Abstract
This paper introduces a GPU (graphics processing unit)-based fast motion synthesis algorithm for a large crowd. The main parts of the algorithms were selecting the most appropriate joint model given adaptive screen-space occupancy of each character and synthesizing motions for the joint model with one or two input motion capture data. The different joint models had a character range from fine-detailed and fully-articulated ones to the most simplified ones. The motion synthesizer, running on a GPU, performed a series of motion blending for each joint of the characters in parallel. For better performance of the motion synthesizer, the GPU maintained a novel cache structure for given speed parameters. Using the high computation power of GPUs, the motion synthesizer could generate arbitrary speeds and orientations for the motions of a vast number of characters. Experiments showed that the proposed algorithm could animate more than 5000 characters in real-time on modest graphics acceleration cards.
1. Introduction
Crowd simulation has been one of the hottest topics among computer animation researchers over the last decade [1]. Its applications range from entertainment industries, such as movies or games, to crowd planning and management of transportation, architectural design, building safety, and so on. For instance, when a sports stadium where a large crowd would gather is built, the architectural design must consider the safety of the crowd in case of an emergency. Virtual crowds have an important role in those applications for estimating the behaviors of a crowd in reality. Most research in those applications focuses on improving the controllability over crowds or creating convincing and aggregate crowd movements. However, animating a large crowd in real time still has many challenges to overcome. First, because most motion synthesizing algorithms are based on complicated mathematical models, those algorithms cannot be applied directly to large crowds while maintaining real-time performance. As a result, most crowd simulation research often ignores the quality of the individual motions and, rather, focuses on the overall aggregate behaviors of crowds. Thus, they are often described as simple polygons, such as circles and triangles. Second, when large crowds are rendered, the camera often moves dynamically, zooming in and out to show the entire crowd. Therefore, when we create detailed motions for each character, their contribution for the scene should be considered from the given camera viewpoint. This is also quite important when we deal with a large number of 3D characters to achieve real-time performance.
In this paper, we proposed a GPU (graphics processing unit)-based motion synthesis algorithm for a large number of characters. The algorithm fully utilized the high-performance computing power of a GPU. First, it checked the screen-space pixel coverage of each character, which corresponds to the contribution or importance of the character from the given camera’s perspective. The larger the coverage is, the more important the character is at that moment. Then, the algorithm automatically selected a joint skeleton model for given pixel coverage. The different joint models had a different number of joints. The factors for selecting a particular joint model included the character’s distance from the camera and its orientation to the camera that takes space in the image plane. Once the algorithm determined a set of joints for a character, it performed motion blending with the input motion capture data on the GPU. In the proposed algorithm, only two cyclic input motions of high-speed running and the slow running motion were used. By changing the weight value for blending these motions, a continuously changing speed motion could be generated with an arbitrary orientation spontaneously. To process the motions in a GPU-friendly manner, the input motions were converted into so-called motion textures, in which each pixel represents a unit quaternion value representing a local orientation of the joint. The joint hierarchy was also represented as an array to find a parent or child joint index easily. For better performance, our algorithm maintained a cache structure, where motion clips with speed parameters were stored. When a motion synthesis for a desired speed was requested, the algorithm checked the motion in the cache and applied one to the character; otherwise, it started to synthesize the motion. The experiments showed that the GPU-based motion synthesis has at least a 10 magnitude faster performance than that of CPU-based methods.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows: Previous approaches for crowd motion simulation are reviewed in Section 2. The main algorithms for the GPU-based fast motion synthesis of large crowds are described in Section 3. The experimental results for animating a large number of characters in real time are demonstrated in Section 4. We conclude this paper with a discussion of potential improvements in Section 5.
2. Related Work
Many different approaches have been proposed for simulating and editing crowd motions [1]. Classical approaches usually viewed the entire crowd as a single group and focused the overall moving patterns of it. Continuum crowds or aggregate dynamics [2] were one of those classical crowd simulation approaches. Some researchers consider those approaches as macroscopic models. Those techniques did not focus on individual behaviors. Instead, they concentrated on the crowd flow and density control. Although those methods were able to generate interesting movements for special situations, like queuing and jamming during a crowd’s exit [1], they usually did not consider the quality of individual motions of crowds.
