Abstract
An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using monoclonal antibody (MAb), Fab antibody, and single-chain variable fragment (scFv) antibody has become one of the most promising analytical methods owing to its rapidity, sensitivity, and reliability. Recently, a chimera of green fluorescent protein (GFP) with a scFv antibody, named fluobody, was proposed as a probe for an alternative immunosorbent assay; i.e., fluorescence-linked immunosorbent assay (FLISA). In this FLISA, an even more sensitive, simple, and rapid immunoassay can be performed by detecting the highly sensitive fluorophore of GFP that is genetically and directly fused to the scFv antibody. In addition, the time- and cost-consuming secondary antibody reaction and the following enzyme-substrate reaction, necessary for conventional ELISA, can be avoided, making it possible to complete the assay more rapidly. Focusing on naturally occurring bioactive products, fluobody recognizing 1,4-naphthoquinone, plumbagin and triterpenoid saponin, ginsenosides were successfully expressed in Escherichia coli (E. coli) and applied to FLISA. The construction, the expression, and the potential use of fluobody in quantitative/qualitative analysis of bioactive natural products are reviewed in this article.
1. Introduction
Antibody-based analytical methods have recently received much attention due to high-binding affinity and specificity of antibodies to target molecules. To date, the antibody-based analytical method has been expanded from enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) [1], surface plasmon resonance (SPR) [2,3], flow cytometry [4,5], hand-held immunochromatographic assay [6,7,8] to novel eastern blotting techniques [9,10,11]. Among them, ELISA has a great advantage in quantitative and qualitative analysis of bioactive natural products since multi-sample can be continuously determined /detected in the one plate. In addition, the accuracy and reliability of ELISA are sufficiently high enough to be used in the quality control of medicinal plants [12]. The probes used in ELISA are rich in variety such as monoclonal antibody (MAb) [13], polyclonal antibody (PAb), Fab antibody, single-chain variable fragment (scFv) antibody [14], and bispecific antibody [15].
In our previous study, we focused on the development of an antibody-based analytical method for two promising natural products, plumbagin (5-hydroxy-2-methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone; PL; Figure 1a) and ginsenoside Re (G-Re; Figure 1b) [16,17]. PL is a naturally occurring bioactive product mainly produced from the root of the family Plumbaginaceae which includes Plumbago zeylanica, P. indica, and P. europaea [18,19,20]. Much work has been carried out regarding PL since it was found to have diverse and interesting pharmacological properties such as anti-cancer, anti-cardiotonic, anti-microbial, anti-fertility, anti-atherosclerotic, anti-filarial, and anti-amyloidogenic activities [21,22,23,24,25,26]. Thus, PL has recently been a remarkable natural product as a drug candidate. However, the biokinetics of PL need to be monitored from the point of view of appropriate usage and the avoidance of adverse effects due to its strong pharmacological activities. To date, high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), coupled with a diode array detector (HPLC-DAD), and liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS-MS) have been developed for quantitative/qualitative analysis of PL [27,28,29]. On the other hand, ginsenosides are major triterpenoid saponins mainly produced and isolated from the root of Panax ginseng (white ginseng) and its related species including P. japonicus (Japanese ginseng), P. quinquefolium (American ginseng), and P. notoginseng (Tienchi ginseng). Recently, their demand has been dramatically increased worldwide as ingredients of dietary health supplements and additives in foods and beverages due to their pharmacological activities such as tonic, immunomodulatory, anti-mutagenic, and anti-aging activities [30,31]. Clinical studies have also raised the possibility that ginseng could be used for the treatment of psychological function, immune function, and conditions associated with diabetes [32,33,34]. Ginsenosides are featured as major components of ginseng and are classified into two groups, protopanaxatriol type which includes ginsenoside Re (G-Re) and Rg1 (R-Gg1) and protopanaxadiol types which include ginsenoside Rb1 (G-Rb1), Rc (G-Rc), and Rd (G-Rd) as shown in Figure 1b. So far, various analytical methods for ginsenosides such as HPLC techniques, and ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC), also coupled with tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS) have been developed [35,36,37,38,39] since the ginsenoside constituents controlling the value of the ginseng are different depending on their growing environment such as soil condition and season of harvest to which they are sensitive.
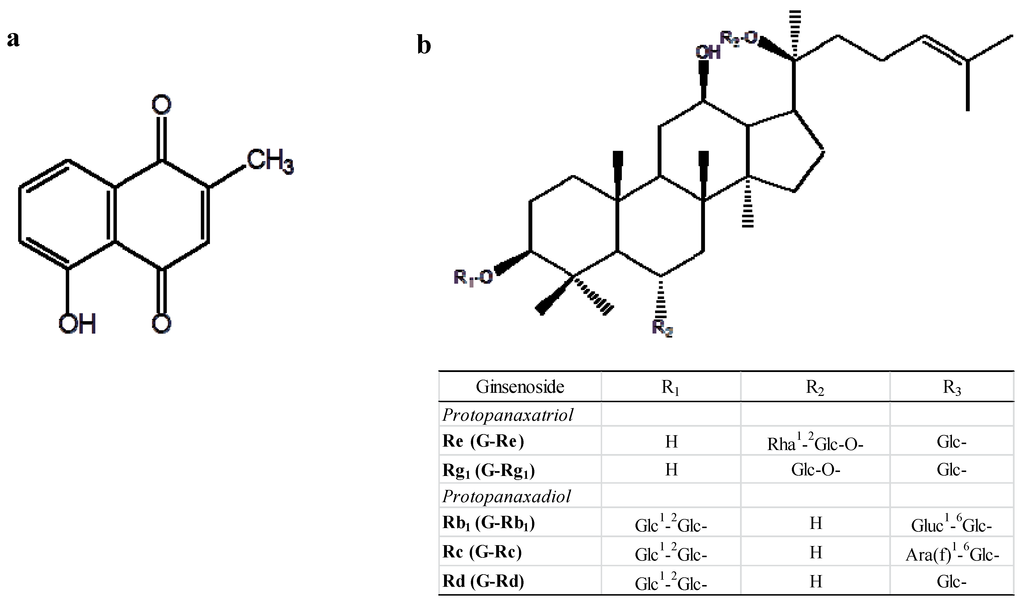
Figure 1.
Structures of 5-hydroxy-2-methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone (PL) (a) and major ginsenosides (b).
Owing to the developed antibody-based analytical method, we primarily prepared MAb against PL (MAb 3A3) and G-Re (MAb-4G10) which possess high specificity to PL and wide cross-reactivity to ginsenosides, respectively [16,17]. The developed ELISA using MAbs showed potential as an accurate and reliable assay for assessing the quality of the host plant. We subsequently constructed scFv antibody against PL (PL-scFv) and G-Re (GRe-scFv) using the cDNA of their hybridoma cell lines secreting MAb 3A3 and MAb-4G10, respectively, and expressed in E. coli, Sf9 insect cells, and silkworm (Bombyx mori) to obtain the probes for ELISA more efficiently [40,41,42,43]. However, an even simpler, speedy, and sensitive immunoassay is required to deal with a large number of plant samples serially.
A high level of sensitivity can be gained by fluorescent labels with a wide range of analytical procedures, thus, the conjugation between fluorescent labels and antibodies has conventionally been performed by chemical conjugation of organic fluorophores [44]. Fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) is one of the most popular organic fluorophores, which is widely utilized in various fields. It can be bound to the free amino group of the proteins and peptides, which leads to a stable thiourea bond formation. Therefore, FITC-labeled antibody has been used mainly for flow cytometry and immunohistochemical staining for over half a century [45,46]. With these procedures, however, a large amount of purified protein is required. Moreover, there is a possibility that the fluorophores conjugate with paratope, resulting in a partial or complete loss of reactivity of the antibody. To avoid the disadvantages of chemical conjugation, a fluorescent single domain antibody (fluobody) which is a fusion protein of a green fluorescent protein (GFP) and a scFv antibody has been genetically constructed and used alternatively. In this genetically engineered format, the resultant protein is always expressed in a one-to-one ratio between the fluorochrome and scFv, which should enhance the accuracy of the quantitative analysis. Currently, the usage of fluobody has been expanded from diagnosis, molecular targeted therapy, immunolabeling of cancer cells, probes for immunoassay, fluorescence-activated cell sorter (FACS) to fluorescent-linked immunosorbent assay (FLISA) for the detection of large molecular weight antigens such as proteins, peptides, and microtubules [47,48,49,50,51]. So far the application of a fluobody in FLISA for the detection of small molecules has been rarely reported except against herbicide, picloram [52] and s-triazine [53], and bioactive natural products, PL and G-Re [54,55,56] previously described by our group.
