Abstract
A topological index is a numeric quantity associated with a chemical structure that attempts to link the chemical structure to various physicochemical properties, chemical reactivity, or biological activity. Let be a commutative ring with identity, and is the set of all non-zero zero divisors of . Then, is said to be a zero-divisor graph if and only if , where and . We define if or . Then, ∼ is always reflexive and symmetric, but ∼ is usually not transitive. Then, is a symmetric structure measured by the ∼ in commutative rings. Here, we will draw the zero-divisor graph from commutative rings and discuss topological indices for a zero-divisor graph by vertex eccentricity. In this paper, we will compute the total eccentricity index, eccentric connectivity index, connective eccentric index, eccentricity based on the first and second Zagreb indices, Ediz eccentric connectivity index, and augmented eccentric connectivity index for the zero-divisor graph associated with commutative rings. These will help us understand the characteristics of various symmetric physical structures of finite commutative rings.
MSC:
05C09; 05C25; 13A70
1. Introduction
Chemical graph theory is an area of mathematics that deals with the non-trivial applications of molecular problems. Chemical graph theory is an interdisciplinary science that studies molecular structures using graph theory and attempts to identify structural features involved in structure–property activity relationships using tools from graph theory, set theory, and statistics [1,2,3]. The topological characterization of chemical structures with the desired properties can be used to classify molecules and model unknown structures. In recent decades, much research has been conducted in this field. The topological index is a numerical value associated with chemical structures that purport to link chemical structures to various physicochemical properties, chemical reactivity, or biological activity. Topological indices are based on transforming a molecular graph into a number that describes the topology of the molecular graph [4,5,6,7]. Molecular modeling investigates the relationship between a chemical compound’s structure, properties, and activity. Molecular graphs are frequently used to represent molecules and molecular compounds. A chemical graph is a model for describing the properties of a chemical compound. A molecular graph is a simple graph with vertices representing atoms and edges representing bonds. It can be represented by a drawing, a polynomial, a series of numbers, a matrix, or a derived number known as a topological index, which was first introduced by Wiener [8] in 1947.
2. Definitions and Notations
A non-empty set is said to be a ring if is an abelian group, and is a semi group and satisfies two distributive laws. A ring is a commutative ring if . An element of a commutative ring is said to be zero-divisor if there exists an element in such that . The zero-divisor graph was first introduced in 1988 by Beck [9] where he considered the set of vertices as zero divisors including zero, with an edge set defined by . Later, in 1999, Anderson and Livingston [10] continued their investigation of zero-divisor graphs, but this time they only examined non-zero zero divisors and constructed the zero-divisor graph as a simple graph with all non-zero zero divisors as vertices and an edge set defined by , denoted by .
Let be a commutative ring with identity, and is the set of all non-zero zero divisors of . Then, is said to be a zero-divisor graph if and only if where and .
In a graph , distance is the number of edges in the shortest path between a vertex a and b. Eccentricity is considered to be the maximum distance from a vertex to all other vertices, and degree is the number of edges adjacent to a vertex a and the minimum vertex degree in a graph is denoted by , and the maximum vertex degree is denoted by . Furthermore, the degree sequence is a monotonic, non-increasing sequence of the vertex degrees of the graph vertices.
Farooq, and Malik [11] introduced the total eccentricity index, which is defined as
The eccentric connectivity index was introduced by Sharma et al. [4] which is defined as
The connective eccentric index was introduced by Gupta, Singh, and Madan [6] which is defined as
The eccentricity-based Zagreb indices were introduced by Ghorbani, and Hosseinzadeh [12] which are defined as
and
The Ediz eccentric connectivity index was introduced by Ediz [5] which is defined as
where
The augmented eccentric connectivity index was introduced by Gupta, Singh, and Madan [6] which is defined as
where .
3. Results
Let be a ring and be the ideal of , then the set of all cosets forms a ring known as a factor ring. Let be a polynomial of a commutative ring and be the factor ring. Here, we consider the finite commutative rings and to investigate some topological indices such as total eccentricity index, eccentric connectivity index, connective eccentric index, eccentricity based on first and second Zagreb indices, Ediz eccentric connectivity index and augmented eccentric connectivity index of zero-divisor graph for the commutative rings.
For with any prime , then be a zero-divisor graph with zero divisors of considered to be vertices and edges.
Then,
Now, the vertex set has been divided by
Additionally, and are subdivided by
It is clear to see that if , then every vertex is adjacent to each other in A, if , then every vertex in A is adjacent to every vertex in B and if , then every vertex in A is adjacent to every vertex in C.