Microscopic models, on the other hand, were more interested in individual behaviors and interactions between them. The agent-based approach falls into that category. The social force model and Boids model [3,4] were two popular models for animating flocks based on interactions between characters. Most of those agent-based models focused on how to get collision-free trajectories of each agent by predicting other characters’ future positions even when they are in a jammed situation [5]. Barnett et al. proposed a method that could obtain congestion-free paths for crowds using topological scene analysis techniques [6]. This method was especially useful when we needed a sort of ordered behavior, such as a soldiers’ marching scene. It produced a sample path called a “guideline” from the globally coordinated graph. This approach was quite efficient for simulating group behaviors but had difficulties in manipulating each trajectory in a highly detailed manner. More recently, inspired by observation on the real crowds, a statistical model has been proposed [7], which reveals a simple power law interaction based on the projected time to a potential future collision between crowds. Through experiments, they found out that the proposed model quite resembles the real crowds in terms of their speeds and densities. Furthermore, they extended it to the generalized collision avoidance model where arbitrary time steps are allowed [8]. However, in their approaches, the characters were represented as a simple 3D humanoid model and were not realistic in movements as they did not support subtle changes of the limb for the dynamically changing velocity of a character. Overall, most of microscopic models did not address the problem of solving the motion synthesis where the 3D character must adjust their poses for supporting arbitrary changing speed and orientations of crowds.
In the meantime, researchers working on synthesizing realistic human motions through a set of motion capture data have extended their methods to the multi-character cases [9,10]. Their algorithms put efforts on editing a group of character motions in a controllable manner without damaging the fidelity of the original motions. For example, inspired by the mesh deformation technique where users are manipulating a vertex and deform the whole mesh interactively, they can put each character in the position of a vertex of mesh and effectively specify the formation of crowds. Although these techniques produced the natural motions of crowds, the number of characters that a system could manipulate was just less than several hundred because the editing was a tedious manual work. The approach proposed in this paper is similar to those mentioned above in that individual motions were also synthesized with motion capture data. However, unlike their approaches, this study introduced a method that fully utilized the power of a GPU and created motions for more than 10,000 characters in real time rate. For better performance, our method considered the viewpoint of the camera and divided whole crowds into a set of different joint-level groups. The factors for splitting characters into specific groups included the pixel coverage of the joints of the characters and their distance from the camera. Different joint levels had different numbers of joints. Joint models varied from fine-detailed to the most simplified ones. The proposed approach is equivalent to the LOD (Level of Detail) technique that has been widely used for rendering complicated terrain scene [11]. A major difference is that rather than simplifying surface meshes dynamically, our algorithm selects the best joint model for the given camera parameters. This makes sense for rendering a large crowd where camera is often set at a wide, top down angle to show the entire movement of whole crowds. In this case, the motions for every single joint of the characters do not need to be synthesized because the characters are barely seen.
Our motion synthesizing method was based on motion blending techniques [12]. To calculate a joint orientation given the skeleton hierarchy, motion data, and speed parameter, a GPU-friendly data structure was created called “motion textures”, in which each texel had joint orientation data represented as a unit quaternion instead of color. This structure was efficient for being processed in the GPU like regular image-based textures. Therefore, the blending could be done in parallel in the GPU shaders.
3. Algorithms
The algorithm proposed in this paper is divided into CPU-bound jobs and GPU-bound jobs. The CPU-bound jobs are first described including data initialization for motion textures, while the GPU-bound jobs are explained including the calculation of the pixel coverage and the motion synthesis. Figure 1 shows an overall step of the proposed algorithm.

Figure 1.
Overview of the proposed algorithm.
3.1. Motion Textures
One of the important CPU-bound jobs is data initialization. The data used include a couple of motion capture data and joint hierarchy of the characters. For our algorithm, two input motions of running motions with different speeds and the Biovision hierarchy (BVH) are used for the motion data [13]. The BVH file format specifies the joint hierarchy, joint position, and orientation data in a text file. Those motion data are read and then stored in a floating-point 2D texture. It is called motion textures because each texel of texture represents a unit quaternion and a 3D offset instead of a color. Figure 2 shows an example of a motion texture. The x coordinate values are joint orientations represented as unit quaternions and 3D offset vectors indicating the positions of the local joints relative to their parent joints. The y coordinate values represent the frame numbers. For the root joint, which does not have an offset, the 3D global position of the joint is stored instead of a 3D offset. A texel has four floating-point values representing the x, y, z, and w values of a unit quaternion. In addition to the 3D offset or global position data, each joint needs two four-floating point data. If 16-bit floating point is used, each joint requires 2 × 16 × 4 bits. Because the original BVH data have an Euler angle representation with a particular order of multiplication for each joint in the file, a process is needed that converts from Euler to unit quaternion. In addition to the motion texture, an additional single integer array is needed that contains the parent joint index number for joints to specify a hierarchy in the motion texture. For example, in the bottom of Figure 2, a parent array contains the index that indicates a joint number and its value representing the parent joint number. Because the root joint at the index 0 does not have a parent joint, its value is set to –1. Also, because a joint may have multiple child joints, some values of the array can be same.
