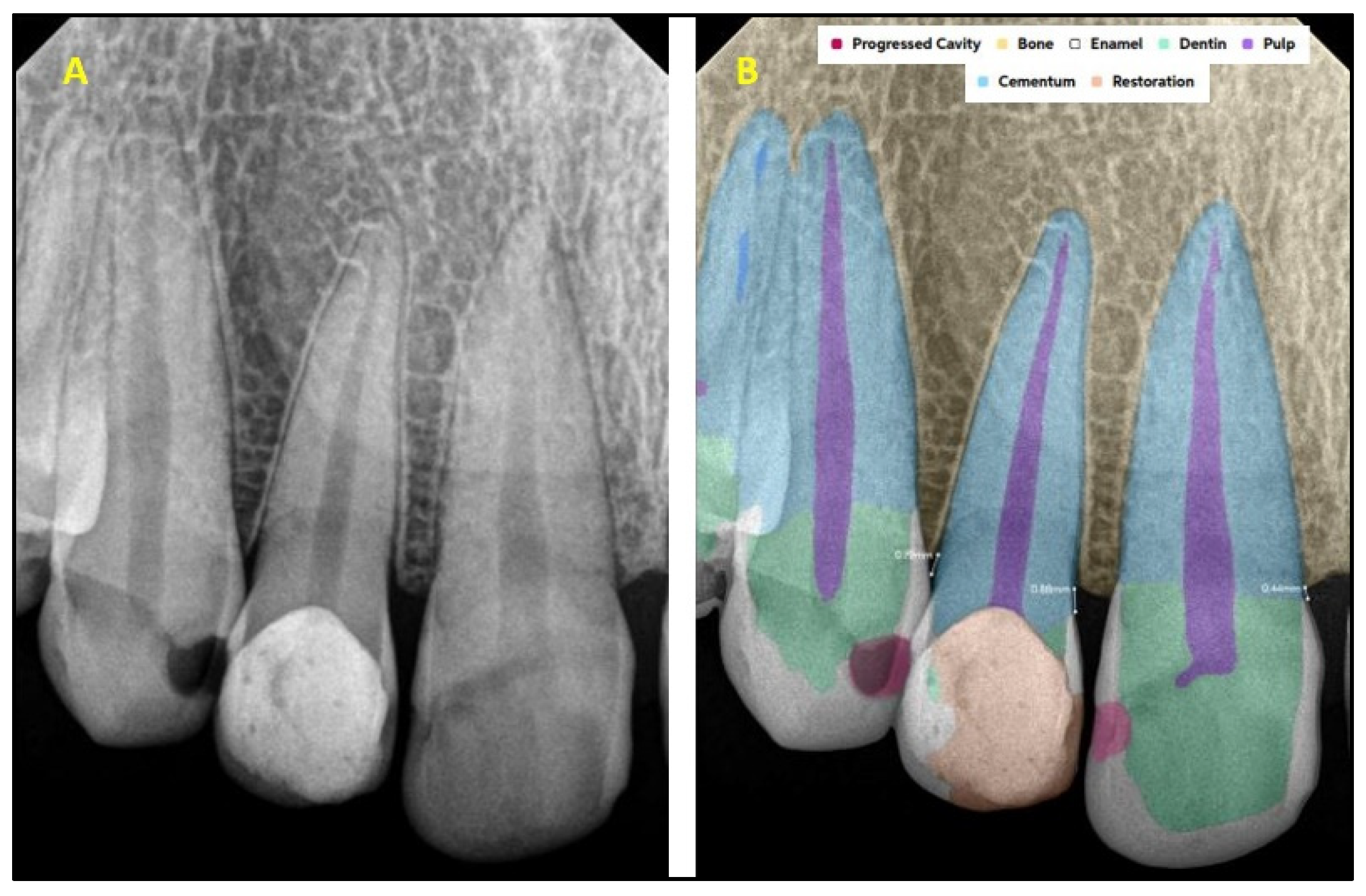
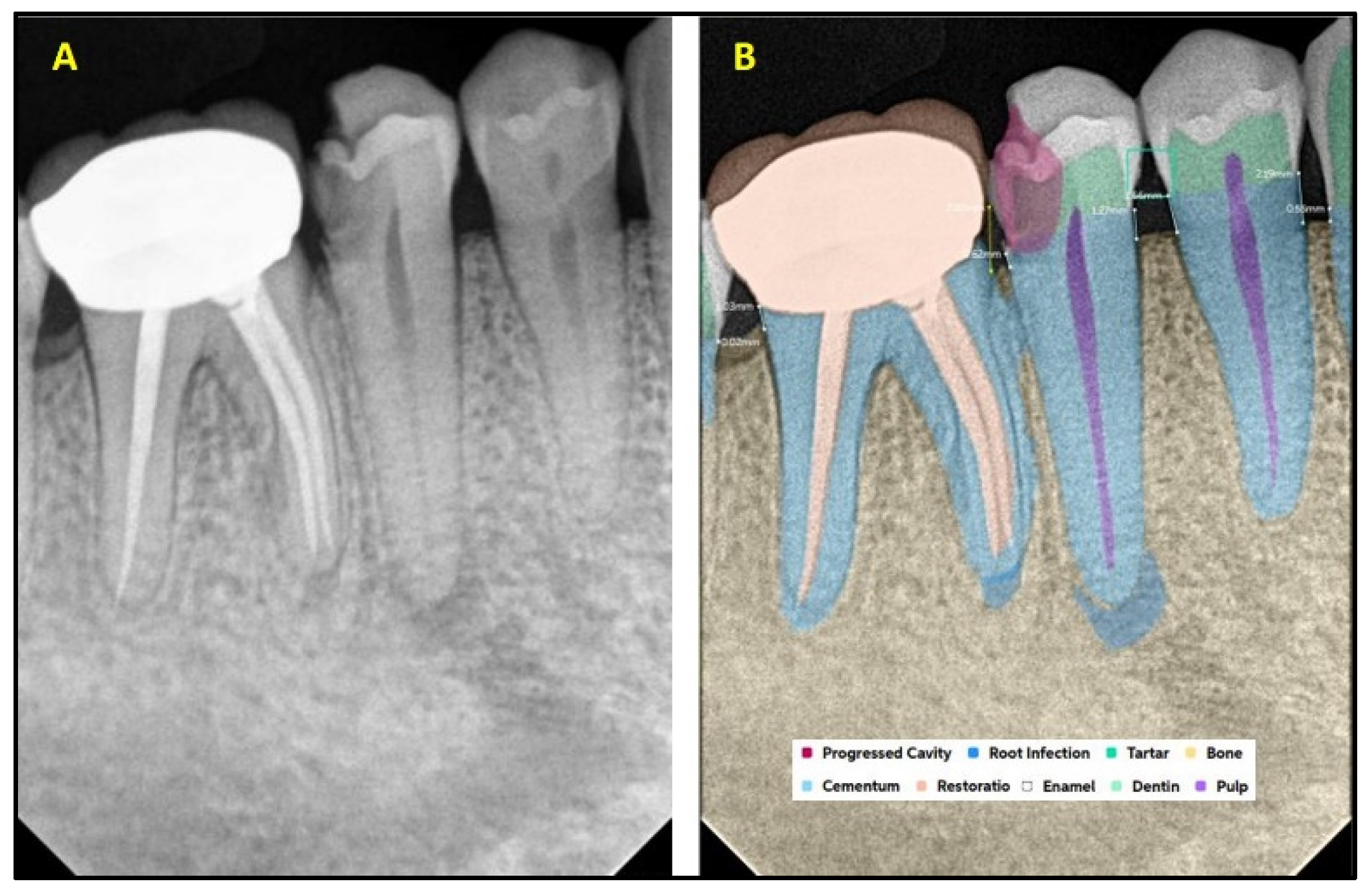
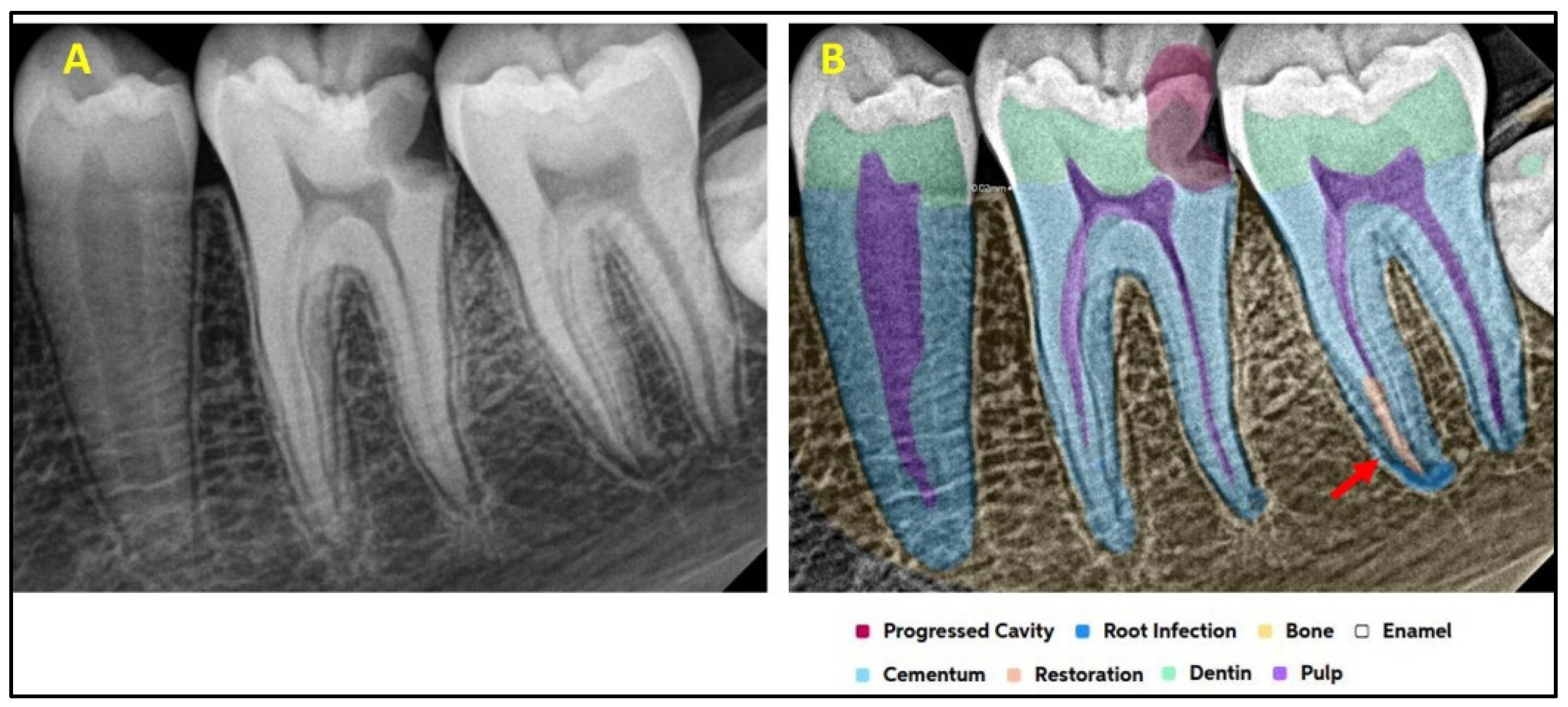
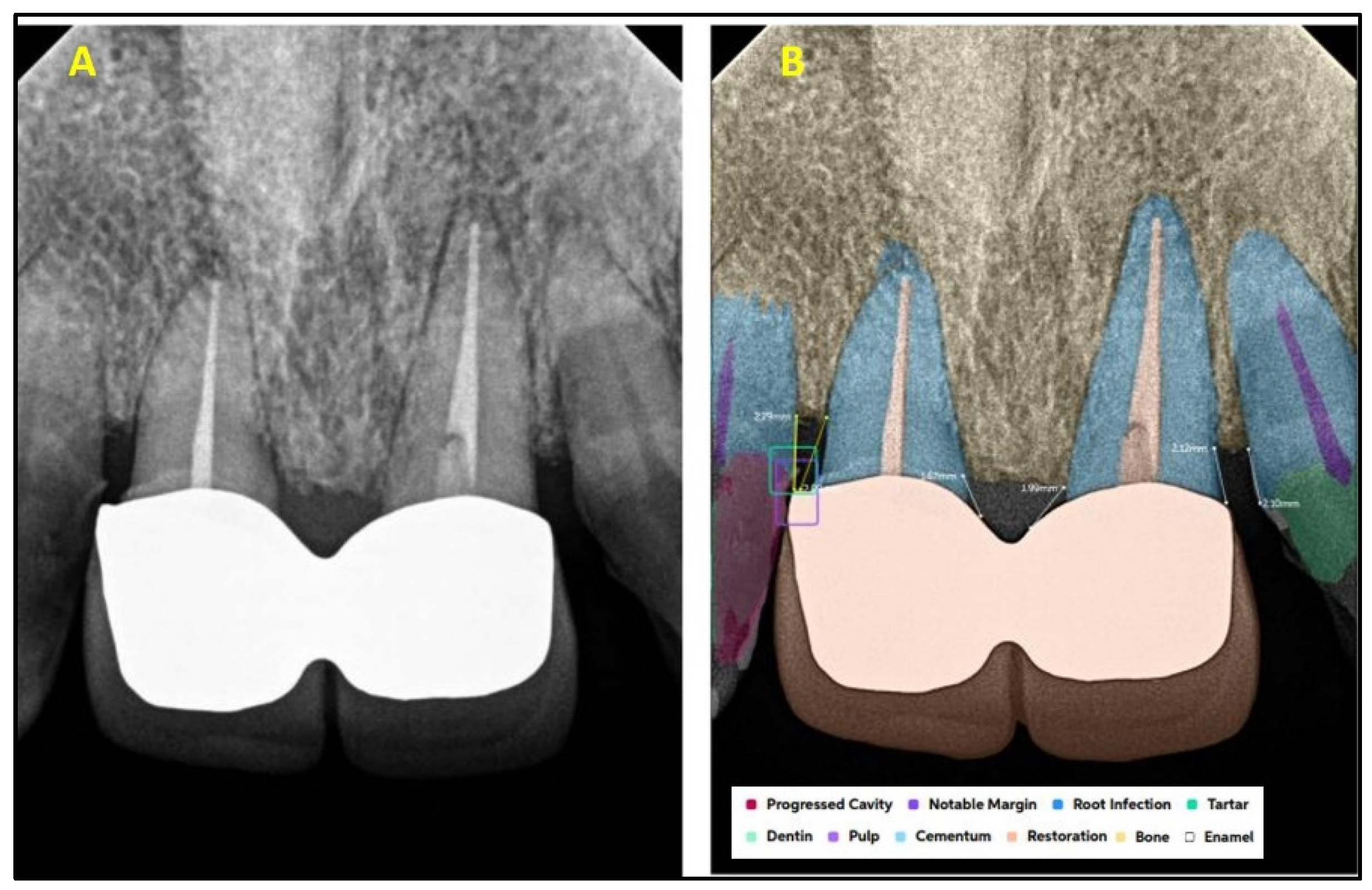
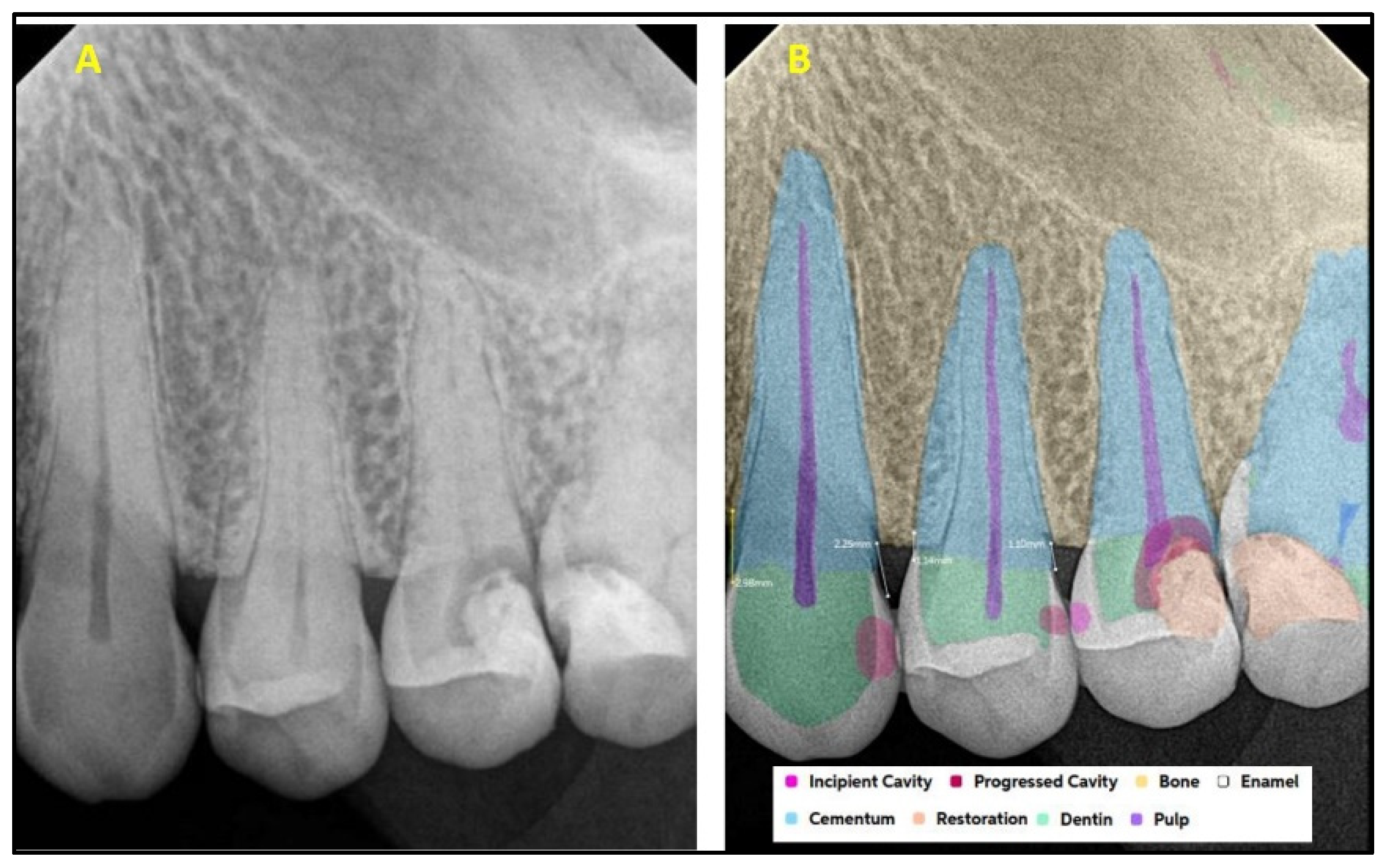
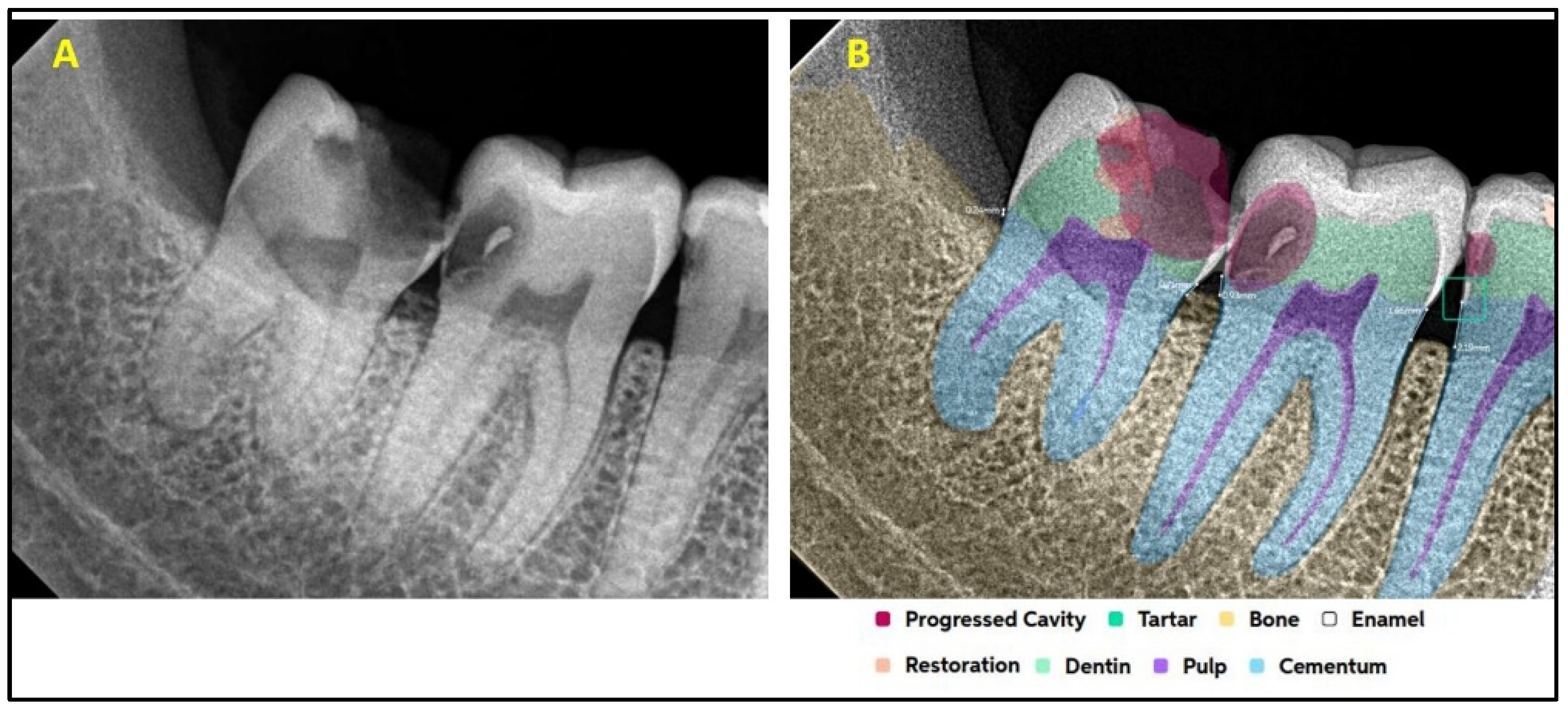
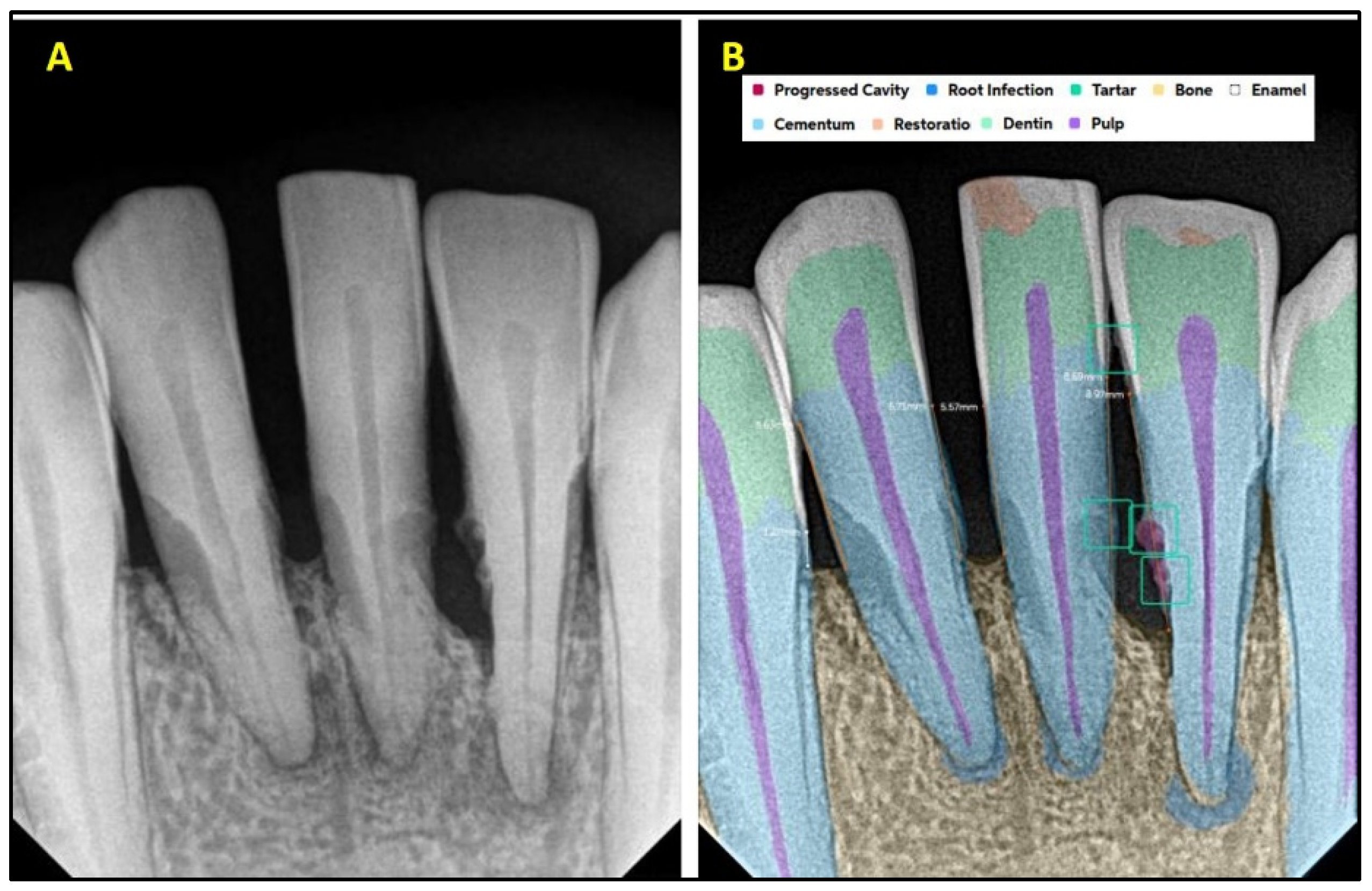


| Present | Absent | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AI software | Positive | TP | FP | TP + FP |
| Negative | FN | TN | FN + TN | |
| Total | TP + FP | FP + TN | TP + FP + FP + TN |
| Conditions | AI Software | Diagnosis by Radiologist | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Present | Absent | Total | |||||||
| Caries | Positive | 721 | 31 | 752 | 91.0% | 87.0% | 95.9% | 74.5% | <0.0001 |
| Negative | 71 | 207 | 378 | ||||||
| Total | 792 | 238 | 1030 | ||||||
| PA lesions | Positive | 233 | 13 | 246 | 86.6% | 98.3% | 94.7% | 95.4% | <0.0001 |
| Negative | 36 | 748 | 784 | ||||||
| Total | 269 | 761 | 1030 | ||||||
| Crowns | Positive | 201 | 3 | 204 | 97.1% | 99.6% | 98.5% | 99.3% | <0.0001 |
| Negative | 6 | 820 | 826 | ||||||
| Total | 207 | 823 | 1030 | ||||||
| Open crown margins | Positive | 38 | 13 | 51 | 82.6% | 91.9% | 74.5% | 94.9% | <0.0001 |
| Negative | 8 | 148 | 156 | ||||||
| Total | 46 | 161 | 207 | ||||||
| Restoration | Positive | 150 | 31 | 181 | 89.3% | 96.4% | 82.9% | 97.9% | <0.0001 |
| Negative | 18 | 831 | 849 | ||||||
| Total | 168 | 862 | 1030 | ||||||
