Abstract
This study evaluated the effects of different types and rates of locally produced organic residues on soil organic matter (SOM) and soil health in highly degraded loamy soils of olive orchards in arid southern Tunisia. Three residues were tested: poultry manure, raw date palm waste, and composted date palm waste mixed with manure. A randomised field trial was conducted over three years. Two years after application, soil samples were analysed for physical and chemical properties, basal respiration, nitrogen mineralisation, microbial biomass, enzyme activities (dehydrogenase, phosphomonoesterase, β-glucosidase, urease, arylsulphatase), and community-level physiological profiles. All residues increased SOM and available phosphorus (Pi), with dose-dependent effects sustained over time, though significant increases were only observed at the highest application rates. The most notable improvements occurred in soils amended with composted date palm waste. In contrast, biological and biochemical parameters showed little response, even after remoistening to stimulate microbial activity. This limited response was attributed to the absence of vegetation and, consequently, of root exudates and plant residues. This will be further investigated by assessing changes in the same biological and biochemical properties following the implementation of an intercropping system, which is expected to enhance both SOM content and microbial activity in these soils.
1. Introduction
The degradation of agricultural land is a serious and rapidly accelerating global problem, especially in arid and semi-arid regions, which are characterised by very low rainfall, high temperatures and extremely high evapotranspiration rates [1]. Moreover, the problem is expected to be exacerbated by climate change. In the Maghreb countries, the complex interactions between the hot and dry climate, heavy wind erosion, repeated cropping on the same land and scarcity of water for irrigation accelerate soil degradation [2]. The degradation is further aggravated by the low organic matter content of soils (<1%), the lack of structure typical of loamy textured soils and the high rate of application of chemical fertilisers typically used to increase crop yields. All of these factors pose short, medium and long-term problems for agricultural land, in terms of both the ecological and the economic impact [3].
The Entisols and Aridisols, which are characteristic of the Matmata region in southern Tunisia—one of the Maghreb areas with a long tradition of olive cultivation—are severely affected by high temperatures, water scarcity, extremely low organic matter content, and reduced microbial activity. In addition, these soils are further degraded by wind erosion. Management practices involving annual deeply rooted tillage have exacerbated this problem [2,4]. Furthermore, the dry conditions induce further reduction of soil organic matter content and, consequently, of microbial activity in the soil [5,6,7]. All these factors negatively affect the health of these soils and compromise their ability to produce crops and provide ecosystem services [2].
Numerous studies have been conducted in recent years with the aim of developing crop management practices capable of maintaining or increasing soil fertility and productivity in arid and semi-arid regions, while preserving soil health, in the context of global change [8]. Among these, in the case of woody crops, various forms of agroforestry are particularly noteworthy—especially the intercropping of different plant species (such as cereals, legumes, and aromatic herbs) between the rows of woody plants [8,9,10,11]. This practice offers several advantages: (i) it helps stabilise the soil and prevent erosion [10]; (ii) it improves soil quality by increasing organic matter content, mainly through root exudates and the resulting stimulation of biological activity [12]; and (iii) it provides economic benefits for plantation owners by not only enhancing olive oil production but also generating additional income from the sale of the intercropped harvest [9,10]. Some species, such as aromatic and medicinal plants, offer additional advantages [11]: they are well adapted to arid and semi-arid climates, and many of them are perennial, which means the soil remains covered year-round—an important factor in reducing erosion. Recent studies conducted in collaboration with some of the authors of the present study in Morocco (unpublished results, A. Boularbah, personal communication) and in Tunisia (unpublished results, A. Sahli, personal communication) have shown that the use of aromatic plants can improve several soil properties, including organic matter content and enzymatic activity, while also enhancing the quality of olives in olive groves. Therefore, this could be a promising practice to implement in the Matmata region. However, the extremely low organic matter content and harsh soil conditions in the area could limit the chances of successful establishment of intercrops, including aromatic crops [9]. The fastest way to improve plant production is to apply inorganic amendments to the soil. However, excessive use of fertilisers can lead to nitrogen volatilisation, soil acidification, eutrophication of surface waters, and a decrease in soil biodiversity [13]. In addition to the environmental cost of inorganic amendments, the high cost of chemical fertilisers is a major obstacle for small farmers, especially in countries with the lowest per capita income [14], a situation that has been exacerbated in recent years as the price of fertilisers, especially phosphate fertilisers, has risen disproportionately.
In different parts of the world over the past 20 years, inorganic fertilisers have gradually been replaced or complemented with either unprocessed or composted waste material (such as manure, poultry litter, green wastes, crop residues, etc.) as soil amendments [9]. The application of these residues to land has been shown to enhance the fertility of dryland soils by increasing soil nutrients, water infiltration, microbial community abundance, and soil enzymatic activities [15,16]. Thus, in line with the growing worldwide concerns regarding environmental conservation, there is increasing reliance on the use of abundant locally available natural resources in farming, with a tendency to reduce the use of chemical fertilisers. Organic amendments are generally important for agro-environmental health [17]. Moreover, as waste products that require proper disposal, they also represent an environmental problem. Thus, the use of these organic waste products as soil amendments provides a sustainable solution to both problems. Nevertheless, to avoid possible harmful effects related to excessive and unregulated application [18], careful selection of the quantity, type and timing of organic fertiliser application is particularly important [19,20].
The use of organic amendments, comprised of either plant residues or animal waste, is key to improving the physico-chemical and biological properties of soil, and such amendments have many functions in cultivated ecosystems [21]. Cattle manure and poultry litter have traditionally been used for many years to increase the soil organic carbon content, which may increase by 10–38% after the addition of these residues [22]. Poultry manure is predominantly used as a soil amendment in the southern region of Tunisia. Given the high pH of poultry manure, citric acid is usually added to reduce the pH and make the product more suitable as a pH-ameliorating agent [23], as soils in this area are calcareous and typically alkaline.
The more suitable plant residue for soil amendment will depend on the region considered and the crops (and consequently the residues) produced [21,24]. In southern Tunisia, palm trees yield large amounts of waste, approximately 16 kg per tree annually, mainly in the form of palm leaves [25]. The use of palm tree waste as an amendment in regions where this crop predominates contributes to the circular economy while also providing economic and social benefits for many small companies in the region. Although palm tree residues can be applied to land without being processed, they are usually composted before use [18]. This process, among other factors, contributes to minimising the huge quantity of palm tree waste and thus facilitating its management [26]. On the other hand, combining organic manure with date palm waste to produce compost not only supplies many nutrients to the soil but also increases the microbiological activity and balances the carbon/nitrogen (C/N) ratio in the soil, thus facilitating microbial decomposition and reducing nitrogen immobilisation [27,28].
All soil properties (physical, chemical, biological, and biochemical) are important for determining soil quality or health [29,30]. However, the properties that are most sensitive to environmental stress will determine soil metabolism and functionality [31,32]. These include properties directly related to the abundance and activity of soil microbiota (such as microbial biomass, basal respiration, and oxidoreductase activity) and also those associated with the decomposition of organic compounds and nutrient release, such as hydrolytic enzyme activities [32,33,34].
The effects of different organic amendments on soil physicochemical properties in arid and semi-arid areas have been widely studied [18,35,36]. The effects of the rate, type, and timing of organic fertiliser application on soil physicochemical and biological properties have also been investigated [18]. However, studies addressing the impact of such practices (especially the application of date palm residues in combination with livestock manure) on the biological and biochemical properties (enzymatic activities and microbial activity) of loamy-textured soils in semi-arid climate zones are scarce [37,38], despite the important role of these practices in organic matter decomposition and biogeochemical element cycling. Another important, often overlooked, factor is that organic residues are typically applied to dry soil, unless the soil has been wetted by irrigated or scarce, infrequent rainfall. In either case, the amount of water that reaches the soil is minimal. However, even small amounts of water can be sufficient to induce a pulse of microbial activity, potentially increasing microbial activity and basal soil respiration [39]. This short burst of activity may lead to higher CO2 emissions, thereby reducing the amount of carbon accumulated in the soil.
Considering the soil-related challenges in the Matmata region—exacerbated by common agricultural practices such as deep tillage and keeping the soil bare for long periods, which leads to severe erosion—the implementation of intercropping has been proposed as the most effective way to improve soil health [40].
The main objective of this study was to assess the feasibility of agroforestry practices in loamy soils of olive groves located in the semi-arid region of Southern Tunisia, through the enhancement of soil organic matter, fertility, and soil health. With this aim, a two-phase approach was adopted. In the first phase, the study evaluated whether the application of different types and amounts of locally produced organic residues could enhance the accumulation of soil organic matter, along with key biological and biochemical properties essential for soil health and functionality. In addition, changes in these properties were examined after moistening the soil to 40% of field capacity, to simulate conditions typical of irrigation or rainfall. The second phase will assess whether the prior application of organic wastes facilitates the subsequent implementation of intercropping with aromatic herbs in the olive groves. Date palm waste—either fresh or composted with cattle manure—was selected because this plant residue is highly abundant in the region, and a local company is actively producing compost and preparing the fresh material for use in agricultural soils. These two forms of date palm residue were compared with poultry manure combined with citric acid, a type of organic fertiliser commonly used by farmers in the area. We hypothesised the following: (1) the application of organic residues will increase soil organic matter content, along with biochemical and microbiological activity; (2) the effect of organic residue application on soil metabolic activity will vary depending on the type and quantity of organic waste used; (3) re-wetting the soil will induce a pulse of biological and biochemical activity in organically amended soils; (4) the increase in organic matter content and microbial activity resulting from the application of different organic residues to the soil will facilitate the subsequent establishment of intercropping in these extremely poor soils, where such implementation would otherwise be extremely difficult.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
The present study was conducted in arable land in the Djeffara Plain (southeastern Tunisia), in the Northern part of the Dahar series formed by accumulation of loess loam (Tertiary Permian). The experimental site is an olive grove located in New Matmata, approximately 27 km north of Gabes city (southeastern Tunisia), at an altitude of 600 m above mean sea level (33°30′ N Latitude and 9°49′ Elongitude). The climate in the area is semi-arid Mediterranean, characterised by a highly irregular rainfall patterns and amounts. According to the data obtained from the Meteorological National Institute of Tunisia (INM) during the period 2014–2022, the most precipitation events occur in winter and autumn, with an average annual rainfall of approximately 175 mm; the summers are hot and dry. The highest temperature recorded was 46 °C, in August, while the lowest temperature reached was 25 °C, in January; the average annual temperature is around 19.8 °C. The area has a standardised precipitation index (SPI) between −0.7 to 1.3, corresponding to a typically dry region [41]. The soil in the experimental site is classified as an Aridisol [42]. The experimental site is only used for olive cultivation, and no other plants were cultivated in the past or during the study period. The olive trees were watered by drip irrigation, while the experimental plots relied completely on natural rainfall. No organic amendments or fertilisers had ever been applied to the site. The soil used in the field experiment was characterised by an alkaline pH (pH in water 8.6), a loam texture (92% of silt), very low organic matter content (total carbon (C): 1.37%, organic C: 0.49%, total nitrogen (N): 0.05%, C/N: 9.8) and total phosphorus (P) (15 mg kg−1), low electrical conductivity (0.06 dS cm−1), and a moderate carbonate content (5.26%).
