Genesis of the Aït Abdellah Copper Deposit, Bou Azzer-El Graara Inlier, Anti-Atlas, Morocco
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Geological Setting
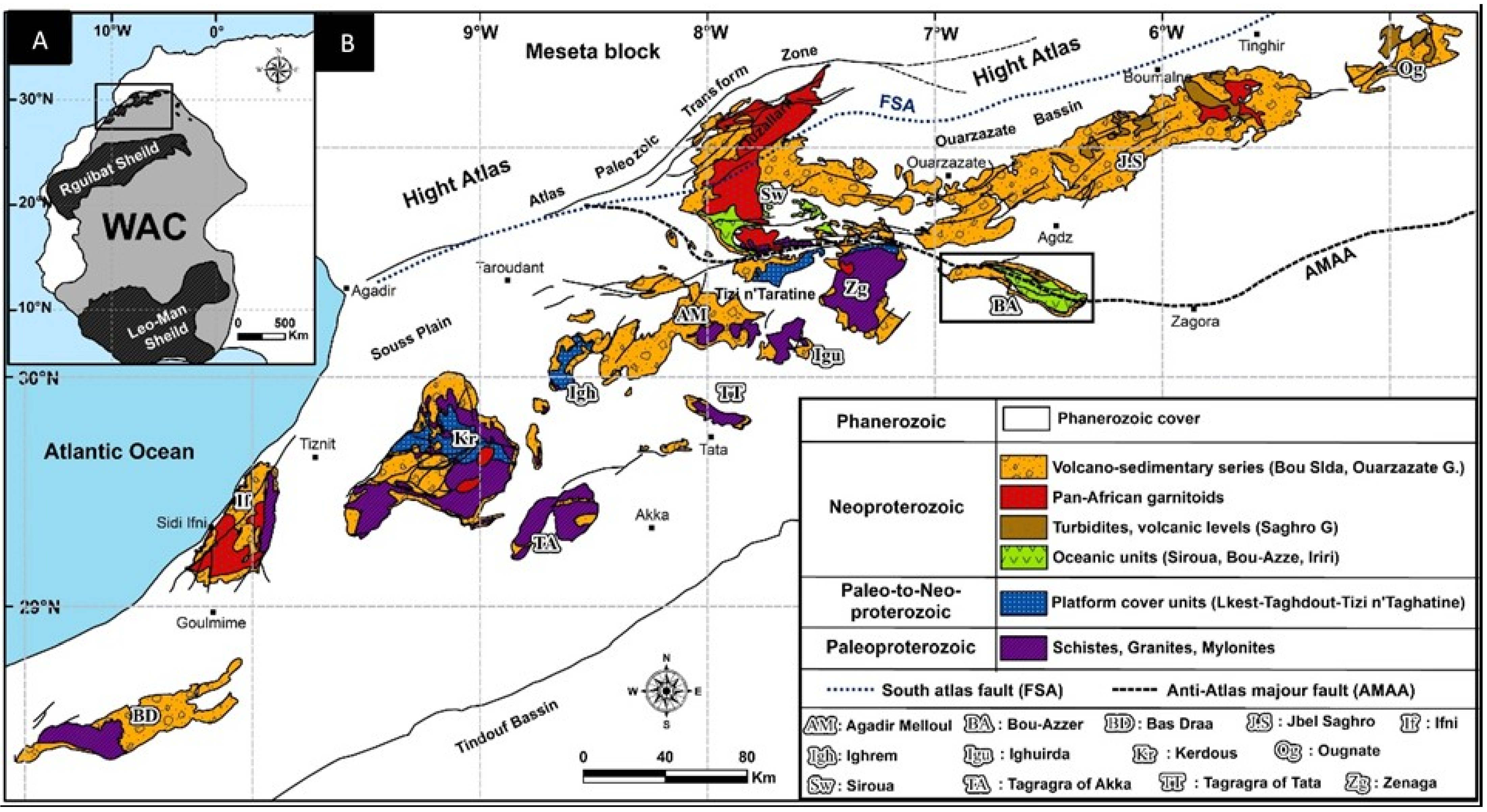
2.1. The Anti-Atlas Belt
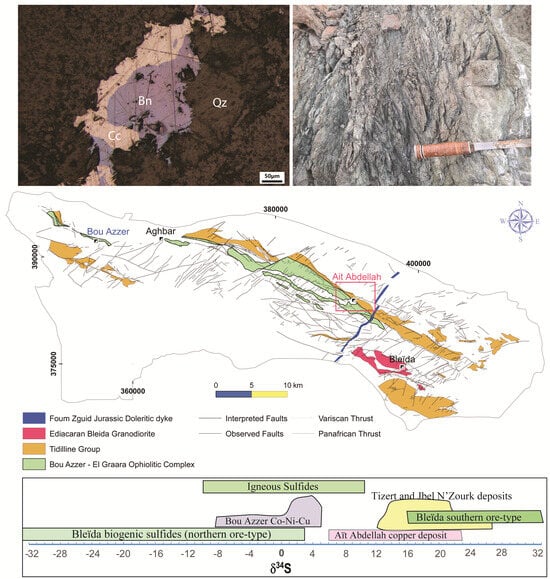
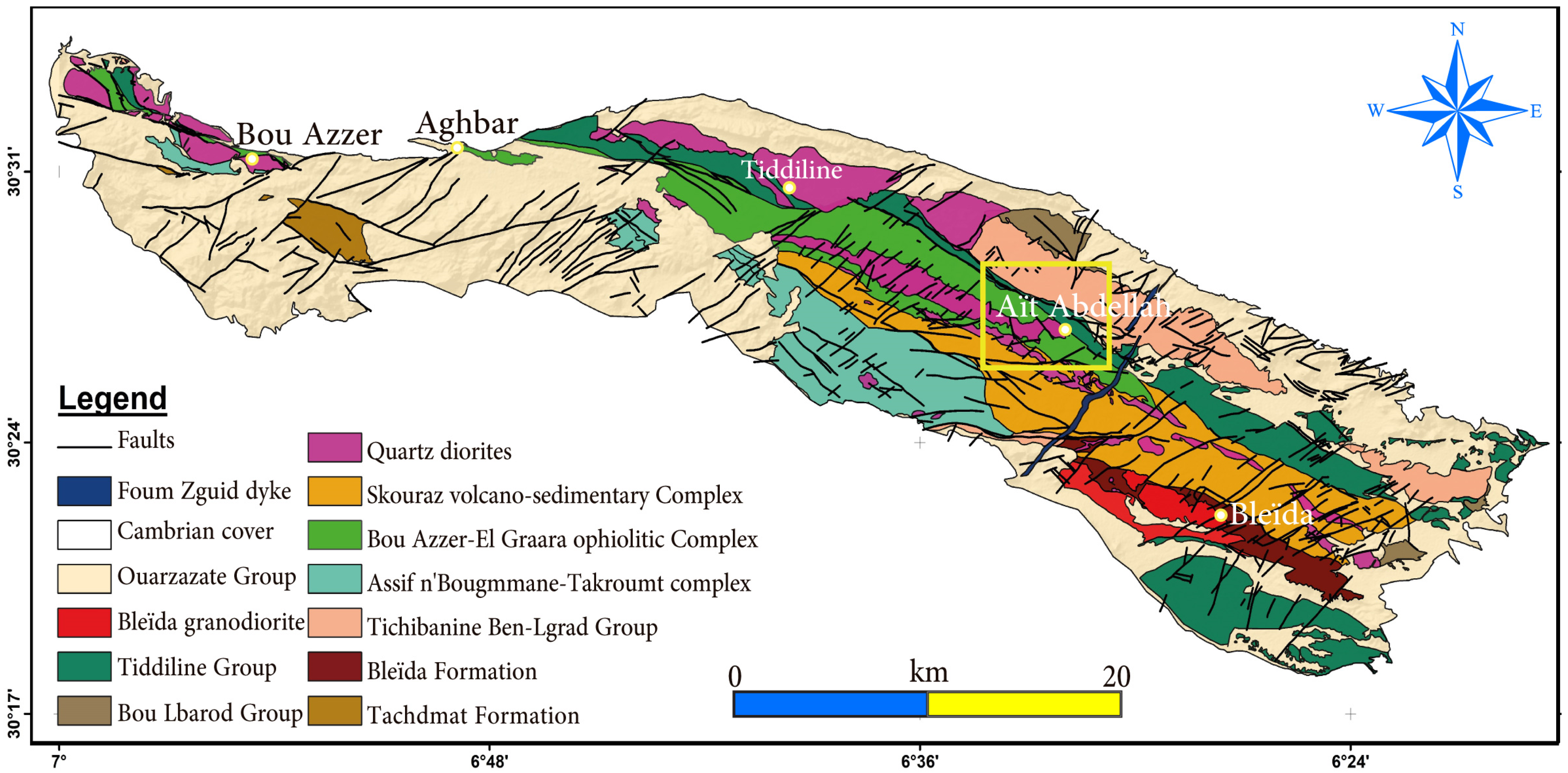
2.2. The Bou Azzer-El Graara Inlier
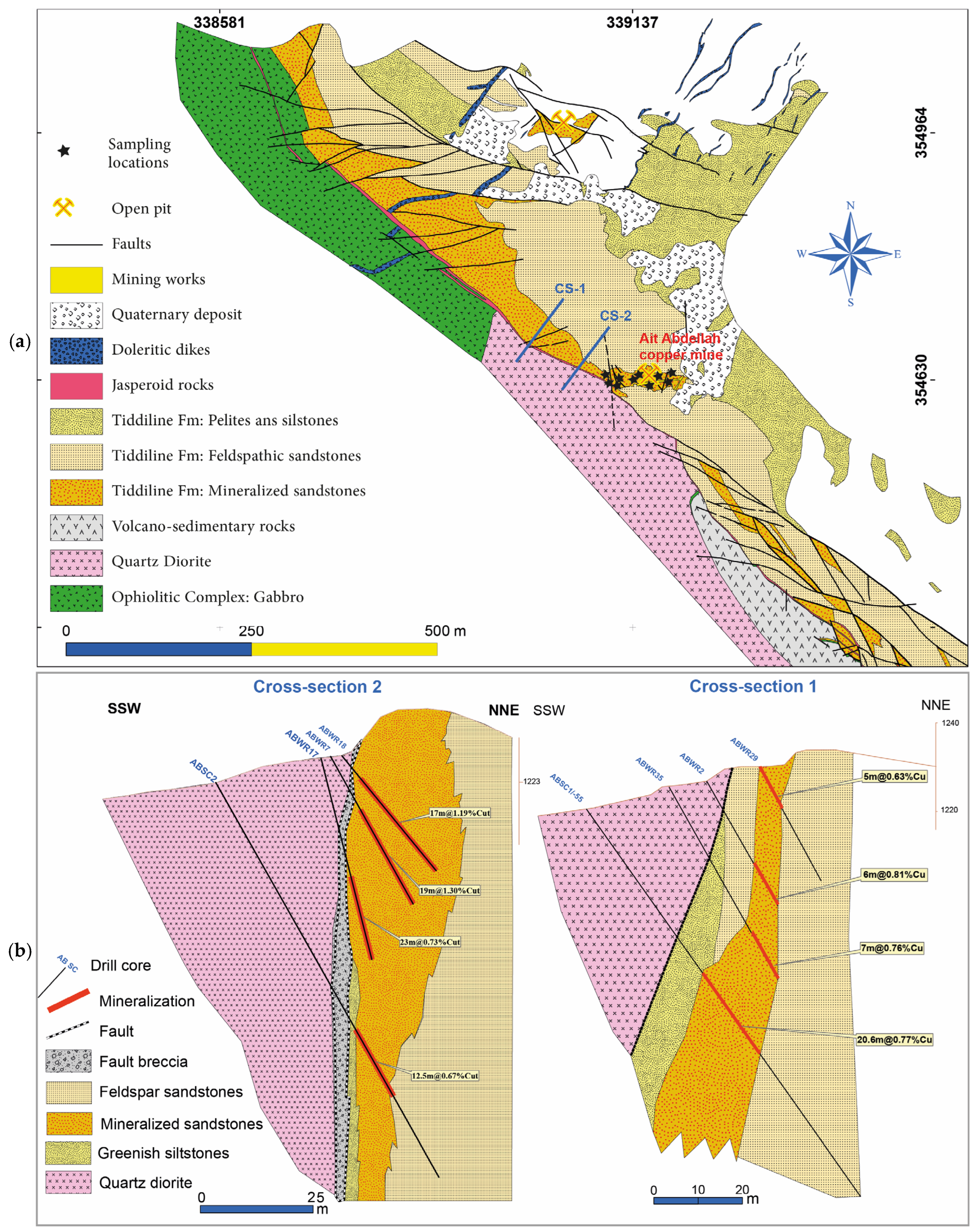
2.3. Deposit Geology and Field Observations
3. Methods
3.1. Microscopic Studies
3.2. Mineralogical Studies