In this study, the construction, bacterial expression, and characterization of fluobodies that have binding affinity to PL and G-Re have been demonstrated. Furthermore, the adequate formation of a fluobody has been assessed by constructing two chimera proteins of GFP fused at the C-terminus of scFv (C-fluobody) and the N-terminus of scFv (N-fluobody). The potential use of a fluobody in quantitative/qualitative analysis of bioactive natural products has been additionally reviewed in this article.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Construction and Expression of the Fluobodies
Splicing by overlap extension PCR (SOE-PCR) is an effective technique to engineer hybrid genes for fusion of proteins [57]. To fuse scFv with AcGFP domains by SOE-PCR, they were primarily amplified by PCR from pET28a expression vector encoding PL-scFv and GRe-scFv gene and pAcGFP1-N1 vector encoding AcGFP gene. After purification of two domains, these domains were assembled by SOE-PCR to generate two constructs (C-fluobody and N-fluobody) with flexible linker (Gly4Ser)2 and restriction enzyme sites at both ends (BamH I and Sal I). The assembled fluobodies gene was purified, digested and ligated downstream of T7 promoter of pET28a vector to express it as chimera protein with His6-tag and T7-tag. Sequencing of the nucleotide acid revealed that C-, and N-fluobody against PL (C-, N-fluobody/PL) and C-, and N-fluobody against G-Re (C-, N-fluobody/G-Re) possess 1461-bp nucleotides encoding 487 amino acids and 1446-bp nucleotides encoding 482 amino acids, respectively. These results also indicated that the flexible linker sequences that are composed of repetitive sequences of four glycine and serine residues, (Gly4Ser)2, had been successfully placed between scFv and AcGFP genes but with a different format of AcGFP-linker-scFv (C-format) and scFv-linker-AcGFP (N-format) with each other (Figure 2). The plasmids encoding the fluobodies were transformed into the E. coli (BL21) strain for overexpression. The expression of the fluobodies was induced by the addition of 0.5 mM isopropyl-thio-β-D-galactopyranoside (IPTG) when the optimal density at 660 nm reached 0.6, with further culturing at 25 °C for 12 h.
2.2. Purification and Refolding of the Fluobodies
Purification and refolding of fluobodies that are mainly expressed as inclusion bodies were carried out by immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography (IMAC) using His-bind resin and stepwise dialysis following the Umetsu method [58], respectively. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE), followed by Coomassie brilliant blue staining was performed to estimate purity after IMAC. In this purification, the four kinds of the fluobodies, C-, N-fluobody/PL and C-, N-fluobody/G-Re were estimated at more than 90% (Figure 3). The yields of each of the fluobodies were in the range of 29 to 53 mg per 1 L of bacterial cell culture as shown in Table 1. When MAb 3A3 were prepared by culturing hybridoma cells, the yield was approximately 8 mg per 500 mL culture medium (equivalent to 16 mg per 1 L) [16]. Considering the labor-intensive and long-term culture of hybridoma cells, which requires advanced techniques to avoid contamination from microorganisms, bacterial expression using E. coli has a big advantage in preparing probes for immunoassay even if the refolding steps of inclusion bodies are sometimes required. SDS-PAGE analysis demonstrated that the fluobody monomer was successfully expressed and purified as a chimeric protein containing His6- and T7-tags with a molecular mass with theoretical values of fluobody/PL (57 kDa) and fluobody/G-Re (55.5 kDa).
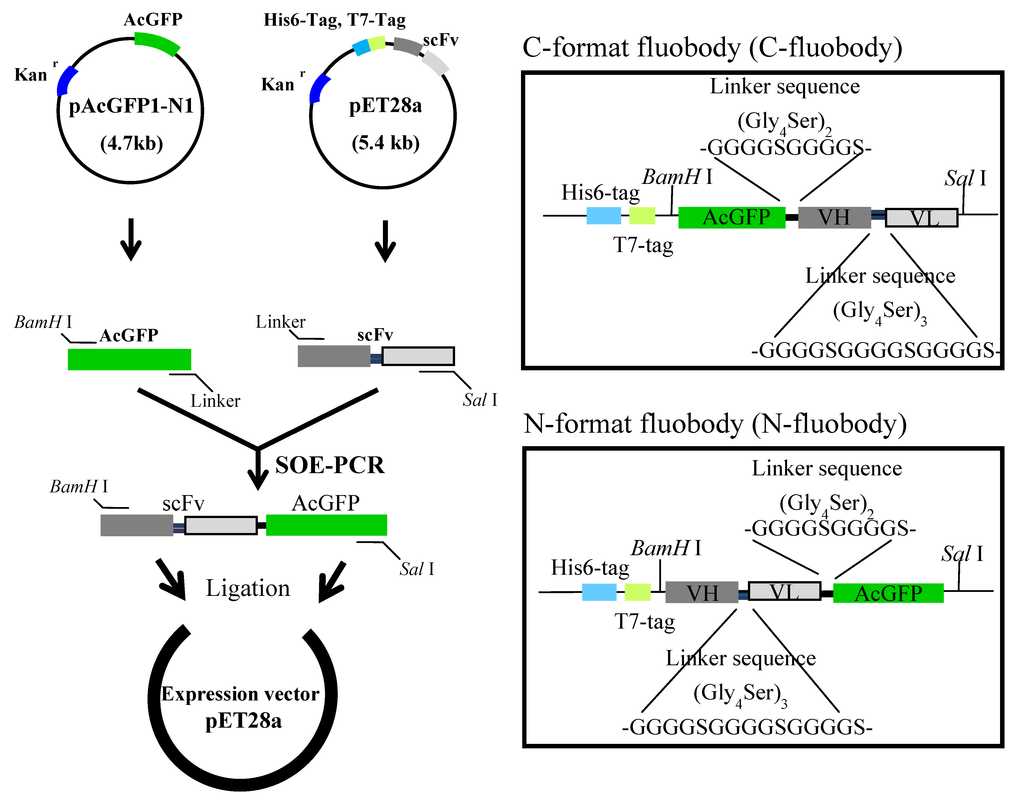
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of the construction of fluobody. The AcGFP and scFv genes were fused by splicing by overlap extension PCR (SOE-PCR) with the flexible linker sequence consisting of repetitive sequence of glycine and serine.

Table 1.
The yields of fluobodies after purification by immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography.
| C-format | N-format | |
|---|---|---|
| Fluobody/PL | 29.0 mg | 41.4 mg |
| Fluobody/G-Re | 32.9 mg | 52.6 mg |
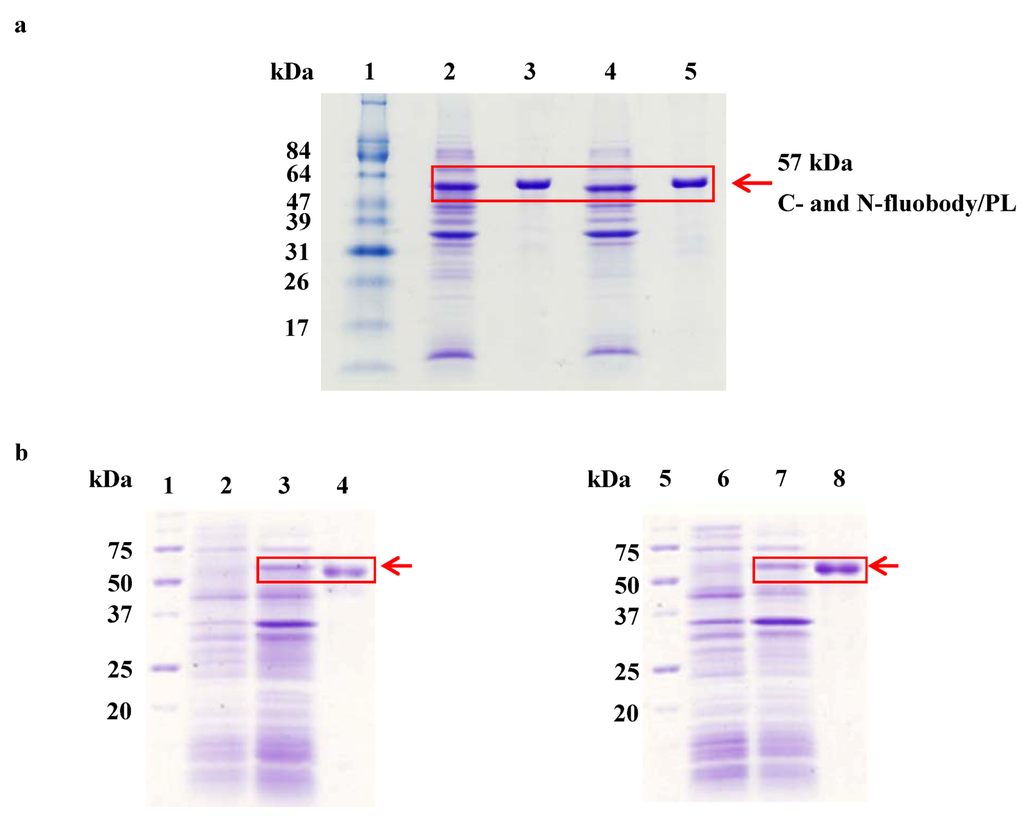
Figure 3.
