Abstract
Stochastic SIRS models play a key role in formulating and analyzing the transmission of infectious diseases. These models reflect the environmental changes of the diseases and their biological mechanisms. Therefore, it is very important to study the uniqueness and existence of the global positive solution to investigate the asymptotic properties of the model. In this article, we investigate the dynamics of the stochastic SIRS epidemic model with a saturated incidence rate. The effects of both deterministic and stochastic distribution from infectious to susceptible are analyzed. Our findings show that the occurrence of symmetry breaking as a function of the stochastic noise has a significant advantage over the deterministic one to prevent the spread of the infectious diseases. The larger stochastic noise will guarantee the control of epidemic diseases with symmetric Brownian motion. Periodic outbreaks and re-infection may occur due to the existence of feedback memory. It is shown that the endemic equilibrium is stable under some suitable initial conditions, taking advantage of the symmetry of the large amount of contact structure. A numerical method based on Legendre polynomials that converts the given stochastic SIRS model into a nonlinear algebraic system is used for the approximate solution. Finally, some numerical experiments are performed to verify the theoretical results and clearly show the sharpness of the obtained conditions and thresholds.
1. Introduction
Mathematical models became a vital tool after the fundamental work of McKendrick and Kermack []. This study seeks to learn about the causes and the control of infectious diseases. In ecological systems, random changes in the external environment constantly influence the human power. For example, models of the rate of disease transmission during an epidemic have been modified for a number of meteorological factors, such as the survival and spread of many viruses and bacteria in wet conditions and the amount of ultraviolet (UV) light [,,]. Growth of the population and environmental impacts tend to combine with changes in the range of food supplies, which in turn is largely affected by unpredictable precipitation fluctuations []. In the literature, a very popular method is to randomly change modes in such a way that the Markov chain continuous-time values are separated with values in space in a finite state, which leads a change in basic parameters with the Markov chain state switching [,,]. The dynamical system becomes regime switching via a mathematical equation in the form of Markov process, which is piecewise deterministic. Based on a biological system in terms of stochastic environmental circumstances, the epidemic models along with their deterministic primary parameters are not likely to be realistic. It is essential to examine the disease effect of irregular mutations in natural psychological states on the spread of the infection in the proposed population. Despite the significance of environmental noise, it has gained little consideration in the literature on infectious diseases. Initially, Gray, Greenhalgh and Mao et al. proposed an epidemic SIS model for Markovian switching []. For time discretization, some authors obtained reliable results taking the irregular switching of environmental regimes [,]. For the approximate solution of the stochastic differential models, some authors used LSCM [,]. Moreover, Legendre polynomials are also used for the numerical approximation of integrals, as well as differential equations [,,,,]. The effect of Markov switching on a deterministic SIRS model is investigated in []. Due to the COVID-19 epidemic, SIRS stochastic models became more essential and many scholars have adopted them to study the transmission of COVID-19. For example, in [], the authors used the classical deterministic SIR epidemic model to construct a more compatible model for COVID-19 transmission. Differential equations of fractional order for the mathematical modeling of COVID-19 were used by Khan et al., where they provided a detailed analysis by considering Saudi Arabia as a case study []. An approach based on piecewise differential and integral operators was developed by Atangana, Seda and Prolonger [,]. The dynamics of COVID-19 with the fuzzy Caputo approach are discussed in []. In all these works, the authors used deterministic approaches to formulate mathematical models for the transmission of COVID-19. However, these models have some limitations in describing the reality compared with the stochastic models, because the system parameters are not constant and fluctuate around an average value [].
The connection between the Lie symmetry of a SIRS stochastic differential equation and its integrability is established in []. The derived equation is used to find the admitted Lie point symmetries of the stochastic SIRS model. We provide the message passing system of equations for this model and prove, for the first time, that it has a unique feasible solution. A generalized upper bound is obtained for the expected epidemic size at a fixed time , where the graph (network) is symmetric with a homogeneous special case in []. In real life, external fluctuation is a key factor in the transmission of epidemic diseases. Therefore, it is important to include the randomness in the model, and hence stochastic SIRS models are considered to be more practical and realistic to study and simulate the evaluation of any epidemic disease. A great deal of work has been done on the application of stochastic SIRS models in epidemiology [,,,,,,,,,,,,,,].