2.2. Experimental and Sampling Design
The field amendment experiment was started in March 2019. Twelve plots (1.5 m × 7 m) were established (Figure 1), and each was separated by a 4 m buffer zone in all directions. Nine plots were established to apply three treatments, each at three different doses, along with three plots of unamended soil. The following types of organic waste were used: poultry manure plus citric acid fertiliser (FPCA), fresh raw date palm waste (FDPW), and date palm waste and cattle manure compost (MDPW). All three types of amendments were applied to the soil at three doses: Q1 = 20 t ha−1, Q2 = 40 t ha−1, and Q3 = 80 t ha−1. The amendments were applied to the soil surface and mixed into the top 30 cm using a hand shovel, to ensure that they were well incorporated in the soil.
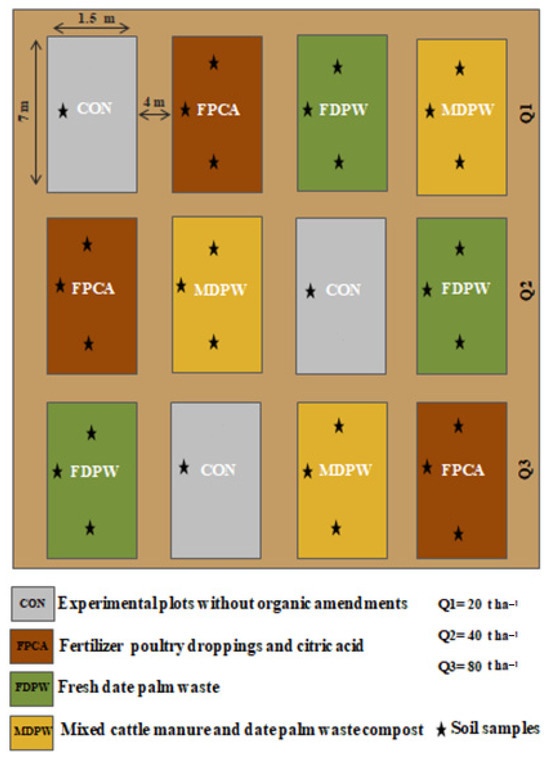
Figure 1.
Experimental design showing the distribution of plots treated with different amendments. CON: experimental plots without organic amendments (control soils); FPCA: poultry manure plus citric acid fertiliser; FDPW: fresh raw date palm waste; MDPW: date palm waste and cattle manure compost; Q1 = 20 t ha−1, Q2 = 40 t ha−1 and Q3 = 80 t ha−1.
The organic amendments were produced at a composting station (run by the Chenini Oasis Conservation Association in Gabes) from bio-waste generated in agricultural areas in southern Tunisia. The FPCA was prepared by mixing poultry manure with citric acid. The FDPW amendment was produced by grinding date palm leaves (pruning waste), and the MDPW was obtained by composting cattle manure and date palm waste without any other additives. The characteristics of the organic amendments are summarised in Table 1.

Table 1.
Values of pH in water (pH H2O), electrical conductivity (EC), total phosphorous (P), potassium (K) and calcium (Ca), total carbon (TC), and nitrogen (TN) contents of the organic materials, and total carbon/total nitrogen ratio (C/N). FPCA: poultry manure plus citric acid fertiliser; FDPW: fresh raw date palm waste; MDPW: date palm waste and cattle manure compost. % = values in percentage (g 100 g−1).
The soil was re-amended with the same types of organic amendments and application rates in March 2021, i.e., two years after establishment of the field experiment. In August 2022, soil samples were collected from a depth of 0–10 cm in each plot, with the aid of a handle shovel. Three subsamples were taken from different points in each of the amended plots, and one sample was taken from each of the three control plots (Figure 1). All samples were analysed separately as individual replicates. In total, 30 soil samples were obtained: 3 organic amendments × 3 doses × 3 replicates + 3 control plots × 1 replicate each. All soil samples were air-dried, sieved through a 2 mm mesh and stored in polyethylene bags. As the soil samples were collected in August, when temperatures were very high (42 °C) and the soils were dry, they were stored at an ambient temperature rather than at 4 °C, as usually required for samples from temperate climates [43].
2.3. Analytical Methods and Incubation Under Different Moisture Conditions
2.3.1. Soil Chemical and Physico-Chemical Properties
Soil pH and electrical conductivity (EC) were determined in a soil suspension prepared at 1:5 soil-to-water ratio, as described by [44]. Total nitrogen (TN) and total carbon (TC) contents were determined in finely ground, air-dried samples, by complete combustion at 960 °C, and the resulting gases were measured using a thermal conductivity detector (TCD) in a controlled heating column (ELEMENTAR Rapid N; Elementar Analysensysteme, Gesellschaft mit beschränkter Haftung (GmbH), Hanau, Germany). Total organic carbon (OC) content was measured in air-dried, finely ground samples, by potassium dichromate oxidation in acid medium, following the method described by [45]. The C/N ratio was calculated as the ratio of total organic carbon content to total nitrogen content. Available phosphorous (P) was extracted with 0.5 M sodium bicarbonate, pH 8.5 (soil/extractant ratio 1:50; extraction time 16 h), according to [46], and inorganic phosphorus (Pi) in the bicarbonate extracts was determined following the method described by [47]. Field water capacity was determined as the amount of water retained by the soil at a potential of −30.39 kPa, which was measured in undisturbed soil samples with a Richards plate-and-membrane apparatus [45]. The soil moisture content was determined after oven-drying the soil at 105 °C for 24 h.
Before establishment of the field experiment and application of the organic amendments, the soil was analysed to determine the particle size distribution and total phosphorus and carbonate contents. The particle size distribution was determined using Robinson’s pipette method, and the soil texture was classified according to the [42]. Total phosphorus (P) was determined using the colorimetric method described by [48], after digestion of finely ground soil samples with concentrated sulfuric acid at 300 °C, and the carbonate content was determined using the Bernard calcimeter method.
The effects of the different organic amendments on soil basal respiration, soil N mineralisation capacity, microbial biomass C, enzyme activities and community-level physiological profiling (CLPP) were evaluated under both dry and moist conditions (40% of field capacity), as proxies for the processes occurring under the predominant dry conditions of the area, and also after soil moistening due to occasional precipitation events. The soils were first incubated under dry conditions for 10 days to determine the C and N mineralisation capacity. Distilled water was then added to each soil sample until they reached 40% of the field capacity (moisture content, 3.38%), and the samples were incubated under moist conditions for another 10 days. The CLPP and all soil enzyme activities were then measured in the moistened samples. Microbial biomass C was also determined; however, the results were extremely variable, and these data are not reported here.
2.3.2. Soil Basal Respiration and Soil N Mineralisation Capacity
Dry soil: Soil basal respiration was determined in triplicate by static incubation [45]. Briefly, 25 g of dry soil was incubated in tightly sealed 1000 mL glass jars at 25 °C for 10 days. To prevent additional moistening of the soil, the distilled water typically placed at the bottom of the jar to maintain humidity in the headspace was not added. The CO2 produced was collected in 10 mL of a 0.1 M NaOH solution, which was then titrated against HCl with an automatic titrator. Two Mason jars with NaOH solution but without soil were also incubated under the same conditions to enable measurement of the CO2 in the jars. The soil basal respiration was expressed as mg CO2-C produced kg−1 dry soil 10 days−1.
To determine the nitrogen mineralisation capacity, duplicate amounts (10 g) of dry soil were extracted for 30 min with 50 mL of 2 M KCl before and after incubation for 10 days at 25 °C (as used for soil C mineralisation), and ammoniacal N and total inorganic N were determined in the extracts by Kjeldahl distillation [49]. The nitrate content was estimated as the difference between total inorganic and ammoniacal N. The nitrogen mineralisation capacity (mg kg−1 dry soil 10 days−1) was calculated as the difference between the values obtained before and after incubation.
Moist soil: After the initial 10-day incubation period, all soil samples were moistened with distilled water to 40% of field capacity. Distilled water (25 mL) was then added to the bottom of each jar to maintain headspace moisture. The soil samples were incubated for another 10-days, and the CO2 produced was captured in 10 mL of a 0.5 M NaOH solution. At the end of the second 10-day incubation period, the NaOH solutions were titrated against HCl in an automatic titrator, and the amount of CO2-C was measured for estimation of the CO2 emissions from the moist soil (mg CO2-C produced kg−1 soil 10 days−1).
To determine the nitrogen mineralisation capacity of the moist soil, duplicate amounts (10 g) of moist soil were extracted for 30 min with 50 mL of 2 M KCl after incubation for 10 days. Ammoniacal N and total inorganic N in the extracts were determined by Kjeldahl distillation [49]. The amount of N mineralised in the moist soil was calculated as the difference between the values obtained at the end of dry and moist soil incubation periods and expressed as mg kg−1 soil 10 days−1.
2.3.3. Microbial Biomass
Soil microbial biomass C (MBC) was determined by the fumigation–extraction method developed by [50]. Briefly, 10 g aliquots of soil (dry soil or the moist soil equivalent to 10 g dry soil) were placed in centrifuge tubes held inside a desiccator containing a beaker with ethanol-free chloroform and maintained for 24 h at 25 °C. After removal of the chloroform (by leaving the centrifuge tubes open in a fume hood), carbon was extracted from both fumigated and non-fumigated samples with 0.5 N K2SO4. The carbon content of the extracts was determined by oxidation with potassium dichromate, and microbial biomass C was calculated as the difference between fumigated and non-fumigated samples, divided by the C extraction efficiency coefficient (Kec) = 0.45 [51].
2.3.4. Soil Enzyme Activities
Dehydrogenase activity was determined with iodonitrotetrazolium violet (INT) as substrate, by incubation with 1 M TRIS-HCl buffer pH 7.5 for 1 h. The iodonitrotetrazolium formazan (INTF) produced was extracted with a 1:1 (v:v) mixture of ethanol and dimethylformamide and measured spectrophotometrically at 490 nm [52]. The activity was quantified by reference to a calibration curve constructed using INTF standards and is expressed in µmol INTF g−1 h−1. Urease activity was determined by incubating the samples with 1065.6 mM urea as substrate, for 1.5 h in 0.2 M phosphate buffer (pH 8.0; to ensure the reaction mixture has this pH, it was measured), and measuring the NH4+ released with an ammonia electrode [53]. The enzyme activity is expressed as µmol NH3 g−1 h−1.
