Abstract
The Awulale Iron Metallogenic Belt (AIMB) located in Central Tianshan is a significant iron ore belt in China. The Beizhan area exhibits extensive volcanic and intrusive rocks that formed during or close to the iron mineralization period. The iron ores in Beizhan are found in Early Carboniferous rhyolite and dacite tuff. The rhyolite is enriched in LILEs and LREEs, depleted in HFSEs, and shows high positive εNd(t) values (+3.0–+4.0). Late Carboniferous intrusive rocks include a granite stock and diabase and diorite dykes. The zircon grains from the granite yield a weighted mean 206Pb/238U age of 311.8 ± 2.6 Ma. The geochemical features of the granite are similar to those of rhyolite, but with pronounced negative anomalies of Eu, Sr, P, and Ti and higher positive εNd(t) values (+4.9–+5.1). The zircons in the diorite dyke yield a weighted mean 206Pb/238U age of 299.2 ± 1.4 Ma. Both the diabase and diorite dykes show an enrichment of LREEs and depletion of HFSEs with high positive εNd(t) values (+3.3–+7.3 and +2.3–+2.6, respectively), although the Eu, Th, and Sr anomalies are more negative in the diorite compared to the diabase. The rhyolite displays high positive εNd(t) values and young Nd model ages (TDM2 = 760–838 Ma) and has Nb/Ta ratios (11.3–12.8) close to that of the continental crust, indicating that it originated from the partial melting of the juvenile lower crust. The granite has similar geochemical characteristics (TDM2 = 656–673 Ma and Nb/Ta ratio = 8.7–10.9) and is also believed to have originated mainly from the partial melting of the juvenile lower crust. The diabase and diorite dykes have low (Tb/Yb)N ratios (<2) and high Ba/Th (31.8–353.2 and 185.3–251.3, respectively) and Sr/Th (113.8–312.9 and 144.7–163.1) ratios, and exhibit a pronounced depletion of HREEs and Y and negative Th anomalies, suggesting that they originated from a spinel-garnet lherzolite mantle source. The Early Carboniferous rhyolite erupted in a continental arc setting, whereas the Late Carboniferous granites, diabase dykes, and diorite dykes formed in an extensional setting associated with the upwelling of the asthenosphere. Therefore, the magmatism and Fe mineralization in the AIMB are correlated with an extensional setting associated with oceanic slab breakoff.
1. Introduction
The Central Asian Orogenic Belt (CAOB) is globally acknowledged as one of the world’s largest accretionary orogenic systems (Figure 1a) [1,2,3,4,5], recognized for its abundant copper, gold, lead–zinc, molybdenum, nickel, and chromium ore deposits [6,7,8,9]. Additionally, the CAOB is known for its significant iron deposits concentrated in three distinct areas: the Turgai belt in Uralides [10], the Southern Altay in China [11,12], and the Awulale Belt in Tianshan [7,13]. Given the economic significance of these resources, the geological evolution of the CAOB has garnered enduring attention from geologists and economic experts worldwide [6,7,9,14,15,16].
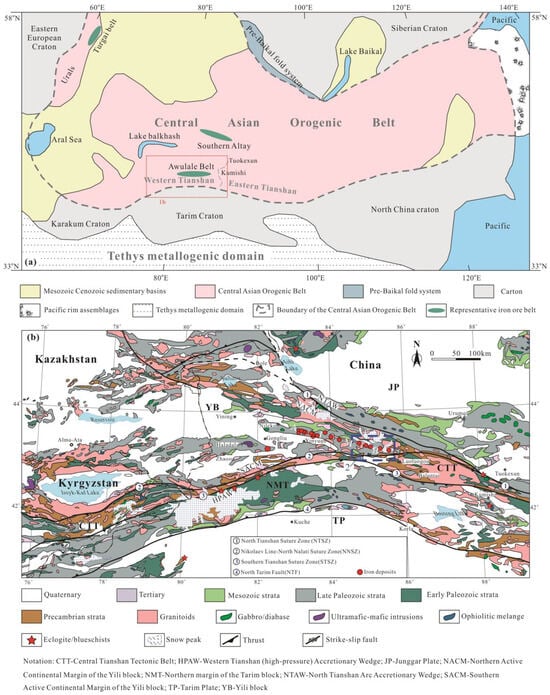
Figure 1.
(a) Simplified Central Asian orogenic collage and adjacent structures (modified after Gao et al. [15]). (b) Geological map of the Chinese West Tianshan and adjacent region (modified after Gao et al. [16]). (Blue-square with number 2 in the subfigure (b) refer to the enlargement of Figure 2).
The Awulale Iron Metallogenic Belt (AIMB), as one significant iron metallogenic belt within China, boasts numerous iron deposits and occurrences (Figure 1b) [13,17,18]. These include Beizhan (468 Mt at 41% Fe), Dunde (185 Mt at 35% Fe), Zhibo (337 Mt at 26%–68% Fe), Chagangnuo’er (210 Mt at 35% Fe), Nixintage-Akesayi (106 Mt), and Songhu (63 Mt) (Figure 2) [13,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29]. Although extensive geological, geochemical, and geochronological research has been conducted on these iron deposits, the metallogenic origin and its link to volcanic and intrusive rocks remains subject to controversy. Previously, scholars believed that iron ore mineralization took place during the whole Carboniferous period [7,13]. However, recent high-precision dating indicates that the mineralization was primarily concentrated in the Late Carboniferous [21,27,29,30]. Consequently, there is considerable interest in Late Carboniferous volcanic and intrusive rocks surrounding the iron deposits. While a few recent studies have examined the ore-hosting volcanics [19,23,26,31,32,33,34], previous research has predominantly focused on igneous rocks outside the AIMB, which are neither contemporaneous nor spatially associated with the iron mineralization [35,36,37,38,39,40,41].
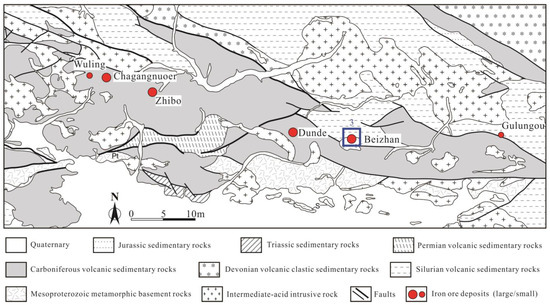
Figure 2.
Geological map of the Eastern segment of the Awulale Metallogenetic Belt showing the locality of iron deposits (modified after Tian et al. [29]). (Blue-square with number 3 refer to the enlargement of Figure 3).
In this study, we conduct detailed petrological investigations, zircon U–Pb isotopic dating, and whole-rock geochemical and Sr–Nd isotope analyses of volcanic and intrusive rocks found in the Beizhan Fe deposit within the AIMB. Our objective is to assess the petrogenesis of these magmatic rocks, as well as to determine the metallogenic setting of the AIMB. To achieve this, we incorporate previously published geological data for a comprehensive evaluation.
2. Geological Setting
The Chinese Tianshan is divided into two segments: the Eastern Tianshan and the Western Tianshan, which are separated by the Tuokexun–Kumishi High Road [42,43]. The Western Tianshan is located along the southwestern margin of the CAOB (Figure 1a). It lies between the Junggar Plate (JP) to the north and the Tarim Plate (TP) to the south and is a Paleozoic Orogenic belt. In the Western Tianshan, Gao et al. [44] identified seven tectonic units (Figure 1b): the North Tianshan Arc accretionary wedge (NTAW), the northern active continental margin of the Yili Block (NACM), the Yili Block itself (YB), the southern active continental margin of the Yili Block (SACM), the Central Tianshan composite arc terrane (CTT), the Western Tianshan (high-pressure) accretionary wedge (HPAW), and the northern margin of the Tarim Block (NMT).
The Terskey Ocean, an early Paleozoic ocean basin, once separated the Yili Block and the Central Tianshan composite arc terrane. It is believed to have closed during the Middle Ordovician [35]. The South Tianshan Ocean, on the other hand, separated the northern margin of the Tarim Block from the Central Tianshan composite arc terrane. The associated Western Tianshan (high-pressure) accretionary wedge is a metamorphic mélange belt that experienced deep subduction and exhumation, and it might have closed during the late Paleozoic [16]. The North Tianshan Ocean, which separated the Junggar Plate from the northern active continental margin of the Yili Block, is thought to have closed in the Late Carboniferous [45]. Following the closure of the South Tianshan Ocean and the North Tianshan Ocean, the Junggar Plate, Yili Block, and Tarim Plate merged into a unified block. Subsequently, the Western Tianshan entered a postcollisional extension stage [16,38,44,46,47,48].
The AIMB is a linear belt located in the center of the Yili Block. It consists of a Precambrian basement and Paleozoic volcanic–sedimentary strata (Figure 1b). The basement rocks primarily consist of Mesoproterozoic gneiss, schist, and quartzite. The Paleozoic volcanic-sedimentary strata include various rock types from different time periods. Specifically, these strata comprise Silurian carbonate-rich volcanic rocks, Middle Devonian marine volcaniclastic and sedimentary rocks, Upper Devonian littoral volcanic and terrigenous clastic–carbonate rocks, Lower Carboniferous marine volcanic–sedimentary clastic–carbonate rocks, Upper Carboniferous marine volcanic rocks with limestone interbeds, Lower Permian terrigenous clastic rocks, Lower to Middle Triassic terrigenous clastic rocks, and Jurassic terrigenous clastic rocks with coal seams (Figure 2) [49,50,51,52].
The Beizhan iron deposit, which is the focus of this study, is situated in the eastern part of the AIMB. The lithological units in this area mainly consist of littoral facies, volcanic/volcaniclastic rocks, and sedimentary rocks that dip northward. These rocks include rhyolite, dacite, shard tuff, crystal tuff, lithic tuff, conglomerate, sandstone, limestone, and dolomite (Figure 3) [53]. Additionally, there are minor occurrences of marble and phyllite to the north of the iron orebodies. Intrusions in these rocks include a granite stock and numerous diorite and diabase dykes (Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5a,b). Notably, diabase dykes also intrude the granite (Figure 5c).
Three platy-shaped magnetite orebodies were identified within the rhyolite and tuff formations (numbered as L1, L2, and L3). The hydrothermal alteration associated with mineralization includes a narrow “skarn envelope” that closely wrapped the L2 and L3 orebodies (Figure 5m), a broader orebody-centered carbonate alteration in the dacite and tuff, and irregularly distributed sparse veins of epidote, tourmaline, and/or chlorite close to the orebodies (Figure 5n,o). The ore minerals are dominated by magnetite with minor pyrite and pyrrhotite. The gangue minerals mainly include calcite, ankerite, chlorite, serpentine, tourmaline, epidote, and muscovite with minor garnet, diopside, forsterite, tremolite, and apatite. Based on mineral assemblage and texture, four successive stages are identified: an early skarn mineral stage, magnetite stage, sulfide stage, and late carbonate stage. The Beizhan iron deposit is classified as an iron skarn due to the mineral assemblage mentioned above. Its mineralization age is constrained to 302–308 Ma [21]. The presence of an abundance of tourmaline and scarcity of quartz in the ores suggests the involvement of a silica-deficient but volatile-rich ore-forming fluid.
Nineteen representative samples from the Beizhan volcanic lava and intrusions were carefully chosen for geochemical analyses. As the dating of rhyolite and diabase has been completed previously [54,55], we opted to focus on granite and diorite for geochronology purposes. The locations of the samples can be seen in Figure 3.
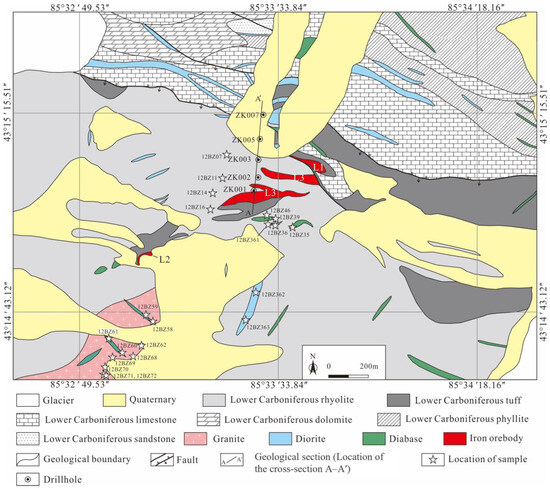
Figure 3.
Geological map of the Beizhan iron deposit (modified after the No. 11 Geological Party of the Xinjiang Bureau of Geology and Mineral Exploration and Development [53]).
