Cardiovascular Disease and Cardiac Imaging in Inflammatory Arthritis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Rheumatoid Arthritis
3.1.1. Cardiovascular Risk Factors
3.1.2. Inflammation and (Subclinical) Cardiovascular Disease
3.2. Axial Spondyloarthritis (Radiographic and Non-Radiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis)
3.2.1. Cardiovascular Risk Factors
3.2.2. Inflammation and (Subclinical) Cardiovascular Disease
3.2.3. Other Cardiovascular Abnormalities and Potential Association with CVD
3.3. Psoriatic Arthritis
3.3.1. Cardiovascular Risk Factors
3.3.2. Inflammation and Cardiovascular Disease
3.3.3. Subclinical Cardiovascular Disease
3.4. Screening for CVD in Inflammatory Arthritis and the Role of the Rheumatologist
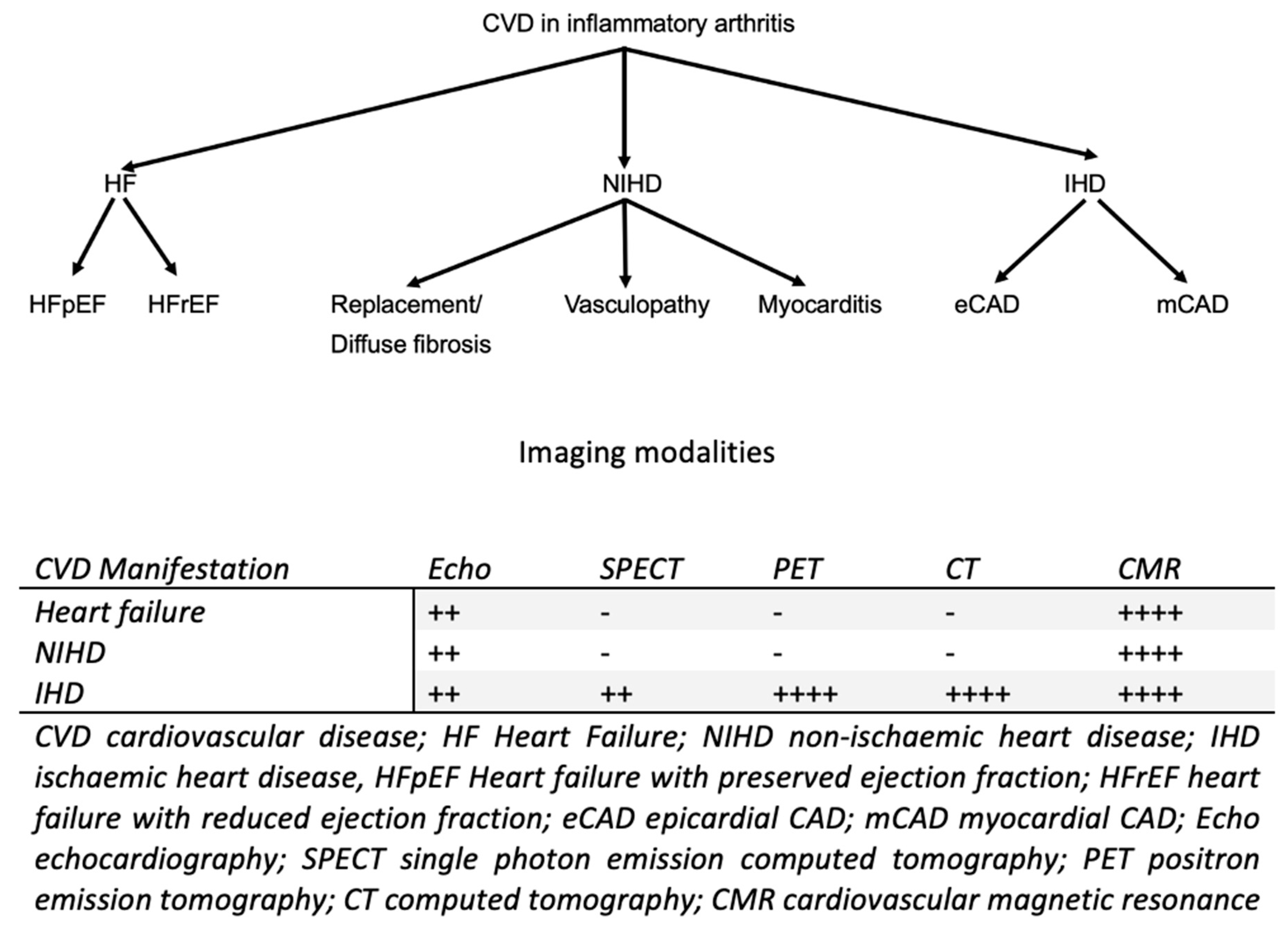
4. Role of Non-Invasive Imaging Modalities in the Evaluation of Cardiovascular Disease in Inflammatory Arthritides
4.1. Biventricular Function Assessment
4.2. Wall Motion Evaluation
4.3. Myocardial Ischemia Assessment
4.4. Non-Invasive Coronary Artery Evaluation
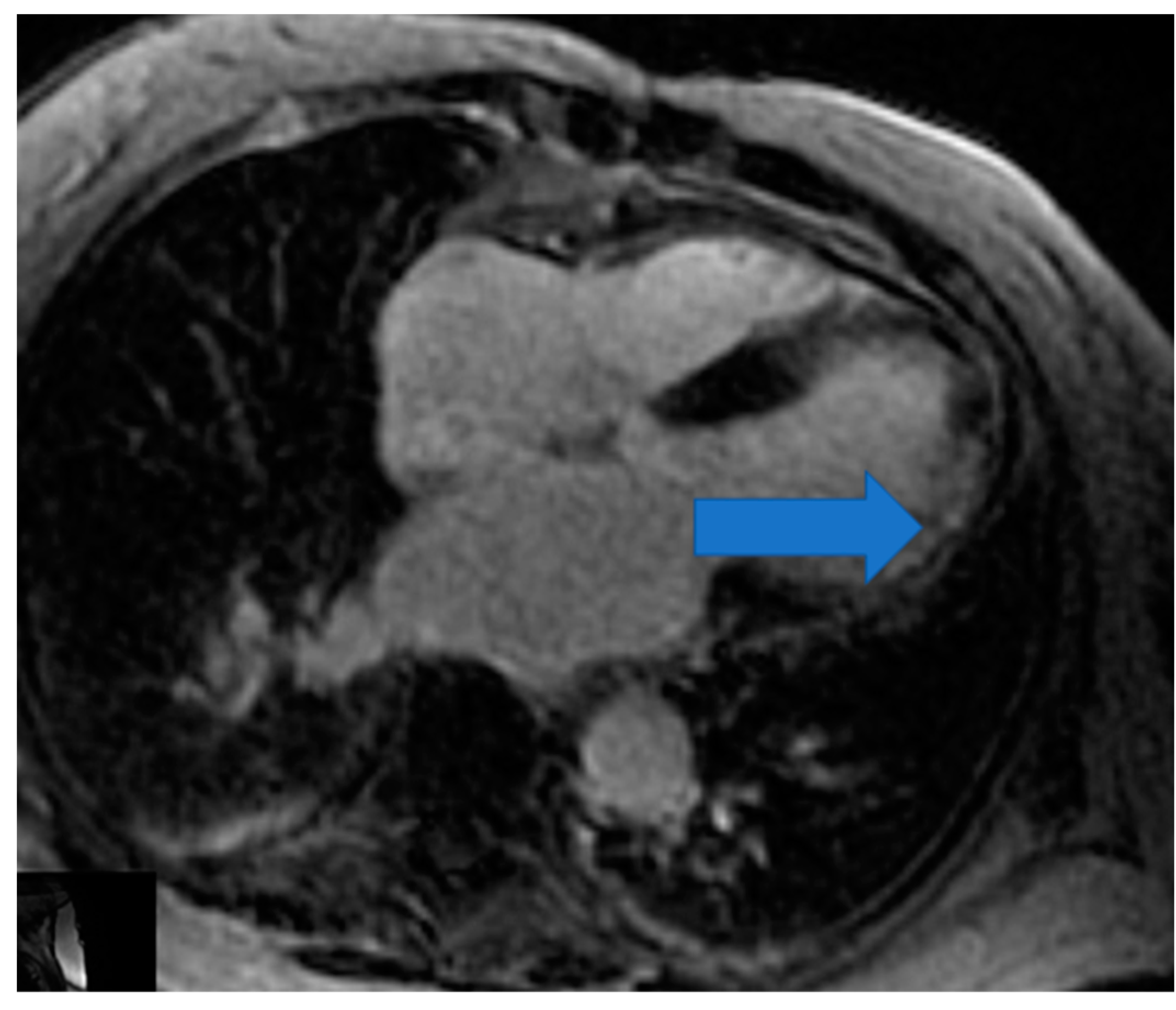
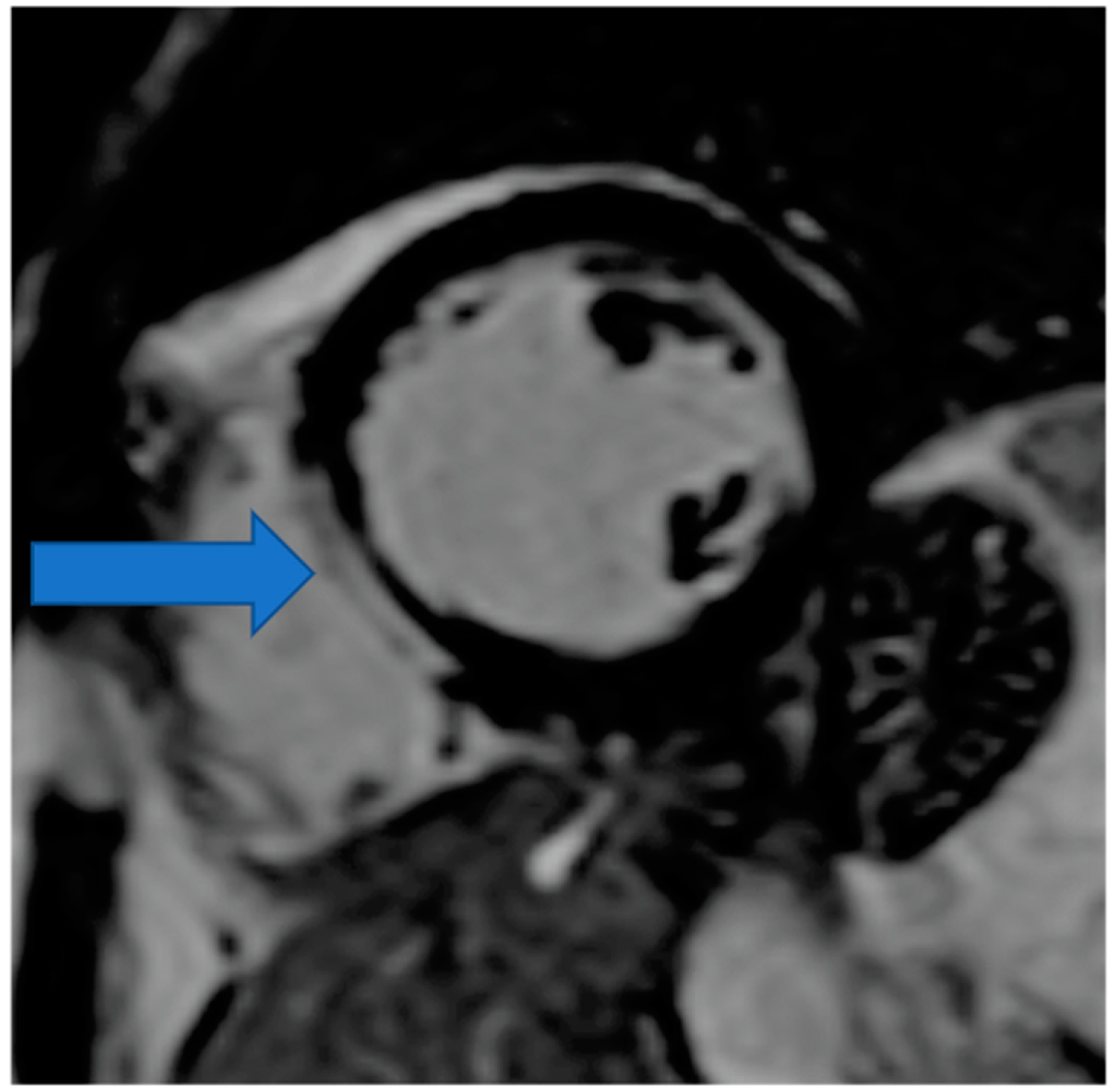
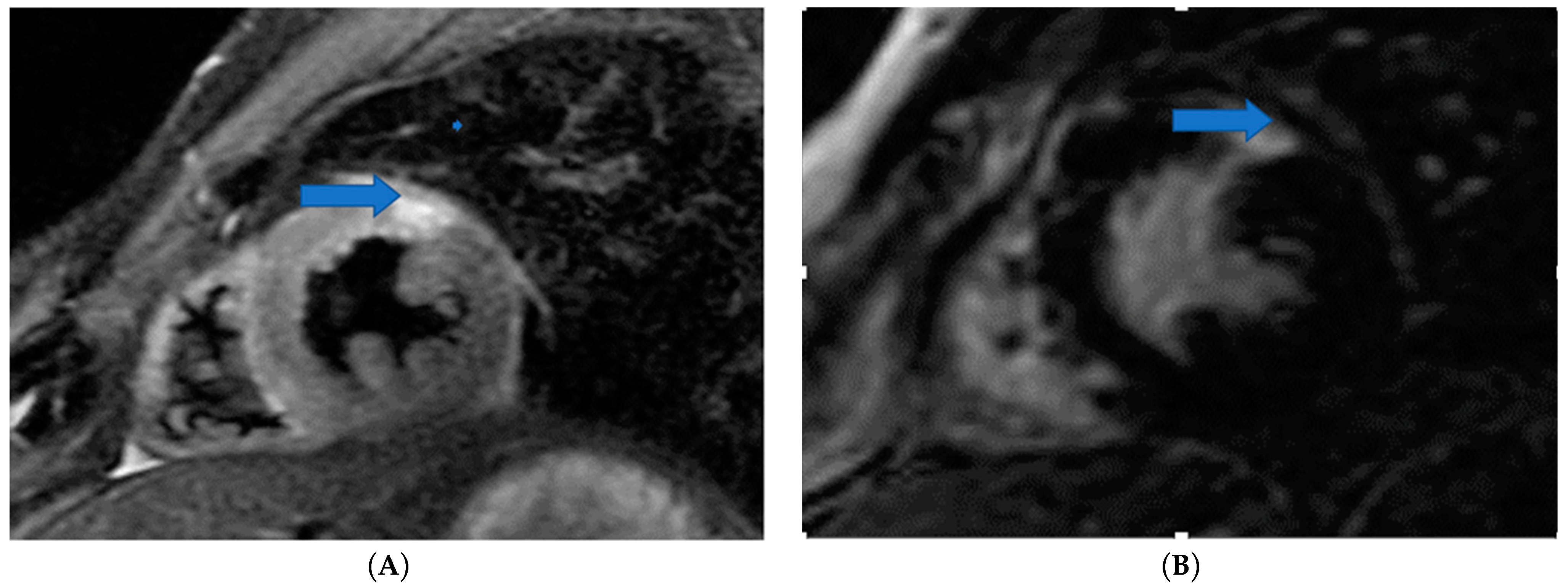
4.5. Myocardial Edema-Fibrosis Assessment
4.6. Future Directions
- Oxygen-sensitive CMR imaging. This technique has been correlated with endothelial function and inducible myocardial ischemia and has recently been suggested as a means of assessing myocardial vascular function and improving the diagnosis of vasculopathy in cardiac allografts [168]. The inflammatory mechanisms seen with ARDs may impair endothelial function, as shown in cardiac allografts, and oxygen-sensitive imaging may offer an interesting and novel approach to studying these diseases.
- Molecular imaging. The use of superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO) nanoparticles for cellular tracking has been attracting much interest [169]. Briefly, when imaging immune-mediated diseases such as multiple sclerosis, leukocytes, most often macrophages, are labeled with SPIO through either in vivo or in vitro phagocytosis or with transfection agents under MR imaging, a blooming artefact can be seen. This effect is mediated through T2 signal reduction; in one study, the magnitude of T2 signal reduction was found to correlate with macrophage content in the atherosclerotic plaque. As the abundance of leukocytes in cardiac tissue can indicate the severity of the condition, cell-labeling approaches with SPIO have potential useful implications for ARDs [169].
- Hyperpolarized magnetic resonance (MR). This is an emerging imaging technology that generates contrast agents with 10- to 20,000-fold improvements in MR signal, enabling cardiac metabolite mapping. The use of hyperpolarized MR using [1–13C] pyruvate provides a novel method for the assessment of innate immune cell-driven inflammation in the heart after myocardial infarction, with broad potential applicability across other cardiovascular and inflammatory diseases and suitability for early clinical translation [167]. Furthermore, an experimental model of re-perfused myocardial infarction could be of value for testing new drugs to treat reperfusion injury and facilitate translational research [170].