Acid phosphomonoesterase, ß-glucosidase, and arylsulphatase activities were determined by incubating the soils with a substrate containing a p-nitrophenyl moiety and then measuring the amount of p-nitrophenol released during enzymatic hydrolysis by spectrophotometry. The enzymatic activities were quantified by reference to calibration curves corresponding to p-nitrophenol standards incubated under the same conditions as for the samples and the activities are expressed as µmol p-nitrophenol g−1 h−1. The original protocols were modified slightly for each of the three enzymes; the modifications are described for each case. Phosphomonoesterase activity was determined following the method of [54], with 16 mM p-nitrophenyl phosphate as substrate and by incubating the samples with Modified Universal Buffer (the method described by [55] was used to ensure that the pH of the reaction mixture was maintained at pH 11.0 for 30 min). At the end of this period, 2 M CaCl2 was added, and the p-nitrophenol released was extracted with 0.2 M NaOH. ß-glucosidase activity was determined as described for phosphomonoesterase activity, except that the substrate was 25 mM p-nitrophenyl-ß-D-glucopyranoside, the pH of the reaction mixture was 6.0, the incubation time was 1 h and the released p-nitrophenol was extracted with 0.1 M (Tris(hydroxymethyl) aminomethane)-NaOH (THAM-NaOH), pH 12 [56]. Arylsulphatase activity was determined by incubating the samples with 5 mM p-nitrophenyl sulphate as substrate, with 0.5 M acetate buffer (pH 5.8), for 1 h [57]. The activity of each of the above four enzymes is expressed as µmol p-nitrophenol g−1 h−1.
To normalise the enzyme activity, the specific activity of each enzyme was calculated by dividing the activity in each sample by the total organic carbon content [58]. The results are expressed as µmol of product per gram of carbon per hour (µmol product g−1 C h−1).
2.3.5. Community-Level Physiological Profiling (CLPP)
Community-level physiological profiling (CLPP) of the soil bacterial community was evaluated using the Biolog EcoPlates™ technique, as described by [59]. Briefly, soil sample suspensions were prepared in sterile 1% sodium hexametaphosphate (HMP) at a 1:10 (w/v) ratio and shaken for 30 min at 150 rpm and 22 °C. After 10 min, 1 mL of the supernatant was diluted in 9 mL of sterile 0.85% NaCl solution. Aliquots (125 μL) of this suspension were then pipetted into the wells of the microplate, which was then incubated at 26 °C in the dark for one week. Colour development was measured every 24 h at 490 nm in a DIALAB EL800 Microplate Reader (DIALAB GmbH, Vienna, Austria) [60,61,62].
2.3.6. Statistical Analysis
The mean values were calculated for three replicate plots and three measurements for each sample. The data were examined by one-way ANOVA, followed by Duncan’s multiple range tests for post hoc comparisons, using SPSS version 20.0 for Windows (IBM SPSS Statistics, Armonk, NY, USA). p values ≤ 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Organic Amendments on the Main Physico-Chemical Properties of the Soil
The carbonate content of the soil used in the field experiment was moderate. However, given the very low organic carbon (OC) content, there was a notable difference between total carbon and total organic carbon content in both the control soil (unamended) and in soils treated with the different types of organic amendments (Figure 2). The application of all types of amendments at all dosages resulted in an increase in soil organic carbon content. However, statistically significant increases were only observed for the highest dose for poultry manure plus citric acid (FPCA) and for date palm waste (FDPW). By contrast, for the compost derived from date palm waste and cattle manure, both the highest (Q3) and the intermediate (Q2) doses produced significant increases in organic carbon content. Moreover, while in the latter case the increase in organic C was proportional to the amount of compost applied, for the other two types of waste, both of the lower doses produced similar increases, and the increase only being statistically significant for the highest dose. The high variability among the different amended plots across all treatments (especially the compost) contributed to the lack of statistical significance in some cases. The increase in organic C content was similar in soils amended with poultry manure and in those amended with date palm waste, and greater increases were observed in soils amended with compost (Figure 2b).

Figure 2.
Effect of different treatments and applications rates on (a) total carbon (TC), (b) total organic carbon (TOC), (c) total nitrogen (TN), and (d) inorganic available phosphorus (P). CON: experimental plots without organic amendments (control soils); FPCA: poultry manure plus citric acid fertiliser; FDPW: fresh raw date palm waste; MDPW: date palm waste and cattle manure compost; Q1 = 20 t ha−1, Q2 = 40 t ha−1 and Q3 = 80 t ha−1. Vertical bars indicate standard deviations of means (n = 6) Different letters indicate significant differences between the treatment effects at different doses (Duncan’s test at p < 0.05).
The effect of applying the organic residues on total soil nitrogen (TN) content was similar to that observed for total organic carbon (Figure 2c). Thus, all three types of amendments produced an increase in total nitrogen content. However, while only the highest doses of poultry manure and date palm waste produced a relevant and statistically significant increase, both the highest and intermediate doses of compost yielded significant increases in total soil N. Furthermore, as with organic C, a dose-dependent increase was only observed for the compost, with higher doses producing greater increases in total N content. As previously noted for organic C, high variability between plots was also evident across all treatments in this case.
The available inorganic phosphorus (P) content was very low in the unamended soil. All three organic amendments produced significant increases in the content of this element, which were generally related to the dose of organic residue applied and which were significant for the highest doses. As with C and N, the compost derived from date palm waste and cattle manure produced the greatest increases in bioavailable inorganic P (Figure 2d).
The soil used in the experiment was alkaline (pH in water = 8.6). All three residues produced a slight increase in pH, but for each the increase was independent of the dose applied. In contrast to the observed changes in C, N and bioavailable inorganic P content, the variability in pH among the different plots (in both the control and in organic residue amended soils) was very low. As a result, the differences in pH between amended and control soils were statistically significant in all cases (Figure 3a). However, these slight differences are not considered biologically significant.
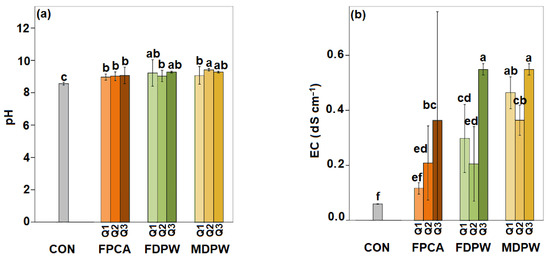
Figure 3.
(a) pH and (b) electrical conductivity (EC) of the soil under organic amendments and application doses. CON: experimental plots without organic amendments (control soils); FPCA: poultry manure plus citric acid fertiliser; FDPW: fresh raw date palm waste; MDPW: date palm waste and cattle manure compost; Q1 = 20 t ha−1, Q2 = 40 t ha−1, and Q3 = 80 t ha−1. Vertical bars indicate standard deviations of means (n = 6) Different letters indicate significant differences between the treatment at different doses (Duncan’s test at p < 0.05).
The electrical conductivity (EC) was very low in the control soil (Figure 3b). All three organic residues increased the EC at all doses, although the values were not excessively high for any of the amendments or doses. The highest EC values were recorded in the soil amended with the highest dose of date palm waste, whether composted with cattle slurry or applied in its raw form, with EC reaching values of 0.55 and 0.36 mS cm−1, respectively (Figure 3b). The increases in EC were only proportional to the dose of amendment for poultry manure.
3.2. Effect of the Organic Amendments on Microbial Biomass C
Microbial biomass contents in the different plots (both the unamended control and those amended with the three types of organic residues) were extremely variable (Figure 4a).
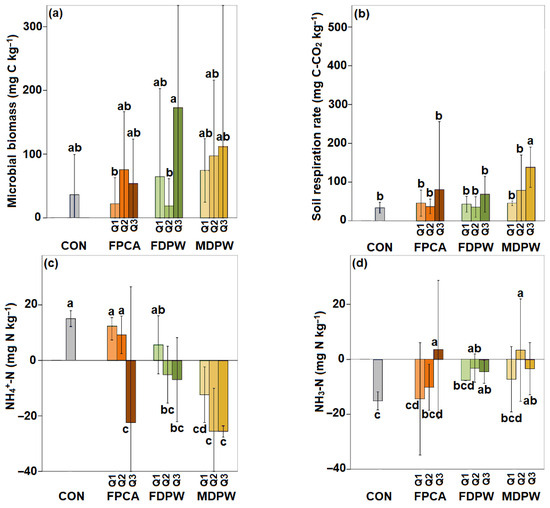
Figure 4.
Changes in (a) microbial biomass C, (b) soil respiration rate, (c) ammonification (NH4+–N), and (d) nitrification (NO3–N) in dry samples of soils treated with different amounts of the different types of organic amendments. CON: experimental plots without organic amendments (control soils); FPCA: poultry manure plus citric acid fertiliser; FDPW: fresh raw date palm waste; MDPW: date palm waste and cattle manure compost; Q1 = 20 t ha−1, Q2 = 40 t ha−1, and Q3 = 80 t ha−1. Vertical bars indicate standard deviations of means (n = 6). Different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) between treatment effects, according to Duncan’s tests.
Thus, the observed differences between treatments and doses were generally not statistically significant, and only general trends can be described. Microbial biomass levels in the control soil were very low and increased with the application of all three types of residues, although not with all doses. Application of the poultry manure and date palm waste increased the microbial biomass, but the increases varied widely in relation to the dose applied. By contrast, all doses of compost derived from date palm waste and cattle manure increased the microbial biomass, in a dose-dependent trend. However, none of these increases were statistically significant owing to the already indicated high variability, which was particularly pronounced in the control soil (Figure 4a).
3.3. Effect of the Organic Amendments on Soil Basal Respiration and Nitrogen Mineralisation Capacity
As observed for microbial biomass, the basal respiration also varied widely among plots, and many of the differences between treatments and doses were not statistically significant. Nevertheless, basal respiration tended to increase after application of all three types of organic amendments. For poultry manure and date palm waste, however, the increases for the two lowest doses (Q1 and Q2) were minimal and almost identical. By contrast, the highest dose (Q3) caused a notable increase in respiration. The compost derived from date palm waste and cattle slurry produced clear increases in respiration at all three doses, with greater increases corresponding to higher application rates. The increases were also more pronounced than caused by the other two amendments (Figure 4b).
Regarding the nitrogen mineralisation capacity, ammonification and nitrate immobilisation clearly occurred in the control soil during the 10-day incubation of the dry soil. The results obtained for soils treated with the different amendments were, once again, very variable, and as a result, the observed changes were generally not statistically significant. For the lowest doses of poultry manure and date palm waste, slight ammonification occurred, similar to that observed in the control soil (Figure 4c). In all other cases, ammonium nitrogen was immobilised, particularly in soils receiving the highest dose of poultry manure and across all three doses of compost. In general, nitrate was immobilised in all treatments, with the effect being more pronounced in soils amended with poultry manure than with the other two residues. An exception to this pattern was observed with the highest dose of poultry manure and the intermediate dose of compost; however, the amount of mineralised nitrate was very low in these cases (Figure 4d).