In addition, if , then every vertex is adjacent to each other in . Similarly, it holds for . However, , then no vertex in is adjacent to vertex in .
Additionally, if then is adjacent to in but no two or has zero product by modulo or in . Similarly, it holds for .
For example, then we have a graph in Figure 1.
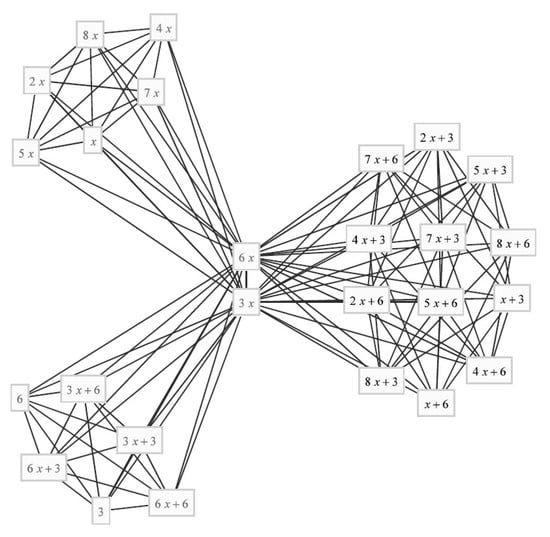
Figure 1.
.
The vertex set has been divided by
Lemma 1.
Let be a zero-divisor graph with any prime . Then,
where and are degree sequences and their eccentricity sequences of .
Theorem 1.
Let be a zero-divisor graph with any prime . Then,
Proof.
Let be a zero-divisor graph with vertices and edges. Then,
By Lemma 1, we have
It is clear that is adjacent to all divisors of , then and .
However, is adjacent only to divisors in A & B, then and .
Additionally, is adjacent to divisors in A and & C but no two or has zero product by modulo or in C. and .
□
Theorem 2.
Let be a zero-divisor graph with any prime . Then,
and
Proof.
By Lemma 1, we have
and
and
and
and
and
and
and
and
□
Theorem 3.
Let be zero-divisor graph with any prime . Then,
Proof.
By Lemma 1, we have
and
and
and
where
where
□
For with any prime , then be a zero-divisor graph with zero divisors of considered as a vertices and edges.
Then
By using these vertices, there exists an edge defined between a and b by and .
It is clear to see that if , then every vertex is adjacent to each other in . Similarly, it holds and . In addition, if or then every vertex in is adjacent to every vertex in . Similarly, every vertex in is adjacent to every vertex in and every vertex in is adjacent to every vertex in . Additionally, every vertex in is adjacent to every vertex in .
For example, if and , then we have a graph in Figure 2.
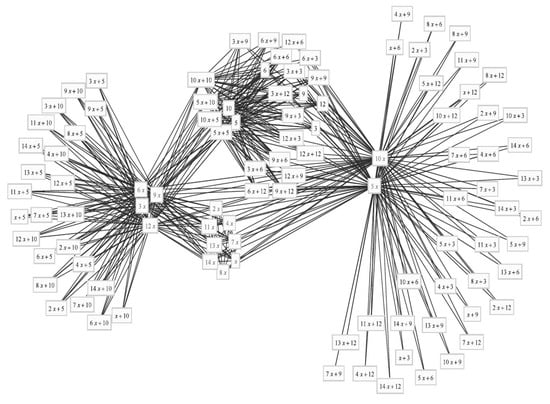
Figure 2.
.
The vertex set has been divided by
Lemma 2.
Let be a zero-divisor graph with any prime . Then,
where and are degree and eccentricity sequences of .
Theorem 4.
Let be a zero-divisor graph with any prime . Then
Proof.
Let be zero-divisor graph with zero divisors of vertices and edges.
By Lemma 2, we have
□
Theorem 5.
Let be a zero-divisor graph with any prime . Then,
and
Proof.
By Lemma 2, we have
□
Theorem 6.
Let be a zero-divisor graph with any prime . Then,
and
Proof.
By Lemma 2, we have
where
where
□
4. Discussions and Applications
Algebraic structures were investigated separately because of their strong links to representation theory and number theory, as well as their widespread use in combinatorics [2,3]. As a result of extensive mathematical research in this area, finite rings and fields have received a significant amount of focus for their applications to cryptography and coding theory [13,14,15,16].
Here, we investigated the eccentricity-based indices associated with factor ring and obtained the zero-divisor graph of the factor rings and .