| Endodontic treatment | Positive | 171 | 6 | 177 | 93.4% | 99.3% | 96.6% | 98.6% | <0.0001 |
| Negative | 12 | 841 | 853 | ||||||
| Total | 183 | 847 | 1030 | ||||||
| Calculus | Positive | 77 | 12 | 89 | 80.2% | 97.8% | 86.5% | 96.5% | <0.0001 |
| Negative | 19 | 528 | 547 | ||||||
| Total | 96 | 540 | 636 | ||||||
| Marginal bone loss | Positive | 338 | 18 | 356 | 91.1% | 93.1% | 94.9% | 88.0% | <0.0001 |
| Negative | 33 | 242 | 275 | ||||||
| Total | 371 | 260 | 631 | ||||||
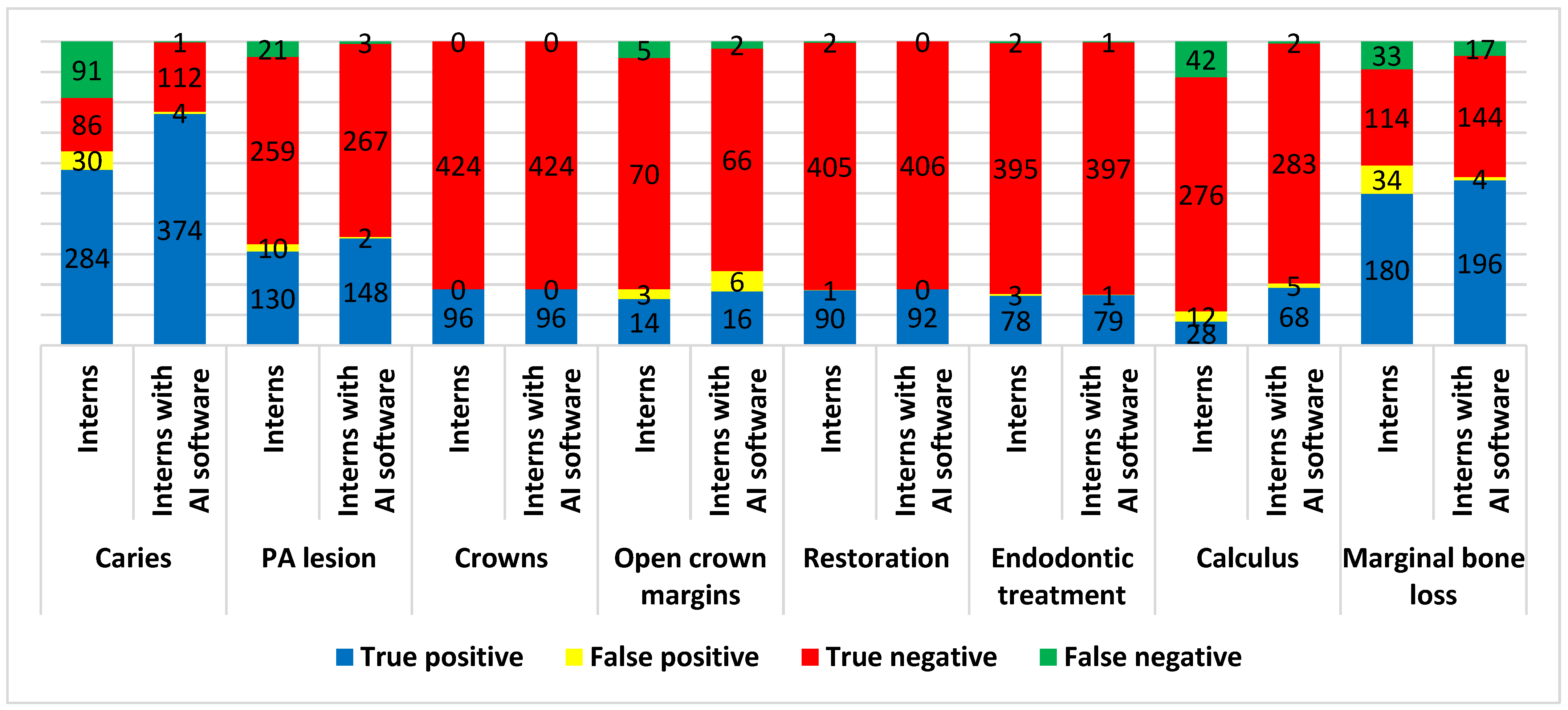
| Conditions | Operators | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | Youden’s Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caries | Interns | 75.36% | 75.73% | 74.14% | 90.45% | 48.59% | 0.499 |
| Interns with AI software | 98.98% | 99.73% | 96.55% | 98.94% | 99.12% | 0.963 | |
| Difference | 23.62% | 24.00% | 22.41% | ||||
| p value | 0.0037 | 0.0103 | 0.1739 | ||||
| PA lesions | Interns | 92.62% | 86.09% | 96.28% | 92.86% | 92.50% | 0.824 |
| Interns with AI software | 98.81% | 98.01% | 99.26% | 98.67% | 98.89% | 0.973 | |
| Difference | 6.19% | 11.92% | 2.98% | ||||
| p value | 0.5121 | 0.4358 | 0.8041 | ||||
| Crowns | Interns | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 1.000 |
| Interns with AI software | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 1.000 | |
| Difference | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | ||||