3.3. Stable Isotopes Analysis
3.4. Fluid Inclusion
4. Results
4.1. Structural Control and Hydrothermal Alteration
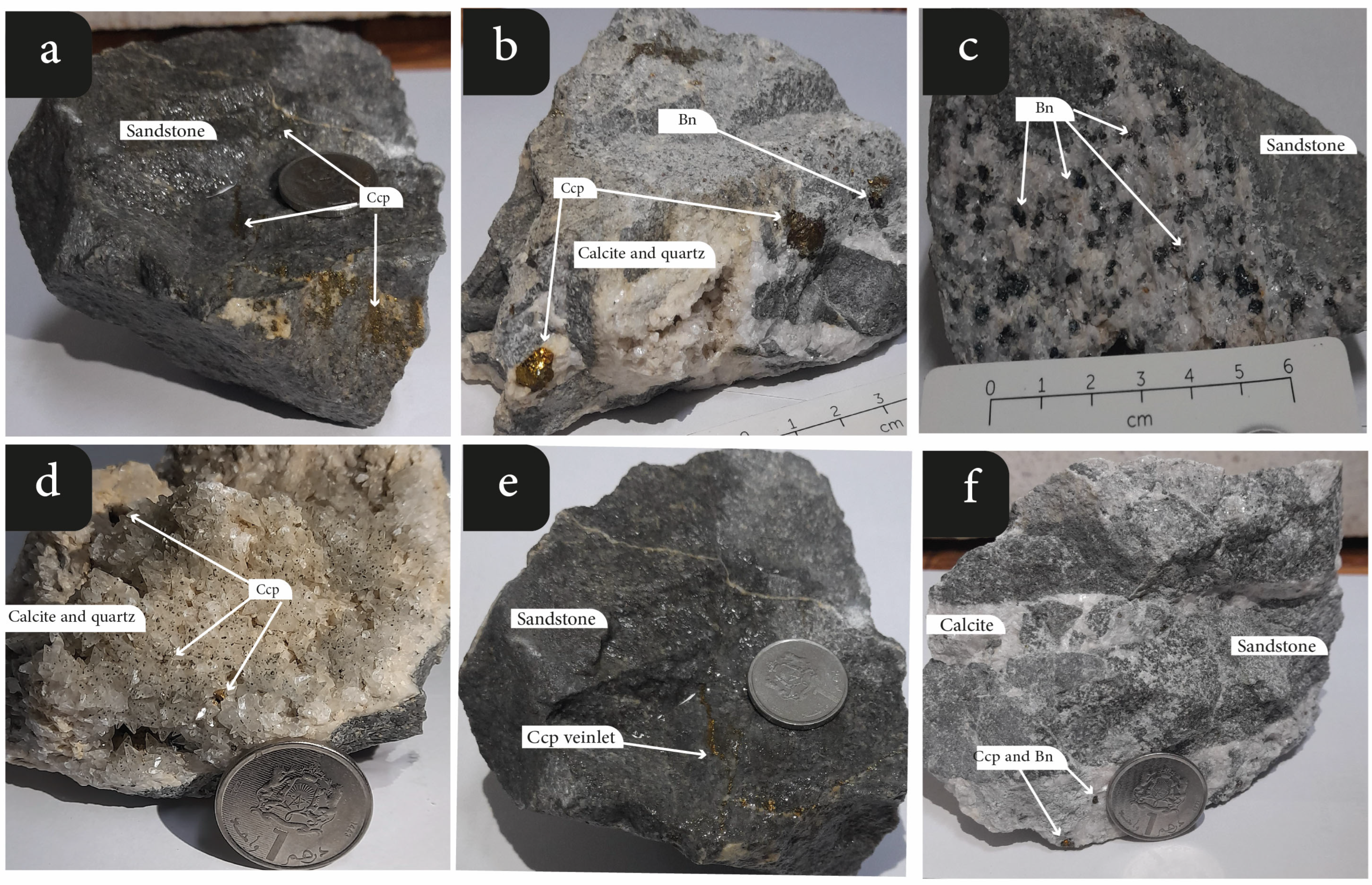
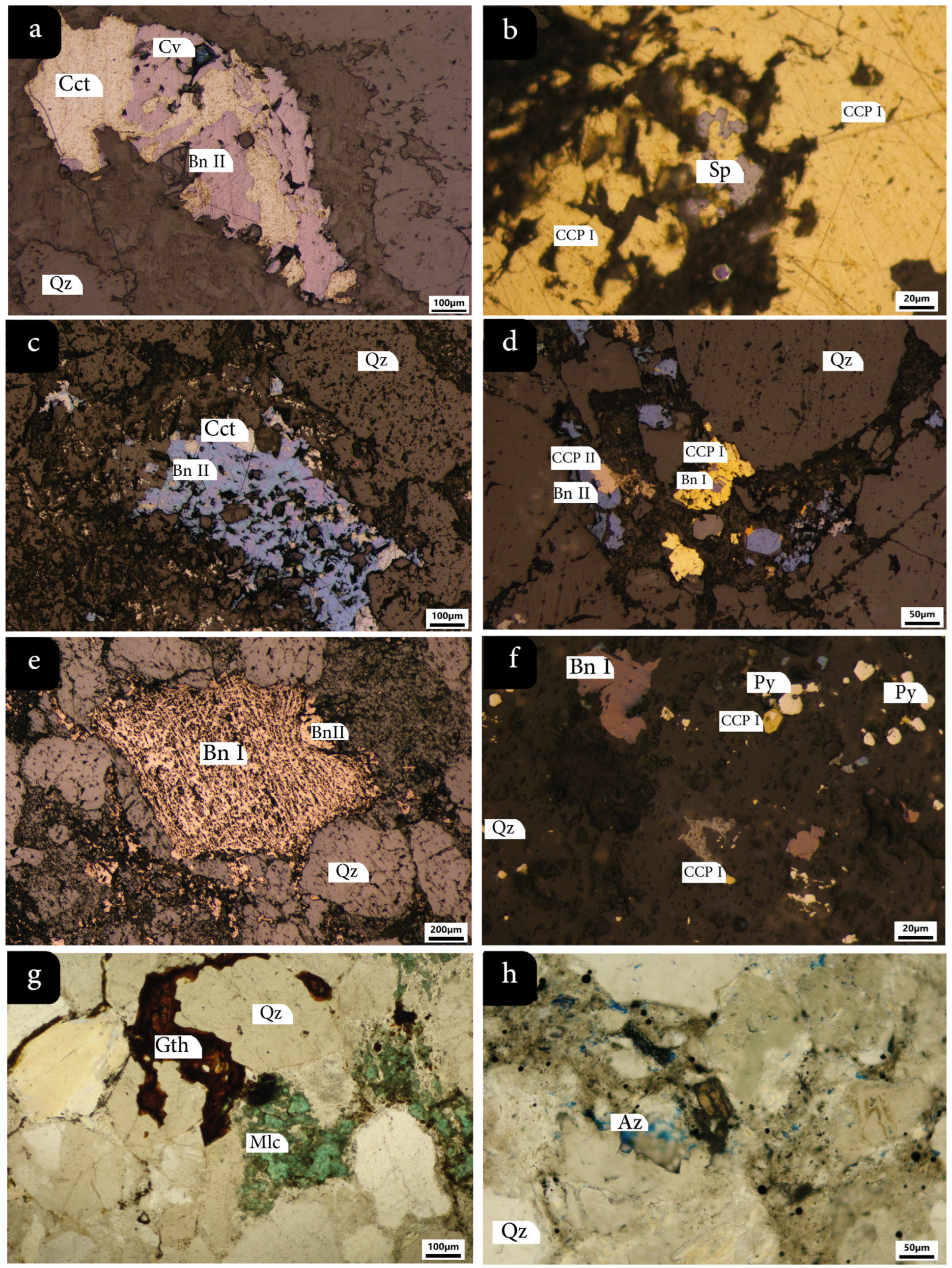
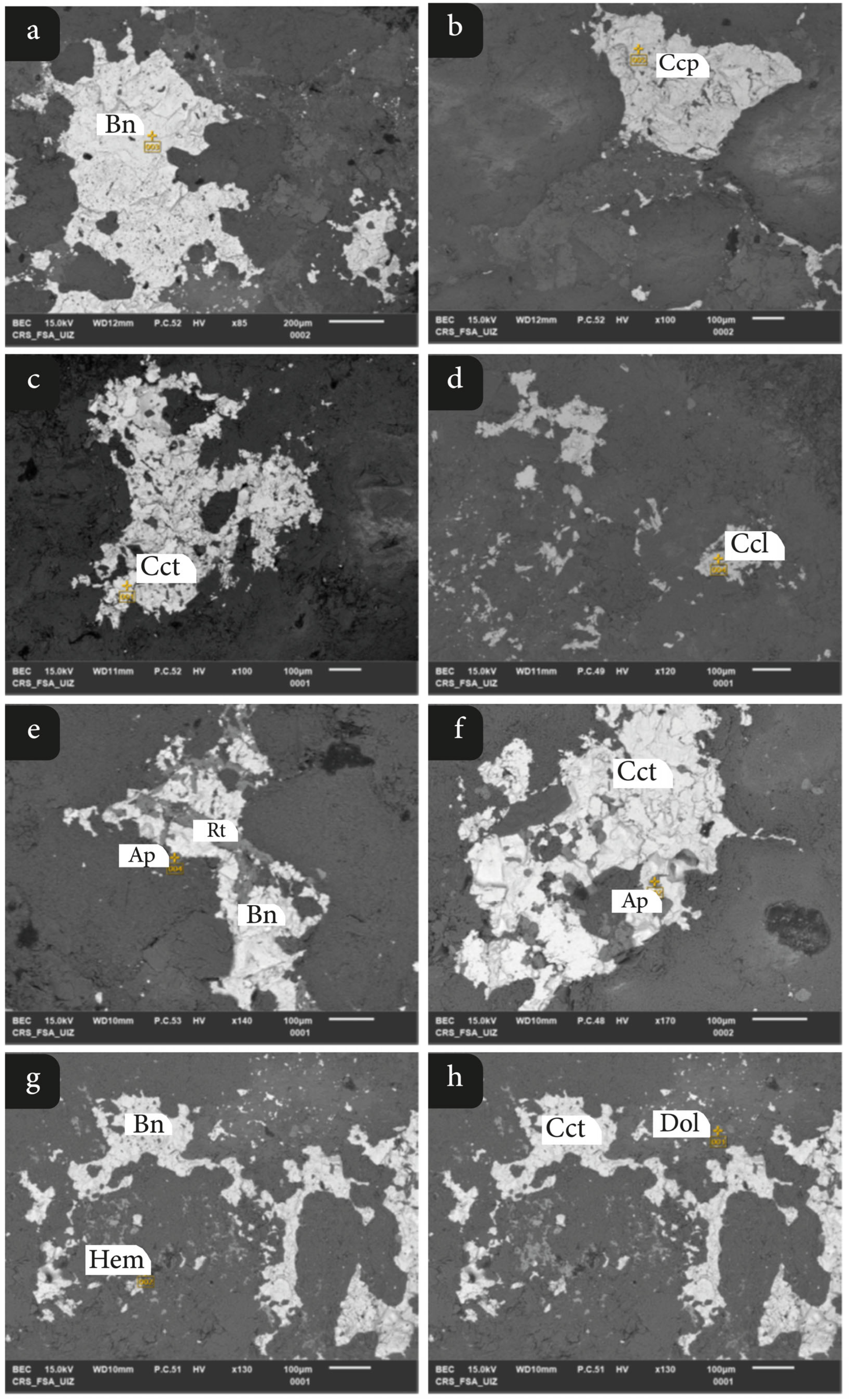
4.2. Mineralogy, Texture, and Paragenesis
4.3. Mineral Chemistry
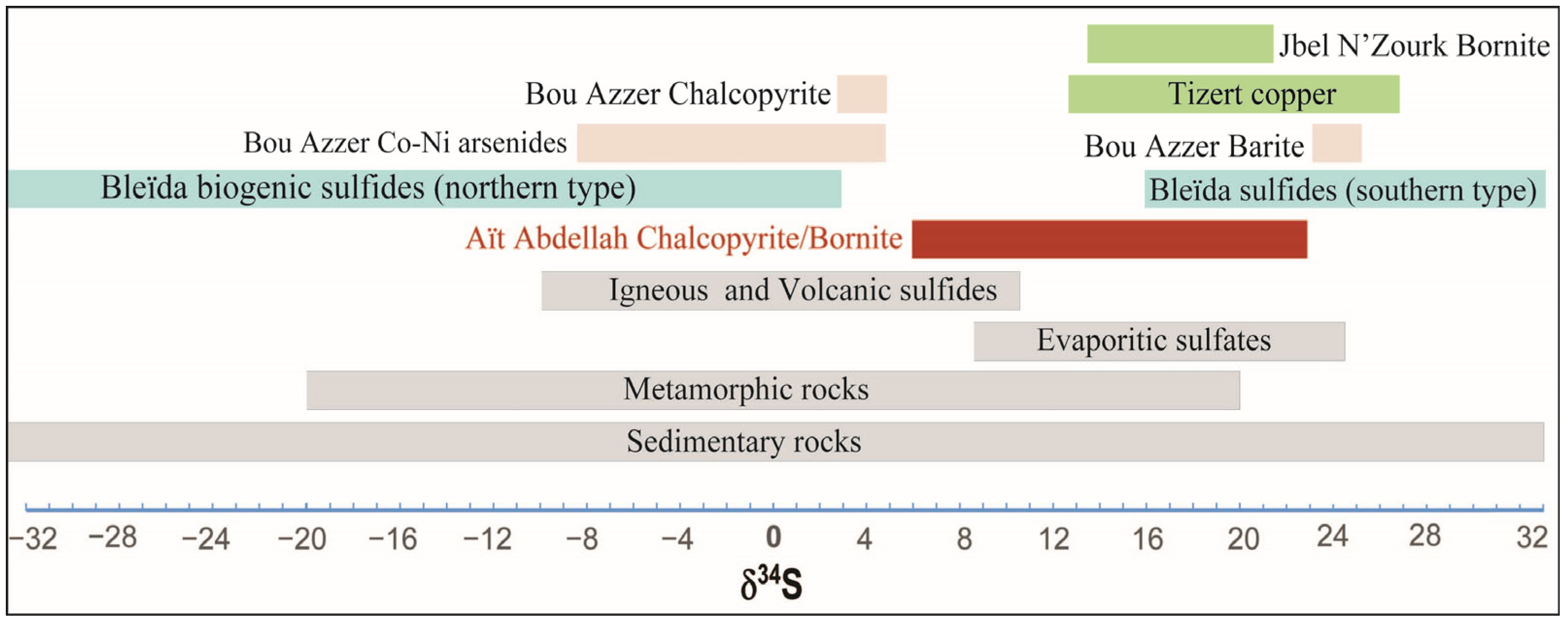
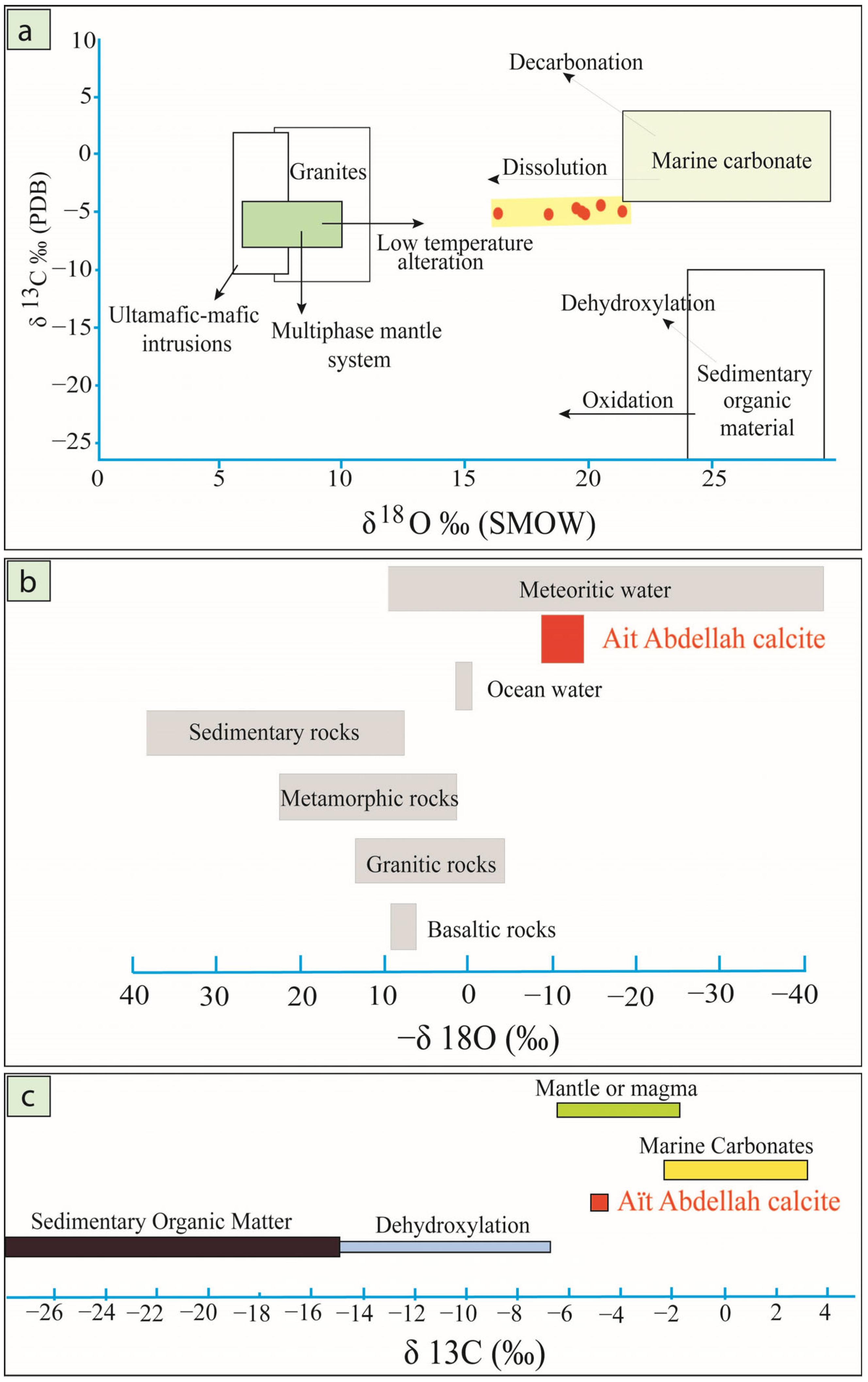
4.4. Stable Isotopes
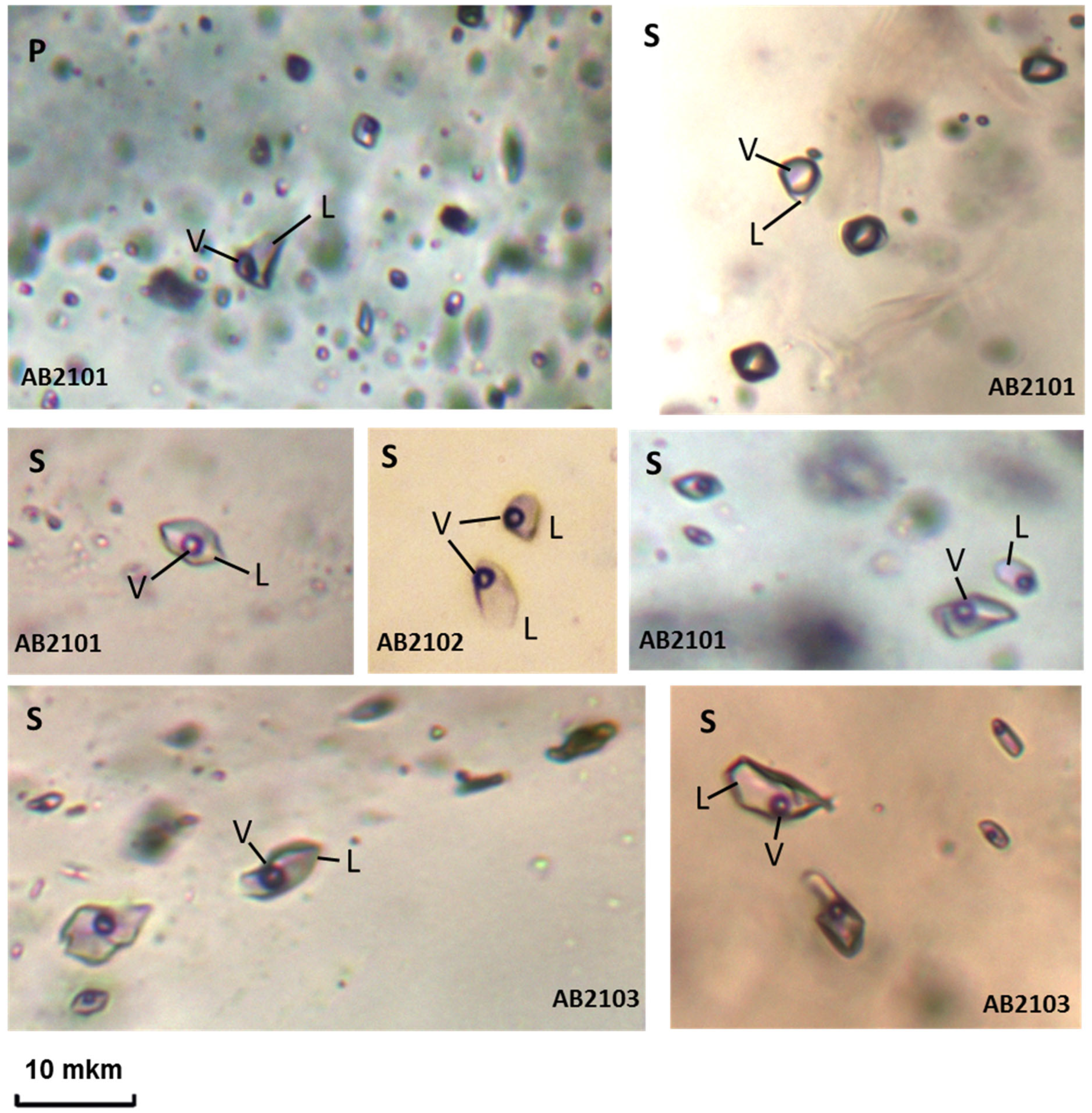
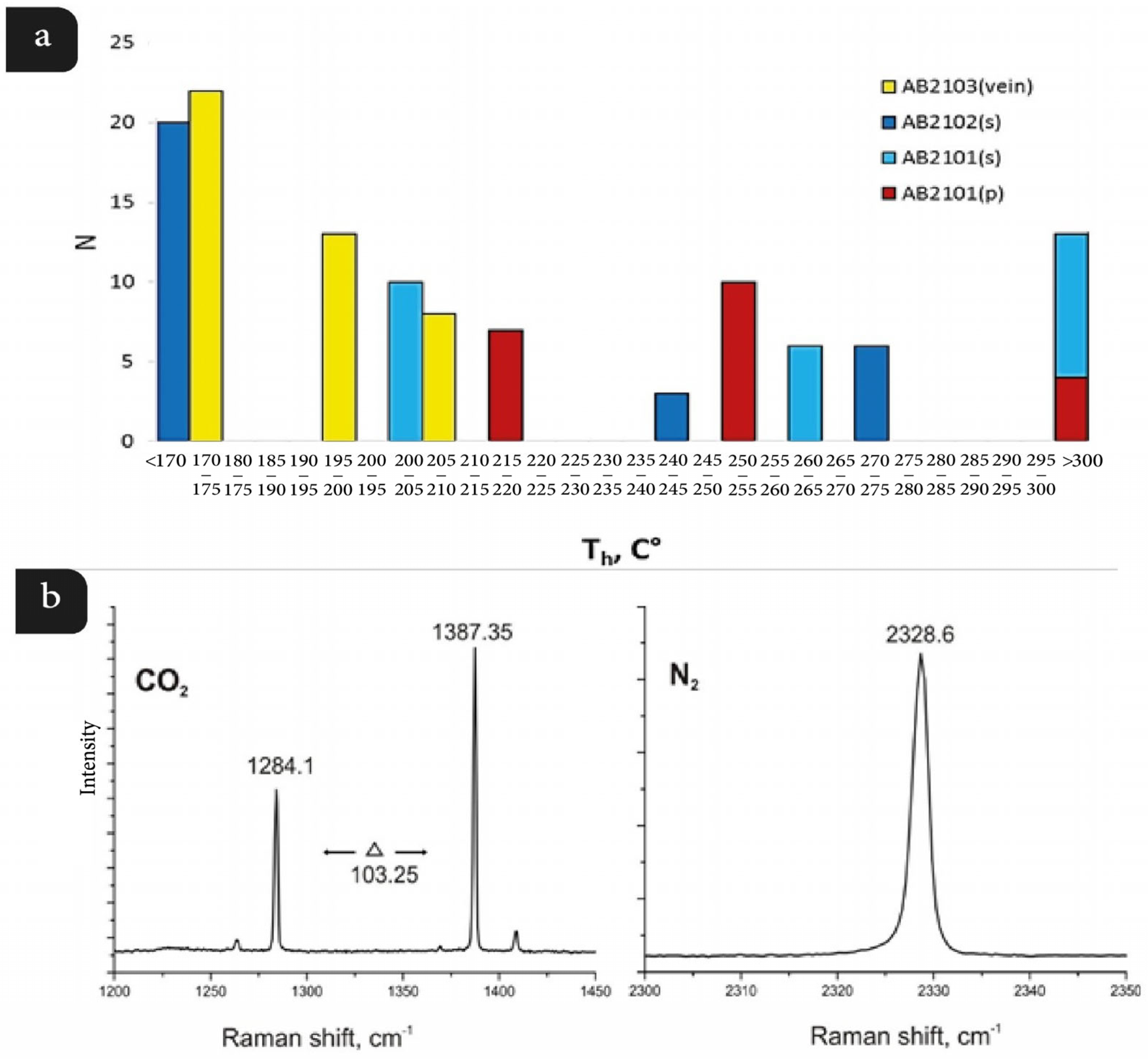