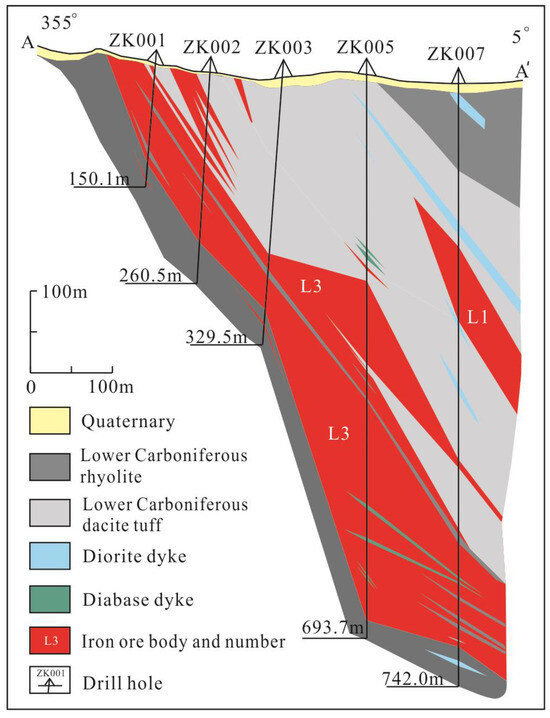
Figure 4.
Geological details along the cross-section A–A′. (See Figure 3 for location of the section; modified after the No. 11 Geological Party of the Xinjiang Bureau of Geology and Mineral Exploration and Development [53]).
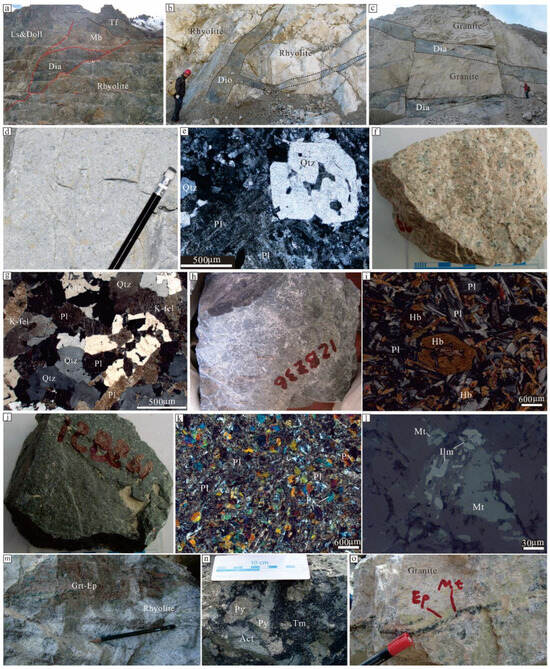

Figure 5.
Photographs of outcrops, hand specimens and microscopy of rocks from the Beizhan iron deposit. (a) Fault contact between rhyolite and interbedded limestone–dolomite (Ls and Doll), and carbonate rocks close to diabase (Dia) recrystallized into marble (Mb); look east. (b) Diorite (Dio) dyke in rhyolite. (c) Diabase dykes in granite. (d) Massive porphyritic rhyolite. (e) Quartz (Qtz) and plagioclase (Pl) phenocrysts of rhyolite, and early euhedral quartz phenocryst with internal sieve structure and resorption borders; with cross-polarized light. (f) Massive granite hand specimen. (g) Subhedral inequigranular granite composed mainly of K-feldspar (K-fel), plagioclase (oligoclase), and quartz; with cross-polarized light. (h) Fine-grained diorite dyke specimen, about 20 cm × 20 cm. (i) Hornblende (Hb) crystal of diorite is partially replaced by epidote or chlorite; with cross-polarized light. (j) Fine-grained diabase dyke hand specimen. (k) Euhedral plagioclase and anhedral pyroxene (Px) in diabase; the former experienced strong alteration; with cross-polarized light. (l) Magnetite (Mt) and ilmenite (Ilm) in diabase; with reflective polarized light. (m) Garnet (Grt)–epidote (Ep) skarn veins in rhyolite. (n) Tourmaline (Tm)–pyrite (Py) veins in actinolite skarn. (o) Epidote–magnetite vein in granite.
3. Analytical Methods
Petrographic investigations were conducted using an optical microscope. The separation of zircon grains was accomplished through conventional density and magnetic techniques at the Institute of Regional Geology and Resource Survey, Hebei Province, China. Zircon cathodoluminescence (CL) imaging was carried out using a JSM6510 scanning electron microscope equipped with a GATAN Chroma CL mini detector, which was housed at Beijing GeoAnalysis Co., Ltd., Beijing, China.
U–Pb isotope analyses were conducted using a Finnigan Neptune inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer that connected to NewWave UP–213 laser ablation in the LA–ICP–MS laboratory at the Institute of Mineral Resources, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences. Details regarding the instrument settings and operation conditions are as described by Hou et al. [56,57]. The laser beam had a diameter of 25 μm, frequency of 10 Hz, and energy density of about 2.5 J/cm2. Helium gas was used as the carrier gas to enhance transport efficiency of the ablated materials. The external standard GJ-1 was used to monitor the age of zircon and was analyzed twice every 5–10 analyses. Preferred U–Th–Pb isotopic ratios for the GJ-1 were derived from Jackson et al. [58]. The standard M127 (U: 923 × 10−6, Th: 439 × 10−6, and Th/U: 0.475 [59]) was used to calibrate U and Th concentrations and was analyzed once every 5–10 analyses. For detailed parameter settings and analysis steps, please refer to Hou et al. [60]. Data were processed using ICPMSDataCal according to the procedure of Liu et al. [61] and assessed using Isoplot 3 [62]. The analytical data are presented with 1σ on the concordia plots. Uncertainties in the mean age are quoted at the 95% confidence level. The reference zircon Plesovice was dated as an unknown sample and yielded a weighted mean 206Pb/238U age of 337.8 ± 2.8 Ma (2σ, n = 4), in good agreement with the recommended 206Pb/238U age of 337.13 ± 0.37 Ma (2σ) [63].
The samples for bulk-rock geochemical analysis were finely crushed and ground to a 200-mesh powder at the Institute of Regional Geology and Resource Survey, Hebei Province, China. The analysis of major, trace, and rare-earth elements was conducted at the National Research Center for Geoanalysis, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, located in Beijing, China. Major oxides such as SiO2, Al2O3, TFe2O3, Na2O, K2O, CaO, MgO, TiO2, MnO, and P2O5 were tested based on the GB/T14506.28–2010 standard [64] and using a PW4400 X-ray fluorescence spectrometer with a relative standard deviation (RSD) <2%–8%. FeO was determined using the titration method (RSD < 10%) based on the GB/T14506.14–2010 standard [65]. The loss on ignition (LOI) was determined by calculating the weight difference after subjecting the samples to high temperature combustion (1000 °C) with a relative standard deviation (RSD) of less than 5%, following the LY/T1253–1999 standard [66]. Trace and rare-earth elements were analyzed using an XSeries inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (ICP–MS) with a relative standard deviation (RSD) ranging from 2% to 10%, in accordance with the DZ/T0223–2001 standard [67].
Sr and Nd isotopic ratios were determined at the Isotope Laboratory of the Institute of Geology, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Beijing, China. The instrument used for Sr isotope analysis was the MAT262 solid isotope mass spectrometer, while a Nu Plasma HR Multi-Collector magnetic sector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (MC–ICP–MS) was used for the Nd isotope. Sample preparation and chemical separation followed the methods of He et al. [68] and Zhang et al. [69]. The mass fractionation corrections for Sr and Nd isotopic ratios were based on 88Sr/86Sr = 8.37521 and 146Nd/144Nd = 0.7219. The results calculated from the repeated analysis of international standards were as follows: the Sr value (SRM 987 SrCO3) 87Sr/86Sr = 0.710238 ± 0.000012 (2σ) and the Nd value (JMC Nd2O3) 143Nd/144Nd = 0.511124 ± 10 (2σ).
4. Results
4.1. Petrography
The rhyolites found within the Beizhan iron deposit exhibit a porphyritic texture, characterized by the presence of phenocrysts comprising approximately 10%–15% volume of quartz, 10%–15% volume of plagioclase, and 3%–5% volume of K-feldspar (Figure 5). The quartz phenocrysts exhibit rounded shapes due to resorption, while the plagioclase phenocrysts display euhedral forms with polysynthetic twinning. The K-feldspar phenocrysts consist mainly of microcline, displaying tartan or Carlsbad twin structures and appearing as short laths. The groundmass exhibits fine-grained, anhedral textures primarily composed of an approximately 30%–35% volume of quartz and 35%–40% volume of plagioclase. The distinction between rhyolite and dacite lies mainly in the relative content of quartz and feldspar phenocrysts (with occasional scattered hornblende) at different horizons. Additionally, some localized occurrences of chlorite are observed in the rhyolite, likely resulting from the alteration of hornblende.
The granite stock primarily exhibits a medium-coarse-grained texture (Figure 5f,g), with a more pronounced porphyritic feature towards the margins. The composition of the rock is primarily consists of an approximately 30% volume of K-feldspar, 32% volume of plagioclase, 30% volume of quartz, around 6% volume of mafic minerals (altered to chlorite while maintaining the morphology of hornblende), and minor accessory minerals including zircon, apatite, and magnetite. The margins of the stock exhibit phenocrysts of K-feldspar (20%–25% volume) and quartz (10%–15% volume), accompanied by a subhedral fine-grained groundmass consisting of quartz, plagioclase, and perthite.
The diabase dykes, ranging from 0.2 m to 2 m in width and several hundred meters in length, primarily trend in a W–NW or NE direction as they intrude the granite and surrounding strata. These dykes exhibit a porphyritic texture with phenocrysts comprising approximately 5% volume of clinopyroxene and 5% volume of plagioclase (Figure 5j,k). The groundmass of the dykes displays a fine-grained ophitic texture, primarily composed of an approximately 40% volume of clinopyroxene, 40% volume of plagioclase, 5% volume of hornblende, and contains chlorite, ilmenite, and magnetite in higher proportions exceeding 5% in volume. The diabase is distinctive due to its high content of ilmenite and magnetite (Figure 5l).
The diorite dykes share similarities with the diabase dykes in terms of occurrence. These rocks exhibit a medium-grained texture (Figure 5h,i) and are composed of an approximately 50% volume of plagioclase, 15% volume of K-feldspar, 15% volume of quartz, 14% volume of hornblende, less than 2% volume of chlorite, and also contain some accessory minerals such as zircon, apatite, and magnetite.
4.2. Zircon Geochronology
The analytical results are provided in Supplementary Table S1 and depicted in both Figure 6 and Figure 7. The zircon grains found in both the granite and diorite samples exhibit a similar crystal morphology, mostly appearing euhedral and measuring between 50 and 160 μm in length, with an average length-to-width ratio of approximately 2:1 (Figure 6). These zircon grains are predominantly transparent with a light yellow color, displaying characteristic oscillatory zoning. In the granite sample (12BZ72), some zircon grains exhibit a core-rim structure. The cores of these grains are unzoned and show signs of resorption, with a slightly weaker cathodoluminescent (CL) brightness compared to the rims (e.g., zircon 18 in Figure 6a). It is suggested that these core regions may have been inherited from the magma source or country rocks at greater depths, while the rims represent a subsequent magmatic overgrowth.
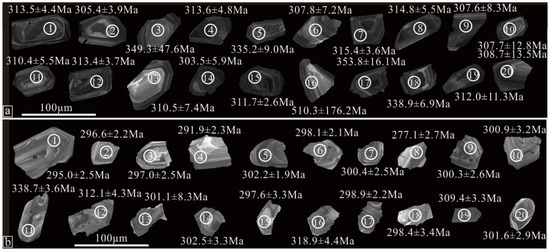
Figure 6.
Cathodoluminescence images of zircon grains from granite sample (a): sample 12BZ72 and diorite dyke sample (b): sample 12BZ36. The circles are analysis spots marked with ages.
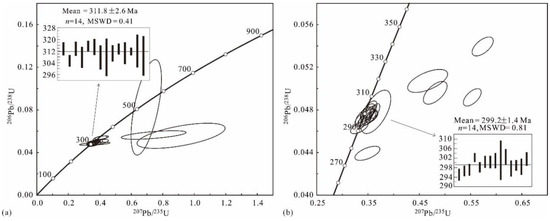
Figure 7.
Laser ablation–ICP–MS U–Pb zircon concordia diagrams for granite and diorite dyke from the Beizhan iron deposit. (a) Sample 12BZ72 and(b) sample 12BZ36.
The analysis of 20 zircon grains from the granite revealed a range of 8–204 ppm U and 8–149 ppm Th, with Th/U values ranging from 0.53 to 0.99, indicating a magmatic origin [70]. Two analyses (zircon 3 and 17 in Figure 6a) fall outside the concordia plot (Figure 7a) and are considered to represent instances of Pb loss. Two other analyses (zircon 5 and 16 in Figure 6a) exhibit relatively higher 206Pb/238U model ages (335 Ma and 510 Ma, respectively), suggesting that they are inherited grains. The remaining 15 analyses form a tight cluster on the concordia plot (Figure 7a), with 14 of them yielding a well-weighted mean 206Pb/238U age of 311.8 ± 2.6 Ma (MSWD = 0.41) and a concordia 206Pb/238U age of 312.1 ± 1.2 Ma (MSWD = 14). Analysis 14 (zircon 14 in Figure 6a) was excluded due to a higher discordance. The weighted mean age of 311.8 ± 2.6 Ma is interpreted as the most reliable estimate for the crystallization age of the granite.
