Abstract
Based on 143 Sentinel-1A images from January 2020 to December 2022, this study used SBAS-InSAR technology to monitor the surface deformation of the tailings pond and analyzed and predicted the surface deformation laws in southeast Tibet. Overall, the surface deformation of the tailings pond was significant and there were many areas where the deformation was uneven. The typical subsidence areas were mainly located in the northern part of the right tailings pond and the southern part of the left tailings pond. From a temporal perspective, the subsidence in the tailings pond showed a certain periodic downward fluctuation. Specifically, cumulative subsidence from January to September each year displayed a clear downward trend, reaching its maximum around September. This was followed by a slight uplift in October and November, after which a notable downward trend resumed from December until the following September. Based on spatial scale analysis, the changes in the tailings pond were relatively stable before May 2020. After that, the northern part of the right tailings pond showed a sinking trend, while the southern part exhibited uplift, and the central part remained relatively stable. Conversely, the southeastern part of the left tailings pond showed an uplifting trend, while the northern, central, and western parts experienced subsidence. Based on the Holt–Winters exponential smoothing model, we predicted the cumulative subsidence for 10 monitoring points in 2023. The northern part of the right tailings pond is expected to continue showing a significant subsidence trend in 2023. A prominent subsidence center is projected to emerge in the central part of the left tailings pond, and we should strengthen monitoring to avoid the disaster risk in the mining area.
1. Introduction
Southeast Tibet is situated at the junction of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau and the Asian continent plate. Influenced by the natural geographical environment and climatic factors, this area features complex topography, including various landforms such as high mountains, rivers, lakes, and canyons [1,2]. It is also characterized by extensive permafrost and glaciers, and there are significant changes in its geomorphological features. Permafrost undergoes freeze–thaw cycles influenced by seasonal temperature changes, resulting in surface uplift and subsidence [3]. The effects of alternate freezing and thawing can lead to damage to the geological environment and trigger geological hazards such as foundation cracks, ground fissures, debris flows, and landslides, posing severe threats to the stability of buildings in permafrost regions and the safety of local residents’ lives and property [4,5,6,7,8]. Moreover, the collision between the Eurasian and Indian plates has caused crustal shortening and uplift of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, leading to intense geological activity and frequent geological hazards in the region, which seriously threaten the production and life of residents in southeast Tibet [9,10]. Therefore, understanding the pattern and trend of surface deformation in southeast Tibet is essential for early warning and prevention of geological disasters.
The tailings pond serves as a site for storing waste materials generated during the mining process, and its surface deformation can directly reflect the stability and safety of the tailings pond [11,12]. Throughout the long-term filling and storage processes, the tailings pond may experience surface deformation, subsidence, and damage. The impact of the tailings pond on the surrounding environment is a long process, as solid pollutants, wastewater and waste gas accumulated during ore dressing will change in response to variations in the surface deformation of the tailings pond. Consequently, studying the surface deformation law and trend of the tailings pond is crucial for ensuring their safety, stability, and sustainable development.
Despite the advantages of high precision and convenient deployment, traditional field ground survey methods, such as the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) and precise leveling [11,12,13,14], can only provide deformation data at specific monitoring points. These methods are unable to continuously acquire surface deformation data over large uninhabited areas under all-weather conditions, which make it difficult to meet the demands for extensive and long-term surface measurements. In recent years, with the launch of the Sentinel-1 satellites by the European Space Agency (ESA), the sources of SAR data have been broadened and their quality has improved considerably [5]. Meanwhile, Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) technology has developed rapidly. This technology is a new and advanced earth observation technology [15,16]. Based on Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR), it employs active microwave remote sensing to transmit electromagnetic waves and applies the technique of interferometry to capture single-look complex (SLC) images of the study area by recording the returned signals and phase information [17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25]. The precision of surface deformation data can be achieved at the centimeter level, and even the millimeter level. Due to its advantages such as all-weather capability, all-time capability, high precision, high processing speed, and continued stability, InSAR technology enables high-precision measurements of surface deformation [26,27,28,29], providing important data and a scientific basis for the study of surface micro-relief evolution characteristics in southeast Tibet.