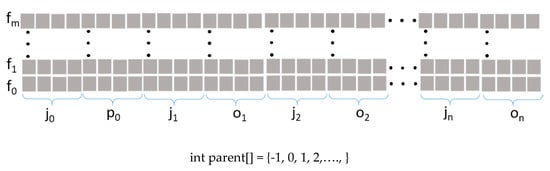
Figure 2.
A layout of motion texture: m is the number of frames, n is the number of joints, ji is the offset of the ith joint, p0 is the global position, and oi is the orientation of the ith joint.
Once a floating-point motion texture is built, then it can be read in the GPU efficiently using a texture coordinate that indicates the joint and the frame number. Given a motion texture called motex, a joint number j, and a frame number f, the orientation of joint r and its offset o can be obtained using the following GPU shader codes:
vec2 to = vec2(j × 2, f)
vec2 tp = vec2(j × 2 + 1, f)
vec4 r = texelFetch(motex, to)
vec3 o = texelFetch(motex, tp).xyz
Because there were two input motions with different speed parameters, two motion textures were used and blended together to obtain the joint orientation for an arbitrary speed parameter.
3.2. Pixel Coverage of Characters
In a crowd simulation, the camera is often zoomed out so that it can oversee the overall movement of the crowds from a remote location. In this scenario, characters may use small spaces on the final image plane. Similar to LOD-based techniques, our motion synthesis algorithm took the pixel coverage of the characters into account. In our approach, joint models were reduced depending on the pixel coverage of the characters. That is, the number of joints for each character was changing dynamically, according to their current pixel coverage on the view image plane. One of the important requirements for calculating the pixel coverage of the characters is that it should be fast enough such that the camera can change its position at any time through a user interface, such as mouse dragging. To calculate the pixel coverage, the whole body of a character was divided into five different parts, four limbs and the body, and a bounding sphere was put on each part, and then, the number of pixels that the bounding sphere was covering was counted on the image screen. Rather than having a fixed number of joint models with different LOD levels, each character had a different number of joints, depending on the camera position and orientation. Figure 3 illustrates the five bounding spheres put upon the five different parts of body, and Figure 4 shows their projections on the image plane. The centers of the bounding spheres present the global positions of two elbows, the middle of spine, and two knees of the character. The size of bounding spheres was changing dynamically depending on the frames of motions.
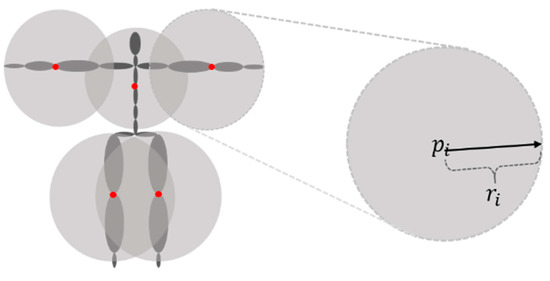
Figure 3.
Five bounding spheres centered at the joints (denoted as red circles).
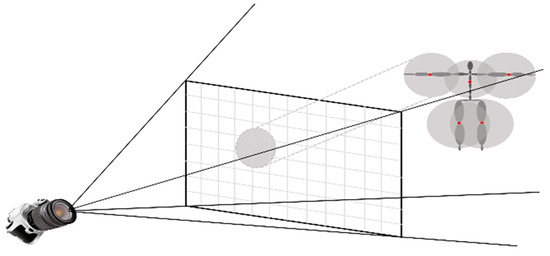
Figure 4.
Projection of bounding spheres on the image plane and their pixel coverages.
A point p on a sphere can be described as a parametric form as follows:
Here, o is the center of the sphere and r is the radius of the sphere.
