Abstract
Uterine arteriovenous malformations are a rare cause of puerperal haemorrhage, but their incidence is increasing due to both improved diagnosis and the more frequent use of uterine surgery in recent years. The use of ultrasound, both B-mode and Doppler, is recommended for diagnosis and follow-up, as it has been shown to be the simplest and most cost-effective method. Endometrial thickening associated with an anechoic and vascular intramiometrial structure is very useful for diagnosis and can help to exclude other causes of dysfunctional bleeding. Pulsed Doppler shows low-resistance vessels and high pulsatility indices with a high peak systolic velocity (PSV). In a healthy myometrium, the vessels have a peak systolic velocity of 9–40 cm/s and a resistance index between 0.6 and 0.8, whereas in the case of AVMs, the systolic and diastolic velocities are 4–6 times higher (PSV 25–110 cm/s with a mean of 60 cm/s and a resistance index of 0.27–0.75 with a mean of 0.41). For treatment, we must individualise each case, taking into account haemodynamic stability, the patient’s reproductive wishes, and the severity of the AVM as assessed by its size and PSV.
1. Introduction
Uterine arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) are an uncommon cause of puerperal metrorrhagia and haemorrhage [1]. Understanding them is important as they are potentially fatal [2,3] and because there has been an increase in their occurrence in recent years due to the new diagnostic techniques available.
Their clinical and radiological suspicion is fundamental since common interventions to control uterine haemorrhage, such as curettage in the case of a uterine arteriovenous malformation, can lead to massive haemorrhage and a fatal outcome [1].
Uterine arteriovenous malformations can be congenital or acquired, the latter being the most frequent [1]. Congenital ones originate from an alteration in the embryological differentiation of primitive vascular structures, creating abnormal vascular connections (fine capillaries intertwined with myometrial vessels) that can reach large pelvic vessels in addition to the uterine arteries (especially in women of reproductive age) [1,4].
Acquired arteriovenous malformations constitute true arteriovenous fistulas between the intramural arterial branches and the myometrial venous plexus. They are related to iatrogenic uterine trauma, such as obstetric curettage, uterine surgery (caesarean section, myomectomy), or even traumatic childbirth [5,6]. Other less frequent causes of AVMs are those coexisting with endometrial cancer, gestational trophoblastic disease, or infections [1,7].
Abnormal intramiometrial and endometrial vessel formation can cause severe uterine bleeding, constituting a threat to life and hindering future pregnancies. We describe the case of a 40-year-old patient diagnosed with a uterine AVM after severe metrorrhagia secondary to curettage for delayed abortion.
The main aim of our study was to review the diagnostic and therapeutic management of uterine arteriovenous malformation, a rare but potentially fatal entity.
2. Case Report
A 40-year-old woman presented to the gynaecological emergency department with severe metrorrhagia two months after aspiration curettage for delayed abortion (obstetric formula G1A1). She had no allergies or other medical or surgical history of interest. Upon arrival at the emergency department, moderate bleeding was observed.
Ultrasonography showed an endometrial cavity occupied by a protruding formation in the uterine cavity measuring 38 × 15 mm, compatible with a uterine AVM (Figure 1). The presence of vascularisation of the right lateral uterine wall was noted, and pulsed Doppler showed a peak systolic velocity > 100 cm/s (Figure 2).
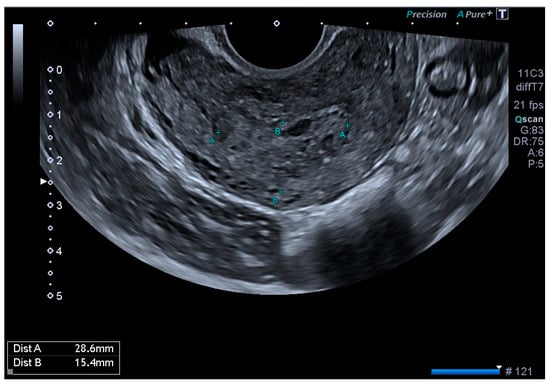
Figure 1.