Expression analysis of fluobody by SDS-PAGE. (a) SDS-PAGE analysis of C- and N-fluobody/PL. Lane 1; molecular protein marker, lane 2; C-fluobody in insoluble fraction after IPTG induction, lane 3; C-fluobody/PL after IMAC purification (1.5 µg), lane 4; N-fluobody in insoluble fraction after IPTG induction, lane 5; N-fluobody/PL after IMAC purification (1.5 µg). (b) SDS-PAGE analysis of C- and N-fluobody/G-Re. lane 1 and 5; molecular protein marker, lane 2 and 6; total proteins before IPTG induction, lane 3; C-fluobody/G-Re in insoluble fraction after IPTG induction, lane 4; C-fluobody/G-Re after IMAC purification (2.1 µg), lane 7; N-fluobody/G-Re in insoluble fraction after IPTG induction, lane 8; N-fluobody/G-Re after IMAC purification (2.1 µg).
2.3. Measurement of Fluorescence Intensity
The fluorescence intensity of each fluobody was analyzed using the MTP-600FE fluorescent microplate reader at an emission wavelength of 490 nm and an excitation wavelength of 530 nm. In this assay, phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) was used as both a negative control and as solvent to adjust the concentration of fluobodies. Interestingly, in both cases of fluobody/PL and fluobody/G-Re, the fluorescence intensity of C-fluobody was higher than that of N-fluobody (Figure 4), making it possible to apply C-fluobody to FLISA. In support of our results, the superiority of C-fluobody in fluorescence intensity has been recently reported by Ohshima [59]. It is supposed that the differences in fluorescence intensity between C-fluobody and N-fluobody are mainly derived from the flexibility of the linker domains between AcGFP and scFv. The 10 amino acids (30 bp) of the C-terminus of the AcGFP are well known as a flexible sequence [60], which can function as an additional linker in the C-fluobody fusing scFv at the C-terminus of AcGFP. Since the length of the linker peptide of the fluobodies was designed to contain 10 amino acids encoded by 30 bp, C-fluobody is equivalent to having a 2-fold longer linker sequence compared to N-fluobody.
Although the length of linker peptide (Gly4Ser)2 of both fluobodies is the same, the flexibility between the AcGFP and scFv domains is structurally different due to their joining format, resulting in the fluorescence intensity of C-fluobody being superior to that of N-fluobody.
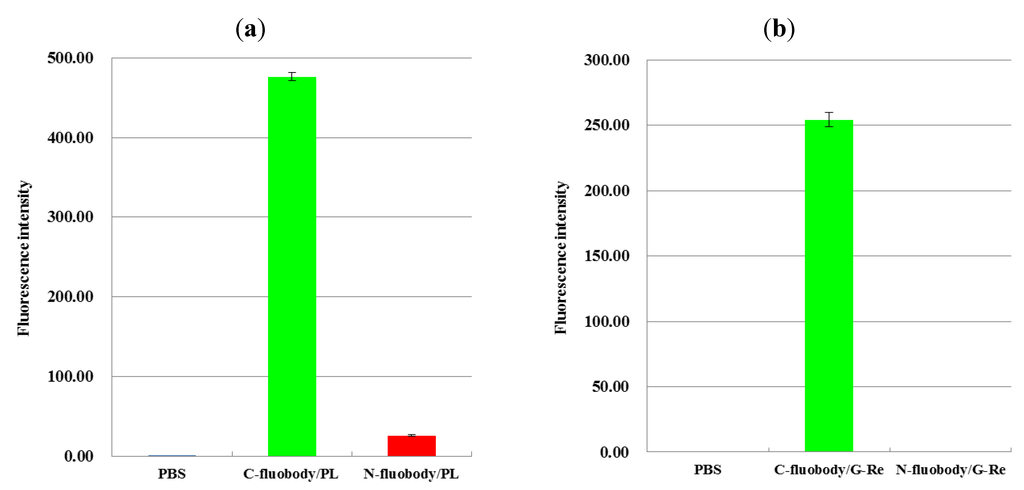
Figure 4.
Measurement of fluorescence intensity. Fluorescence intensity of fluobody was detected by MTP-600FE fluorescent microplate reader at an emission wavelength of 490 nm and an excitation wavelength of 530 nm. (a) Fluorescence intensity of C-, and N-fluobody/PL. Concentrations of C-fluobody/PL and N-fluobody/PL were equalized by addition of PBS at a concentration of 160 µg/mL. (b) Fluorescence intensity of C-, and N-fluobody/G-Re. Concentrations of C-fluobody/G-Re and N-fluobody/G-Re were equalized by addition of PBS at a concentration of 200 µg/mL.
2.4. Indirect ELISA and Indirect Competitive ELISA (icELISA)
The reactivity of the fluobody/PL and fluobody/G-Re was evaluated by indirect ELISA using PL-ovalbumin (PL-Ova) and G-Re-human serum albumin (GRe-HSA) conjugates, respectively. The reactivity response curve was drawn by plotting the absorbance at 405 nm against the logarithm of the fluobody concentration in indirect ELISA. The concentration of each fluobody positively correlated with the absorbance value in a logical manner (Figure 5). Interestingly, indirect ELISA revealed that the performance of N-fluobody is superior (up to one order of magnitude) to that of C-fluobody in both cases (Figure 5), although the C-fluobody exhibits higher fluorescence intensity compared to the N-fluobody (Figure 4). In both cases, it was found that the characteristics of N-terminal protein (AcGFP for C-fluobody and scFv for N-fluobody) have a tendency to be expressed stronger than those of C-terminal protein.
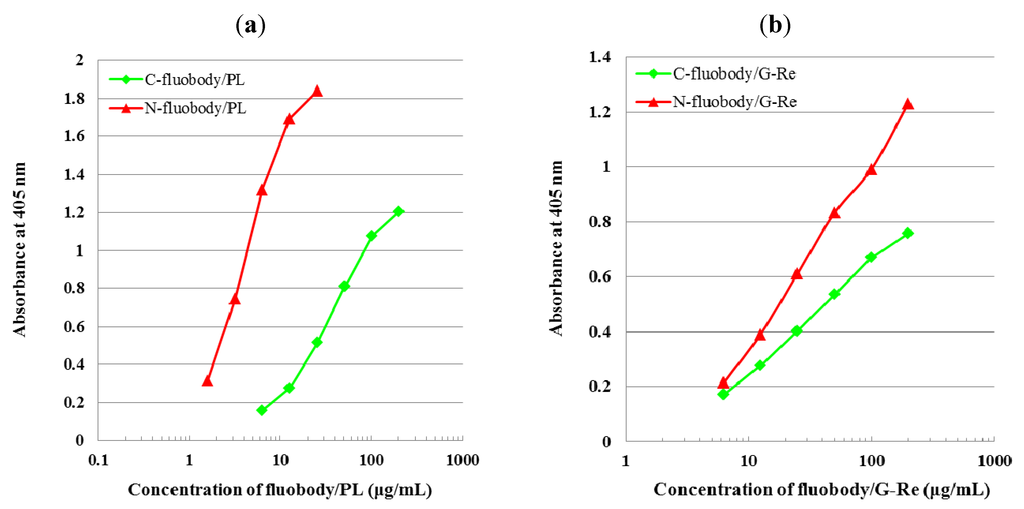
Figure 5.