Let us assume that a ray is shot from the camera to the image plane in a pinhole camera model. Then, the ray arrives at point p on the sphere as it intersects the image plane at (x, y, 1), if the focal length equals to 1 as follows:
Here, is the ray direction represented as a vector, and . The corresponds to the distance from the camera to the intersection point. If we associate Equation (1) with Equation (2) with point p, the following equation is derived:
If Equation (3) is rearranged with respect to t, a quadratic equation is defined with A, B, and C, as follows:
Here represents a dot product. This quadratic function has solutions only when its discriminant is positive. Therefore, if we expand the discriminant, , and arrange it, we derive the following inequality:
By plugging defined in Equation (2), eliminating positive constants, into Equation (5), we derive the following equation:
If an implicit equation is preferred rather than parametric ones, any rotated ellipse including circles can be represented as a general second-degree equation in which the coefficients from to are defined as follows [14]:
Given this general implicit representation of an ellipse, the major and minor axis, a and b, of the general conic section of an ellipse is given as follows [14]:
If we put a to f terms and simplify them, we have a final major and minor axis, a and b, as follows:
Once a and b were obtained, the area could be simply calculated by . The five bounding spheres on the four limbs and the body of a character were separately projected on the image plane, and their pixel coverage could be calculated. If the pixel coverage was smaller than the threshold, the motions for the joints that belonged to the bounding sphere were not synthesized. In terms of implementation, our algorithm computed those areas in a shader function such that they could be running at the GPU, which drastically improved the calculation speed.
3.3. Motion Synthesis
After determining all active joints for a character that covered the image plane, the motion synthesizing module generated the motions for the character using input motions. For each frame, the motion synthesizer determined the local orientations of all active joints and the global position of the root joint. The root joint, which corresponds to the root node of the joint hierarchy, is usually located in pelvis. The global position of the root joint represented the location of the character. To synthesize the motions of crowds, the initial positions, direction, and frame number of characters were randomly distributed. The initial frame numbers were also given randomly so that the whole crowd did not animate the same poses at the same time. Given the speed parameter w, which is between 0 and 1, the algorithm synthesized motions frame-by-frame for a character by blending two input cyclic motions. The algorithm could not change the speed parameter until it synthesized the final frame of the input motions in order to prevent non-smooth artifacts in the blended motion.
First, the motion synthesizer determined the global position of root joint. The default position of the root joint at frame f is denoted as which could be obtained from a motion texture. It was noticeable that the default position was different from the initial position which was assigned randomly; instead, it was given from the input motion. A 2D rigid transformation matrix could be applied to the input motion to translate the character to the initial position. The two input motions had fixed transformation between frames, and our algorithm blended them together for the given speed parameter. That is, the new for speed parameter w could be calculated by transforming the previous . The transformation could be done by multiplying the scaling, rotation, and translation matrix in a row. Here, the scaling matrix adjusted the size difference between original motions and 3D characters. The rotation matrix was the 2D rotation on the x and z plane, where y (up vector) became the rotation axis from the orientation parameter . The translation matrix was built from a 3D offset vector obtained by linear interpolation of the frame distances between the high-speed motion and the low speed motion . As shown in Equation (10), T, R, and S represent the translation, rotation, and scaling matrix, respectively, while the and are the high and low speed motion, respectively, as follows:
After the root joint position is determined, the local orientation of joints for the frame f needs to be calculated. Let us say that a user wants to synthesize a motion for joint j at frame number f. Our method represents a joint orientation as a single matrix, say where it can be further decomposed into two separate transformation matrices and . They are called a fixed transformation matrix and joint transformation matrix, respectively. The final matrix is the multiplication of matrix and . As the matrix is independent of the speed parameter w, they can be built as a pre-processing step. The matrix corresponds to the world transformation of a joint offset, which can be easily obtained from a motion texture. This matrix is quite useful for rendering the character motion because it can locate meshes representing joints in the right position. For example, to represent each joint with an ellipse, the matrix transforms the ellipse such that it can be aligned to the joint offset at the middle of the joint. To compute , the orientation between the y axis and the joint offset in quaternion form needs to be calculated and converted into a matrix. Additionally, depending on the applications, the translation and scaling matrix can be also multiplied to transform the mesh associated with the joint. On the other hand, the joint transformation matrix , which represents the global orientation of the joint at the speed parameter w for each frame, can be obtained by multiplying all local orientations of ancestry joints in the hierarchy. The orientations of ancestry joints are calculated by interpolating two location orientations of input motions at the same level of hierarchy using the weight value w. This process of algorithm is explained in Figure 5.
