Abstract
B lymphocyte receptors are generated randomly during the bone marrow developmental phase of B cells. Hence, the B cell repertoire consists of both self and foreign antigen specificities necessitating specific tolerance mechanisms to eliminate self-reactive B cells. This review summarizes the major mechanisms of B cell tolerance, which include clonal deletion, anergy and receptor editing. In the bone marrow presentation of antigen in membrane bound form is more effective than soluble form and the role of dendritic cells in this process is discussed. Toll like receptor derived signals affect activation of B cells by certain ligands such as nucleic acids and have been shown to play crucial roles in the development of autoimmunity in several animal models. In the periphery availability of BAFF, a B cell survival factor plays a critical role in the survival of self-reactive B cells. Antibodies against BAFF have been found to be effective therapeutic agents in lupus like autoimmune diseases. Recent developments are targeting anergy to control the growth of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells.
1. Introduction
The development of an adaptive immune system requires generation of antibody receptors with varied affinities some of which will have reactivity to self-antigens. In the B-cell lineage, self-reactive B cells are eliminated in the bone marrow (Central tolerance) and the spleen (Peripheral tolerance). By utilizing a variety of transgenic mouse models, researchers have demonstrated that the central tolerance mechanisms exclude autoreactive immature B cells and prevent cells that exhibit self-reactive B-cell receptors from entry into the peripheral B-cell compartment. Additional studies have revealed mechanisms that promote the differentiation of non-autoreactive immature B cells and their positive selection into the peripheral B-cell compartment. These central tolerance mechanisms are fundamental to the generation of a naive B-cell repertoire that is largely devoid of self-reactivity while capable of reacting with any foreign antigen.
B-cells are generated in the bone marrow in a tightly regulated manner. Productive rearrangement of immunoglobulin heavy (IgH) and light (IgL) chain gene segments results in the generation and expression of the mature B-cell antigen receptor (BCR) at the cell surface. While specific combination of Ig H and L chains determines the antigenic specificity of the newly formed BCR, its association with Ig-α and Ig-β allows transduction of a signal inside the cell that directs cell fate [1,2]. Developing B cells first express a mature BCR on the cell surface in the form of IgM and as such are classified as immature B cells (Figure 1) [3,4,5]. It is at the immature B-cell stage that the BCR is exposed to autoantigens in the bone marrow. Central B-cell tolerance is the process that negatively selects newly generated immature B cells that react with a self-antigen in the bone marrow environment. This is considered the first checkpoint of B-cell tolerance, and the outcome of this checkpoint mechanism is fundamental to the generation of a naive B cell repertoire that contains BCRs reactive to foreign antigens and is mostly devoid of self-reactive specificities. Once the central checkpoint is successfully overcome, immature B cells differentiate into transitional and mature B cells in the spleen [4,6,7]. However, a fraction of autoreactive immature B cells, that retains low reactivity to self-antigens, escapes the central checkpoint of tolerance and migrates into the periphery [6,7,8].
2. Central Tolerance: Clonal Deletion, Anergy and Receptor Editing
Burnet’s clonal selection theory suggested that lymphocyte clones that react to self are eliminated to prevent immune responses against self-antigens [9]. Seminal work from many investigators involved injecting antibodies reactive toward immunoglobulin (Ig) chains into newborn mice and rabbits to test whether newly generated B cells reacted with a “self-antigen,” (in this case, the rabbit anti-Ig antibody acts like a self-antigen), would either be deleted or modulated [10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17]. Consistent with such a hypothesis, injection of anti-Ig antibody and anti-idiotypic antibodies in newborn animals resulted in the elimination of Ig and idiotype-expressing B cells, respectively. Later on, with the advancement of transgenic mice technology, anti-hen egg lysozyme (HEL) and anti-H-2Kk (and H-2Kb) Ig transgenic mice were developed with the purpose of testing whether newly generated autoreactive B cells were either eliminated or suppressed on recognition of their specific self-antigen. These studies indicated that when an immature B cell reacts with a self-antigen with high avidity, such as a highly expressed membrane-bound protein, it undergoes apoptosis within 2–3 d [3,18]. In contrast, low avidity interactions of B cells with self-antigens induce unresponsiveness to subsequent stimulation or anergy but allowed for migration into peripheral compartment. The anergic B cells fail to enter follicle and have reduced life-span [3]. Therefore, it was concluded that clonal deletion and anergy were major mechanisms mediating central tolerance of developing autoreactive B cells, resulting in the elimination of autoreactive clones, and preventing immune responses against self. However, later studies showed that clonal deletion and anergy are not the only modes of selection against autoreactive immature B cells, but there operates another system, namely, receptor editing. Several important studies that utilized immunoglobulin heavy and/or light chain transgenic mouse models in which the self-antigens were either MHC class I or DNA showed that autoreactive immature B cells “edit” their antigen receptors [19,20]. Specifically, autoreactive immature B cells reactivated their Ig gene rearrangement program at the Ig light chain loci resulting in the expression of a new light chain that paired with the existing H chain to form a non-autoreactive BCR, an event that promoted the selection of these edited B cells into the periphery. The concept of “receptor editing” was thus born. Several studies with human B cells have shown that receptor editing also plays a role in shaping human B cell repertoire and failures in regulation of these mechanisms are involved in lupus like autoimmune diseases [21]. Despite a critical role for BCR affinity in deciding the fate of immature B cells, their selection is also influenced by the bone marrow microenvironment [2].