Twenty spots on zircon grains from the diorite show 49–376 ppm of U, 47–357 ppm of Th, and Th/U values in the range of 0.61–1.42, suggesting a magmatic origin. Five analyses (zircon 8, 11, 12, 16, and 19 in Figure 6b) fall out of the concordia plot (Figure 7b) and are excluded. One analysis (zircon 4 in Figure 6b) was discarded due to a high discordance. The remaining 14 analyses form a single and tight cluster on the concordia plot (Figure 7b) and yield a weighted mean 206Pb/238U age of 299.2 ± 1.4 Ma (MSWD = 0.81). This age is interpreted as the best estimation of the crystallization age of the diorite.
4.3. Whole-Rock Geochemistry
The analytical results are listed in Supplementary Table S2. The rhyolite samples have SiO2 = 66.92%–73.35% and Na2O + K2O = 5.00%–8.05% and are subalkaline (Figure 8a). One sample has relatively high K2O = 4.25%, while the other four have a very low K2O content (0.29%–1.28%) but a relatively high CO2 and CaO content (0.77%–1.11% and 3.14%–6.61%, respectively) which are interpreted to be due to mild carbonate alteration. These samples show calc-alkaline and metaluminous characteristics (Figure 8b,d). On the chondrite-normalized REE patterns (Figure 9), they show a variable enrichment of light rare earth elements (LREEs), approximately parallel flat heavy rare earth elements (HREEs) and slightly negative Eu anomalies with δEu between 0.45 and 0.70. On the primitive mantle-normalized spidergram (Figure 9), they show high concentrations of the large ion lithophile elements (LILEs) Th and U, an obvious depletion in P and Ti, and negative anomalies of Nb and Ta due to the variable content of La and Ce.
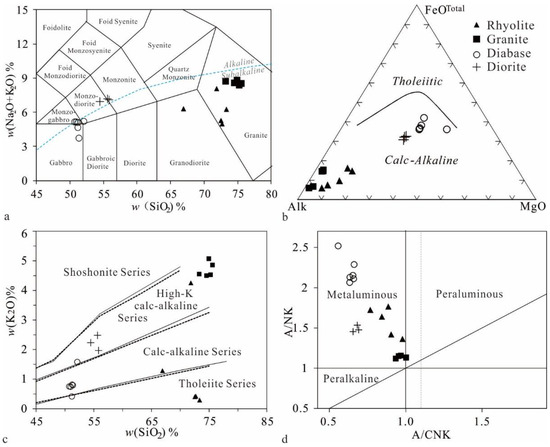
Figure 8.
(a) TAS diagram (modeled after Middlemost [71]) and dividing line for alkaline and subalkaline rocks (dashed line; modeled after Irvine and Baragar [72]). (b) AFM plot (Irvine and Baragar [72]). (c) SiO2–K2O plot (solid line modeled after Peccerillo and Taylor [73]; dashed line modeled after Middlemost [74]). (d) Aluminum saturation index.
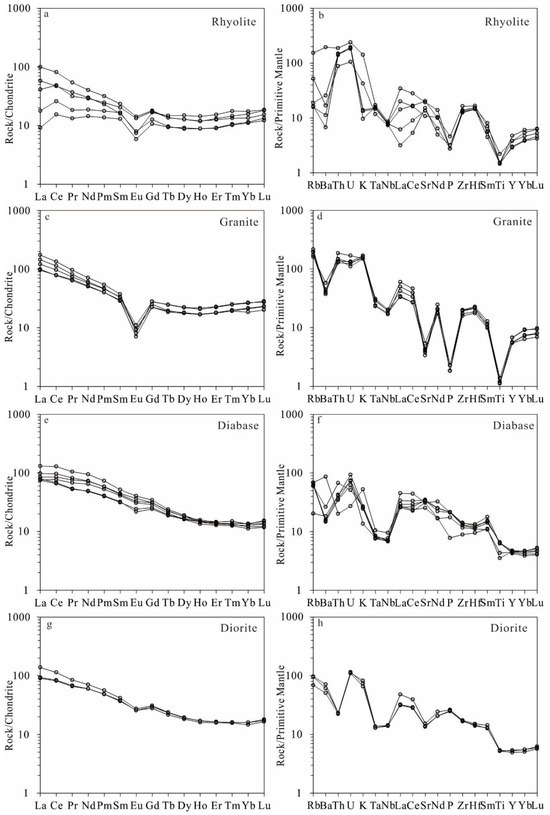
Figure 9.
Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (Left) and primitive mantle-normalized trace element patterns (Right) of the representative samples from the Beizhan area. Chondrite and primitive mantle normalized values are from Sun and McDonough [75]. (a,b) show two patterns of rhyolite; (c,d) show two patterns of granite; (e,f) show two patterns of diabase; (g,h) show two patterns of diorite.
The granite samples have high SiO2 (73.97%–77.61%) and Na2O + K2O (8.34%–8.82%) contents, slightly low Na2O/K2O ratios (0.74–0.91) and are subalkaline (Figure 8a). They display calc-alkaline and metaluminous affinities, and plot in the field of high-K calc-alkaline igneous rocks (Figure 8b–d). Their chondrite-normalized rare earth element pattern is characterized by a pronounced LREE-enrichment (steep negative slope), relatively flat HREEs (slightly concave downward) and an obvious negative Eu anomaly with δEu between 0.25 and 0.36. The primitive mantle-normalized spidergrams show high concentrations of the LILEs Rb, U, Th, and K, but strong negative anomalies in Ba, Nb, Ta, Sr, P, and Ti elements.
The diabase samples show high Na2O/K2O ratios (2.28–10.29) and show subalkaline (Figure 8a) and metaluminous features, plotting in the field of calc-alkaline igneous rocks (Figure 8c,d). They are characterized by the relatively strong enrichment of LREEs but depletion of HREEs and show approximately parallel steep negative slope on the chondrite-normalized REE patterns and have very mild negative Eu anomalies (δEu = 0.77–0.97). They also have apparent negative Nb and Ta anomalies, and are depleted in HFSEs (Ti, Y, Yb, and Lu).
The diorite samples have SiO2 = 54.48%–55.83% and Na2O + K2O = 6.94%–7.19% and are slightly alkaline and metaluminous (Figure 8a). These samples are similar to the diabase samples on the chondrite-normalized REE patterns and primitive mantle-normalized spidergram. They are relatively strongly enriched in LREEs but depleted in HREEs and show slightly negative Eu anomalies (δEu = 0.75–0.80). They also display strong negative anomalies of Th, Nb, Ta, and Sr, and are depleted in HFSEs such as Ti, Y, Yb, and Lu.
4.4. Sr–Nd Isotopic Geochemistry
Measured and age-corrected initial isotopic ratios of Sr and Nd are presented in Table 1 and illustrated in Figure 10. The Sm, Nd, Rb, and Sr contents of these rocks are given in Supplementary Table S2. Because the fSm/Nd (fractionation factor of Sm and Nd) for these samples mainly range from −0.47 to −0.29 (except for two rhyolite samples of −0.09 and −0.10, respectively), the two stage model ages (TDM2) were calculated. The rhyolite samples have initial 87Sr/86Sr ratios (ISr) ranging from 0.7055 to 0.7060, εNd(t) values ranging from +3.0 to +4.0, and TDM2 values of 760–838 Ma. The granite samples have ISr values of 0.6986–0.7029, εNd(t) values of +4.9 to +5.1, and TDM2 values of 656–673 Ma. However, owing to the extremely high Rb/Sr ratios of the Beizhan granite, their calculated initial 87Sr/86Sr ratios are not meaningful (e.g., Tang et al. [76]). For the diabase samples, the ISr, εNd(t) and TDM2 values are 0.7043 to 0.7049, +3.3 to +7.3, and 466 to 797 Ma, respectively. For the diorite samples, these values are 0.7050 to 0.7053, +2.3 to +2.6, and 852 to 872 Ma, respectively.

Table 1.
Sr and Nd isotopic data for volcanic and intrusive rocks from the Beizhan iron deposit.
Table 1.
Sr and Nd isotopic data for volcanic and intrusive rocks from the Beizhan iron deposit.
| Sample | Rock | Rb (ppm) | Sr (ppm) | 87Rb/86Sr | 87Sr/86Sr | 2σ | ISr | Sm (ppm) | Nd (ppm) | 147Sm/144Nd | 143Nd/144Nd | 2σ | INd | εNd(t) | fSm/Nd | TDM2 (Ma) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12BZ07 | R | 97.2 | 405 | 0.69 | 0.708772 | 15 | 0.7055 | 3.57 | 18.8 | 0.12 | 0.512668 | 7 | 0.512419 | 4.0 | −0.41 | 760 |
| 12BZ11 | R | 10.4 | 227 | 0.13 | 0.706282 | 14 | 0.7057 | 2.44 | 14 | 0.11 | 0.51264 | 6 | 0.512412 | 3.9 | −0.46 | 772 |
| 12BZ14 | R | 10 | 319 | 0.09 | 0.706426 | 11 | 0.7060 | 1.98 | 6.73 | 0.18 | 0.512761 | 10 | 0.512376 | 3.1 | −0.09 | 829 |
| 12BZ16 | R | 11.9 | 286 | 0.12 | 0.706362 | 15 | 0.7058 | 2.55 | 8.72 | 0.18 | 0.512784 | 5 | 0.512401 | 3.6 | −0.10 | 789 |
| 12BZ35 | R | 33.1 | 428 | 0.22 | 0.707012 | 15 | 0.7060 | 3.11 | 13.5 | 0.14 | 0.512672 | 9 | 0.512370 | 3.0 | −0.29 | 838 |
| 12BZ62 | G | 109 | 91.7 | 3.44 | 0.716508 | 15 | 0.7012 | 4.52 | 23.5 | 0.12 | 0.512728 | 6 | 0.512489 | 4.9 | −0.41 | 670 |
| 12BZ68 | G | 102 | 113 | 2.61 | 0.714482 | 15 | 0.7029 | 5.13 | 27.1 | 0.12 | 0.512733 | 6 | 0.512498 | 5.1 | −0.41 | 656 |
| 12BZ69 | G | 137 | 85.3 | 4.65 | 0.719238 | 14 | 0.6986 | 4.38 | 24.1 | 0.11 | 0.512717 | 6 | 0.512491 | 5.0 | −0.44 | 666 |
| 12BZ70 | G | 123 | 71.6 | 4.97 | 0.723082 | 14 | 0.7010 | 5.01 | 28.3 | 0.11 | 0.512707 | 10 | 0.512487 | 4.9 | −0.45 | 673 |
| 12BZ71 | G | 126 | 80.3 | 4.54 | 0.721549 | 13 | 0.7014 | 5.71 | 33.2 | 0.10 | 0.512707 | 5 | 0.512493 | 5.0 | −0.47 | 663 |
| 12BZ39 | Dia | 43.7 | 535 | 0.24 | 0.70596 | 12 | 0.7049 | 4.79 | 22.6 | 0.13 | 0.512734 | 11 | 0.512478 | 4.5 | −0.34 | 698 |
| 12BZ46 | Dia | 37.8 | 652 | 0.17 | 0.705606 | 14 | 0.7049 | 4.94 | 23 | 0.13 | 0.512675 | 5 | 0.512416 | 3.3 | −0.34 | 797 |
| 12BZ58 | Dia | 39.5 | 717 | 0.16 | 0.705074 | 14 | 0.7044 | 6.26 | 30.1 | 0.13 | 0.512867 | 7 | 0.512616 | 7.2 | −0.36 | 478 |
| 12BZ59 | Dia | 40.4 | 659 | 0.18 | 0.705037 | 15 | 0.7043 | 7.91 | 44.1 | 0.11 | 0.51284 | 8 | 0.512624 | 7.3 | −0.45 | 466 |
| 12BZ61 | Dia | 41.9 | 699 | 0.17 | 0.705337 | 14 | 0.7046 | 6.81 | 33.6 | 0.12 | 0.512863 | 5 | 0.512618 | 7.2 | −0.37 | 475 |
| 12BZ361 | Dio | 60.3 | 323 | 0.54 | 0.707616 | 14 | 0.7053 | 6.36 | 32.9 | 0.12 | 0.512602 | 6 | 0.512372 | 2.3 | −0.40 | 872 |
| 12BZ362 | Dio | 61.4 | 285 | 0.62 | 0.707666 | 13 | 0.7050 | 5.75 | 27.9 | 0.13 | 0.512627 | 10 | 0.512382 | 2.5 | −0.36 | 856 |
| 12BZ363 | Dio | 43.6 | 294 | 0.43 | 0.707152 | 13 | 0.7053 | 5.62 | 27.9 | 0.12 | 0.512624 | 6 | 0.512384 | 2.6 | −0.38 | 852 |
Note: Dia—diabase dyke; Dio—diorite dyke; G—granite; and R—rhyodacite. Chondrite uniform reservoir (CHUR) values [(143Sm/144Nd)CHUR(0) = 0.512638 and (143Nd/144Nd)CHUR(0) = 0.1967] and depleted mantle (DM) values [(143Nd/144Nd)DM = 0.513151 and (147Sm/144Nd)DM = 0.2137] are used for the calculation. fSm/Nd = (147Sm/144Nd)m/(147Sm/144Nd)CHUR(0) − 1. λRb = 1.42 × 10−11/year [77] and λSm = 6.54 × 10−12/year [78]. The initial Sr and Nd isotopic ratios were corrected to 329 Ma, 312 Ma, 303 Ma, and 299 Ma for rhyolite, dacite granite, diabase dyke, and diorite dyke, respectively.