4.5. Fluid Inclusion Studies
| Sample | Host Mineral | Type | Phase | Th. C° | Tm(ice). C° | Salinity (wt.% NaCl equiv.) | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AB2101 | Quartz | primary | L + V | 219 ± 0.5. 254 ± 0.5. 311 ± 1.2 | −4.5–−7.5 | 7.2–11.1 | 7, 10, 4 |
| Quartz | secondary | L + V | 205 ± 1.5. 263 ± 0.5 | −4.1–−7.1 | 6.7–10.6 | 10, 6 | |
| Quartz | secondary | V >> L | 309 ± 1.2 * | 9 | |||
| AB2102 | Quartz | secondary | L + V | 132 ± 2.5. 244 ± 0.5. 275 ± 0.5 | −3.5–−7.6 | 5.7–11.22 | 20, 3, 6 |
| AB2103 | Quartz | secondary | L + V | 174 ± 1.5. 195 ± 0.5. 208 ± 2.5 | −21.1 | 23.2 | 22, 13, 8 |
5. Discussion
5.1. Genetic and Structural Framework of Mineralization
5.2. Isotopic Constraints on Ore Fluid Evolution
6. Conclusions
- -
- The mineralization is structurally controlled by a major NE–SW-trending shear zone, which served as a primary conduit for hydrothermal fluid flow and facilitated ore emplacement.