3. Peripheral Tolerance – Role of BAFF (BLyS)
The central tolerance mechanisms eliminate approximately 90% of the self-reactive B cell pool [5,22]. Despite the presence of clonal deletion, anergy and receptor editing mechanisms, several autoreactive clones bypass these checkpoints and are found in peripheral B cell pool [8,23,24]. Immature B cells that survived the central tolerance leave the bone marrow and continue their development as transitional B cells in the periphery. Here they undergo peripheral tolerance based on their BCR specificity and signal strength. The BCR signal strength must fall within the range for further maturation and selection: above the “tonic” signaling for positive selection and below the threshold signaling for negative selection [2,25,26]. The “transitional B cell tolerance” is the first B cell tolerance check point in the periphery, which eliminates about two-thirds of the transitional B cells [5]. Unlike the central tolerance mechanisms, the stringency of transitional B-cell tolerance is plastic and selection depends on the interplay between BCR-mediated signals and a B cell survival factor, called B lymphocyte stimulator (BAFF, also known as BLyS) signaling [27].
BAFF is a soluble type II transmembrane protein that promotes key biological functions including peripheral B-cell survival and homeostasis [28]. In addition to promoting B-cell survival, BAFF also regulates expression of CD21/35 on the surface of B cells [27,29]. BAFF deficiency results in a reduction in the number of peripheral B cells and a diminished capacity to mount robust humoral immune responses. Overexpression of BAFF has been linked to human autoimmunity, and recent data provide clues as to how excessive secretion of BAFF may allow the emergence of autoreactive B cells in mice and humans [28,29]. BAFF binds to three receptors: BAFF receptor 3 (BR3; also known as BAFF-R), transmembrane activator-1 and calcium modulator and cyclophilin ligand-interactor (TACI), and B cell maturation antigen (BCMA). BAFF-R is one of the BAFF receptors expressed on all peripheral blood B cells in both mice and humans. In the mouse spleen, BAFF-R is most highly expressed on transitional type 2 (T2) B cells, followed by mature and marginal zone (MZ) B cells, while T1 cells having lower levels of BAFF-R on the surface, and GC B cells have reduced expression compared to mature follicular B cells. Human tonsillar B cells have a high level of BAFF-R expression, and like mouse, tonsillar B cells with a GC phenotype express BAFF-R in reduced levels [30,31,32]. It was shown that BAFF-R is not expressed on B-cell precursors in the bone marrow. BAFF-R was initially believed to be expressed exclusively by B cells; however, BAFF-R was recently found to be expressed on a subset of mouse splenic T cells and on human anti-CD3-activated peripheral blood T cells [33,34,35,36]. Close examination of tonsillar T cells revealed that a large proportion of effector and memory T cells express BAFF-R, while naive T cells are negative [31,32]. Although mRNA for BCMA, another receptor for BAFF can be found in the spleen, lymph nodes, and several B-lineage cell lines, cell-surface BCMA is undetectable. TACI, a third receptor for BAFF was found to be expressed on B cells and a subset of activated T cells [31,32]. In the mouse, splenic MZ and T2 B cells have the highest level of TACI expression, while expression on T1 and mature B cells is low or absent. In the absence of BAFF, B cell development remains normal in the bone marrow, but peripheral B cells are reduced significantly. BAFF signaling is crucial for the survival of late transitional (T2 and T3), follicular and marginal zone B cells, whereas B-1 B cells remain unaffected due to lack of BAFF [37,38].
Elevated levels of BAFF lead to defect in transitional B cell tolerance and a breach in the peripheral tolerance. Studies with the immunoglobulin knock-in mice that express self-reactive BCRs show that most of the transitional B cells are negatively selected during transitional B cell tolerance. However, administration of exogenous BAFF in these mice results in an increase in number of self-reactive B cells in the mature B cell pool [39,40]. Thus, B cells that would normally be deleted through negative selection instead survive because of BAFF signaling and join the mature naïve B-cell pool. These studies suggest that BAFF is a limiting factor in transitional B-cell tolerance. Increased levels of BAFF lowered the BCR affinity threshold required for positive selection with a consequence that self-reactive B cells with a low affinity BCR were rescued into the peripheral repertoire. Consistent with this idea, aberrant transitional tolerance processes because of elevated levels of BAFF have been identified in patients with antibody mediated autoimmune diseases [41,42,43,44]. These observations made BAFF an attractive therapeutic target, and subsequently a BAFF-blocking monoclonal antibody, Belimumab (Benlysta), received FDA approval in 2011 as a treatment for patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) [45,46]. Treatment with Belimumab leads to a significant reduction in autoantibodies and selected B cell subsets (naïve, transitional but not memory B cells) in SLE patients [47]. Though Belimumab has promising potential, it does have reduced benefits in long term clinical care of patients. Clinical trials comparing two doses of Belimumab (1 or 10 mg/kg), were performed in adult patients (n = 1684). It was shown that after 52 weeks patients who responded to the drug were about 10% higher with belimumab (10 mg/kg) than with placebo. However, this response was not observed in one of the trials at 76 weeks [48]. Although it was demonstrated that treating patients with Belimumab provided no statistically significant therapeutic benefit, the positive outcome of these two trials is that patients with highly active disease had clinical benefit. Belimumab has been shown to be immunosuppressive and to exacerbate the effects when combined with other immunosuppressive drugs [48,49,50]. Different mechanisms of B cell tolerance in bone marrow and periphery are summarized in Figure 1.
