Abstract
Purpose: To differentiate inflammatory breast cancer (IBC) from mastitis in Asian women presenting with symptoms of inflammation. Methods: Between January 2012 and June 2024, 101 Asian women with symptoms of inflammation underwent breast ultrasound (US). Clinical and demographic data were extracted from patients’ medical records. US analysis assessed lesion bilaterality, location, type, size, internal changes, and lymph node status. Patients with suspicious findings had US-guided biopsies, and pathology reports were reviewed for tumor histology and immunohistochemical markers. Logistic regression was used to determine odds ratios. Results: Of the 101 participants, 14 (13.9%) were diagnosed with IBC and 87 (86.1%) were diagnosed with mastitis. Patients with IBC were significantly older (46.4 vs. 38.4 years, p = 0.020) and showed a higher prevalence of postmenopausal status (57.1% vs. 12.6%, p < 0.0001). These patients experienced a longer symptom onset duration (37.7 vs. 12.7 days, p = 0.002) and more frequent localized symptoms like swelling (50.0% vs. 13.8%, p = 0.004). US findings showed that 21.4% of IBC lesions involved the entire breast, compared to only 1.1% in patients with mastitis (p = 0.001). Biopsy results revealed that invasive ductal carcinoma was the most common malignancy (78.6%). Logistic regression identified symptom onset duration (adjusted odds ratio (OR) 1.07, p = 0.014) and swelling (adjusted OR 15.24, p = 0.016) as significant predictors of IBC. Conclusion: In Asian women, age, menopausal status, symptom onset duration, and swelling are effective in differentiating IBC from mastitis. Logistic regression confirmed that symptom onset duration and swelling are significant predictors of IBC, with US findings indicating larger lesion sizes and more frequent whole-breast involvement.
1. Introduction
Inflammatory breast, sometimes referred to as red breast syndrome, is a classic but rare complaint among women in both primary care settings and dedicated breast centers [1,2]. It typically manifests as redness and warmth of the breast and is frequently accompanied by breast pain [3,4]. The spectrum of possible diagnoses for women presenting with inflammatory breast symptoms is broad, ranging from benign, self-limited conditions to progressive, malignant diseases [1]. The malignant form of this condition, known as inflammatory breast cancer (IBC), has a high risk of metastasis and recurrence [5]. Lee and Tannebaum first described inflammatory carcinoma of the breast in 1924 [6]. In the United States, IBC is estimated to account for approximately 2–4% of new breast cancer diagnoses annually, yet it is responsible for 7–10% of breast cancer-related deaths [7].
Based on an estimated incidence of 125 breast cancer cases per 100,000 women, the incidence of IBC is approximately 2–3 cases per 100,000 women [8]. Consequently, many generalists may never encounter IBC during their careers. Studies indicate that among women presenting with an inflamed breast, the incidence of IBC ranges from 5–50%, underscoring its relevance in cases of breast inflammation, particularly in non-pregnant or non-postpartum patients [1,9,10].
All IBC studies, with the exception of a single study from France [9], have been conducted in the United States [1,11,12,13,14] and have generally excluded Asian women from their analyses. Additionally, original research has included cohorts ranging from 22–76 participants [1,9]. Jagsi et al. [14] proposed a quantitative scoring system to distinguish IBC from non-inflammatory locally advanced breast cancer based on clinical, pathological, and imaging features.
Breast cancer constitutes 24.5% of all cancers in female patients, with nearly half of breast cancer patients (45.4%) diagnosed in Asia [15]. Breast cancer tends to affect Asian women at an earlier age compared to Western women, with peak incidence occurring between 40 and 50 years in Asian countries and between 60 and 70 years in Western countries [16,17].
Therefore, this study aimed to investigate and differentiate IBC from mastitis in Asian women presenting with inflammatory symptoms. Our study included women of all ages, both postpartum and non-postpartum, in a large consecutive cohort.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
This study was approved by our Institutional Review Board (IRB No. 2024-07-009), and the requirement for informed consent was waived due to its retrospective nature. The study adhered to the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki. From January 2012 to June 2024, a total of 118 women presenting with inflammatory breast symptoms underwent breast ultrasound (US) at our facility. Nine patients were excluded owing to incomplete demographic and clinical information, and eight patients were excluded owing to poor US image quality or the removal of images from data storage. Consequently, 101 participants were included in the study; among them, 25 were diagnosed with clinical mastitis, 62 underwent biopsy for mastitis, and 14 had biopsies confirming IBC (Figure 1).