Reactivity of fluobody to coated antigen in indirect ELISA. (a) Reactivity response curve of fluobody/PL to PL-Ova conjugates (1 µg/mL as protein amount). (b) Reactivity response curve of fluobody/G-Re to GRe-HSA conjugates (2 µg/mL as protein amount).
Subsequently, the inhibitory activity of fluobody against free antigen (PL or G-Re) was analyzed by icELISA. After blocking with phosphate-buffered saline containing 10% (w/v) skimmed milk (SPBS), fluobodies were incubated with serially double diluted concentrations of free antigen (PL or G-Re) on an immunoplate. Any fluobodies binding to free antigen were washed out. The fluobodies bound to either PL-Ova or GRe-HSA were then incubated with secondary antibody followed by 2,2′-azino-bis (3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) diammonium salt (ABTS) substrate solution for coloring. In this icELISA, the detectable range of PL using C-fluobody and N-fluobody expanded from 0.2 to 25 µg/mL, while that of G-Re ranged from 100 ng/mL to 3.1 µg/mL (Figure 6). These results demonstrated that icELISA using both C-, N-fluobody/PL and C-, N-fluobody/G-Re displayed the same sensitivity as that using the original PL-scFv [40] and GRe-scFv [41], respectively, suggesting that the complementarity-determining regions (CDRs) for binding antigen are not inhibited by fusing AcGFP at termini. The analysis of these fluobodies by X-ray crystallography is necessary to gain more insight into structural characterization.
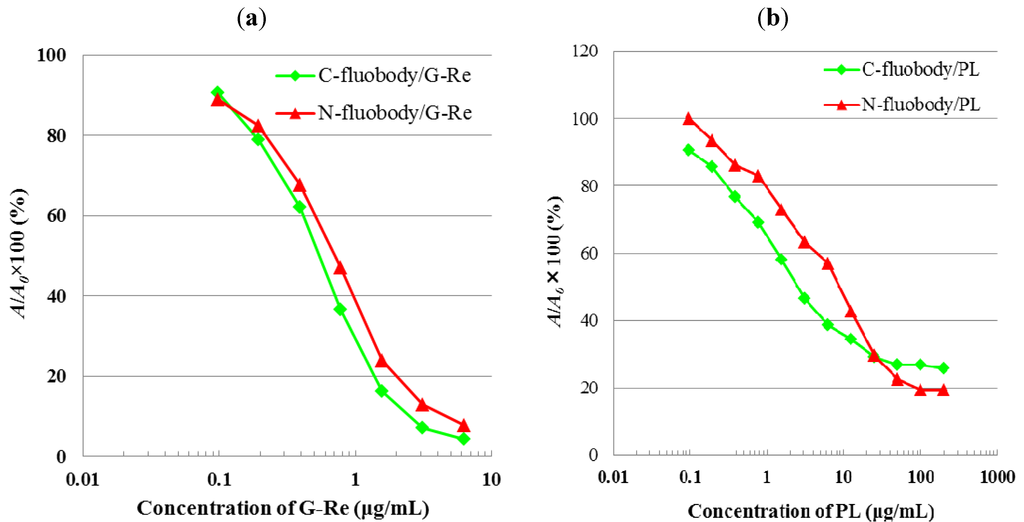
Figure 6.
Calibration curve of PL (a) and G-Re (b) in icELISA. A/A0, A0 is the absorbance in the absence of PL (a) or G-Re (b), and A is the absorbance in the presence of PL (a) or G-Re (b).
2.5. Characterization of Fluobodies/PL and Fluobodies/G-Re
Characterization of C-, and N-fluobody/PL has been done by icELISA to examine the specificity of recombinant fluobodies against structure related compounds and binding affinity against PL.
The dissociation constant (KD) of fluobodies in solution was evaluated by the ELISA method proposed by Friguet et al. [61]. This method is equally available for antibodies against both small and large molecular weight antigens without labeling of either antibodies or antigens. Briefly, a fixed concentration of fluobody and various concentrations of PL were mixed and then allowed to reach equilibrium. Subsequently, the concentrations of free fluobody in the mixtures were measured by ELISA. Various concentrations of PL were incubated with C- or N-fluobody at 37 °C for 1 h until they reached equilibrium. Free fluobody amounts in the incubation mixture were determined by ELISA as described above. The KD of C-fluobody/PL and N-fluobody/PL in solution were 5.93 × 10−6 M and 2.43 × 10−5 M, respectively from the typical Scatchard plot. When the KD of MAb 3A3 (6.18 × 10−6 M) was compared to that of both fluobodies, C-fluobody/PL (5.93 × 10−6 M) exhibited about a 4-fold higher binding affinity than that of N-fluobody/PL (2.43 × 10−5 M), although C-fluobody/PL exhibited almost the same binding affinity as that of MAb 3A3.
The specificity of fluobodies as a probe for immunoassay was evaluated by calculating cross-reactivities (CRs) followed by the Weiler and Zenk method [60]. As shown in Table 2, CRs of C fluobody/PL displayed almost the same specificity as that of N-fluobody/PL except against 1,2-naphthoquinone (C-fluobody/PL; 23%, N-fluobody/PL; 83%). Furthermore, it was also found that CRs of C-fluobody/G-Re exhibited nearly the same CRs as that of N-fluobody/G-Re. This result raised the possibility that fluobody/G-Re could be applicable to develop FLISA for the specific detection/determination of G-Re and G-Rb1, which is classified into protopanaxatriol.
Though the CRs of C-format fluobody were not different from that of N-format fluobody, C-fluobody was found to be superior to N-fluobody in the fluorescence intensity of AcGFP, using as a fluorophore. As we described in the previous paragraph, it may be due to the flexibility of the C-terminus of AcGFP.

Table 2.
Cross-reactivities (CRs) of fluobodies against PL or G-Re.
| Compounds | CRs (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| C-fluobody/PL | N-fluobody/PL | |
| Plumbagin (2-methyl-5-hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone) | 100 | 100 |
| Menadion (2-methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone) | 11 | 4.4 |
| Juglone (5-hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone) | 20 | 22 |
| Lawsone (2-hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone) | <0.005 | <0.005 |
| 1,4-Naphthoquinone | 2.5 | 0.9 |
| 1,2-Naphthoquinone | 23 | 83 |
| Shikonin | 0.4 | 0.1 |
| Sennoside A | <0.005 | <0.005 |
| Sennoside B | <0.005 | <0.005 |
| 1-Naphthol | <0.005 | <0.005 |
| 2-Naphthol | <0.005 | <0.005 |
| C-fluobody/G-Re | N-fluobody/G-Re | |
| Ginsenoside Re (G-Re) | 100 | 100 |
| Ginsenoside Rg1 (G-Rg1) | 72 | 79 |
| Ginsenoside Rd (G-Rd) | 15 | 13 |
| Ginsenoside Rb1 (G-Rb1) | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| Ginsenoside Rc (G-Rc) | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| Glycyrrhizin | <0.005 | <0.005 |
| Saikosaponin A | <0.005 | <0.005 |
| Digitonin | <0.005 | <0.005 |
| Swertiamarin | <0.005 | <0.005 |
| Sennoside A | <0.005 | <0.005 |
| Sennoside B | <0.005 | <0.005 |
| Deoxycholic acid | <0.005 | <0.005 |
2.6. Indirect FLISA and Indirect Competitive FLISA (icFLISA)
The characterized fluobodies were then applied to fluorescence-linked immunosorbent assay (FLISA) to develop a simple, speedy, and sensitive antibodies-based analytical method. Since scFv antibody was genetically fused with AcGPF which enabled it to be directly detected by the MTP-600FE fluorescent microplate reader (Corona), the time- and cost-consuming enzyme substrate reaction could be avoided, making it possible to complete the assay within 3 h.