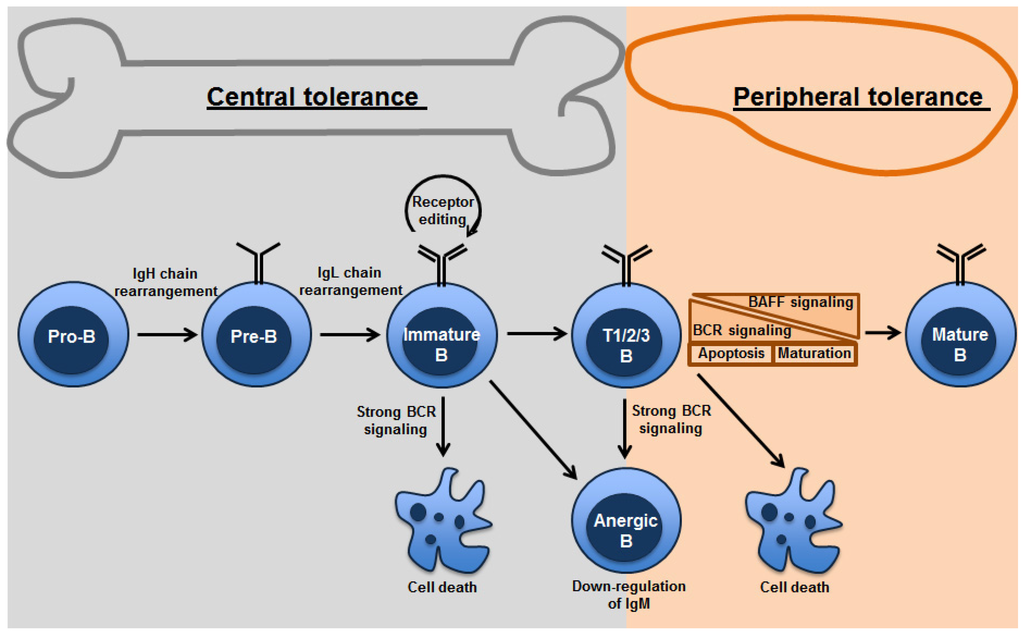
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of B-cell tolerance in bone marrow and periphery: Both clonal deletion and anergy are mechanisms utilized in the primary as well as peripheral lymphoid organs. Strength of BCR signaling affects the fate of the B cells undergoing tolerance. Receptor editing occurs primarily in the bone marrow. Transitional B cells are found in the bone marrow and spleen. Peripheral tolerance is primarily found in splenic transitional B cells, which depends on tonic BCR signaling thresholds and survival signals from BAFF.
4. Peripheral Tolerance - Role of Toll-Like Receptors
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are pattern recognition receptors that recognize pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) [51,52]. TLR-mediated recognition of PAMPS leads to activation of innate immune cells [53]. TLR signaling promotes activation and maturation of innate immune cells, which instructs and supports T-cell activation, leading to cell-mediated adaptive immune response. Activated antigen-specific T cells and naïve B cells interact with each other (cognate interaction), which leads to B-cell clonal expansion and differentiation and antibody secretion. Recent evidence suggests that in addition to TLR signaling in cells of the innate immune system, direct TLR mediated activation of B cells is also required for eliciting humoral immune response. However, multiple B cell subsets exists that play distinct roles during humoral immune responses. For example, follicular B cells are shown to be important for T-dependent immune responses whereas marginal zone B cells are important for T-independent immune responses. Marginal zone B cells are shown to be in a pre-activated state and respond rapidly to LPS and secrete antibody in vitro. Peyer’s patch B cells in the intestine play critical role in mucosal immune response by secreting IgA that binds to pathogens and prevents enteric infections. B-1 B cells, a subset of B cells in the peritoneal cavity is the source of natural IgM present in the serum and plays an important role in immunity against blood borne pathogens [6,54]. It was shown that B-cell subsets express all known TLRs except 5 and 8 [55].
In a series of landmark studies, it was demonstrated that TLRs expressed by B cells can also recognize self-antigens released from host tissues that are damaged, and such self-recognition by the B cell intrinsic TLR can potentially promote the development of autoimmune disease by breaking B-cell tolerance. Studies from transgenic mice reveal that immune complexes (ICs) consisting of IgG bound to mammalian DNA have been shown to effectively activate transgenic rheumatoid factor (RF) specific B cells through a process that involves BCR recognition of the IC and subsequent delivery of the DNA to TLR9 sequestered in an endosomal/lysosomal compartment [56,57,58]. These low affinity RF specific B cells do not proliferate in response to protein-containing ICs. The chromatin ICs, but not protein ICs, stimulate myeloid and plasmacytoid DCs to secrete cytokines, through coengagement of both FcγRs and TLR9. Under specific conditions, mammalian DNA can also directly stimulate DNA-reactive cells, through a TLR9-dependent process. However, the role of TLR9 in lupus appears more complex since deletion of Tlr9 gene in some mouse models protects against autoimmunity [59].
In addition to the DNA and DNA containing ICs, RNA and RNA binding proteins, such as Sm/RNP, constitute a second major category of autoantigens frequently targeted in systemic autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Sm/RNP particles consist of the U1 RNA bound by Sm and other associated proteins. Recent studies suggest that TLR7 and TLR8 act as receptors for single stranded RNA expressed by the viruses. In this context, the ssRNA was found to be a particularly effective ligand for TLR7 and TLR8 [56,60]. These observations raised the possibility that the interactions between BCR and TLRs that lead to DNA dependent activation of autoreactive B cells and DCs, would also apply to TLR7/8 involvement in the activation of B cells by RNA-associated autoantigens [59]. In agreement with such a concept, TLR7 deficiency ameliorated autoimmunity in murine models [59]. Thus, these observations in mouse models are consistent with the fact that autoantibodies reactive with DNA or DNA-associated proteins are the earliest and most commonly prevalent serological markers of human SLE [47,57].