| p value | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||||
| Open crown margins | Interns | 91.30% | 73.68% | 95.89% | 82.35% | 93.33% | 0.696 |
| Interns with AI software | 91.11% | 88.89% | 91.67% | 72.73% | 97.06% | 0.806 | |
| Difference | −0.19% | 15.21% | −4.22% | ||||
| p value | 0.9463 | 0.7029 | 0.8504 | ||||
| Restoration | Interns | 99.40% | 97.83% | 99.75% | 98.90% | 99.51% | 0.976 |
| Interns with AI software | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 1.000 | |
| Difference | 0.60% | 2.17% | 0.25% | ||||
| p value | 0.9921 | 0.9163 | 0.9802 | ||||
| Endodontic treatment | Interns | 98.95% | 97.50% | 99.25% | 96.30% | 99.50% | 0.967 |
| Interns with AI software | 99.58% | 98.75% | 99.75% | 98.75% | 99.75% | 0.985 | |
| Difference | 0.63% | 1.25% | 0.50% | ||||
| p value | 0.9450 | 0.9548 | 0.9599 | ||||
| Calculus | Interns | 84.92% | 40.00% | 95.83% | 70.00% | 86.79% | 0.358 |
| Interns with AI software | 98.04% | 97.14% | 98.26% | 93.15% | 99.30% | 0.954 | |
| Difference | 13.12% | 57.14% | 2.43% | ||||
| p value | 0.1842 | 0.0014 | 0.8330 | ||||
| Marginal bone loss | Interns | 81.44% | 84.51% | 77.03% | 84.11% | 77.55% | 0.615 |
| Interns with AI software | 94.18% | 92.02% | 97.30% | 98.00% | 89.44% | 0.893 | |
| Difference | 12.74% | 7.51% | 20.27% | ||||
| p value | 0.1823 | 0.5475 | 0.1716 |
