Abstract
The Daliuhang gold deposit in the Qipengfu (Qixia–Penglai–Fushan) ore concentration area is a typical gold deposit of medium-low temperature hydrothermal veins. Uncertainties regarding the primary sources of ore-forming fluids, as well as whether host rocks contribute materials to the mineralization of the gold deposits in the Jiaodong Peninsula, are still subject to intense debate. Hydrogen–oxygen isotope results show that atmospheric water is involved in ore-forming fluids. According to the results of the helium–argon isotopes of pyrite, it is hypothesized that the initial fluid source was located in the oceanic crust or upper mantle lithosphere above the Early Cretaceous Paleo-Pacific Plate, as it was subducted into the eastern part of the eastern North China Craton. In situ sulfur isotope results show that high δ34S values characterize the pyrite in the main mineralization period. It is inferred that during the thinning and melting process of the lithospheric mantle, the volatile components enriched in pyrite contributed to the release of δ34S. At the same time, when the fluids ascended to the weak zones, such as fissures of ore-endowed peripheral rocks, the δ34S in the peripheral rocks were extracted, and the two processes acted together to cause high δ34S values to occur. Similarly, the lead and strontium isotopic compositions indicate a crust–mantle mixing attribute of the mineralized material source. The zircon U–Pb age of the ore-hosting granodiorite was 130.35 ± 0.55 Ma, and the Rb–Sr isochron age of the pyrite from the main mineralization period was 117.60 ± 0.10 Ma, which represents the timing of felsic magmatism and gold mineralization, respectively, with at least 10 Ma between the magmatism and mineralization. The magma gradually cooled over time after its formation, and when the granodiorite cooled down to 300 ± 50 °C, the temperature and pressure conditions were most conducive to the precipitation of gold. It is inferred that gold-rich initial mantle fluids with volatile components, rising along tectonically weak zones, such as fractures, underwent fluid phase separation in the fractured position of the granite and extracted the gold from the granodiorite, forming gold deposits.
1. Introduction
The Jiaodong Peninsula is located on the southeastern edge of the North China Craton (NCC), and it is China’s most productive gold province, with more than 5400 t of gold resources [1]. The preserved resource reserves exceed 4000 t, which accounts for more than one-quarter of China’s total. The Jiaodong gold province is the third-largest gold mining area in the world [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]. There are three ore concentration areas in the region: the Jiaoxibei (Laizhou–Zhaoyuan) ore concentration area, the Qipengfu (Qixia–Penglai–Fushan) ore concentration area, and the Muru (Muping–Rushan) ore concentration area [8,10]. The Daliuhang gold field is located in the northern part of the Qipengfu ore concentration area. It consists of several gold deposits, including Daliuhang, Menlou, Ankou, Hexi, and other gold deposits. The ore bodies exist in Early Cretaceous granodiorite. They belong to middle-low-temperature hydrothermal vein-type gold deposits, and they are one of the most important types of gold deposits in the Jiaodong Peninsula.
Early studies have suggested several genetic types of gold deposits in the Jiaodong Peninsula, but its genesis remains enigmatic. Studies have indicated that the gold mineralization in Jiaodong Peninsula, and even eastern North China, is closely related to the destruction of the eastern North China Craton, and it is proposed that the eastern North China gold deposits belong to the “Decratonic gold deposits” [11]. During the Early Cretaceous, against a strong extensional tectonic background, the Paleo-Pacific plate was subducted beneath the eastern North China Craton. The lithospheric mantle, which was strongly metasomatized, underwent large-scale partial melting [11,12]. The produced basaltic magma reacted with the strongly enriched mantle and the lower crust, and the interaction between the fluids and crustal-source felsic magma formed gold-rich magma [11]. The auriferous fluids were exsolved from the magma and uplifted along the deep faults, which were mineralized by filling in the subtectonic levels [11]. Other works believe that the gold deposits formed during the dehydration and metamorphism of the subducting slab of the Paleo-Pacific Plate. Gold may have come from the devolatilization of stalled subducting slabs and oceanic crustal sediments [7,13,14]. Tectonic stress conversion resulted in ultra-high pressure gold-rich fluids, which migrated along the abyssal fault and other crustal hierarchical rupture systems and were further deposited to form the minerals, thus being considered “orogenic gold deposits” [7,15]. Additionally, some other studies also suggest that these gold deposits belong to the greenstone belt gold deposit, and its mineralization is likely related to the Mesozoic granitic magmatism. This indicates that the Jiaodong gold deposit may represent post-magmatic hydrothermal deposits [14,16]. However, some recent studies suggest that the gold deposits in this area are “Jiaodong-type gold deposits”, in contrast to all the above types [6,17,18,19,20]. One of the focal points of the various genetic models mentioned above is the origin of gold-bearing fluids. Therefore, the study of the geological characteristics, the origin of the ore-forming fluids and materials, and the mineralization chronology of the Daliuhang gold deposit can enrich the theoretical study of medium-low temperature hydrothermal vein-type gold deposits, enhance our understanding of the origin of ore-forming fluids in the Qipengfu (Qixia–Penglai–Fushan) ore concentration area, and provide a theoretical basis for prospecting work on the same types of gold deposits in this area.
In this study, the Rb–Sr ages of pyrite in ores were obtained to determine the precise timing of gold mineralization in the Daliuhang gold deposit. In addition, the U–Pb ages of zircon from ore-hosting granodiorite were obtained to determine the timing of felsic magmatic events. In situ sulfur isotopic analyses of gold-hosted pyrite, hydrogen–oxygen isotopic analyses of quartz, lead isotopic analyses of pyrite, and helium–argon isotopic analyses of primary ore-forming fluids entrapped in pyrite were conducted in order to place constraints on the sources and temporal evolution of the ore-forming fluids, as well as on the probable origins of the sulfur and ore metals. The integrated results contribute to a better understanding of the genesis of the Daliuhang deposit.
2. Regional Geology
The Jiaodong Peninsula consists of three parts: the Jiaobei Terrane in the north, the Weihai Terrane in the east, and the JiaoLai Basin in the south. The Qipengfu ore concentration area is located in the north-central part of the Jiaobei Terrane, which mainly consists of Precambrian basement rocks and Mesozoic igneous intrusions (Figure 1). The Precambrian basement rocks mainly include the Archean granite–greenstone belt (Tonalite–Trondhjemite–Grandiorite (TTG) gneisses, known as the Jiaodong Group) and Paleoproterozoic metamorphic strata. The Mesozoic igneous intrusions are divided into the following groups: Late Jurassic (165–150 Ma) granite (Linglong granite), Early Cretaceous (132–123 Ma) porphyritic granodiorite (Guojialing granodiorite), Early Cretaceous (118–110 Ma) granite (Weideshan granite) [21,22,23,24], and various kinds of dikes dominated by lamprophyres and diorite–porphyrites. The structures in the area are mainly fault structures, divided into three groups: NNE-, NE-, and NNW-trending crustal-scale fault zones. The NNE- and NE-trending fault zones are the most developed and the main ore-controlling structures in the area, including the Sanshandao, Jiaojia, Zhaoyuan–Pingdu, Qixia, and Muping–Rushan fault zones.
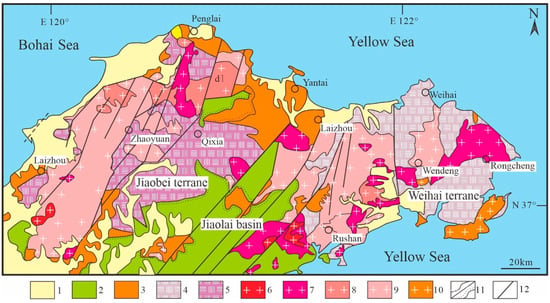
Figure 1.