5. Role of Dendritic Cells in Central and Peripheral Tolerance
Interaction of dendritic cells (DCs) with B cells and T cells plays an important role in the regulation of immune responses. DCs express a variety of TLRs and respond to TLR stimuli. DCs were found to present antigen to both T cells and B cells in a tolerogenic form [61,62]. Immature DCs have been shown to inhibit and tolerize T cells in vivo because of the absence of a costimulatory signal, whereas maturation of DCs by TLR or CD40 overcomes this inhibitory effect on T cells [62,63]. Recent studies suggest that immature bone marrow DCs (iBMDCs) or bone marrow resident DCs, but not mature bone marrow DCs or Splenic resident DCs [64], strongly inhibited B cell proliferation and differentiation responses induced by TLR ligation. iBMDCs specifically inhibited TLR2, TLR3, and TLR4, as well as BCR-induced proliferation, but did not inhibit anti-CD40 or PMA-ionomycin-induced B cell proliferation [54,65]. Cell-cycle analysis revealed that iBMDCs block B cell proliferation by inducing G1-S growth arrest [54]. Similar to the DC-mediated regulation of T cell responses, maturation of immature BMDCs with TLR ligands overcame the inhibitory effect of DCs on B cells. Many different TLR ligands can mature DCs in either a MyD88-dependent or MyD88-independent manner [66]. Maturation of immature BMDCs via the MyD88-dependent pathway (LPS, peptidoglycan) or the MyD88-independent pathway [poly(I:C)] had similar effects in overcoming the inhibitory effect of iBMDCs on B cells.
CD22 expression by B cells is critical for the immature BMDC-mediated inhibition of TLR-induced B cell proliferation [54]. Interestingly, it has been shown that maturation of BMDCs decreases the expression of sialic acid ligands [67], which is consistent with the role of CD22 in DC–B cell interaction. It is also possible that the sialic acid binding proteins such as Siglec G, which have been shown to be important for B-1 cell responses and for Ag-induced tolerance in B cells could play a role in this process [68]. Unstimulated splenic resident DCs were immature as evident by low CD86 and class II expression on the surface, compared with LPS mature Spl-RDCs but they did not inhibit TLR-induced B cell responses. In contrast, bone marrow resident DCs strongly inhibited TLR induced proliferation of B cells from both the bone marrow and the spleen. Although immature BMDCs normally are a heterogeneous population of DCs, flow cytometric sorting established that myeloid DCs in this population have potent inhibitory effects on B cells [64]. It is of interest to note that Kilmon et al. [69] found that myeloid DCs and macrophages, but not plasmacytoid DCs, inhibited autoantibody production by self-reactive B cells, but not Ab production by normal B cells.
In thymus, DCs present self-antigen in the context of their MHC and play a role in the negative selection of T cells. Thus, the DCs in the bone marrow might play a similar role in B cell negative selection by presenting soluble self-antigens to B cells in membrane bound form in the context of CD22/SIGLEC-mediated inhibitory signals. In this context, recently it has been shown that ligation of T-independent Ags with sialic acid epitopes induced B-cell tolerance through their ability to crosslink SIGLEC family proteins [70,71]. It was proposed that self-antigens that behave like T independent Ags may use this pathway for self-tolerance. In support of such an idea, mice doubly deficient for CD22 and Siglec G developed autoantibodies and a moderate form of immune complex mediated glomerular nephritis [71]. Although the significance of inhibition of TLR responses of bone marrow B cells is currently unclear, it must be noted that several endogenous TLR ligands have been identified and have been implicated in the breakdown of self-tolerance in several autoimmune models [72,73]. Some of the endogenous TLR ligands such as high mobility group box 1 and heat shock proteins have their origin in cell death [74], which is known to occur extensively during B cell development. Defects in clearance of dead cells have a critical role in the development of autoimmune diseases such as lupus [75]. In the periphery, DCs in mucosal areas and epidermal Langerhans cells (sites of extensive cell turnover) have anti-inflammatory properties.
6. Human B Cell Tolerance and Its Impact on Human Autoimmune Diseases
In the previous sections, we discussed immunological tolerance in B cells based on studies performed with transgenic mouse models of B cell tolerance and knockout mice that develop autoimmune diseases. In humans, most developing autoreactive B cells in healthy individuals are removed at two distinct steps. A vast majority of B cell clones expressing self-reactive B cell receptors are eliminated by the central tolerance mechanisms in the bone marrow. A peripheral B cell tolerance checkpoint further eliminates autoreactive new emigrant B cells before they enter the mature naive B cell compartment. In patients with active autoimmune diseases including rheumatoid arthritis (RA) or type 1diabetes (T1D), both the central and peripheral checkpoints are defective [76,77]. In autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis (MS), RA and to a lesser extent T1D, anti-CD20 therapy that depletes B cells has shown some efficacy in ameliorating the disease suggesting that the deletion of autoreactive B cell clones may reduce disease symptoms in these autoimmune diseases [78]. It was reported that a defective peripheral B cell tolerance checkpoint is observed in all three autoimmune diseases including MS, T1D, and RA, whereas central B cell tolerance is only impaired in two out of three autoimmune diseases (T1D and RA but not in MS) [79]. Hence, defects in the deletion of autoreactive B cell clones in the bone marrow seem to be critical for the development of RA and T1D, but are dispensable for MS. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have demonstrated that several susceptibility alleles are shared among many different autoimmune diseases [77]. For example, it has been shown that C1858T polymorphism in the PTPN22 gene is associated with high risk T1D and RA, but not MS [80]. This PTPN22 mutant blocks both T cell receptor (TCR) and B cell receptor (BCR) signaling that regulates central tolerance. Consistent with this hypothesis, it was shown that healthy donors carrying the PTPN22 risk allele lack the ability to eliminate autoreactive B cells in the bone marrow. This finding is similar to that observed in T1D and RA patients, revealing that this susceptibility allele is sufficient to confer the impaired central B cell tolerance associated with these autoimmune diseases. Other susceptibility genes associated with T1D and RA, include BLK, LYN, PTPN2, and BANK1, all of which affect BCR signaling pathways and may interfere with the removal of emerging autoreactive B cells [81]. In contrast, none of these polymorphisms, including the PTPN22 variant, are associated with MS, further demonstrating that alterations in B cell intrinsic pathways controlling central B cell tolerance may not be necessary for the development of all autoimmune diseases. It has been demonstrated that disease-associated polymorphisms in MS mainly affect T helper differentiation and B cell-T cell interactions and not B cell intrinsic pathways [79]. In contrast to central tolerance mechanisms, the maintenance of the peripheral B cell tolerance checkpoint is specifically defective in MS patients, which is postulated to be due to defects in regulatory T cell function [79].
