Abstract
Splenic torsion is an unusual condition that results in congenital abnormality, especially in the visceral abnormal arrangement. We report the case of an 8.5-year-old boy with features in the right upper quadrant. Radiological investigations revealed heterotaxy syndrome with polysplenia and a hypodense tumor in the right upper quadrant adjacent to several spleens. We initially treated it as an intra-abdominal tumor. Laparoscopy was performed to check the tumor condition and revealed a congestive tumor located in the abdomen of the right upper quadrant below the central liver, which was suspected to be a torsion spleen without attaching ligaments. Laparoscopic splenectomy was successfully carried out without complications. The pathological report shows splenic tissue with hemorrhagic infarction. Physicians should be vigilant of the differential diagnosis of the acute abdomen in adolescents.
1. Introduction
The normal anatomy of the internal organs is known as the situs solitus. Situs inversus refers to the mirror image of situs solitus, in which there is a reversal of the placement of the abdominal and thoracic structures. Heterotaxy is defined as abnormal arrangements of the abdominal and thoracic organs, which are caused by a change in the orientation of the left–right axis in early embryonic development [1,2] (Figure 1).
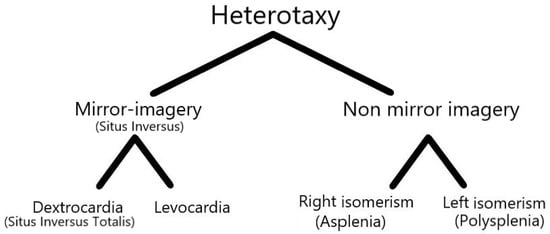
Figure 1.
Anomalies of situs (visceral arrangement).
Heterotaxy, a term that originates from Greek (hetero, meaning “different”; taxy, meaning “arrangement”), is also referred to as visceral heterotaxy or heterotaxy syndrome. Patients with heterotaxy are classified into two subsets: right isomerism (asplenia syndrome) and left isomerism (polysplenia syndrome). Heterotaxy syndrome has an estimated incidence of 1 in 6000 to 20,000 live births, with a female predominance [3].
There are several modalities of genetic inheritance associated with heterotaxy, such as primary ciliary dyskinesia, Patau syndrome (trisomy 13), Edwards syndrome (trisomy 18), or DiGeorge syndrome (22q11.2 deletion syndrome). In addition, other factors, such as maternal cocaine use, maternal diabetes, and monozygotic twinning are also associated with heterotaxy [4]. In the molecular study of the anomalies of situs, some mutations of genes affect the cilia and the normal asymmetry of the left–right axis. They encode proteins in the TGF-beta pathway, including NODAL, NKX2-5, CRELD1, LEFTY2, ZIC3, and ACVR2B [5,6,7,8]. Famous mutations in the ZIC3 gene, which encodes the zinc finger transcription factor, are described in about 75% of X-linked familial cases and 5% of sporadic cases [9].
The clinical findings in heterotaxy syndrome are variable and range from asymptomatic to serious cyanotic presentation. The level of cardiac malformation, the severity of the disease and the prognosis are complex; and the polysplenia group has a better prognosis than the asplenia group. The hemodynamic compromise is less severe due to the rarity of pulmonary atresia and an anomalous pulmonary vein. However, atrioventricular block is more severe in patients with polysplenia [10]. Intestinal obstruction and rotation are common in both groups. Intestinal rotational disorders (such as malrotation) can occur in 40 to 90% of heterotaxy syndrome, and Hill et al. reported that the asplenia group may have a higher rate of malrotation [11,12,13].
The organ in abdominal cavity can rapidly be illustrated by plain films of the chest or abdomen. Echocardiography is also a diagnostic tool for diagnosing variable and often complex cardiovascular abnormalities in patients with heterotaxy syndrome, but it depends on the efficacy and experience of the sonographer. Computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be a useful additional diagnostic tool [14,15].
This article presents a special case of abdominal pain in the right upper quadrant as a splenic torsion and increases the awareness of heterotaxy syndrome.