Indirect FLISA was carried out to evaluate the binding reactivity to coated antigen, PL-Ova or GRe-HSA conjugates in a 96-well black microtiter plate (FluoroNunc). In the reactivity response curve in indirect FLISA using C-format fluobodies, the concentration of the C-fluobody positively correlated with the fluorescence intensity values in a logical manner, while the concentration of the N-format fluobodies did not show any correlation with the fluorescence intensity values (data not shown), as was predicted by the data in Figure 4.
We then analyzed the inhibitory activities of fluobodies against free antigen (PL or G-Re) in icFLISA. Figure 7 shows the calibration curves for various concentrations of PL or G-Re in diluted methanol solution. In this icFLISA, the detectable range of PL using C-fluobody/PL ranged from 25 ng/mL to 3.1 μg/mL, whereas that of G-Re using C-fluobody/G-Re ranged from 10 ng/mL to 3.1 μg/mL. However, in the case of N-format fluobody, the signal was undetectable due to its low fluorescence intensity as well as in indirect FLISA, even though competitive inhibitory activity was detected in the ELISA system. More interestingly, both limits of detection (LOD) for PL and G-Re determinations in FLISA system using the C-fluobody were found to be about 10-fold lower than that in the conventional ELISA using scFv (PL-scFv and GRe-scFv) [40,41] and their parental MAb (MAb 3A3 and MAb-4G10) [16,17], where the LOD for PL and G-Re showed 200 ng/mL and 100 ng/mL, respectively. It was estimated that the improvement of LOD comes from the highly sensitive fluorescence of AcGFP detected by the fluorescent microplate reader compared to that of the enzyme. These results indicate not only a simple and speedy immunoassay but also that a sensitive immunoassay could be generally developed using C-fluobody instead of MAb or scFv.
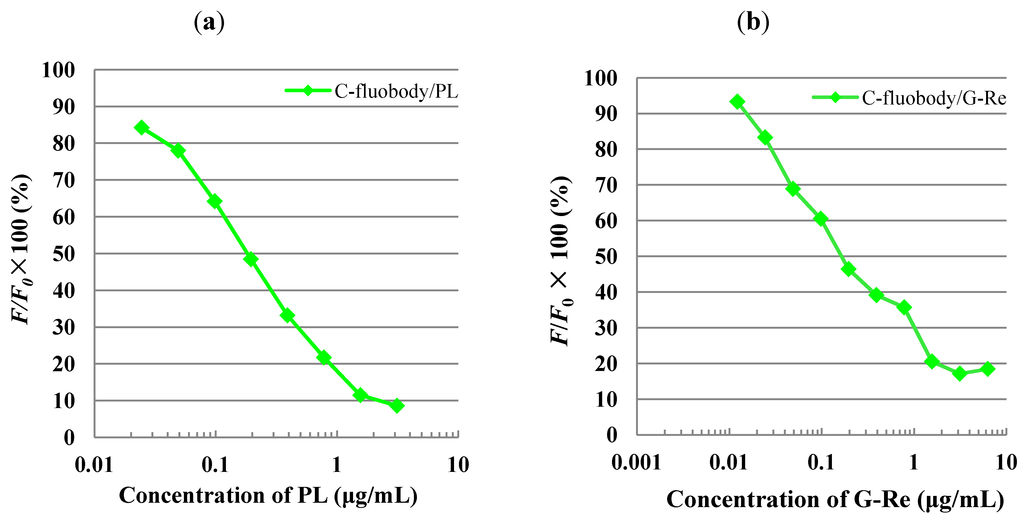
Figure 7.
Calibration curve of PL (a) and G-Re (b) using C-fluobody in icFLISA. F/F0, F0 is the absorbance in the absence of PL, and F is the absorbance in the presence of PL. Green squares and curves shows the standard curve produced using C-fluobody/PL (a; 25 µg/mL) and C-fluobody/G-Re (b; 125 µg/mL).
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Chemicals and Immunochemicals
PL, ginsenoside Re (G-Re), ginsenoside Rb1 (G-Rb1), ginsenoside Rc (G-Rc), ginsenoside Rg1 (G-Rg1), and ginsenoside Rd (G-Rd) were purchased from Wako Pure Chemical (Osaka, Japan). Ovalbumin (Ova), human serum albumin (HSA), and monoclonal anti-T7 tag antibodies produced in mice were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Steinheim, Germany). Horseradish peroxidase (HRP) labeled anti-T7-tag conjugates reagent was obtained from Invitrogen (San Diego, CA, USA). HRP-labeled anti-mouse IgG goat antibody was obtained from Santa Cruz (CA, USA). DNA polymerase and DNA restriction enzyme were purchased from Takara (Kyoto, Japan). The pAcGFP1-N1 vector was obtained from Clontech (Palo Alto, CA, USA). All other chemicals used in the experiments were standard commercial products of an analytical reagent grade.
3.2. Preparation of PL-Ova and GRe-HSA Conjugates for Coated Antigen
Since a free low molecular weight compound is usually hard to be adsorbed on a plate without modifications, PL and G-Re have thus been chemically conjugated to Ova and HSA by the 1-ethyl-3-(3'-dimethylaminopropyl)-carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC) method [16] and the periodate oxidation method [62], respectively. Briefly, 1-ethyl-3-(3'-dimethylaminopropyl)-carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC; 6 mg) dissolved in MES buffer consisting of 0.1 M 2-(N-morpholino) ethanesulfonic acid and 0.9% (w/v) sodium chloride (0.3 mL) were added to the 3'-(5-hydroxy-2-methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone-3-yl) propanoic acid (3 mg) solution dissolved in 35% (w/w) pyridine (0.3 mL) and MES buffer (0.3 mL). The resultant mixture was then added dropwise to 3 mg Ova solution in MES buffer (0.3 mL), and stirred at room temperature for 13 h. Subsequently, the precipitates were then removed by centrifugation, and the supernatants were dialyzed against five batches of distilled water for 2 d at 4 °C and lyophilized to yield 1.0 mg of PL-Ova conjugates. In the case of synthesis of GRe-HSA conjugates, G-Re (3 mg) in dimethyl sulfoxide (0.4 mL) was added dropwise to 3 mg NaIO4 solution (0.6 mL) and then stirred at room temperature for 1 h. After that, 8 mg HSA in 50 mM carbonate buffer (pH 9.6; 1.0 mL) was added to the mixture and stirred for 5 h. The reaction mixture was dialyzed against five batches of distilled water and then lyophilized to yield 6.7 mg of GRe-HSA conjugates.
3.3. Construction of Expression Vector for Fluobody
To construct both C-format and N-format fluobody expression vector, pET28a expression vector (Novagen) encoding scFv gene, whose DDBJ accession numbers of PL-scFv and GRe-scFv are AB470492 and AB537502, respectively, and a pAcGFP1-N1 vector (Clontech) encoding AcGFP gene were used as templates. For constructing two kinds of chimera fused with scFv at the C-terminus of AcGFP (C-fluobody) or the N-terminus of AcGFP (N-fluobody), eight primers were designed based on the sequence information of scFv and AcGFP.
The AcGFP domains for C-, and N-fluobody were primarily amplified from the pAcGFP1-N1 vector by PCR using the two primers sets containing a BamH I restriction enzyme site at the 5′ end with a linker sequence at the 3′ end, and a linker sequence at the 5′ end with a Sal I restriction enzyme site at the 3′ end. Subsequently, scFv domains for C-, and N-fluobody were amplified from the pET28a expression vector by PCR using the two primers sets containing a linker sequence at the 5′ end with a Sal I restriction enzyme site at the 3′ end, and a BamH I restriction enzyme site at the 5′ end with a linker sequence at the 3′ end. The PCR conditions for both AcGFP and scFv domains were as follow: 30 cycles of denaturation (98 °C, 10 s), annealing (55 °C, 5 s), and extension (72 °C, 1 min) with PrimeStar HS DNA polymerase (Takara, Kyoto, Japan).
After amplification and gel purification of individual domains, these domains were combined together with the standard 10 amino acid linker (Gly4Ser)2 between two domains. C-fluobody was constructed by SOE-PCR using the purified AcGFP and scFv domains for C-fluobody and the primers containing restriction enzyme site (BamH I and Sal I) with C-format as was described in Figure 2. While, N-fluobody was constructed by SOE-PCR using the purified scFv and AcGFP domains for N-fluobody and the primers containing restriction enzyme site at both ends (BamH I and Sal I) with N-format. The PCR conditions for amplification of C- and N-fluobody were as follows: 30 cycles of denaturation (98 °C, 10 s), annealing (55 °C, 5 s), and extension (72 °C, 3 min) with PrimeStar HS DNA polymerase (Takara). The amplified genes encoding the C-fluobody and N-fluobody were then purified, digested with BamH I and Sal I, and ligated downstream of the His6 and T7-tags of the pET28a expression vector (Novagen) to generate the pET28a/C-fluobody and pET28a/N-fluobody plasmids.