- -
- Three distinct mineralizing stages have been identified: (1) an early hydrothermal phase marked by the deposition of quartz, dolomite, pyrite, bornite, and chalcopyrite; (2) a subsequent stage characterized by intense fracturing and fluid flow, leading to the precipitation of bornite, chalcopyrite, and Ag-bearing sulfosalts; and (3) a supergene enrichment phase during which primary sulfides were oxidized to form secondary copper minerals such as chalcocite and malachite.
- -
- Sulfur isotope compositions (δ34S values of chalcopyrite and bornite ranging from +5.9% to +22.8%) suggest a mixed magmatic-hydrothermal sulfur source.
- -
- Carbon isotope signatures in calcite (δ13C from –5.2% to –4.4%, VPDB) are consistent with a mantle-derived carbon source. In contrast, oxygen isotopes (δ18O between 16.3% and 21.4%, VSMOW) reflect fluid mixing between magmatic/metamorphic and marine sources.
- -
- Fluid inclusion data reveal homogenization temperatures ranging from 195 °C to 310 °C and salinities between 5.7 wt.% and 23.2 wt.% NaCl equivalent, supporting a model involving mixing of magmatic-hydrothermal fluids with basin or volcano-sedimentary fluids.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hitzman, M.W.; Selley, D.; Bull, S. Formation of sedimentary rock-hosted stratiform copper deposits through earth history. Econ. Geol. 2010, 105, 627–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, D.L.; Sangster, D.F. Geology and Genesis of Sediment-Hosted Copper Deposits; Special Publication 12; Society of Economic Geologists: Littleton, CL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Barton, M.D.; Bowers, T.S. Sedimentary rock-hosted copper deposits. Miner. Depos. 1999, 34, 93–104. [Google Scholar]
- Huston, D.L.; Groves, D.I.; Vearncombe, J.R. The genesis of sandstone-hosted copper deposits. Geol. Ore Depos. 2006, 6, 37–54. [Google Scholar]
- El Ghorfi, M.; Oberthür, T.; Melcher, F.; Lüders, V.; El Boukhari, A.; Maacha, L.; Ziadi, R.; Baoutoul, H. Gold–palladium mineralization at Bleïda Far West, Bou Azzer–El Graara Inlier, Anti-Atlas, Morocco. Miner. Depos. 2006, 41, 549–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essarraj, S.; Boiron, M.C.; Cathelineau, M.; Banks, D.A.; Benharref, M. Penetration of surface-evaporated brines into the Proterozoic basement and deposition of Co and Ag at Bou Azzer (Morocco): Evidence from fluid inclusions. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2005, 41, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ez-Zghoudy, M.; Ikenne, M.; Souhassou, M.; Belfoul, M.A.; Gouiza, M.; Ilmen, S.; Zouhair, M. Structural controls on the Co and Ni-bearing arsenides from the Bou Azzer mine (Case of Aït Ahmane F53 vein deposit): Implications for mineral exploration. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2023, 202, 104929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajjar, Z.; Gervilla, F.; Fanlo, I.; Jiménez, J.M.G.; Ilmen, S. Formation of serpentinite-hosted, Fe-rich arsenide ores at the latest stage of mineralization of the Bou-Azzer mining district (Morocco). Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 128, 103926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikenne, M.; Madi, A.; Gasquet, D.; Cheilletz, A.; Hilal, R.; Mortaji, A.; Mhaili, E. Petrogenetic significance of podiform chromitites from the Neoproterozoic ophiolitic complex of Bou Azzer (Anti-Atlas, Morocco). Afr. Geosci. Rev. 2005, 12, 131–143. [Google Scholar]
- Ikenne, M.; Souhassou, M.; Cousens, B.; Montero, P.; Bea, F.; Askkour, F.; Toummite, A. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and Sm-Nd and Rb-Sr isotope systematics of Neoproterozoic granitoids from Bou Azzer (Anti-Atlas-Morocco): The obduction trigger of the central Anti-Atlas terrane. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2023, 202, 104900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leblanc, M. Ophiolites Précambriennes et Gîtes Arséniés de Cobalt (Bou Azzer-Maroc). Unpublished Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Paris VI, Paris, France, 1975; p. 367. [Google Scholar]
- Saintilan, N.J.; Ikenne, M.; Bernasconi, S.M.; Toma, J.; Creaser, R.A.; Souhassou, M.; Allaz, J.M.; Karfal, A.; Maacha, L.; Spangenberg, J.E. The world’s highest-grade cobalt mineralization at Bou Azzer associated with Gondwana supercontinent breakup, serpentinite and Kellwasser hydrocarbon source rocks. Am. J. Sci. 2023, 323, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmi, S.; Errami, E.; Jouhari, A.; El Kabouri, J.; Ennih, N.; Outaaoui, O.; Maacha, L. Constraints of the regional deformation on the hydrothermal veins in Ousdrat and Aït Ahmane ore deposits (Bou Azzer-El Graara inlier, central Anti-Atlas, Morocco): Implications for mineral exploration. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2024, 220, 105441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, A.; Marignac, C.; Bouabdelli, M. Les dykes basiques du massif ancien de l’Ourika (Atlas de Marrakech, Maroc): Géochimie et signification. Comptes Rendus Geosci. 2002, 334, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkabir, A.; Jébrak, M.; Maacha, L.; Samir, M.R.A.; Madi, A. Gold Mineralization in the Proterozoic Bleida Ophiolite, Anti-Atlas, Morocco; Special Publications; Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2008; Volume 297, pp. 249–264. [Google Scholar]
- Benaouda, R.; Kraemer, D.; Sitnikova, M.; Goldmann, S.; Schwarz-Schampera, U.; Errami, A.; Bau, M. Discovery of high-grade REE-Nb-Fe mineralization associated with calciocarbonatite in south Morocco. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 124, 103631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- En-Naciri, A.; Barbanson, L.; Touray, J.-C. Brine inclusions from the Co-As-(Au) Bou Azzer District, Anti-Atlas Mountains, Morocco. Econ. Geol. 1997, 92, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinin, Y.A.; Borovikov, A.A.; Maacha, L.; Zouhair, M.; Palyanova, G.A.; Zhitova, L.M. Au-Pd mineralization and ore-forming fluids of the Bleïda Far West deposit (Anti-Atlas, Morocco). Geol. Ore Depos. 2022, 64 (Suppl. S2), S237–S256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leblanc, M. Ophiolites précambiennes et gîtes arséniés de cobalt (Bou Azzer–Maroc). Notes Mém. Serv. Géol. Maroc 1981, 280, 306. [Google Scholar]
- Maacha, L. Étude Métallogéniques et Géophysiques des Minéralisations Cobaltifères et Cuprifères de Bou-Azzer El Graara Anti-Atlas, Maroc. Unpublished Ph.D. Thesis, Cadi Ayyad University, Marrakech, Morocco, 2013; p. 344. [Google Scholar]
- Mouttaqi, A.; Sagon, J.P. Le gisement de cuivre de Bleïda (Anti-Atlas central): Une interférence entre les processus de remplacement et d’exhalaison dans un contexte de rift. Chron. Rech. Minière 1999, 536–537, 5–21. [Google Scholar]
- Bourque, H. Le Cuivre de l’Anti-Atlas, un Problème Complexe: Synthèse des Occurrences Cuprifères de la Boutonnière de Bou Azzer-El Graara et Nouvelles Données (Anti-Atlas, Maroc). Ph.D. Thesis, Université d’Orléans, Orléans, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- El Ghorfi, M.; Melcher, F.; Oberthür, T.; Boukhari, A.E.; Maacha, L.; Maddi, A.; Mhaili, M. Platinum group minerals in podiform chromitites of the Bou Azzer ophiolite, Anti Atlas, Central Morocco. Mineral. Petrol. 2008, 92, 59–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennih, N.; Liégeois, J.-P. The Moroccan Anti-Atlas: The West African craton passive margin with limited Pan-African activity. Implications for the northern limit of the craton. Precambrian Res. 2001, 112, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodel, F.; Triantafyllou, A.; Berger, J.; Macouin, M.; Baele, J.M.; Mattielli, N.; Monnier, C.; Trindade, R.I.F.; Ducea, M.N.; Chatir, A.; et al. The Moroccan Anti-Atlas ophiolites: Timing and melting processes in an intra-oceanic arc-back-arc environment. Gondwana Res. 2020, 86, 182–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourque, H.; Barbanson, L.; Sizaret, S.; Branquet, Y. The copper history in the Anti-Atlas belt, from Pan-African to Variscan orogeny, a persistence of tectonic controls: An overview of Bou Azzer-El Graara inlier. In 25ème Réunion des Sciences de la Terre (RST 2016); SIGES Seine-Normandie: Paris, France, 2016; p. 60. [Google Scholar]