3.4. Effect of the Organic Amendments on Soil Enzyme Activities
As indicated in the Materials and Methods section, specific enzyme activities (i.e., activities per unit of organic carbon) were calculated in order to normalise the activities and make them comparable across the different soils, regardless of the organic matter content. The absolute enzymatic activity values (expressed per unit of weight) are presented as Supplementary Material (Table S1). Application of the organic residues produced an increase in the absolute values of dehydrogenase and urease activities in all cases. These increases were generally dose-dependent, with higher activities corresponding to greater amounts of organic residue added. Moreover, the poultry manure caused the smallest increases in enzymatic activity, while composted palm waste caused the largest increases (Table S1). Although the activities of the other three enzymes (β-glucosidase, alkaline phosphomonoesterase, and arylsulfatase) were slightly higher than in the control soil, the differences were minimal and generally not statistically significant. Moreover, the slight variations relative to the control soil did not follow a dose-dependent trend (Table S1).
In general, due to the high variability between plots, particularly in the amended soils, the difference in the effect of the organic amendments on the specific enzymatic activities in the control soil and the soils treated with the different amendments and doses were not statistically significant (Figure 5).
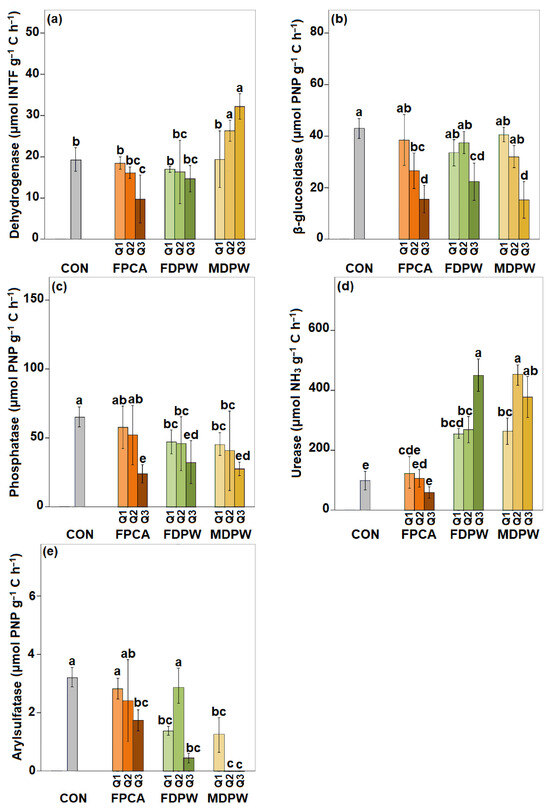
Figure 5.
Specific enzyme activities in the dry soil treated with different amounts of the organic amendments. CON: experimental plots without organic amendments (control soils); FPCA: poultry manure plus citric acid fertiliser; FDPW: fresh raw date palm waste; MDPW: date palm waste and cattle manure compost; Q1 = 20 t ha−1, Q2 = 40 t ha−1 and Q3 = 80 t ha−1. INTF: iodonitrotetrazolium formazan; PNP: p-nitrophenol. Vertical bars indicate standard deviations of means (n = 6). Different letters indicate significant differences between treatment effects at different doses (Duncan’s test at p < 0.05).
None of the amendments produced increases in the specific β-glucosidase, phosphomonoesterase, and arylsulfatase activities, and in most cases, there was a dose-dependent reduction in the activities. Poultry manure and palm waste either did not affect dehydrogenase activity or caused a decrease at the highest doses, while the composted palm waste produced a dose-dependent increase in dehydrogenase activity (Figure 5a). Unlike the other enzymatic activities investigated, all of the organic amendments produced increases in the specific urease activity. However, the increase produced by poultry manure was very slight and tended to decrease with higher application rates. By contrast, the increases induced by both untreated and composted palm waste were much more pronounced and statistically significant. Although the specific enzyme activities generally increased with increasing doses, the dose-response relationship was not clearly defined in either case. Furthermore, the effect on specific urease activity was very similar for both types of palm waste (Figure 5d).
3.5. Effect of the Organic Amendments on Community Level Physiological Profile (CLPP)
In general, the average well colour development (AWCD) from Biolog EcoPlates™ did not show a consistent pattern across soils amended with the different types of organic residues. In soils amended with poultry manure, the AWCD tended to be higher than in the unamended control, but only for the lowest and highest doses. For soils treated with raw date palm residue, the AWCD increased markedly and significantly at the lowest dose, whereas no significant changes were observed at the highest two doses. The composted date palm waste produced a significant increase in AWCD, although the increase was not dose-dependent (Figure 6a).
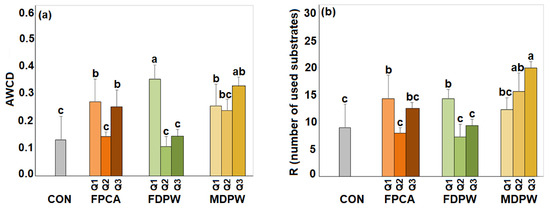
Figure 6.
Changes in (a) the AWCD and (b) Richness index (R) values of different C substrates degraded by aerobic bacterial communities in dry soils different amounts of the organic amendments. CON: experimental plots without organic amendments (control soils); FPCA: poultry manure plus citric acid fertiliser; FDPW: fresh raw date palm waste; MDPW: date palm waste and cattle manure compost; Q1 = 20 t ha−1, Q2 = 40 t ha−1, and Q3 = 80 t ha−1. Vertical bars indicate standard deviations of means (n = 6). Different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) between treatment effects according to Duncan’s tests.
In soils amended with poultry manure and raw date palm residue, the R index (number of substrates utilised) followed the same trend as the AWCD. However, in the soil amended with composted date palm waste and cattle slurry, the R index increased sharply, consistent with the AWCD response. In this case, the increase was statistically significant at all application rates and was clearly dose-dependent (Figure 6b).
Regarding the degradation of the different types of C substrates, a positive influence of the amendments, especially of the poultry manure and composted palm waste, on the degradation of polymers and organic acids was observed. Thus, the AWCD of these substrates, relative to the total colour development in the plate, was generally higher in amended than in non-amended soils (Figure 7).

Figure 7.
Average colour development for polymers, organic acids and pyruvic acid methyl ester relative to the total colour development in Biolog EcoPlates™. CON: experimental plots without organic amendments (control soils); FPCA: poultry manure plus citric acid fertiliser; FDPW: fresh raw date palm waste; MDPW: date palm waste and cattle manure compost; Q1 = 20 t ha−1, Q2 = 40 t ha−1 and Q3 = 80 t ha−1. Vertical bars indicate standard deviations of means (n = 6). Different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) between treatment effects, according to Duncan’s tests.
Degradation of the pyruvic acid methyl ester was also generally stimulated, especially by the composted palm residue. The degradation of other C substrates was not significantly affected by the amendments (Figure 8).

Figure 8.
Percent of total carbon source utilisation response to application of organic amendments. CH = Carbohydrates, OA = Organic acids, PO = Polymers, AA = amino acids, AM = Amines (only Putrescie was degraded), MIS = Miscellaneous compounds (only Pyruvic acid was degraded). CON: experimental plots without organic amendments (control soils); FPCA: poultry manure plus citric acid fertiliser; FDPW: fresh raw date palm waste; MDPW: date palm waste and cattle manure compost; Q1 = 20 t ha−1, Q2 = 40 t ha−1, and Q3 = 80 t ha−1.
3.6. Effect of the Organic Amendments on Soil Basal Respiration and Nitrogen Mineralisation Capacity in Moist Soils
After the soils were re-wetted, the microbial biomass values fluctuated widely. It was not possible to repeat the experiment, due to the lack of additional soil, and therefore these values are not reported.
After the soils were re-wetted, basal respiration increased markedly in both the control and amended soils. In all cases, respiration was higher in the amended soils than in the control soil, although the response varied depending on the type of organic residue applied. In soils amended with poultry manure, the lowest and highest doses induced greater increases in respiration than the intermediate dose. However, due to the high variability among plots, none of the differences between the treated and control plots were statistically significant.
In soils amended with date palm residue, the CO2 emissions at the two lower application rates were similar to those from the control soil, while the highest dose caused release of significantly more CO2. In compost-amended soils, CO2 emissions increased gradually with the dose of amendment: the lowest dose produced values similar to the control, while the higher doses resulted in significantly greater emissions (Figure 9c).
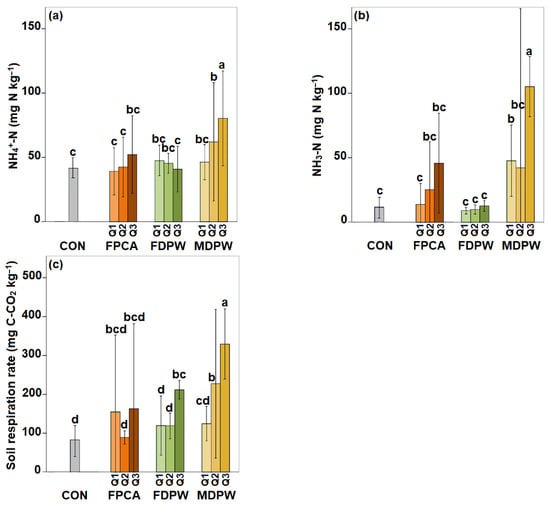
Figure 9.
Changes in (a) ammonification (NH4+–N), (b) nitrification (NO3–N) and (c) respiration rate in moist soils treated with different amounts of the organic amendments. Vertical bars indicate standard deviations of means (n = 6). CON: experimental plots without organic amendments (control soils); FPCA: poultry manure plus citric acid fertiliser; FDPW: fresh raw date palm waste; MDPW: date palm waste and cattle manure compost; Q1 = 20 t ha−1, Q2 = 40 t ha−1, and Q3 = 80 t ha−1. Vertical bars indicate standard deviations of means (n = 6). Different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) between treatment effects according to Duncan’s tests.
Re-wetting the control soil induced mineralisation, resulting in both ammonification and nitrification (Figure 9). In the amended soils, nitrogen mineralisation was also observed in all treatments, with increases in both ammonium and nitrate concentrations by the end of the 10-day incubation period. Again, owing to the high variability among plots, many of the differences between amended and control soils were not statistically significant, and thus, in general, only the observed trends can be discussed.
In soils amended with poultry manure, ammonification increased with the amount of residue applied, and the highest dose produced higher ammonium levels than in the control. By contrast, in soils amended with date palm residue, the highest degree of ammonification (greater than in the control) was induced by the lowest dose, with a gradual decrease at higher doses, reaching values similar to the control at the highest dose. In soils amended with compost, the lowest dose produced higher ammonium levels than in the control; the levels increased gradually with the application rate, with the two highest doses producing significantly higher levels than in the control (Figure 9a).