The aim of this work is to improve numerous studies existing in the field of stochastic SIRS models and provide an alternative technique to treat and analyze more complex biological and epidemiological models. To this end, we use a stable, robust and efficient numerical technique based on the Legendre collocation method with theoretical justifications.
The classical deterministic SIR epidemic model is given by:
In the proposed model, we observe that the whole population is divided into a further three categories: the first category is susceptible S(t), the second one is infectious I(t) and the last one is recovered R(t). All the parameters are assumed to be positive. Constant recruitment of new susceptible individuals is denoted by , where is the transmission rate; shows the per-capita natural mortality rate; disease causing mortality is denoted by ; the rate of recovery of the infected individuals per capita is denoted by ; hosts initially recovered are immune. The loss of immunity is denoted by , by the symmetry of Brownian motion []. Using the invariance principle of LaSalle, the basic reproduction number are influenced by threshold dynamics. If , then Equation (1) would indicate disease-free equilibrium and will be stable asymptotically, and otherwise, endemic equilibrium of the proposed system will be stable when reproduction number . The stochastic perturbations are assumed to be white noise. The system given in Equation (1) can be extrapolated to the following stochastic SIRS model:
where the initial conditions are
are independent standard Brownian motion, where the intensities of are denoted by . This study includes the solution of the stochastic SIRS model in Equation (2) using the Legendre spectral collocation method (LSCM). Many authors have been used Legendre polynomials and their operational matrix for the approximation of integral and differential equations [,].
Sections of this research article are organized as follows: Section 2 includes a concise description of Legendre polynomials and the description of the scheme to solve the proposed model. Section 3 consists of stability analysis of the SIRS model. Numerical results and discussion are given in Section 4, while conclusions are drawn in Section 5.
2. Description of the Method
Before we describe the proposed scheme in detail for the stochastic SIRS model given in (2), we first briefly discuss Legendre polynomials.
Legendre Polynomials
Consider the Nth order Legendre polynomial, which is denoted by . We use Legendre interpolating polynomials to approximate any function in interval, which are defined as
where are interpolating points and satisfy
and denotes unknown Legendre coefficients, and Nth Legendre polynomials are denoted by and defined as
To solve the proposed model given in Equation (2), we use Legendre Gauss quadrature along with a weight function. We consider, for the LSCM, the Legendre Gauss Lobatto points .
Our aim in this study is to develop an efficient approximate solution to Equation (2). Integrating Equation (2) from , we obtain
where and are initial conditions for the functions and , respectively. Taking linear transformation to analyze the LSCM over standard interval on Equation (5), we obtain
The spectral equations (semi-discretized) of Equation (6) are given by
where Legendre Gauss quadrature with weights is
Similarly, is the stochastic weight function.
To find the approximate solution for each class, we use the Legendre polynomials given in Equation (3):
In the above equation, Legendre coefficients of each class are denoted by and , respectively. Incorporating Equation (8) into Equation (7), we have
taking for simplicity. Thus, there are unknowns in the system given in Equation (9) with non-linear algebraic equations. After incorporating the initial conditions, we obtain
These two equations—Equations (9) and (10)—consist of non-linear systems of algebraic equations having variables (unknowns). We obtain a numerical solution to the system given in Equation (2) by incorporating the values of these unknowns into Equation (8).
3. Stability Analysis
In this section, we take into account both the stochastic SIRS model of Equation (2) and the deterministic SIRS model of Equation (1) considering saturated incident rate and a time describing inherent period. The basic reproduction number for Equation (1) is defined by Below, we have given some important results about the basic reproduction number.
Theorem 1.
Proof.
Let the endemic equilibrium of the system given in Equation (1) be , and the given classes satisfy the stationary system
We will consider two cases. Case 1: ; case 2: .
- Case 2: Here, . In this case, the calculation has been done using Maple software version 13. We successfully obtain the following stable endemic equilibrium :and
Thus, if , we must have , which implies that . This means that we must ensure that . This completes the proof of the theorem. □
Lemma 1.
Initial values , for the system given in Equation (2), have almost surely a unique positive solution for .
Lemma 2.
Total region are positive; have a positively invariant solution for the proposed system given in Equation (2).
Proof.
As the total population are , differentiating and using Equation (2), we obtain the following:
Integrating and using the initial values gives
□
Lemma 3.
Using the initial conditions, the solution of of the system in Equation (2) satisfies the following properties:
Definition 1.
The infected class “I(t)” is said to be extinctive if .