This study focuses on the tailings pond in southeast Tibet. Based on 143 Sentinel-1A images from January 2020 to December 2022, we used SBAS-InSAR technology to monitor the surface deformation of the tailings pond in the study area and analyzed the surface deformation rate and the cumulative subsidence to explore the patterns of surface deformation under conditions of human disturbances and natural evolution in southeast Tibet. Additionally, by using the Holt–Winters exponential smoothing model, we deeply analyzed the typical subsidence points to predict the changing trends of surface deformation at these locations.
2. Study Area
The tailings pond in southeast Tibet is located 67 km east of Lhasa (Figure 1), Tibet. This area belongs to the temperate semi-arid monsoon climate of the plateau, featuring thin air, cold and dryness, strong winter and spring monsoons, a minor annual temperature difference, and large diurnal temperature variation. The average annual temperature is about 5.1~9 °C, with the highest temperature occurring in June, reaching around 30 °C, and the lowest temperature in occurring January, up to around −16 °C. The area receives an average of 2813.5 h of sunshine annually, and its precipitation is mainly concentrated from June to September, with an annual rainfall of approximately 515.9 mm [24]. The mining area falls into the junction zone of the Kailas Range and the Nyainqêntanglha Mountains, where the terrain is steep and complicated due to intense erosion. With an average elevation exceeding 5000 m, glacial landforms are distributed in this area. The geological formation of the mining area is a volcanic–sedimentary rock series of Middle Jurassic Yeba Formation and the main host rocks are biotite adamellite and monzonitic granite-porphyry of the Miocene. The wall rocks are strongly altered, and fractures and fissures are well developed. The elevation of the ore body ranges from 1800 m to 1000 m, and it is elliptical in plan view and irregularly cylindrical in its cross-section. The ore body consists of veinlet-dissemination primary sulfide ore, with chalcopyrite as the main mineral and copper as the major useful element, in addition to associated elements such as molybdenum, silver, and sulfur. The mineral deposit is a typical porphyry copper deposit [25].
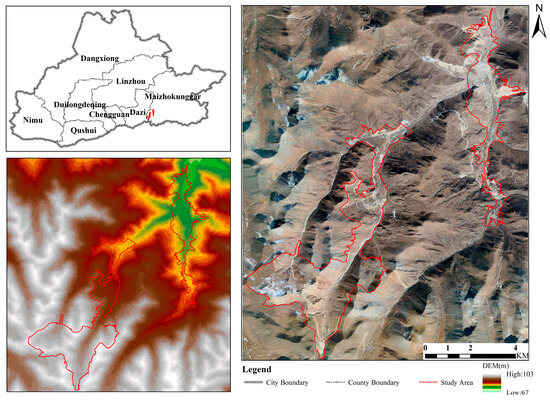
Figure 1.
Location of study area.
3. Data and Methodology
3.1. Data and Process
3.1.1. InSAR Data
This study downloaded 143 scenes of Sentinel-1A ascending and descending orbit data from the ASF Data Search. Further details regarding the basic parameter information of Sentinel-1A IW-mode image data can be found in Table 1. Table 2 lists the imaging times of 72 scenes of Sentinel-1A ascending and descending radar images of the tailings pond.

Table 1.
Basic parameter information of Sentinel-1A IW-mode image data.

Table 2.
Imaging time of Sentinel-1A tailings pond.
Sentinel-1 data include two common types of orbital data. The precise orbit ephemeris data (AUX_POEORB) are the most accurate type. Precise orbit files are published once per day, each covering 26 h of data, with a positioning accuracy of 5 cm in 3D RMS. However, these data can only be used 21 days after the GNSS downlink. Another type, the restituted orbit data (AUX_RESORB), is also quite accurate. Restituted orbit files are generated within 3 h from sensing time and distributed daily, with a positioning accuracy of 10 cm in 2D RMS. This study selects the AUX_RESORB files to correct the orbital information. These files can be downloaded from the European Space Agency portal, ensuring that the sensing time of the files corresponds with the imaging times of Sentinel-1A.