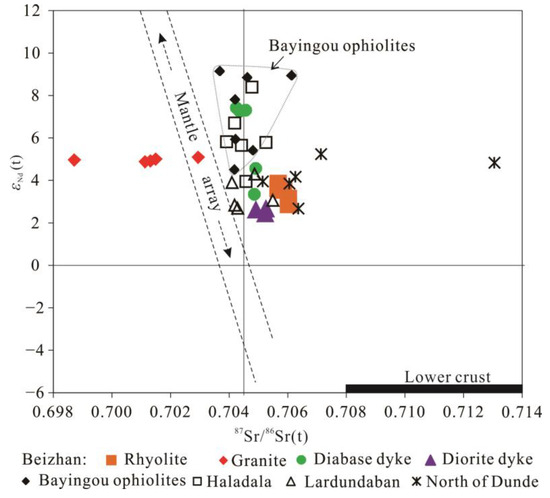
Figure 10.
Diagram of εNd(t) (t = 310 Ma) versus initial 87Sr/86Sr(t) for the representative samples from the Beizhan area and peripheral region. The mantle array is modeled after Zindler and Hart [79]. Data sources: the Bayingou ophiolite [80], the Halada mafic-ultramafic complex [81], the Lardun basalt [39], the andesites from the North of Dunde [37] and the lower crust [82,83].
5. Discussion
5.1. Magmatic Episodes and Speculative Causative Pluton for the Beizhan Iron Deposit
The rhyolite and dacite found in the Beizhan iron deposit have been classified as part of the Early Carboniferous Dahalajunshan Formation, based on regional lithologic correlation (No. 11 Geological Party of the Xinjiang Bureau of Geology and Mineral Exploration and Development [53]). LA–ICP–MS zircon U–Pb analyses of dacite from the Beizhan deposit yielded a weighted mean 206Pb/238U age of 329.1 ± 1.0 Ma [54], consistent with the results of lithologic correlation. However, Zhang et al. [84] reported a zircon U–Pb age of 301.3 ± 0.8 Ma for the dacite in the Beizhan deposit. Since the dacite is intruded by granite and the zircons from granite yielded a weighted mean 206Pb/238U age of 311.8 ± 2.6 Ma in this study, we consider that the 301.3 ± 0.8 Ma age reported by Zhang et al. [84] cannot represent the age of wall-rock dacite from the Beizhan iron ores. Recently, Luo et al. [85] reported a LA–IC–PMS zircon U–Pb age of 302.5 ± 1.3 Ma for diabase dyke in the Beizhan deposit. Our zircon U–Pb age of 299.2 ± 1.4 Ma for the diorite dyke is consistent with that of the diabase dyke within the error range. Considering their proximity, it is inferred that the diabase and diorite formations originated from the same magma chamber in the shallow crust, suggesting a sequential process. At this point, we can deduce the following: Following the eruption of rhyolite and dacite during the Early Carboniferous period, subsequent intrusions occurred in the Late Carboniferous. These included granite stocks, diabase, and diorite dykes in the existing volcanic rock formations.
Duan et al. [21] reported an isochron age of 302.5 ± 8.2 Ma using pyrite Re–Os isotopic dating, along with four muscovite 40Ar/39Ar plateau ages for the Beizhan iron ores: 304.7 ± 1.8 Ma, 304.5 ± 1.9 Ma, 308.1 ± 1.9 Ma, and 307.2 ± 1.8. Based on these ages, it can be inferred that the iron mineralization is associated with Late Carboniferous intrusive rocks. However, the age of the iron mineralization overlaps with the estimated ages of granite, diabase, and diorite veins, making it challenging to definitively identify the metallogenic intrusions based solely on isotopic age. Several geological pieces of evidence support a genetic relationship between iron mineralization and diabase:
- (1)
- Spatial association: The iron mineralization is spatially associated with diabase and diorite dykes, indicating a potential connection between the two.
- (2)
- Mineral composition: The assemblage of gangue minerals suggests that the fluid responsible for forming the iron ores had a low SiO2 content but high volatile content. This observation contrasts with the expected characteristics of high SiO2 granite but aligns with the properties of mafic diabase and diorite dykes.
- (3)
- Alteration occurrence: The alteration of chlorite and carbonate is common in diabase dyke, but very few are found in its wall-rock rhyolite, suggesting that diabase is rich in water.
- (4)
- Cutting relationship: Several long and straight epidote-magnetite veins were observed along the edge of the granite (Figure 5o), indicating that the iron mineralization is associated with a later structure-hydrothermal event, rather than being part of the granite itself.
- (5)
- Similar mineralization nearby: The Yikaiharenguo iron deposit is located adjacent to the Beizhan iron deposit, occurring specifically at the contact zone between a diabase stock and limestone (Figure 2).
Therefore, there appears to be a connection between mineralization and the diabase. The diabase dyke mapped at present may be from the shallower portion of a deeper diabase stock. This is supported by ground magnetic surveys which show a larger strong positive magnetic anomaly except the peak-style anomaly induced by magnetite ores in the Beizhan deposit, interpreted as the effect of a concealed gabbroic pluton (No. 11 Geological Party of the Xinjiang Bureau of Geology and Mineral Exploration and Development [53]). The skarn iron deposits associated with mafic intrusions are commonly referred to as “Cornwall-type” deposits, named after the well-known example found in Cornwall, Pennsylvania [86,87,88]. A comparable iron deposit has also been documented in the Eastern Tianshan region, specifically the Cihai iron skarn deposit [88].
5.2. Petrogenesis and Source Characteristics
5.2.1. Rhyolite and Granite
The absence of primary peraluminous minerals such as muscovite, cordierite, garnet, and tourmaline (Figure 5), along with over 8% CIPW normative diopside but less than 1% normative corundum and relatively low A/CNK ratios (≤1.0; Figure 8d) differentiate the Beizhan rhyolite and granite from S-type granites [89]. Additionally, moderate concentrations of Rb, Nb, Ce, and Zr, as well as moderate FeO*/MgO ratios and 10,000 × Ga/Al ratios below 2.6 exclude the possibility of an A-type granite affinity [90]. Therefore, based on their mineralogical and geochemical characteristics, the Beizhan rhyolite and granite can be reasonably classified as calc-alkaline I-type granites. Furthermore, their depleted Nd isotopic composition and their decrease in P concentration with the increase of SO2 (Figure 11) further confirm their I-type nature.
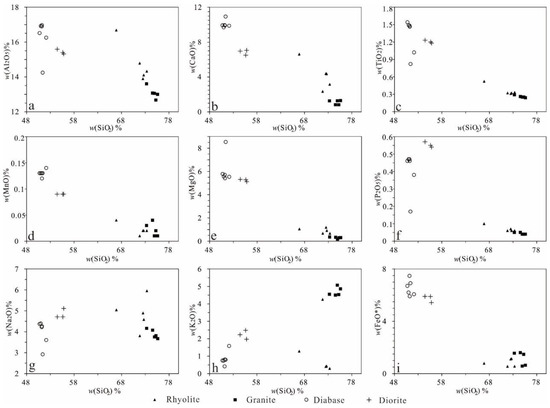
Figure 11.
SiO2 versus oxides of other major elements for the representative samples from the Beizhan deposit. Symbols are the same as in Figure 8. (a) SiO2 vs. Al2O3 diagram; (b) SiO2 vs. CaO diagram; (c) SiO2 vs.TiO2 diagram; (d) SiO2 vs. MnO diagram; (e) SiO2 vs. MgO diagram; (f) SiO2 vs. P2O5 diagram; (g) SiO2 vs. Na2O diagram; (h) SiO2 vs. K2O diagram; (i) SiO2 vs. FeO* diagram.
I-type granites are generally believed to form through the partial melting of older igneous rocks [89,91]. The Beizhan granite stands out from typical adakite series, which are produced by the partial melting of subducting slabs, due to its low Sr content (<113 ppm) but high Y (>24.8 ppm) and Yb (>3.13 ppm) contents [92]. Moreover, its high 87Sr/86Sr initial ratio (≥0.7055), along with its low concentrations of Cr (<15 ppm), Co (<10 ppm), Ni (<6 ppm), and Sr/Y ratios (<25) excludes the Beizhan rhyolite from being classified as typical adakitic rocks [92].
The Nb/Ta ratios of both the Beizhan rhyolite and granite, ranging from 11.3 to 12.8 and 8.7 to 10.9, respectively, closely resemble those of the continental crust (approximately 11 [93,94]) but differ significantly from the ratios observed in the mantle or mantle-derived melts (17.5 ± 2.0 [95]). However, the high positive εNd(t) values (+3.0–+4.0 and +4.9–+5.1, respectively) and young Nd model ages (TDM2, 760–838 Ma and 656–673 Ma, respectively) align closely with the depleted mantle values (Figure 10), suggesting that the Beizhan rhyolite and granite resulted from the partial melting of a newly underplated lower crust. This interpretation is supported by the absence of contemporaneous basaltic and intermediate magmatic rocks in the Beizhan area, thus ruling out the possibility of derivation through fractional crystallization of the mantle-derived melts. Similar conclusions have been drawn in previous studies on I-type granitoids with high positive εNd(t) values in the AIMB [76,96,97]. Therefore, it is plausible to consider a source consisting of a newly underplated lower crust, with contributions from a mantle that was previously modified by subduction-related fluids and sediments.
In the Harker diagram (Figure 11), most major elements in the rhyolite and granite exhibit a weak correlation with SiO2, except for Al2O3 and TiO2. This suggests that the chemical compositions of these rocks were primarily controlled by the partial melting rather than by fractional crystallization. This observation is consistent with the findings of Zhang et al. [98], who also suggested that fractional crystallization is unlikely in granitic magmas due to their high viscosity and the similarity in density between primary minerals and granitic magmas.
The rhyolite displays negative anomalies in P and Ti, which likely indicates the presence of apatite and Fe-Ti oxides in the residual material. Additionally, its flat pattern of MREEs (Middle Rare Earth Elements) to HREEs (Heavy Rare Earth Elements) (Figure 9a) suggests the involvement of amphibole as cumulates in the residual material.
On the other hand, the granite exhibits highly fractionated LREEs to HREEs, characterized by flat to listric-shaped patterns. It also displays more pronounced negative anomalies in Eu, Ba, Sr, P, and Ti in the REE patterns and spider diagrams compared to the rhyolite. These anomalies likely indicate the presence of apatite, Fe-Ti oxides, plagioclase, and amphibole in the residual material from the deep source.
Saturation temperatures of zircon, calculated based on bulk-rock compositions, exhibit a range of 748 °C to 774 °C for rhyolites, suggesting a relatively low initial magma temperature at the source. The presence of water appears to be crucial in generating such “cold” felsic magma in the source area [99]. Additionally, the breakdown of amphibole could have played a significant role in the process of dehydration partial melting, contributing to the initial water content necessary for melt production [100].
On the other hand, granite exhibits zircon saturation temperatures ranging from 787 °C to 816 °C, indicating a comparatively high initial magma temperature at the source. The generation of this “hot” felsic magma might require advective heat input into the crust [99] and is likely connected to the underplating of mafic magmas [97].
5.2.2. Diabase and Diorite Dykes
The diabase and diorite dykes found in the Beizhan deposit underwent a mild alteration, as indicated by their relatively high loss on ignition values ranging from 1.69% to 2.69% for diabase and 1.57% to 1.84% for diorite. A petrographic examination further revealed that chlorite and carbonate partially replaced clinopyroxene and plagioclase minerals. Given the limited occurrence of alteration minerals, it can be inferred that certain major elements and LILEs (such as Na, K, Ba, Rb, and U) were mobile during the low-temperature alteration process, while other major elements, HFSEs, and REEs remained relatively unaffected (e.g., Yan et al. [33] and references therein). Consequently, the major elements (excluding Na and K), REEs, and HFSE contents of the diabase and diorite dykes serve as valuable indicators for understanding their petrogenesis and tectonic setting.
