A Novel Tongue Pressure Measurement Instrument with Wireless Mobile Application Control Function and Disposable Positioning Mouthpiece
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
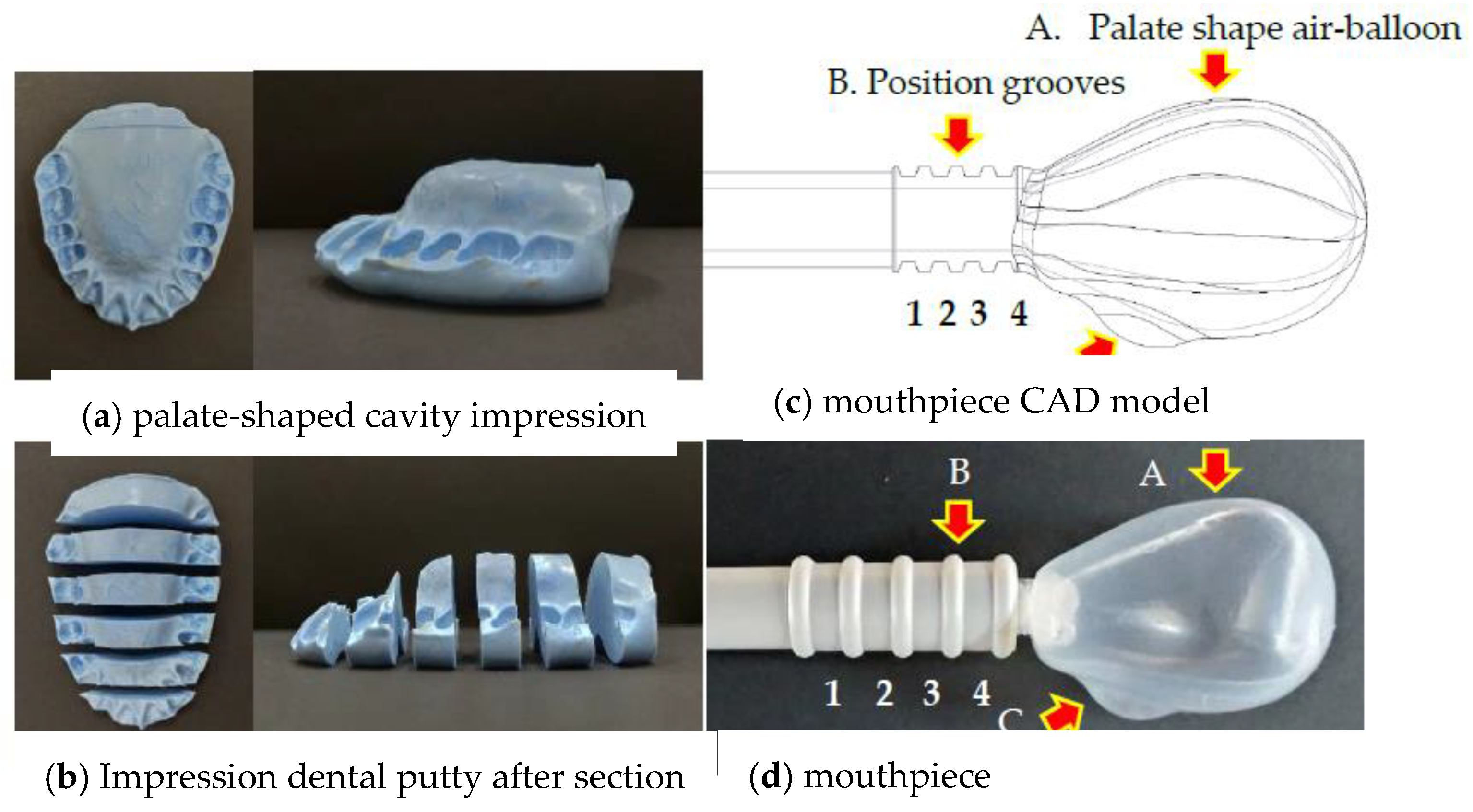
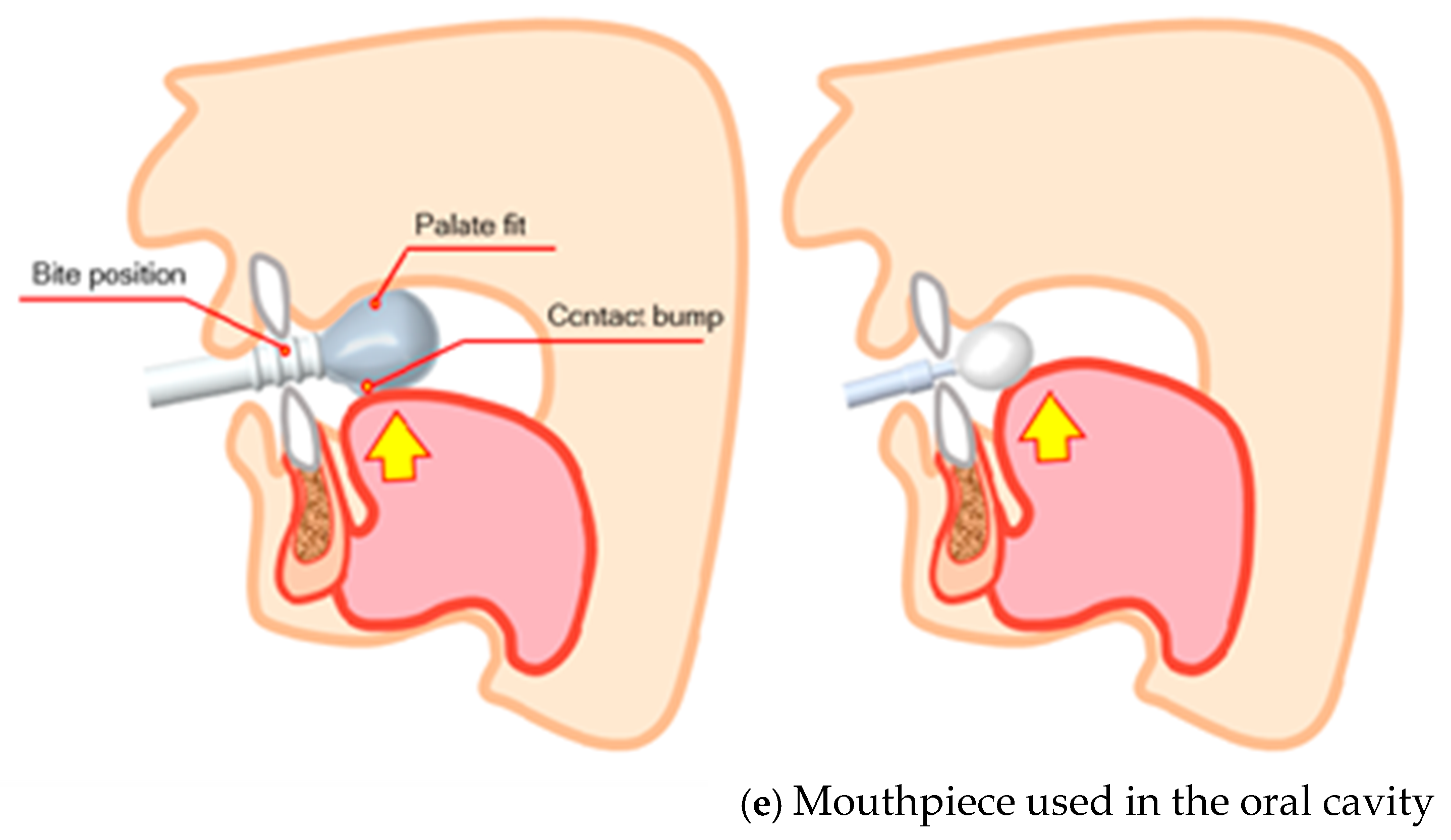
2.1. Mouthpiece Device Design
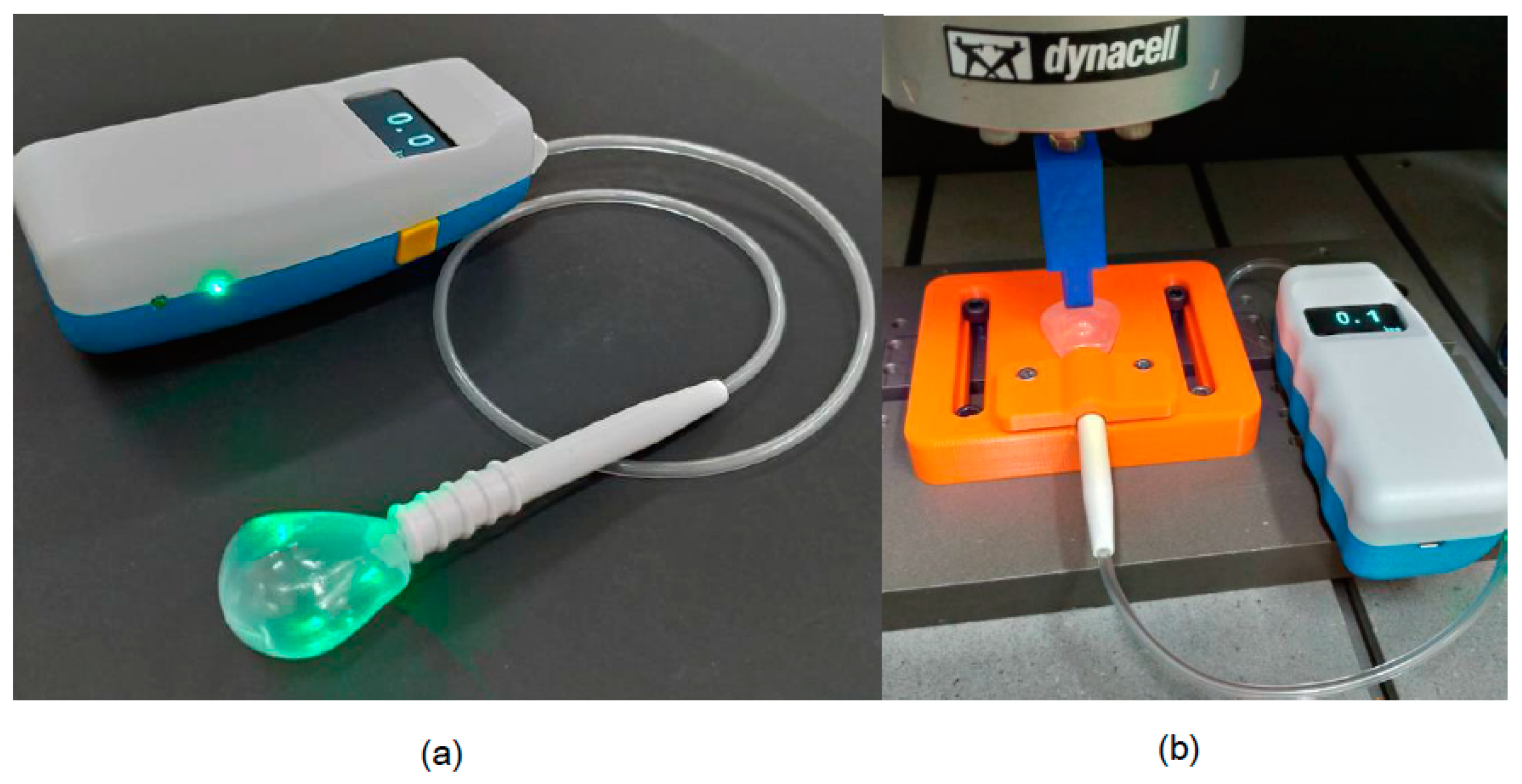
2.2. Mouthpiece Fatigue Testing
2.3. TP Instrument Development
2.4. Participants and TP Measuring Method
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Ethical Approval
References
- Adams, V.; Mathisen, B.; Baines, S.; Lazarus, C.; Callister, R. Reliability of measurements of tongue and hand strength and endurance using the Iowa Oral Performance Instrument with healthy adults. Dysphagia 2014, 29, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, A.; Hind, J.; Kays, S.; Nicosia, M.; Doyle, J.; Tompkins, W.; Gangnon, R.; Robbins, J. Standardized instrument for lingual pressure measurement. Dysphagia 2008, 23, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, K.; Akagi, J. Decreased tongue pressure is associated with sarcopenia and sarcopenic dysphagia in the elderly. Dysphagia 2015, 30, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.C. Effects of Tongue Strength Training and Detraining on Tongue Pressures in Healthy Adults. Dysphagia 2015, 30, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utanohara, Y.; Hayashi, R.; Yoshikawa, M.; Yoshida, M.; Tsuga, K.; Akagawa, Y. Standard values of maximum tongue pressure taken using newly developed disposable tongue pressure measurement device. Dysphagia 2008, 23, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Yoshida, M.; Tsuga, K.; Akagawa, Y.; Groher, M.E. Comparison of three types of tongue pressure measurement devices. Dysphagia 2011, 26, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higa, C.; Mori, T.; Hiraoka, A.; Takeda, C.; Kuroki, A.; Yoshikawa, M.; Yoshida, M.; Tsuga, K. Five-year change in maximum tongue