Map showing the regional geology in the Jiaodong Peninsula (modified after [9,10]). (1) Quaternary sediments; (2) Cretaceous sedimentary basin; (3) Paleoproterozoic and Neoproterozoic; (4) Neoproterozoic bearing eclogite granitic gneiss; (5) Archean granite–greenstone belt; (6) Late Cretaceous granite (Laoshan granite); (7) Early Cretaceous granite (Late, Weideshan granite); (8) Early Cretaceous granite (Early, Guojialing granite); (9) Late Jurassic granite (Linglong granite); (10) Triassic granitoid; (11) geological boundary of conformity/unconformity; (12) fault.
3. Ore Deposit Geology
The Daliuhang deposit mainly developed from the Late Jurassic biotite granite and Early Cretaceous porphyritic granodiorite (Figure 2). Ultramafic to intermediate dikes are also developed, including granite pegmatite, lamprophyre, and quartz–diorite porphyrite.
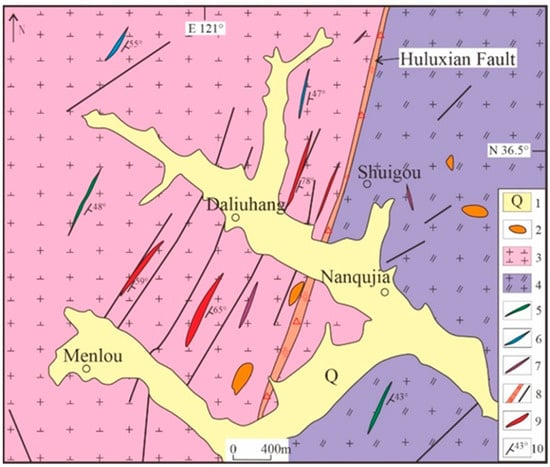
Figure 2.
Geological map of the Daliuhang deposit. (1) Quaternary sediments; (2) Neoproterozoic; (3) Early Cretaceous porphyritic granodiorite (Guojialing granodiorite); (4) Late Jurassic granite (Linglong biotite granite); (5) quartz diorite porphyrite; (6) lamprophyre; (7) granite pegmatite; (8) fault; (9) ore vein; (10) occurrence.
The Huluxian Fault exerts full control over the ore veins in the area, and the occurrence of ore veins is in complete alignment with it. The ore veins consistently strike 20–30° and dip 59–78° SE, with a gentle upward slope and a steep downward slope. The ore-hosting enclosing rocks mainly consist of pyrite–seritic cataclastic rock and porphyritic granodiorite. The width of quartz–pyrite veins is generally more than ten to dozens of centimeters (Figure 3a), with uneven development. The gold grade is generally higher in the areas where quartz–polymetallic sulfide veins are well-developed (Figure 3b). The mineral composition of the ore comprises two main parts: metallic minerals and non-metallic minerals. Sulfides, including pyrite, and a small amount of galena, dominate the metallic minerals. The non-metallic minerals include quartz, feldspar, calcite, sericite, chlorite, etc. (Figure 3c–f). The main ore textures are automorphic granular, pressure, and hypidiomorphic–itomorphic granular, etc. (Figure 3e,f), and they exhibit veinlet-disseminated, mottled, massive, and other structures (Figure 3e,f). The main alterations of the surrounding rocks include potashization, pyriteization, silicification, and sericitization, followed by carbonatization, chloritization, and kaolinization. Sericitization of the surrounding rocks is the most developed alteration phenomenon in the deposit. The width of its alteration zone ranges from tens of centimeters to several meters. The alteration is more substantial closer to the main fault surface and gradually weakens on both sides.
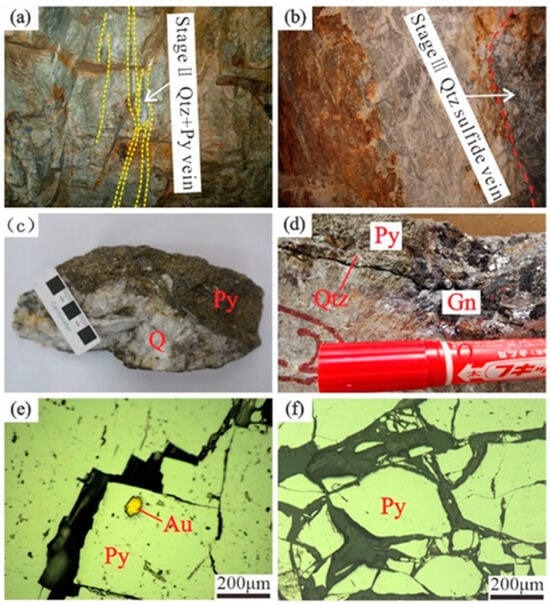
Figure 3.
Photographs of major wall rocks and various mineralized veins in the Daliuhang gold deposit. (a) Pyrite sericite cataclastic rock and quartz–pyrite veins (Stage II); (b) quartz vein (Stage II) and its adjacent quartz–galena–pyrite vein (Stage III); (c) representative specimens of quartz–pyrite veins (Stage II); (d) representative specimens of quartz–galena–pyrite veins (Stage III); (e) euhedral pyrite and gold grains occur inside pyrite crystals; (f) pyrite with an automorphic-semi-automorphic structure. Au, gold; Gn, galena; Py, pyrite; Qtz, quartz.
Based on the interpenetration relationship of ore veins, mineral assemblage characteristics, and observations using backscattered electron (BSE) images, the mineralization can be roughly divided into four stages: Stage I consists of pyrite and quartz, with a small amount of medium and fine-grained pyrite. Stage II contains quartz and pyrite, where white-grey quartz fills cavities, and pyrite occurs as coarse euhedral cubes (Py2), displaying a smooth surface and a single component in the backscattered electron (BSE) images (Figure 4a,b). Stage III is characterized by gold, quartz, and polymetallic sulfide phases. The quartz is grey to pale with relatively coarse particles, and the pyrite (Py3) and galena are medium-coarse-grained and more automorphic. Locally, Stage III minerals are superimposed on Py2, forming an irregular, dark inner core (Py3a) with a bright outer rim (Py3b) in the BSE images (Figure 4c,d). Milky carbonate–quartz veins represent Stage IV. Stages II and III represent the main gold mineralization episodes.
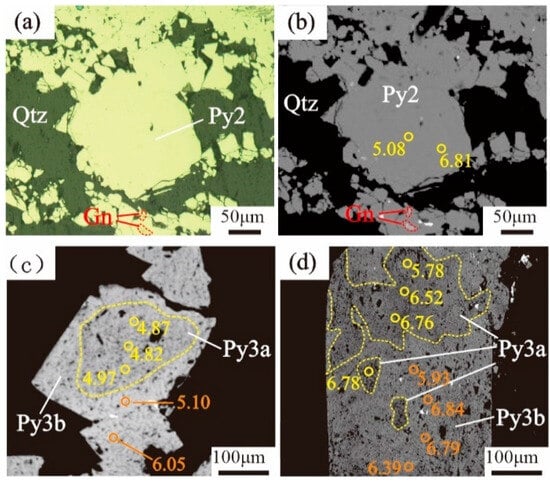
Figure 4.
Reflected light photomicrographs (a) and backscattered electron (BSE) images (a–d) showing textural features of pyrite from main mineralizing stages II and III. (a) Cataclastic texture of pyrite, pyrite intergrowth with galena; (b) Py2 from quartz–pyrite veins (Stage II) is homogeneous in composition; (c) regular Py3a is overgrown by zoned and brighter Py3b from quartz polymetallic sulfide veins (Stage III); (d) irregular Py3a is overgrown by zoned and brighter Py3b from quartz polymetallic sulfide veins (Stage III). Gn, galena; Py, pyrite; Qtz, quartz.
4. Sampling and Analytical Methods
A total of 23 samples were collected from the pit at a depth of +200 m of the Daliuhang gold deposit, including pyrite, galena, and other sulfides, which were intergrown with quartz veins.