When mantle-derived magmas ascend or accumulate within a magma chamber in the Earth’s crust, they can undergo varying degrees of contamination from the surrounding crustal materials [101]. The Beizhan diabase samples exhibit a relatively wide range of εNd(t) values (Figure 12), indicating the involvement of crustal components. However, several lines of evidence suggest that the impact of crustal contamination on the diabase and diorite magma is limited. Firstly, although the diabase samples display varying εNd(t) values, the presence of high positive εNd(t) values (+3.3–+7.3 and +2.3–+2.6 for diabase and diorite, respectively) contradicts the significant assimilation of crustal material. This is because such a process would inevitably alter the Sr–Nd isotopic composition of the magmas [97]. Secondly, the lack of a strong correlation between εNd(t) and SiO2 indicates that any crustal contamination is minor. Thirdly, the Nb/Ta ratios of the diabase (14.1–17.0) and diorite (17.9–18.7) are close to those of the mantle or mantle-derived melts (17.5 ± 2.0 [95]) but differ from the ratios found in the continental crust (around 11 [93,94]). Fourthly, both the diabase and diorite display high Ti/Yb ratios: 2165 to 4831 for diabase and 2654 to 2840 for diorite. These ratios suggest a minimal contribution from the crustal material [102]. Lastly, the negative Zr–Hf anomalies observed in the spider diagrams for the diabase and diorite samples (Figure 9) imply that little to no crustal contamination occurred. Consequently, it can be inferred that crustal contamination played an insignificant role in the formation of the diabase and diorite rocks.
The diabase and diorite samples exhibit Mg# values (58–69 and 62–63, respectively) as well as lower concentrations of compatible elements such as Cr (86–364 ppm and 83–108 ppm, respectively) and Ni (30–62 ppm and 58–76 ppm, respectively) compared to the mantle-derived primary melts (Mg# = 73–81, Ni > 400 ppm, Cr > 1000 ppm [103,104]). This suggests that the diabase and diorite were not primary magmas and underwent some degree of crystal fractionation. The presence of weak negative anomalies for Ba, Eu, and Sr indicates fractional crystallization of plagioclase. Additionally, the positive correlations between Cr, Ni, CaO, and Mg# suggest fractionation of olivine and clinopyroxene.
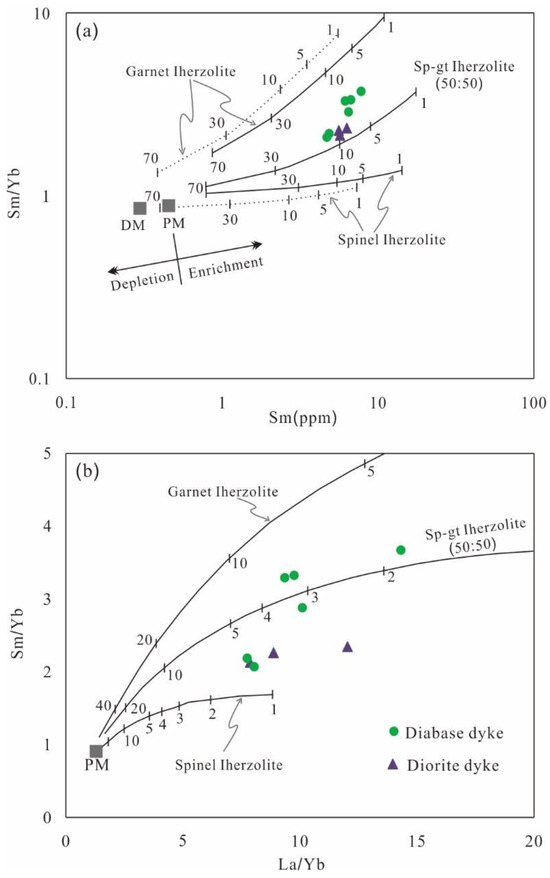
Figure 12.
(a) Sm/Yb versus Sm and (b) Sm/Yb versus La/Yb for the diabase and diorite samples from the Beizhan deposit. Mantle array is defined by depleted MORB mantle (DM, [105]) and primitive mantle (PM, [75]). Melting curves for spinel lherzolite (Ol0.53 + Opx0.27 + Cpx0.17 + Sp0.03) and garnet lherzolite (Ol0.60 + Opx0.20 + Cpx0.10 + Gt0.10) with both DM and PM compositions are modeled after Aldanmaz et al. [106] and Zhao and Zhou [107,108]. Dashed and solid curves are the melting trends for DM and PM, respectively. Numbers along lines represent the degree of partial melting.
The diabase and diorite dykes show indications of possibly originating from the same magma chamber, as evidenced by their close spatial relationship, similar zircon ages, and comparable initial Sr isotope composition (ISr) and εNd(t) values (Figure 10). There is also a notable correlation between TiO2, Al2O3, TFeO, MnO, MgO, CaO, Na2O, K2O, and P2O5 vs. SiO2 (Figure 11). These similarities are further supported by their comparable chondrite-normalized REE patterns and primitive mantle-normalized spidergrams (Figure 9). Therefore, it is highly likely that the diorite in Beizhan originated from diabase through crystal fractionation.
Both the diabase and diorite samples exhibit low initial 87Sr/86Sr ratios (ranging from 0.7043 to 0.7050 and 0.7050 to 0.7053, respectively) and high positive εNd(t) values (ranging from +3.3 to +7.3 and +2.3 to +2.6, respectively), indicating their derivation from a depleted mantle source. The significant negative anomalies of Ta and Nb (Figure 9) distinguish them from magmas derived from the asthenosphere and are more reminiscent of trace-element patterns observed in oceanic island basalts [109]. Moreover, the (Th/Nb)PM ratios (ranging from 2.1 to 9.8 and 1.6 to 1.7, respectively) and Zr/Nb ratios (ranging from 19.3 to 30.3 and 18.9 to 19.2, respectively) of both the diabase and diorite are notably higher than those of asthenosphere-derived basalts, with (Th/Nb)PM < 1 and Zr/Nb ≈ 5.8 [110,111], effectively excluding the possibility of an asthenospheric origin.
The low (Tb/Yb)N ratios (<2) in the diabase and diorite samples indicate their derivation from spinel-bearing peridotite sources [112]. The pronounced depletion of HREEs and Y (Figure 9) suggests the presence of garnet as an important residual mineral in their source [96]. In the Sm/Yb versus Sm and La/Yb diagrams (Figure 12), both the diabase and diorite plot near the melting curve of garnet and spinel Iherzolite, further suggesting a lithospheric mantle source comprising spinel and garnet lherzolite. The evident negative Th, Ta, and Nb anomalies and high Ba/Th and Sr/Th ratios also indicate prior metasomatism of the lithospheric mantle source by subduction-related fluids (Figure 13) (e.g., Sun et al. [97]).
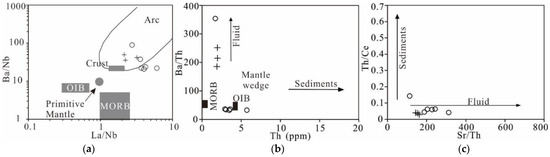
Figure 13.
Plots of (a) La/Nb and Ba/Nb, (b) Th and Ba/Th, and (c) Sr/Th and Th/Ce [97] for the representative samples from the Beizhan deposit. Lengend: ○ diabase; + diorite.
5.3. Implications for Metallogenic Setting
The AIMB’s iron deposits were formed in the Late Carboniferous according to the latest isotopic dating and geological inferences [21]. Nevertheless, there is a current debate about the tectonic setting of the AIMB during the Late Carboniferous. Previous studies have proposed varied tectonic models, including Carboniferous rifting [36,37,113], extension induced by orogenic root detachment [97], extension induced by slab rollback [18,33,40,76], a tectonic transition from slab breakoff (320–310 Ma) to postcollisional setting (309–290 Ma) [114,115], and island arcs [16,38,39,40,44].
The volcanic rocks in the YP during the Early Carboniferous belong to a calc-alkaline basalt–andesite–dacite–rhyolite association, indicating a volcanic arc setting. This is supported by various studies [4,5,16,44,76,116]. The Beizhan rhyolite, as well as similar rhyolite found in other locations such as the Zhibo, Songhu, and Tiemulike iron deposits show specific geochemical characteristics like a Ta–Nb depletion and the enrichment of LREEs and LILEs, which further support the volcanic arc setting [20,26,117]. Additionally, the presence of adakite, high-Mg andesite, Nb-enriched arc basalt, porphyry copper, and epithermal gold deposits in the Early Carboniferous on the northern margin of the YP aligns well with the presence of Early Carboniferous Bayingou ophiolites (located north of the YP), suggesting the subduction of the North Tianshan Ocean from the north during that time [116,118]. In the Permian period, the YP witnessed the presence of bimodal volcanic rocks as well as peralkaline and alkaline granites, indicating a postcollisional setting. This tectonic transition from a continental arc to a postcollisional setting took place in the Late Carboniferous. The Carboniferous rift model is not considered applicable based on previous studies.
The Late Carboniferous igneous rock assemblages in the AIMB primarily indicate an extensional setting; for instance, the presence of extensional-type granites such as the 319 Ma A-type granite in Muhanbasitao, the 306 Ma A-type granite in Qunjisayi, and the 304 Ma A-type granite in Zhibo [18,31,119]. Additionally, bimodal igneous rock associations have been observed, such as the association of Fe-rich basalt (318 Ma) and rhyolite (319 Ma) in the Chagangnuoer district [120], and the association of mafic dykes (317 Ma) and granitoids (319 Ma) in the Muhanbasitao district of the AIMB [119]. Potassic and ultrapotassic volcanic and intrusive rocks (syenites, trachyandesites, and trachybasalts) dating back to 312 Ma have also been identified in Gongnaisi [97]. The 308 Ma Haladala mafic-ultramafic intrusion in the Yishijilike district (within the Yili Plate) to the west of the AIMB is another example of an extension-related formation [81,121,122]. The Beizhan granite deposits are found around the triple junction of volcanic arc granite, collisional granite, and within-plate granite (Figure 14a–c) or between the syn-collision field and the post-orogenic field (Figure 14d). Similar granites can also be observed in the Zhibo iron deposit (29). These observations suggest a non-subduction environment. The Late Carboniferous diabase samples plot in the within-plate tholeiites and volcanic arc basalts fields, while the contemporaneous diorite samples plot in the within-plate alkali and tholeiitic basalts fields (Figure 14), possibly indicating a within-plate setting. Therefore, the transition from an arc to a postcollisional setting in the AIMB likely occurred in the early Late Carboniferous. Iron mineralization in the AIMB took place in an extensional environment, excluding the possibility of an island arc model.
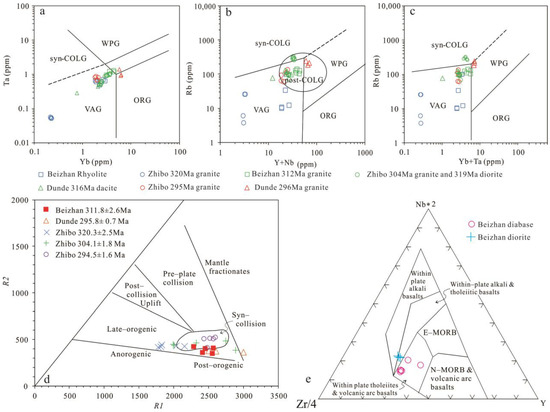
Figure 14.
Tectonic discriminating diagrams for the Beizhan magmatic rocks. (a) Ta vs. Yb, (b) Rb vs. Y + Nb and (c) Rb vs. Yb + Ta diagrams [123]. (d) Factor R1–R2 diagram of igneous rock (modeled after Batchelor and Bowden [124]). (e) Zr–Nb–Y discrimination diagram of Meschede [125]. Data for the Zhibo and the Dunde granite are from Zhang et al. [31] and Duan et al. [19].
The Late Carboniferous volcanism in the Western Tianshan region is characterized by a narrow linear zone of magmatism along the AIMB, which poses challenges to understanding the tectonic transition mechanism. The orogenic root detachment model suggests the presence of large diffuse and non-linear magmatic zones, with intense asthenosphere-derived magmas within the affected area [111,126,127,128]. However, this model does not align with the observed narrow linear distribution of Late Carboniferous volcanic activity in the Western Tianshan. Additionally, the subducted oceanic slab rollback model proposes the existence of a Late Carboniferous arc, but this is contradicted by the igneous rock suites found in the Late Carboniferous formations mentioned above. Furthermore, the zircon age data from the granitoids intruding into the CTT (Central Tianshan Tectonic Belt) indicate that the peak of granitic magmatism occurred between 460 and 320 million years ago, with Late Carboniferous ages being very rare [16]. This suggests that a Late Carboniferous arc on the southern margin of the amalgamated YP–CTT is unlikely. The age data on high-pressure metamorphism to the south of the YP–CTT support the idea of a Late Carboniferous collision between the Tibetan Plateau (TP) and the YP–CTT [16,44,129]. This collision is further confirmed by the widespread occurrence of postcollisional igneous rocks such as syenites, nepheline syenites, aegirine syenites, two-mica peraluminous leucogranites, and A-type rapakivi granites, which have been dated to the Permian period (296 to 269 million years ago) in the South Tianshan region [16]. On the northern side of the YP–CTT, the Late Carboniferous volcanic activity is limited in distribution. The Sikeshu granitic pluton, which crosscuts the North Tianshan suture zone (including the Bayingou and Motuogou ophiolites), provides important chronological information. The pluton has been dated to 316 ± 3 million years ago using the SHRIMP zircon U–Pb dating method [129], setting an upper age limit for the collision between the YP and JP (Junggar Plate) during the Late Carboniferous period. Therefore, the Late Carboniferous arc model may not be applicable to both sides of the YP–CTT.