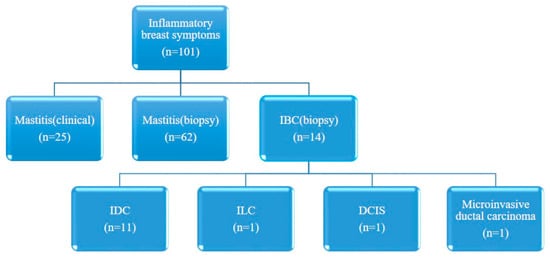
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram for the inclusion of participants.
All study participants underwent initial evaluation for inflammatory breast symptoms at the time of diagnosis and were not receiving any treatment.
IBC denotes inflammatory breast cancer; IDC denotes invasive ductal carcinoma; ILC denotes invasive lobular carcinoma; and DCIS denotes ductal carcinoma in situ.
2.2. Clinical and Demographic Data
Clinical and demographic data were collected, including age, body mass index (BMI, weight/height2) [18], pregnancy or lactation status, menopause status, history of mastitis, personal history of breast or other cancers, and underlying conditions such as diabetes, metabolic syndrome, or immunocompromised state. Information on current regular alcohol consumption and smoking habits was also gathered from the patients’ electronic medical records. For breast-related aspects, data on inflammatory symptoms included duration of symptom onset, types of localized symptoms (erythema, swelling, skin changes, warmth, palpable mass/lesion, and pain/discomfort), and systemic symptoms (fever, malaise, myalgia, flu-like symptoms, or none).
2.3. Ultrasound Examination and Analysis
Two breast radiologists, with 13 and 15 years of experience in breast imaging, conducted preoperative US examinations. Images were obtained using various high-resolution US units, including the ATL HDI 5000 (Philips-Advanced Technology Laboratories, Bothell, WA, USA) equipped with a 12–5 MHz linear array transducer, the iU22 (Philips Healthcare, Bothell, WA, USA) with a 12–5 MHz linear array transducer, and the Epic-7 and Epic Elite (Philips Healthcare, Bothell, WA, USA) with an eL18-4 MHz linear array transducer.
All patients underwent bilateral breast and axillary examinations. US images were analyzed in consensus by the radiologists using a INFINITT PACS system (Version: 3.0.11, INFINITT Healthcare, Seoul, Republic of Korea). The findings documented included bilaterality of the lesions, whether they were located in the right breast, left breast, or both, lesion type, and whether they were masses or non-mass formations. The location of the lesions was noted as central or peripheral, and their focality was classified as either single or multiple lesions. Echogenicity was assessed as hypoechoic, isoechoic, or hyperechoic, while the echo pattern was determined to be either homogeneous or heterogeneous. The size of the lesions was evaluated in relation to the whole breast, with categories including less than half, the same or larger than half, or involving the entire breast.
Additionally, internal changes within the lesions, such as cystic or necrotic alterations, were noted, as well as the presence or absence of lesion vascularity, categorized as minimal/mildly increased, moderate-to-severely increased, or none. Other findings included the presence of skin thickening, parenchymal edema, nipple inversion, calcification, and ductal changes. The status of the axillary lymph nodes was also assessed, with nodes being classified as enlarged, equivocal, or within the normal range.