2. Detailed Case Description
An 8.5-year-old boy, who had asthma treated with the usual use of inhalers and Montelukast, was admitted to the emergency department upon referral from the local medical department. He suffered from intermittent dull abdominal pain in the right upper quadrant (RUQ) after a long running activity during a sports lesson at school. Physical examination revealed a tenderness over the RUQ region but normal presentation otherwise. A laboratory investigation showed leukocytosis (18,100/μL) with neutrophilia (76.8%); elevated C-reactive protein (2.56 mg/dL) and d-dimer (1670 ng/mL); and decreased hemoglobin (13.0 g/dL). Plain films of the chest and abdomen showed right-side stomach gas and levocardia as well as midline liver shadow and colonic gas on the left side, suggesting heterotaxy syndrome and malrotation (Figure 2). Abdominal computed tomography (CT) revealed hypodense tumor and polysplenia (six spleens) in the right upper quadrant; midline liver, right-sided stomach, ipsilateralization of the abdominal aorta, and IVC were also suspected (Figure 3). He was admitted to the ward for further surveillance.
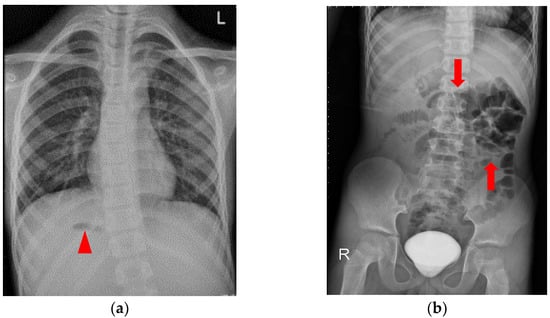
Figure 2.
Plain film of the chest and abdomen: (a) right-sided stomach gas (arrow head) and levocardia; (b) midline liver shadow and colon gas on the left side (arrows), suggesting heterotaxy syndrome and malrotation. Contrast medium that had not finished metabolism was retained in the urinary bladder.
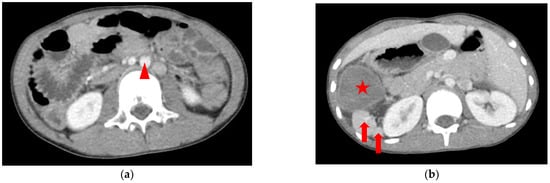
Figure 3.
CT of the abdomen showing that the liver is full in the midline of the abdomen: (a) the hypodense tumor is located in the right abdomen <star>, and the superior mesentery vein <arrow head> lies to the left of the superior mesentery artery; (b) seven arrowhead spleens <arrows> are suspected beside the tumor (all spleens cannot be shown in two pictures). See the complete series of CT in Supplementary Materials Figure S1: CT of abdomen.
During hospitalization, no elevated levels of tumor makers, such as alpha feto-protein (<0.5 ng/mL) and carcinoembryonic antigen (0.3 ng/mL), were observed. A whole-body positron emission tomography (PET) scan revealed tumor or inflammation in the right upper abdomen (Figure 4). A clinical diagnosis of a right upper abdominal tumor was made. Surgical intervention was agreed upon after discussion with the patient’s family. Preoperative cardiac sonography showed an interruption of IVC with a continuation of the azygos vein, ipsilateralization of the abdominal aorta and IVC, and juxtaposition of the atrial appendage. Furthermore, normal intra-cardiac structures and cardiac function with functioning left ventricular ejection fraction (68%) were observed.
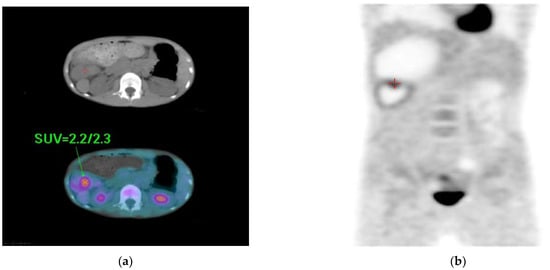
Figure 4.
Whole-body PET scan showing: (a,b) persistent focal increase in FDG uptake in the right upper abdomen (early/delayed SUV max = 2.2/2.3) and a tumor or inflammation was pointed out <red duplex and arrow>. SUV = standard uptake volume.
Laparoscopic tumor excision (Figure 5) was performed. He was discharged 4 days after the operation, and his condition was cured without any complications. The pathological report showed splenic tissue with hemorrhagic infarction.
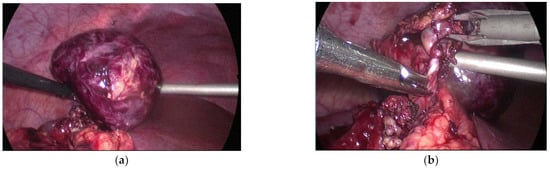
Figure 5.
Laparoscopy showing: (a) a 5 cm × 5 cm intra-abdominal tumor beneath the liver—a suspected spleen; (b) twisted feeding vessels are also observed without ligaments connected around them.