- Bourque, H.; Barbanson, L.; Sizaret, S.; Branquet, Y.; Ramboz, C.; Ennaciri, A.; Badra, L. A contribution to the synsedimentary versus epigenetic origin of the Cu mineralizations hosted by terminal Neoproterozoic to Cambrian formations of the Bou Azzer–El Graara inlier: New insights from the Jbel Laassel deposit (Anti Atlas, Morocco). J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2015, 107, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leblanc, M.; Arnold, M. Sulfur isotope evidence for the genesis of distinct mineralizations in the Bleida stratiform copper deposit (Morocco). Econ. Geol. 1994, 89, 931–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchchen, M.; Abia, E.H.; Soulaimani, A.; Abioui, M.; Lutz, B.; Benssaou, M.; Boutaleb, S. The missing link in the genesis of the Lower Paleozoic copper deposits of the Anti-Atlas (Morocco): The Late Triassic Central Atlantic Magmatic Province event. Minerals 2023, 13, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasquet, D.; Ennih, N.; Liégeois, J.-P.; Soulaimani, A.; Michard, A. The Pan-African belt. In Continental Evolution: The Geology of Morocco; Michard, A., Saddiqi, O., Chalouan, A., Frizon de Lamotte, D., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Earth Sciences; Springer-Verlag: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 116, pp. 33–64. [Google Scholar]
- Ait Malek, H.; Gasquet, D.; Bertrand, J.M.; Leterrier, J. Géochronologie U-Pb sur zircon de granitoïdes éburnéens et panafricains dans les boutonnières protérozoïques d’Igherm, du Kerdous et du Bas Drâa (Anti-Atlas occidental, Maroc). Comptes Rendus L’académie Sci.-Ser. IIA-Earth Planet. Sci. 1998, 327, 819–826. [Google Scholar]
- Askkour, F.; Ikenne, M.; Chelle-Michou, C.; Cousens, B.L.; Markovic, S.; Ousbih, M.; Souhassou, M.; El Bilali, H.; Ernst, R. Geochronology and petrogenesis of granitoids from the Bas Draa inlier (Western Anti-Atlas, Morocco): Revived debate on the tectonic regime operating during early Paleoproterozoic at the NW edge of the West African Craton. Geochemistry 2024, 84, 126044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askkour, F.; Saintilan, N.J.; Madi, A.; Chelle-Michou, C.; Souhassou, M.; Icame, N.; Ousbih, M.; Spangenberg, J.E.; Ikenne, M. A lower Cambrian Moroccan Copperbelt? (Tizert copper deposit, Igherm inlier Anti Atlas, Morocco): Preliminary results of Cu-Fe-sulfide Re-Os geochronology and stable sulfur isotope data. In Proceedings of the 17th SGA Biennial Meeting, Zürich, Switzerland, 28 August–1 September 2023; Volume 2, pp. 272–275, Society for Geology Applied to Mineral Deposits. [Google Scholar]
- Barbey, P.; Oberli, F.; Burg, J.P.; Nachit, H.; Pons, J.; Meier, M. The Palaeoproterozoic in western Anti-Atlas (Morocco): A clarification. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2004, 39, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasquet, D.; Chevremont, P.; Baudin, T.; Chalot-Prat, F.; Guerrot, C.; Cocherie, A.; Roger, J.; Hassenforder, B.; Cheilletz, A. Polycyclic magmatism in the Tagragra and Kerdous-Tafeltast inliers (western Anti-Atlas, Morocco). J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2004, 39, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, E.A.; Barnes, R.P.; Beddoe Stephens, B.; Fletcher, T.; Gillespie, M.R.; Hawkins, M.P.; Loughlin, S.C.; Smith, M.; Smith, R.A.; Waters, C.N.; et al. Geology of the Drâa, Kerdous, and Boumalne Districts, Anti-Atlas, Morocco; British Geological Survey: Nottingham, UK, 2010; p. 324. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberger, H.T. A magnificent record—The Pennsylvania Historical Association’s first thirty-seven years. Pa. Hist. A J. Mid-Atl. Stud. 1970, 75, 448–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saquaque, A.; Benharref, M.; Abia, H.; Mrini, Z.; Reuber, I.; Karson, J.A. Evidence for a Panafrican volcanic arc and wrench fault tectonics in the Jbel Saghro, Anti-Atlas, Morocco. Geol. Rundsch. 1992, 81, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söderlund, U.; Ibanez-Mejia, M.; El Bahat, A.; Ernst, R.E.; Ikenne, M.; Soulaimani, A.; Hafid, A. Reply to Comment on “U–Pb baddeleyite ages and geochemistry of dolerite dykes in the Bas-Drâa inlier of the Anti-Atlas of Morocco: Newly identified 1380 Ma event in the West African Craton” by André Michard and Dominique Gasquet. Lithos 2013, 174, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baidada, B.; Ikenne, M.; Barbey, P.; Soulaimani, A.; Cousens, B.; Haissen, F.; Ilmen, S.; Alansari, A. SHRIMP U–Pb zircon geochronology of the granitoids of the Imiter Inlier: Constraints on the Pan-African events in the Saghro massif, Anti-Atlas (Morocco). J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2019, 150, 799–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Haïbi, H.; El Hadi, H.; Pesquera, A.; Tahiri, A.; Martìnez-Poyatos, D.; Zahour, G.; Mehdioui, S. Geochemical and Sr–Nd isotopic constraints on the petrogenesis of the Tiflet granitoids (Northwestern Moroccan Meseta): Geological implications. J. Iber. Geol. 2021, 47, 347–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errami, E.; Bonin, B.; Laduron, D.; Lasri, L. Petrology and geodynamic significance of the post-collisional Pan-African magmatism in the Eastern Saghro area (Anti-Atlas, Morocco). J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2009, 55, 105–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasquet, D.; Levresse, G.; Cheilletz, A.; Azizi-Samir, M.R.; Mouttaqi, A. Contribution to a geodynamic reconstruction of the Anti-Atlas (Morocco) during Pan-African times with the emphasis on inversion tectonics and metallogenic activity at the Precambrian-Cambrian transition. Precambrian Res. 2005, 140, 157–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikenne, M.; Youbi, N.; Ernst, R.; Söderlund, U.; Ait Lahna, A.; Ousbih, M.; Boumehdi, M.A.; Bekker, A.; Bensalah, M.K. Discussion on “From Pan-African transpression to Cadomian transtension at the West African margin: New U-Pb zircon ages from the Eastern Saghro Inlier (Anti-Atlas, Morocco)” by Errami et al. 2020. J. Geol. Soc. 2021, SP 503, 209–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, G.J.; Benziane, F.; Aleinikoff, J.N.; Harrison, R.W.; Yazidi, A.; Burton, W.C.; Quick, J.E.; Saadane, A. Neoproterozoic tectonic evolution of the Jebel Saghro and Bou Azzer-El Graara inliers, eastern and central Anti-Atlas, Morocco. Precambrian Res. 2012, 216–219, 23–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouyaté, D.; Söderlund, U.; Youbi, N.; Ernst, R.; Hafid, A.; Ikenne, M.; Soulaimani, A.; Bertrand, H.; El Janati, M.; Chaham, K.R. U-Pb baddeleyite and zircon ages of 2040 Ma, 1650 Ma, and 885 Ma on dolerites in the West African Craton (Anti-Atlas Inlier): Possible links to break-up of Precambrian supercontinents. Lithos 2013, 174, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bahat, A.; Ikenne, M.; Soderlund, U.; Cousens, B.; Youbi, N.; Ernst, R.; Soulaimani, A.; Janati, M.; Ahmid Hafid, A. U–Pb baddeleyite ages and geochemistry of dolerite dykes in the Bas Draa inlier of the Anti-Atlas of Morocco: Newly identified 1380 Ma event in the West African Craton. Lithos 2013, 174, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikenne, M.; Söderlund, U.; Ernst, R.E.; Pin, C.; Youbi, N.; Hafid, A. A c. 1710 Ma mafic sill emplaced into a quartzite and calcareous series from Ighrem, Anti-Atlas, Morocco: Evidence that the Taghdout passive margin sedimentary group is nearly 1 Ga older than previously thought. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2017, 127, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oummouch, A. Environnement Métallogénique, Géochimique, Paléogéographique et Géophysique des Minéralisations Stratiformes à Cu-Ag de la Boutonnière d’Igherm Anti-Atlas Occidental (Maroc): Cas du Gisement de Tizert. Unpublished Ph.D. Thesis, Cadi Ayyad University, Marrakech, Morocco, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chabane, A.; El Boukhari, A.; Rocci, G.; Tane, J.L. Découverte d’un Magmatisme D’affinité Boninitique d’arc Associé à L’ophiolite Panafricaine de Khzama (Massif du Siroua, Anti-Atlas Marocain); Comptes rendus de l’Académie des sciences. Série 2, Mécanique, Physique, Chimie, Sciences de l’univers, Sciences de la Terre; Gauthier-Villars: Paris, France, 1991; Volume 313, pp. 1301–1304. [Google Scholar]