Nitrification rates were higher in the soils amended with poultry manure and those amended with compost than in the control soil, for all doses. However, while nitrification increased gradually with the dose in the soils amended with poultry manure (with significantly higher values than the control at the two highest rates), the level was significantly higher in compost-amended soils, for all doses, than in the control soil, with very similar values at the lowest two doses and a much higher value at the highest dose (Figure 9b).
3.7. Effect of the Organic Amendments on Soil Enzyme Activities in Moist Soils
When considering the absolute values of enzymatic activities, re-wetting the soil appeared to have little effect on any of the enzymes studied (Figure 10). The β-glucosidase, arylsulfatase, and phosphomonoesterase activities were only slightly different from those in dry soils. Urease activity tended to decrease after re-wetting; however, it remained consistently higher in amended soils than in the control soil, generally increasing with the dose of amendment. The highest urease activity was observed in soils amended with composted palm waste. Phosphomonoesterase activity was slightly higher in re-wetted soils than in dry soils across all treatments, including the control. Overall, phosphomonoesterase activity was higher in amended soils than in the control soil, with the highest values recorded in soils treated with untreated palm waste (Figure 10c).

Figure 10.
Specific enzyme activities in the moist soil amended with different amounts of diverse organic wastes. CON: experimental plots without organic amendments (control soils); FPCA: poultry manure plus citric acid fertiliser; FDPW: fresh raw date palm waste; MDPW: date palm waste and cattle manure compost; Q1 = 20 t ha−1, Q2 = 40 t ha−1, and Q3 = 80 t ha−1. INTF: iodonitrotetrazolium formazan; PNP: p-nitrophenol. Vertical bars indicate standard deviations of means (n = 6). Different letters indicate significant differences between effects of the different amendment doses (Duncan’s test at p < 0.05).
When considering the specific activity values rather than absolute ones, some slight differences were observed. Dehydrogenase activity was generally higher in amended soils than in the control, soil, although most of the differences were not statistically significant (Figure 10a). Moreover, the activity tended to decrease as the dose of amendment increased. For all four hydrolytic enzymes investigated (β-glucosidase, phosphomonoesterase, urease, and arylsulfatase), and for each of the three types of amendments applied, the enzymatic activity was similar to that of the control soil and the soils treated with the lowest dose of amendment. Furthermore, with the exception of urease activity in soils amended with composted date palm waste, the activity decreased as the dose of amendment increased, with the lowest values of activity corresponding to the highest doses of amendment. No clear differences were observed among the three types of amendments.
4. Discussion
Soils in semi-arid and arid regions are rather unproductive due to water limitation (very scarce precipitation), low fertility, and erosion caused by wind or rainfall [63]. The usual management practices in the study area in southern Tunisia do not include the cultivation of crops between the olive trees (intercropping), and the soil is typically left bare [64]. Occasionally some farmers plant cereals, such as wheat and barley, in the olive plantations, but only when there is enough rainfall [9,65]. The adverse conditions of the region also prevent the development of spontaneous vegetation, leaving the soil bare and thus increasing the risk of soil erosion [65]. The aim of the present study was to investigate the potential use of different organic residues to increase soil organic matter content, as well as soil fertility and quality, in the short- to medium-term. The overall objective was to establish a base for the implementation of an intercropping system aimed at enhancing soil health, improving long-term fertility, and reducing erosion [65]. This approach also offers potential economic benefits for plantation owners. Soil organic matter (SOM) content is fundamental to soil fertility and quality, as SOM plays a critical role in improving the soil physical, chemical and biological properties. Moreover, it is closely linked to nutrient cycling and soil fertility, making it essential for the sustainability and productivity of agroecosystems. Increasing soil organic carbon (SOC) also contributes to carbon sequestration and helps ensure long-term productivity [66]. The study assessed whether various locally abundant organic residues could be used to increase the organic matter content of very poor soils in the arid and semi-arid regions of Tunisia. This approach addresses several issues. On the one hand, it seeks to tackle the environmental problem posed by the accumulation of various organic residues abundant in the region [67], whose management represents a significant environmental challenge due to difficulties in their disposal. On the other hand, the residues are applied to soils with extremely low organic matter content in order to enhance carbon sequestration and organic matter accumulation [66,68]. In the medium to long term, this may facilitate the establishment of crops planted between olive trees and potentially increase the soil productivity, as the soils are currently underutilised in this type of plantation [69]. Ultimately, this could promote the re-establishment of biogeochemical nutrient cycles, increase microbial biomass and activity, and improve soil health and fertility [69,70,71].
4.1. Effects of Organic Amendments on the Main Physico-Chemical Properties of the Soil
The three organic amendments caused slight increases in soil pH. However, the increases were not dose-dependent, and there were no significant differences in relation to the type of residue applied (Figure 3a). Although the differences in pH between the treated soils and the untreated control were statistically significant, they were very small in magnitude. The pH of the amended soils remained very close to that of the unamended soil, which was already alkaline. Therefore, these slight increases are not biologically relevant and would not affect the potential soil fertility [72]. Despite all three amendments having a near-neutral pH (Table 1), they produced a slight increase rather than a decrease in soil pH. This may be due to the slight increase in electrical conductivity (EC) observed across all amended soils (Figure 3b), which was probably due to the relatively high EC of the three organic amendments (Table 1) [11]. Additionally, although the carbonate content of the soil was relatively low [68,73], it was probably sufficient to buffer any changes in soil pH [7]. As a result, the soil pH increased slightly, rather than decreasing, as might be expected given that the pH of the three organic amendments was slightly lower than that of the soil. This may also explain why the pH increase was not related to the amendment dose, unlike in the case of EC (Figure 3b). Moreover, despite the slight increases in EC, the values reached after the application of any of the amendments remain well below the threshold that could pose a salinity hazard [74].
The organic amendments produced only minor variations in most of the chemical, biochemical and biological properties evaluated, with the most notable changes being observed in soil organic matter content, carbon mineralization capacity, and available inorganic phosphorus levels. All three types of residues improved the soil fertility. These findings are consistent with those of other studies that have evaluated the application of various organic wastes (composted or not) in arid and semi-arid regions, with positive effects on both organic matter content [75,76] and available phosphorus levels [77]. However, due to the high variability observed among plots, the differences in the soil treated with the lowest doses of amendment and the control soil were not statistically significant (Figure 2). Moreover, only the composted date palm waste appeared to have a dose-dependent effect, whereas the effects of poultry manure and raw date palm residues were more variable. The residues were carefully incorporated into the soil to a depth of 30 cm with the aid a hand shovel, to ensure maximum mixing. However, the resulting mixtures were not as homogeneous as desired, even two years after preparation. The lack of homogeneity may be partly due to the fact that the residues were applied in different years, as well as to the dry conditions, which further hindered thorough mixing. In addition, the soil was devoid of vegetation, further contributing to the incomplete homogenisation. Of the three organic residues tested, the composted date palm waste produced the best results with the greatest improvement in soil fertility, especially at the highest dose (80 t ha−1).
4.2. Effects of Organic Amendments on the Biological and Biochemical Properties of Dry Soil
Regarding the soil biological properties considered, none of the effects of any of the three residues, regardless of the application rate, were very clear, with rather limited, variable and inconsistent results being obtained. The two highest doses (40 and 80 t ha−1) of each of the three residues produced a slight increase in microbial biomass and basal soil respiration, as previously observed in arid soils after the application of diverse organic residues [78,79,80]. However, except for the compost, the increases were not generally dose dependent. None of the residues produced a decrease in nitrate and ammonium levels, probably due to microbially induced immobilisation of these nitrogen forms [81,82], in response to the increased abundance and activity of soil microorganisms. Nonetheless, the increases in both microbial biomass and the rate of respiration were minimal (Figure 4). This can be partly attributed to the fact that the soils were very dry (soil moisture content ranging from 0.82 to 1.56%, and the measurements were therefore not made under optimal conditions, as is standard practice in such types of assessments in laboratory [83]. Measurements were instead made under the prevailing dry conditions, to better reflect field conditions and the actual environmental context.
Considering the absolute values of enzymatic activities measured in dry soil, and contrary to expectations, not all of the organic residues caused an increase in these activities. Only the composted date palm residue produced a significant increase in soil enzymatic activities (Table S1). Moreover, the increase was not observed for all the enzymes investigated, as phosphomonoesterase and arylsulfatase were not affected by the compost application. By contrast, the dehydrogenase, β-glucosidase, and urease activities generally increased significantly. In the case of dehydrogenase and urease activities, the increase was also dose dependent. Conversely, the effects of poultry manure and untreated date palm waste on enzyme activities were minimal and, in general, not statistically significant. All of the organic amendments generally produced an increase, not always statistically significant, in urease activity; for poultry manure, the increase was not related to the dose applied.
Given the usually strong relationship between soil enzyme activities and soil organic matter content [13,84,85], the increased in soil organic matter content produced by the organic amendments would be expected to influence the enzyme activity levels [13,68,86]. Thus, in order to normalise the activities and make them comparable across the soils amended with the different organic residues, the values of specific activity, i.e., the activity per unit of organic carbon, were calculated [58] (Figure 5). In general, none of the organic residues enhanced the specific enzyme activities, and in most cases a decrease was observed. Only the date palm waste (both composted and untreated) produced a significant and dose-dependent increase in urease activity. Additionally, the composted date palm produced an increase in dehydrogenase activity, possibly related to the higher respiration rate in the soil amended with compost than in soils amended with poultry manure or raw date palm waste, as dehydrogenase is an intracellular enzyme, whose activity reflects microbial degradative activity in the soil [52]. The higher degradative activity caused by the organic amendments was also reflected in the increase of average well colour development (AWCD) and the richness index (R), both of which indicated enhanced degradation of various carbon-based compounds by the soil bacterial communities, as observed through the Biolog assay. This increase was observed for all three amendments, although again it was only dose-dependent for the compost (Figure 6). Not all carbon compounds behaved in the same way, as only the degradation of polymers, organic acids, and pyruvic acid methyl ester appeared to be stimulated by the application of organic residues to the soil. Furthermore, while no significant differences were observed between amendments or doses for the degradation of organic acids and pyruvic acid methyl ester, compost again caused the greatest increase in polymer degradation, although in this case also poultry manure had a similar effect (Figure 7).