3. Discussion
In general, splenic torsion has been described in individuals with wandering spleen or accessory spleen and in those patients without underlying congenital anomalies of the situs. The first successful resection of splenic torsion associated with wandering spleen was described by Martin in 1877 [16]. Wandering spleen can be caused by the acquired laxity of the peri-splenic ligaments, congenital underdevelopment, or the absence of the primary ligament attachments of the spleen [17]. Accessory spleens arise from incomplete fusion of the spleen during embryonic development [18].
The pathological condition that causes splenic torsion was described as abnormal visceral fixation, including twisted intraperitoneal pancreas in the pedicle, anomalies of gastric attachment or diaphragmatic anatomy. Furthermore, the secondary consequences of torsion can also be a mechanism, such as obstruction due to mass effects, gastric varices, or hemoperitoneum due to the interruption of vascular flow. Bough GM et al. used a large modern dataset of 408 cases for splenic torsion in the first systematic review. It showed that only 8% of the patients had a coexisting congenital anomaly, such as a congenital diaphragmatic hernia, diaphragmatic eventration, and abdominal wall defect. Females were predominant in presenting splenic torsion, but an inverse presentation occurred at a younger age and during infancy [19].
There were no specific symptoms or signs that can be used to evaluate splenic torsion. Nonspecific gastrointestinal presentations were commonly described, including abdominal pain, vomiting, fever, and abdominal distension. In some cases, the inflammation reaction may affect adjacent organs, such as the stomach, intestines, and pancreas, due to compromised vascular systems. Therefore, gastric volvulus, intestinal obstruction, pancreatic torsion, or shock may occur simultaneously [19,20]. A recent study described that preoperative thrombocytosis may predict splenic infarction [19]. Therefore, imaging exams play a critical character for the clinical diagnosis. Ultrasound can seldom be used to diagnose, but abdomen CT with intravenous contrast is frequently required.
Surgical intervention and conservative management are the two main splenic torsion treatment options. Splenectomy is the main choice of treatment for splenic torsion, but the spleen can also be preserved using detorsion, splenopexy, and an autotransplant [21]. More than 50% of patients who chose conservative management require subsequent surgery. The splenopexy technique can be carried out using three different methods: direct fixation of the spleen to the abdominal wall with non-absorbable sutures, indirect fixation using an artificial mesh pocket, or indirect fixation using an extraperitoneal or intraperitoneal pouch [22,23,24]. Each option may have complications. The main complications of splenectomy are thrombocytosis, sepsis, and subsequent immunity of capsuled bacterial organisms, which requires triple vaccination boosters (Hemophilus influenzae, Neisseria meningitidis, and Streptococcus pneumoniae), seasonal influenza vaccination, COVID-19 vaccination, and even prophylactic antibiotics. Some studies of long-term outcomes after splenectomy described the additional increased risk of hematologic malignancy and thromboembolism [25,26]. For de-torsion and splenopexy, patients may present recurrent splenic torsion, splenomegaly due to venous obstruction, and sequestration of blood [20].
Splenic torsion is an unusual surgical condition that may present in a time-critical manner with a diagnostic challenge [20]. In our case, the challenge was greater due to the association of heterotaxy syndrome. In our review of the literature, we found that only five cases (not including our case) of splenic torsion in heterotaxy syndrome with polysplenia have been reported thus far [27,28,29,30,31] (Table 1), with a female predominance.

Table 1.
Previous reports of splenic torsion in heterotaxy syndrome.
Anamnesis is not a major tool for diagnosis to offer a suggestion of whether splenic torsion and heterotaxy syndrome are present, as described above. These conditions gradually become clear until imaging examination can definitively diagnose them [32,33]. In our case, abdominal pain in the right upper quadrant was the only presentation. We could not ensure that the intra-abdominal tumor was the torsion spleen, even by CT and PET scan, until laparoscopy and histology. Therefore, we delayed diagnosis for several days.
We chose the minimally invasive laparoscopic splenectomy because our technique was available [34]. In addition, during laparoscopy, we found that the ligaments around the resected spleen were absent and could easily twist. The patient was placed in the reverse Trendelenburg position. A vertical incision was made on the umbilicus. A modified Hassen method was used to place a 10 mm Trocar. Insufflation started with the flow about 5 L/min of CO2, and the pressure was set at 12 mmHg. A 5 mm telescope was inserted through the umbilical port, allowing for a good visualization of the right upper quadrant abdominal cavity. The second 5 mm port was placed in the subxiphoid area, and the third 5 mm port was placed in the right lumbar region. A fourth port may be placed in the right upper quadrant to assist with retraction. The infarcted left upper quadrant spleen was recognized and was adherent to greater omentum. The twisted feeding vessels of the spleen were clipped and divided. Then, we extended the umbilical wound to take the spleen out.