3.1.2. DEM Data
Reference DEM data play a crucial role in SEA data processing, providing essential terrain information and reference geographic coordinate systems. The Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) is an international research effort aimed at remotely sensing and mapping the Earth’s surface. This project was implemented in collaboration with the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA), the German Aerospace Center (DLR), and the Italian Space Agency (ASI). The SRTM system flew on board the Space Shuttle Endeavour launched by the U.S., and SRTM3 version 4 is the latest version, which fills the voids using ancillary data, including generating contour lines and elevation points, as well as re-interpolating and converting these ancillary data to DEM data. This study selects the strip number of the study area from the Geospatial Data Cloud and then downloads the SRTM3 version 4 DEM data from the SRTM Tile Grabber based on the obtained strip number.
3.2. Research Methods
3.2.1. Surface Deformation Monitoring Method Based on SBAS-InSAR
The basic idea of SBAS-InSAR technology is to connect independent SAR images caused by long baselines to form a collection of short-baseline SAR images. Specifically, this technology can divide the existing SAR image dataset into several small subsets, where the baselines between the SAR images in each small subset are relatively short, while the baselines between the subsets are longer. The basic operating principle and method of this technique are as follows:
We collect K SAR images, denoted as (t1, t2, …, tk). The SAR images are then registered and sampled according to established baseline thresholds and time baseline thresholds. This process results in M interferometric pairs, with their quantity satisfying the following relationship (Equation (1)):
If time tA is less than time tB, the differential interferometric phase at the coordinate point (x, y), for the i interferogram, which is generated by SAR images at time tA and tB, can be expressed as Equation (2) [28]:
where is the line-of-sight (LOS) cumulative deformation, expresses the atmospheric delay phase difference, is the residual terrain phase difference, and is the noise phase difference.
After estimating and removing the phases related to atmospheric and elevation variations using a Spatial–Temporal Filter, the M interferometric phases can be organized in the following matrix (Equation (3)):
where B represents an M × N matrix. The generalized inverse matrix of B is then obtained using Singular Value Decomposition (SVD), calculating the deformation rate and the cumulative deformation time series.
The specific implementation process is as follows (Figure 2). Firstly, Sentinel-A data are preprocessed to form the connection diagram of interference image pairs. Then, according to different temporal and spatial baselines, interference results with better image quality are selected as the superior main image and the rest are used as secondary images, where secondary images are registered with the superior main image. Interference processing is performed on the data to generate differential interferogram, and then de-leveling, adaptive filtering, coherence calculation, and phase unwinding are carried out. Then, according to the phase unwinding diagram and de-leveling interferogram, a sufficient number of points in the surface deformation region should be selected as GCP control points, and these should be evenly distributed in the study area. After two inversions of the data, geocoding is carried out to obtain the surface deformation rate in the study area.
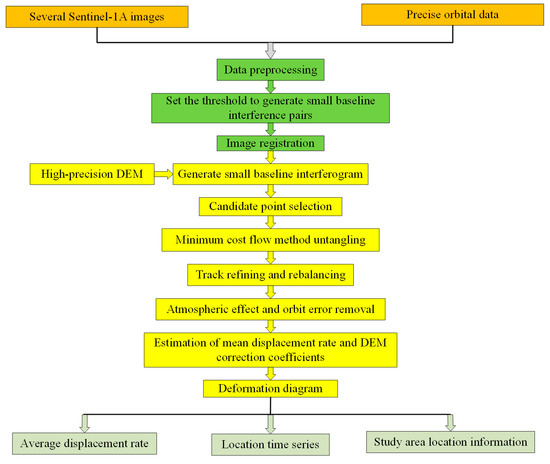
Figure 2.
Processing workflow of SBAS-InSAR.
3.2.2. Holt–Winters Time Series Models
The Holt–Winters formulation has three components: trend, seasonality, and level. The validity of the Holt–Winters model depends mainly on the stationarity of the time series, and the model is suitable for cases where the magnitude of seasonal fluctuations increases or decreases over time. The trend considers the long-term change in the time series data, which mainly includes linear trends and nonlinear trends. The model can be expressed as Equation (4):
where observed represents the level, trend represents the trend, and seasonal is seasonality.
Exponential smoothing in year t can be denoted as st. Let st denote the smoothed level in year t, tt denote the smoothed trend, and ot be seasonal factor smoothing. The equations used in the model are as follows:
Here, we have the following:
is the exponential smoothing parameter for the level (0 < < 1); xt is the observed data at time t; ot−m is the seasonal component; st−1 is the previously smoothed level; tt−1 is the previously smoothed trend; is the exponential smoothing parameter for the trend (0 < < 1); is the exponential smoothing parameter for seasonality (0 < < 1).