Transvaginal ultrasound with suspected uterine arteriovenous malformation.
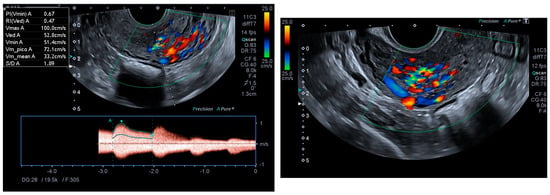
Figure 2.
Colour and pulsed Doppler studies of the uterine arteriovenous malformation.
Following these findings, the patient was advised to avoid pregnancy, so combined hormonal contraception was prescribed, and an angio-CT scan of the pelvis was requested with a referral to the Vascular Surgery Department.
CT angiography showed a complex network of millimetre-sized vessels of tortuous appearance with rapid contrast enhancement in the late arterial phase and isodensity in the portal phase (similar to systemic venous vessels). This network extended through the right parametrium, through the myometrial fundus, and apparently into the endometrium (Figure 3 and Figure 4). The radiological findings were compatible with a uterine arteriovenous malformation.
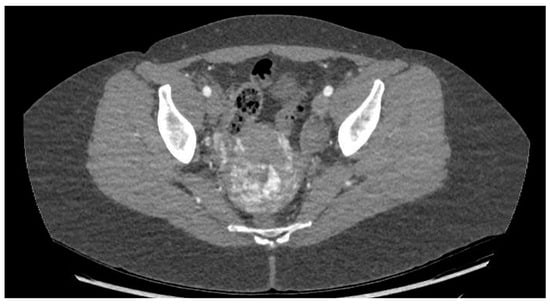
Figure 3.
Cross-sectional pelvic CT angiography.
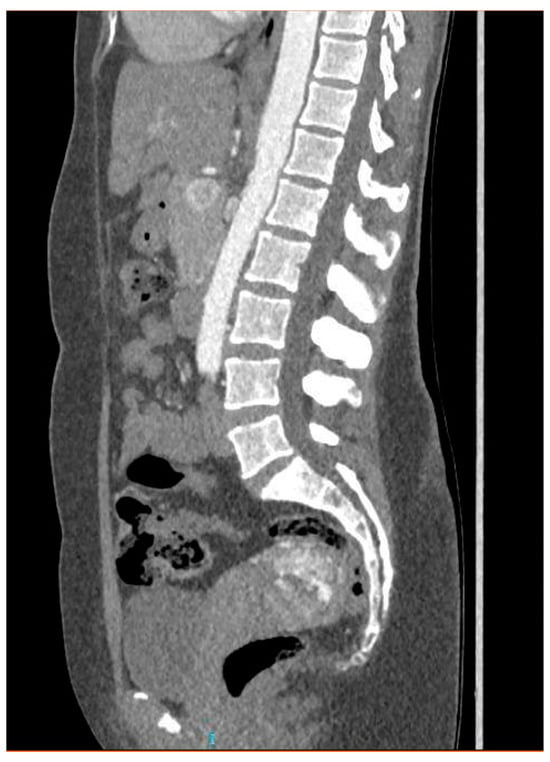
Figure 4.
Coronal pelvic CT angiography.
Finally, the vascular surgeons ruled out selective arterial embolisation because the size of the lesion made complete and effective embolisation impossible. Conservative treatment with combined hormonal contraceptives was chosen because the patient’s reproductive desires were not fulfilled. After four months of being asymptomatic and under treatment with combined hormonal contraceptives, the patient presented for follow-up, at which time no AVM was observed on the ultrasound, either in B-mode or colour Doppler (Figure 5 and Figure 6).