- Cardiac energetics using Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (MRS). Magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) is a non-invasive tool to analyze cardiac energy metabolism both in clinical and pre-clinical settings.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Humphreys, J.H.; Warner, A.; Chipping, J.; Marshall, T.; Lunt, M.; Symmons, D.P.M.; Verstappen, S.M.M. Mortality trends in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis over 20 years: Results from the Norfolk Arthritis Register. Arthritis Care Res. 2014, 66, 1296–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakland, G.; Gran, J.T.; Nossent, J.C. Increased mortality in ankylosing spondylitis is related to disease activity. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 1921–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadoun, S.; Zeboulon-Ktorza, N.; Combescure, C.; Elhai, M.; Rozenberg, S.; Gossec, L.; Fautrel, B. Mortality in rheumatoid arthritis over the last fifty years: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Jt. Bone Spine 2013, 80, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elalouf, O.; Muntyanu, A.; Polachek, A.; Pereira, D.; Ye, J.Y.; Lee, K.-A.; Chandran, V.; Cook, R.J.; Gladman, D.D. Mortality in psoriatic arthritis: Risk, causes of death, predictors for death. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2020, 50, 571–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, A.; Maradit Kremers, H.; Crowson, C.S.; Nicola, P.J.; Davis, J.M., 3rd; Therneau, T.M.; Roger, V.L.; Gabriel, S.E. The widening mortality gap between rheumatoid arthritis patients and the general population. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 3583–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naz, S.M.; Farragher, T.M.; Bunn, D.K.; Symmons, D.P.; Bruce, I.N. The influence of age at symptom onset and length of followup on mortality in patients with recent-onset inflammatory polyarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 985–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawler, P.R.; Bhatt, D.L.; Godoy, L.C.; Lüscher, T.F.; O Bonow, R.; Verma, S.; Ridker, P.M. Targeting cardiovascular inflammation: Next steps in clinical translation. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 113–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myasoedova, E.; Chandran, A.; Ilhan, B.; Major, B.T.; Michet, C.J.; Matteson, E.L.; Crowson, C.S. The role of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) flare and cumulative burden of RA severity in the risk of cardiovascular disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallberg-Jonsson, S.; Johansson, H.; Ohman, M.L.; Rantapaa-Dahlqvist, S. Extent of inflammation predicts cardiovascular disease and overall mortality in seropositive rheumatoid arthritis. A retrospective cohort study from disease onset. J. Rheumatol. 1999, 26, 2562–2571. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bonek, K. Associations of IL-18 with Altered Cardiovascular Risk Profile in Psoriatic Arthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 3, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batun-Garrido, J.S.; Salas-Magana, M.; Juarez-Rojop, I.E. Association between leptin and IL-6 concentrations with cardiovascular risk in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 3, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.L.; Sinnathurai, P.; Buchbinder, R.; Hill, C.; Lassere, M.; March, L. Biologics and cardiovascular events in inflammatory arthritis: A prospective national cohort study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roubille, C.; Richer, V.; Starnino, T.; McCourt, C.; McFarlane, A.; Fleming, P.; Siu, S.; Kraft, J.; Lynde, C.; Pope, J.; et al. The effects of tumour necrosis factor inhibitors, methotrexate, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and corticosteroids on cardiovascular events in rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angel, K.; Provan, S.A.; Gulseth, H.L.; Mowinckel, P.; Kvien, T.K.; Atar, D. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha antagonists improve aortic stiffness in patients with inflammatory arthropathies: A controlled study. Hypertension 2010, 55, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.S.; Lin, N.N.; Li, L.; Li, Y. The Effect of TNF Inhibitors on Cardiovascular Events in Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis: An Updated Meta-Analysis. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2016, 51, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Provan, S.; Lillegraven, S.; Sexton, J.; Angel, K.; Austad, C.; A Haavardsholm, E.; Kvien, T.K.; Uhlig, T. Trends in all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in patients with incident rheumatoid arthritis: A 20-year follow-up matched case-cohort study. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myasoedova, E.; Gabriel, S.E.; Matteson, E.L.; Davis, J.M., 3rd; Therneau, T.M.; Crowson, C.S. Decreased Cardiovascular Mortality in Patients with Incident Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) in Recent Years: Dawn of a New Era in Cardiovascular Disease in RA? J. Rheumatol. 2017, 44, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.J.L.; Symmons, D.; McCarey, D.; Dijkmans, B.A.C.; Nicola, P.J.M.Z.; Kvien, T.K.; McInnes, I.; Haentzschel, H.; Gonzalez-Gay, M.A.; Provan, S.; et al. EULAR evidence-based recommendations for cardiovascular risk management in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other forms of inflammatory arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agca, R.; Heslinga, S.C.; Rollefstad, S.; Heslinga, M.; McInnes, I.B.; Peters, M.J.; Kvien, T.K.; Dougados, M.; Radner, H.; Atzeni, F.; et al. EULAR recommendations for cardiovascular disease risk management in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other forms of inflammatory joint disorders: 2015/2016 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avina-Zubieta, J.A.; Thomas, J.; Sadatsafavi, M.; Lehman, A.J.; Lacaille, D. Risk of incident cardiovascular events in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 1524–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, S.; Koduri, G.; Nikiphorou, E.; Dixey, J.; Williams, P.; Young, A. A study of baseline prevalence and cumulative incidence of comorbidity and extra-articular manifestations in RA and their impact on outcome. Rheumatology 2013, 52, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindhardsen, J.; Ahlehoff, O.; Gislason, G.H.; Madsen, O.R.; Olesen, J.B.; Torp-Pedersen, C.; Hansen, P.R. The risk of myocardial infarction in rheumatoid arthritis and diabetes mellitus: A Danish nationwide cohort study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 929–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosentino, F.; Grant, P.; Aboyans, V.; Bailey, C.J.; Ceriello, A.; Delgado, V. 2019 ESC Guidelines on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases developed in collaboration with the EASD. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 255–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agca, R.; Hopman, L.H.; Laan, K.J.; van Halm, V.P.; Peters, M.J.; Smulders, Y.M.; Dekker, J.M.; Nijpels, G.; Stehouwer, C.D.; Voskuyl, A.E.; et al. Cardiovascular Event Risk in Rheumatoid Arthritis Compared with Type 2 Diabetes: A 15-year Longitudinal Study. J. Rheumatol. 2020, 47, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meune, C.; Touze, E.; Trinquart, L.; Allanore, Y. Trends in cardiovascular mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis over 50 years: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Rheumatology 2009, 48, 1309–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoek, J.V.D.; Roorda, L.D.; Boshuizen, H.C.; Tijhuis, G.J.; Dekker, J.; Bos, G.A.V.D.; Nurmohamed, M.T. Trend in and predictors for cardiovascular mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis over a period of 15 years: A prospective cohort study. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2016, 34, 813–819. [Google Scholar]
- Kerola, A.M.; Nieminen, T.; Virta, L.J.; Kautiainen, H.; Kerola, T.; Pohjolainen, T.; Kauppi, M.J.; Puolakka, K. No increased cardiovascular mortality among early rheumatoid arthritis patients: A nationwide register study in 2000–2008. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2015, 33, 391–398. [Google Scholar]