pressure and physical function in community-dwelling elderly adults. J. Dent. Sci. 2020, 15, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machida, N.; Tohara, H.; Hara, K.; Kumakura, A.; Wakasugi, Y.; Nakane, A.; Minakuchi, S. Effects of aging and sarcopenia on tongue pressure and jaw-opening force. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2017, 17, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, M.; Kikutani, T.; Tsuga, K.; Utanohara, Y.; Hayashi, R.; Akagawa, Y. Decreased tongue pressure reflects symptom of dysphagia. Dysphagia 2006, 21, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, H.M. Specificity of training in the lingual musculature. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2012, 55, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, V.; Mathisen, B.; Baines, S.; Lazarus, C.; Callister, R. A systematic review and meta-analysis of measurements of tongue and hand strength and endurance using the Iowa Oral Performance Instrument (IOPI). Dysphagia 2013, 28, 350–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderwegen, J.; Guns, C.; Van Nuffelen, G.; Elen, R.; De Bodt, M. The influence of age, sex, bulb position, visual feedback, and the order of testing on maximum anterior and posterior tongue strength and endurance in healthy belgian adults. Dysphagia 2013, 28, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kugimiya, Y.; Watanabe, Y.; Igarashi, K.; Hoshino, D.; Motokawa, K.; Edahiro, A.; Ueda, T.; Takano, T.; Sakurai, K.; Taniguchi, Y.; et al. Factors associated with masticatory performance in community-dwelling older adults: A cross-sectional study. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2020, 151, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaker, R.; Cook, I.J.; Dodds, W.J.; Hogan, W.J. Pressure-flow dynamics of the oral phase of swallowing. Dysphagia 1988, 3, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagao, K.; Kitaoka, N.; Kawano, F.; Komoda, J.; Ichikawa, T. Influence of changes in occlusal vertical dimension on tongue pressure to palate during swallowing. Prosthodont. Res. Pract. 