After the collision of continents, the subducted oceanic lithosphere may detach from the lighter continental lithosphere due to buoyancy, ultimately resulting in slab breakoff [130,131]. Many researchers have invoked the slab breakoff mechanism to explain postcollisional magmatism and metamorphism, as seen in the Alps, Dabie, Himalayas, and Eastern Junggar [111,130,131,132]. In addition, slab breakoff has been used to explain Early Permian magmatism in the Western Tianshan [133], Late Carboniferous granite in the Nalati Mountain [134], and iron mineralization in the AIMB [115]. Wang et al. [115] proposed two periods for the tectonic setting of the AIMB in the Late Carboniferous: a slab breakoff period (320–310 Ma) and a subsequent postcollisional period (309–290 Ma), identifying the former as the setting for iron mineralization. However, the latest isotopic dating has constrained the age of iron deposits in AIMB to 316–302 Ma (e.g., Duan et al. [21] and references therein). While we agree with Wang et al. [115] regarding the role of slab breakoff in the tectonic setting of iron mineralization (Figure 15), we disagree with their claim that the geological evidence from the Late Carboniferous can be clearly divided into two periods. The feasibility of slab breakoff during the Late Carboniferous is based on several geological events and geochemical data, including the closure of the South and North Tianshan Oceans and the corresponding arc magmatism in the Late Carboniferous [16,44,129], as well as the presence of volcanic and intrusive rocks showing syn-collision or intraplate characteristics, simultaneous mafic and felsic magmatism, and A-type granites, potassic and ultrapotassic volcanic and intrusive rocks, and mafic-ultramafic intrusions [18,81,97,119,120,135].
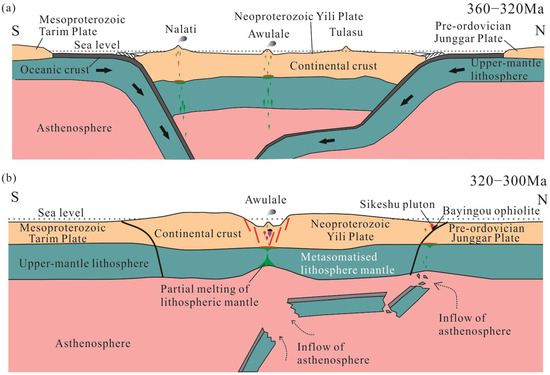
Figure 15.
Schematic diagrams showing the tectonic evolution of the Chinese Western Tianshan Orogen: (a) Early Carboniferous subduction; (b) Late Carboniferous slab breakoff and extension (slab breakoff or delamination of the mantle lithosphere under the Sikeshu area is from Han et al. [129]).
Slab breakoff leads to the intrusion of a hot asthenosphere into a narrow gap in the lithosphere above the sinking slab. This intrusion causes the formation of a relatively narrow and linear zone of magmatism in the upper crust, which is consistent with the case of the AIMB. The heat input from the ascending asthenosphere results in the partial melting of the overlying lithospheric mantle and lower continental crust [133]. This partial melting produces “hot” felsic magmas, such as the Beizhan granite, in contrast to the “cold” rhyolite of the Early Carboniferous period. The shallow extension induced by slab breakoff provides a pathway for rapid magma ascent. The ore-forming magma, which is rich in water and volatiles (likely inherited from the previous subduction process [136]), and its shallow to ultra-shallow emplacement are considered the two key factors contributing to the occurrence of iron ore deposits. In summary, the Late Carboniferous magmatism and associated iron mineralization in the AIMB are believed to be the result of an extensional setting caused by the breakoff of the oceanic slab.
6. Conclusions
The Beizhan iron deposit provides evidence of Late Carboniferous granite intrusion (311.8 ± 2.6 Ma) as well as diabase and diorite intrusions (299.2 ± 1.4 Ma) into Early Carboniferous rhyolite. The rhyolite and granite exhibit enriched LILEs (large ion lithophile elements) and LREEs (light rare earth elements), depleted HFSEs (high field strength elements), high positive εNd(t) values, and young Nd model ages. These characteristics suggest that they originated from the partial melting of a juvenile lower crust.
The diabase and diorite samples are believed to have originated from a spinel-garnet lherzolite mantle source. It is suggested that these magmatic suites formed in two distinct tectonic settings: an Early Carboniferous continental arc setting and a Late Carboniferous within-plate extensional setting induced by slab breakoff. The iron mineralization in the area is likely associated with the latter tectonic setting.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/min14010016/s1, Table S1: LA–ICP–MS U–Pb data for intrusive rocks in the Beizhan iron ore deposit, Western Tianshan; Table S2: Major (wt.%) and trace element (ppm) compositions of volcanic and intrusive rocks in the Beizhan iron ore deposit, Western Tianshan.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.D.; methodology, S.D.; software, S.D.; validation, S.D.; formal analysis, S.D.; investigation, S.D.; resources, S.D.; data curation, S.D.; writing—original draft preparation, S.D.; writing—review and editing, S.D. and W.L.; visualization, S.D.; supervision, S.D., Z.J. and W.L.; project administration, S.D. and Z.J.; funding acquisition, S.D. and Z.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant numbers 42172104 and 41203035; the Chinese Geological Survey Program, grant number DD20230033; and the Fundamental Research Funds for the MNR Key Laboratory of Metallogeny and Mineral Assessment, grant number KK2014.
Data Availability Statement
All data are contained within this article and the Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our gratitude to the engineers Xincheng Guo, Zhengang Zhao, and Xiejun Xu from the No. 11 Geological Party of the Xinjiang Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources for their valuable assistance during the fieldwork. Additionally, we would like to extend our appreciation to the anonymous reviewers for providing constructive comments and suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sengör, A. Evolution of the Altaid tectonic collage and Palaeozoic crustal growth in Eurasia. Nature 1993, 364, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahn, B.M.; Wu, F.Y.; Chen, B. Massive granitoid generation in Central Asia: Nd isotope evidence and implication for continental growth in the Phanerozoic. Episodes 2000, 23, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovalenko, V.I.; Yarmolyuk, V.V.; Kovach, V.P.; Kotov, A.B.; Kozakov, I.K.; Salnikova, E.B.; Larin, A.M. Isotopic provinces, mechanism of generation and sources of the continental crust in the Central Asian mobile belt: Geological and isotopic evidence. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2004, 23, 605–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.J.; Han, C.M.; Yuan, C.; Sun, M.; Lin, S.F.; Chen, H.L.; Li, Z.L.; Li, J.L.; Sun, S. Middle Cambrian to Permian subduction–related accretionary orogenesis of Northern Xinjiang, NW China: Implications for the tectonic evolution of central Asia. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2008, 32, 102–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.J.; Santosh, M. The western Central Asian Orogenic Belt: A window to accretionary orogenesis and continental growth. Gondwana Res. 2014, 25, 1429–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakubchuk, A. Architecture and mineral deposit settings of the Altaid orogenic collage: A revised model. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2004, 23, 761–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Liu, D.Q.; Tang, Y.L.; Wang, D.H.; Dong, L.H.; Xu, X.; Wang, X.D. Mineral Resources and Mineralization System in Tianshan, China Vol. 1; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2008; pp. 246–287. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.Q.; Liu, F.; Li, Q.; Geng, X.X. In situ LA–MC–ICP–MS U–Pb geochronology of igneous rocks in the Ashele Basin, Altay orogenic belt, northwest China: Constraints on the timing of polymetallic copper mineralization. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2014, 79, 477–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Klemd, R.; Zhu, M.T.; Wang, X.S.; Li, J.L.; Wan, B.; Xiao, W.J.; Zeng, Q.D.; Shen, P.; Sun, J.G.; et al. Large-scale porphyry-type mineralization in the Central Asian metallogenic domain: A review. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2018, 165, 7–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, T.; Smith, M.P.; Herrington, R.J.; Maslennikov, V.; Boyce, A.J.; Jeffries, T.; Creaser, T.A. The geology and genesis of the iron skarns of the Turgai belt, northwestern Kazakhstan. Ore. Geol. Rev. 2017, 85, 216–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.Q.; Mao, J.W.; Liu, F.; Chai, F.M.; Geng, X.X.; Zhang, Z.X.; Guo, X.J.; Liu, G.R. A review of the geological characteristics and mineralization history of iron deposits in the Altay orogenic belt of the Xinjiang, Northwest China. Ore. Geol. Rev. 2013, 54, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.Q.; Geng, X.X.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Z.X.; Guo, X.J. A synthesis of mineralization styles and geodynamic settings of the Paleozoic and Mesozoic metallic ore deposits in the Altay Mountains, NW China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2018, 159, 233–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Hong, W.; Jiang, Z.S.; Duan, S.G.; Li, F.M.; Shi, F.P. Geological characteristics and metallogenesis of iron deposits in western Tianshan, China. Ore. Geol. Rev. 2014, 57, 425–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldfarb, R.J.; Taylor, R.D.; Collins, G.S.; Goryachev, N.A.; Orlandini, O.F. Phanerozoic continental growth and gold metallogeny of Asia. Gondwana Res. 2014, 25, 48–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhu, M.T.; Wang, X.S.; Hong, T.; Li, G.M.; Li, J.L.; Xiao, W.J.; Qin, K.Z.; Zeng, Q.D.; Shen, P.; et al. Large scale porphyry type mineralization in the Central Asian metallogenic domain: Tectonic background, fluid feature and metallogenic deep dynamic mechanism. Acta Geol. Sin. 2019, 93, 24–71. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Qian, Q.; Long, L.L.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.L.; Su, W. Accretionary orogenic process of Western Tianshan, China. Geol. Bull. China 2009, 28, 1804–1816. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, T.; Zhang, Z.; Pirajno, F.; Santosh, M.; Encarnacion, J.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, L. Geology, tectonic settings and iron ore metallogenesis associated with submarine volcanism in China: An overview. Ore. Geol. Rev. 2014, 57, 498–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.M.; Li, L.X.; Yang, X.Q.; Cheng, Y.B. Types and geological characteristics of iron deposits in China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 103, 2–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.G.; Zhang, Z.H.; Jiang, Z.S.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.P.; Li, F.M.; Tian, J.Q. Geology, geochemistry, and geochronology of the Dunde iron–zinc ore deposit in western Tianshan, China. Ore. Geol. Rev. 2014, 57, 441–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.G.; Zhang, Z.H.; Jiang, Z.S.; Li, F.M.; Ren, Y.; Xiao, Y.H.; Shi, W.X. Geochronology and rock geochemistry of volcnaic rocks from Songhu iron deposit in West Tianshan Mountains, Xinjiang. Miner. Depos. 2016, 35, 913–932. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, S.G.; Zhang, Z.H.; Wang, D.C.; Jiang, Z.S.; Luo, W.J.; Li, F.M. Pyrite Re–Os and muscovite 40Ar/39Ar dating of the Beizhan iron deposit in the Chinese Tianshan Orogen and its geological significance. Int. Geol. Rev. 2018, 60, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.G. Metallogenesis of Iron Ores in the Awulale Mineralization Belt, Western Tianshan, Xinjiang, China; Postdoctoral Research Report; Chang’an University: Xi’an, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, S.G.; Zhang, Z.H.; Wei, M.Y.; Tian, J.Q.; Jiang, Z.S.; Li, F.M.; Zhao, J.; Wang, H.F. Geochemistry and zircon U–Pb geochronology of the diorite associated with the Wuling iron deposit in Western Tianshan Mountains, Xinjiang. Geol. China 2014, 41, 1757–1770. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, W.; Zhang, Z.H.; Li, H.Q.; Li, F.M.; Liu, X.Z. Metallogenic epoch of Chagangnuoer iron deposit in western Tianshan Mountains, Xinjiang: Information for garnet Sm-Nd isochron age. Miner. Depos. 2012, 31, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, W.; Zhang, Z.H.; Baker, M.J.; Jiang, Z.S.; Duan, S.G. Zircon U-Pb dating and stable isotopic compositions for constraining the genesis of the Chagangnuoer magnetite deposit in western Tianshan, NW China. Ore. Geol. Rev. 2020, 121, 103478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.S.; Zhang, Z.H.; Wang, Z.H.; Duan, S.G.; Li, F.M.; Tian, J.Q. Geology, geochemistry, and geochronology of the Zhibo iron deposit in the Western Tianshan, NWChina: Constraints on metallogenesis and tectonic setting. Ore. Geol. Rev. 2014, 57, 406–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.S.; Wang, D.C.; Zhang, Z.H.; Duan, S.G.; Kang, Y.J.; Li, F.M. Application of in situ titanite U–Pb geochronology to volcanic-hosted magnetite deposit: New constraints on the timing and genesis of the Zhibo deposit, Western Tianshan, NW China. Ore. Geol. Rev. 2018, 95, 325–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.X.; Zhang, Z.C.; Liu, B.X.; Jin, Y.L.; Santosh, M. The genetic link between iron oxide-apatite and iron skarn mineralization in the Beizhan deposit, Western Tianshan, NW China: Evidence from magnetite and gangue mineral geochemistry. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2023, 241, 105460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.Q.; Duan, S.G.; Peng, W.L.; Li, M.; Jiang, Z.S.; Yan, R. Geochemistry of volcanic and intrusive rocks in Zhibo iron ore deposit of western Tianshan Mountains. Miner. Depos. 2015, 34, 119–138. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.J. Ore Genesis of the Dunde Iron-Zinc-Gold Polymetallic Deposit, West Tianshan, Xinjiang. Ph.D. Dissertation, Peking University, Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Tian, J.Q.; Gao, J.; Klemd, R.; Dong, L.H.; Fan, J.J.; Jiang, T.; Hu, C.J.; Qian, Q. Geochronology and geochemistry of granitoid rocks from the Zhibo syngenetic volcanogenic iron ore deposit in the Western Tianshan Mountains NW–China: Constraints on the age of mineralization and tectonic setting. Gondwana Res. 2012, 22, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.S.; Zhai, M.G.; Safonova, I.; Li, D.P.; Zhu, X.Y.; Zuo, P.F.; Shan, H.X. Whole-rock geochemistry and Sr–Nd–Pb isotope systematics of the Late Carboniferous volcanic rocks of the Awulale metallogenic belt in the western Tianshan Mountains NW China: Petrogenesis and geodynamical implications. Lithos 2015, 228–229, 62–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Shan, Q.; Niu, H.C.; Yang, W.B.; Li, N.B.; Zeng, L.J.; Jiang, Y.H. Petrology and geochemistry of late Carboniferous hornblende gabbro from the Awulale Mountains, western Tianshan NW China: Implication for an arc–nascent back–arc environment. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 113, 218–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.L.; Zhu, W.N.; Wang, Y.T. Genesis of the Kiruna-type Nixintage iron deposit, Chinese Western Tianshan, NW China: Constrains of ore geology, geochemistry and geochronology. J. Geochem. Explor. 2022, 243, 107094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.F.; He, G.Q.; Wu, T.R.; Li, H.M. Zircon U–Pb dating and geochemical features of early Paleozoic granites from Tianshan, Xinjiang: Implications for tectonic evolution. Xinjiang Geol. 2004, 22, 4–11. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, L.Q.; Xu, X.Y.; Xia, Z.C.; Li, X.M.; Ma, Z.P.; Wang, L.S. Petrogenesis of Carboniferous rift–related volcanic rocks in the Tianshan, northwestern China. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2004, 116, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.Q.; Xia, Z.C.; Xu, X.Y.; Li, X.M.; Ma, Z.P. Relative contributions of crust and mantle to the generation of the Tianshan Carboniferous rift–related basic lavas, northwestern China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2008, 31, 357–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhao, Z.H.; Xu, J.F.; Wyman, D.A.; Xiong, X.L.; Zi, F.; Bai, Z.H. Carboniferous adakite–high–Mg andesite–Nb–enriched basaltic rock suites in the Northern Tianshan area: Implications for phanerozoic crustal growth in the Central Asia Orogenic Belt and Cu–Au mineralization. Acta. Petrol. Sin. 2006, 22, 11–30. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.F.; Zhou, J.; Guo, X. Petrology and Sr–Nd isotopic geochemistry of the Carboniferous volcanic rocks in the western Tianshan Mountains, NW China. Acta. Petrol. Sin. 2006, 22, 1341–1350. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, G.J.; Chung, S.L.; Wang, Q.; Wyman, D.A.; Dan, W.; Chen, H.Y.; Zhao, Z.H. Petrogenesis of a Late Carboniferous mafic dike–granitoid association in the western Tianshan: Response to the geodynamics of oceanic subduction. Lithos 2014, 202–203, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H.; Xue, C.J.; Zhao, X.B.; Symons, D.T.A.; Niu, P.Q. Petrogenesis and tectonic implications of the Early Carboniferous shoshonitic to calc-alkaline magmatic rocks of the southern Yili terrane, western Tianshan. Geol. Mag. 2023, 160, 855–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.S.; Wang, C.Y.; Ye, S.F. Tectonic Framework and Crustal Evolutional of Eastern Tianshan Mountains; Publishing House of Nanjing University: Nanjing, China, 1993; pp. 1–225. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, R.S.; Shu, L.S.; Sun, J.Q. Tectonic Evolution and Metallogeny of Eastern Tianshan Mountains; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1997; pp. 1–202. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Long, L.L.; Klemd, R.; Qian, Q.; Liu, D.Y.; Xiong, X.M.; Su, W.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y.T.; Yang, F.Q. Tectonic evolution of the South Tianshan orogen and adjacent regions, NW China: Geochemical and age constraints of granitoid rocks. Int. J. Earth. Sci. 2009, 98, 1221–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.F.; Guo, Z.J.; Zhang, Z.C.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J.F.; Song, B. Age, geochemistry, and tectonic implications of a late Paleozoic stitching pluton in the North Tian Shan suture zone, western China. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2010, 122, 627–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windley, B.F.; Allen, M.B.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Wang, G.R. Paleozoic accretion and Cenozoic redeformation of the Chinese Tien Shan range, central Asia. Geology 1990, 18, 128–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.B.; Windley, B.F.; Zhang, C. Palaeozoic collisional tectonics and magmatism of the Chinese Tien Shan, central Asia. Tectonophysics 1992, 220, 89–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Shu, L.S.; Cluzel, D.; Faure, M.; Charvet, J. Geochemical constraints on Carboniferous volcanic rocks of the Yili Block Xinjiang, NW China: Implication for the tectonic evolution of Western Tianshan. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2007, 29, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, X.D.; Zhang, B.; Gao, Y.L.; Yang, J.Q.; Li, Y.J. New materials of stratigraphic classification and correlation of the carboniferous in Awulale area, Western Tianshan. Xinjiang Geol. 2008, 26, 231–235. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.J.; Li, Z.C.; Zhou, J.B.; Gao, Z.H.; Gao, Y.L.; Tong, L.M.; Liu, J. Division of the Carboniferous lithostratigraphic units in Awulale area, wetern Tianshan. Acta. Petrol. Sin. 2009, 25, 1332–1340. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.J.; Gao, Y.L.; Tong, L.L.; Guo, W.J.; Tong, L.M. Tempestite of Akeshake Formation in Awulale Area, Western Tianshan and its significance. Earth Sci. Front. 2009, 16, 341–348. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.X.; Shi, F.P.; Wang, B.Y.; Hu, J.M.; Wang, J.T.; Tian, J.Q. Volcanogenic Iron Deposits in the Awulale Metallogenic Belt in Western Tianshan; Geological Publishing Hous: Beijing, China, 2010; pp. 16–112. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- No. 11 Geological Party of the Xinjiang Bureau of Geology and Mineral Exploration and Development. Geological survey and evaluation of iron deposits in the Dunde-Beizhan area in Hejing County, Xinjiang province. Internal report. 2011.
- Sun, J.M.; Ma, Z.P.; Xu, X.Y.; Li, X.Y.; Weng, K.; Zhang, T. The formation epoch of the host wall rock of the Beizhan iron deposit in West Tianshan Mountains of Xinjiang and its geological significance. Geol. Bull. China 2012, 31, 1973–1982. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Yu, J.J.; Chai, F.M.; Mao, J.W.; Hou, K.J. Metallogenic Regularity and Mechanism of Volcanic Type Rich Iron Ore; Research Report of the National Basic Research Program, Institute of Mineral Resources, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences: Beijing, China, 2016; pp. 45–48. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hou, K.J.; Li, Y.H.; Qu, X.M.; Shi, Y.R.; Xie, G.Q. Laser ablation–MC–ICP–MS technique for Hf isotope microanalysis of zircon and its gelolgical applications. Acta. Petrol. Sin. 2007, 23, 2595–2604. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, K.J.; Li, Y.H.; Tian, Y.R.; Qin, Y.; Xie, G.Q. High precision Cu-Zn isotope measurements by multi–collector ICP–MS. Miner. Depos. 2008, 27, 774–781. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, S.E.; Pearson, N.J.; Griffin, W.L.; Belousova, E.A. The application of laser ablation–inductively coupled plasma–mass spectrometry LA–ICPMS to in situ U–Pb zircon geochronology. Chem. Geol. 2004, 211, 47–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasdala, L.; Hofmeister, W.; Norberg, N.; Martinson, J.M.; Corfu, F.; Dörr, W.; Kamo, S.L.; Kennedy, A.K.; Kronz, A.; Reiners, P.W.; et al. Zircon M257: A homogeneous natural reference material for the ion microprobe U–Pb analysis of zircon. Geostand. Geoanal. Res. 2008, 32, 247–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, K.J.; Li, Y.H.; Tian, Y.R. In situ U–Pb zircon dating using laser ablation–multi ion counting–ICP–MS. Miner. Depos. 2009, 28, 481–492. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.S.; Gao, S.; Hu, Z.C.; Gao, C.G.; Zong, K.Q.; Wang, D.B. Continental and oceanic crust recycling–induced melt–peridotite interactions in the Trans–North China Orogen: U–Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths. J. Petrol. 2010, 51, 537–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, K.R. User’s manual for Isoplot 3.00: A geochronological toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Berkeley Geochronol. Cent. Spec. Publ. 2003, 4, 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Sláma, J.; Kosler, J.; Condon, D.J.; Crowley, J.L.; Gerdes, A.; Hanchar, J.M.; Horstwood, M.S.A.; Morris, G.A.; Nasdala, L.; Norberg, N.; et al. Plesovice zircon—A new natural reference material for U–Pb and Hf isotopic microanalysis. Chem. Geol. 2008, 249, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T14506.28–2010; Methods for Chemical Analysis of Silicate Rocks—Part 28: Determination of 16 Major and Minor Elements Content. Standards Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2010.
- GB/T14506.14–2010; Methods for Chemical Analysis of Silicate Rocks—Part 14: Determination of Ferrous Oxide Content. Standards Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2010.
- LY/T1253–1999; Determination of Mineral Total Elements (Silica, Iron, Aluminium, Titanium, Manganese, Calcium, Magnesium, Phosphorus) Ignition Loss in Forest Soil. Standards Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1999.
- DZ/T 0223–2001; General Rule for Inductively Coupled Plasma Massspectrometry(ICP-MS)Analytical Method. Standards Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2001.