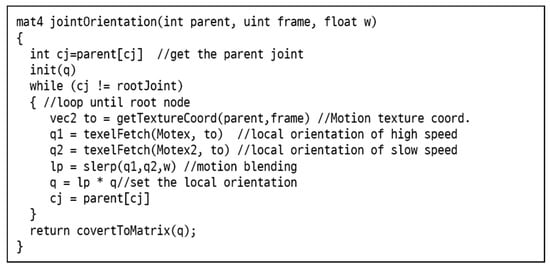
Figure 5.
Algorithm for joint orientation estimation: This function returns a 4 × 4 orientation matrix for given three input parameters. The parent is the index number of parent joint, the frame is the frame number of motion data, and w is the speed parameter. To calculate a joint orientation in the hierarchical joint structure for the given parameters, the algorithm blends two input motions (i.e., slow and fast motion) from the current joint to the root joint. For the blending operation, spherical linear interpolation (SLERP) is used between two input joint orientations. All the joint orientations are represented as unit quaternions.
At the final step, all matrices are combined into a single matrix for the joint as follows:
where f is the frame number, and j is the joint number.
3.4. Motion Catching
Once a short motion is synthesized with a desired speed, it can be reused for other output motions by building a cache structure in the GPU memory. When a motion synthesis for a desired speed was requested, our algorithm first checked the motion in the cache and applied one to the character. Otherwise, it started the synthesizing process and stored the result motion into the cache. The cache structure consists of a key and its associated data. In our approach, the speed parameter and the local orientations of joints were used as the key and the associated data, respectively. Finding a motion with an exact speed parameter is ambiguous due to the floating-point continuous value of the speed parameter. For this reason, a small range of speed parameters are used to increase the chances of cache-hit. In addition, when a cache-hit occurs, a small number of matrices are applied for the motion synthesis as our algorithm needs only a subset of joints for the pixel coverage. Figure 6 shows the motion cache structure. The size of cache depends on the capacity of the GPU memory. In our approach, the maximum size of cache was set to 20 megabytes. As the cache operates in a First-In-First-Out (FIFO) manner, the oldest data were removed first when it was full.
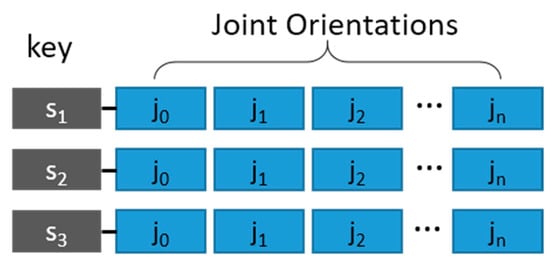
Figure 6.
Motion cache: s is the speed, and ji is the ith joint orientation.
4. Experimental Results
We built a crowd simulation system on a Microsoft Windows 10 platform. The hardware specifications were a single Intel i7 CPU with 16 GB main memory and a Nvidia GeForce GTX 1060 graphic card. OpenGL library was used to render the 3D characters. The two input cyclic motions were fast-running and slow-running motions in a BVH format. Each motion had a skeleton model consisting of 25 joints and around 30 frames. To represent a character, the joints were rendered with a set of squashed spheres. All simulation algorithms were implemented with OpenGL Shading Language (GLSL) to run on the GPU. Updating the character positions and building all the required matrices were implemented with a compute shader that OpenGL 4.3 or higher version provides.
Figure 7 shows a screenshot of 5000 characters simulated by our system. Figure 8 shows a screenshot of the three different joint levels determined by their pixel coverage on the image plane. In this experiment, the yellow characters had less than five joints because they were located far away from the camera. The red characters had around eight joints due to their mid-range distance from the camera, and the blue characters has a full number of joints as they were within a close distance. Even though we used only three levels for simplicity, we could set any number of different joint levels. The picture on the bottom of Figure 8 compares the three different approaches. Throughout all experiments, the speed parameter w was set randomly between 0 and 1 for every character. Figure 9 shows the crowd motions of 1000 characters forming a circle. In this case, our algorithm sets the orientation parameters automatically such that the characters can stay in the boundary of the circle during the simulation.