4.1. Isotopes Analysis
Quartz grains were crushed into 40–60 mesh and handpicked from under a binocular (purity > 99%). Hydrogen and oxygen isotopic composition analyses were performed at the MLR Key Laboratory of Metallogeny and Mineral Assessment, Institute of Mineral Resources, CAGS. The samples were heated to approximately 500 °C in an induction furnace to release moisture. The samples were heated to 180–200 °C until the vacuum degree was less than 10−1 Pa, and then the volatile substances in the sample were degassed. At a temperature of 400 °C, water was converted into hydrogen gas by a heated zinc powder, which was then analyzed with a MAT–253 mass spectrometer. The analysis results of the standard water samples show that the accuracy of the δD was ±2‰. The pure mineral was crushed into 200 mesh, and then the crushed material was reacted with BrF5 at 500–600 °C for 14 h to produce O2, and then reacted with graphite at 700 °C to produce CO2 under the action of a platinum catalyst. The carbon dioxide’s oxygen isotopes were then measured using a MAT–253 mass spectrometer. The reproducibility of the isotopically homogeneous pure quartz was approximately ±0.2‰. More detailed analytical conditions and procedures are described by previous researchers [25].
In situ sulfur isotopic compositions of four pyrite samples from Stage II in thin sections were analyzed using a 193 nm ArF excimer laser ablation system (RESOlution S–155) connected to an MC–ICP–MS (Nu Plasma II) at the State Key Laboratory for Geological Processes and Mineral Resources at the China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), China. Helium delivered the ablative material into the plasma at a gas flow rate of 0.4 L/min. Argon (0.8 L/min) and a small amount of nitrogen (~4 mL/min) were mixed with the carrier gas before entering the MC–ICPMS. The addition of a small amount of N2 gas is effective in removing polyatomic interferences (e.g., 16O2+) from 32S [26,27]. The laser diameter was 23 μm, and the laser repetition frequency was 8 Hz for single-site analysis. The energy flux of the laser was about 3–4 J/cm2. The internal pyrite standard (WS–1) consisted of natural pyrite crystals from the Wenshan polymetallic deposit in Yunnan Province, southern China, and was used to calibrate the mass bias of the S isotopes. The δ34SVCDT value of WS–1 (1.1 ± 0.2‰) was determined by SIMS at the China Institute of Geochemistry, Guangzhou [28]. The analytical precision was evaluated to be better than 0.5‰.
Lead isotope analysis was performed at the Beijing Research Institute of Uranium Geology, Beijing. Pb isotope samples were taken from pyrite and galena in Stage III mineralization. After dissolution and separation of the samples, the lead isotope analyses were conducted using a thermal ionization mass spectrometer (ISOPROBE–T) produced by GV, UK, at a relative humidity of 36% and a room temperature of 20 °C. The measured Pb isotopic ratios of the international standard NBS981 are approximately 0.2‰. The analytical results of the standard NBS981 are as follows: 206Pb/204Pb = 16.937 ± 0.002, 207Pb/204Pb = 15.457 ± 0.002, and 208Pb/204Pb = 272 36.611 ± 0.004.
Helium–argon isotope analyses were performed at the MLR Key Laboratory of Metallogeny and Mineral Assessment, Institute of Mineral Resources, CAGS. The samples were taken from pyrite in Stage III mineralization. The Helix SFT™ Split Flight Tube noble gas mass spectrometer was used. The system consists of crushing, purification, and mass spectrometry systems. Tests were performed under high-vacuum conditions, with the vacuum of the crushing and purification systems at 5 × 10−9–10 × 10−9 mbar and the vacuum of the mass spectrometry system at 7 × 10−9–9 × 10−10 mbar. The mass spectrometry ion source was Nier, with a sensitivity better than 2 × 10−4 amps/Torr for helium at a trap current of 800 μA, and 1 × 10−3 amps/Torr for argon at a trap current of 200 μA. The static rate of rise was less than 1 × 10−12 cm3 STP/min for 40Ar, and the background was less than 5 × 10−14 cm3 STP for 36Ar. The Faraday background was less than 5 × 10−14 STP/min for 36Ar, the static rate of rise was less than 1 × 10−12 cm3 STP/min, and the 36Ar background was less than 5 × 10−14 STP/min. The Faraday cup resolution was >400 and the ion counter resolution was >700, which allowed for complete separation of the 3He, 4He, HD + H3, and 3He peaks. A program blank was performed before each measurement. The blanks for both helium and argon were negligible (3He < 3 × 10−17 cm3 STP, 40Ar < 4 × 10−17 cm3 STP), approximately 0.1% of the sample signal. The sample test results were corrected using the test results of the day’s air standards and the air standard values. The standard value of 3He/4He for air was 1.4 × 10−6 (Ra). The 40Ar/36Ar and 36Ar/38Ar standard values were adopted as 295.5 and 5.35, respectively.
4.2. Zircon U-Pb Dating
Zircon crystals for U–Pb dating were separated from the ore-hosting porphyritic granodiorite (Early Cretaceous granodiorite). Zircon LA–ICP–MS U–Pb dating was conducted using a Resonetics–M50 laser ablation system equipped with a 193 nm ArF excimer laser connected to a multi-collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (Neptune), at the Tianjin Center, China Geological Survey, Tianjin. Helium was used as the carrier gas to enhance the transport efficiency of the ablated material. The spot diameter was 35 μm, and the ablation frequency was 9 Hz. The silicate glass standard NIST SRM 612 was used to calibrate U, Th, and Pb concentrations. All measurements were performed using zircon GJ–1 as the external standard, with a recommended 206Pb/238U age of 609 Ma [29]. In contrast, the Plesǒvice zircon standard = 337.13 ± 0.37 Ma [30] was used as a blind sample to monitor the data quality. The raw data were processed using ICPMS DataCal software [31], and the 208Pb method was used for the common Pb correction [32]. Concordia diagrams and weighted mean ages were generated using the ISOPLOT program version 3.75 [33]. Errors for individual analyses were at the 2σ level, and deviations of the pooled analyses are given at the 95% confidence level.
4.3. Rb-Sr Dating
The Rb–Sr isotope system was used to date five samples of pyrite from Stage III mineralization. The Rb–Sr isotope analysis was performed in the Laboratory of Isotope Chronology at the Tianjin Center, China Geological Survey, Tianjin. The pyrite samples were accurately weighed and dissolved with HNO3 + HClO4. The dissolved sample solution was evenly divided into two parts. One part was mixed with 87Rb + 84Sr diluent. After separation and purification, the rubidium and strontium contents were determined. The other portion was purified and used for strontium isotope ratio determination. To determine the 87Sr/86Sr isotope ratio, a mass fractionation correction was made using 88Sr/86Sr = 8.375209, and the instrumental state was monitored using the international SRM987 standard solution: the ratio obtained was 87Sr/86Sr = 0.710242 ± 0.000008 (2σ). The reliability of the analytical method was monitored using the international rock standard BCR–2, which gave a ratio of 87Sr/86Sr = 0.705015 ± 0.000009 (2σ). For the full-flow blank, the rubidium content was less than 103 pg, and the strontium content was less than 276 pg. The detailed experimental separation process and instrument test parameters followed those of previous researchers [24,34], and the ISOPLOT program was used to calculate the isochron age.
5. Results
5.1. Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopes
This paper conducted H–O isotope analysis on quartz samples from the Daliuhang gold deposit during its main gold mineralization episodes and collected previous research results on the Jiaojia and Jinqingding gold deposits (Table 1). The δ18O values of the hydrothermal quartz (δ18OSMOW‰) ranged from 15.8 to 18.3‰, with a median value of 16.5‰. The hydrogen isotope composition δDsmow value varied from −101.0 to −84.0‰, with an average value of −89.0‰ (Table 1). Assuming that quartz is isotopically equilibrated with the ore-forming hydrothermal fluids, the oxygen isotope composition of the ore-forming hydrothermal fluids can be estimated following the temperature-dependent quartz–water oxygen isotope fractionation equation: 1000lnαQ–W = 3.38 × 106/T2 − 2.90 [35], that is, δ18OH2O = δ18Osmow − 1000lnαQ–W. The δ18OH2O value ranged from 7.63 to 10.90‰, with an average of 8.52‰. The hydrogen and oxygen isotope values of the Daliuhang gold deposit are relatively similar to those of the Jiaojia and Jinqingding gold deposits (Figure 5).