- Innala, L.; Möller, B.; Ljung, L.; Magnusson, S.; Smedby, T.; Södergren, A.; Öhman, M.-L.; Rantapää-Dahlqvist, S.; Wållberg-Jonsson, S. Cardiovascular events in early RA are a result of inflammatory burden and traditional risk factors: A five year prospective study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2011, 13, R131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argnani, L.; Zanetti, A.; Carrara, G.; Silvagni, E.; Guerrini, G.; Zambon, A.; Scirè, C.A. Rheumatoid Arthritis and Cardiovascular Risk: Retrospective Matched-Cohort Analysis Based on the RECORD Study of the Italian Society for Rheumatology. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 745601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.J.L.; van Halm, V.P.; Voskuyl, A.E.; Smulders, Y.M.; Boers, M.; Lems, W.F.; Visser, M.; Stehouwer, C.D.A.; Dekker, J.M.; Nijpels, G.; et al. Does rheumatoid arthritis equal diabetes mellitus as an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease? A prospective study. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 61, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghdadi, L.R.; Woodman, R.J.; Shanahan, E.M.; Mangoni, A.A. The impact of traditional cardiovascular risk factors on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barra, L.J.; Pope, J.; Hitchon, C.; Boire, G.; Schieir, O.; Lin, D.; Thorne, C.J.; Tin, D.; Keystone, E.C.; Haraoui, B.; et al. The effect of rheumatoid arthritis-associated autoantibodies on the incidence of cardiovascular events in a large inception cohort of early inflammatory arthritis. Rheumatology 2017, 56, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadwen, B.; Stranges, S.; Barra, L. Risk factors for hypertension in rheumatoid arthritis patients-A systematic review. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, K.G.; Zimmet, P.; Shaw, J. The metabolic syndrome—A new worldwide definition. Lancet 2005, 366, 1059–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, W.; Tang, X.; Pang, M. Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 855141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manrique-Arija, S.; Mena-Vazquez, N.; Ureña, I.; Rioja, J.; Valdivielso, P.; Ginel-Mendoza, L.; Abad-Sánchez, S.; Jiménez-Núñez, F.G.; Oliver-Martos, B.; Fernandez-Nebro, A. Cumulative inflammatory burden and obesity as determinants of insulin resistance in patients with established rheumatoid arthritis: Cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e044749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikiphorou, E.; Norton, S.; Carpenter, L.; Dixey, J.; Walsh, D.A.; Kiely, P.; Young, A.; on behalf of the Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Study and the Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Network Cohorts. Secular Changes in Clinical Features at Presentation of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Increase in Comorbidity But Improved Inflammatory States. Arthritis Care Res. 2017, 69, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulman, E.; Bartlett, S.J.; Schieir, O.; Andersen, K.M.; Boire, G.; Pope, J.; Hitchon, C.; Jamal, S.; Thorne, J.C.; Tin, D.; et al. Overweight, Obesity, and the Likelihood of Achieving Sustained Remission in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis: Results from a Multicenter Prospective Cohort Study. Arthritis Care Res. 2018, 70, 1185–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiphorou, E.; Norton, S.; Young, A.; Dixey, J.; Walsh, D.; Helliwell, H.; Kiely, P.; Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Study and the Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Network. The association of obesity with disease activity, functional ability and quality of life in early rheumatoid arthritis: Data from the Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Study/Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Network UK prospective cohorts. Rheumatology 2018, 57, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linauskas, A.; Overvad, K.; Symmons, D.; Johansen, M.B.; Stengaard-Pedersen, K.; de Thurah, A. Body Fat Percentage, Waist Circumference, and Obesity as Risk Factors for Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Danish Cohort Study. Arthritis Care Res. 2019, 71, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubreuil, M.; Rho, Y.H.; Man, A.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Löve, J.; Ogdie, A.; Gelfand, J.; Choi, H.K. Diabetes incidence in psoriatic arthritis, psoriasis and rheumatoid arthritis: A UK population-based cohort study. Rheumatology 2014, 53, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semb, A.G.; Rollefstad, S.; Ikdahl, E.; Wibetoe, G.; Sexton, J.; Crowson, C.; van Riel, P.; Kitas, G.; Graham, I.; Rantapää-Dahlqvist, S.; et al. Diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular risk management in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: An international audit. RMD Open 2021, 7, e001724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruscitti, P.; Cipriani, P.; Liakouli, V.; Iacono, D.; Pantano, I.; Margiotta, D.P.E.; Navarini, L.; Castaniti, G.M.D.; Maruotti, N.; Di Scala, G.; et al. Subclinical and clinical atherosclerosis in rheumatoid arthritis: Results from the 3-year, multicentre, prospective, observational GIRRCS (Gruppo Italiano di Ricerca in Reumatologia Clinica e Sperimentale) study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido, J.A.B.; Olan, F.; Hernandez Nunez, E. Dyslipidemia and atherogenic risk in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Investig. Arterioscler. 2016, 28, 123–131. [Google Scholar]
- Boyer, J.F.; Gourraud, P.A.; Cantagrel, A.; Davignon, J.L.; Constantin, A. Traditional cardiovascular risk factors in rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis. Jt. Bone Spine 2011, 78, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; Delzell, E.; Muntner, P.; Hillegass, W.B.; Safford, M.M.; Navarro-Millán, I.; Crowson, C.S.; Curtis, J.R. The association between inflammatory markers, serum lipids and the risk of cardiovascular events in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 1301–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelsgaard, I.K.; Ikdahl, E.; Rollefstad, S.; Wibetoe, G.; A Esbensen, B.; Kitas, G.D.; Van Riel, P.; Gabriel, S.; Kvien, T.K.; Douglas, K.; et al. Smoking cessation is associated with lower disease activity and predicts cardiovascular risk reduction in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 1997–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikiphorou, E.; de Lusignan, S.; Mallen, C.D.; Khavandi, K.; Bedarida, G.; Buckley, C.D.; Galloway, J.; Raza, K. Cardiovascular risk factors and outcomes in early rheumatoid arthritis: A population-based study. Heart 2020, 106, 1566–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauper, K.; Courvoisier, D.S.; Chevallier, P.; Finckh, A.; Gabay, C. Incidence and Prevalence of Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Rheumatoid Arthritis, Psoriatic Arthritis, and Axial Spondyloarthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2018, 70, 1756–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, D.H.; Polak, J.F.; Kronmal, R.A.; Manolio, T.A.; Burke, G.L.; Wolfson, S.K., Jr.; Carotid-artery intima and media thickness as a risk factor for myocardial infarction and stroke in older adults. Cardiovascular Health Study Collaborative Research Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 14–22. [Google Scholar]
- Inaba, Y.; Chen, J.A.; Bergmann, S.R. Carotid plaque, compared with carotid intima-media thickness, more accurately predicts coronary artery disease events: A meta-analysis. Atherosclerosis 2012, 220, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosino, P.; Lupoli, R.; Di Minno, A.; Tasso, M.; Peluso, R.; Di Minno, M.N. Subclinical atherosclerosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. A meta-analysis of literature studies. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 113, 916–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maradit-Kremers, H.; Nicola, P.J.; Crowson, C.S.; Ballman, K.V.; Gabriel, S.E. Cardiovascular death in rheumatoid arthritis: A population-based study. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 722–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arts, E.A.; Fransen, J.; den Broeder, A.A.; Popa, C.D.; van Riel, P.L. The effect of disease duration and disease activity on the risk of cardiovascular disease in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 6, 998–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, S.; Kahlon, S.S.; Sikandar, R.; Peddemul, A.; Tejovath, S.; Hassan, D.; Patel, K.K.; Mostafa, J.A. Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha Inhibitors and Cardiovascular Risk in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e26430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naranjo, A.; the QUEST-RA Group; Sokka, T.; Descalzo, M.A.; Calvo-Alén, J.; Hørslev-Petersen, K.; Luukkainen, R.K.; Combe, B.; Burmester, G.R.; Devlin, J.; et al. Cardiovascular disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Results from the QUEST-RA study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2008, 10, R30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, D.H.; Reed, G.W.; Kremer, J.M.; Curtis, J.R.; Farkouh, M.E.; Harrold, L.R.; Hochberg, M.C.; Tsao, P.; Greenberg, J.D. Disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis and the risk of cardiovascular events. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 1449–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ytterberg, S.R.; Bhatt, D.L.; Mikuls, T.R.; Koch, G.G.; Fleischmann, R.; Rivas, J.L.; Germino, R.; Menon, S.; Sun, Y.; Wang, C.; et al. Cardiovascular and cancer risk with Tofacitinib in rheumatoid arthritis. N. Eng. J. Med. 2022, 386, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.