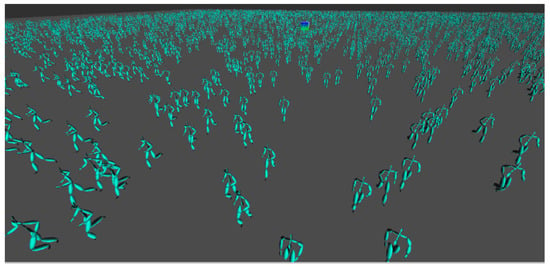
Figure 7.
Animation of 5000 characters.
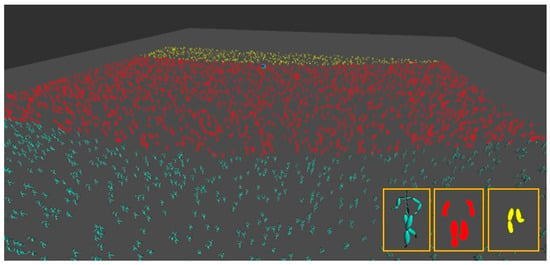
Figure 8.
Three levels of the joint models.
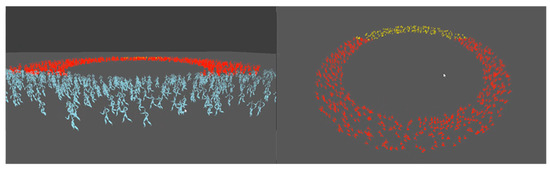
Figure 9.
A circle formation of a crowd (1000 characters).
Figure 10 shows a performance graph. As the number of characters was increased, the frame rates for three different methods were calculated. In the first case, crowds were only simulated on the CPU. In the second case, crowds were simulated on the GPU, but the multi-joint models were not used. Instead, only the full number of joints were used for the entire characters. In the third case, the crowds were simulated on the GPU, but multi-joint models were used depending on their pixel coverage on the image plane without using cache structure. As shown in the picture, the frame rate dropped down significantly for the CPU-only method as the number of character increased. The GPU-based method without the multi-joint model, however, maintained the frame rate around 60 frames per second, even when we increased the number of characters to 10,000. The performance got better when we used the GPU-based method with the multi-joint model, where we provided three different joint models. Since the model selection depends on the camera position, we kept changing the camera position and calculated the average frame rate. We found that the performance did not drop that much when we used the multi-joint levels. It was slightly more saturated than the case of a single joint level. We also noted that performance difference between the single joint and adaptive multi-joint case was getting bigger as we increased the number of characters, which proved the performance upgrade of our approach. Through several experiments, we verified that the proposed method could carry out at least a 6-times faster performance than that of CPU-based methods and animate more than 10,000 characters at the real time rate. Also, there was no artifact, such as foot-skating, and unnatural movement on the characters, even when we randomly changed their orientation and speed of characters.
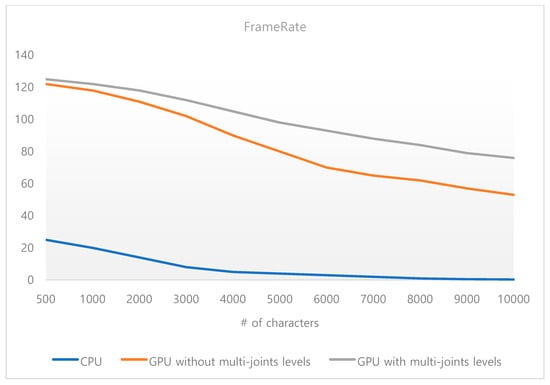
Figure 10.
Comparison of the performance between CPU and GPU (graphics processing unit) methods.
Figure 11 compares the performances of two cases in which the cache structure was used for the first case and not used for the second case as the number of characters are increased. The number of cache-hits is highly related to the frequency of changes of the speed parameter. If the speed parameter was changing frequently, the cache-hit did not occur many times. If the same speed was used constantly, there was a high chance that the motion synthesized with the speed was stored in the cache. In our experiments, the speed varied every five seconds between 0 and 1. As seen in Figure 11, if the stored motions in the cache were applied without using the motion synthesis, the average of around 15% performance improvement had been achieved. The experiment results can be seen on the YouTube video that captured the animations in real time (Supplementary Materials located at https://youtu.be/GXGdKyhPBBc).