2.4. Histopathology Review
After undergoing US examination, selected patients recommended by clinicians or radiologists underwent US-guided biopsy to confirm the diagnosis of mastitis and exclude other diseases, especially malignancy. Pathology reports were reviewed to determine tumor histology. Additional information regarding tumor grade and immunohistochemical (IHC) subtypes was collected from the patients’ electronic medical records after breast malignancy was confirmed. The following biomarkers were evaluated via IHC: estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), and Ki-67. IHC staining was performed using an automated Ventana BenchMark XT Slide Stainer (Ventana, Tucson, AZ, USA). Tumor subtypes were classified as hormone receptor (HR) positive/HER2 negative, HR positive/HER2 positive, HR negative/HER2 positive, or HR negative/HER2 negative (triple-negative). Positive Ki-67 expression was defined as Ki-67 positivity in ≥20% of cancer cell nuclei.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Clinical and demographic data of study participants were analyzed by calculating the mean, standard deviation, and numbers (%). To determine the distribution differences between IBC and mastitis for categorical variables, Fisher’s Exact Test or the Pearson Chi-Square Test was employed. For assessing mean differences in continuous variables, we performed a t-test. Additionally, logistic regression was used to calculate the crude odds ratio (OR), and an analysis was conducted to determine the adjusted OR, evaluating the impact of differences between IBC and mastitis. All statistical analyses were performed using SAS version 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA), and two-tailed p-values < 0.05 were considered to be statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Clinical and Demographic Characteristics
The study included 101 participants, with 14 (13.9%) diagnosed with IBC and 87 (86.1%) diagnosed with mastitis (Table 1). Patients with IBC had a significantly higher mean age of 46.4 years compared to 38.4 years in the mastitis group (p = 0.020). Additionally, a greater proportion of patients with IBC were aged 40 years or older (78.6%) compared to those with mastitis (26.4%) (p < 0.001).

Table 1.
Clinical and demographic data of the study participants.
Body mass index (BMI) also differed significantly between the groups. Patients with IBC had a higher mean BMI of 28.8 compared to 24.4 in the mastitis group (p = 0.009). All patients were either overweight or obese, with 87.5% categorized as obese; only 53.5% of patients fell into these categories (p = 0.012).
Menopausal status was significantly associated with IBC. Approximately 57.1% of patients with IBC were postmenopausal, compared to only 12.6% of patients with mastitis (p < 0.0001). The onset of symptoms was longer in patients with IBC, with a mean duration of 37.7 days compared to 12.7 days for patients with mastitis (p = 0.002). Localized symptoms such as swelling were more common in patients with IBC (50.0%) than in those with mastitis (13.8%) (p = 0.004). Other localized or systemic symptoms did not differ significantly between the groups. However, a history of previous mastitis was significantly less common in patients with IBC (7.1%) compared to those with mastitis (37.9%) (p = 0.019).
3.2. Ultrasound Features
US findings revealed significant differences between patients with IBC and those with mastitis (Table 2). IBC lesions were notably larger, with 21.4% involving the whole breast versus 1.1% in mastitis (p = 0.001) (Figure 2). Cystic/necrotic changes were less common in IBC (7.1%) compared to mastitis (33.3%) (p = 0.039) (Figure 3). Although the difference was not statistically significant, patients with IBC had a higher frequency of non-mass lesions (78.6%) and centrally located lesions (61.5%) compared with those with mastitis (67.8% and 38.8%, respectively). This group also exhibited more minimal to mild vascularity and skin thickening (85.7% and 92.9%, respectively) than patients with mastitis (59.8% and 80.5%). Parenchymal edema was present in all patients with IBC, compared to 86.2% of patients with mastitis. Additionally, patients with IBC had slightly higher rates of nipple inversion (28.6%) and calcifications (7.1%) compared to patients with mastitis (14.9% and 2.3%). Ductal changes and lymphadenopathy were more common in patients with IBC (35.7% and 57.1%) than in those with mastitis (32.2% for both), although these differences were not statistically significant.

Table 2.
Ultrasound findings of the study participants (n = 101).
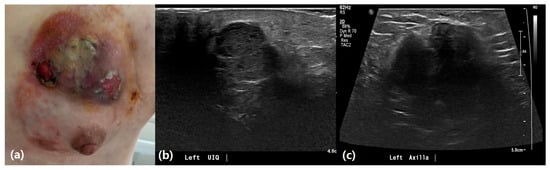
Figure 2.
Inflammatory breast cancer. A 40-year-old female patient presented with a palpable mass and skin changes in her left breast. (a) Clinical appearance showing erythema, skin thickening, and ulcerative changes at the time of the visit. (b) Ultrasound imaging demonstrates an irregular hypoechoic mass with diffuse skin thickening and edematous changes, primarily in the left upper inner quadrant. (c) Ultrasound imaging also shows a conglomerated lymph node, approximately 4.7 cm in size, in the left axillary level I, suggestive of metastatic involvement.
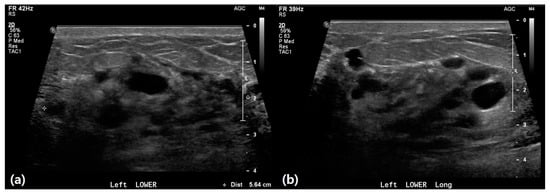
Figure 3.