| Conditions | Operators | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | Youden’s Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caries | Specialists | 88.68% | 88.49% | 89.34% | 96.60% | 69.43% | 0.778 |
| Specialists with AI software | 97.77% | 97.84% | 97.54% | 99.27% | 92.97% | 0.954 | |
| Difference | 9.09% | 9.35% | 8.20% | ||||
| p value | 0.2660 | 0.3140 | 0.6339 | ||||
| PA lesions | Specialists | 99.02% | 96.61% | 99.59% | 98.28% | 99.19% | 0.962 |
| Specialists with AI software | 99.67% | 99.15% | 99.80% | 99.15% | 99.80% | 0.989 | |
| Difference | 0.65% | 2.54% | 0.21% | ||||
| p value | 0.9351 | 0.8884 | 0.9820 | ||||
| Crowns | Specialists | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 1.000 |
| Specialists with AI software | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 1.000 | |
| Difference | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | ||||
| p value | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||||
| Open crown margins | Specialists | 99.13% | 96.30% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 98.88% | 0.963 |
| Specialists with AI software | 99.15% | 96.43% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 98.89% | 0.964 | |
| Difference | 0.02% | 0.13% | 0.00% | ||||
| p value | 0.9626 | 0.9972 | 1.0000 | ||||
| Restoration | Specialists | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 1.000 |
| Specialists with AI software | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 1.000 | |