- He, X.X.; Tang, S.H.; Zhu, X.K.; Wang, J.H. Precise measurement of Nd isotopic ratios by means of multi–collector magnetic sector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2007, 28, 405–410. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.Q.; Zhang, G.W.; Tang, S.H. Geochronology of Metamorphic Sequences from the Southern Qinling; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2002; pp. 1–256. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Belousova, E.A.; Griffin, W.L.; Suzanne, Y.O.R.; Fisher, N.I. Igneous zircon: Trace element composition as an indicator of source rock type. Contrib. Mineral. Petr. 2002, 143, 602–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middlemost, E.A.K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system. Earth-Sci. Rev. 1994, 37, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvine, T.N.; Baragar, W.R.A. A guide to the chemical classification of the common volcanic rocks. Can. J. Earth. Sci. 1971, 8, 523–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peccerillo, R.; Taylor, S.R. Geochemistry of Eocene calc–alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, Northern Turkey. Contrib. Mineral. Petr. 1976, 58, 63–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middlemost, E.A.K. Magmas and Magmatic Rocks; Longman: London, UK, 1985; p. 266. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.S.; McDonough, W.F. Chemical and isotopic systematics in ocean basalt: Implication for mantle composition and processes. In Magmatism in the Ocean Basins; Saunders, A.D., Norry, M.J., Eds.; Geological Society of London Special Publications: London, UK, 1989; Volume 42, pp. 313–345. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, G.J.; Wang, Q.; Wyman, D.A.; Sun, M.; Li, Z.X.; Zhao, Z.H.; Sun, W.D.; Jia, X.H.; Jiang, Z.Q. Geochronology and geochemistry of Late Paleozoic magmatic rocks in the Lamasu–Dabate area, northwestern Tianshan west China: Evidence for a tectonic transition from arc to post–collisional setting. Lithos 2010, 119, 393–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiger, R.H.; Jäger, E. Subcommission on geochronology: Convention on the use of decay constants in geochronology and cosmochronology. Earth. Planet. Sc. Lett. 1977, 36, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugmair, G.W.; Harti, K. Lunar initial 143Nd/144Nd: Differential evolution of the lunar crust and mantle. Earth. Planet. Sc. Lett. 1978, 39, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zindler, A.; Hart, S. Chemical geodynamics. Annu. Rev. Earth. Pl. Sc. 1986, 14, 493–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.Y.; Xia, L.Q.; Ma, Z.P.; Wang, Y.B.; Xia, Z.C.; Li, X.M.; Wang, L.S. SHRIMP zircon U–Pb geochronology of the plagiogranites from Bayinggou ophiolite in North Tianshan Mountains and the petrogenesis of the ophiolite. Acta. Petrol. Sin. 2006, 22, 83–94. [Google Scholar]
- Long, L.L.; Wang, Y.W.; Tang, P.Z.; Wang, L.J.; Wang, J.B.; Liao, Z. A debate on the special circumstance of rock-forming and ore-forming of Haladala pluton, a mafic-ultralmafic complex related to CuNi-VTiFe composite mineralization in western Tianshan. Acta. Petrol. Sin. 2012, 28, 2015–2028. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.F.; Zhou, T.X.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, X.; Guo, X.S. Formation of positive εNd(t) granitoids from the Alataw Mountains, Xinjiang, China, by mixing and fractional crystallization: Implication for Phanerozoic crustal growth. Tectonophysics 2000, 328, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A.Q.; Jahn, B.M.; Zhang, G.X.; Chen, Y.B.; Zhang, Q.F. Crustal evolution and Phanerozoic crustal growth in northern Xinjiang: Nd isotopic evidence. Part I. Isotopic characterization of basement rocks. Tectonophysics 2000, 328, 15–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Hong, W.; Jiang, Z.S.; Duan, S.G.; Xu, L.G.; Li, F.M.; Guo, X.C.; Zhao, Z.G. Geological characteristics and zircon U–Pb dating of volcanic rocks from the Beizhan iron deposit in western Tianshan Mountains, Xinjiang, NW China. Acta Geol. Sin.-Engl. 2012, 86, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.J.; Zhang, Z.H.; Duan, S.G.; Jiang, Z.S.; Wang, D.C.; Chen, J. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Beizhan basic-ultrabasic pluton in West Tianshan, Xinjiang: Petrogenesis and geodynamical implications. Acta Petrol. Et Mineral. 2018, 37, 733–753. [Google Scholar]
- Eugster, H.P.; Chou, I.M. A model for the deposition of Cornwall-type magnetite deposits. Econ. Geol. 1979, 74, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, A.W.; Herrick, D.C.; Deines, P. An oxygen and sulfur isotope study of skarn-type magnetite deposits of the Cornwall type, Southeastern Pennsylvania. Econ. Geol. 1985, 80, 418–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.; Zhang, Z.C.; Santosh, M.; Encarnacion, J.; Wang, M. The Cihai diabase in the Beishan region, NW China: Isotope geochronology, geochemistry and implications for Cornwall-style iron mineralization. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2013, 70–71, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, B.W.; White, A.J.R. Two contrasting granite types: 25 years later. Aust. J. Earth. Sci. 2001, 48, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalen, J.B.; Currie, K.L.; Chappell, B.W. A-type granites: Geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis. Contrib. Mineral. Petr. 1987, 95, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, B.W.; Stephens, W.E. Origin of infracrustal I–type granite magmas. Trans. R. Soc. Edinb. Earth Sci. 1988, 79, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defant, M.J.; Drummond, M.S. Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere. Nature 1990, 347, 662–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.R.; McLennan, S.M. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution; Black Well: Oxford, UK, 1985; pp. 1–312. [Google Scholar]
- Green, T.H. Significance of Nb/Ta as an indicator of geochemical processes in the crust–mantle system. Chem. Geol. 1995, 120, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, A.W. Chemical differentiation of the Earth: The relationship between mantle, continental crust, and oceanic crust. Earth. Planet. Sc. Lett. 1988, 90, 297–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Zhang, Z.C.; Encarnacion, J.; Xue, C.J.; Duan, S.G.; Zhao, Z.D.; Liu, J.L. Petrogenesis of the Kekesai composite intrusion, western Tianshan, NW China: Implications for tectonic evolution during late Paleozoic time. Lithos 2012, 146–147, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.H.; Wang, Y.J.; Fan, W.M.; Zi, J.W. Post–collisional potassic magmatism in the Southern Awulale Mountain, western Tianshan Orogen: Petrogenetic and tectonic implications. Gondwana Res. 2008, 14, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Pan, G.Q.; Li, C.D.; Jin, W.J.; Jia, X.Q. Does fractional crystallization occur in granitic magma? Some crucial questions on granite study. Acta. Petrol. Sin. 2007, 23, 1239–1251. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, C.F.; McDowell, S.M.; Mapes, R.W. Hot and cold granites? Implications of zircon saturation temperatures and preservation of inheritance. Geology 2003, 31, 529–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapp, R.P.; Watson, E.B. Dehydration melting of metabasalt at 8–32 kbar: Implications for continental growth and crust-mantle recycling. J. Petrol. 1995, 36, 891–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, E.B. Basalt contamination by continental–crust–some experiments and models. Contrib. Mineral. Petr. 1982, 80, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, W.K.; Gabriel, G.W.; Walter, R.C.; Mertzman, S.A. Basaltic volcanism in Ethiopia: Constraints on continental rifting and mantle interactions. J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 94, 7721–7748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M. Siberian traps. In Large Igneous Provinces: Continental, Oceanic, and Planetary Flood Volcanism; Mahoney, J.J., Coffin, M.F., Eds.; Geophysical Monographs, American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; Volume 100, pp. 273–295. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, M. Igneous Petrogenesis; Harper Collins Academic: London, UK, 1989; p. 466. [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie, D.; O’Nions, R.K. Partial melt distribution from inversion of rare earth element concentrations. J. Petrol. 1991, 32, 1021–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldanmaz, E.; Pearce, J.A.; Thirlwall, M.F.; Mitchell, J.G. Petrogenetic evolution of late Cenozoic, post-collision volcanism in western Anatolia, Turkey. J. Volcanol. Geoth. Res. 2000, 102, 67–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.H.; Zhou, M.F. Geochemistry of Neoproterozoic mafic intrusions in the Panzhihua district (Sichuan Province, SW China): Implications for subduction related metasomatism in the upper mantle. Precambrian Res. 2007, 152, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.H.; Zhou, M.F. Secular evolution of the Neoproterozoic lithospheric mantle underneath the northern margin of the Yangtze Block, South China. Lithos 2009, 107, 152–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.B.; Zindler, A.; Xu, X.S.; Qu, Q. Major, trace element, and Nd, Sr and Pb isotope studies of Cenozoic basalts in SE China: Mantle sources, regional variations, and tectonic significance. Chem. Geol. 2000, 171, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, A.D.; Storey, M.; Kent, R.W.; Norry, M.J. Consequences of plume–lithosphere interactions. In Magmatism and the Cause of Continental Breakup; Storey, B.C., Alabaster, T., Pankhurst, R.J., Eds.; Geological Society of Special Publication: London, UK, 1992; pp. 41–60. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.P.; Zheng, J.P.; Griffin, W.L.; Zhao, J.H.; Tang, H.Y.; Ma, Q.; Lin, X.Y. Geochemistry and geochronology of Carboniferous volcanic rocks in the eastern Junggar terrane, NW China: Implication for a tectonic transition. Gondwana Res. 2012, 22, 1009–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Plank, T.; Walker, J.D.; Smith, E.I. A mantle melting profile across the Basin and Range, SW USA. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, ECV 5-1–ECV 5-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Z.C.; Liu, L.; Liu, H.F.; Luo, J.H. Review on the Ancient Yili Rift, Xinjiang, China. Acta. Petrol. Sin. 1996, 12, 478–490. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, W.Y.; Zhu, Y.F. Petrogenesis and tectonic implications of the late Carboniferous calc-alkaline and shoshonitic magmatic rocks in the Awulale mountain, western Tianshan. Gondwana Res. 2019, 76, 44–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.S.; Zhang, X.; Gao, J.; Li, J.L.; Jiang, T.; Xue, S.C. A slab break-off model for the submarine volcanic-hosted iron mineralization in the Chinese Western Tianshan: Insights from Paleozoic subduction-related to post-collisional magmatism. Ore. Geol. Rev. 2018, 92, 144–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, F.; Zhu, Y.F.; Wei, S.N.; Lai, S.C. An Early Devonian to Early Carboniferous volcanic arc in North Tianshan, NW China: Geochronological and geochemical evidence from volcanic rocks. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2013, 78, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.C.; Duan, S.G.; Chen, J.; Jiang, Z.S.; Zhang, Z.H.; Jia, J.D. Hf isotopic and geochemistry of volcanic rocks from Tiemulike iron deposit in western Tianshan, Xinjiang, and their geological significance. Acta. Petrol. Sin. 2016, 32, 1391–1408. [Google Scholar]
- An, F.; Zhu, Y.F.; Wei, S.N.; Lai, S.C. The zircon U–Pb and Hf isotope constraints on the basement nature and Paleozoic evolution in northern margin of Yili block, NW China. Gondwana Res. 2017, 43, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Qian, Q.; Su, W.; Li, J.L. Pluton from Muhanbasitao in the western of Awulale, western Tianshan: Geochemistry, geochronology and geological implications. Acta. Petrol. Sin. 2012, 28, 2401–2413. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, H.C.; Shan, Q.; Yang, W.B.; Luo, Y.; Li, N.B.; Yu, X.Y. The discovery of Fe rich basalt–Rhyolite association in the Chagangnuoer area, western Tianshan, Xinjiang Abstract. Bull. Mineral. Petrol. Geochem. 2011, 30, 85. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.M.; Zhao, Z.H.; Xiong, X.L.; Han, J.W. Petrogeochemistry of late Paleozoic gabbroic rocks from Tekes County in West Tianshan Mountains. Acta Petrol. Et Mineral. 2010, 29, 675–690. [Google Scholar]
- He, P.L.; Huang, X.L.; Li, H.Y.; Li, J.; Yu, Y.; Li, W.X. Mechanism of Fe-Ti enrichment in the Haladala gabbros: Implication for the tectonic evolution of the western Tianshan orogenic belt. Acta. Petrol. Sin. 2013, 29, 3457–3472. [Google Scholar]
- Pearce, J.A.; Harris, N.B.W.; Tindle, A.G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks. J. Petrol. 1984, 25, 956–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelor, R.A.; Bowden, P. Petrogenetic interpretation of granitoid rock seires using multicationic parameters. Chem. Geol. 1985, 48, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meschede, M. A method of discriminating between different types of mid ocean ridge basalts and continental tholeiite with the Nb–Zr–Y diagram. Chem. Geol. 1986, 56, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalen, J.B.; McNicoll, V.J.; van Staal, C.R.; Lissenberg, C.J.; Longstaffe, F.J.; Jenner, G.A.; van Breeman, O. Spatial, temporal and geochemical characteristics of Silurian collision-zone magmatism, Newfoundland Appalachians: An example of a rapidly evolving magmatic system related to slab break-off. Lithos 2006, 89, 377–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalen, J.B.; Wodicka, N.; Taylor, B.E.; Jackson, G.D. Cumberland batholith, Trans-Hudson Orogen, Canada: Petrogenesis and implications for Paleoproterozoic crustal and orogenic processes. Lithos 2010, 117, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, F.; Karsli, O.; Chen, B. Petrogenesis of the Neogene alkaline volcanics with implications for post-collisional lithospheric thinning of the Eastern Pontides, NE Turkey. Lithos 2008, 104, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.F.; He, G.Q.; Wang, X.C.; Guo, Z.J. Late Carboniferous collision between the Tarim and Kazakhstan–Yili terranes in the western segment of the South Tian Shan Orogen, Central Asia, and implications for the Northern Xinjiang, western China. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2011, 109, 74–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.H.; von Blanckenburg, F. Slab breakoff: Amodel of lithosphere detachment and its test in the magmatism and deformation of collisional orogens. Earth. Planet. Sc. Lett. 1995, 129, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Blanckenburg, F.; Davies, J.H. Slab-breakoff: A model for syncollisional magmatism and tectonics in the Alps. Tectonics 1995, 14, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.Y.; Chung, S.L.; Lo, C.H.; Ji, J.Q.; Lee, T.Y.; Qian, Q.; Zhang, Q. Eocene Neotethyan slab breakoff in southern Tibet inferred from the Linzizong volcanic record. Tectonophysics 2009, 477, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.X.; Shu, L.S.; Meert, J.G. Early Permian slab breakoff in the Chinese Tianshan belt inferred from the post-collisional granitoids. Gondwana Res. 2015, 27, 228–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.C.; Zhu, Y.F.; Fen, W.Y.; Tan, Y.W.; An, F.; Zheng, J.H. Paleozoic intrusive rocks in the Nalati mountain range (NMR), southwest Tianshan: Geodynamic evolution based on petrology and geochemical studies. J. Earth Sci.-China 2017, 28, 196–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.B.; Niu, H.C.; Shan, Q.; Yang, W.B. Two episodes of Late Paleozoic A-type magmatism in the Qunjisayi area, western Tianshan: Petrogenesis and tectonic implications. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 113, 238–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.F.; Zhang, L.F.; Gu, L.B.; Guo, X.; Zhou, J. The zircon SHRIMP chronology and trace element geochemistry of the Carboniferous volcanic rocks in western Tianshan Mountains. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2005, 50, 2201–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).