A 43-year-old female presented with erythema, a palpable mass, and pain in the breast. (a,b) Ultrasound imaging revealed heterogeneous echo texture in both breasts. The lower portion of the left breast exhibited diffuse skin thickening and edematous changes, with an indistinct heterogeneous hypoechoic lesion containing cystic components. These findings suggest a high likelihood of an infectious condition, such as mastitis. The patient was treated with medication, and clinical follow-up indicated improvement in symptoms.
3.3. Pathological and Biopsy Results
Among benign mastitis cases (n = 62), the most common finding was chronic granulomatous inflammation (50.0%) (Figure 4), followed by inflammation with abscess formation (37.1%). For malignant biopsies (n = 14), invasive ductal carcinoma was predominant (78.6%), with one case each of microinvasive ductal carcinoma, invasive lobular carcinoma, and ductal carcinoma in situ (each 7.1%) (Table 3).
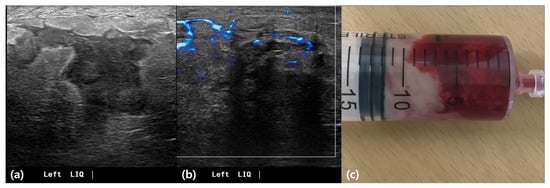
Figure 4.
Idiopathic granulomatous mastitis with abscess. A 35-year-old female patient presented with breast discomfort persisting for 14 days. (a) Ultrasound imaging demonstrates a hypoechoic lesion with diffuse skin thickening and edematous changes in the lower inner quadrant of the left breast. (b) Doppler ultrasound imaging reveals a moderate increase in blood flow, shown in blue. (c) Ultrasound-guided needle aspiration was performed, and 12 cc of bloody pus was aspirated.

Table 3.
Histopathologic results of ultrasound-guided biopsy, suggesting mastitis versus IBC (n = 86).
Among the 13 invasive cancer cases found in US-guided biopsies, 38.5% were moderately differentiated and 61.5% were poorly differentiated. Estrogen receptor positivity was found in 53.8%, while progesterone receptor positivity was found in 46.2%. HER2 positivity was observed in 61.5% of tumors. The Ki-67 proliferation index exceeded 20% in 61.5% of cases, indicating high tumor aggressiveness. The tumor subtypes were HR+/HER2+ (38.5%), HR-/HER2+ (23.1%), HR-/HER2- (23.1%), and HR+/HER2- (15.4%) (Table S1).
3.4. Logistic Regression Analysis of Factors Associated with IBC
Table 4 presents the logistic regression analysis of factors associated with IBC. Statistically significant variables from clinical and demographic data, as well as US findings, were used for this analysis, as shown in Table 1 and Table 2. The crude analysis identified age, BMI, menopausal status, symptom onset duration, breast swelling, and lesion size as significant predictors. However, BMI was excluded from the adjusted model owing to potential data issues suggested by an extremely high crude OR. After adjusting for other variables, symptom onset duration and breast swelling emerged as clinically significant predictors of inflammatory breast cancer. The adjusted OR for symptom onset duration was 1.07 (95% CI: 1.02–1.14) with a p-value of 0.014, and breast swelling had an adjusted OR of 15.24 (95% CI: 1.68–138.69) with a p-value of 0.016.

Table 4.
Logistic regression analysis of factors associated with inflammatory breast cancer.
4. Discussion
We analyzed 101 Asian women presenting with inflammatory symptoms; of them, 14 (13.9%) were diagnosed with IBC and 87 (86.1%) were diagnosed with mastitis. In 2009, Kamal et al. [10] found that 5.6% of patients had IBC in a cohort of 197 patients with mastitis. Similarly, Froman et al. [1] reported a rate of 4.5% of IBC in a cohort of 23 patients presenting with red breast syndrome after screening more than 3700 women at their breast unit over a two-year period. In another report [9], non-pregnant or postpartum women presenting with inflammatory breast symptoms had a breast cancer incidence of 50%. Our study included participants aged 22–82, both postpartum and non-postpartum, and found that the incidence of IBC in non-postpartum cases was 16.7% (13/78), which is within the range of previous studies.