Table 1.
Hydrogen and oxygen isotope compositions in the Daliuhang gold deposit.
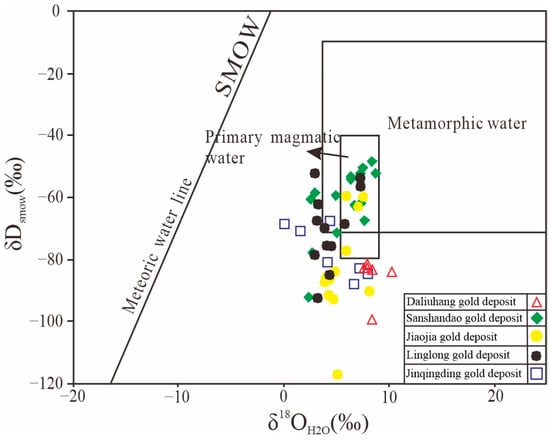
Figure 5.
Isotopic compositions of oxygen and hydrogen in the Daliuhang gold deposit.
5.2. In Situ Sulfur Isotopic Compositions
The in situ sulfur isotopic compositions of pyrite from the ores are listed in Table 2. The δ34S values of the pyrite ranged from 4.82‰ to 7.04‰ (average of 6.12‰), which were all positively biased away from meteoric sulfur and had a narrow variation, with a high degree of sulfur homogenization characterized by a mild enrichment of δ34S (Figure 6). Based on the backscattered electron (BSE) images (Figure 4c,d), the pyrite can be divided into a dark inner core (Py3a) and a bright outer rim (Py3b). As shown in Figure 4c,d, the core (Py3a) had δ34S values of 4.82–6.78‰ (average of 5.37‰), with an increase to 5.10–7.04‰ (average of 6.33‰) on the rim (Py3b).

Table 2.
In situ sulfur isotopic analyses in the Daliuhang gold deposit.
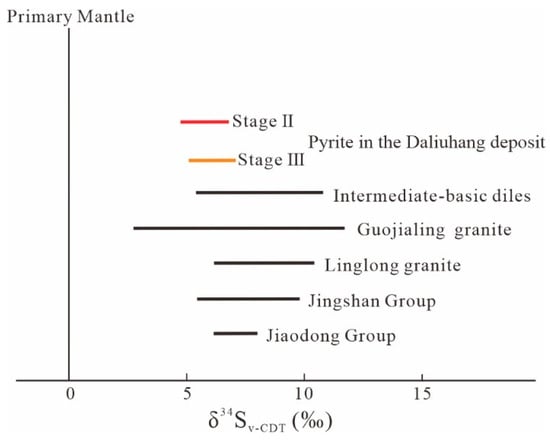
Figure 6.
Sulfur isotopic composition of pyrite from the ore deposits in the Daliuhang gold deposit and regional rocks.
5.3. Lead Isotope Compositions
The analytical results of the lead isotopes of ten sulfides separated from the Daliuhang gold deposit during Stage III mineralization are presented in Table 3 (attached at the end of the article). For comparison, five published Pb isotopic data of sulfides [36,37] are also listed in Table 3. The pyrite had 206Pb/204Pb ratios ranging from 17.365 to 17.566 (mean of 17.493), 207Pb/204Pb from 15.514 to 15.576 (mean of 15.536), and 208Pb/204Pb from 38.118 to 38.462 (mean of 38.258). The galena had 206Pb/204Pb ratios ranging from 17.503 to 17.577 (mean of 17.532), 207Pb/204Pb from 15.515 to 15.60 (mean of 15.548), and 208Pb/204Pb from 38.272 to 38.548 (mean of 38.374).

Table 3.
Pb isotope compositions of sulfides from the Daliuhang gold deposit.
5.4. Helium-Ar Isotopes of Pyrite
The results of the He and Ar isotope analyses of fluid inclusions in pyrite are listed in Table 4 (attached at the end of the article). The contents of 4He varied from 0.28 × 10−8 cm3/gSTP to 8.63 × 10−8 cm3/gSTP, and the 3He/4He ratios ranged mainly from 1.43 to 1.92 Ra, where Ra represents the standard value of helium in air (3He/4He = 1.4 × 10−6). The 40Ar/36Ar ratios were in the range of 446.30–753.80.

Table 4.
The He-Ar samples analysis results in the Dliuhang gold deposit. Note: 40Ar*(%) = [(40Ar/36Ar)sample − 295.5]/(40Ar/36Ar)sample × 100.
5.5. Zircon U-Pb Age of Granodiorite
Zircon crystals from the Early Cretaceous porphyritic granodiorite are generally euhedral, pale yellow, and translucent. Most of them are equiprismatic to prismatic, with a few short columnar grains. Most of the grains are 100 to 200 μm in diameter, but a few grains are 300 to 400 μm in diameter. Based on cathodoluminescence (CL) images (Figure 7), magmatic oscillatory zoning is present in most grains. However, some zircon cores are residual. Many of the residual cores show signs of partial melting and are clearly bounded by oscillatory zones. A total of 26 spots were analyzed in the regions with oscillatory zoning. All analyses agree on a weighted average 206Pb/238U age of 130.35 ± 0.55 Ma (Figure 7).
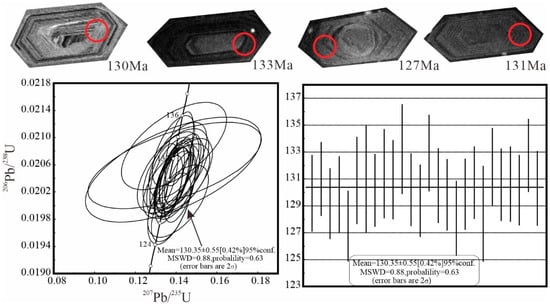
Figure 7.
Representative zircon crystals and U–Pb Concordia diagram for granodiorite.
5.6. Pyrite Rb-Sr Age
The mass fractions and isotope ratios of Rb and Sr in pyrite from the Daliuhang gold deposit are listed in Table 5. The Rb and Sr mass fractions were 0.1369–6.2452 ppm and 0.9369–19.8666 ppm, respectively. The 87Rb/86Sr ratios ranged from 0.0446–5.6666, and the 87Sr/86Sr ratios ranged from 0.71340 to 0.72280. The graphs of 87Rb/86Sr and 87Sr/86Sr for pyrite in the Daliuhang gold deposit show an excellent linear relationship. ISOPLOT software was used to calculate the isochron age, which was t = 117.60 ± 0.10 Ma, and the initial 87Sr/86Sr (Isr) value was 0.713319 ± 0.000028 (Figure 8).

Table 5.
The mass fractions and isotope ratios of Rb and Sr in pyrite from the Daliuhang gold deposit.
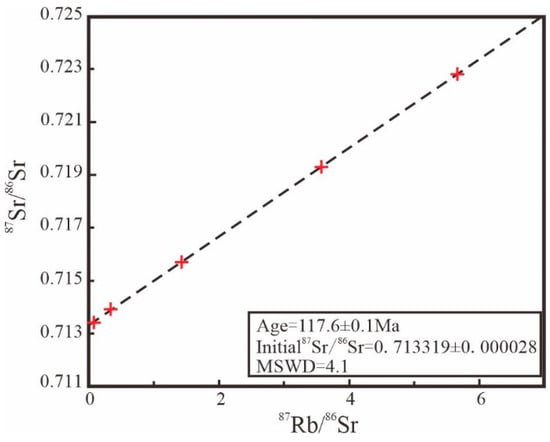
Figure 8.