Let us propose
and we have the theorem as given below.
Theorem 2.
When or along , then infected class of the above stochastic system given in Equation (2) exponentially approaches zero. Here,
Proof.
Consider the solution of the above system given in Equation (2) entertaining the initial conditions . Then, by using the It formula, we find
Now, taking the integration of the system in Equation (3) from 0 to t shows
Here, we discuss two cases:
Theorem 3.
If , then are present in Equation (2).
Proof is given in [].
Remark 1.
After the above discussion, we can make the following remarks. Making use of Theorem 1, Equation (1) is disease-free if and it has a unique endemic equilibrium if . By Theorem 2, if , the infectious disease in the system of Equation (2) is almost surely extinct, whereas the system in (2) has a disease-free equilibrium for small intensities and , which shows that is the threshold dynamics along with the extinction of of infectious diseases.
4. Numerical Discussion
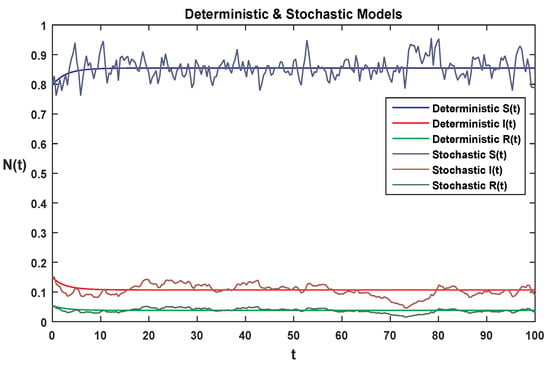
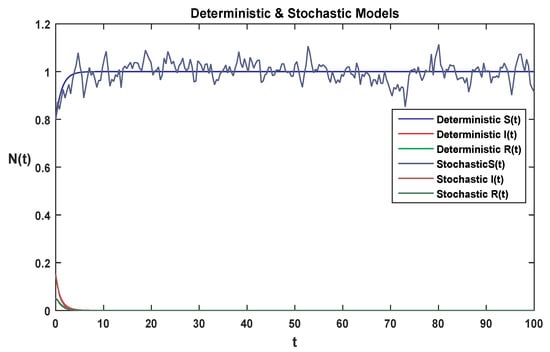
Numerical simulations are performed using our proposed numerical scheme for both the deterministic and stochastic SIR models to show the different behaviors of reproduction number using different parameter values involved in both mathematical models shown in Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8. In all simulations, we use . In Figure 1, we use the parameter values , . For each class, we compare both the models given in Equations (1) and (2), respectively. Using the above parameter values, simple calculation shows that both reproduction numbers and . Using Theorems 1 and 2, we clearly observe in Figure 1 that the given systems have a stable disease-free equilibrium , where the susceptible class is . The parameter values , were used to obtain Figure 2. For each class, we compare both the models given in Equations (1) and (2), where calculation gives and . Applying Theorems 1 and 2, both systems in Equations (1) and (2) have stable endemic equilibrium . Moreover, Figure 2 shows that all the classes are greater than zero. Using parameter values in Equation (1), Figure 3 is obtained with reproduction number . Using Theorem 1, we notice from Figure 3 that the given systems satisfy the disease-free equilibrium. Moreover, the susceptible class is given by and all the remaining classes approach zero. For Figure 4, we use parameter values and we draw the numerical solution of the deterministic system given in Equation (1), with reproduction number . Again, using Theorem 1, Figure 4 satisfies the stable endemic equilibrium. Moreover, all the classes become greater than zero. Figure 5 is obtained using the parameter values in Equation (1), with reproduction number . Now, using Theorem 2, we observe from Figure 5 that the given systems satisfy the disease-free equilibrium. Moreover, the susceptible class is given by and all the remaining classes approach zero. Using parameter values, the result is as shown in Figure 6. The numerical solution of the stochastic system given in Equation (1) is obtained with . Again, by Theorem 2, Figure 6 shows that the systems satisfy the stable endemic equilibrium. Moreover, all the classes become greater than zero. Using the parameter values and and , Figure 7 is obtained. By Theorem 2, Figure 7 satisfies the disease-free equilibrium. Moreover, the susceptible class is given by and all the remaining classes approach zero. For the parameter values , the numerical solution for both systems given in Equations (1) and (2) with reproduction numbers and is as shown in Figure 8. Now, by using Theorem 2, we evidently notice from Figure 8 that the given systems satisfy the stable endemic equilibrium. Moreover, all the classes become greater than zero.