2002, 1, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.L.; Watkin, K.L. The influence of bolus volume and viscosity on anterior lingual force during the oral stage of swallowing. Dysphagia 1996, 11, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuga, K.; Hayashi, R.; Sato, Y.; Akagawa, Y. Handy measurement for tongue motion and coordination with laryngeal elevation at swallowing. J. Oral Rehabil. 2003, 30, 985–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouderoux, P.; Kahrilas, P.J. Deglutitive tongue force modulation by volition, volume, and viscosity in humans. Gastroenterology 1995, 108, 1418–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crow, H.C.; Ship, J.A. Tongue strength and endurance in different aged individuals. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 1996, 51, M247–M250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, R.; Tsuga, K.; Hosokawa, R.; Yoshida, M.; Sato, Y.; Akagawa, Y. A novel handy probe for tongue pressure measurement. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2002, 15, 385–388. [Google Scholar]
- McKenna, V.S.; Zhang, B.; Haines, M.B.; Kelchner, L.N. A Systematic Review of Isometric Lingual Strength-Training Programs in Adults With and Without Dysphagia. Am. J. Speech Lang. Pathol. 2017, 26, 524–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Steen, L.; De Bodt, M.; Guns, C.; Elen, R.; Vanderwegen, J.; Van Nuffelen, G. Tongue-Strengthening Exercises in Healthy Older Adults: Effect of Exercise Frequency—A Randomized Trial. Folia Phoniatr. Logop. 2020, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, N.P.; Clark, H.M. The effect of an anti-slip surface on objective measures of tongue strength in healthy adults. Int. J. Orofac. Myol. Myofunct. Ther. 2020, 46, 13–21. [Google Scholar]