The diagnostic criteria for IBC include typical symptoms such as erythema occupying more than one-third of the breast, edema, peau d’orange, and warmth. These symptoms may or may not be associated with an underlying palpable mass [12]. The time from onset to full presentation is usually within three months and never more than six months, which distinguishes IBC from locally advanced non-IBC. In our study, the most common presenting symptoms among patients diagnosed with IBC included swelling and palpable mass (50% each), pain/discomfort (42.9%), and erythema (35.7%). A retrospective review identified erythema (62%), edema or fullness (48%), and skin dimpling or discoloration (46%) as the most common presenting clinical signs. However, Lê et al. [19] found that, in most patients with IBC, no discrete mass is palpable on clinical examination. This may be because breast enlargement due to swelling may cause confusion.
Our findings indicate that older age, higher BMI, postmenopausal status, longer symptom duration, and absence of previous mastitis history are associated with an increased likelihood of IBC compared to mastitis. Dabi et al. [9] reported that patients with malignant lesions were significantly older and had a significantly larger palpable mass compared to those with benign disease. Another study identified high BMI as one of the strongest risk factors for IBC [13]. These findings are consistent with our results. Although there is no report on symptom onset duration, patients with IBC statistically had a longer duration of symptoms than those with mastitis in our study.
Despite multimodal treatment approaches, survival outcomes for IBC remain poor compared to matched non-inflammatory controls [20]. Historical data estimate that the 5- and 10-year overall survival rates for stage 3 IBC are between 40–45% and 30–35%, respectively [21,22,23]. Due to the aggressive nature of IBC, early diagnosis is crucial. Routine screening mammography is not effective in the early detection of IBC and is the least sensitive among breast imaging modalities [22].
For women at average risk of breast cancer, one study demonstrated that adding US to mammography detected more cases of breast cancer during screening [24]. In women with dense breasts, cohort studies more reflective of real-life clinical settings confirmed these results, while studies on women with non-dense breasts showed no statistically significant differences between the two modalities. Regarding neoadjuvant tumor size prediction, another study suggested that both mammography and breast US outperformed clinical palpation [25]. While mammography was slightly more accurate than US in estimating the exact tumor size, the difference was not statistically significant. Notably, 29 out of 193 (15%) tumors were assessable solely by breast US.
In patients with symptoms but no precise initial diagnosis, bilateral breast and nodal USs may be helpful. Our US findings suggest that larger lesion size and absence of cystic/necrotic changes are important characteristics that may help differentiate IBC from mastitis. Other studies have revealed that the presence of precise limits of the mass is only associated with IBC [9,10,26].
Although published data on MRI findings in patients with IBC are limited, MRI is the most accurate test for detecting a primary breast lesion in these patients [27]. For contrast-enhanced MRI, non-mass-like enhancement, rapid initial enhancement with a washout pattern, and diffuse cutaneous/subcutaneous and prepectoral edema on T2-weighted images are key indicators of IBC [28]. However, MRI is not easily accessible in our daily practice for patients presenting with inflammatory symptoms before undergoing US examinations.
Pathologic analysis should confirm invasive breast carcinoma. IBC is often associated with the infiltration of dermal lymphatics by tumor emboli, accounting for the characteristic edema and skin changes. However, this is not required for diagnosis nor always seen in biopsy specimens. In our study, invasive ductal carcinoma was predominant (78.6%). Previous studies have revealed that lobular histologic characteristics are less common in IBC than in non-IBC cases [29]. However, our study did not include lobular histology, possibly due to its small sample size. Among biopsy-proven benign pathologies, 47.1% showed abscess formation or granulomatous inflammation, which may have affected US findings suggestive of cystic/necrotic changes.
To the best of our knowledge, no previous studies have used regression analysis to identify the impact of variables in distinguishing IBC from mastitis. Logistic regression analysis identified symptom onset duration and breast swelling as clinically significant predictors of IBC, even after adjusting for other variables. The adjusted OR for symptom onset duration was 1.07, and for breast swelling, it was 15.24, both indicating strong associations with IBC.