- El Boukhari, A.; Chabane, A.; Rocci, G.; Tane, J.L. Upper Proterozoic ophiolites of the Siroua Massif (Anti-Atlas, Morocco): A marginal sea and transform fault system. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 1992, 14, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blein, O.; Baudin, T.; Chèvremont, P.; Soulaimani, A.; Admou, H.; Gasquet, P.; Cocherie, A.; Egal, E.; Youbi, N.; Razin, P.; et al. Geochronological constraints on the polycyclic magmatism in the Bou Azzer-El Graara inlier (central Anti-Atlas Morocco). J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2014, 99, 287–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hefferan, K.; Soulaimani, A.; Samson, S.D.; Admou, H.; Inglis, J.; Saquaque, A.; Chaib, L.; Heywood, N. A reconsideration of Pan African orogenic cycle in the Anti-Atlas Mountains, Morocco. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2014, 98, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodel, F.; Macouin, M.; Triantafyllou, A.; Carlut, J.; Berger, J.; Rousse, S.; Ennih, N.; Trindade, R.I.F. Unusual massive magnetite veins and highly altered Cr-spinels as relics of a Cl-rich acidic hydrothermal event in Neoproterozoic serpentinites (Bou Azzer ophiolite, Anti-Atlas, Morocco). Precambrian Res. 2017, 300, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samson, S.D.; Inglis, J.D.; D’Lemos, R.S.; Admou, H.; Blichert-Toft, J.; Hefferan, K. Geochronological, geochemical, and Nd-Hf isotopic constraints on the origin of Neoproterozoic plagiogranites in the Tasriwine ophiolite, Anti-Atlas orogen, Morocco. Precambrian Res. 2004, 135, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouougri, E.H.; Ait Lahna, A.; Tassinari, C.G.; Basei, M.; Youbi, N.; Admou, H.; Saquaque, A.; Boumehdi, M.A.; Maacha, L. Time constraints on Early Tonian rifting and Cryogenian Arc terrane-continent convergence along the northern margin of the West African craton: Insights from SHRIMP and LA-ICP-MS zircon geochronology in the Pan-African Anti-Atlas belt (Morocco). Gondwana Res. 2020, 85, 169–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouougri, E.H.; Saquaque, A. Lithostratigraphic framework and correlation of the Neoproterozoic northern western African craton passive margin sequence (Siroua Zenaga Bou Azzer-El Graara inliers, central Anti-Atlas, Morocco): An integrated approach. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2004, 39, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Lemos, R.S.; Inglis, J.D.; Samson, S.D. A newly discovered orogenic event in Morocco: Neoproterozoic ages for supposed Eburnean basement of the Bou Azzer inlier, Anti-Atlas Mountains. Precambrian Res. 2006, 147, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevremont, P.; Baudin, T.; Blein, O.; Admou, H.; Ahmid, H.; Bouabdelli, M.; Soulaimani, A. Carte Géologique du Maroc au 1/50 000, Feuille d’Ighriy; Service Géologique du Maroc: Rabat, Morocco, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Admou, H.; Razin, P.; Egal, E.; Youbi, N.; Soulaimani, A.; Blein, O.; Chevremont, P.; Gasquet, D.; Barbanson, L.; Bouabdelli, M.; et al. Notice Explicative de la Carte géologiques du Maroc (1/50 000), Feuille Aït Ahmane; Notes et Mémoires du Service Géologique No. 533 bis; Service Géologique du Maroc: Rabat, Morocco, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Blein, O.; Baudin, T.; Soulaimani, A.; Cocherie, A.; Chèvremont, P.; Admou, H.; Ouanaimi, H.; Hafi, A.; Razin, P.; Bouabdelli, M.; et al. New geochemical, geochronological and structural constraints on the Ediacaran evolution of the south Sirwa, Agadir-Melloul and Iguerda inliers, Anti-Atlas, Morocco. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2014, 98, 47–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulaimani, A.; Blein, O.; Chèvremont, P.; Ouanaimi, H.; Hafid, A.; Admou, H.; Beni Akhy, R. Notice Explicative Carte Géologique du Maroc (1/50 000), Feuille Agadir Melloul; Notes et Mémoires du Service Géologique No. 549; Service Géologique du Maroc: Rabat, Morocco, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Soulaimani, A.; Chakiri, S.; Soulaimani, S.; Bejjaji, Z.; Miftah, A.; Manar, A. Gradiometry processing techniques for large-scale aeromagnetic data for structural and mining implications: The case study of Bou Azzer Inlier, Central Anti-Atlas, Morocco. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulaimani, A.; Razin, P.; Youbi, N.; Barbanson, L.; Admou, H.; Blein, O.; Anzar, C. Notice Explicative de la Carte Géologique du Maroc (1/50 000), Feuille Al Gloa; Notes et Mémoires du Service Géologique No. 532 bis; Service Géologique du Maroc: Rabat, Morocco, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bodinier, J.L.; Dupuy, C.; Dostal, J. Geochemistry of Precambrian ophiolites from Bou Azzer, Morocco. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1984, 87, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidoo, D.D.; Bloomer, S.H.; Saquaque, A.; Hefferan, K. Geochemistry and significance of metavolcanic rocks from the Bou Azzer-El Graara ophiolite (Morocco). Precambrian Res. 1991, 53, 79–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllou, A.; Berger, J.; Baele, J.M.; Bruguier, O.; Diot, H.; Ennih, N.; Monnier, C.; Plissart, G.; Vandycke, S.; Watlet, A. Intra-oceanic arc growth driven by magmatic and tectonic processes recorded in the Neoproterozoic Bougmane arc complex (Anti-Atlas, Morocco). Precambrian Res. 2018, 304, 39–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllou, A.; Berger, J.; Baele, J.M.; Mattielli, N.; Ducea, M.N.; Sterckx, S.; Samson, S.; Hodel, F.; Ennih, N. Episodic magmatism during the growth of a Neoproterozoic oceanic arc (Anti-Atlas, Morocco). Precambrian Res. 2020, 339, 105610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choubert, G. Histoire Géologique du Précambrien de l’Anti-Atlas. Ph.D. Thesis, Service Géologique du Maroc, Rabat, Morocco, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Deynoux, M.; Affaton, P.; Trompette, R.; Villeneuve, M. Pan-African tectonic evolution and glacial events registered in Neoproterozoic to Cambrian cratonic and foreland basins of West Africa. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2006, 46, 397–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernhet, E.; Youbi, N.; Chellai, E.H.; Villeneuve, M.; El Archi, A. The Bou-Azzer glaciation on the West African Craton (Anti-Atlas, Morocco). Precambrian Res. 2012, 196–197, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letsch, D.; Large, S.J.E.; Buechib, M.W.; Winkler, W.; Quadta, A.V. Ediacaran glaciations of the West African Craton: Evidence from Morocco. Precambrian Res. 2018, 310, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.J.; Fekkak, A.; Ennih, N.; Errami, E.; Loughlin, S.C.; Gresse, P.G.; Chevallier, L.P.; Liégeois, J.P. A new lithostratigraphic framework for the Anti-Atlas Orogen, Morocco. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2004, 39, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ousbih, M.; Ikenne, M.; Cousens, B.; Chelle-Michou, C.; El Bilali, H.; Gaouzi, A.; Ernst, R. Stratigraphy, geochronology, geochemistry and Nd isotopes of the Ouarzazate Group, Anti-Atlas, Morocco: Evidence of a Late Neoproterozoic large igneous province in the northwestern part of the West African Craton. Lithos 2024, 474, 107593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toummite, A.; Liégeois, J.P.; Gasquet, D.; Bruguier, O.; Beraaouz, E.H.; Ikenne, M. Field, geochemistry and Sr-Nd isotopes of the Pan-African granitoids from the Tifnoute Valley (Sirwa, Anti-Atlas, Morocco): A post-collisional event in a metacratonic setting. Mineral. Petrol. 2013, 107, 739–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maacha, L.; El Ghorfi, M.; Ennaciri, A.; Sadiqqi, O.; Soulaimani, A.; Alansari, A.; Bhilisse, M. Nouvelles données isotopiques et d’inclusions fluides des minéralisations cobaltifères de Bou Azzer: Apport à la géologie économique de la boutonnière (Anti-Atlas central, Maroc). Notes Et Mémoires Du Serv. Géologique du Maroc 2015, 579, 133–139. [Google Scholar]
- Bouabdellah, M.; Maacha, L.; Levresse, G.; Saddiqi, O. The Bou Azzer Co-Ni-Fe-As (±Au±Ag) district of central Anti-Atlas (Morocco): A long-lived late Hercynian to Triassic magmatic-hydrothermal to low-sulphidation epithermal system. In Mineral Deposits of North Africa; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 229–247. [Google Scholar]
- Dolansky, L.M. Controls on the Genesis of Hydrothermal Cobalt Mineralization: Insights from the Mineralogy and Geochemistry of the Bou Azzer Deposits, Morocco. Unpublished Master Thesis, McGill University, Montreal, QC, Canada, 2007; p. 162. [Google Scholar]
- El Ghorfi, M.; Melcher, F.; Oberthür, T.; El Boukhari, A.; Maacha, L. Carbonate-hosted gold and palladium mineralization in the Anti-Atlas (Morocco): Geochemistry, mineralogy and tectonic setting. In Mineral Deposit Research: Meeting the Global Challenge; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 1127–1130. [Google Scholar]
- Maacha, L.; Ennaciri, A.; Saquaque, A.; Soulaimani, A. A promising prospect: The Jbel N’Zourk deposit (Central Anti-Atlas). Notes Et Mémoires Du Serv. Géologique du Maroc 2011, 564, 123–127. [Google Scholar]