7. Targeting B Cell Anergy for Therapy
Several studies demonstrate that the constitutive B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling and response have a critical role in the survival and expansion of both B cell lymphoma and the chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) clones. CLL patients represent a heterogeneous group with one subset exhibiting an indolent disease whereas others progress rapidly necessitating early therapy. It was observed that patients with indolent form of CLL are characterized by an expansion of clonal B cells with anergic features. In this subset of patients, B cells fail to respond to BCR cross-linking as measured by calcium mobilization and protein tyrosine phosphorylation [82,83]. This was characterized as B cell anergy and was associated with low levels of surface IgM expression, constitutive activation of ERK1/2 and NFATc1 signaling. Chronic BCR triggering promoted CLL cell survival selectively in p-ERK+ve subset and treatment with ERK or NF-AT signaling inhibitors specifically induced apoptosis in this group of patients. The initial phase of reversal of anergy consists of loss of ERK phosphorylation and NF-AT nuclear translocation and restoration of B cell unresponsiveness, reinforcing the notion that the anergic signaling favors the chronic survival of leukemic lymphocytes. Thus, it appears that the constitutive signaling observed in B-cell anergy can be efficiently targeted in CLL for therapeutic purposes [82].
8. Conclusions
The studies of central B-cell tolerance performed in the last 3 decades in mouse models have given us an understanding of forces that shape the murine naive B-cell repertoire. Future challenges will be determining the contributions of different forms of tolerance (clonal deletion, anergy, receptor editing and BAFF thresholds) to the repertoire of human B cells, and to understanding which of these mechanisms is primarily affected in autoimmune diseases. Another challenge will be to increase our knowledge of the bone marrow microenvironment to establish whether a specific niche exists for the self-antigen presentation to newly generated B cells, and for the processes of negative and positive selection. In particular, we will need to define the cytokines and chemoattractants that influence immature B-cell selection and their distribution in the marrow environment. Another major challenge will be to determine what factors regulate tonic BCR signaling in immature B cells, and particularly what defines the signaling threshold that separates negative and positive selection.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported in part by grants from Edward P. Evans Foundation and an NIH grant to SB.
Author Contributions
Murali Gururajan and Vishal J. Sindhava wrote the manuscript in consultation with Subbarao Bondada. Final revisions were made by Subbarao Bondada.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest
References
- Tze, L.E.; Schram, B.R.; Lam, K.P.; Hogquist, K.A.; Hippen, K.L.; Liu, J.; Shinton, S.A.; Otipoby, K.L.; Rodine, P.R.; Vegoe, A.L.; et al. Basal immunoglobulin signaling actively maintains developmental stage in immature B cells. PLoS Biol. 2005, 3, e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroe, J.G.; Bannish, G.; Fuentes-Panana, E.M.; King, L.B.; Sandel, P.C.; Chung, J.; Sater, R. Positive and negative selection during B lymphocyte development. Immunol. Res. 2003, 27, 427–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, J.I.; Goodnow, C.C. Positive versus negative signaling by lymphocyte antigen receptors. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1998, 16, 645–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allman, D.; Lindsley, R.C.; DeMuth, W.; Rudd, K.; Shinton, S.A.; Hardy, R.R. Resolution of three nonproliferative immature splenic B cell subsets reveals multiple selection points during peripheral B cell maturation. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 6834–6840. [Google Scholar]
- Allman, D.M.; Ferguson, S.E.; Lentz, V.M.; Cancro, M.P. Peripheral B cell maturation. Ii. Heat-stable antigen(hi) splenic B cells are an immature developmental intermediate in the production of long-lived marrow-derived B cells. J. Immunol. 1993, 151, 4431–4444. [Google Scholar]
- Hardy, R.R.; Hayakawa, K. Positive and negative selection of natural autoreactive B cells. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2012, 750, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, K.; Asano, M.; Shinton, S.A.; Gui, M.; Allman, D.; Stewart, C.L.; Silver, J.; Hardy, R.R. Positive selection of natural autoreactive B cells. Science 1999, 285, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardemann, H.; Yurasov, S.; Schaefer, A.; Young, J.W.; Meffre, E.; Nussenzweig, M.C. Predominant autoantibody production by early human B cell precursors. Science 2003, 301, 1374–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnet, F.M. A modification of jerne’s theory of antibody production using the concept of clonal selection. CA Cancer J. Clin. 1976, 26, 119–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahana, W.; Guilbert, B.; Avrameas, S. Suppression of anti-DNA antibody production in MRL mice by treatment with anti-idiotypic antibodies. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1987, 70, 538–545. [Google Scholar]
- Rajewsky, K. From a dream to reality. Eur J. Immunol. 2007, 37 (Suppl. 1), S134–S137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, A.C.; Denman, A.M. Self-tolerance and autoimmunity. Br. Med. Bull. 1976, 32, 124–129. [Google Scholar]