3.4. Expression and Purification of Recombinant Fluobodies
Resultant plasmids were then transformed into the E. coli BL21 (DE3) strain (Novagen) for the expression and purification of the fluobodies. The E. coli were cultured at 25 °C in 1 L of Luria-Bertani (LB) supplemented with 25 μg/mL kanamycin until the optimal density at 660 nm reached 0.6. The expression of C-, and N-fluobody was induced by addition of 0.5 mM IPTG followed by shaking the culture for 12 h at 25 °C, and then the E. coli cells were harvested by centrifugation at 8,000 rpm for 10 min at 4 °C before being treated with lysis buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, 500 mM NaCl, 10% (v/v) glycerol, and 0.01% (v/v) Nonidet P40; pH 8.0), and 1 mg/mL lysozyme. In this lysis step, 1 mL of lysis buffer was used to 1 g wet weight cell pellets. Next, the cells were ultrasonically lysated and then centrifuged at 14,000 rpm for 20 min at 4 °C to give pellets as inclusion bodies. Since the fluobodies were designed to be expressed as a chimera containing His6-tag at their N-termini, IMAC using His-bind resin (Novagen) could be a potentially effective tool in this purification. The pellets were suspended in binding buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, 8 M urea, 500 mM NaCl, and 5 mM imidazole, pH 8.0) for further purification and ultrasonically extracted. The solubilized inclusion bodies were then applied to the resin column charged with Ni2+, and the resins were washed with binding buffer followed by washing buffer (50 mM Tri-HCl, 8 M urea, 500 mM NaCl, and 20 mM imidazole; pH 8.0) to remove nonspecific binding of background proteins. The target proteins were then eluted with elution buffer (50 mM Tri-HCl, 8 M urea, 500 mM NaCl, and 500 mM imidazole; pH 8.0). The yield of purified fluobodies was estimated by the method of Bradford [63].
3.5. Refolding of Recombinant Fluobodies
The purified recombinant C-, and N-fluobody/PL (250 μg/mL) and C-, and N-fluobody/G-Re (200 μg/mL) were refolded by stepwise dialysis following the methods of Umetsu with slight modifications [56]. The fluobody protein was reduced by addition of 100-fold molar excess of β-mercaptoethanol (β-ME) in the dialysis buffer which consisted of 50 mM Tris-HCl, 8 M urea/6 M guanidine hydrochloride (GuHCl), 200 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, and β-ME was then removed by dialysis against the same buffer lacking β-ME. After that, the fluobodies were refolded by gradual removal of urea/GuHCl using stepwise dialysis against Tris buffer containing urea (4, 2, 1, 0.5, 0.1, and 0 M) or GuHCl (3, 2, 1, 0.5, 0.1, 0 M). At the 2 M to 0.5 M urea or 1 M to 0.5 M GuHCl stages, 400 mM L-arginine and 50-fold molar excess oxidized glutathione (GSSG) were added to facilitate the formation of disulfide bonds. At the last step, the fluobodies were dialyzed against PBS for 24 h at 4 °C. Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) was performed according to the methods of Laemmli [64].
3.6. Measurement of Fluorescence Intensity
To compare the fluorescence intensity between C-fluobody and N-fluobody, the concentrations of the purified fluobodies were equalized in PBS, which was also used as a negative control. A black microtiter plate (FluoroNunc, MaxiSorp) was used to reduce the background fluorescence. 50 μL of each of the samples (C-fluobody, N-fluobody, and PBS) were added to one-wells and the fluorescence intensity was measured with an MTP-600FE fluorescent microplate reader (Corona) at excitation and emission wavelengths of 490 nm and 530 nm, respectively. This assay was carried out at least five times for each sample.
3.7. Indirect ELISA and icELISA
Indirect ELISA was carried out to analyze the binding activity of fluobodies to the coated antigen, which is either PL-Ova or GRe-HSA conjugate. PL-Ova (1 µg/mL) or GRe-scFv (2 µg/mL) conjugates were dissolved in 50 mM carbonate buffer (pH 9.0), added to a 96-well immunoplate (100 µL/well) (Nunc, Maxisorb, Roskilde, Denmark), and incubated for 1 h. The plate was then washed three times with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) containing 0.05% (v/v) Tween 20 (PBS-T) and then treated with 300 µL of PBS containing 10% (w/v) skimmed milk (PBS-sm) for 1 h to reduce non-specific adsorption. Subsequently, various concentrations of fluobodies (100 μL/well) were incubated for 1 h. After washing the plate three times with PBS-T, the fluobodies bound to the coated antigen were incubated with 100 µL of a 5,000-fold diluted solution of secondary antibody, which is horse radish peroxidase (HRP)-labeled anti-T7-tag conjugates (Invitrogen) for 1 h. The plate was then washed with PBS-T, 100 µL of ABTS substrate solution mixed with 0.1 M citrate buffer (pH 4.0) supplemented with 0.003% (v/v) H2O2 were added to each well and incubated for 15 min. All incubation steps of the ELISA were carried out at 37 °C. Absorbance was measured at 405 nm with a microplate reader (Immuno Mini NJ-2300, Nalge Nunc International).
An icELISA was also carried out to analyze the inhibitory activity of fluobodies against PL or G-Re. The same procedures as used in the indirect ELISA were used until the blocking step. After washing the blocked-plate three times with PBS-T, 50 µL of various concentrations of PL or G-Re in diluted methanol solution were incubated with 50 µL of each fluobody solution for 1 h. The plate was then washed three times with PBS-T, and the fluobody bound to GRe-HSA conjugates was combined with 100 µL of a 5,000-fold diluted solution of HRP-labeled anti-T7-tag conjugates for 1 h. After washing the plate three times with PBS-T, 100 µL of ABTS substrate solution was added to each well and incubated for 15 min. Absorbance at 405 nm was measured using a microplate reader.
To evaluate the specificity of fluobodies, the cross-reactivities (CRs) of the purified fluobodies against various compounds were calculated using the method of Weiler and Zenk [65] as follows:
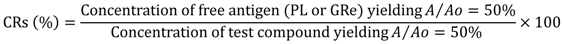
where A is the absorbance in the presence of the test compound, and A0 is the absorbance in the absence of the test compound.
3.8. Indirect FLISA and icFLISA
For the indirect FLISA, a black microtiter plate (FluoroNunc, MaxiSorp, Roskilde, Denmark) was coated with PL-Ova (1 µg/mL) or GRe-HSA (2 µg/mL) conjugates in 100 µL of 50 mM carbonate buffer (pH 9) and incubated at 37 °C for 1 h. The plate was washed three times with PBS-T and then treated with 300 µL of PBS-sm for 1 h at 37 °C to reduce non-specific adsorption. Subsequently, various concentrations of fluobodies (100 μL/well) were incubated for 1 h at 25 °C. After washing the plate a further three times with PBS-T and adding 100 µL PBS to each well, the remaining fluorescence was measured at an excitation wavelength of 490 nm and an emission wavelength of 530 nm using a fluorescent microplate reader (MTP-600FE, Corona).
In icFLISA, the same procedure as was used in the indirect FLISA was used until the blocking step. After washing the blocked-plate three times with PBS-T, various concentrations of PL or G-Re (50 µL) in diluted methanol were incubated with 50 µL of purified fluobody solution for 1 h at 25 °C to observe the competition of fluobody between free antigen (PL or G-Re) and coated antigen (PL-Ova or GRe-HSA conjugates). After washing the plate a further three times with PBS-T and adding 100 µL of PBS to each well, the remaining fluorescence was measured with a MTP-600FE fluorescent microplate reader.