Rb-Sr isotope data and isochron ages of pyrite from the Daliuhang gold deposit.
6. Discussion
6.1. Evolution of Ore-Forming Fluid
The hydrogen and oxygen isotope compositions of the ore-forming fluids in the Daliuhang gold deposit in this study had a limited range of variation. The oxygen isotope composition δ18Osmow values ranged from 15.80‰ to 18.30‰, and the δ18OH2O values ranged from 7.63‰ to 10.90‰. The hydrogen isotope composition δDsmow values ranged from −101.0‰ to −84.0‰. The magmatic water had typical hydrogen isotope compositions of −80.0‰ and −40.0‰ and oxygen isotopes of 5.0‰ to 10.0‰ [39,40,41,42]. The results of this study do not entirely fall into the category of magma water (Figure 5). According to the isotopic compositions of oxygen and hydrogen in the Daliuhang gold deposit (Figure 5), it can be seen that the projection points of each group of data were mainly concentrated in the lower part of the metamorphic water and magma water side, which was closer to the magma water, indicating that magma fluids dominated the fluids in the initial period of the gold deposits. With the advancement of mineralization, there is a mixing of meteoric water.
Generally, after the formation of the deposit, the fluid inclusions in the ore sulfides were susceptible to diffusive loss, which may have been affected by later geological processes. However, if the host minerals were sulfides, the inert gases inside them were generally not significantly lost after being captured [43,44], and the U and Th contents of sulfides such as pyrite are very low, which can rule out the adverse effects caused by late diffusion loss. In addition, noble gas isotopes will not produce obvious isotope fractionation during the capture and extraction process of inclusions [43,45,46]. Therefore, the He isotope analysis results of pyrite can represent the initial value when fluid inclusions were captured. The He and Ar isotopic compositions of the fluid inclusions in pyrite are shown in Figure 9. The proportions of mantle fluids (Rm) and crustal fluids (Rc) in the binary mixing model can be deduced by using the 3He/4He ratio with the following equation: Mantle 4He (%) = [(R − Rc)/(Rm − Rc)] × 100, where Rc, Rm, and R represent the 3He/4He ratio of crustal fluid, mantle fluid, and the sample, respectively [47]. According to the calculations, the mantle fluid participation ratio in the Daliuhang gold deposit is only 10.39 to 21.55%, with an average value of 14.86% (Table 4). The above data indicate that the ore-forming fluids are mainly from crustal sources, with mantle fluids mixed in.
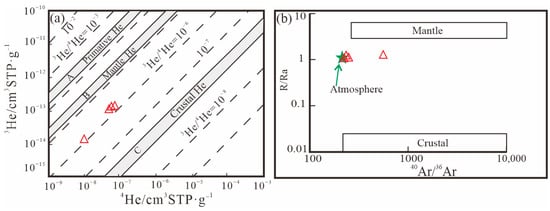
Figure 9.
(a) Helium isotopes of pyrite from the Daliuhang gold deposit. A–C From Mamyin and Tolstikhin (1984) [48]; (b) He (R/Ra) vs. 40Ar/36Ar diagram for fluid in pyrite from the Daliuhang gold deposit. Values of crustal and mantle end-members [47,49,50,51].
The pyrite 40Ar/36Ar ratio of the Daliuhang gold deposit ranged from 446.30 to 753.80 (Table 4), which is higher than the 40Ar/36Ar ratio in the atmosphere of 295.5, but much lower than the 40Ar/36Ar ratio of the mantle (generally greater than 40,000), suggesting that the argon in the fluid is not from a single source. Atmospheric argon and radiotracer 40Ar* in the crust have both contributed to mineralization, but the mantle argon participation ratio is low and can be nearly negligible [38]. The radioactive origin 40Ar* (%) in the crust can be obtained according to the formula: 40Ar* (%) = [(40Ar/36Ar)sample − 295.5]/(40Ar/36Ar)sample × 100 [49,52]. The calculated 40Ar* (%) is 33.79–60.80%, with a wide range, and atmospheric Ar also had a particular contribution. There was an addition of an atmospheric noble gas component to the mantle through subduction [53,54,55,56].
It is speculated that the ore-forming fluids were produced during the dehydration and decarbonization of the overlying sediments during the subduction of the Paleo-Pacific plate beneath the eastern North China Craton in the Early Cretaceous, and the atmospheric components were also mixed in during this process.
6.2. Sources of Ore-Forming Material
Earth has three main sources of sulfur: sulfur in the mantle, seawater, and continental crust. The average value of δ34S in the mantle is close to zero, with a variation range of 0 ± 3.0‰, and it mainly exists in a reduced state. The average value of δ34S in seawater is +20.0‰. In addition, the sulfur in crustal sources is affected by its original rock, and its δ34S may be greater or less than the value of the above two sources. The in situ sulfur isotope results of pyrite in this study show that the δ34S values were all greater than 4.82‰, and the test results generally show higher δ34S values (Figure 6), indicating that the possibility of sulfur only coming from mantle-derived magma is relatively tiny. Sulfur in ore-forming fluids mainly comes from δ34S-rich magmatic rocks [57] or mantle degassing with high oxygen fugacity in the subduction zones [11]. The results of these two processes will have the characteristics of high δ34S values. According to previous research results, the δ34S value of pyrite in the Jiaodong Group ranges from 6.10‰ to 7.80‰ [58,59], in the Jingshan Group, it ranges from 5.60‰ to 9.80‰ [58,60], in the Late Jurassic granite, it ranges from 6.10‰ to 10.70‰ [59,60,61], in the early Early Cretaceous porphyritic granodiorite, it ranges from 2.7‰ to 11.8‰ [59,61], and in the intermediate–basic dike rocks, it ranges from 5.30‰ to 10.80‰ [62]. The δ34S values of pyrite from the Daliuhang gold deposit overlap somewhat with the δ34S values of all types of rocks, and in general, overlap more with the Jingshan Group, Early Cretaceous porphyritic granodiorite, and intermediate–basic dike rocks. The δ34S value of pyrite (Py3) in Stage III is slightly higher than the pyrite (Py2) in Stage II, which indicates that new sulfur was added to the mineralized hydrothermal fluids as mineralization proceeded. A large number of isotopic exchanges were presumed to exist between the mineralized fluids and host rocks. It can be assumed that during the thinning and melting of the lithospheric mantle, the enriched volatile fraction promoted the release of δ34S. In contrast, the δ34S in the surrounding rock was extracted when the fluid rose to the location of the enclosing rock, and the two effects resulted in the generation of high δ34S values.
Pyrite, galena, and other ore minerals are generally free of U and Th, or their contents are low enough to be negligible. The composition of lead in the ore is mainly affected by the initial Pb, μ (238U/204Pb), ω (232Th/204Pb) in the source area and the initial formation time. It has little impact on the geochemical environment after its formation. Therefore, the lead isotope composition was analyzed to obtain information about the source of the minerals [63]. Previous studies have believed that lead with μ values of <9.74 [64] or <9.58 [65] is derived from the lower crust or upper mantle, respectively. Samples from the Daliuhang deposit have Pb μ values of 9.41–9.58 (average of 9.476), suggesting a lower crust or upper mantle source. It is generally believed that the 206Pb/207Pb ratio between 0.89 and 1.20 belongs to the range of normal lead, while a range between 1.20 and 1.95 belongs to the content of abnormal Pb (J–type Pb). It is known that the lead source of the Daliuhang gold deposit is normal lead according to the 206Pb/207Pb ratio. According to the lead isotopic tectonic environment model of the deposit (Figure 10), it can be seen that the injection points mainly fall within the lower crust and are close to the upper mantle, which indicates that the sources of the ore-forming materials have the characteristics of a mixed crust–mantle source.