- Coutinho, A.; Moller, G. Editorial: Immune activation of B cells: Evidence for ‘one nonspecific triggering signal’ not delivered by the ig receptors. Scand. J. Immunol. 1974, 3, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taussig, M.J. Induction of hapten-specific B cell tolerance by low doses of hapten-carrier conjugate. Nature 1973, 245, 34–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiller, J.M.; Romball, C.G.; Weigle, W.O. Induction of immunological tolerance in neonatal and adult rabbits. Differences in the cellular events. Cell. Immunol. 1973, 8, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siskind, G.W.; Benacerraf, B. Cell selection by antigen in the immune response. Adv. Immunol. 1969, 10, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denman, A.M.; Frenkel, E.P. Mode of action of anti-lymphocyte globulin. Ii. Changes in the lymphoid cell population in rats treated with anti-lymphocyte globulin. Immunology 1968, 14, 115–126. [Google Scholar]
- Nemazee, D.; Kouskoff, V.; Hertz, M.; Lang, J.; Melamed, D.; Pape, K.; Retter, M. B-cell-receptor-dependent positive and negative selection in immature B cells. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2000, 245, 57–71. [Google Scholar]
- Radic, M.Z.; Erikson, J.; Litwin, S.; Weigert, M. B lymphocytes may escape tolerance by revising their antigen receptors. J. Exp. Med. 1993, 177, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiegs, S.L.; Russell, D.M.; Nemazee, D. Receptor editing in self-reactive bone marrow B cells. J. Exp. Med. 1993, 177, 1009–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luning Prak, E.T.; Monestier, M.; Eisenberg, R.A. B cell receptor editing in tolerance and autoimmunity. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1217, 96–121. [Google Scholar]
- Forster, I.; Rajewsky, K. The bulk of the peripheral B-cell pool in mice is stable and not rapidly renewed from the bone marrow. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 4781–4784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandien, A.; Fucs, R.; Nobrega, A.; Andersson, J.; Coutinho, A. Negative selection of multireactive B cell clones in normal adult mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 1994, 24, 1345–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Brill-Dashoff, J.; Shinton, S.A.; Asano, M.; Hardy, R.R.; Hayakawa, K. Evidence of marginal-zone B cell-positive selection in spleen. Immunity 2005, 23, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.P.; Stadanlick, J.E.; Cancro, M.P. Space, Selection, and surveillance: Setting boundaries with BLyS. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 6405–6410. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, S.H.; Reth, M. Perspectives on the nature of BCR-mediated survival signals. Mol. Cell 2004, 14, 696–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, J.L.; Oropallo, M.A.; Sindhava, V.; Goenka, R.; Cancro, M.P. The role of B lymphocyte stimulator in B cell biology: Implications for the treatment of lupus. Lupus 2013, 22, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, P.; MacKay, F.; Steiner, V.; Hofmann, K.; Bodmer, J.L.; Holler, N.; Ambrose, C.; Lawton, P.; Bixler, S.; Acha-Orbea, H.; et al. BAFF, a novel ligand of the tumor necrosis factor family, stimulates B cell growth. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 189, 1747–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, P.A.; Belvedere, O.; Orr, A.; Pieri, K.; LaFleur, D.W.; Feng, P.; Soppet, D.; Charters, M.; Gentz, R.; Parmelee, D.; et al. BLyS: Member of the tumor necrosis factor family and B lymphocyte stimulator. Science 1999, 285, 260–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Jiang, X.; Kubo, S.; Sakashita, M.; Narita, N.; Yamamoto, H.; Sunaga, H.; Fujieda, S. B type CpG-DNA suppresses poly(I:C)-induced BLyS expression and production in human tonsillar fibroblasts. Clin. Immunol. 2011, 141, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darce, J.R.; Arendt, B.K.; Wu, X.; Jelinek, D.F. Regulated expression of BAFF-binding receptors during human B cell differentiation. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 7276–7286. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Park, C.S.; Yoon, S.O.; Li, L.; Hsu, Y.M.; Ambrose, C.; Choi, Y.S. BAFF supports human B cell differentiation in the lymphoid follicles through distinct receptors. Int. Immunol. 2005, 17, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, F.; Chen, R.; Liu, B.; Zhang, X.; Han, J.; Wang, H.; Shen, G.; Tao, J. BAFF induces spleen CD4+ T cell proliferation by down-regulating phosphorylation of Foxo3a and activates cyclin D2 and D3 expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 425, 854–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Chen, S.J.; Zhang, W.; Ma, H.W.; Zhang, S.Q.; Chen, L. hsBAFF regulates proliferation and response in cultured CD4(+) T lymphocytes by upregulation of intracellular free Ca(2+) homeostasis. Cytokine 2011, 53, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavie, F.; Miceli-Richard, C.; Ittah, M.; Sellam, J.; Gottenberg, J.E.; Mariette, X. B-cell activating factor of the tumour necrosis factor family expression in blood monocytes and T cells from patients with primary sjogren’s syndrome. Scand. J. Immunol. 2008, 67, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimoto, K.; Takahashi, Y.; Ogasawara, M.; Setoyama, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Tsuzaka, K.; Abe, T.; Takeuchi, T. Aberrant expression of BAFF in T cells of systemic lupus erythematosus, which is recapitulated by a human T cell line, Loucy. Int. Immunol. 