Both composted and non-composted organic waste have been widely used for agricultural purposes and for environmental restoration [16]. The properties of these residues make them particularly suitable for enhancing soil fertility and restoring soils with low organic matter content in arid and semi-arid regions [7,18,87]. However, most studies conducted in the arid and semi-arid areas of Tunisia have focused on the effects of organic waste on physical and physicochemical properties, such as pH, water retention capacity, and organic matter content [88,89,90]. By contrast, studies investigating the impact of these residues on biological and biochemical parameters are relatively scarce, and consequently, related data are virtually non-existent. Various studies in other arid and semi-arid areas of the Mediterranean region have investigated the effects of different organic residues on a broad range of parameters, including biological and biochemical indicators [87], which are considered particularly sensitive to environmental changes and are therefore closely linked to soil health [29,30,31,91]. In general, biological and biochemical soil properties are very sensitive to amendments made with different organic residues. The amendments typically cause an increase in the abundance and activity of soil microorganisms, as well as an overall improvement in soil health [13,68,92], which is often sustained in the long term [93,94]. In the present study, the limited response of soil enzyme activities to the application of organic amendments may be due to multiple factors. First, the residues were applied three years (first application) and one year (second application) before soil sampling. Furthermore, from the time of the first and second applications, the soil remained bare, without any vegetation cover. The absence of vegetation probably had both direct and indirect effects on soil enzymes. On the one hand, because of the absence of plants, there was no input of root exudate or plant debris to the soil. Without the input of labile substrates, there is probably no need for the synthesis and excretion of enzymes [86,94]. On the other hand, the lack of labile substrates also limits microbial biomass and activity, which further restricts soil enzyme production and activity [86]. Finally, among the three organic residues applied, only the compost was expected to actively contribute microorganisms and enzymes to the soil, whereas the other amendments probably would not do so in significant amounts.
The main objective of applying the amendments was to increase soil organic matter as a base for facilitating the establishment of an intercropped system between olive trees, while also improving soil fertility and health in the medium to long term. Given that the soils in the study area remain dry for most of the year, the results obtained seem promising, as all three residues produced significant increases in the soil organic matter content and nutrients such as phosphorus (P). This result is especially promising considering that the most recent organic amendment was applied two years before the study and that the soil remained bare throughout this period. A faster and more pronounced improvement would be expected if vegetation were present. It is also important to highlight that the study was conducted under dry conditions. Nonetheless, although infrequent, precipitation does occur at certain times of the year. While rainfall is limited, it may be sufficient to trigger a pulse of organic matter mineralisation, given the very low field capacity of these soils (8.45 ± 0.39%), as generally found in soils in arid and semi-arid regions [73]. Thus, small amounts of water are sufficient to bring the soil into optimal moisture conditions. Combined with the high temperatures prevalent in the area, this could lead to an undesirable increase in organic matter mineralisation [85], which would in turn increase CO2 emissions (a greenhouse gas), with potentially unintended consequences on the organic matter accumulation expected with the application of the residues.
4.3. Effects of Organic Amendments on the Biological and Biochemical Properties of Re-Wetted Soil
The soils were re-wetted and incubated under optimal moisture and temperature conditions to assess nitrogen mineralisation capacity, basal soil respiration and the hydrolase and oxidoreductase activities previously measured in dry soil. Re-wetting caused an increase in soil respiration in both the unamended soil and the soils amended with the three organic residues. However, unlike in the dry soil, respiration was higher than in the control for all residues and application rates. The increase was only significant at all doses of the composted date palm waste, with a clear dose-dependent pattern (Figure 9). Similarly, and unlike in dry soils, ammonification and nitrification processes occurred in all amended and unamended soils. Both poultry manure and composted date palm waste caused an increase in ammonification and nitrification rates relative to the control soil, and the increases were dose dependent. By contrast, untreated date palm waste did not affect the ammonification or nitrification rates relative to those in the control soil (Figure 9). Microbial biomass could not be measured in the re-wetted soils due to the excessively low difference in labile carbon (extractable with potassium sulphate) between non-fumigated and chloroform-fumigated samples, as well as the high variability among soils. This, in turn, suggests that re-wetting did not result in a detectable increase in microbial biomass, despite the higher respiration and nitrogen mineralisation observed in these soils. This is probably a methodological limitation, indicating that a more sensitive method may be required to assess microbial biomass in soils of this type. The absence of any such methodology in our laboratory, along with the limited amount of soil available, prevented us from conducting these measurements.
The increased carbon dioxide efflux due to the increase in soil respiration does not appear to be of significant environmental concern [95], and it would not substantially affect the expected accumulation of organic carbon in amended soils [95]. On the one hand, the amount of CO2 emitted from dry soils and its proportion relative to the total soil organic carbon remained fairly consistent regardless of the type or amount of organic amendment applied. For instance, in the control soil, the CO2-C emitted from the dry soil represents 0.69% of the total organic carbon, a value comparable to those observed in soils amended with various types and doses of organic residues, where the proportion ranged from 0.54% to 0.97%, with a mean of 0.64 ± 0.16%. In the re-wetted soil, the amount of CO2-C emitted increased. However, even in this case, the proportion of carbon loss relative to total organic carbon remains low. In the control soil, 1.70% of the total organic carbon was lost as CO2, while in amended soils (across all application rates), the value ranged from 1.23% to 2.18%, with an average loss of 1.81 ± 0.51%. Moreover, in the three years after the initial application of organic amendments (and despite the soil being bare and probably exposed to several rainfall events) all types and doses of residues tested led to accumulation of soil organic carbon. Although the increases were not always statistically significant (largely due to the high variability among soils from different plots), positive trends were observed for all amendment rates, including the lowest ones (Figure 2). By contrast, both ammonification and nitrification levels were high in all soils, including the control and the amended treatments. However, among the amended soils, only those treated with composted palm date waste (at any application rate) released significant amounts of ammonium and nitrate relative to the control soil. Thus, irrigating the soil shortly after sowing is important for effective soil management, particularly considering the intention to fully utilise available land and agricultural residues in the arid and semi-arid regions of Tunisia through intercropping systems in olive groves, as recently recommended [36]. This would enable crops to take advantage of the inorganic nitrogen released by the soil upon re-wetting, thereby supporting their early development.
Soil re-wetting had little effect on the enzymatic activities assessed, whether considering absolute activity values or specific activity (Table S2, Figure 10). The only noteworthy changes observed were a large reduction in urease activity in soils amended with all three types of organic residues and at all application rates, probably associated with the sharp increase in inorganic nitrogen content resulting from mineralisation. In addition, although absolute dehydrogenase activity values were similar to (or even lower than) those observed in dry soils, the activity per unit of organic C (specific activity) increased consistently across all treatments once the soils were re-wetted, consistent with the enhanced soil respiration. Interestingly, however, the dehydrogenase activity was inversely related to the amount of organic waste applied, decreasing as the application rate increased (Figure 10, Table S2). Given the opposite trend observed for both nitrogen mineralisation and respiration, both closely linked to microbial activities, it is difficult to determine the reason for this contrasting behaviour.
4.4. Future Perspectives
As previously mentioned, the next step in this research will be to evaluate whether the increased levels of organic matter and improved soil fertility can facilitate the establishment of intercropped plant species within olive groves. This will require the careful selection of plant species that are both drought-tolerant and capable of producing sufficient root exudates and biomass to support the development of an active and stable soil microbial community. Among the species to be tested are fast-growing, deep-rooted aromatic and medicinal plants, which can yield high-value products and therefore offer significant economic potential for olive plantation owners [11]. This is consistent with results (personal communication) reported by several researchers from Morocco and Tunisia (Professor Sahli and Boularbah), as part of a project in which they collaborate with some of the co-authors of the present study. These researchers observed that aromatic species have the potential to improve not only soil quality but also the quality of olives and the resulting oil.
5. Conclusions
The application of different organic residues (poultry manure plus citric acid, raw date palm waste, and composted date palm waste plus manure) to olive grove soils in the arid southeastern region of Tunisia significantly increased their organic matter content, one of the main study objectives. The bioavailable inorganic phosphorus content also increased, with both improvements showing a clear dose-dependent pattern. Despite the absence of vegetation throughout the entire period, the effects were sustained over time, with the organic matter content and fertility remaining higher in the soils amended three years prior to sampling than in the unamended control.
In contrast to chemical properties directly related to fertility and carbon sequestration, parameters associated with soil biological activity (microbial biomass, basal respiration, nitrogen mineralisation, and both hydrolytic and oxidoreductase enzymatic activities) were only minimally affected by application of the residues, even after soils were re-wetted to simulate post-rainfall conditions. The only consistent biological response observed was an increase in respiration in re-wetted soils relative to the dry soils. However, in all cases, the amount of CO2 released (whether in dry or moist soils) was minimal relative to the total organic carbon content, suggesting that applying agricultural waste residues is a sustainable disposal strategy that promotes soil organic carbon accumulation without significantly increasing CO2 emissions during wet periods.