| Difference | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | ||||
| p value | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||||
| Endodontic treatment | Specialists | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 1.000 |
| Specialists with AI software | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 1.000 | |
| Difference | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | ||||
| p value | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||||
| Calculus | Specialists | 96.76% | 80.77% | 98.41% | 84.00% | 98.02% | 0.792 |
| Specialists with AI software | 98.20% | 88.46% | 99.21% | 92.00% | 98.81% | 0.877 | |
| Difference | 1.44% | 7.69% | 0.80% | ||||
| p value | 0.9027 | 0.8245 | 0.9493 | ||||
| Marginal bone loss | Specialists | 94.07% | 94.30% | 93.75% | 95.51% | 92.11% | 0.881 |
| Specialists with AI software | 97.78% | 98.10% | 97.32% | 98.10% | 97.32% | 0.954 | |
| Difference | 3.71% | 3.80% | 3.57% | ||||
| p value | 0.7536 | 0.8059 | 0.8450 |
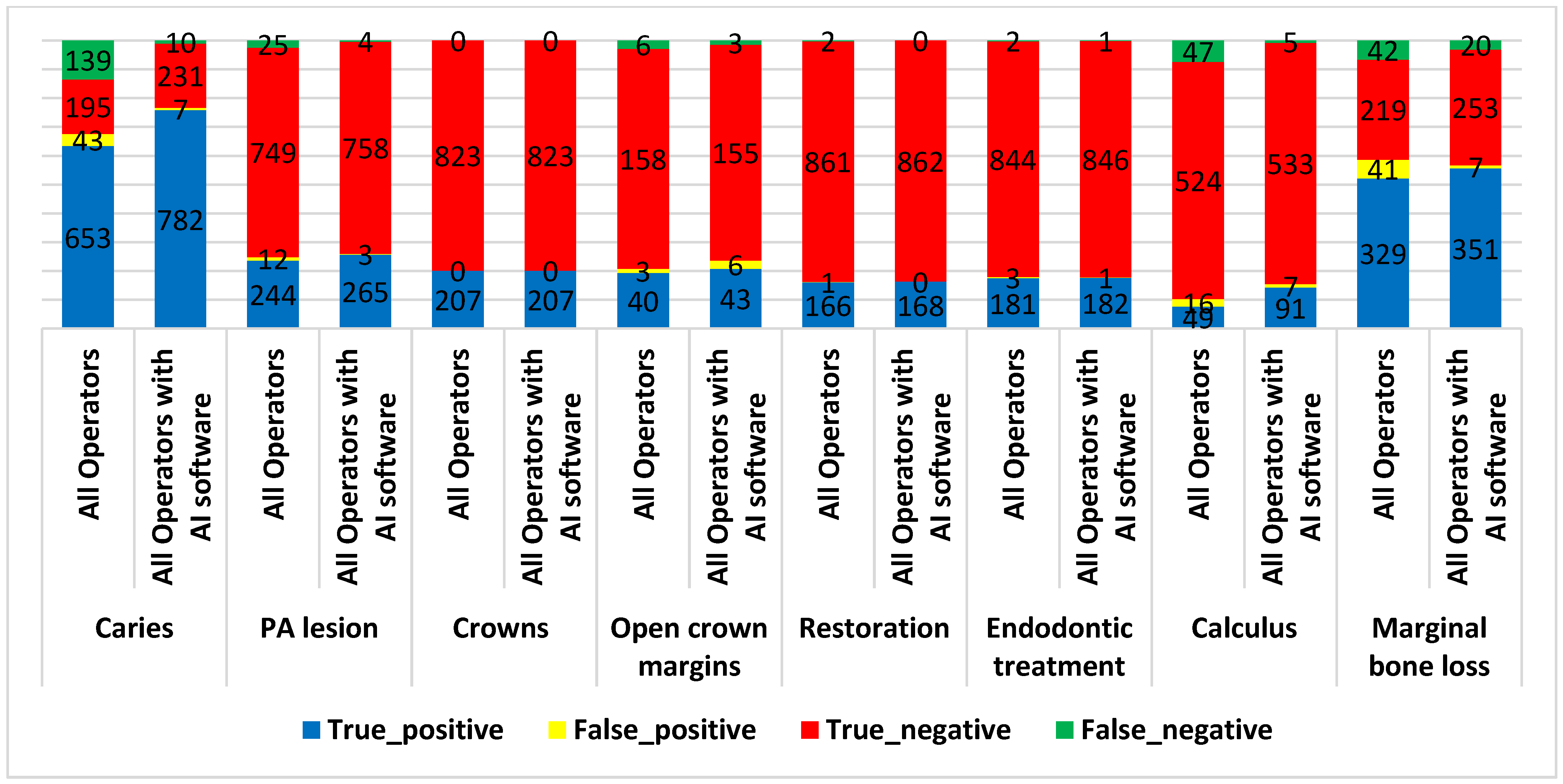
| Conditions | Operators (Interns and Specialists) | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | Youden’s Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caries | Interns and specialists | 82.33% | 82.45% | 81.93% | 93.82% | 58.38% | 0.644 |
| Interns and specialists with AI software | 98.35% | 98.74% | 97.06% | 99.11% | 95.85% | 0.958 | |