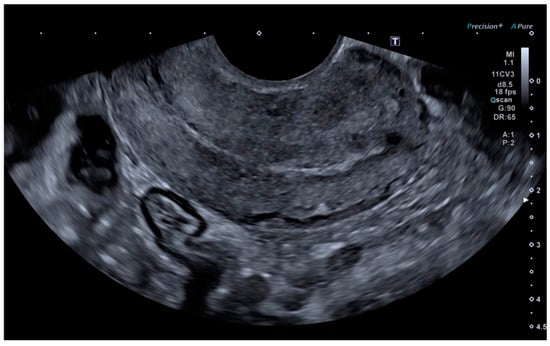
Figure 5.
Linear endometrium after conservative treatment for 4 months.
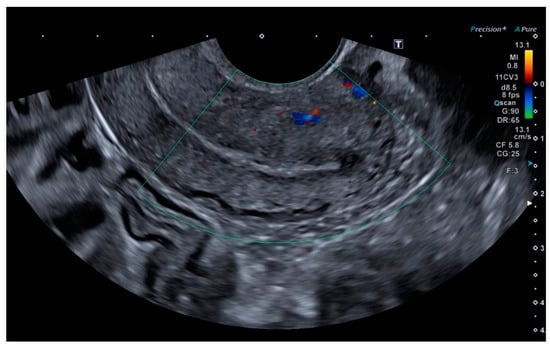
Figure 6.
Absence of colour Doppler uptake.
3. Discussion
The therapeutic approach for this patient was guided by the rapid control of symptoms with conservative treatment and the fact that she had not yet fulfilled her reproductive desires.
AVMs are conditions for which we do not know the prevalence and current incidence in the general population (they are common formations in the pulmonary or cerebral territory but are rarely found in the uterus). Due to the paucity of reported cases and available research, many remain undetected after responding to conservative treatment. They may account for 1–2% of metrorrhagias [8]. It is likely that the frequency of this pathology will increase in the coming years due to the wider use of ultrasound and increased awareness of this pathology.
Histologically, we find fistulae between the myometrial venous plexus and the intramural layer of the arterioles.
Clinically, we can observe this in asymptomatic patients to those with severe metrorrhagia and cardiovascular consequences with the need for haemotransfusions (30%) [9]. In these cases, it is important to make a diagnosis upon suspicion. This will allow us to prolong the study and offer the patient all the therapeutic alternatives available.
3.1. Diagnosis of AVMs
Several techniques can be used to diagnose AVMs, such as ultrasound, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or angiography, depending on the patient’s condition and the availability of the techniques.
The differential diagnosis of uterine arteriovenous malformations is mainly made by ultrasound: colour and pulsed Doppler [10]. The visualisation of endometrial thickening with an anechoic and vascular intramiometrial structure is very useful in the diagnosis and can help to exclude other causes of dysfunctional uterine bleeding such as retained placental debris, uterine sarcoma, pelvic varices, or gestational trophoblastic disease [11,12,13]. The most common ultrasound findings with colour Doppler are multidirectional myometrial hypervascularisation in the area of the lesion, with turbulent flow and multiple tortuous vessels in the bed [14].
Pulsed Doppler shows low-resistance vessels and high pulsatility indices with a high systolic peak velocity (PSV). In a healthy myometrium, the vessels have a peak systolic velocity of 9–40 cm/s and a resistance index between 0.6 and 0.8, with systolic and diastolic velocities four to six times higher in the case of uterine arteriovenous malformation (PSV between 25 and 110 cm/s with a mean of 60 cm/s and a resistance index of 0.27–0.75 with a mean of 0.41) [15,16].
Depending on the PSV of the lesions, they can be classified as follows [17,18]:
- -
- Mild: PSV < 40 cm/s, where expectant management is recommended.
- -
- Moderate: PSV of 40–60 cm/s, where medical treatment is recommended.
- -
- Severe: PSV > 60–70 cm/s, where arterial embolisation or surgical treatment is recommended.
Therefore, if an AVM is suspected, a Doppler scan should be performed prior to obstetric curettage, as this may worsen the bleeding and even make it fatal, requiring an urgent hysterectomy [1,18].