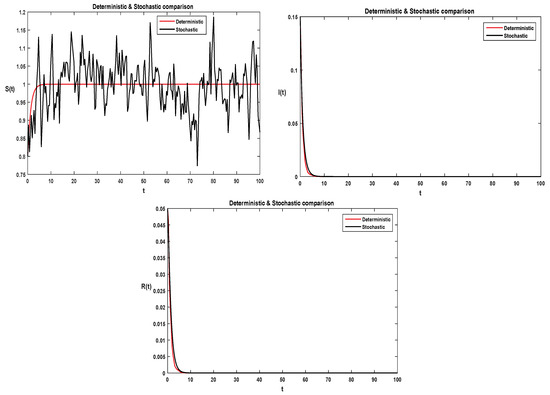
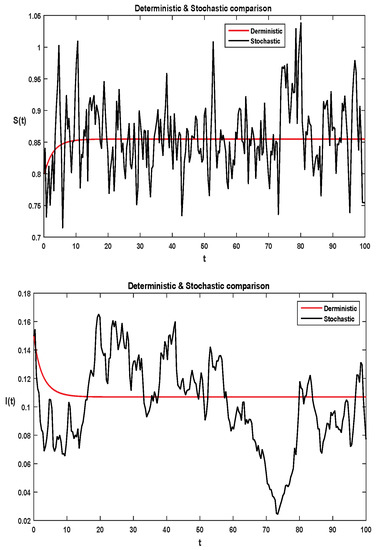
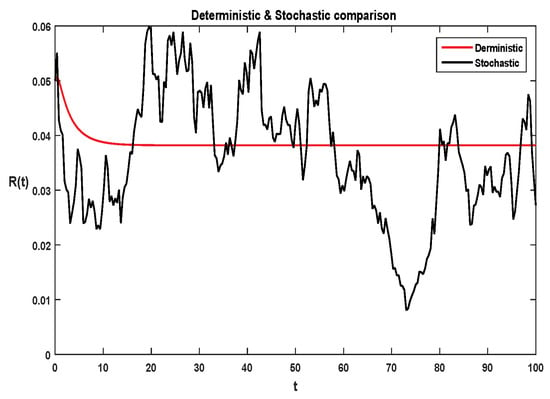
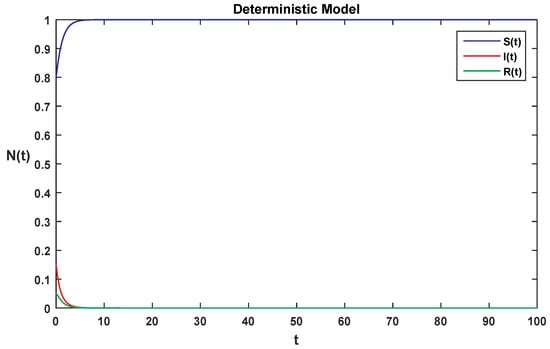
Figure 3.
Solution for each class of deterministic system Equation (1), where is less than 1.
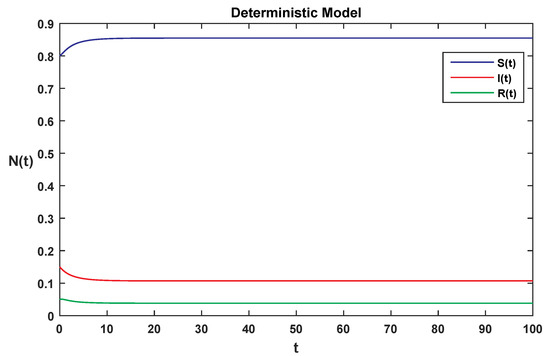
Figure 4.
Solution for each class of deterministic system Equation (1), where is greater than 1.
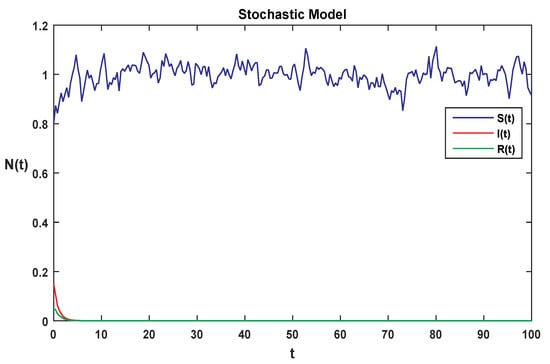
Figure 5.