| Difference | 16.02% | 16.29% | 15.13% | ||||
| p value | 0.0055 | 0.0136 | 0.2048 | ||||
| PA lesions | Interns and specialists | 96.41% | 90.71% | 98.42% | 95.31% | 96.77% | 0.891 |
| Interns and specialists with AI software | 99.32% | 98.51% | 99.61% | 98.88% | 99.48% | 0.981 | |
| Difference | 2.91% | 7.80% | 1.19% | ||||
| p value | 0.6348 | 0.5045 | 0.8695 | ||||
| Crowns | Interns and specialists | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 1.000 |
| Interns and specialist with AI software | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 1.000 | |
| Difference | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | ||||
| p value | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||||
| Open crown margins | Interns and specialists | 95.65% | 86.96% | 98.14% | 93.02% | 96.34% | 0.851 |
| Interns and specialists with AI software | 95.65% | 93.48% | 96.27% | 87.76% | 98.10% | 0.898 | |
| Difference | 0.00% | 6.52% | −1.87% | ||||
| p value | 1.0000 | 0.8113 | 0.9039 | ||||
| Restoration | Interns and specialists | 99.71% | 98.81% | 99.88% | 99.40% | 99.77% | 0.987 |
| Interns and specialists with AI software | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 1.000 | |
| Difference | 0.29% | 1.19% | 0.12% | ||||
| p value | 0.9627 | 0.9382 | 0.9864 | ||||
| Endodontic treatment | Interns and specialists | 99.51% | 98.91% | 99.65% | 98.37% | 99.76% | 0.986 |