Our study has some limitations that should be acknowledged. First, like other retrospective analyses, there is a risk of selection bias and potential inaccuracies in chart data extraction. Similarly, the granularity of the extracted electronic medical records was limited. Second, we did not analyze mammography findings. Mammography is generally less specific in distinguishing between mastitis and IBC [30], especially since our study included post-partum and young patients. This limitation is consistent with the study’s primary focus on utilizing US as the main diagnostic tool. Third, due to the rarity of IBC, the number of patients we studied was small despite our relatively large study population. This may have limited our ability to detect subtle differences between IBC and mastitis. However, one of the strengths of our study is the inclusion of consecutive Asian women over a 12-year period. Finally, due to prompt referral to an academic tertiary care center with an established multidisciplinary clinic for the treatment of IBC upon diagnosis, our study did not include details on the treatment course or surgical outcomes of patients.
In conclusion, age, BMI, menopausal status, symptom onset duration, and breast swelling significantly differentiated IBC from mastitis in Asian women. Logistic regression identified symptom onset duration and breast swelling as significant IBC predictors. US findings showed larger lesion size and more frequent whole-breast involvement in patients.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/life15010005/s1. Table S1. Histopathologic results of invasive malignancy.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.Y.O.; methodology, H.Y.O.; validation, H.Y.O.; formal Analysis, H.S.M.; investigation, H.S.M.; resources, H.S.M. and H.Y.O.; data curation, H.S.M.; writing—original draft preparation, H.S.M.; writing—review and editing, H.Y.O.; visualization, H.S.M.; supervision, H.Y.O.; project administration, H.Y.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by a research grant from Kangwon National University in 2024.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved by our Institutional Review Board (IRB No. 2024-07-009). The study adhered to the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki.
Informed Consent Statement
The requirement for informed consent was waived due to the study’s retrospective nature.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available but are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analysis, or interpretation of the data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Froman, J.; Landercasper, J.; Ellis, R.; De Maiffe, B.; Theede, L. Red breast as a presenting complaint at a breast center: An institutional review. Surgery 2011, 149, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferron, S.; Asad-Syed, M.; Boisserie-Lacroix, M.; Palussière, J.; Hurtevent, G. Imaging benign inflammatory syndromes. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2012, 93, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisserie-Lacroix, M.; Debled, M.; Tunon de Lara, C.; Hurtevent, G.; Asad-Syed, M.; Ferron, S. The inflammatory breast: Management, decision-making algorithms, therapeutic principles. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2012, 93, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutet, G. Breast inflammation: Clinical examination, aetiological pointers. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2012, 93, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, S.; Cristofanilli, M. Inflammatory breast cancer: What progress have we made? Oncology 2011, 25, 264–270, 273. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, B.J.; Tannenbaum, N.E. Inflammatory carcinoma of the breast. Surg. Gynecol. Obstet. 1924, 39, 580–595. [Google Scholar]
- Menta, A.; Fouad, T.M.; Lucci, A.; Le-Petross, H.; Stauder, M.C.; Woodward, W.A.; Ueno, N.T.; Lim, B. Inflammatory Breast Cancer: What to Know About This Unique, Aggressive Breast Cancer. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 98, 787–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le-Petross, H.T.; Balema, W.; Woodward, W.A. Why diagnosing inflammatory breast cancer is hard and how to overcome the challenges: A narrative review. Chin. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 10, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabi, Y.; Darrigues, L.; Pons, K.; Mabille, M.; Abd Alsamad, I.; Mitri, R.; Skalli, D.; Haddad, B.; Touboul, C. Incidence of inflammatory breast cancer in patients with clinical inflammatory breast symptoms. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamal, R.M.; Hamed, S.T.; Salem, D.S. Classification of inflammatory breast disorders and step by step diagnosis. Breast J. 2009, 15, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, S.; Tadros, A.B. New Strategies for Locally Advanced Breast Cancer: A Review of Inflammatory Breast Cancer and Nonresponders. Clin. Breast Cancer 2024, 24, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hester, R.H.