The limited response of microbial abundance and enzymatic activity, despite the increased organic matter content, can be at least partly attributed to the absence of vegetation. The lack of plant cover leads to a scarcity of labile carbon inputs from plant residues and root exudates. Although the composted date palm waste generally yielded the best results regarding improving the soil fertility and health parameters investigated, its use instead of raw date palm waste would only be justified if the preparation and application did not entail significant additional costs, as the advantages were relatively limited.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/land14071414/s1, Table S1: Absolute values of enzymatic activities in dry soils amended with different organic wastes Table S2: Absolute values of enzymatic activities in moist soils amended with different organic wastes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.B. and C.T.-C.; methodology, A.B., Á.P.-F. and C.T.-C.; formal analysis, A.B. and N.C.; investigation, A.B., Á.P.-F. and C.T.-C.; resources, A.B. and C.T.-C.; data curation, N.C. and Z.O.; writing—original draft preparation, N.C. and C.T.-C.; writing—review and editing, N.C., Á.P.-F. and C.T.-C.; visualisation, A.B., N.C., Á.P.-F. and C.T.-C.; supervision, S.M., A.B. and C.T.-C.; project administration, S.M.; funding acquisition, N.C. and C.T.-C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Tunisian Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research, University of Gabès and by the Xunta de Galicia through the RCG project IN607A 2021-06.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
N. Chniguir is grateful for the support from all the team of the Soil Biochemistry Department of the MBG Santiago-CSIC (Santiago de Compostela, Spain). The authors thank A. Iglesias-Tojo, L. Debernardo, M. Loureiro and B. Rodríguez-Garrido, for assistance in carrying out the analyses.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Huang, J.; Yu, H.; Dai, A.; Wei, Y.; Kang, L. Drylands Face Potential Threat under 2 °C Global Warming Target. Nat. Clim. Change 2017, 7, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Belghiti, F.-Z.; Benidire, L.; M’Barki, K.; Dounas, H.; Boularbah, A. Soil System Status, Threats, Utilization Pattern, and Sustainable Management Strategies in the Global South: Overview of the Agriculture Soils in Maghreb Countries. In Sustainable Soil Systems in Global South; Ogwu, M.C., Izah, S.C., Dessureault-Rompré, J., Gasparatos, D., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2024; pp. 689–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahim, N.; Ibrahim, H.; Hatira, A. Tunisian Soil Organic Carbon Stock–Spatial and Vertical Variation. Procedia Eng. 2014, 69, 1549–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Bowman, D.; Shi, W. Seasonal Variations of Soil Microbial Biomass and Activity in Warm-and Cool-Season Turfgrass Systems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1536–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastida, F.; Moreno, J.L.; Hernandez, T.; García, C. Microbiological Activity in a Soil 15 Years after Its Devegetation. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 2503–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fterich, A.; Mahdhi, M.; Mars, M. Seasonal Changes of Microbiological Properties in Steppe Soils from Degraded Arid Area in Tunisia. Arid Land Res. Manag. 2014, 28, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madline, A.; Benidire, L.; Pereira, S.I.; Khalil, H.E.; Michalski, A.; Castro, P.M.; Charzyński, P.; Boularbah, A. Optimizing Biological and Physicochemical Properties of Acidic Mine Tailings through Combined Organo-Mineral Amendments and Topsoil Application. J. Soils Sediments 2025, 25, 609–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wezel, A.; Casagrande, M.; Celette, F.; Vian, J.-F.; Ferrer, A.; Peigné, J. Agroecological Practices for Sustainable Agriculture. A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 34, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahim, N.; Karbout, N.; Dhaouadi, L.; Bouajila, A. Global Landscape of Organic Carbon and Total Nitrogen in the Soils of Oasis Ecosystems in Southern Tunisia. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittrich, F.; Iserloh, T.; Treseler, C.-H.; Hüppi, R.; Ogan, S.; Seeger, M.; Thiele-Bruhn, S. Crop Diversification in Viticulture with Aromatic Plants: Effects of Intercropping on Grapevine Productivity in a Steep-Slope Vineyard in the Mosel Area, Germany. Agriculture 2021, 11, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobeh, M.; Boularbah, A.; Yasri, A. Chemically Degraded Soil Rehabilitation Process Using Medicinal and Aromatic Plants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 73–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenwerth, K.; Belina, K.M. Cover Crops Enhance Soil Organic Matter, Carbon Dynamics and Microbiological Function in a Vineyard Agroecosystem. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2008, 40, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; He, Z.; Zhou, X.; Powell, C.A.; Yang, Y.; He, L.M.; Stoffella, P.J. Impact of Mixed Land-Use Practices on the Microbial Water Quality in a Subtropical Coastal Watershed. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 449, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D.; Cassman, K.G.; Matson, P.A.; Naylor, R.; Polasky, S. Agricultural Sustainability and Intensive Production Practices. Nature 2002, 418, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejada, M.; Moreno, J.L.; Hernández, M.T.; García, C. Soil Amendments with Organic Wastes Reduce the Toxicity of Nickel to Soil Enzyme Activities. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2008, 44, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastida, F.; Kandeler, E.; Hernández, T.; García, C. Long-Term Effect of Municipal Solid Waste Amendment on Microbial Abundance and Humus-Associated Enzyme Activities under Semiarid Conditions. Microb. Ecol. 2008, 55, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammad, H.M.; Khaliq, A.; Abbas, F.; Farhad, W.; Fahad, S.; Aslam, M.; Shah, G.M.; Nasim, W.; Mubeen, M.; Bakhat, H.F. Comparative Effects of Organic and Inorganic Fertilizers on Soil Organic Carbon and Wheat Productivity under Arid Region. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2020, 51, 1406–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbout, N.; Brahim, N.; Mlih, R.; Moussa, M.; Bousnina, H.; Weihermuller, L.; Bol, R. Bentonite Clay Combined with Organic Amendments to Enhance Soil Fertility in Oasis Agrosystem. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Hu, F.; Chen, X.; Huang, Q.; Jiao, J.; Zhang, B.; Li, H. Organic Amendments with Reduced Chemical Fertilizer Promote Soil Microbial Development and Nutrient Availability in a Subtropical Paddy Field: The Influence of Quantity, Type and Application Time of Organic Amendments. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2009, 42, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfstrand, S. Impact of Green Manure on Soil Organisms: With Emphasis on Microbial Community Composition and Function. Ph.D. Thesis, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences, Uppsala, Sweden, 2007. Available online: https://pub.epsilon.slu.se/1349/1/SE_thesis.pdf (accessed on 2 May 2025).
- Eid, E.M.; Shaltout, K.H.; Abdallah, S.M.; Galal, T.M.; El-Bebany, A.F.; Sewelam, N.A. Uptake Prediction of Ten Heavy Metals by Eruca Sativa Mill. Cultivated in Soils Amended with Sewage Sludge. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 104, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasoulzadeh, A.; Yaghoubi, A. Effect of Cattle Manure on Soil Physical Properties on a Sandy Clay Loam Soil in North-West Iran. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2010, 8, 976–979. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, M.J.; Worrall, F. Charcoal Addition to Soils in NE England: A Carbon Sink with Environmental Co-Benefits? Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1704–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.N.; Finck, A.; Blair, G.J.; Tandon, H.L.S. Plant Nutrition for Food Security. Guide Integr. Nutr. Manag. FAO Fertil. Plant Nutr. Bull. 2006, 16, 201–214. [Google Scholar]
- Zrelli, A.; Elfalleh, W.; Ghorbal, A.; Chaouachi, B. Valorization of Date Palm Wastes by Lignin Extraction to Be Used for the Improvement of Polymeric Membrane Characteristics. Period. Polytech. Chem. Eng. 2022, 66, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oueriemmi, H.; Kidd, P.S.; Trasar-Cepeda, C.; Rodríguez-Garrido, B.; Zoghlami, R.I.; Ardhaoui, K.; Prieto-Fernández, Á.; Moussa, M. Evaluation of Composted Organic Wastes and Farmyard Manure for Improving Fertility of Poor Sandy Soils in Arid Regions. Agriculture 2021, 11, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, M.P.; Alburquerque, J.A.; Moral, R. Composting of Animal Manures and Chemical Criteria for Compost Maturity Assessment. A Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5444–5453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, R.; Rao, K.J.; Reza, S.K.; Padua, S.; Dinesh, D.; Dharumarajan, S. Influence of Inorganic Fertilizers and Organic Amendments on Plant Nutrients and Soil Enzyme Activities under Incubation. Int. J. Bio-Resour. Stress Manag. 2016, 7, 924–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, M.A.; Coen, G.M. Characterization of Soil Quality: Physical and Chemical Criteria. Am. J. Altern. Agric. 1992, 7, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, J.F.; Papendick, R.I.; Hornick, S.B.; Meyer, R.E. Soil Quality: Attributes and Relationship to Alternative and Sustainable Agriculture. Am. J. Altern. Agric. 1992, 7, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ros, M.; Rodríguez, I.; García, C.; Hernández, M.T. Bacterial Community in Semiarid Hydrocarbon Contaminated Soils Treated by Aeration and Organic Amendments. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2014, 94, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Sotres, F.; Trasar-Cepeda, C.; Leirós, M.C.; Seoane, S. Different Approaches to Evaluating Soil Quality Using Biochemical Properties. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 877–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nannipieri, P.; Greco, S.; Ceccanti, B. Ecological Significance of the Biological Activity in Soil. In Soil Biochemistry; Bollag, J.-M., Stotzky, G., Eds.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 1990; Volume 6, Chapter 6; pp. 293–356. [Google Scholar]
- Visser, S.; Parkinson, D. Soil Biological Criteria as Indicators of Soil Quality: Soil Microorganisms. Am. J. Altern. Agric. 1992, 7, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordán, A.; Zavala, L.M.; Gil, J. Effects of Mulching on Soil Physical Properties and Runoff under Semi-Arid Conditions in Southern Spain. Catena 2010, 81, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahim, N.; Ibrahim, H.; Mlih, R.; Bouajila, A.; Karbout, N.; Bol, R. Soil OC and N Stocks in the Saline Soil of Tunisian Gataaya Oasis Eight Years after Application of Manure and Compost. Land 2022, 11, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armas, C.M.; Santana, B.; Mora, J.L.; Notario, J.S.; Arbelo, C.D.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, A. A Biological Quality Index for Volcanic Andisols and Aridisols (Canary Islands, Spain): Variations Related to the Ecosystem Degradation. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 378, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannachi, N.; Cocco, S.; Fornasier, F.; Agnelli, A.; Brecciaroli, G.; Massaccesi, L.; Weindorf, D.; Corti, G. Effects of Cultivation on Chemical and Biochemical Properties of Dryland Soils from Southern Tunisia. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 199, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miralles, I.; Trasar-Cepeda, C.; Leirós, M.C.; Barbosa-Pereira, L.; Gil-Sotres, F. Capacity of Biological Soil Crusts Colonized by the Lichen Diploschistes to Metabolize Simple Phenols. Plant Soil 2014, 385, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benidire, L.; Madline, A.; Pereira, S.I.A.; Castro, P.M.L.; Boularbah, A. Synergistic Effect of Organo-Mineral Amendments and Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) on the Establishment of Vegetation Cover and Amelioration of Mine Tailings. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 127803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.A.E.-H.; Moursy, F.I.; Darrag, M.H.; El-Mahdy, M.E.-S. Assessment of Long-Term Trends and Mapping of Drought Events in Tunisia. Sci. Afr. 2023, 21, e01766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014, Update 2015 International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps. World Soil Resources Reports No. 106. Rome, Italy, FAO. 2015. Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/server/api/core/bitstreams/bcdecec7-f45f-4dc5-beb1-97022d29fab4/content (accessed on 15 April 2025).
- Dick, R.P. Methods of Soil Enzymology; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mylavarapu, R.; Bergeron, J.; Wilkinson, N. Soil pH and Electrical Conductivity: A Country Extension Soil Laboratory Manual. IFAS Extension. University of Florida, USA. Available online: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss118 (accessed on 15 April 2025).