| Interns and specialists with AI software | 99.81% | 99.45% | 99.88% | 99.45% | 99.88% | 0.993 | |
| Difference | 0.30% | 0.54% | 0.23% | ||||
| p value | 0.9626 | 0.9703 | 0.9725 | ||||
| Calculus | Interns and specialists | 90.09% | 51.04% | 97.04% | 75.38% | 91.77% | 0.481 |
| Interns and specialists with AI software | 98.11% | 94.79% | 98.70% | 92.86% | 99.07% | 0.935 | |
| Difference | 8.02% | 43.75% | 1.66% | ||||
| p value | 0.2899 | 0.0065 | 0.8440 | ||||
| Marginal bone loss | Interns and specialists | 86.85% | 88.68% | 84.23% | 88.92% | 83.91% | 0.729 |
| Interns and specialists with AI software | 95.72% | 94.61% | 97.31% | 98.04% | 92.67% | 0.919 | |
| Difference | 8.87% | 5.93% | 13.08% | ||||
| p value | 0.2328 | 0.5422 | 0.2569 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ibraheem, W.I.; Jain, S.; Ayoub, M.N.; Namazi, M.A.; Alfaqih, A.I.; Aggarwal, A.; Meshni, A.A.; Almarghlani, A.; Alhumaidan, A.A. Assessment of the Diagnostic Accuracy of Artificial Intelligence Software in Identifying Common Periodontal and Restorative Dental Conditions (Marginal Bone Loss, Periapical Lesion, Crown, Restoration, Dental Caries) in Intraoral Periapical Radiographs. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1432. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15111432