For the Holt–Winters exponential smoothing forecast value, the following equation is used:
where m is the period to be predicted, and mod is an operator used to obtain the remainder from a division.
It should be noted that when the Holt–Winters algorithm is used for time series prediction, different model parameters and smoothing coefficients should be selected for fitting according to the actual data to improve the prediction accuracy, and they are determined by minimizing the mean square error and iteratively optimizing by the L-BFGS-B algorithm until the error converges. Furthermore, the confidence of the predicted value should be evaluated to judge the reliability of the forecast results.
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. Analysis of Surface Micro-Relief Deformation Patterns in the Tailings Pond Based on the SBAS
Leveraging Sentinel-1A ascending and descending orbit data and using InSAR-SBAS technology, we obtained radar line-of-sight (LOS) deformation rates (Figure 2) from January 2020 to December 2022. Positive values indicate vertical surface uplift (i.e., moving closer to the satellite), while negative values represent vertical subsidence (i.e., moving away from the satellite). This study validated the deformation results by comparing the results obtained by the SBAS-InSAR and PS-InSAR processing methods; the difference in the surface deformation rate between the two methods was calculated, and the difference in most areas was ±6 mm/a. In addition, 120 deformation points were randomly selected as sample points in the study area for linear regression analysis, and the correlation coefficient was obtained as 0.877. This indicates that InSAR technology is reliable in monitoring land subsidence.
The results showed that during the study period, the monitoring points selected by SBAS technology through temporal coherence and phase stability show significant characteristics in spatial distribution. The monitoring points with high coherence (including some distributed scatterers (DSs)) in the west sunny slope area are mainly distributed in the ascending orbit image data, while the east sunny slope area is more common in the descending orbit image data. In the flat terrain area, the lifting rail data can effectively obtain stable monitoring points. It is worth noting that DSs usually occur on the surface with uniform scattering properties (such as vegetated areas or loose sedimentary layers). The spatial distribution features are closely related to the right-side imaging geometry of the Sentinel-1A satellite, and the deformation monitoring capability in hilly and mountainous areas with large topography can be improved by integrating the InSAR deformation field of the lifting rail [26].
Overall, significant and uneven deformation was observed in the tailings pond (Figure 3), with a cumulative subsidence rate ranging from −77.58 mm/a to 31.78 mm/a. There were multiple subsidence centers in the tailings pond, primarily located in the northern part of the right tailings pond and the southern part of the left tailings pond. The subsidence rates in these locations were relatively high, making them prone to geological hazards. As presented in Figure 4, time series subsidence data of the tailings pond exhibited a fluctuating decreasing trend from January 2020 to December 2022. The cumulative subsidence dramatically increased from January to September, reaching its maximum around September. Subsequently, there was a slight uplift in October and November, after which subsidence resumed in December and continued until the following September. This indicated a noticeable periodic fluctuating subsidence trend.

Figure 3.
Sentinel-1A line-of-sight deformation results in tailings pond.
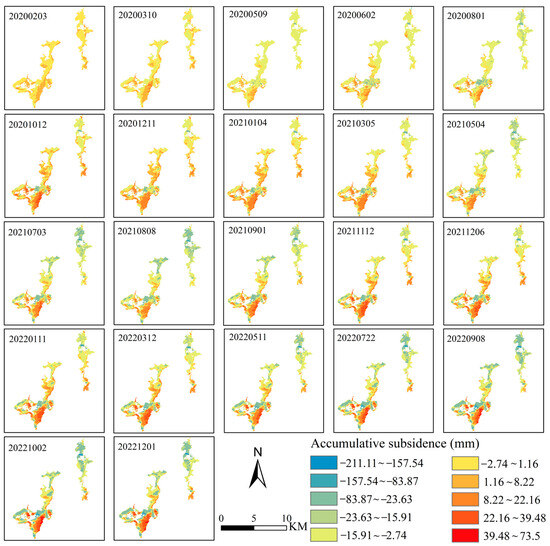
Figure 4.
Sequence of accumulative subsidence in tailings pond from 2020 to 2022.