On the other hand, the diagnosis of heterotaxy is relatively challenging. This is because there are so many systems of viscera that need to be evaluated to distinguish the isomeric subset. The comparison of visceral presentation between both groups is listed in Table 2 [2,35,36,37,38,39,40,41] (Table 2). However, it is based on the atrial appendage structures that are the truly isomeric, whereas this is not always the case for the arrangement of pulmonary, bronchial, and abdominal organs [2].

Table 2.
Comparison of cardiac and extracardiac presentation in heterotaxy syndrome.
Our patient presents relatively typical left isomerism features. For instance, in the thoracic cavity, there is a juxtaposition of the atrial appendage. Unfortunately, we cannot accurately confirm the location and morphology of the juxtaposed atrial appendage due to lack of cardiac surgery necessity. In our case, cardiac anomalies were not always present in left isomerism. Singhi et al. described that the structurally normal heart or minor cardiac anomalies can be present in patients who had a juxtaposition of the left atrial appendage [42]. There are bilateral bilobed lungs with hyparterial bronchi in our patient, as shown in Supplementary Materials Figure S2: PET-CT of lung window. However, the details of heart anatomy cannot be evaluated by CT since a contrast medium was not used, whereas echocardiography showed normal intra-cardiac structures. Furthermore, bilateral SVC and interrupted IVC with continuation of the azygos vein are also presented. The abdominal cavity contains the midline liver, hepatic vein returning into the right atrium in confluence, ipsilateralization of the abdominal aorta and IVC, right-sided stomach, multiple spleens in the right upper quadrant abdomen, and malortation. The limitation of our study is the quality of the image series. We applied image studies, initially focusing on the surveillance of the acute abdomen, so only the lower part of the lungs and partial cardiac structure can be shown in the CT of abdomen. The lungs and bronchi were occasionally investigated using a whole-body PET-CT scan.
Our patient was cured and did not need a follow-up in the outpatient department for 7 years. He remains alive without any sequelae. We cannot expect a normal splenic function even though he still has six spleens. However, he has no post-operative record of any infective course; therefore, we did not remind him to take prophylactic antibiotics or have boosters of triple vaccinations for the encapsulated organisms. Additionally, malrotation is clearly observed. However, the surgeon was forced to choose a balance between morbidity and mortality from congenital heart disease and the risk of midgut volvulus. Hill et al. suggested that patients with left atrial isomerism could be easily treated due to fewer congenital heart problems [13]. Our patient did not have congenital heart disease for surgical correction and had good cardiac function.
4. Conclusions
Splenic torsion in heterotaxy syndrome with polysplenia is a rare condition that presents with abdominal pain in the right upper quadrant, and it can cause delayed diagnosis. Additionally, the stabilization of the spleens in this case of polysplenia may be weak due to the lack of attached ligaments. Physicians should be vigilant of the differential diagnosis of the acute abdomen that may affect adolescent patients.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/diagnostics12122920/s1, Figure S1: CT of abdomen; Figure S2: PET CT of lung window.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.-W.F. and T.-W.C.; methodology, Y.-W.F.; software, I.N.C.; validation, Y.-J.H., Y.-W.F. and T.-W.C.; investigation, C.-Y.W.; resources, C.-Y.W.; data curation, I.N.C.; writing—original draft preparation, I.N.C.; writing—review and editing, I.N.C.; visualization, I.N.C.; supervision, Y.-W.F.; project administration, Y.-W.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research did not receive external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was waived because of the absence of sensitive photos or private information.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge all participants and the MDPI English editing team involved in this study for their collaboration.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Varga, I.; Babala, J.; Kachlik, D. Anatomic variations of the spleen: Current state of terminology, classification, and embryological background. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2018, 40, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, R.H.; Spicer, D.E.; Loomba, R. Is an Appreciation of Isomerism the Key to Unlocking the Mysteries of the Cardiac Findings in Heterotaxy? J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2018, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, A.E.; Krikov, S.; Riehle-Colarusso, T.; Frías, J.L.; Belmont, J.; Anderka, M.; Geva, T.; Getz, K.D.; Botto, L.D.; the National Birth Defects Prevention Study. Laterality defects in the national birth defects prevention study (1998–2007): Birth prevalence and descriptive epidemiology. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2014, 164, 2581–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, S. Cardiac and Non-Cardiac Abnormalities in Heterotaxy Syndrome. Indian J. Pediatr. 2015, 82, 1135–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Xia, H.; Deng, S. Genetic basis of human left–right asymmetry disorders. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2015, 16, e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaki, R.; Gebbia, M.; Kosaki, K.; Lewin, M.; Bowers, P.; Towbin, J.A.; Casey, B. Left-right axis malformations associated with mutations in ACVR2B, the gene for hu-man activin receptor type IIB. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1999, 82, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, B.; Casey, B.; Li, H.; Ho-Dawson, T.; Smith, L.; Fernbach, S.D.; Molinari, L.; Niesh, S.R.; Jefferies, J.L.; Craigen, W.J.; et al. Identification and functional characterization of NODAL rare variants in heterotaxy and isolated cardiovascular malformations. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedard, J.E.J.; Haaning, A.M.; Ware, S.M. Identification of a Novel ZIC3 Isoform and Mutation Screening in Patients with Heterotaxy and Congenital Heart Disease. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellchambers, H.M.; Ware, S.M. ZIC3 in Heterotaxy. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1046, 301–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.-H.; Wang, J.-K.; Chiu, S.-N.; Tseng, W.-C.; Lu, C.-W.; Lin, H.-C.; Lin, M.-T.; Chen, C.-A. Twin atrioventricular nodes, arrhythmias, and survival in pediatric and adult patients with heterotaxy syndrome. Heart Rhythm 2021, 18, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buca, D.I.P.; Khalil, A.; Rizzo, G.; Familiari, A.; Di Giovanni, S.; Liberati, M.; Murgano, D.; Ricciardulli, A.; Fanfani, F.; Scambia, G.; et al. Outcome of prenatally diagnosed fetal heterotaxy: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 51, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartram, U.; Wirbelauer, J.; Speer, C.P. Heterotaxy Syndrome–Asplenia and Polysplenia as Indicators of Visceral Malposition and Complex Congenital Heart Disease. Neonatology 2005, 88, 278–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, M.S.; Guleserian, K.J.; Forbess, J.M. Ladd’s Procedure in Functional Single Ventricle and Heterotaxy Syndrome: Does Timing Affect Outcome? Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2013, 95, 1403–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawfik, A.M.; Batouty, N.; Zaky, M.M.; Eladalany, M.A.; Elmokadem, A.H. Polysplenia syndrome: A review of the relationship with viscero-atrial situs and the spectrum of extra-cardiac anomalies. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2013, 35, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.K.; Park, Y.W.; Ryu, S.J.; Won, J.W.; Choi, J.Y.; Sul, J.H.; Lee, S.K.; Cho, B.K.; Choe, K.O. Efficacy of MRI in Complicated Congenital Heart Disease with Visceral Heterotaxy Syndrome. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2000, 24, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A. A Successful Case of Splenotomy. BMJ 1878, 1, 191–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, Y.; Mo, Z.; Tian, Z.; Yang, F.; Wang, Y.; Yao, L. Wandering spleen with splenic torsion in a toddler. Medicine 2020, 99, e22063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglietta, P.M.; Moran, C.J.; Ryan, D.P.; Sagar, P.; Huck, A.E. Case 3-2016. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bough, G.M.; Gargan, K.E.; Cleeve, S.J.; Farrell, S. Diagnosis, management and outcome of splenic torsion; A systematic review of published studies. Surgeon 2021, 20, e296–e305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, A.S.A.; Streit, U.; Uhlig, J.; Biggemann, L.; Kahl, F.; Ahmed, S.; Markus, D. Splenic torsion with involvement of pancreas and descending colon in a 9-year-old boy. BJR Case Rep. 2018, 5, 20180051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Peng, C.; Wu, D.; Wang, K.; Chen, Y. Diagnosis and treatment of splenic torsion in children: Preoperative thrombocytosis predicts splenic infarction. BMC Pediatr. 2022, 22, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palanivelu, C.; Rangarajan, M.; Senthilkumar, R.; Parthasarathi, R.; Kavalakat, A.J. Laparoscopic Mesh Splenopexy (Sandwich Technique) for Wandering Spleen. JSLS J. Soc. Laparoendosc. Surg. 2007, 11, 246–251. [Google Scholar]