2006, 18, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, J.A.; Dillon, S.R.; Mudri, S.; Johnston, J.; Littau, A.; Roque, R.; Rixon, M.; Schou, O.; Foley, K.P.; Haugen, H.; et al. TACI-Ig neutralizes molecules critical for B cell development and autoimmune disease. Impaired B cell maturation in mice lacking BLyS. Immunity 2001, 15, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiemann, B.; Gommerman, J.L.; Vora, K.; Cachero, T.G.; Shulga-Morskaya, S.; Dobles, M.; Frew, E.; Scott, M.L. An essential role for BAFF in the normal development of B cells through a BCMA-independent pathway. Science 2001, 293, 2111–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hondowicz, B.D.; Alexander, S.T.; Quinn, W.J., 3rd; Pagan, A.J.; Metzgar, M.H.; Cancro, M.P.; Erikson, J. The role of BLyS/BLyS receptors in anti-chromatin B cell regulation. Int. Immunol. 2007, 19, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesley, R.; Xu, Y.; Kalled, S.L.; Hess, D.M.; Schwab, S.R.; Shu, H.B.; Cyster, J.G. Reduced competitiveness of autoantigen-engaged B cells due to increased dependence on BAFF. Immunity 2004, 20, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheema, G.S.; Roschke, V.; Hilbert, D.M.; Stohl, W. Elevated serum B lymphocyte stimulator levels in patients with systemic immune-based rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44, 1313–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariette, X.; Roux, S.; Zhang, J.; Bengoufa, D.; Lavie, F.; Zhou, T.; Kimberly, R. The level of BLyS (BAFF) correlates with the titre of autoantibodies in human sjogren’s syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2003, 62, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohl, W.; Metyas, S.; Tan, S.M.; Cheema, G.S.; Oamar, B.; Xu, D.; Roschke, V.; Wu, Y.; Baker, K.P.; Hilbert, D.M. B lymphocyte stimulator overexpression in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: Longitudinal observations. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 3475–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Roschke, V.; Baker, K.P.; Wang, Z.; Alarcon, G.S.; Fessler, B.J.; Bastian, H.; Kimberly, R.P.; Zhou, T. Cutting edge: A role for B lymphocyte stimulator in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Lamore, R., 3rd; Parmar, S.; Patel, K.; Hilas, O. Belimumab (Benlysta): A breakthrough therapy for systemic lupus erythematosus. Pharm. Ther. 2012, 37, 212–226. [Google Scholar]
- Stohl, W.; Scholz, J.L.; Cancro, M.P. Targeting BLyS in rheumatic disease: The sometimes-bumpy road from bench to bedside. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2011, 23, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohl, W.; Hiepe, F.; Latinis, K.M.; Thomas, M.; Scheinberg, M.A.; Clarke, A.; Aranow, C.; Wellborne, F.R.; Abud-Mendoza, C.; Hough, D.R.; et al. Belimumab reduces autoantibodies, normalizes low complement levels, and reduces select B cell populations in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 2328–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coca, A.; Sanz, I. Updates on B-cell immunotherapies for systemic lupus erythematosus and Sjogren’s syndrome. Curr. Opin Rheumatol. 2012, 24, 451–456. [Google Scholar]
- Stohl, W.; Merrill, J.T.; McKay, J.D.; Lisse, J.R.; Zhong, Z.J.; Freimuth, W.W.; Genovese, M.C. Efficacy and safety of Belimumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A phase ii, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study. J. Rheumatol. 2013, 40, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, D.J.; Stohl, W.; Furie, R.A.; Lisse, J.R.; McKay, J.D.; Merrill, J.T.; Petri, M.A.; Ginzler, E.M.; Chatham, W.W.; McCune, W.J.; et al. A phase II, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study of belimumab in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 61, 1168–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medzhitov, R.; Janeway, C. The Toll receptor family and microbial recognition. Trends Microbiol. 2000, 8, 452–456. [Google Scholar]
- Medzhitov, R.; PrestonHurlburt, P.; Janeway, C.A. A human homologue of the drosophila toll protein signals activation of adaptive immunity. Nature 1997, 388, 394–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinman, R.M.; Hemmi, H. Dendritic cells: Translating innate to adaptive immunity. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2006, 311, 17–58. [Google Scholar]
- Sindhava, V.J.; Bondada, S. Multiple regulatory mechanisms control B-1 B cell activation. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gururajan, M.; Jacob, J.; Pulendran, B. Toll-like receptor expression and responsiveness of distinct murine splenic and mucosal B-cell subsets. PLoS One 2007, 2, e863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.M.; Broughton, C.; Tabor, A.S.; Akira, S.; Flavell, R.A.; Mamula, M.J.; Christensen, S.R.; Shlomchik, M.J.; Viglianti, G.A.; Rifkin, I.R.; et al. Rna-associated autoantigens activate B cells by combined B cell antigen receptor/Toll-like receptor 7 engagement. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 1171–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leadbetter, E.A.; Rifkin, I.R.; Marshak-Rothstein, A. Toll-like receptors and activation of autoreactive B cells. Curr. Dir. Autoimmun. 2003, 6, 105–122. [Google Scholar]
- Leadbetter, E.A.; Rifkin, I.R.; Hohlbaum, A.M.; Beaudette, B.C.; Shlomchik, M.J.; Marshak-Rothstein, A. Chromatin-IgG complexes activate B cells by dual engagement of IgM and Toll-like receptors. Nature 2002, 416, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celhar, T.; Magalhaes, R.; Fairhurst, A.M. TLR7 and TLR9 in SLE: When sensing self goes wrong. Immunol. Res. 2012, 53, 58–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herlands, R.A.; Christensen, S.R.; Sweet, R.A.; Hershberg, U.; Shlomchik, M.J. T cell-independent and toll-like receptor-dependent antigen-driven activation of autoreactive B cells. Immunity 2008, 29, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelman, F.D.; Lees, A.; Birnbaum, R.; Gause, W.C.; Morris, S.C. Dendritic cells can present antigen in vivo in a tolerogenic or immunogenic fashion. J. Immunol. 1996, 157, 1406–1414. [Google Scholar]