In the spatial dimension, deformation in the tailings pond remained relatively stable before May 2020, with cumulative subsidence generally ranging between −23.63 and 1.16 mm. After that, the northern part of the right tailings pond showed a subsidence trend, while the southern part experienced uplift, and the central part showed small changes in surface deformation. Except for the southeastern part of the left tailings pond, which exhibited an uplifting trend, other parts showed a subsidence trend. Among them, the western part of the left tailings pond remained relatively stable without significant deformation before May 2021, but afterwards, it also began to show a subsidence trend.
4.2. Analysis of Surface Micro-Relief Deformation Patterns at Typical Subsidence Points in the Tailings Pond Based on the SBAS
To conduct further analysis of the time series of deformation in typical areas of the tailings pond from 2020 to 2022, this study employed 10 typical subsidence points and explored their surface deformation characteristics (Table 3).

Table 3.
Cumulative surface deformation information of the pond and 10 typical settling points in the tailings pond.
As depicted in Figure 5, point 1, located in the northern part of the tailings pond, showed the maximum cumulative subsidence rate of −71.22 mm/a and exhibited a severe periodic fluctuating downward trend. Specifically, there was a continuous subsidence trend from January to September each year, with the maximum subsidence occurring in September. This was followed by a slight uplift from September to November, after which it continued to exhibit a subsidence trend. Points 2 to 6 were located in the central part of the tailings pond, and their cumulative deformation rates fell within the range of −40.95 to −23.38 mm/a, with a moderate subsidence trend. Point 7 was located in the central part of the left tailings pond, and its cumulative deformation rate reached −64.11 mm/a, second only to Point 1. Points 8 to 10 were located in the southwestern part of the tailings pond, exhibiting a moderate level of surface subsidence development. Their cumulative subsidence rates ranged from −38.93 to −28.66 mm/a, with point 8 having the lowest deformation rate.
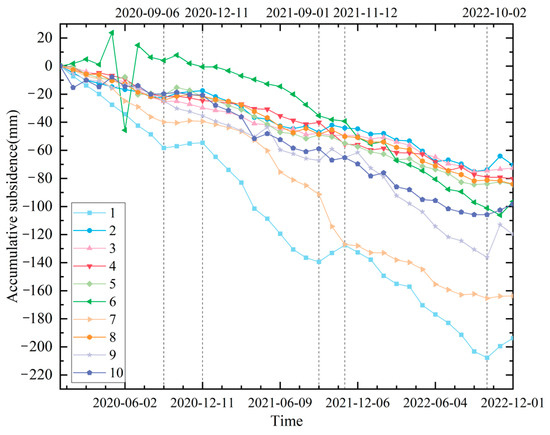
Figure 5.
Time series of displacements of 10 key settlement areas in tailings pond from 2020 to 2022.
4.3. Prediction of Surface Micro-Relief Deformation in the Tailings Pond
This study predicted the surface deformation at each subsidence point of the tailings pond in 2023 using the Holt–Winters exponential smoothing additive model (Figure 6). Overall, the 10 typical subsidence points of the tailings pond kept their sinking trend in 2023. Among them, the cumulative subsidence of typical point 1 remains far greater than that of the other subsidence points, and is expected to reach a maximum of −275.71 mm in September. This value is anticipated to increase slightly to −275.04 mm from September to November. After November, it will resume the sinking trend, with the cumulative subsidence projected to reach −274.17 mm. The cumulative subsidence of points 2, 3, 4, 5 and 8 are close to each other, with a small variation range, basically ranging from −116.75 to −71.23 mm. Furthermore, the surface deformation of points 6, 9, and 10 is also expected to remain relatively stable, but the cumulative subsidence is larger than that of the 5 points mentioned above, approximately −161.48 to −108.67 mm. The cumulative subsidence of point 7 is still in second place and will reach a maximum of −200.81 mm in November.
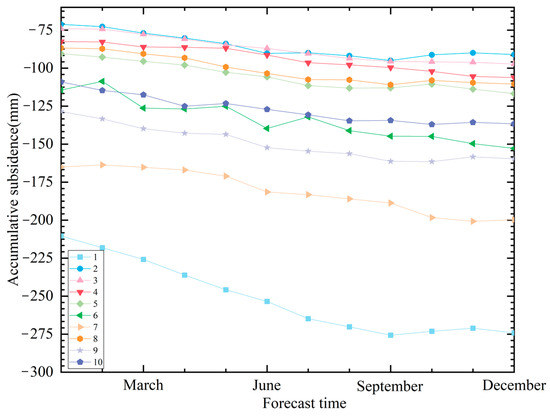
Figure 6.