The use of CT is also widespread but is usually limited to urgent cases due to a patient’s metrorrhagia, when MRI does not provide good resolution, or before surgery to implement the approach plan. One of the advantages of CT over MRI is its better resolution in areas close to bone or the bowels, while the main disadvantage is the radiation it produces.
The images obtained with MRI allow for controlling and monitoring the pathology, including the possibility of assessing arterial supply and venous drainage, as well as high-resolution three-dimensional reconstruction and aiding in therapeutic management.
However, the gold standard for the diagnosis of this pathology is angiography, which is not only a diagnostic but also a therapeutic method. As this technique usually produces high levels of radiation, digital subtraction angiography [19] can be performed with less exposure to ionising radiation and less contrast than conventional studies, with the possibility of obtaining three-dimensional reconstructions of the vessels studied. Nowadays, although angiography is the gold standard, it is reserved for therapeutic embolisation to delay or avoid surgery, while ultrasound is preferred as a diagnostic technique [1,10].
Ultrasound, both two-dimensional B-mode and colour and pulsed Doppler, for the diagnosis of AVMs has proven to be the simplest method with the best diagnostic results [11,20]. It is also the most cost-effective method for patient follow-up [17].
3.2. Treatment of AVMs
Treatment options include conservative management with combined hormonal contraception, uterine artery embolisation, or a hysterectomy. An individualised approach to the treatment of AVMs is crucial, as there is no consensus on the superiority of one treatment over another. Treatment is usually selected on the basis of the patient’s symptoms, haemodynamic stability, and the maximum ultrasound PSV of the lesion.
In asymptomatic patients, treatment with norethisterone has been shown to stop bleeding and significantly reduce the lesion in 90% of cases [21]; however, patients with a PSV > 83 cm/s usually require surgical treatment.
In patients who still have reproductive desires and have large AVMs with a PSV > 60–70 cm/s, selective embolisation of the region should be the first choice, provided the patient is haemodynamically stable. This technique has not been shown to affect subsequent pregnancies or placental vascularisation and therefore does not appear to result in intrauterine growth restriction [22,23,24,25]. Embolisation can be repeated if a partial response is achieved, with a success rate of 71–93% [26]. Cases of congenital AVMs have a lower success rate, as they are more extensive lesions that may involve other pelvic and extrapelvic territories.
If embolisation fails, the patient is haemodynamically unstable, or her reproductive wishes are already fulfilled, the last therapeutic option is a hysterectomy. Some cases of fertility preservation surgery, such as uterine artery ligation, have been described without conclusive results [27].
There are numerous cases published in the literature on the surgical management of haemorrhage due to uterine arteriovenous malformations. One published article presented the case of a 32-year-old female patient who arrived to the emergency department 15 days after eutocic delivery with massive haemorrhage. In the immediate puerperium, she presented with severe haemorrhage, requiring the transfusion of two red blood cell concentrates. Transvaginal ultrasound in the emergency department showed a 22 × 44 mm hyperechogenic intrauterine lesion on colour Doppler imaging, compatible with a uterine arteriovenous malformation. Intracavitary tamponade with a Foley catheter was initially used to control the haemorrhage, and it eventually ceased. Conservative management was attempted due to the patient’s age and having only one child. After the vascular surgery team declined to embolise the uterine arteries due to the size of the arteriovenous malformation, a simple total hysterectomy was performed at the patient’s request. [28]
4. Conclusions
Uterine arteriovenous malformations are rare, but their incidence is increasing due to both improved diagnosis and the increase in uterine surgery in recent years. The use of ultrasound, both two-dimensional B-mode and colour and pulsed Doppler, is recommended for the diagnosis of AVMs, as it has been shown to be the simplest method with the best diagnostic results. It is also the most cost-effective method for patient follow-up.
As far as treatment is concerned, we need to individualise each case, taking into account haemodynamic stability, the patient’s reproductive wishes, and the severity of the AVM, as assessed by its size and SPV. This assessment will lead us to opt for conservative treatment in mild cases where the patient wishes to conceive, whereas in cases where the patient’s life is at risk, there is no reproductive desire, or the size of the lesion prevents pregnancy, we will opt for embolisation or surgical treatment.