Ibraheem WI, Jain S, Ayoub MN, Namazi MA, Alfaqih AI, Aggarwal A, Meshni AA, Almarghlani A, Alhumaidan AA. Assessment of the Diagnostic Accuracy of Artificial Intelligence Software in Identifying Common Periodontal and Restorative Dental Conditions (Marginal Bone Loss, Periapical Lesion, Crown, Restoration, Dental Caries) in Intraoral Periapical Radiographs. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(11):1432. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15111432
Chicago/Turabian StyleIbraheem, Wael I., Saurabh Jain, Mohammed Naji Ayoub, Mohammed Ahmed Namazi, Amjad Ismail Alfaqih, Aparna Aggarwal, Abdullah A. Meshni, Ammar Almarghlani, and Abdulkareem Abdullah Alhumaidan. 2025. "Assessment of the Diagnostic Accuracy of Artificial Intelligence Software in Identifying Common Periodontal and Restorative Dental Conditions (Marginal Bone Loss, Periapical Lesion, Crown, Restoration, Dental Caries) in Intraoral Periapical Radiographs" Diagnostics 15, no. 11: 1432. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15111432
APA StyleIbraheem, W. I., Jain, S., Ayoub, M. N., Namazi, M. A., Alfaqih, A. I., Aggarwal, A., Meshni, A. A., Almarghlani, A., & Alhumaidan, A. A. (2025). Assessment of the Diagnostic Accuracy of Artificial Intelligence Software in Identifying Common Periodontal and Restorative Dental Conditions (Marginal Bone Loss, Periapical Lesion, Crown, Restoration, Dental Caries) in Intraoral Periapical Radiographs. Diagnostics, 15(11), 1432. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15111432