- Rotta, G.; Edwards, E.W.; Sangaletti, S.; Bennett, C.; Ronzoni, S.; Colombo, M.P.; Steinman, R.M.; Randolph, G.J.; Rescigno, M. Lipopolysaccharide or whole bacteria block the conversion of inflammatory monocytes into dendritic cells in vivo. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 1253–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisch, R. Immunogenic versus tolerogenic dendritic cells: A matter of maturation. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 29, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindhava, V.J.; Tuna, H.; Gachuki, B.W.; DiLillo, D.J.; Avdiushko, M.G.; Onami, T.M.; Tedder, T.F.; Cohen, D.A.; Bondada, S. Bone marrow dendritic cell-mediated regulation of TLR and B cell receptor signaling in B cells. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 3355–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.; Draves, K.E.; Boton, M.; Grewal, P.K.; Marth, J.D.; Clark, E.A. Dendritic cell-dependent inhibition of B cell proliferation requires CD22. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 4561–4569. [Google Scholar]
- Kaisho, T.; Akira, S. Dendritic-cell function in Toll-like receptor- and MyD88-knockout mice. Trends Immunol. 2001, 22, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenner, J.; Kerst, G.; Handgretinger, R.; Muller, I. Increased alpha2,6-sialylation of surface proteins on tolerogenic, immature dendritic cells and regulatory T cells. Exp. Hematol. 2006, 34, 1212–1218. [Google Scholar]
- Duong, B.H.; Tian, H.; Ota, T.; Completo, G.; Han, S.; Vela, J.L.; Ota, M.; Kubitz, M.; Bovin, N.; Paulson, J.C.; et al. Decoration of T-independent antigen with ligands for CD22 and SIGLEC-G can suppress immunity and induce B cell tolerance in vivo. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilmon, M.A.; Rutan, J.A.; Clarke, S.H.; Vilen, B.J. Low-affinity, smith antigen-specific B cells are tolerized by dendritic cells and macrophages. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Jellusova, J.; Nitschke, L. Regulation of B cell functions by the sialic acid-binding receptors SIGLEC-G and CD22. Front. Immunol. 2011, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellusova, J.; Wellmann, U.; Amann, K.; Winkler, T.H.; Nitschke, L. CD22 x SIGLEC-G double-deficient mice have massively increased B1 cell numbers and develop systemic autoimmunity. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 3618–3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, M.; Liang, Y.; Noronha, A.; Coukos, J.; Kasper, D.L.; Farraye, F.A.; Ganley-Leal, L.M. Systemic Toll-like receptor ligands modify B-cell responses in human inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2011, 17, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagannathan, M.; McDonnell, M.; Liang, Y.; Hasturk, H.; Hetzel, J.; Rubin, D.; Kantarci, A.; van Dyke, T.E.; Ganley-Leal, L.M.; Nikolajczyk, B.S. Toll-like receptors regulate B cell cytokine production in patients with diabetes. Diabetologia 2010, 53, 1461–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jube, S.; Rivera, Z.S.; Bianchi, M.E.; Powers, A.; Wang, E.; Pagano, I.; Pass, H.I.; Gaudino, G.; Carbone, M.; Yang, H. Cancer cell secretion of the damp protein hmgb1 supports progression in malignant mesothelioma. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 3290–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, L.E.; Lauber, K.; Schiller, M.; Manfredi, A.A.; Herrmann, M. The role of defective clearance of apoptotic cells in systemic autoimmunity. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2010, 6, 280–289. [Google Scholar]
- Menard, L.; Samuels, J.; Ng, Y.S.; Meffre, E. Inflammation-independent defective early B cell tolerance checkpoints in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotsapas, C.; Voight, B.F.; Rossin, E.; Lage, K.; Neale, B.M.; Wallace, C.; Abecasis, G.R.; Barrett, J.C.; Behrens, T.; Cho, J.; et al. Pervasive sharing of genetic effects in autoimmune disease. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, J.C.; Szczepanski, L.; Szechinski, J.; Filipowicz-Sosnowska, A.; Emery, P.; Close, D.R.; Stevens, R.M.; Shaw, T. Efficacy of B-cell-targeted therapy with rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 2572–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnunen, T.; Chamberlain, N.; Morbach, H.; Cantaert, T.; Lynch, M.; Preston-Hurlburt, P.; Herold, K.C.; Hafler, D.A.; O’Connor, K.C.; Meffre, E. Specific peripheral B cell tolerance defects in patients with multiple sclerosis. J. Clin. Invest. 2013, 123, 2737–2741. [Google Scholar]
- Arimura, Y.; Yagi, J. Comprehensive expression profiles of genes for protein tyrosine phosphatases in immune cells. Sci. Signal. 2010, 3, rs1. [Google Scholar]
- Menard, L.; Saadoun, D.; Isnardi, I.; Ng, Y.S.; Meyers, G.; Massad, C.; Price, C.; Abraham, C.; Motaghedi, R.; Buckner, J.H.; et al. The PTPN22 allele encoding an R620W variant interferes with the removal of developing autoreactive B cells in humans. J. Clin. Invest. 2011, 121, 3635–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apollonio, B.; Scielzo, C.; Bertilaccio, M.T.; Ten Hacken, E.; Scarfo, L.; Ranghetti, P.; Stevenson, F.; Packham, G.; Ghia, P.; Muzio, M.; et al. Targeting B-cell anergy in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2013, 121, 3879–3888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woyach, J.A. Survival of the weak (signalers): Anergy in CLL. Blood 2013, 121, 3781–3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).