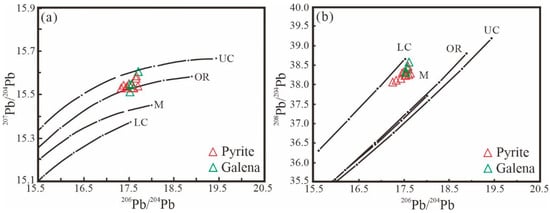
Figure 10.
207Pb/204Pb vs. 206Pb/204Pb diagram (a) and 208Pb/204Pb vs. 206Pb/204Pb diagram (b) of sulfides from the Daliuhang gold deposit (after [66]). Abbreviations: LC, lower crust; UC, upper crust; M, mantle; OR, orogenic belt.
The 87Sr/86Sr initial value is an essential indicator for determining the diagenetic source of ore-forming materials. The determination of the Sr isotope composition can be used in deposit geology research on sources to trace the deep origins or crust–mantle mixing of magmatic fluids and the source of ore-forming fluids. Generally, values of 87Sr/86Sr > 0.710 are considered to reflect a crustal source, whereas values of 87Sr/86Sr < 0.705 are considered to reflect a mantle source [13,36,67,68]. The initial value of pyrite in the Daliuhang gold deposit was lower than the continental crust, but significantly higher than the mantle. The Sr isotope composition also shows that the source of the minerals has the attributes of a mixed crust–mantle source.
6.3. Relationship between Gold Mineralization and Ore-Hosting Intrusions
The LA–ICP–MS zircon U–Pb age of the granodiorite was 130.35 ± 0.55 Ma, which is consistent with the results of previous studies [69,70,71]. The Rb–Sr isochron age of the pyrite from the main mineralization period was 117.60 ± 0.10 Ma, representing the ore formation age of the gold deposit belonging to the Early Cretaceous. This is consistent with the metallogenic age of gold deposits in the Jiaodong Peninsula (120 ± 5 Ma) [17,72,73,74], indicating that the gold mineralization in the Jiaodong Peninsula was accomplished in the same structure within a short period of time. Microscopic thermometry data of fluid inclusions in the Jiaodong gold deposits show that the maximum temperature of the mineralizing fluids was about 350 °C [75,76]. The granite of the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous cooled to 300 ± 50 °C at 123 Ma ± [77,78], indicating that the P–T conditions of the granite in this period were most conducive to the beginning of gold precipitation. The diagenetic time of the surrounding rocks (granodiorite) was more than 10 Ma earlier than the mineralization time. There is no direct association between magmatism and mineralization in terms of time [79]. However, more than 90% of the gold deposits in the Jiaodong Peninsula are hosted between the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous granite, and there is a particular connection between the magmatism and the mineralization in terms of spatial location. The geochemical composition of Guojialing granodiorite shows that its origin was crust–mantle mixing, which is related to the subduction of the North China Craton by the Paleo-Pacific Plate in the Mesozoic [80,81,82]. The lead and strontium isotopic compositions also show that the source of gold mineralization has the attribute of crust–mantle-mixed source, and the isotope composition is highly similar to the surrounding rocks. The tectonics of the Jiaodong Peninsula changed from compressional to extensional tectonics in the Jurassic–Cretaceous [83,84]. It is inferred that gold-rich initial mantle fluids containing volatile matter followed structural weak zones, such as faults. During the ascent and intrusion, a large amount of crustal sulfur was mixed, forming mixed sulfur dominated by crustal sulfur. The fluid carried the minerals and continued to rise. The fluid had the mineralized material and continued to rise, and in the crushed zone of the granite with increased tectonic space, fluid phase separation and sulfidation occurred, and the gold in the surrounding rock was extracted, thus forming the gold deposits.
7. Conclusions
The ore-forming fluids were the result of the dehydration and decarbonization of the overlying sediments during the subduction of the Paleo-Pacific plate beneath the eastern North China Craton in the Early Cretaceous. The magma fluids dominated the formation of the gold deposits in the early stages, with atmospheric components mixed in during later stages.
The LA–ICP–MS zircon U–Pb age of the granodiorite was 130.35 ± 0.55 Ma. The Rb–Sr isochron age of the pyrite from the main mineralization period was 117.60 ± 0.10 Ma, representing the ore formation age of gold deposits, belonging to the Early Cretaceous.
The mineralization of the gold deposits originated from the fluid of mantle magma mixed with a large amount of crustal material during their ascent. Fluid phase separation and sulfidation occurred under suitable temperature and pressure conditions, leading to the extraction of gold from the granite and the formation of gold deposits in the Early Cretaceous.
Author Contributions
J.T. conceived and designed the research ideas; J.L., J.T., C.F., Z.D., and P.Z. participated in the field investigation; J.T., X.W., P.Z., J.H., and R.T. performed the data processing; J.T., J.L., and W.T. reviewed and edited the draft. All the data were obtained from previous work performed by the project team. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (grant 2016YFC0600107), the projects from the China Geological Survey (grants DD20190379-31, DD20221695-30 and 200110200038), and the Doctoral Research Foundation of Shandong Jianzhu University (grant X21005Z).
Data Availability Statement
All data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Tian, R.C.; Li, D.P.; Zhang, W.; Tian, J.X.; Yu, X.W.; Geng, K.; Zhang, Y. The mixing of Mesozoic crust-mantle magma is the key to the source of large amounts of gold deposits in the Jiaobei uplift, China. Acta Pet. Sin. 2022, 38, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Luo, Z.K.; Liu, X.Y.; Xu, W.D.; Luo, H. Geodynamic setting for formation of large-superlarge gold deposits and Mesozoic granites in Jiaodong area. Miner. Depos. 2005, 24, 361–372. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Yang, L.Q.; Ge, L.S.; Wang, Q.F.; Zhang, J.; Gao, B.F.; Zhou, Y.F.; Jiang, S.Q. Research advances in the Mesozoic tectonic regimes during the formation of Jiaodong ore cluster area. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2006, 16, 777–784. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Wang, C.M.; Bagas, L.; Carranza, E.J.M.; Lu, Y.J. Cretaceous-Cenozoic tectonic history of the Jiaojia Fault and gold mineralization in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China: Constraints from zircon U-Pb, illite K-Ar, and apatite fission track thermochronometry. Min. Depos. 2015, 50, 987–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.R.; Santosh, M. Metallogeny and craton destruction: Records from the North China Craton. Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 56, 376–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.Q.; Deng, J.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhang, L.; Guo, L.N.; Song, M.C.; Zheng, X.L. Mesozoic gold metallogenic system of the Jiaodong gold province, eastern China. Acta Pet. Sin. 2014, 30, 2447–2467. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb, R.J.; Santosh, M. The dilemma of the Jiaodong gold deposits: Are they unique? Geosci. Front. 2014, 5, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.R.; Feng, K.; Li, X.H.; Hu, F.F.; Yang, K.F. Mesozoic gold mineralization in the Jiaodong and Korean peninsulas. Acta Pet. Sin. 2016, 32, 3225–3238. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Song, M.C.; Ding, Z.J.; Zhang, J.J.; Song, Y.X.; Bo, J.W.; Wang, Y.Q.; Liu, H.B.; Li, S.Y.; Li, J.J.; Li, R.X. Geology and mineralization of the Sanshandao supergiant gold deposit (1200 t) in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China: A review. China Geol. 2021, 4, 686–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.C.; Song, Y.X.; Ding, Z.Z.; Li, S.Y. Jiaodong Gold Deposits:Essential Characteristics and Major Controversy. Gold Sci. Technol. 2018, 26, 406–422. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, R.X.; Fan, H.R.; Li, J.W.; Meng, Q.R.; Li, S.R.; Zeng, Q.D. Decratonic gold deposits. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2015, 58, 1523–1537. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.F.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, Z.F.; Dai, L.Q. Mesozoic mafic magmatism in North China: Implications for thinning and destruction of cratonic lithosphere. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2018, 61, 353–385. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.J.; Pirajno, F.; Lai, Y.; Li, C. Metallogenic time and tectonic setting of the Jiaodong gold province, eastern China. Acta Pet. Sin. 2004, 20, 907–922. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.J.; Yan, F. Ore fluid evolution and ore prediction of magmatic hydrothermal gold deposits in Jiaodong area. Conributions Geol. Miner. Resour. Res. 2002, 17, 169–174. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb, R.J.; Hart, C.; Davis, G.; Groves, D. East Asian gold: Deciphering the anomaly of phanerozoic gold in precambrian cratons. Econ. Geol. 2007, 102, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.Z. The Geochemistry of Wallrock Alteration Zone of Gold Deposits—As Exemplified by Jiaodong Gold Deposits; Geology Press: Beijing, China, 1998; pp. 109–122. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, M.G.; Fan, H.R.; Yang, J.H.; Miao, L.C. Large-scale cluster of gold deposits in east shandong: Anorogenic metallogenes. Earth Sci. Front. 2004, 11, 85–98. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Santosh, M.; Li, S.R. The ‘Jiaodong type’ gold deposits: Characteristics, origin and prospecting. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 65, 589–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Wang, Q.F. Gold mineralization in China: Metallogenic provinces, deposit types and tectonic framework. Gondwana Res. 2016, 36, 219–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.C.; Song, Y.X.; Li, J.; Liu, H.B.; Li, J.; Dong, L.L.; He, C.Y.; Wang, R.S. Thermal doming-extension metallogenic system of Jiaodong type gold deposits. Acta Pet. Sin. 2023, 39, 1241–1260. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.C.; Luo, Z.K.; Guan, K.; Huang, J.Z. The implication of the SHRIMP U-Pb age in zircon to the petrogenesis of the Linglong granite, East Shangdong Province. Acta Pet. Sin. 1998, 14, 198–206. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, L.G.; Ren, F.L.; Cao, Z.X.; Zhang, Y.Q. Late mesozoic magmatic activities and their constraints on geotectonics of jiaodong region. Geotecton. Metallog. 2008, 1, 117–123. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.C.; Song, Y.X.; Li, J.; Li, S.Y. Metallogenic series of gold and nonferrous metal deposits related to cretaceous granites in eastern Shandong Peninsula, China. Geotecton. Metallog. 2015, 39, 828–843. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.P. The Mesozoic Gold Polymetallic Regional Metallogeny in Qipengfu Ore Concentration Area, Jiaodong Peninsula. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2020. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Wan, D.F.; Fan, T.Y.; Tian, S.H. The chromium analytical technique for hydrogen isotopes. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2005, 26, 35–38. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.Q.; Zhao, K.D.; Jiang, S.Y.; Chen, W. In-situ sulfur isotope and trace element analysis of pyrite from the Xiwang uranium ore deposit in South China: Implication for ore genesis. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 195, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.L.; Hu, Z.C.; Zhang, W.; Yang, L.; Liu, Y.S.; Li, M.; Zong, K.Q.; Gao, S.; Hu, S.H. In situ sulfur isotopes (δ34S and δ33S) analyses in sulfides and elemental sulfur using high sensitivity cones combined with the addition of nitrogen by laser ablation MC-ICP-MS. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 911, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.Y.; Cook, N.J.; Yang, T.; Ciobanu, C.L.; Zhao, K.D.; Jiang, S.Y. Mapping of Sulfur Isotopes and Trace Elements in Sulfides by LA-(MC)-ICP-MS: Potential Analytical Problems, Improvements and Implications. Minerals 2016, 6, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.E.; Pearson, N.J.; Griffin, W.L.; Belousova, E.A. The application of laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry to in situ U-Pb zircon geochronology. Chem. Geol. 2004, 211, 47–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slama, J.; Kosler, J.; Condon, D.J.; Crowley, J.L.; Gerdes, A.; Hanchar, J.M.; Horstwood, M.S.A.; Morris, G.A.; Nasdala, L.; Norberg, N.; et al. Plesovice zircon—A new natural reference material for U-Pb and Hf isotopic microanalysis. Chem. Geol. 2008, 249, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.S.; Hu, Z.C.; Zong, K.Q.; Gao, C.G.; Gao, S.; Xu, J.A.; Chen, H.H. Reappraisement and refinement of zircon U-Pb isotope and trace element analyses by LA-ICP-MS. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2010, 55, 1535–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, T. Correction of common lead in U–Pb analyses that do not report 204 Pb. Chem. Geol. 2002, 192, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, K.R. User’s Manual for Isoplot 3.75, A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel; Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2012; Volume 5, pp. 1–75. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.G.; Liu, H.B.; Li, G.Z.; Xiao, Z.B.; Tu, J.R.; Li, H.M. The Application of Ion Exchange Resins in Sr-Nd Isotopic Assay of Geological Samples. Acta Geol. Sin. 2017, 91, 2584–2592. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Clayton, R.N.; O’Neil, J.R.; Mayeda, T.K. Oxygen isotope exchange between quartz and water. J. Geophys. Res. 1972, 77, 3057–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.L.; Jiang, S.Y.; Jiang, Y.H.; Ling, H.F. S-Pb isotope geochemistry and Rb-Sr geochronology of the Penglai gold field in the eastern Shangdong province. Acta Pet. Sin. 2006, 22, 2525–2533. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.F. GeoKit—A geochemical toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Geochimica 2004, 33, 459–464. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Simmons, S.F.; Sawkins, F.J.; Schlutter, D.J. Mantle-derived helium in two Peruvian hydrothermal ore deposits. Nature 1987, 329, 429–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugh, P.; Taylor, J.R. The Application of Oxygen and Hydrogen Isotope Studies to Problems of Hydrothermal Alteration and Ore Deposition. Econ. Geol. 1974, 69, 843–883. [Google Scholar]
- Ohmoto, H. Stable isotope geochemistry of ore deposits. Rev. Mineral. 1986, 16, 491–559. [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard, S.M.F. Characterization and isotopic variations in natural waters. Reviews of Mineralogy. Rev. Mineral. 1986, 16, 165–183. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.W.; Li, H.M.; Wang, Y.T.; Zhang, C.Q.; Wang, R.T. The relationship between mantle-drived fluid gold ore-formation in the eastern Shandong peninsula: Evidences from D-O-C-S isotopes. Acta Pet. Sin. 2005, 79, 839–857. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Baptiste, P.J.; Fouquet, Y. Abundance and isotopic composition of helium in hydrothermal sulfides from the East Pacific Rise at 13 °N. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trull, T.W.; Kurz, M.D.; Jenkins, W.J. Diffusion of cosmogenic 3He in olivine and quartz: Implications for surface exposure dating. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1991, 103, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podosek, K.A.; Bernatowica, T.J.; Kramer, F.E. Absorption of xenon and krypton on shales. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1980, 45, 2401–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, G.; Stuart, F. Helium/heat ratios and deposition temperatures of sulphides from the ocean floor. Nature 1992, 375, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolstikhin, I.N. A Review—Some Recent Advances in Isotope Geochemistry of Light Rare Gases. Adv. Earth Planet. Sci. 1978, 3, 33–62. [Google Scholar]
- Mamyrin, B.A.; Tolstikhin, I.N. Helium Isotopes in Nature; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1984; pp. 1–273. [Google Scholar]