Let be a zero-divisor graph with prime , then and
Let be a zero-divisor graph with prime , then and
These values help understand the characteristics of various symmetric physical structures of finite commutative rings and have received significant focus for their applications to cryptography and coding theory. They may also help design strong symmetric physical structures for robotics and identify computer network issues associated with speed, distance, and time. This research will aid in the understanding the properties of various physical structures such as carbohydrates, silicone structures, polymers, hexagonal chains, and cylindrical fullerenes [17,18,19]. They can also create a productive physical design in mechanics and solve various computer network problems.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, we explored various topological indices and discussed the total eccentricity index, eccentric connectivity index, connective eccentric index, eccentricity based on the first and second Zagreb indices, Ediz eccentric connectivity index, and augmented eccentric connectivity index for the zero-divisor graph associated with commutative rings. Additionally, we showed that the boundaries are related to topological indices for the zero-divisor graph.
Author Contributions
C.J.R. contributes for conceptualization, methodology, software, and writing-original draft preparation. R.S.J. contributes for supervision, validation, formal analysis, writing-review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Vellore Institute of Technology, Vellore—632014.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors like to thank the management of VIT University for their support to carry out this research work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ali Koam, N.A.; Ali, A.; Azeem, H. On eccentric topological indices based on edges of zero divisor graphs. Symmetry 2019, 11, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkaew, S.; Boonklurb, R. k-Zero-Divisor and Ideal-Based k-Zero-Divisor Hypergraphs of Some Commutative Rings. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Rather, B.A.; Fatima, N.; Sarfraz, M.; Ullah, A.; Alharbi, K.A.M.; Dad, R. On the topological indices of commuting graphs for finite non-Abelian groups. Symmetry 2022, 14, 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Goswami, R.; Madan, A.K. Eccentric connectivity index: A novel highly discriminating topological descriptor for structure property and structure activity studies. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1997, 37, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ediz, S. On the Ediz eccentric connectivity index of a graph. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. Rapid Commun. 2011, 5, 1263–1264. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.; Singh, M.; Madan, A.K. Connective eccentricity index: A novel topological descriptor for predicting biological activity. J. Mol. Graph. Modelling 2000, 18, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Singh, M.; Madan, A.K. Application of graph theory: Relationship of eccentric connectivity index and Wiener’s index with anti-inflammatory activity. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2002, 266, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiener, H. Structural determination of paraffin boiling points. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1947, 69, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, I. Coloring of commutative rings. J. Algebra 1988, 116, 208–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.F.; Axtell, M.C.; Stickles, J.A. The zero-divisor graph of a commutative ring. J. Algebra 1999, 217, 434–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, R.; Malik, M.A. On some eccentricity based topological indices of nanostar dendrimers. Optoelectron. Adv.-Mater.-Rapid Commun. 2015, 9, 842–849. [Google Scholar]
- Ghorbani, M.; Hosseinzadeh, M.A. A new version of Zagreb indices. Filomat 2012, 26, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Bhat, V.K. Adjacency matrix and Wiener index of zero divisor graph Γ(Zn). J. Appl. Math. Comput. 2021, 66, 717–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rather, B.A.; Pirzada, S.; Naikoo, T.A.; Shang, Y. On Laplacian eigenvalues of the zero-divisor graph associated to the ring of integers modulo n. Mathematics 2021, 9, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rather, B.A.; Ali, F.; Ullah, A.; Fatima, N.; Dad, R. Aγ eigenvalues of zero divisor graph of integer modulo and Von Neumann regular rings. Symmetry 2022, 14, 1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppan, A.; Ravi Sankar, J. Prime Decomposition of Zero Divisor Graph in a Commutative Ring. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2022, 2152513. Available online: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/mpe/2022/2152513/ (accessed on 24 September 2022). [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.R.; Jahani-Nezhad, R. Energy and Wiener index of zero divisor graph Γ(Zn). Iran. J. Math. Chem. 2011, 2, 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Elahi, K.; Ahmad, A.; Hasni, R. Construction algorithm for zero divisor graphs of finite commutative rings and their vertex-based eccentric topological indices. Mathematics 2018, 6, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadini, A.A.H.; Koam, A.N.; Ahmad, A.; Bača, M.; Semaničová–Feňovčíková, A. Computing Vertex-Based Eccentric Topological Descriptors of Zero-Divisor Graph Associated with Commutative Rings. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 2056902. Available online: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/mpe/2020/2056902/ (accessed on 24 August 2020). [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).