-H.; Lin, M.-C.; Peng, C.-L.; Wu, Y.-C.; Sung, F.-C.; Kao, C.-H.; Liu, S.-H. A nationwide population-based retrospective cohort study: Increased risk of acute coronary syndrome in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2014, 43, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.J.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, J.G.; Han, I.-B.; Han, K.D.; Choi, J.M.; Sohn, S. Association of Acute Myocardial Infarction with ankylosing Spondylitis: A nationwide longitudinal cohort study. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 56, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Exarchou, S.; Lie, E.; Lindström, U.; Askling, J.; Forsblad-D′Elia, H.; Turesson, C.; Kristensen, L.E.; Jacobsson, L.T. Mortality in ankylosing spondylitis: Results from a nationwide population-based study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 1466–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Choi, I.A. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in patients with spondyloarthritis: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 24, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moltó, A.; Etcheto, A.; Van Der Heijde, D.; Landewé, R.; Bosch, F.V.D.; Bautista-Molano, W.; Burgos-Vargas, R.; Cheung, P.P.; Estévez, E.C.; Deodhar, A.; et al. Prevalence of comorbidities and evaluation of their screening in spondyloarthritis: Results of the international cross-sectional ASAS-COMOSPA study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molto, A.; Nikiphorou, E. Comorbidities in Spondyloarthritis. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.S.; Goodson, N.J.; Robertson, S.; Gaffney, K. Smoking in spondyloarthritis: Unravelling the complexities. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 1472–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glintborg, B.; Højgaard, P.; Hetland, M.L.; Krogh, N.S.; Kollerup, G.; Jensen, J.; Chrysidis, S.; Hansen, I.M.J.; Holland-Fischer, M.; Hansen, T.H.; et al. Impact of tobacco smoking on response to tumour necrosis factor-alpha inhibitor treatment in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: Results from the Danish nationwide DANBIO registry. Rheumatology 2016, 55, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulger, S.; Karlibel, I.A.; Aksoy, M.K.; Altan, L.; Dikis, O.S.; Yildiz, T. How Does Smoking Cessation Affect Disease Activity, Function Loss, and Quality of Life in Smokers with Ankylosing Spondylitis? J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2019, 25, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciurea, A.; Scherer, A.; Weber, U.; Exer, P.; Bernhard, J.; Tamborrini, G.; Riek, M.; Müller, R.B.; Weiss, B.; Nissen, M.J.; et al. Impaired response to treatment with tumour necrosis factor alpha inhibitors in smokers with axial spondyloarthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, G.; Gallagher, P.; O’Shea, F.D. Multimorbidity in Axial Spondyloarthropathy and Its Association with Disease Outcomes: Results from the Ankylosing Spondylitis Registry of Ireland Cohort. J. Rheumatol. 2020, 47, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maas, F.; Arends, S.; Van Der Veer, E.; Wink, F.; Efde, M.; Bootsma, H.; Brouwer, E.; Spoorenberg, A. Obesity Is Common in Axial Spondyloarthritis and Is Associated with Poor Clinical Outcome. J. Rheumatol. 2016, 43, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Chen, H.A.; Liu, C.H.; Liao, H.T.; Chou, C.T.; Chen, C.H. Association of obesity with inflammation, disease severity and cardiovascular risk factors among patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 23, 1165–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, K.F.; Kuo, Y.H.; Lai, S.W. Diabetes mellitus in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, e134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiortsis, D.N.; Mavridis, A.K.; Vasakos, S.; Nikas, S.N.; Drosos, A.A. Effects of infliximab treatment on insulin resistance in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2005, 64, 765–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda-Filloy, J.A.; Llorca, J.; Carnero-Lopez, B.; Gonzalez-Juanatey, C.; Blanco, R.; Gonzalez-Gay, M.A. TNF-alpha antagonist therapy improves insulin sensitivity in non-diabetic ankylosing spondylitis patients. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2012, 30, 850–855. [Google Scholar]
- Papadakis, J.A.; Sidiropoulos, P.I.; Karvounaris, S.A.; Vrentzos, G.E.; Spanakis, E.K.; Ganotakis, E.S.; Kritikos, H.D.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Boumpas, D.T. High prevalence of metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular risk factors in men with ankylosing spondylitis on anti-TNFalpha treatment: Correlation with disease activity. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2009, 27, 292–298. [Google Scholar]
- Maia, D.G.; Augusto, K.L.; Bezerra, M.C.; Rodrigues, C.E.M. Metabolic syndrome in patients with ankylosing spondylitis receiving anti-TNFalpha therapy: Association with predictors of cardiovascular risk. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 36, 2371–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malesci, D.; Niglio, A.; Mennillo, G.A.; Buono, R.; Valentini, G.; La Montagna, G. High prevalence of metabolic syndrome in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2007, 26, 710–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucuk, A.; Uslu, A.U.; Icli, A.; Cure, E.; Arslan, S.; Turkmen, K.; Toker, A.; Kayrak, M. The LDL/HDL ratio and atherosclerosis in ankylosing spondylitis. Z. Rheumatol. 2017, 76, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dregan, A.; Chowienczyk, P.; Molokhia, M. Cardiovascular and type 2 diabetes morbidity and all-cause mortality among diverse chronic inflammatory disorders. Heart 2017, 103, 1867–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazón, I.G.; Rueda-Gotor, J.; Ferraz-Amaro, I.; Genre, F.; Corrales, A.; Rio, V.C.; Fontana, N.P.; Portilla, V.; Llorca, J.; Mata, C.; et al. Subclinical atherosclerotic disease in ankylosing spondylitis and non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis. A multicenter study on 806 patients. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2021, 51, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueda-Gotor, J.; Ferraz-Amaro, I.; Genre, F.; González-Mazón, I.; Corrales, A.; Calvo-Rio, V.; Portilla, V.; Llorca, J.; Expósito, R.; Hernández-Hernández, V.; et al. Factors associated with atherosclerosis in radiographic and non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis. A multicenter study on 838 patients. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2022, 55, 152037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarini, L.; Currado, D.; Marino, A.; Di Donato, S.; Biaggi, A.; Caso, F.; Costa, L.; Tasso, M.; Ruscitti, P.; Pavlych, V.; et al. Persistence of C-reactive protein increased levels and high disease activity are predictors of cardiovascular disease in patients with axial spondyloarthritis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 1, 7498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Sijl, A.M.; van Eijk, I.C.; Peters, M.J.; Serné, E.H.; van der Horst-Bruinsma, I.E.; Smulders, Y.M.; Nurmohamed, M.T. Tumour necrosis factor blocking agents and progression of subclinical atherosclerosis in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genre, F.; López-Mejías, R.; Miranda-Filloy, J.A.; Ubilla, B.; Mijares, V.; Carnero-López, B.; Gomez-Acebo, I.; Dierssen-Sotos, T.; Remuzgo-Martínez, S.; Blanco, R.; et al. Anti-TNF-alpha therapy reduces endothelial cell activation in non-diabetic ankylosing spondylitis patients. Rheumatol. Int. 2015, 35, 2069–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arida, A.; Protogerou, A.D.; Konstantonis, G.; Konsta, M.; Delicha, E.M.; Kitas, G.D.; Sfikakis, P.P. Subclinical Atherosclerosis Is Not Accelerated in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis with Low Disease Activity: New Data and Metaanalysis of Published Studies. J. Rheumatol. 2015, 42, 2098–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eder, L.; Sadek, M.; McDonald-Blumer, H.; Gladman, D.D. Aortitis and spondyloarthritis—An unusual presentation: Case report and review of the literature. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 39, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slobodin, G.; E Naschitz, J.; Zuckerman, E.; Zisman, D.; Rozenbaum, M.; Boulman, N.; Rosner, I. Aortic involvement in rheumatic diseases. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2006, 24, S41–S47. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shawn, R.; Jenny, D.; Corina, M.; Haley, B.N.; Siegel, E.L.; Nehal, N.M. Psoriatic arthritis and sacroiliitis are associated with increased vascular inflammation by 18-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography computed tomography: Baseline report from the Psoriasis Atherosclerosis and Cardiometabolic Disease Initiative. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, R161. [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen, N.H.; Horslev-Petersen, K.; Beyer, J.M. Ambulatory 24-hour continuous electrocardiographic monitoring in 54 patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Eur. Heart J. 1986, 7, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dik, V.; Peters, M.; Dijkmans, P.; Van der Weijden, M.; De Vries, M.; Dijkmans, B.; Van der Horst-Bruinsma, I.; Nurmohamed, M. The relationship between disease-related characteristics and conduction disturbances in ankylosing spondylitis. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2010, 39, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, K.; Klingberg, E.; Deminger, A.; Wallberg, H.; Jacobsson, L.T.H.; Bergfeldt, L.; Forsblad-D’Elia, H. Cardiac conduction disturbances in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: Results from a 5-year follow-up cohort study. RMD Open 2019, 5, e001053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergfeldt, L.; Edhag, O.; Vallin, H. Cardiac conduction disturbances, an underestimated manifestation in ankylosing spondylitis. A 25-year follow-up study of 68 patients. Acta Med. Scand. 1982, 212, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldan, C.A.; Chavez, J.; Wiest, P.W.; Qualls, C.R.; Crawford, M.H. Aortic root disease and valve disease associated with ankylosing spondylitis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1998, 32, 1397–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergfeldt, L. HLA-B27-associated cardiac disease. Ann. Intern. Med. 1997, 127, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerges, L.; D’Angelo, K.; Bass, D.; Haghshenas, A.; Kersten, D.J.; Ahluwalia, M.; Zelster, R.; Makaryus, A.N. Cardiac conduction disturbances in rheumatologic disease: A cross-sectional study. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2022, 1, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Kerola, A.M.; Kazemi, A.; Rollefstad, S.; Lillegraven, S.; Sexton, J.; Wibetoe, G.; A Haavardsholm, E.; Kvien, T.K.; Semb, A.G. All-cause and cause-specific mortality in rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and axial spondyloarthritis: A nationwide registry study. Rheumatology 2022, 61, 4656–4666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degboé, Y.; Koch, R.; Zabraniecki, L.; Jamard, B.; Couture, G.; Ruidavets, J.B.; Ferrieres, J.; Ruyssen-Witrand, A.; Constantin, A. Increased Cardiovascular Risk in Psoriatic Arthritis: Results from a Case-Control Monocentric Study. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 785719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eder, L.; Wu, Y.; Chandran, V.; Cook, R.; Gladman, D.D. Incidence and predictors for cardiovascular events in patients with psoriatic arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 1680–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horreau, C.; Pouplard, C.; Brenaut, E.; Barnetche, T.; Misery, L.; Cribier, B.; Jullien, D.; Aractingi, S.; Aubin, F.; Joly, P.; et al. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: A systematic literature review. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2013, 27 (Suppl. S3), 12–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladman, D.D.; Ang, M.; Su, L.; Tom, B.D.; Schentag, C.T.; Farewell, V.T. Cardiovascular morbidity in psoriatic arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 1131–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Ma, W.; Liu, H.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Z.; Zang, C.; et al. Stroke risk in arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogdie, A.; Maliha, S.; Shin, D.; Love, T.J.; Baker, J.; Jiang, Y.; Choi, H.; Gelfand, J.M. Cause-specific mortality in patients with psoriatic arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2017, 56, 907–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, H.; Bohra, N.; Syed, K.; Donato, A.; Murad, M.H.; Karmacharya, P. All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality in Psoriatic Arthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arthritis Care Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Syrimi, Z.; Hughes, D.M.; Zhao, S.S. Comorbidities in psoriatic arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatol. Int. 2021, 41, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibari, A.; Cohen, A.D.; Gazitt, T.; Bitterman, H.; Lavi, I.; Feldhamer, I.; Shalom, G.; Greenberg-Dotan, S.; Zisman, D. Cardiac and cardiovascular morbidities in patients with psoriatic arthritis: A population-based case control study. Clin. Rheumatol. 2019, 38, 2069–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiro, R.; Lorenzo, A.; Tejon, P.; Coto, P.; Pardo, E. Obesity in psoriatic arthritis: Comparative prevalence and associated factors. Medicine 2019, 98, e16400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husted, J.A.; Thavaneswaran, A.; Chandran, V.; Eder, L.; Rosen, C.F.; Cook, R.J.; Gladman, D.D. Cardiovascular and other comorbidities in patients with psoriatic arthritis: A comparison with patients with psoriasis. Arthritis Care Res. 2011, 63, 1729–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radner, H.; Lesperance, T.; Accortt, N.A.; Solomon, D.H. Incidence and Prevalence of Cardiovascular Risk Factors Among Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis, Psoriasis, or Psoriatic Arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2017, 69, 1510–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, C.C.; Ko, G.T.; Ho, L.Y.; Yu, K.L.; Chan, P.T.; To, C.H. Prevalence of atherosclerotic risk factors and the metabolic syndrome in patients with chronic inflammatory arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2011, 63, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafri, K.; Bartels, C.M.; Shin, D.; Gelfand, J.M.; Ogdie, A. Incidence and Management of Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Psoriatic Arthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Population-Based Study. Arthritis Care Res. 2017, 69, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Xie, L.; Wang, Y.; Vaidya, N.; Baser, O. Comorbidity and economic burden among moderate-to-severe psoriasis and/or psoriatic arthritis patients in the US Department of Defense population. J. Med. Econ. 2018, 21, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Li, W.Q.; Han, J.; Sun, Q.; Qureshi, A.A. Hypercholesterolemia and risk of incident psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis in US women. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haroon, M.; Gallagher, P.; Heffernan, E.; FitzGerald, O. High prevalence of metabolic syndrome and of insulin resistance in psoriatic arthritis is associated with the severity of underlying disease. J. Rheumatol. 2014, 41, 1357–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Queiro, R.; Lorenzo, A.; Tejon, P.; Pardo, E.; Coto, P.; Ballina, J. Polyarticular evolution and late-onset psoriasis may be associated with cardiovascular disease in psoriatic arthritis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 22, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaine, J.; Song, X.; Kim, G.; Hur, P.; Palmer, J.B. Higher Incidence Rates of Comorbidities in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis Compared with the General Population Using U.S. Administrative Claims Data. J. Manag. Care Spec. Pharm. 2019, 25, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindez, E.; Carmona, L. Is obesity in psoriatic arthritis associated with a poorer therapeutic response and more adverse effects of treatment with an anchor drug? Reumatol. Clin. 2016, 12, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejo-Yague, E.; Burkard, T.; Micheroli, R.; Burden, A.M. Minimal disease activity and remission in patients with psoriatic arthritis with elevated body mass index: An observational cohort study in the Swiss Clinical Quality Management cohort. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e061474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingberg, E.; Bilberg, A.; Björkman, S.; Hedberg, M.; Jacobsson, L.; Forsblad-D′Elia, H.; Carlsten, H.; Eliasson, B.; Larsson, I. Weight loss improves disease activity in patients with psoriatic arthritis and obesity: An interventional study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eder, L.; Thavaneswaran, A.; Chandran, V.; Cook, R.J.; Gladman, D.D. Obesity is associated with a lower probability of achieving sustained minimal disease activity state among patients with psoriatic arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 813–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Han, J.; Qureshi, A.A. Obesity and risk of incident psoriatic arthritis in US women. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 1267–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loganathan, A.; Kamalaraj, N.; El-Haddad, C.; Pile, K. Systematic review and meta-analysis on prevalence of metabolic syndrome in psoriatic arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 24, 1112–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marra, M.; Campanati, A.; Testa, R.; Sirolla, C.; Bonfigli, A.R.; Franceschi, C.; Marchegiani, F.; Offidani, A. Effect of etanercept on insulin sensitivity in nine patients with psoriasis. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2007, 20, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Mutairi, N.; Shabaan, D. Effects of tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibitors extend beyond psoriasis: Insulin sensitivity in psoriasis patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cutis 2016, 97, 235–241. [Google Scholar]