- Thambidorai, C.R.; Imtiaz, A.; Nafiqudin, M. Torsion of a wandering spleen with whorled appearance of the splenic hilum in CT scan. Med. J. Malays. 2005, 60, 653–654. [Google Scholar]
- Fukuzawa, H.; Urushihara, N.; Ogura, K.; Miyazaki, E.; Matsuoka, T.; Fukumoto, K.; Kimura, S.; Mitsunaga, M.; Hasegawa, S. Laparoscopic splenopexy for wandering spleen: Extraperitoneal pocket splenopexy. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2006, 22, 931–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyaw, M.H.; Holmes, E.M.; Toolis, F.; Wayne, B.; Chalmers, J.; Jones, I.G.; Campbell, H. Evaluation of Severe Infection and Survival After Splenectomy. Am. J. Med. 2006, 119, 276.e1–276.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristinsson, S.Y.; Gridley, G.; Hoover, R.N.; Check, D.; Landgren, O. Long-term risks after splenectomy among 8149 cancer-free American veterans: A cohort study with up to 27 years follow-up. Haematologica 2013, 99, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, M.; Abe, Y.; Kodera, A.; Kitada, K.; Araki, T. Splenic torsion and polysplenia syndrome in a 10-year-old girl. Pediatr. Int. 2019, 61, 192–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachmann, R.; Loff, S.; Düber, C.; Neff, K.W. Visceral heterotaxia with polysplenia syndrome and haemorrhagic splenic infarction as a rare cause of the acute paediatric abdomen. Pediatr. Radiol. 2006, 36, 572–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, N.B.; Smith, M.D.; Strobel, C.T.; Wheller, J.J. Splenic Torsion in the Polysplenia Syndrome. South. Med. J. 1982, 75, 897–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, F.; Mirza, B. Polysplenia syndrome associated with situs inversus abdominus and type I jejunal atresia. APSP J. Case Rep. 2011, 2, 18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dash, M.R.; Upasani, A.V.; Chandna, S.B.; Rathod, P.B.; Prajapati, K.K.; Patel, D.N. Splenic Torsion in a Child with Polysplenia and Situs Inversus: A Very Rare Presentation. Indian J. Surg. 2013, 75, 236–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sanders, S.P.; Geva, T. Classifying Heterotaxy Syndrome. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2018, 11, e007490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yim, D.; Nagata, H.; Lam, C.Z.; Grosse-Wortmann, L.; Seed, M.; Jaeggi, E.; Yoo, S.-J. Disharmonious Patterns of Heterotaxy and Isomerism. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2018, 11, e006917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, H.; Yamaoka, N.; Tamai, M.; Kamiya, H.; Kamada, Y.; Nagata, T.; Fukuda, K.-I.; Otsuji, E. Laparoscopic splenectomy for polysplenia with splenic torsion: A case report. Surg. Case Rep. 2019, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, S.J.; Heiss, K.F.; Mittal, R.; Clabby, M.L.; Durham, M.M.; Ricketts, R.; Wulkan, M.L. Heterotaxy syndrome and malrotation: Does isomerism influence risk and decision to treat. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2014, 49, 934–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, J.P.; Anderson, R.H.; Weinberg, P.M.; Walters, H.L.; Tchervenkov, C.I.; Del Duca, D.; Franklin, R.C.G.; Aiello, V.D.; Béland, M.J.; Colan, S.D.; et al. The nomenclature, definition and classification of cardiac structures in the setting of heterotaxy. Cardiol. Young 2007, 17 (Suppl. S2), 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Praagh, R.; Van Praagh, S. Atrial isomerism in the heterotaxy syndromes with asplenia, or polysplenia, or normally formed spleen: An erroneous concept. Am. J. Cardiol. 1990, 66, 1504–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macartney, F.J.; Zuberbuhler, J.R.; Anderson, R.H. Morphological considerations pertaining to recognition of atrial isomerism. Consequences for sequential chamber localisation. Heart 1980, 44, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-J. Heterotaxy Syndrome. Korean Circ. J. 2011, 41, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, A.L.; Miller, D.V.; Porter, C.-B.J.; Edwards, W.D. Characterization of atrial morphology and sinus node morphology in heterotaxy syndrome: An autopsy-based study of 41 cases (1950–2008). Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2012, 21, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, S.; Parthiban, A. Progressive fetal atrioventricular block in heterotaxy syndrome. Cardiol. Young 2007, 17, 432–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivakumar, K.; Singhi, A.K.; Pradhan, P.; Agarwal, R. Juxtaposed atrial appendages: A curiosity with some clinical relevance. Ann. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2016, 9, 186–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).