4. Conclusions
To date, many antibody-based analytical approaches have been developed, which include ELISA, SPR, flow cytometry, and hand-held immunochromatographic assay [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11]. We have mainly focused on the preparation of monoclonal antibodies against natural products and the application in ELISA for the serial determination of bioactive compounds in medicinal plants in order to select high quality strains after breeding [12]. The advantage of the ELISA method using monoclonal antibody (MAb) is rapid determination/detection, easy handling, high sensitivity, and selectivity. However, even simpler, speedy, and sensitive immunoassay is required to deal with a large number of plant samples continually. Recent advance in gene technology makes it possible to construct various antibodies [14] by dealing with the original hybridoma and filamentous bacteriophage displaying antibody fragments [66,67].
In this review, construction of the fluobody, which is a chimera protein of GFP and scFv antibody, against PL and G-Re, and characterization has been described to develop fluorescence-linked immunoassay, FLISA. The fluobody used in FLISA can overcome the disadvantage of cost, time, and labor, when preparing MAb. To obtain MAb as a probe for ELISA, an expensive medium, sophisticated technique for culture of hybridoma cells to avoid contamination with microorganisms, and a long period of time are required. On the other hand, the fluobody can be easily expressed in E. coli or other hosts [42,43,56], when genes are constructed. In the case of E.coli expression as mentioned in this review, an adequate amount of fluobody can be obtained within 1 week including the refolding step. In addition, it can be commonly performed by using low-cost Luria-Bertani (LB) medium consisting of 1% (w/v) polypeptone, 0.5% (w/v) yeast extract, and 0.5% (w/v) NaCl [68]. The FLISA itself can overcome the disadvantage of cost and time, when performing ELISA. The enzyme-substrate reaction that is necessary for ELISA can be avoided in FLISA. Therefore, the time-saving (1.5 h) and cost-saving analysis, where the expensive secondary antibody is necessary in ELISA, can be carried out in FLISA.
Characterization of fluobodies revealed that the sensitivity in FLISA could be improved by using C-fluobody. Moreover, the specificity of the fluobody is found to be the same as that of the original scFv antibodies. Thus, these results indicate that the rapid, sensitive, and specific immunoassay could be generally developed by using C-format fluobody once scFv antibodies that have interesting characteristics are obtained. Since applications using antibodies have been recently increasing in various fields, fluobodies against bioactive natural products would also be promising tools for qualitative/quantitative analysis in the next-generation.
Acknowledgements
The research in this paper was supported, in part, by the Research Fellowship of the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science for Young Scientists. This work was also funded by a Grant in Aid from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science Asian CORE Program of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan.
References
- Yalow, R.S.; Berson, S.A. Immunoassay of endogenous plasma insulin in man. J. Clin. Invest. 1960, 39, 1157–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lê, H.Q.A.; Sauriat-Dorizon, H.; Korri-Youssoufi, H. Investigation of SPR and electrochemical detection of antigen with polypyrrole functionalized by biotinylated single-chain antibody: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 674, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, D.C.; Brown, R.G.W.; Lowe, C.R. Detection of immuno-complex formation via surface plasmon resonance on gold-coated diffraction gratings. Biosensors 1987, 3, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangl, J.L.; Herzenberg, L.A. Selection of hybridomas and hybridoma variants using the fluorescence activated cell sorter. J. Immunol. Methods 1982, 52, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanier, L.L.; Warner, N.L. Paraformaldehyde fixation of hematopoietic cells for quantitative flow cytometry (FACS) analysis. J. Immunol. Methods 1981, 47, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putalun, W.; Fukuda, N.; Tanaka, H.; Shoyama, Y. A one-step immunochromatographic assay for detecting ginsenosides Rb1 and Rg1. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 378, 1338–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putalun, W.; Morinaga, O.; Tanaka, H.; Shoyama, Y. Development of a one-step immunochromatographic strip test for the detection of sennosides A and B. Phytochem. Anal. 2004, 15, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnegie, P.R.; Pacheco, G. Immunochromatography: A combination of chromatography and immunodiffusion on a micro-scale. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1964, 117, 137–141. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, S.; Tanaka, H.; Shoyama, Y. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for glycyrrhizin using anti-glycyrrhizin monoclonal antibody and an eastern blotting technique for glucuronides of glycyrrhetic acid. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 5784–5790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morinaga, O.; Zhu, S.; Tanaka, H.; Shoyama, Y. Visual detection of saikosaponins by on-membrane immunoassay and estimation of traditional Chinese medicines containing Bupleuri radix. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 346, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Fukuda, N.; Shoyama, Y. Eastern blotting and immunoaffinity concentration using monoclonal antibody for ginseng saponins in the field of traditional Chinese medicines. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 3783–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoyama, Y. Pharmacognosical study during 40 years. Yakugaku Zasshi 2007, 127, 1593–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, G.; Milstein, C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature 1975, 256, 495–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, G.; Milstein, C. Man-made antibodies. Nature 1991, 349, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karawajew, L.; Micheel, B.; Behrsing, O.; Gaestel, M. Bispecific antibody-producing hybrid hybridomas selected by a fluorescence activated cell sorter. J. Immunol. Methods 1987, 96, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, S.; Putalun, W.; Tsuchihashi, R.; Morimoto, S.; Kinjo, J.; Tanaka, H. Development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using highly-specific monoclonal antibodies against plumbagin. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 607, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morinaga, O.; Tanaka, H.; Shoyama, Y. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the determination of total ginsenosides in ginseng. Anal. Lett. 2006, 39, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.T.; Malonne, H.; Duez, P.; Vanhaelen-Fastre, R.; Vanhaelen, M.; Fontaine, J. Cytotoxic constituents from Plumbago zeylanica. Fitoterapia 2004, 75, 500–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangopadhyay, M.; Dewanjee, S.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Bhattacharya, S. Effect of different strains of Agrobacterium rhizogenes and nature of explants on Plumbago indica hairy root culture with special emphasis on root biomass and plumbagin production. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2010, 5, 1913–1916. [Google Scholar]
- Serrilli, A.M.; Sanfilippo, V.; Ballero, M.; Sanna, C.; Poli, F.; Scartezzini, P.; Serafini, M.; Bianco, A. Polar and antioxidant fraction of Plumbago europaea L., a spontaneous plant of Sardinia. Nat. Prod. Res. 2010, 24, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandur, S.K.; Ichikawa, H.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Plumbagin (5-hydroxy-2-methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone) suppresses NF-κB activation and NF-κB-regulated gene products through modulation of p65 and IκBα kinase activation, leading to potentiation of apoptosis induced by cytokine and chemotherapeutic agents. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 17023–17033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itogawa, M.; Takeya, K.; Furukawa, H. Cardiotonic action of plumbagin on guinea-pig papillary muscle. Planta Med. 1991, 57, 317–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, de S.R.; Figueiredo, M.R.; Aragão, T.V.; Kaplan, M.A.C. Antimicrobial activity in vitro of plumbagin isolated from Plumbago species. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo. Cruz. 2003, 98, 959–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, S.K. Effects of plumbagin on reproductive function of male dog. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 1984, 22, 153–156. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan, L.; Mathew, N.; Muthuswamy, K. In vitro antifilarial activity of glutathione S-transferase inhibitors. Parasitol. Res. 2009, 105, 1179–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermejo-Bescós, P.; Martín-Aragón, S.; Jiménez-Aliaga, K.L.; Ortega, A.; Molina, M.T.; Buxaderas, E.; Orellana, G.; Csákÿ, A.G. In vitro antiamyloidogenic properties of 1,4-naphthoquinones. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 400, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stensen, W.; Jensen, E. High-performance liquid chromatrographic separations of naphthoquinones and their derivatives. J. Chromatogr. A 1994, 659, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babula, P.; Mikelova, R.; Adam, V.; Kizek, R.; Havel, L.; Sladky, Z. Using of liquid chromatography coupled with diode array detector for determination of naphthoquinones in plants and for investigation of influence of pH of cultivation medium on content of plumbagin in Dionaea muscipula. J. Chromatogr. B 2006, 842, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.J.; Lin, L.C.; Tsai, T.H. Determination and identification of plumbagin from the roots of Plumbago zeylanica L. by liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1083, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.K.; Johnke, R.M.; Allison, R.R.; O’Brien, K.F.; Dobbs, L.J. Radioprotective potential of ginseng. Mutagenesis 2005, 20, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiefer, D.; Pantuso, T. Panax ginseng. Am. Fam. Physician 2003, 68, 1539–1542. [Google Scholar]