- Pina, T.; Armesto, S.; Lopez-Mejias, R.; Genre, F.; Ubilla, B.; Gonzalez-Lopez, M.; Gonzalez-Vela, M.; Corrales, A.; Blanco, R.; Garcia-Unzueta, M.; et al. Anti-TNF-alpha therapy improves insulin sensitivity in non-diabetic patients with psoriasis: A 6-month prospective study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2015, 29, 1325–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bello, G.D.; Gisondi, P.; Idolazzi, L.; Girolomoni, G. Psoriatic Arthritis and Diabetes Mellitus: A Narrative Review. Rheumatol. Ther. 2020, 7, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uysal, K.T.; Wiesbrock, S.M.; Marino, M.W.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Protection from obesity-induced insulin resistance in mice lacking TNF-alpha function. Nature 1997, 389, 610–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, L.; Caso, F.; Atteno, M.; Del Puente, A.; Darda, M.A.; Caso, P.; Ortolan, A.; Fiocco, U.; Ramonda, R.; Punzi, L.; et al. Impact of 24-month treatment with etanercept, adalimumab, or methotrexate on metabolic syndrome components in a cohort of 210 psoriatic arthritis patients. Clin. Rheumatol. 2014, 33, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, M.; Busby, A.; Elwell, H.; Pratt, A.; Young, A.; Isaacs, J.; Nikiphorou, E. The use and context of the term ′multimorbidity′ in rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic literature review. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 3058–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Minno, M.N.D.; Iervolino, S.; Lupoli, R.; Russolillo, A.; Coppola, A.; Peluso, R.; Scarpa, R.; Di Minno, G. Cardiovascular risk in rheumatic patients: The link between inflammation and atherothrombosis. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2012, 38, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schieir, O.; Tosevski, C.; Glazier, R.H.; Hogg-Johnson, S.; Badley, E.M. Incident myocardial infarction associated with major types of arthritis in the general population: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1396–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juneblad, K.; Rantapaa-Dahlqvist, S.; Alenius, G.M. Disease Activity and Increased Risk of Cardiovascular Death among Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2016, 43, 2155–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, S.H.; So, H.; Cheng, I.T.; Li, E.K.; Wong, P.; Li, T.K.; Lee, A.P.-W.; Tam, L.-S. Association of C-reactive protein and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs with cardiovascular events in patients with psoriatic arthritis: A time-dependent Cox regression analysis. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2021, 13, 1759720X211027712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, E.J.; Harskamp, C.T.; Armstrong, A.W. Psoriasis and major adverse cardiovascular events: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2013, 2, e000062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edson-Heredia, E.; Zhu, B.; Lefevre, C.; Wang, M.; Barrett, A.; Bushe, C.; Cox, A.; Wu, J.; Maeda-Chubachi, T. Prevalence and incidence rates of cardiovascular, autoimmune, and other diseases in patients with psoriatic or psoriatic arthritis: A retrospective study using Clinical Practice Research Datalink. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2015, 29, 955–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brezinski, E.A.; Follansbee, M.R.; Armstrong, E.J.; Armstrong, A.W. Endothelial dysfunction and the effects of TNF inhibitors on the endothelium in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: A systematic review. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 513–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, S.L.; McInnes, I.B.; Sattar, N. Psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis and cardiovascular risk: Are we closer to a clinical recommendation? Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 321–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peluso, R.; Caso, F.; Tasso, M.; Ambrosino, P.; Nicola, M.; Di Minno, D.; Lupoli, R.; Criscuolo, L.; Caso, P.; Ursini, F.; et al. Cardiovascular Risk Markers and Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Psoriatic Arthritis Patients. Rev. Recent. Clin. Trials 2018, 13, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, M.; Aslam, R.; Patel, A.; Nadir, B.; Khan, S. Prevalence and Extent of Subclinical Atherosclerosis and Associated Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Adult Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2021, 13, e16853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, A.; Bahce-Altuntas, A.; Mowrey, W.; Broder, A. Active peripheral inflammation is associated with pro-atherogenic lipid profile in psoriatic arthritis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2016, 46, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szentpetery, A.; Healy, G.M.; Brady, D.; Haroon, M.; Gallagher, P.; Redmond, C.E.; Fleming, H.; Duignan, J.; Dodd, J.D.; FitzGerald, O. Higher Coronary Plaque Burden in Psoriatic Arthritis Is Independent of Metabolic Syndrome and Associated with Underlying Disease Severity. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018, 70, 396–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, I.T.; Shang, Q.; Li, E.K.; Wong, P.C.; Kun, E.W.; Law, M.Y.; Yip, R.M.; Yim, I.C.; Lai, B.T.; Ying, S.K.; et al. Effect of Achieving Minimal Disease Activity on the Progression of Subclinical Atherosclerosis and Arterial Stiffness: A Prospective Cohort Study in Psoriatic Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piepoli, M.F.; Hoes, A.W.; Agewall, S.; Albus, C.; Brotons, C.; Catapano, A.L.; Cooney, M.T.; Corra, U.; Cosyns, B.; Deaton, C.; et al. 2016 European Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice: The Sixth Joint Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and Other Societies on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Clinical Practice (constituted by representatives of 10 societies and by invited experts) Developed with the special contribution of the European Association for Cardiovascular Prevention & Rehabilitation (EACPR). Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 2315–2381. [Google Scholar]
- Joint British Societies Board. Joint British Societies’ consensus recommendations for the prevention of cardiovascular disease (JBS3). Heart 2014, 100 (Suppl. S2), ii1–ii67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hippisley-Cox, J.; Coupland, C.; Brindle, P. Development and validation of QRISK3 risk prediction algorithms to estimate future risk of cardiovascular disease: Prospective cohort study. BMJ 2017, 357, j2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrales, A.; Vegas-Revenga, N.; Atienza-Mateo, B.; Corrales-Selaya, C.; Prieto-Peña, D.; Rueda-Gotor, J.; Portilla, V.; Blanco, R.; Castañeda, S.; Ferraz-Amaro, I.; et al. Combined use of QRISK3 and SCORE as predictors of carotid plaques in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 2801–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulander, E.; Bärebring, L.; Wadell, A.T.; Gjertsson, I.; Calder, P.C.; Winkvist, A.; Lindqvist, H.M. Diet intervention improves cardiovascular profile in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Results from the randomized controlled cross-over trial ADIRA. Nutr. J. 2021, 20, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walldius, G.; Jungner, I. The apoB/apoA-I ratio: A strong, new risk factor for cardiovascular disease and a target for lipid-lowering therapy--a review of the evidence. J. Intern. Med. 2006, 259, 493–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, R.; Molavynejad, S.; Abedi, P.; Rajaei, E.; Haghighizadeh, M.H. Effect of Dietary Education on Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Curr. Rheumatol. Rev. 2021, 17, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrogeni, S.; Pepe, A.; Nijveldt, R.; Ntusi, N.; Sierra-Galan, L.M.; Bratis, K.; Wei, J.; Mukherjee, M.; Markousis-Mavrogenis, G.; Gargani, L.; et al. Cardiovascular magnetic resonance in autoimmune rheumatic diseases: A clinical consensus document by the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2022, 23, e308–e322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thallapally, V.K.; Bansal, R.; Thandra, A.; Gupta, S.; Aurit, S.; Pajjuru, V.S.; Anugula, D.; Ahmed, A.; Nahas, J. Detection of myocardial dysfunction using global longitudinal strain with speckle-tracking echocardiography in patients with vs without rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Echocardiogr. 