- Belafsky, P.C.; Mouadeb, D.A.; Rees, C.J.; Pryor, J.C.; Postma, G.N.; Allen, J.; Leonard, R.J. Validity and reliability of the Eating Assessment Tool (EAT-10). Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2008, 117, 919–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, P.; Chandra, P.; Tandon, R.; Singh, K.; Chauhan, A. Devices used for measuring tongue force: A review. Int. J. Orthod. Rehabil. 2020, 11, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gingrich, L.L.; Stierwalt, J.A.; Hageman, C.F.; LaPointe, L.L. Lingual propulsive pressures across consistencies generated by the anteromedian and posteromedian tongue by healthy young adults. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2012, 55, 960–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuga, K.; Yoshikawa, M.; Oue, H.; Okazaki, Y.; Tsuchioka, H.; Maruyama, M.; Yoshida, M.; Akagawa, Y. Maximal voluntary tongue pressure is decreased in Japanese frail elderly persons. Gerodontology 2012, 29, e1078–e1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doherty, T.J. The influence of aging and sex on skeletal muscle mass and strength. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2001, 4, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, N.P.; Munson, B. The effect of jaw position on measures of tongue strength and endurance. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2004, 47, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Gao, X. Tongue pressure distribution of individual normal occlusions and exploration of related factors. J. Oral Rehabil. 2019, 46, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanashi, H.; Shimizu, Y.; Higashi, M.; Koyamatsu, J.; Sato, S.; Nagayoshi, M.; Kadota, K.; Kawashiri, S.; Tamai, M.; Takamura, N.; et al. Validity of maximum isometric tongue pressure as a screening test for physical frailty: Cross-sectional study of Japanese community-dwelling older adults. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2018, 18, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arakawa, I.; Igarashi, K.; Imamura, Y.; Müller, F.; Abou-Ayash, S.; Schimmel, M. Variability in tongue pressure among elderly and young healthy cohorts: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Oral Rehabil. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Testing Sample | Tongue Pressure during Testing Cycles (kPa) | p-Value | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Cycle 0–10) | (Cycle 300–310) | (Cycle 700–710) | (Cycle 0 v.s. 300) | (Cycle 0 v.s. 700) | |
| Mean(SD) | Mean(SD) | Mean(SD) | |||
| Total | 12.69(0.44) | 12.40(0.11) | 12.14(0.20) | ||
| Sample 1 | 12.84(0.35) | 12.31(1.04) | 11.97(1.28) | 0.14 | 0.05 |
| Sample 2 | 13.04(0.76) | 12.52(1.27) | 12.36(1.35) | 0.28 | 0.18 |
| Sample 3 | 12.20(0.99) | 12.36(1.34) | 12.08(1.29) | 0.76 | 0.82 |
| Testing Sample | Tongue Pressure during Testing Cycles (kPa) | p-Value | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Cycle 0–10) | (Cycle 300–310) | (Cycle 700–710) | (Cycle 0 v.s. 300) | (Cycle 0 v.s. 700) | |||
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | |||||
| Total | 12.69(0.44) | 12.40(0.11) | 12.14(0.20) | ||||
| Sample 1 | 12.84(0.35) | 12.31(1.04) | 11.97(1.28) | 0.14 | 0.05 | ||
| Sample 2 | 13.04(0.76) | 12.52(1.27) | 12.36(1.35) | 0.28 | 0.18 | ||
| Sample 3 | 12.20(0.99) | 12.36(1.34) | 12.08(1.29) | 0.76 | 0.82 | ||
| Variable | TPWA | p-Value | JMS | p-Value | |||
| n | Mean | (SD) | Mean | (SD) | |||
| Total | 52 | 40.77 | (12.48) | 41.51 | (11.01) | ||
| Test sequence | |||||||
| TPWA–JMS | 22 | 42.31 | (13.63) | 0.451 | 42.17 | (12.23) | 0.715 |
| JMS–TPWA | 30 | 39.64 | (11.67) | 41.03 | (10.21) | ||
| Gender | |||||||
| Male | 35 | 43.51 | (11.72) | 0.022 | 44.53 | (10.59) | 0.004 |
| Female | 17 | 35.14 | (12.43) | 35.30 | (9.31) | ||
| Variable | TPWA | p-Value | JMS | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Mean | (SD) | Mean | (SD) | |||