Prediction map of 2023 surface deformation at each settlement point of tailings pond.
Based on the analysis of the locations of ten typical subsidence points in the tailings pond, it can be concluded that the northern part of the right tailings pond was expected to continue experiencing significant subsidence in 2023, warranting main monitoring in the future. The southern part of the right tailings pond, as well as the northern part and southwestern part of the left tailings pond, will also show a subsidence trend, although at a small change range. Additionally, a notable subsidence center can be observed in the central part of the left tailings pond, and it is also recommended to focus on monitoring to prevent potential disaster risks in mining areas.
The following is the prediction of the time series of surface deformation in 2023 within the study area (Figure 7). Over the next 12 months, the surface subsidence of the tailings pond is forecasted to fall within −274.17 mm to −71.23 mm, continuously showing a cyclical fluctuating downward trend. The maximum surface deformation occurs at typical subsidence point 1 in December 2023, where the surface deformation is relatively severe. The confidence interval reflects the reliability of the mean value of surface deformation prediction. A wider confidence interval indicates greater uncertainty, while a narrower interval signifies higher precision in the model’s estimate. It can be seen that the confidence intervals for deformation prediction of typical settlement points 6, 7, 9, and 10 of the tailings pond are relatively large, indicating great uncertainty in the prediction results.
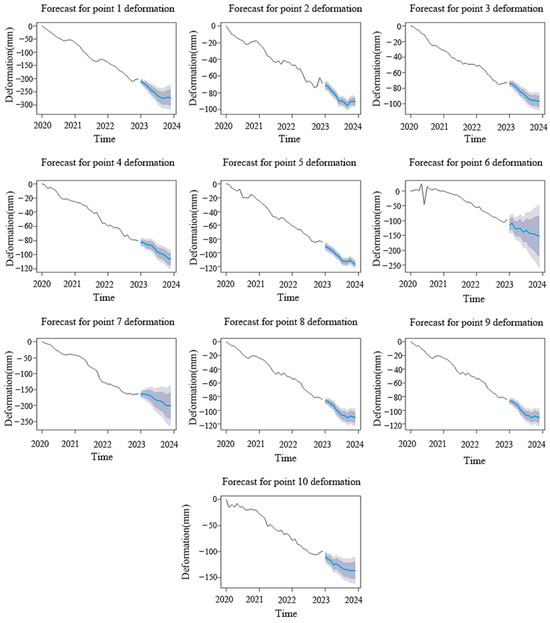
Figure 7.
Time series prediction results and confidence interval graphs of surface deformation of tailings pond in 2023.
5. Discussions and Conclusions
5.1. Discussion
Based on a total of 143 Sentinel-1A images from January 2020 to December 2022, this study utilized SBAS-InSAR technology to monitor surface deformation of the tailings pond and explored the patterns of surface deformation in southeast Tibet. Overall, the surface of the tailings pond experienced significant and uneven deformation, with a cumulative subsidence rate ranging from −77.58 mm/a to 31.78 mm/a, which is similar to the study of Wang in Linzhi, Tibet [10]. Thus, this methodology for monitoring surface deformation can be implicated in southwest Tibet. Multiple subsidence centers were observed in the study area and they are mainly located in the northern part of the right tailings pond and the southern part of the left tailings pond. These areas were influenced by both human activities and environment changes. Although the environment can cause surface uplift due to the plate compression, plenty of mining activities caused more subsidence. Thus, the effects of human activities were more than those of environment changes. What is more, these regions have a high risk of geological hazards.
By using the Holt–Winters exponential smoothing model, the cumulative subsidence for the next 12 months was predicted. The northern part of the right tailings pond was expected to continue exhibiting a significant subsidence trend in 2023 and will require focused monitoring in the future. Although the southern part of the right tailings pond, as well as the northern and southwestern parts of the left tailings pond, will also continue to show a subsidence trend, the change is not as obvious as that in the northern part of the right tailings pond. Additionally, a notable settlement center has emerged in the central area of the left side, which also warrants focused monitoring to prevent the risk of mining area disasters.