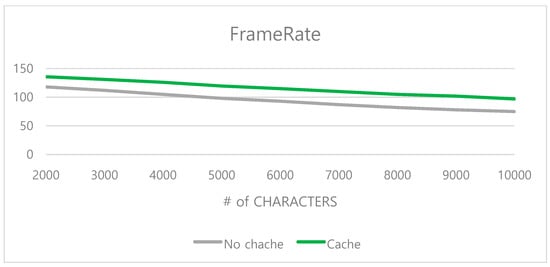
Figure 11.
Comparison of performance with cache and with no cache.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, we introduced a novel GPU-based motion synthesis method for large crowds. The algorithm first built motion textures for input motion capture data so that it could be efficiently read on the GPU. Those data were then blended and updated fully on the GPU. In addition, the algorithm considered how much space each character of the crowd took on the image plane. Depending on this coverage, the algorithm reduced the number of joints dynamically. Through several experiments, we discovered that this algorithm could animate more than 5000 characters in real time. For the performance improvement, a GPU-based cache structure was represented such that the motions stored in the cache could be used without processing a full motion synthesis with all input frames.
As a future work, our approach could be extended to solve the skinning problem where the vertex positions of a mesh needed to be calculated based on the weight values from a set of different joints. We expect that the number of joints can be dynamically adjusted considering their pixel coverage on the image plane. Also, we did not consider the occlusion between the characters. We just let each character being projected individually, without considering others. We believe that we can extend the algorithm by simply checking whether or not there is any overlapping area when we project the bounding ellipses of characters. We believe that this will be able to improve the performance when the crowds are in a highly compact situation.
Supplementary Materials
The experiment results can be seen on the YouTube video located at https://youtu.be/GXGdKyhPBBc.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.S.; Data curation, M.S.; Formal analysis, M.S. and Y.K.; Funding acquisition, M.S. and Y.K.; Investigation, M.S. and Y.K.; Methodology, M.S.; Supervision, Y.K.; Visualization, M.S. and Y.K.; Writing—original draft, M.S.; Writing—review & editing, Y.K.
Funding
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Ministry of Education (2015R1D1A1A01059066 and 2018R1D1A1B07048414).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ijaz, K.; Sohail, S.; Hashish, S. A Survey of Latest Approaches for Crowd Simulation and Modeling using Hybrid Techniques. In Proceedings of the 17th UKSIM-AMSS International Conference on Modelling and Simulation, Cambridge, UK, 25–27 March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, A.; Cooper, S.; Popovic, Z. Continuum Crowds. ACM Trans. Graph. 2006, 25, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Helbing, D. A fluid dynamic model for the movement of pedestrians. Complex Syst. 1992, 6, 391–415. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, C.W. Flocks, Herds, and Schools: A Distributed Behavioral Model. ACM SIGGRAPH Comput. Graph. 1987, 1, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, J.; Patil, S.; Sewall, J.; Manocha, D.; Lin, M. Interactive Navigation of Individual Agents in Crowded Environments. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Interactive 3D Graphics and Games (I3D), Redwood City, CA, USA, 15–17 February 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Barnett, A.; Shum, H.; Komura, T. Coordinated Crowd Simulation with Topological Scene Analysis. Comput. Graph. Forum 2016, 35, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamouzas, I.; Skinner, B.; Guy, S. A universal power law governing pedestrian interaction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 238701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karamouzas, I.; Sohre, N.; Narain, R.; Guy, S. Implicit Crowds: Optimization Integrator for Robust Crowd Simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 2017, 36, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, T.; Lee, K.; Lee, J.; Takahashi, S. Group Motion Editing. ACM Trans. Graph. 2008, 27, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.; Hyun, K.; Kim, J.; Lee, J. Synchronized Multi-Character Motion Editing. ACM Trans. Graph. 2009, 1, 28. [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom, P.; Koller, D.; Ribarsky, W.; Hodges, L.F.; Faust, N.; Turner, G. Real-time, Continuous Level of Detail Rendering of Height Fields. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGARPH, New Orleans, LA, USA, 4–9 August 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Rose, C.; Cohen, M.; Bodenheimer, B. Verbs and Adverbs: Multidimensional Motion Interpolation. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 1998, 18, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, M.; Maddock, S. Motion Capture File Formats Explained. Available online: http://www.dcs.shef.ac.uk/intranet/research/public/resmes/CS0111.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2019).
- Stang, G. Calculus, 3rd ed.; Wellesley-Cambridge Press: Wellesley, MA, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-0980232752. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).