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Lim, B. Inflammatory breast cancer: Early recognition and diagnosis is critical. Am. J. Obs. Gynecol. 2021, 225, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, F.M.; Bondy, M.; Yang, W.; Yamauchi, H.; Wiggins, S.; Kamrudin, S.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Le-Petross, H.; Bidaut, L.; Player, A.N.; et al. Inflammatory breast cancer: The disease, the biology, the treatment. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2010, 60, 351–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagsi, R.; Mason, G.; Overmoyer, B.A.; Woodward, W.A.; Badve, S.; Schneider, R.J.; Lang, J.E.; Alpaugh, M.; Williams, K.P.; Vaught, D.; et al. Inflammatory breast cancer defined: Proposed common diagnostic criteria to guide treatment and research. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2022, 192, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, S.P.; Shen, Z.Z.; Liu, T.J.; Agarwal, G.; Tajima, T.; Paik, N.S.; Sandelin, K.; Derossis, A.; Cody, H.; Foulkes, W.D. Is breast cancer the same disease in Asian and Western countries? World J. Surg. 2010, 34, 2308–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, M.; Raina, V. Epidemiology, screening and diagnosis of breast cancer in the Asia–Pacific region: Current perspectives and important considerations. Asia-Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 4, S5–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, C.B.; Jan, A. BMI Classification Percentile and Cut Off Points. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Lê, M.G.; Arriagada, R.; Contesso, G.; Cammoun, M.; Pfeiffer, F.; Tabbane, F.; Bahi, J.; Dilaj, M.; Spielmann, M.; Travagli, J.P.; et al. Dermal lymphatic emboli in inflammatory and noninflammatory breast cancer: A French-Tunisian joint study in 337 patients. Clin. Breast Cancer 2005, 6, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.C.; Grimm, M.; Sukumar, J.; Schnell, P.M.; Park, K.U.; Stover, D.G.; Jhawar, S.R.; Gatti-Mays, M.; Wesolowski, R.; Williams, N.; et al. Survival outcomes seen with neoadjuvant chemotherapy in the management of locally advanced inflammatory breast cancer (IBC) versus matched controls. Breast 2023, 72, 103591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldini, E.; Gardin, G.; Evagelista, G.; Prochilo, T.; Collecchi, P.; Lionetto, R. Long-term results of combined-modality therapy for inflammatory breast carcinoma. Clin. Breast Cancer 2004, 5, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, N.T.; Fernandez, J.R.E.; Cristofanilli, M.; Overmoyer, B.; Rea, D.; Berdichevski, F.; El-Shinawi, M.; Bellon, J.; Le-Petross, H.T.; Lucci, A.; et al. International Consensus on the Clinical Management of Inflammatory Breast Cancer from the Morgan Welch Inflammatory Breast Cancer Research Program 10th Anniversary Conference. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 1437–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, H.G.; Xia, Y.; Mukherjee, B.; Merajver, S.D. Incidence and survival of inflammatory breast cancer between 1973 and 2015 in the SEER database. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 185, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glechner, A.; Wagner, G.; Mitus, J.W.; Teufer, B.; Klerings, I.; Böck, N.; Grillich, L.; Berzaczy, D.; Helbich, T.H.; Gartlehner, G. Mammography in combination with breast ultrasonography versus mammography for breast cancer screening in women at average risk. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2023, 3, CD009632. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, G.; Findeklee, S.; del Sol Martinez, G.; Georgescu, M.T.; Gerlinger, C.; Nemat, S.; Klamminger, G.G.; Nigdelis, M.P.; Solomayer, E.F.; Hamoud, B.H. Accuracy of Breast Ultrasonography and Mammography in Comparison with Postoperative Histopathology in Breast Cancer Patients after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lequin, M.H.; van Spengler, J.; van Pel, R.; van Eijck, C.; van Overhagen, H. Mammographic and sonographic spectrum of non-puerperal mastitis. Eur. J. Radiol. 1995, 21, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lee, K.W.; Chung, S.Y.; Yang, I.; Kim, H.D.; Shin, S.J.; Kim, J.E.; Chung, B.W.; Choi, J.A. Inflammatory breast cancer: Imaging findings. Clin. Imaging 2005, 29, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Uematsu, T. MRI findings of inflammatory breast cancer, locally advanced breast cancer, and acute mastitis: T2-weighted images can increase the specificity of inflammatory breast cancer. Breast Cancer 2012, 19, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghav, K.; French, J.T.; Ueno, N.T.; Lei, X.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Reuben, J.M.; Valero, V.; Ibrahim, N.K. Inflammatory Breast Cancer: A Distinct Clinicopathological Entity Transcending Histological Distinction. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0145534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Günhan-Bilgen, I.; Üstün, E.E.; Memiş, A. Inflammatory Breast Carcinoma: Mammographic, Ultrasonographic, Clinical, and Pathologic Findings in 142 Cases. Radiology 2002, 223, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).