Solution for each class of stochastic system Equation (2), where is less than 1.
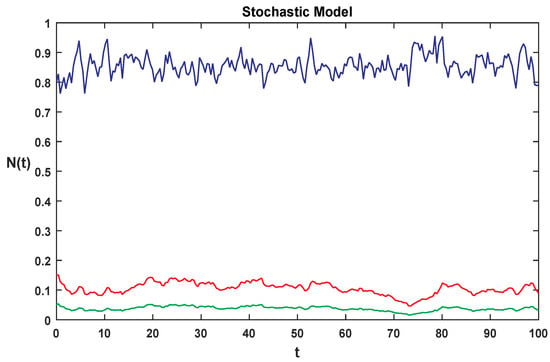
Figure 6.
Solution for each class of stochastic system Equation (2), where is greater than 1.
5. Conclusions
The Legendre spectral method and its orthogonal properties are used to obtain the numerical solution to the proposed SIRS model along with stochastic/random phenomena. To evaluate the integral term more efficiently, Legendre Gauss quadrature along with the weight function are used. Different behavior of the basic reproduction number was observed. It is shown that infected classes approach zero when the reproduction number and the disease-free equilibrium is found. It is observed that the system gives unique stable equilibrium when the reproduction number . Very good agreement between the solutions of both the stochastic and deterministic systems is found. The assumption of the strong symmetry of the initial conditions and parameter values plays a key role in the analysis of the SIRS stochastic model. Our simulations show that the extinction conditions of the disease are weaker in the case of stochastic white noise as compared to its deterministic counterpart. Our findings also show that the rate of saturated incidence has a crucial role in controlling the spread of the disease within the population, which confirms that stochastic epidemic models based on virus dynamics are more realistic as compared to their deterministic counterparts. Our theoretical results provide a solid foundation for the study of similar diseases and has a wide range of applications in the field of biomedical sciences. Our future goal is to apply spectral methods to stochastic SIRS models of fractional order.
Author Contributions
Both authors contributed equally to this work. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Deanship of Scientific Research, Vice Presidency for Graduate Studies and Scientific Research, King Faisal University, Saudi Arabia [Project No. GRANT644].
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Deanship of Scientific Research, Vice Presidency for Graduate Studies and Scientific Research, King Faisal University, Saudi Arabia [Project No. GRANT644].
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kermack, W.O.; McKendrick, A.G. A contribution to the mathematical theory of epidemics. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. 1927, 115, 700–721. [Google Scholar]
- Arundel, A.V.; Sterling, E.M.; Biggin, J.H.; Sterling, T.D. Indirect health effects of relative humidity in indoor envi-ronments. Environ. Health Perspect. 1986, 65, 351–361. [Google Scholar]
- Minhaz Ud-Dean, S.M. Structural explanation for the effect of humidity on persistence of airborne virus: Seasonality of influenza. J. Theoret. Biol. 2010, 264, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keeling, M.J.; Rohani, P. Modeling Infectious Diseases in Human and Animals; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Dexter, N. Stochastic models of foot and mouth disease in feral pigs in the Australian semi-arid rangelands. J. Appl. Ecol. 2003, 40, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, K. Persistence and extinction of a stochastic single-specie model under regime switching in a polluted environment. J. Theor. Biol. 2010, 264, 934–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, A.; Greenhalgh, D.; Mao, X.; Pan, J. The SIS epidemic model with Markovian switching. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2012, 394, 496–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Shao, J. Permanence and extinction of regime-switching predator-prey models. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 2016, 48, 725–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X. Stochastic Differential Equations and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bacar, N.; Khaladi, M. On the basic reproduction number in a random environment. J. Math. Biol. 2013, 67, 1729–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacar, N.; Ed-Darraz, A. On linear birth-and-death processes in a random environment. J. Math. Biol. 2014, 69, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Khan, S.U.; Ali, I. Application of Legendre spectral-collocation method to delay differential and stochastic delay differential equation. AIP Adv. 2008, 8, 035301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.U.; Ali, M.; Ali, I. A spectral collocation method for stochastic Volterra integro-differential equations and its error analysis. J. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2019, 1, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.U.; Ali, I. Numerical analysis of stochastic SIR model by Legendre spectral collocation method. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2019, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenhalgh, D.; Liang, Y.; Mao, X. Modelling the effect of telegraph noise in the SIRS epidemic model using Markovian switching. Phys. A 2016, 462, 684–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Khan, S.U. Analysis of stochastic delayed SIRS model with exponential birth and saturated incidence rate. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 138, 110008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.U.; Ali, I. Convergence and error analysis of a spectral collo- cation method for solving system of nonlinear Fredholm integral equations of second kind. Comput. Appl. Math. 2019, 38, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.U.; Ali, I. Applications of Legendre spectral collocation method for solving system of time delay differential equations. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2020, 12, 1687814020922113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hieu, N.T.; Du, N.H.; Auger, P.; Dang, N.H. Dynamical behavior of a stochastic SIRS epidemic model. Math. Model. Nat. Phenom. 2015, 10, 5673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Din, R.; Algehyne, E.A. Mathematical analysis of COVID-19 by using SIR model with convex incidence rate. Results Phys. 2021, 23, 103970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.M.; Ali, A.; Khan, M.A.; Islam, S.; Ullah, S. Dynamics of fractional order COVID-19 model with a case study of Saudi Arabia. Results Phys. 2021, 21, 103787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atangana, A.; Araz, S.I. New concept in calculus: Piecewise differential and integral operators. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2021, 145, 110638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atangana, A.; Araz, S.I. Modeling Third Waves of COVID-19 Spread with Piecewise Differential and Integral Operators. Turkey, Spain and Czechia. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Arfan, M.; Shah, K.; Gómez-Aguilar, J.F. Investigating a nonlinear dynamical model of COVID-19 disease under fuzzy caputo, random and ABC fractional order derivative. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 140, 110232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Koufi, A.; Bennar, A.; El Koufi, N.; Yousfi, N. Asymptotic properties of a stochastic SIQR epidemic model with Lévy jumps and Beddington–DeAngelis incidence rate. Results Phys. 2021, 27, 104472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matadi, M.B. Lie symmetry analysis of stochastic SIRS model. Commun. Math. Biol. Neurosci. 2019, 23, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson, R.R.; Ball, F.G.; Sharkey, K.J. The relationships between message passing, pairwise, Kermack–McKendrick and stochastic SIR epidemic models. J. Math. Biol. 2017, 75, 1563–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahrouz, A.; Omari, L. Extinction and stationary distribution of a stochastic SIRS epidemic model with non-linear incidence. Stat. Probab. Lett. 2013, 83, 960–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Nanjing, H.; Changwen, Z. European option pricing with time delay. In Proceedings of the 2008 27th Chinese Control Conference, Kunming, China, 16–18 July 2008; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 589–593. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, R.M.; May, R.M. Population biology of infectious diseases: Part I. Nature 1979, 280, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Miao, A.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X.; Liu, J. Extinction and persistence of a stochastic SIRS epidemic model with saturated incidence rate and transfer from infectious to susceptible. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2008, 2018, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capasso, V. Mathematical Structure of Epidemic Systems. In Lecture Notes in Biomathematics; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1993; Volume 97. [Google Scholar]
- Levin, S.A.; Hallam, T.G.; Gross, L.J. Applied Mathematical Ecology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Y.; Gog, J.R.; Grenfell, B.T. Semiparametric estimation of the duration of immunity from infectious disease time series: Influenza as a case-study. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C 2005, 54, 659–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Koufi, A.; Adnani, J.; Bennar, A.; Yousfi, N. Analysis of a stochastic SIR model with vaccination and nonlinear incidence rate. Int. J. Differ. Equ. Appl. 2019, 2019, 9275051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q. A stochastic SIR epidemic model with Lévy jump and media coverage. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2020, 2020, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Sun, W. Periodic solutions of stochastic differential equations driven by Lévy noises. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2021, 31, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Koufi, A.; Adnani, J.; Bennar, A.; Yousfi, N. Dynamics of a stochastic SIR epidemic model driven by Lévy jumps with saturated incidence rate and saturated treatment function. Stoch. Anal. Appl. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Koufi, A.; El Koufi, N. Stochastic differential equation model of COVID-19: Case study of Pakistan. Results Phys. 2022, 21, 105218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieu, N.T.; Nguyen, D.H.; Du, N.H.; Yin, G. Classification of asymptotic behavior in a stochastic SIR model. SIAM J. Appl. Dyn. Syst. 2016, 15, 1062–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).