- Tourneur, E.; Chauvet, A.; Kouzmanov, K.; Tuduri, J.; Paquez, C.; Sizaret, S.; Darfal, A.; Moundi, Y.; El Hassani, A. Co-Ni-arsenide mineralization in the Bou-Azzer district (Anti-Atlas, Morocco): Genetic model and tectonic implications. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 134, 104128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouravsky, G.; De Trey, M. Le Précambrien II supérieur dans la partie nord de la boutonnière du Graara: Ses caractères lithologiques et ses relations stratigraphiques avec le Précambrien III inférieur (série de Tiddiline). Compte Rendu Somm. Séances Société Géologique Fr. 1967, 7, 323–324. [Google Scholar]
- Leblanc, M.; Lancelot, J.R. Interprétation géodynamique du domaine panafricain (Précambrien terminal) de l’Anti-Atlas (Maroc) à partir des données géologiques et géodynamiques. Can. J. Earth Sci. 1980, 17, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassenforder, B. La Tectonique Panafricaine et Varisque de l’Anti-Atlas Dans le Massif de Kerdous (Maroc). Ph.D. Thesis, Université Strasbourg, Strasbourg, France, 1987; p. 249. [Google Scholar]
- Leblanc, M. Minéralisations cuprifères et volcanisme albitophyrique dans les ophiolites précambriennes de Bou Azzer (Anti-Atlas, Maroc). Bull. Volc. 1974, 38, 1095–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leblanc, M.; Billaud, P.I.E.R.R.E. A volcano-sedimentary copper deposit on a continental margin of upper Proterozoic age; Bleïda (Anti-Atlas, Morocco). Econ. Geol. 1978, 73, 1101–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poot, J.; Verhaert, M.; Dekoninck, A.; Oummouch, A.; El Basbas, A.; Maacha, L.; Yans, J. Characterization of weathering processes of the giant copper deposit of Tizert (Igherm Inlier, Anti-Atlas, Morocco). Minerals 2020, 10, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Routhier, P.; Leblanc, M.; Clavel, M. Les gisements de cobalt de Bou Azzer (Maroc) sont portés par un niveau sédimentaire précambrien. Comptes Rendus L’académie Sci. Paris Série D 1970, 270, 1857–1860. [Google Scholar]
- Saadi, M. Les gisements de cuivre de Bleïda (Graara, Anti-Atlas, Maroc). In Les Roches Plutoniques dans leurs Rapports avec les Gîtes Minéraux; Masson: Paris, France, 1973; pp. 288–290. [Google Scholar]
- Barton, P.B.; Bethke, P.M. Chalcopyrite disease in sphalerite; pathology and epidemiology. Am. Mineral. 1987, 72, 451–467. [Google Scholar]
- Hoefs, J. Stable Isotope Geochemistry, 9th ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bouskri, I.; Ilmen, S.; Souhassou, M.; Ikenne, M.; Zoheir, B.; Hajjar, Z.; Maacha, L.; Benzougagh, B.; Kader, S.; Jabbour, M. Geological setting, mineralogy, and isotopic characterization of the Jbel N’Zourk copper deposit, central Anti-Atlas, Morocco. Ore Geol. Rev. 2025, 179, 106533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maacha, L.; Azizi, R.; Bouchta, R. Gisements cobaltifères du district de Bou Azzer (Anti-Atlas): Structure, minéralogie et conditions de genèse. Chron. Rech. Minière 1998, 531–532, 65–75. [Google Scholar]
- Oummouch, A.; Essaifi, A.; Zayane, R.; Maddi, O.; Zouhair, M.; Maacha, L. Geology and metallogenesis of the sediment-hosted Cu-Ag deposit of Tizert (Igherm Inlier, Anti-Atlas Copperbelt, Morocco). Geofluids 2017, 2017, 7508484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liang, J.; Azmy, K.; Zhong, Y. Carbon-isotope stratigraphy of the Lower Cambrian (Cambrian Explosion) in northwestern Yangtze Platform, China: Implications for global correlation. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2024, 166, 106909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmoto, H.; Rye, R.O. Isotopes of sulfur and carbon. In Geochemistry of Hydrothermal Ore Deposits; Barnes, H.L., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1979; pp. 509–567. [Google Scholar]
- Frezzotti, M.L.; Tecce, F.; Casagli, A. Raman spectroscopy for fluid inclusion analysis. J. Geochem. Explor. 2012, 112, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironov, N.L.; Tobelko, D.P.; Smirnov, S.Z.; Portnyagin, M.V.; Krasheninnikov, S.P. Estimation of CO2 content in the gas phase of melt inclusions using Raman spectroscopy: Case study of inclusions in olivine from the Karymsky volcano (Kamchatka). Russ. Geol. Geophys. 2020, 61, 600–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodnar, R.J. Revised equation and table for determining the freezing point depression of H2O–NaCl solutions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1993, 57, 683–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, M.D.; Leach, D.L.; Crofoot, D.C. Sandstone-hosted copper deposits in the Kalahari Basin, Botswana. Econ. Geol. 2015, 110, 625–648. [Google Scholar]
- Seedorff, E.; Krahulec, K.; Vokes, F. Structural and fluid flow controls in sandstone-hosted copper deposits. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2005, 117, 1012–1027. [Google Scholar]
- Tartèse, R.; Boulvais, P.; Poujol, M.; Chevalier, T.; Paquette, J.L.; Ireland, T.R.; Deloule, E. Mylonites of the South Armorican Shear Zone: Insights for crustal-scale fluid flow and water–rock interaction processes. J. Geodyn. 2012, 56–57, 86–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zeng, Y. The Tianger (Bingdaban) shear zone hosted gold deposit, West Tianshan, NW China: Petrographic and geochemical characteristics. Ore Geol. Rev. 2007, 32, 337–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmoto, H. Systematics of sulfur and carbon isotopes in hydrothermal ore deposits. Econ. Geol. 1972, 67, 551–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seal, R.R. Sulfur isotope geochemistry of sulfide minerals. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2006, 61, 633–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, S.; Sasaki, A. Sulfur isotopic ratios of the magnetite-series and ilmenite-series granitoids of the Sierra Nevada batholith: A reconnaissance study. Geology 1989, 17, 788–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santosh, M.; Masuda, H. Reconnaissance oxygen and sulfur isotopic mapping of Pan-African alkali granites and syenites in the southern Indian Shield. Geochem. J. 1991, 25, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, A.; Ishihara, S. Sulfur isotopic composition of the magnetite-series and ilmenite-series granitoids of Japan. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1979, 68, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malitch, K.N.; Belousova, E.A.; Griffin, W.L.; Badanina, I.Y.; Latypov, R.M.; Sluzhenikin, S.F. New insights on the origin of ultramafic-mafic intrusions and associated Ni-Cu-PGE sulfide deposits of the Noril’sk and Taimyr provinces, Russia: Evidence from radiogenic- and stable-isotope data. In Processes and Ore Deposits of Ultramafic-Mafic Magmas through Space and Time; Mondal, S.K., Griffin, W.L., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 97–238. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, H.L. (Ed.) Geochemistry of Hydrothermal Ore Deposits; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]



| Samples ID | Mineral | δ34S |
| AB-01 | Bornite | 14.3 |
| AB-02 | Bornite | 15.7 |
| AB-04 | Bornite | 19.2 |
| AB-05 | Bornite | 14.2 |
| AB-07 | Bornite | 6 |
| AB-G3 | Bornite | 5.9 |
| AB-G4 | Chalocopyrite | 22.8 |
| AB-G5 | Chalocopyrite | 20.6 |
| AB-G6 | Chalocopyrite | 15.6 |
| AB-G7 | Chalocopyrite | 11.1 |
| Samples ID | δ13C-carbs | δ18O-carbs | δ18O-carbs (VSMOW)) |
| AB-G1 | −5.2 | 18.4 | −12.2 |
| AB-G2 | −5.1 | 16.3 | −14.2 |
| AB-G3 | −4.6 | 19.5 | −11.1 |
| AB-G4 | −4.9 | 19.7 | −10.9 |
| AB-G5 | −4.9 | 21.4 | −9.3 |
| AB-G6 | −4.4 | 20.5 | −10.1 |
| AB-G7 | −5.1 | 19.9 | −10.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jabbour, M.; Ilmen, S.; Ikenne, M.; Zoheir, B.; Souhassou, M.; Bouskri, I.; El-Masoudy, A.; Prokopyev, I.; Oulhaj, M.; Ait Addi, M.; et al. Genesis of the Aït Abdellah Copper Deposit, Bou Azzer-El Graara Inlier, Anti-Atlas, Morocco. Minerals 2025, 15, 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050545
Jabbour M, Ilmen S, Ikenne M, Zoheir B, Souhassou M, Bouskri I, El-Masoudy A, Prokopyev I, Oulhaj M, Ait Addi M, et al. Genesis of the Aït Abdellah Copper Deposit, Bou Azzer-El Graara Inlier, Anti-Atlas, Morocco. Minerals. 2025; 15(5):545. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050545
Chicago/Turabian StyleJabbour, Marieme, Said Ilmen, Moha Ikenne, Basem Zoheir, Mustapha Souhassou, Ismail Bouskri, Ali El-Masoudy, Ilya Prokopyev, Mohamed Oulhaj, Mohamed Ait Addi, and et al. 2025. "Genesis of the Aït Abdellah Copper Deposit, Bou Azzer-El Graara Inlier, Anti-Atlas, Morocco" Minerals 15, no. 5: 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050545
APA StyleJabbour, M., Ilmen, S., Ikenne, M., Zoheir, B., Souhassou, M., Bouskri, I., El-Masoudy, A., Prokopyev, I., Oulhaj, M., Ait Addi, M., & Maacha, L. (2025). Genesis of the Aït Abdellah Copper Deposit, Bou Azzer-El Graara Inlier, Anti-Atlas, Morocco. Minerals, 15(5), 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050545