Author Contributions
L.C.B.: conceived and designed the analysis and collected the data. L.C.P.: contributed to data collection and performed the analysis C.F.-C.d.P.: wrote the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were not required for this study as the intervention on the patient was non-invasive and part of the usual follow-up protocol for this pathology. The patient was simply requested to give verbal and written informed consent for the publication of the article.
Informed Consent Statement
Verbal and written informed consent was obtained from the patient for the case publication.
Data Availability Statement
Data is available within the article.
Acknowledgments
In gratitude to the Ultrasound Unit of the Gynaecology and Obstetrics Service of the Valme University Hospital, including doctors, nurses, and other health professionals.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Szpera-Gozdziewicz, A.; Gruca-Stryjak, K.; Breborowicz, G.H.; Ropacka-Lesiak, M. Uterine arteriovenous malformation-diagnosis and management. Ginekol. Polska 2018, 89, 276–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammad, R.; Nausheen, S.; Malik, M. A Case series on uterine arteriovenous malformations: A life-threatening emergency in young women. Cureus 2020, 12, e9410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, F.; Vikneswaran, V.; Yu, K.K. Uterine arteriovenous malformation. Possible association to uterine fibroids? Med. J. Malaysia 2021, 76, 273–274. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.-P.; Sun, Z.-J.; Lang, J.-H.; Pan, J. Clinical characteristic and management of acquired uterine arteriovenous malformation. Chin. Med. J. 2018, 131, 2489–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, D.J.; Choi, S.J.; Jung, J.M.; Choi, J.H. Uterine arteriovenous malformation with repeated vaginal bleeding after dilatation and curettage. Obstet. Gynecol. Sci. 2019, 62, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy, L.L.; Torres, U.S.; D’Ippolito, G. Subinvolution of the placental site associated with focal retained products of conception and placenta accreta mimicking uterine arteriovenous malformation on CT and MRI: A lesson to be learned. Radiol. Bras. 2018, 51, 135–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Blas, A.; Díaz-García, J.D.; Nápoles-Medina, S.; Hernández-Leal, M.; Casián-Castellanos, G. Malformación arteri-ovenosa uterina. Rev. Hosp. Jua. Mex. 2018, 85, 100–104. [Google Scholar]
- Cura, M.; Martinez, N.; Cura, A.; Dalsaso, T.J.; Elmerhi, F. Arteriovenous malformations of the uterus. Acta Radiol. 2009, 50, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manolitsas, T.; Hurley, V.; Gilford, E. Uterine arteriovenous malformation—A rare cause of uterine haemorrhage. Aust. New Zealand J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 1994, 34, 197–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, B.E.; Kaufman, C.S.; Kennedy, A.M.; Ingraham, C.R.; Monroe, E.J. Postpartum hemorrhage—What the interventional radiologist should know. CVIR Endovasc. 2021, 4, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Mejido, J.A.; García-Jiménez, R.; Rodriguez-Cruz, L.; Neguillo-Moguel, R.; Borrero, C.; Sainz-Bueno, J.A. Ultrasound Diagnosis of Uterine Arteriovenous Malformations: A Systematic Review. Clin. Exp. Obstet. Gynecol. 2023, 50, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groszmann, Y.S.; Murphy, A.L.H.; Benacerraf, B.R. Diagnosis and management of patients with enhanced myometrial vascularity associated with retained products of conception. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 52, 396–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampersad, F.; Narine, S.; Rampersad, D.; Diljohn, J.; Ali, R. Uterine arteriovenous malformation mimicking retained products of conception—Treated with embolization. Radiol. Case Rep. 2020, 15, 2076–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lollie, T.K.; Raman, S.S.; Qorbani, A.; Farzaneh, T.; Moatamed, N.A. Rare occurrence of uterine arteriovenous malformation clinically mimicking a malignant growth: A critical reminder for pathologists. Autops. Case Rep. 2020, 10, e2020144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moynihan, H.V.; Richardson, J.; Loveridge, K. Fertility-preserving management of uterine arteriovenous malformation in a 16-year-old female. Cureus 2021, 13, e18162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmerman, D.; Bosch, T.V.D.; Peeraer, K.; Debrouwere, E.; Van Schoubroeck, D.; Stockx, L.; Spitz, B. Vascular malformations in the uterus: Ultrasonographic diagnosis and conservative management. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2000, 92, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, V.T.; Van, H.A.T.; Trinh, C.T.; Pham, N.T.T.; Huynh, C.; Ha, T.N.; Huynh, P.H.; Nguyen, H.Q.; Giao Vo, U.; Nguyen, T.T. Uterine Arteriovenous Malformation: A Pictorial Re-view of Diagnosis and Management. J. Endovasc. Ther. 2021, 28, 659–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giurazza, F.; Corvino, F.; Silvestre, M.; Cavaglià, E.; Amodio, F.; Cangiano, G.; De Magistris, G.; Niola, R. Uterine arteriovenous malformations. Semin. Ultrasound CT MR 2021, 42, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, B.; Royalty, K.; Kowarschik, M.; Rohkohl, C.; Oberstar, E.; Aagaard-Kienitz, B.; Niemann, D.; Ozkan, O.; Strother, C.; Mistretta, C. 4D digital sub-traction angiography: Implementation and demonstration of feasibility. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2013, 34, 1914–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyas, S.; Choi, H.H.; Whetstone, S.; Jha, P.; Poder, L.; Shum, D.J. Ultrasound features help identify patients who can undergo noninvasive management for suspected retained products of conception: A single institutional experience. Abdom. Imaging 2021, 46, 2729–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taneja, A.; Chopra, I.; Kaur, H.; Naik, S.S.; Aggarwal, R.; Sachdeva, E.; Kaur, P. Successful management of abnormal uterine bleeding from uterine arteriovenous mal-formations with proges- terone in postabortal patients. J Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2019, 45, 1114–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poppe, W.; Van Assche, F.A.; Wilms, G.; Favril, A.; Baert, A. Pregnancy after transcatheter embolization of a uterine arteriovenous malfor-mation. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1987, 156, 1179–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javed, A.; Sheikh, S. Admin Pregnancy after embolization for arteriovenous malformation: An uncommon successful outcome. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2021, 71, 1020–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Q.; Chen, X.T.; Zhang, Y.T.; Mai, C.X. The emergent pelvic artery embolization in the management of postpartum hemorrhage: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obstet. Gynecol. Surv. 2021, 76, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delplanque, S.; Le Lous, M.; Proisy, M.; Joueidi, Y.; Bauville, E.; Rozel, C.; Beraud, E.; Bruneau, B.; Levêque, J.; Lavoué, V.; et al. Fertility, pregnancy, and clinical outcomes after uterine arteriovenous malformation management. J. Minim. Invasive Gynecol. 2019, 26, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barral, P.-A.; Saeed-Kilani, M.; Tradi, F.; Dabadie, A.; Izaaryene, J.; Soussan, J.; Bartoli, J.-M.; Vidal, V. Transcatheter arterial embolization with ethylene vinyl alcohol copolymer (Onyx) for the treatment of hemorrhage due to uterine arteriovenous malformations. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2017, 98, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, T.; Kim, N.; Lee, J.; Jee, B.; Kim, Y.; Kim, S. Uterine arteriovenous malformation treated by hysteroscopic excision. Gynecol. Minim. Invasive Ther. 2019, 8, 132–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Conde, C.; García-Jiménez, R.; Valero, I.; Estepa, A.; Macarena, E. Malformación arteriovenosa uterina como causa de hemorragia puerperal tardía. Ginecol. Obstet. Mex. 2023, 91, 631–636. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).