- Guitián-Ojea, F.; Carballas-Fernández, T. Técnicas de Análisis de Suelos, 2nd ed.; Eitorial PS: Santiago de Compostela, España, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Hedley, M.J.; Stewart, J.W.B.; Chauhan, B.S. Changes in Inorganic and Organic Soil Phosphorus Fractions Induced by Cultivation Practices and by Laboratory Incubations. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1982, 46, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trasar-Cepeda, M.C.; Gil-Sotres, F.; Guitian-Ojea, F. Relation between Phosphorus Fractions and Development of Soils from Galicia (NW Spain). Geoderma 1990, 47, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.; Riley, J.P. A Modified Single Solution Method for the Determination of Phosphate in Natural Waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 1962, 27, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremner, J.M. Inorganic Forms of Nitrogen. In Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 2 Agronomy; Black, C.A., Evans, D.D., Clark, F.E., Eds.; American Society of Agronomy Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 1965; pp. 1179–1237. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkinson, D.S.; Powlson, D.S. The Effects of Biocidal Treatments on Metabolism in Soil—V: A Method for Measuring Soil Biomass. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1976, 8, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, E.D.; Brookes, P.C.; Jenkinson, D.S. Microbial Biomass Measurements in Forest Soils: Determination of Kc Values and Tests of Hypotheses to Explain the Failure of the Chloroform Fumigation-Incubation Method in Acid Soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1987, 19, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camiña, F.; Trasar-Cepeda, C.; Gil-Sotres, F.; Leirós, C. Measurement of Dehydrogenase Activity in Acid Soils Rich in Organic Matter. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1998, 30, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nannipieri, P.; Ceccanti, B.; Cervelli, S.; Matarese, E. Extraction of Phosphatase, Urease, Proteases, Organic Carbon, and Nitrogen from Soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 1011–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabai, M.A.; Bremner, J.M. Use of P-Nitrophenyl Phosphate for Assay of Soil Phosphatase Activity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1969, 1, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trasar-Cepeda, M.C.; Gil-Sotres, F. Phosphatase Activity in Acid High Organic Matter Soils in Galicia (NW Spain). Soil Biol. Biochem. 1987, 19, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eivazi, F.; Tabatabai, M.A. Glucosidases and Galactosidases in Soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1988, 20, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabai, M.A.; Bremner, J.M. Arylsulfatase Activity of Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1970, 34, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trasar-Cepeda, C.; Leirós, M.C.; Gil-Sotres, F. Hydrolytic Enzyme Activities in Agricultural and Forest Soils. Some Implications for Their Use as Indicators of Soil Quality. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 2146–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, T.; Rodríguez-Garrido, B.; Saad, R.F.; Soto-Vázquez, J.L.; Loureiro-Viñas, M.; Prieto-Fernández, Á.; Echevarria, G.; Benizri, E.; Kidd, P.S. Assessing the Agromining Potential of Mediterranean Nickel-Hyperaccumulating Plant Species at Field-Scale in Ultramafic Soils under Humid-Temperate Climate. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 630, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garland, J.L. Analysis and Interpretation of Community-Level Physiological Profiles in Microbial Ecology. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 1997, 24, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniz, S.; Lacarta, J.; Pata, M.P.; Jimenez, J.J.; Navarro, E. Analysis of the Diversity of Substrate Utilisation of Soil Bacteria Exposed to Cd and Earthworm Activity Using Generalised Additive Models. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garau, G.; Castaldi, P.; Santona, L.; Deiana, P.; Melis, P. Influence of Red Mud, Zeolite and Lime on Heavy Metal Immobilization, Culturable Heterotrophic Microbial Populations and Enzyme Activities in a Contaminated Soil. Geoderma 2007, 142, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Jiménez, E.; Plaza, C.; Saiz, H.; Manzano, R.; Flagmeier, M.; Maestre, F.T. Aridity and Reduced Soil Micronutrient Availability in Global Drylands. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargouri, K.; Bentaher, H.; Rhouma, A. A Novel Method to Assess Drought Stress of Olive Tree. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2012, 32, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kefi, M.; Yoshino, K.; Setiawan, Y.; Zayani, K.; Boufaroua, M. Assessment of the Effects of Vegetation on Soil Erosion Risk by Water: A Case of Study of the Batta Watershed in Tunisia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 64, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbasiouny, H.; El-Ramady, H.; Elbehiry, F.; Rajput, V.D.; Minkina, T.; Mandzhieva, S. Plant Nutrition under Climate Change and Soil Carbon Sequestration. Sustainability 2022, 14, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherif, H.; Ayari, F.; Ouzari, H.; Marzorati, M.; Brusetti, L.; Jedidi, N.; Hassen, A.; Daffonchio, D. Effects of Municipal Solid Waste Compost, Farmyard Manure and Chemical Fertilizers on Wheat Growth, Soil Composition and Soil Bacterial Characteristics under Tunisian Arid Climate. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2009, 45, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siles, J.A.; García-Sánchez, M.; Gómez-Brandón, M. Studying Microbial Communities through Co-Occurrence Network Analyses during Processes of Waste Treatment and in Organically Amended Soils: A Review. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zriba, Z.; Karbout, N.; Azaiez, F.E.B.; Lamourou, H.; Bousnina, H.; Moussa, M. Effect of Different Soil Amendments on Irrigation and Crop Yields in the Oases of Southern Tunisia. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2023, 35, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanuzzi, A.; Arocena, J.M.; Van Mourik, J.M.; Cano, A.F. Amendments with Organic and Industrial Wastes Stimulate Soil Formation in Mine Tailings as Revealed by Micromorphology. Geoderma 2009, 154, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touceda-González, M.; Álvarez-López, V.; Prieto-Fernández, Á.; Rodríguez-Garrido, B.; Trasar-Cepeda, C.; Mench, M.; Puschenreiter, M.; Quintela-Sabarís, C.; Macías-García, F.; Kidd, P.S. Aided Phytostabilisation Reduces Metal Toxicity, Improves Soil Fertility and Enhances Microbial Activity in Cu-Rich Mine Tailings. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 186, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Z.; Huang, J.; Fallah, N.; Lin, W.; Yuan, Z.; Hu, C. Combining N Fertilization with Biochar Affects Root-Shoot Growth, Rhizosphere Soil Properties and Bacterial Communities under Sugarcane Monocropping. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2022, 182, 114899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Guyader, E.; Morvan, X.; Miconnet, V.; Marin, B.; Moussa, M.; Intrigliolo, D.S.; Delgado-Iniesta, M.J.; Girods, P.; Fontana, S.; Sbih, M. Influence of Date Palm-Based Biochar and Compost on Water Retention Properties of Soils with Different Sand Contents. Forests 2024, 15, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantrell, I.C.; Linderman, R.G. Preinoculation of Lettuce and Onion with VA Mycorrhizal Fungi Reduces Deleterious Effects of Soil Salinity. Plant Soil 2001, 233, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, R.; Bista, P.; Machado, S. Crop Yield Limitation by Soil Organic Matter Decline: A Case Study from the US Pacific Northwest. In Advances in Understanding Soil Degradation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alburquerque, J.A.; Gonzálvez, J.; Tortosa, G.; Baddi, G.A.; Cegarra, J. Evaluation of “Alperujo” Composting Based on Organic Matter Degradation, Humification and Compost Quality. Biodegradation 2009, 20, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinari, S.; Mancinelli, R.; Campiglia, E.; Grego, S. Chemical and Biological Indicators of Soil Quality in Organic and Conventional Farming Systems in Central Italy. Ecol. Indic. 2006, 6, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhadhbi, T.; Pringault, O.; Nouri, H.; Spinelli, S.; Beyrem, H.; Gonzalez, C. Evaluating Polar Pesticide Pollution with a Combined Approach: A Survey of Agricultural Practices and POCIS Passive Samplers in a Tunisian Lagoon Watershed. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 342–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azaiez, N.; Alleoua, A.; Baazaoui, N.; Qhtani, N. Assessment of Soil Loss in the Mirabah Basin: An Overview of the Potential of Agricultural Terraces as Ancestral Practices (Saudi Arabia). Open J. Soil Sci. 2020, 10, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, W.; Ammar, E. Date Palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) Wastes Valorization: A Circular Economy Approach. In Mediterranean Fruits Bio-Wastes: Chemistry, Functionality and Technological Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 403–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieder, R.; Benbi, D.K.; Scherer, H.W. Fixation and Defixation of Ammonium in Soils: A Review. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2011, 47, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, H.W.; Metker, D.J.; Welp, G. Effect of Long-Term Organic Amendments on Chemical and Microbial Properties of a Luvisol. Plant Soil Environ. 2011, 57, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, T.; García, C. Estimación de La Respiración Microbiana Del Suelo. In Técnicas de Análisis de Parámetros Bioquímicos en Suelos; Mundi-Prensa: Madrid, Spain, 2003; pp. 311–346. [Google Scholar]
- Miguéns, T.; Leirós, M.C.; Gil-Sotres, F.; Trasar-Cepeda, C. Biochemical Properties of Vineyard Soils in Galicia, Spain. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 378, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miralles, I.; Ortega, R.; Almendros, G.; Gil-Sotres, F.; Trasar-Cepeda, C.; Leirós, M.C.; Soriano, M. Modifications of Organic Matter and Enzymatic Activities in Response to Change in Soil Use in Semi-arid Mountain Ecosystems (Southern Spain). Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2012, 63, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastida, F.; Torres, I.F.; Moreno, J.L.; Baldrian, P.; Ondoño, S.; Ruiz-Navarro, A.; Hernández, T.; Richnow, H.H.; Starke, R.; García, C. The Active Microbial Diversity Drives Ecosystem Multifunctionality and Is Physiologically Related to Carbon Availability in Mediterranean Semi-arid Soils. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 4660–4673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zornoza, R.; Faz, A.; Carmona, D.M.; Martínez-Martínez, S.; Acosta, J.A. Plant Cover and Soil Biochemical Properties in a Mine Tailing Pond Five Years after Application of Marble Wastes and Organic Amendments. Pedosphere 2012, 22, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbout, N.; Moussa, M.; Gasmi, I.; Bousnina, H. Effect of Clay Amendment on Physical and Chemical Characteristics of Sandy Soil in Arid Areas: The Case of Ground South-Eastern Tunisian. Appl. Sci. Rep. 2015, 11, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douh, B.; Mguidiche, A.; Zouari, I.; Gargouri, K.; Ayachi, M. Impact of Different Organic Amendments on: Hydrodynamic Soil Properties and Olive Tree Behavior Conducted under Deficit Irrigation. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2021, 52, 2256–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masmoudi, S.; Magdich, S.; Rigane, H.; Medhioub, K.; Rebai, A.; Ammar, E. Effects of Compost and Manure Application Rate on the Soil Physico-Chemical Layers Properties and Plant Productivity. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 11, 1883–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ferreiro, J.; Trasar-Cepeda, C.; Leirós, M.C.; Seoane, S.; Gil-Sotres, F. Biochemical Properties of Acid Soils under Native Grassland in a Temperate Humid Zone. N. Z. J. Agric. Res. 2007, 50, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zornoza, R.; Mataix-Solera, J.; Guerrero, C.; Arcenegui, V.; Mayoral, A.M.; Morales, J.; Mataix-Beneyto, J. Soil Properties under Natural Forest in the Alicante Province of Spain. Geoderma 2007, 142, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastida, F.; Hernández, T.; Albaladejo, J.; García, C. Phylogenetic and Functional Changes in the Microbial Community of Long-Term Restored Soils under Semiarid Climate. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 65, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siles, J.A.; José, M.; González-Pérez, J.A.; Fernández-Pérez, V.; García-Díaz, C.; Moreno, J.L.; García, C.; Bastida, F. Long-Term Restoration with Organic Amendments Is Clearer Evidenced by Soil Organic Matter Composition than by Changes in Microbial Taxonomy and Functionality. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 198, 105383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavvadias, V.; Le Guyader, E.; El Mazlouzi, M.; Gommeaux, M.; Boumaraf, B.; Moussa, M.; Lamine, H.; Sbih, M.; Zoghlami, I.R.; Guimeur, K. Using Date Palm Residues to Improve Soil Properties: The Case of Compost and Biochar. Soil Syst. 2024, 8, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).