| Total | 40 | 16.55 | (9.17) | 19.56 | (9.26) | ||
| Test sequence | |||||||
| TPWA–JMS | 20 | 16.12 | (8.78) | 0.772 | 19.12 | (9.02) | 0.768 |
| JMS–TPWA | 20 | 16.98 | (9.75) | 20.00 | (9.71) | ||
| Gender | |||||||
| Male | 9 | 12.97 | (8.30) | 0.187 | 14.91 | (5.57) | 0.087 |
| Female | 31 | 17.59 | (9.27) | 20.91 | (9.74) | ||
| Age | |||||||
| 60–69 yrs | 18 | 19.66 | (10.61) | 0.086 | 22.89 | (10.13) | 0.118 |
| 70–79 yrs | 15 | 15.40 | (6.87) | 17.02 | 6.61 | ||
| ≥80 yrs | 7 | 11.01 | (7.01) | 16.43 | (10.20) | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.-Y.; Chen, C.-H.; Kuo, C.-H.; Feng, M.-C.; Chen, J.-H.; Wang, H.-W.; Chen, K.-C.; Lin, C.-L. A Novel Tongue Pressure Measurement Instrument with Wireless Mobile Application Control Function and Disposable Positioning Mouthpiece. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11030489
Liu H-Y, Chen C-H, Kuo C-H, Feng M-C, Chen J-H, Wang H-W, Chen K-C, Lin C-L. A Novel Tongue Pressure Measurement Instrument with Wireless Mobile Application Control Function and Disposable Positioning Mouthpiece. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(3):489. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11030489
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Hsiu-Yueh, Chun-Hung Chen, Chao-Hung Kuo, Ming-Chu Feng, Jen-Hao Chen, Hsuan-Wen Wang, Kun-Chun Chen, and Chun-Li Lin. 2021. "A Novel Tongue Pressure Measurement Instrument with Wireless Mobile Application Control Function and Disposable Positioning Mouthpiece" Diagnostics 11, no. 3: 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11030489
APA StyleLiu, H.-Y., Chen, C.-H., Kuo, C.-H., Feng, M.-C., Chen, J.-H., Wang, H.-W., Chen, K.-C., & Lin, C.-L. (2021). A Novel Tongue Pressure Measurement Instrument with Wireless Mobile Application Control Function and Disposable Positioning Mouthpiece. Diagnostics, 11(3), 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11030489