- Susin, S.A.; Lorenzo, H.K.; Zamzami, N.; Marzo, I.; Brenner, C.; Larochette, N.; Prévost, M.; Alzari, P.M.; Kroemer, G. Mitochondrial release of caspase-2 and -9 during the apoptotic process. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 189, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.Z.; Luo, L. Ginseng on hyperglycemia: Effects and mechanisms. Evid. Based Complement Altern. Med. 2009, 6, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.T.; Mchendale, S.; Yuan, C.S. Ginseng and diabetes. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2005, 33, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Huang, J.; Hu, X.; Li, K.; Sun, C. Simultaneous determination of ginsenoside (G-Re, G-Rg1, G-Rg2, G-F1, G-Rh1) and protopanaxatriol in human plasma and urine by LC-MS/MS and its application in a pharmacokinetics study of G-Re in volunteers. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2011, 879, 2011–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Luo, G.A.; Liang, Q.L.; Hu, P.; Wang, Y.M. Rapid qualitative and quantitative analyses of Asian ginseng in adulterated American ginseng preparations by UPLC/Q-TOF-MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 52, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanazawa, H.; Nagata, Y.; Matsushima, Y.; Tomoda, M.; Takai, N. Simultaneous determination of ginsenosides and saikosaponins by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. 1990, 507, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, N.; Tanaka, H.; Shoyama, Y. Applications of ELISA, western blotting and immunoaffinity concentration for survey of ginsenosides in crude drugs of Panax species and traditional Chinese herbal medicines. Analyst 2000, 125, 1425–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.F.; Wang, D.L.; Meng, M.X.; Hu, F.; Yao, T.W. Simultaneous determination of notoginsenoside R1, ginsenoside Rg1, Re, Rb1 and icariin in rat plasma by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2009, 877, 2113–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, S.; Taura, F.; Putalun, W.; Pongkitwitoon, B.; Tsuchihashi, R.; Morimoto, S.; Kinjo, J.; Shoyama, Y.; Tanaka, H. Construction and expression of specificity-improved single-chain variable fragments against the bioactive naphthoquinone, plumbagin. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 32, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongkitwitoon, B.; Sakamoto, S.; Morinaga, O.; Juengwatanatrakul, T.; Shoyama, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Morimoto, S. Single-chain variable fragment antibody against ginsenoside Re as an effective tool for the determination of ginsenosides in various ginsengs. J. Nat. Med. 2011, 65, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, S.; Taura, F.; Tsuchihashi, R.; Putalun, W.; Kinjo, J.; Tanaka, H.; Morimoto, S. Expression, purification, and characterization of anti-plumbagin single-chain variable fragment antibody in Sf9 insect cell. Hybridoma (Larchmt) 2010, 29, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, S.; Pongkitwitoon, B.; Nakamura, S.; Maenaka, K.; Tanaka, H.; Morimoto, S. Efficient silkworm expression of single-chain variable fragment antibody against ginsenoside Re using Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedrovirus bacmid DNA system and its application in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for quality control of total ginsenosides. J. Biochem. 2010, 148, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermanson, G.T. Bioconjugate Techniques; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1996; pp. 297–364. [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein, G.; Slizys, I.S.; Chase, M.W. Studies on fluorescent antibody staining. I. Non-specific fluorescence with fluorescein-coupled sheep anti-rabbit globulins. J. Exp. Med. 1961, 114, 89–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommerville, R.G. The production of fluorescent antibody reagents for virus diagnosis in the albino mouse. II. Coupling of mouse immune globulin with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC). Arch. Gesamte. Virusforsch. 1967, 20, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souriu, C.; Hudson, P.J. Recombinant antibodies for cancer diagnosis and therapy. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2001, 1, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, J.L.; Coley, A.M.; Tilley, L.M.; Foley, M. Green fluorescent antibodies: novel in vitro tools. Protein Eng. 2000, 13, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peipp, M.; Saul, D.; Barbin, K.; Bruenke, J.; Zunino, S.J.; Niederweis, M.; Fey, G.H. Efficient eukaryotic expression of fluorescent scFv fusion proteins directed against CD antigens for FACS applications. J. Immunol. Methods 2004, 285, 265–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Cao, P.; Yan, H.J.; Ren, F.; Lu, W.G.; Hu, Y.L.; Zhang, S.Q. Construction and characterization of an enhanced GFP-tagged anti-BAFF scFv antibody. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 79, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olichon, A.; Surrey, T. Selection of genetically encoded fluorescent single domain antibodies engineered for efficient expression in Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 36314–36320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.S.; Shim, J.H.; Suh, Y.T.; Yau, K.Y.F.; Hall, J.C.; Trevors, J.T.; Lee, H. Green fluorescent protein-labeled recombinant antibody for detecting the picloram herbicide. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2002, 66, 1148–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oelschlaeger, P.; Srikant-Iyer, S.; Lange, S.; Schmitt, J.; Schmid, R.D. Fluorophor-linked immunosorbent assay: a time- and cost-saving method for the characterization of antibody fragments using a fusion protein of a single-chain antibody fragment and enhanced green fluorescent protein. Anal. Biochem. 2002, 309, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto, S.; Taura, F.; Pongkitwitoon, B.; Putalun, W.; Tsuchihashi, R.; Kinjo, J.; Tanaka, H.; Morimoto, S. Development of sensitivity-improved fluorescence-linked immunosorbent assay using a fluorescent single-domain antibody against the bioactive naphthoquinone, plumbagin. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 396, 2955–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, S.; Tanizaki, Y.; Pongkitwitoon, B.; Tanaka, H.; Morimoto, S. A chimera of green fluorescent protein with single chain variable fragment antibody against ginsenosides for fluorescence-linked immunosorbent assay. Protein Expr. Purif. 2011, 77, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, S.; Pongkitwitoon, B.; Sasaki-Tabata, K.; Putalun, W.; Maenaka, K.; Tanaka, H.; Morimoto, S. A fluorescent single domain antibody against plumbagin expressed in silkworm larvae for fluorescence-linked immunosorbent assay (FLISA). Analyst 2011, 136, 2056–2063. [Google Scholar]
- Horton, R.M.; Hunt, H.D.; Ho, S.N.; Pullen, J.K.; Pease, L.R. Engineering hybrid genes without the use of restriction enzymes: gene splicing by overlap extension. Gene 1989, 77, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umetsu, M.; Tsumoto, K.; Hara, M.; Ashish, K.; Goda, S.; Adschiri, T.; Kumagai, I. How additives influence the refolding of immunoglobulin-folded proteins in a stepwise dialysis system. Spectroscopic evidence for highly efficient refolding of a single-chain Fv fragment. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 8979–8987. [Google Scholar]
- Ohshima, M.; Inoue, K.; Hayashi, H.; Tsuji, D.; Mizugaki, M.; Itoh, K. Generation of AcGFP fusion with single-chain Fv selected from a phage display library constructed from mice hyperimmunized against 5-methyl 2'-deoxycytidine. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2010, 23, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormo, M.; Cubitt, A.B.; Kallio, K.; Gross, L.A.; Tsien, R.Y.; Remington, S.J. Crystal structure of Aequorea victoria green fluorescent protein. Science 1996, 273, 1392–1395. [Google Scholar]
- Friguet, B.; Chaffotte, A.F.; Djavadi-Ohaniance, L.; Goldberg, M.E. Measurements of the true affinity constant in solution of antigen-antibody complexes by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J. Immunol. Methods 1985, 77, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiyama, M.; Shoyama, Y.; Murakami, H.; Shinohara, H. Production of monoclonal antibodies and development of an ELISA for solamargine. Cytotechnology 1996, 18, 153–158. [Google Scholar]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiler, E.; Zenk, M.H. Radioimmunoassay for determination of digoxin and related compounds in Digitalis lanata. Phytochemistry 1976, 15, 1537–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlandi, R.; Gussow, D.H.; Jones, P.T.; Winter, G. Cloning immunoglobulin variable domains for expression by the polymerase chain reaction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 3833–3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCafferty, J.; Griffiths, A.D.; Winter, G.; Chiswell, D.J. Phage antibodies: Filamentous phage displaying antibody variable domains. Nature (London) 1990, 348, 552–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertani, G. Studies on lysogenesis. I. The mode of phage liberation by lysogenic Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1952, 62, 293–300. [Google Scholar]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).