2022, 21, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrizzetti, G.; Claus, P.; Kilner, P.J.; Nagel, E. Principles of cardiovascular magnetic resonance feature tracking and echocardiographic speckle tracking for informed clinical use. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2016, 18, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciftci, O.; Yilmaz, S.; Topcu, S.; Calıskan, M.; Gullu, H.; Erdogan, D.; Pamuk, B.O.; Yildirir, A.; Muderrisoglu, I.H. Impaired coronary microvascular function and increased intima-media thickness in rheumatoid arthritis. Atherosclerosis 2008, 198, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toutouzas, K.; Sfikakis, P.P.; Karanasos, A.; Aggeli, C.; Felekos, I.; Kitas, G.; Zampeli, E.; Protogerou, A.; Stefanadis, C. Myocardial ischaemia without obstructive coronary artery disease in rheumatoid arthritis: Hypothesis-generating insights from a cross-sectional study. Rheumatology 2013, 52, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggeli, C.; Polytarchou, K.; Varvarousis, D.; Kastellanos, S.; Tousoulis, D. Stress ECHO beyond coronary artery disease. Is it the holy grail of cardiovascular imaging? Clin. Cardiol. 2018, 41, 1600–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Cai, F.; Geng, C.; Wang, Z.; Tang, X. Diagnostic Performance of CMR, SPECT, and PET Imaging for the Identification of Coronary Artery Disease: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 621389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Tang, J.; Zheng, S.; Jiang, H.; Deng, L.; Wang, P. Prognostic significance of coronary artery calcium scoring and single-photon emission computed tomographic myocardial perfusion imaging on major adverse cardiac events in patients at low risk for suspected coronary artery disease. Acta Cardiol. 2019, 74, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaarsma, C.; Leiner, T.; Bekkers, S.C.; Crijns, H.J.; Wildberger, J.E.; Nagel, E.; Nelemans, P.J.; Schalla, S. Diagnostic performance of noninvasive myocardial perfusion imaging using single-photon emission computed tomography, cardiac magnetic resonance, and positron emission tomography imaging for the detection of obstructive coronary artery disease: A meta-analysis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 59, 1719–1728. [Google Scholar]
- Knuuti, J.; Wijns, W.; Saraste, A.; Capodanno, D.; Barbato, E.; Funck-Brentano, C.; Prescott, E.; Storey, R.F.; Deaton, C.; Cuisset, T.; et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of chronic coronary syndromes. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 407–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa-Uva, M.; Neumann, F.-J.; Ahlsson, A.; Alfonso, F.; Banning, A.P.; Benedetto, U.; A Byrne, R.; Collet, J.-P.; Falk, V.; Head, S.J.; et al. 2018 ESC/EACTS Guidelines on myocardial revascularization. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2019, 55, 4–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.; Velasco, A.; Hage, F.G.; Reyes, E. Guidelines in review: Comparison of ESC and ACC/AHA guidelines for the diagnosis and management of patients with stable coronary artery disease. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2018, 25, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Dobashi, H.; Kameda, T. Clinical value of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in patients with connective tissue disease. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2010, 28, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, B.N.; Stevens, E.; Perez-Chada, L.M.; Brown, J.M.; Divakaran, S.; Bay, C.; Bibbo, C.; Hainer, J.; Dorbala, S.; Blankstein, R.; et al. Impaired Coronary Vasodilator Reserve and Adverse Prognosis in Patients with Systemic Inflammatory Disorders. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2021, 14, 2212–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franks, R.; Plein, S.; Chiribiri, A. Clinical Application of Dynamic Contrast Enhanced Perfusion Imaging by Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 768563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, D.M.; Parel, P.; Li, H.; Sorokin, A.V.; Berg, A.R.; Chen, M.; Dey, A.; Hong, C.G.; Playford, M.; Sylvester, M.; et al. PET/CT-Based Characterization of 18F-FDG Uptake in Various Tissues Reveals Novel Potential Contributions to Coronary Artery Disease in Psoriatic Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 909760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, P.R.; Feineis, M.; Abdulla, J. Rheumatoid arthritis patients have higher prevalence and burden of asymptomatic coronary artery disease assessed by coronary computed tomography: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2019, 62, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpouzas, G.A.; Ormseth, S.R.; Hernandez, E.; Budoff, M.J. Biologics May Prevent Cardiovascular Events in Rheumatoid Arthritis by Inhibiting Coronary Plaque Formation and Stabilizing High-Risk Lesions. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 1467–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, S.; Sheth, N.H.; Baker, J.F.; Ogdie, A.; Raper, A.; Saboury, B.; Werner, T.J.; Thomas, P.; Vanvoorhees, A.; Alavi, A.; et al. A comparison of vascular inflammation in psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, and healthy subjects by FDG-PET/CT: A pilot study. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2013, 3, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- van Heeswijk, R.B.; Hullin, R. Oxygen-sensitive Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Noninvasive Step Forward for Diagnosing Vasculopathy in the Cardiac Allograft. Transplantation 2021, 8, 1664–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, S.; Sheth, N.H.; Baker, J.F.; Ogdie, A.; Raper, A.; Saboury, B.; Werner, T.J.; Thomas, P.; Vanvoorhees, A.; Alavi, A.; et al. High-resolution magnetic resonance imaging enhanced with superparamagnetic nanoparticles measures macrophage burden in atherosclerosis. Circulation 2010, 17, 1707–1715. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshihara, H.A.; Bastiaansen, J.A.; Berthonneche, C.; Comment, A.; Schwitter, J. An intact small animalmodel of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion: Characterization of metabolic changes by hyperpolarized 13C MR spectroscopy. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2015, 12, H2058–H2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsampasian, V.; Swift, A.J.; Assadi, H.; Chowdhary, A.; Swoboda, P.; Sammut, E.; Dastidar, A.; Cabrero, J.B.; Del Val, J.R.; Nair, S.; et al. Myocardial inflammation and energetics by cardiac MRI: A review of emerging techniques. BMC Med. Imaging 2021, 1, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterzan, M.A.; Lewis, A.J.M.; Neubauer, S.; Rider, O.J. Non-invasive investigation of myocardial energetics in cardiac disease using 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2020, 3, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
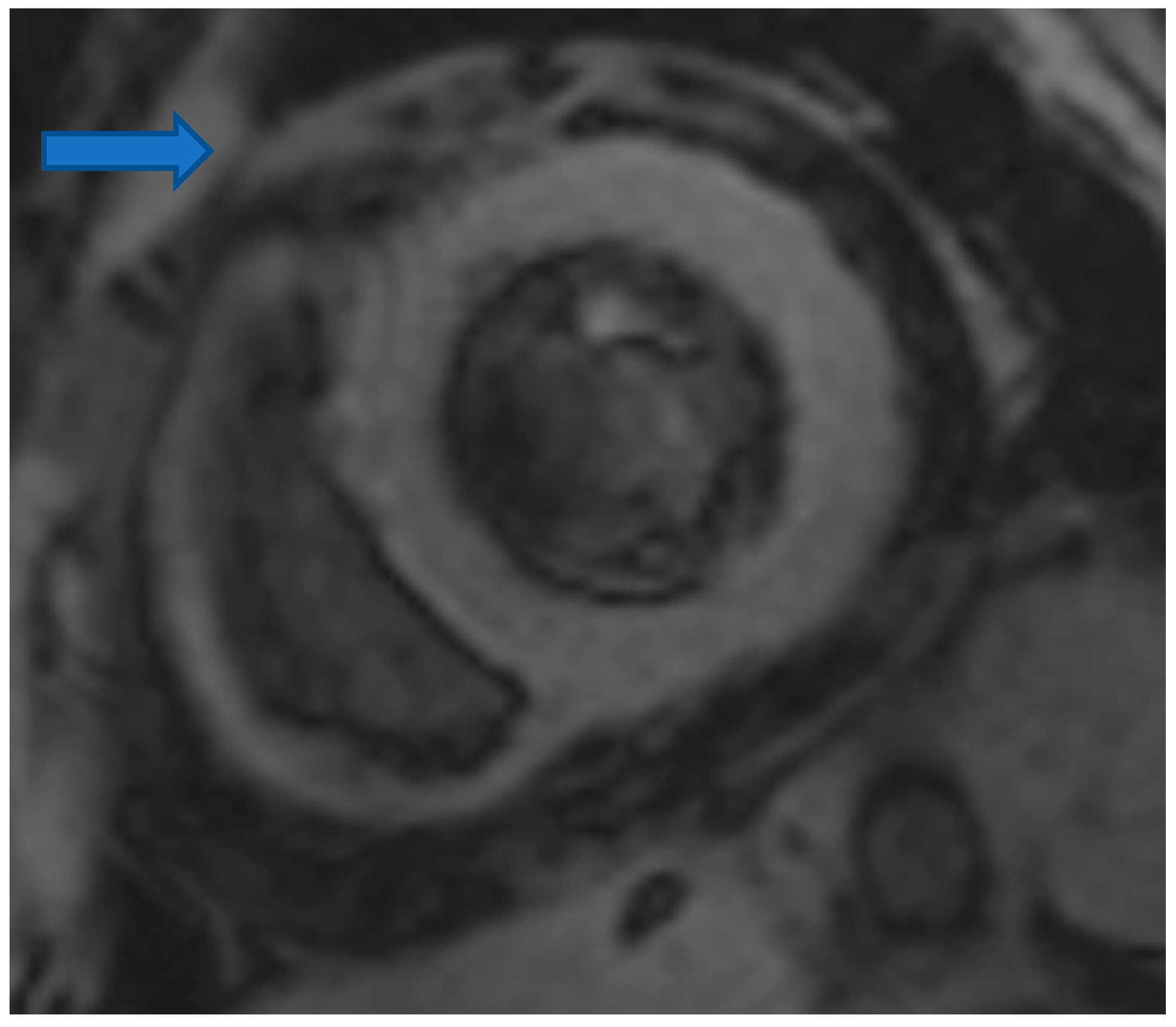
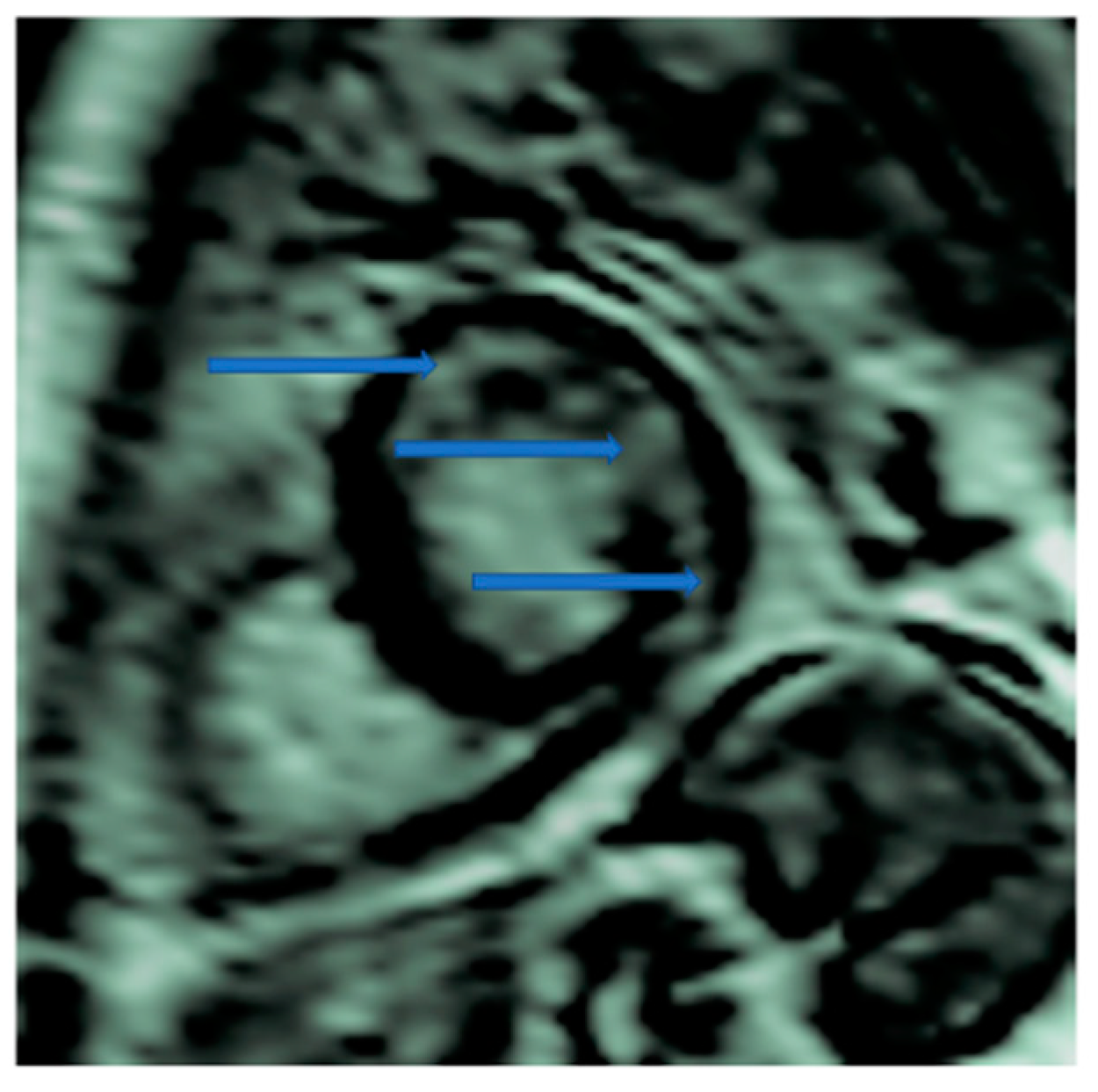
| 1. Cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk is increased in inflammatory arthritis (rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, axial spondyloarthritis) compared to the general population. |
| 2. CVD is associated with increased cardiovascular mortality and morbidity. |
| 3. CVD results from a combination of traditional CV risk factors and inflammation. |
| 4. Traditional CV factors, such as obesity, diabetes, and dyslipidemia, seem to confer a significant burden on cardiovascular disease among patients with inflammatory arthritis (IA). |
| 5. Aggressive screening for CVD, using available tools, such as the SCORE risk calculator, is recommended. |
| 6. Management of CV risk factors is crucial to reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in IA. |
| 7. Disease activity should be optimally controlled, given the pivotal role of inflammation in CVD. |
| 8. Non-invasive cardiovascular imaging modalities offer great potential to detect preclinical lesions in IA. |
| 9. Collaboration between rheumatologists and cardiologists is important for more comprehensive care in patients with IA and cardiovascular disease. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Madenidou, A.-V.; Mavrogeni, S.; Nikiphorou, E. Cardiovascular Disease and Cardiac Imaging in Inflammatory Arthritis. Life 2023, 13, 909. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13040909
Madenidou A-V, Mavrogeni S, Nikiphorou E. Cardiovascular Disease and Cardiac Imaging in Inflammatory Arthritis. Life. 2023; 13(4):909. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13040909
Chicago/Turabian StyleMadenidou, Anastasia-Vasiliki, Sophie Mavrogeni, and Elena Nikiphorou. 2023. "Cardiovascular Disease and Cardiac Imaging in Inflammatory Arthritis" Life 13, no. 4: 909. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13040909
APA StyleMadenidou, A.-V., Mavrogeni, S., & Nikiphorou, E. (2023). Cardiovascular Disease and Cardiac Imaging in Inflammatory Arthritis. Life, 13(4), 909. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13040909