- Ballentine, C.J.; Burgess, R.; Marty, B. Tracing fluid origin, transport and interaction in the crust. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2002, 47, 539–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnard, P.G.; Hu, R.Z.; Turner, G.; Bi, X.W. Mantle, crustal and atmospheric noble gases in Ailaoshan Gold deposits, Yunnan Province, China. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta J. Geochem. Soc. Meteorit. Soc. 1999, 63, 1595–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Liu, Y.L.; Huang, B.L.; Chen, Y.J. The characteristics of noble gases in mantle-derived xenoliths in Wudalianchi and Kuandian, NE China: MORB-like mantle and metasomated mantle. Acta Pet. Sin. 2005, 21, 1373–1381. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kendrick, M.A.; Burgess, R.; Pattrick, R.A.D.; Turner, G. Fluid inclusion noble gas and halogen evidence on the origin of Cu-Porphyry mineralising fluids. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2001, 65, 2651–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, T.; Chen, Y.l.; Matsuda, J.I. Concomitant occurence of primordial and recycled noble gasesin the Earth’s mantle. Earth Planet Sci. Lett. 2001, 185, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautheron, C.; Moreira, M.; Allegre, C. He, Ne and Ar composition of the European lithospheric mantle. Chem. Geol. 2005, 217, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopp, J.; Ionov, D.A. Tracing partial melting and subduction-related metasomatism in the Kamchatkan mantle wedge using noble gas compositions. Earth Planet Sci. Lett. 2011, 302, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadley, M.W.; Ballentine, C.J.; Chavrit, D.; Dallai, L.; Burgess, R. Sedimentary halogens and noble gases within Western Antarctic xenoliths: Implications of extensive volatile recycling to the sub continental lithospheric mantle. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2016, 176, 139–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoefs, J. Stable Isotope Geochemistry, 6th ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 72. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, T.Z.; Zhao, L.S.; Yang, M.Z. Gold mineralization and its evolution in the Muping-Rushan gold deposits, Shandong province. Geotecton. Metallog. 2001, 25, 155–160. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.W.; Zhu, F.S.; Gong, R.T. Tectonic isotope geochemistry--Further study on sulphur isotope of Jiaodong Gold Concentration Area. Gold 2002, 23, 1–16. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Liu, X.F.; Wang, Q.F.; Pan, R.G. Origin of the Jiaodong-type Xinli gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China: Constraints from fluid inclusion and C-D-O-S-Sr isotope compositions. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 65, 674–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.L.; Yang, M.Z. The Geology-Geochemistry of Gold Deposits in Jiaodong Region; Tianjin Science and Technology Press: Tianjin, China, 1993; pp. 1–300. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.Y. Sulfur isotope studies of the metallogenic series of gold deposits in Jiaodong area. Miner. Depos. 1994, 13, 75–86. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, K.X.; Hu, R.Z.; Bi, X.W.; Peng, J.T.; Tang, Q.L. Ore lead isotopes as a tracer for ore-forming material sources: A review. Geol.-Geochem. 2002, 30, 73–81. [Google Scholar]
- Stacey, J.S.; Kramers, J.D. Approximation of terrestrial lead isotope evolution by a two stage model. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1975, 26, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doe, B.R.; Zartman, R.E. Plumbotectonics, the Phanerozoic. In Geochemistry of Hydrothermal Ore Deposits; Barnes, H.L., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1979; pp. 22–70. [Google Scholar]
- Zartman, R.E.; Doe, B.R. Plumbotectonics—The model. Tectonophysics 1981, 75, 135–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, M.; Caridroit, M.; Charvet, J. The Late Jurassic oblique collisional orogen of SW Japan: New structural data and synthesis. Tectonics 1986, 5, 1089–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.L. Sr and O Isotopic Characteristics of Porphyries in the Qinling Molybdenum Deposit Belt and Their Implication to Genetic Mechanism and Type. Ph.D. Thesis, Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu, China, 2001. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Hou, M.L.; Jiang, Y.H.; Jiang, S.Y.; Ling, H.F.; Zhao, K.D. Contrasting origins of late Mesozoic adakitic granitoids from the northwestern Jiaodong Peninsula, east China: Implications for crustal thickening to delamination. Geol. Mag. 2007, 144, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.F.; Fan, H.R.; Santosh, M.; Hu, F.F.; Wilde, S.A.; Lan, T.G.; Lu, L.N.; Liu, Y.S. Reactivation of the Archean lower crust: Implications for zircon geochronology, elemental and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic geochemistry of late Mesozoic granitoids from northwestern Jiaodong Terrane, the North China Craton. Lithos 2012, 146, 112–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Fan, H.R.; Zhang, Y.W.; Hu, F.F.; Yang, K.F.; Liu, X.; Cai, Y.C.; Zhao, K.D. Rapid exhumation of the northern Jiaobei Terrane, North China Craton in the Early Cretaceous: Insights from Al-in-hornblende barometry and U-Pb geochronology. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2018, 160, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Qiu, K.F.; Wang, Q.F.; Goldfarb, R.; Yang, L.Q.; Zi, J.W.; Geng, J.Z.; Ma, Y. In Situ Dating of Hydrothermal Monazite and Implications for the Geodynamic Controls on Ore Formation in the Jiaodong Gold Province, Eastern China. Econ. Geol. 2020, 115, 671–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.F.; Jiang, P.; Fan, H.R.; Zuo, Y.B.; Yang, Y.H. Tectonic transition from a compressional to extensional metallogenic environment at similar to 120 Ma revealed in the Hushan gold deposit, Jiaodong, North China Craton. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2018, 160, 408–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Weinberg, R.F.; Yang, L.Q.; Groves, D.I.; Sai, S.X.; Matchan, E.; Phillips, D.; Kohn, B.P.; Miggins, D.P.; Liu, Y.; et al. Mesozoic Orogenic Gold Mineralization in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China: A Focused Event at 120 +/− 2 Ma During Cooling of Pregold Granite Intrusions. Econ. Geol. 2020, 115, 415–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.R.; Zhai, M.G.; Xie, Y.H.; Yang, J.H. Ore-forming fluids associated with granite-hosted gold mineralization at the Sanshandao deposit, Jiaodong gold province, China. Min. Depos. 2003, 38, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.J.; Fan, H.R.; Santosh, M.; Hu, F.F.; Pirajno, F.; Yang, K.F. Genesis of two different types of gold mineralization in the Linglong gold field, China: Constrains from geology, fluid inclusions and stable isotope. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 65, 643–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.W.; Vasconcelos, P.M.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, M.F.; Zhang, X.J.; Yang, F.H. 40Ar/39Ar constraints on a temporal link between gold mineralization, magmatism, and continental margin transtension in the Jiaodong Gold Province, eastern China. J. Geol. 2003, 111, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, N.; Augier, R.; Gumiaux, C.; Monie, P.; Chen, Y.; Faure, M.; Zhu, R.X. Timing, duration and role of magmatism in wide rift systems: Insights from the Jiaodong Peninsula (China, East Asia). Gondwana Res. 2013, 24, 412–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Fan, H.R.; Groves, D.I.; Yang, K.F.; Hu, F.F.; Liu, X.; Cai, Y.C. Geochronological and sulfur isotopic evidence for the genesis of the post-magmatic, deeply sourced, and anomalously gold-rich Daliuhang orogenic deposit, Jiaodong, China. Min. Depos. 2020, 55, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.M.; Wang, H.M.; Rao, B. Partial melting experiments of Jiaodong Group and their implication for the origin of the granites. Geochimica 2000, 2, 153–161. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.H.; Zhou, X.H. The Rb-Sr isochron of ore and pyrite sub-samples from Linglong gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China and their geological significance. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2000, 45, 2272–2277. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.H.; Chu, M.F.; Liu, W.; Zhai, M.G. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of Guojialing granodiorites from the northwestern Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China. Acta Pet. Sin. 2003, 19, 692–700. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama, S.; Isozaki, Y.; Kimura, G.; Terabayashi, M. Paleogeographic maps of the Japanese Islands: Plate tectonic synthesis from 750 Ma to the present. Isl. Arc. 1997, 6, 121–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Niu, M.L.; Xie, C.L.; Wang, Y.S. Sinistral to Normal Faulting along the Tan-Lu Fault Zone: Evidence for Geodynamic Switching of the East China Continental Margin. J. Geol. 2010, 118, 277–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).