This study extracted the surface deformation information of tailings ponds and analyzed and predicted the spatial–temporal evolution of surface deformation. However, due to the large volume of data, there are still many shortcomings in this study. First of all, due to the large amount of data, this study only analyzed the spatio-temporal evolution of the surface deformation rate and cumulative settlement of the tailings pond during 2020–2022 based on SBAS-InSAR technology and did not explore the surface deformation of the entire southeast Tibet region. In future studies, the research area should be further expanded. The influence of major human activity areas on land surface settlement in southeast Tibet was analyzed. Secondly, due to the small volume of time series data, the prediction results of the time series prediction model can be further improved, and more deformation data of time series can be obtained in future research.
5.2. Conclusions
This study used SBAS-InSAR technology to monitor the surface deformation of the tailings pond and explored the patterns of surface deformation in southeast Tibet. Additionally, prediction models for surface deformation in the southeastern Tibet region were constructed using the Holt–Winters algorithm to forecast and analyze the surface deformation of typical subsidence points in the tailings pond. Overall, the surface of the tailings pond experienced significant and uneven deformation, with a cumulative subsidence rate ranging from −77.58 mm/a to 31.78 mm/a. Multiple subsidence centers were observed in the study area and they are mainly located in the northern part of the right tailings pond and the southern part of the left tailings pond. These areas have a high risk of geological hazards. The northern part of the right tailings pond is expected to continue exhibiting a significant subsidence trend in 2023 and will require focused monitoring in the future. Although the southern part of the right tailings pond, as well as the northern and southwestern parts of the left tailings pond, will also continue to show a subsidence trend, the change is not as obvious as that in the northern part of the right tailings pond. Additionally, a notable settlement center has emerged in the central area of the left side, which also warrants focused monitoring to prevent the risk of mining area disasters. Especially for the safety and stability of tailings pond, the seepage monitoring should be strengthened, and vegetation reclamation should be carried out to prevent soil erosion and reduce geological disasters such as landslides.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.C. and G.; methodology, Z.H.; software, Z.H.; validation, G., Z.H. and L.C.; formal analysis, G.; investigation, Z.H.; resources, G.; data curation, Z.H.; writing—original draft preparation, G.; writing—review and editing, L.C.; visualization, Z.J.; supervision, L.C.; project administration, Q.J.; funding acquisition, Q.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42371291 and No. 41901234), the National Key R&D Program of China (2023YFF1304204), and the Geological Survey Project of China Geological Survey “Remote Sensing Monitoring and Evaluation of Human Activities in National Nature Reserves” (No. DD20230488).
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the authors. Restrictions apply to the availability of these data, which were used under license for this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Cigna, F.; Tapete, D. Present-day land subsidence rates, surface faulting hazard and risk in Mexico City with 2014–2020 Sentinel-1 IW InSAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 253, 112161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Gong, X.; Zhang, G.; Chen, Z. Wide-Area Subsidence Monitoring and Analysis Using Time-Series InSAR Technology: A Case Study of the Turpan Basin. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, E.; Dinar, A.; Calvo, E.; Albiac, J.; Calatrava, J.; Herrera, G.; Teatini, P.; Tomás, R.; Ezquerro, P.; Li, Y. Modeling the Optimal Management of Land Subsidence Due to Aquifers Overexploitation. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 349, 119333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rott, H. Advances in interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) in earth system science. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2009, 33, 769–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lian, X.; Ge, L.; Liu, X.; Du, Z.; Yang, W.; Wu, Y.; Hu, H.; Cai, Y. Surface Subsidence Monitoring Induced by Underground Coal Mining by Combining DInSAR and UAV Photogrammetry. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royden, L.H.; Burchfiel, B.C.; King, R.W.; Wang, E.; Chen, Z.; Shen, F.; Liu, Y. Surface Deformation and Lower Crustal Flow in Eastern Tibet. Science 1997, 276, 788–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Ding, L.; Guo, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wei, L.; Zheng, Y.; Cui, X.; Wang, J. Spatiotemporal evolution of surface deformation based on MT-InSAR and mechanism analysis along Zhengzhou Metro, China. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2025, 156, 106182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A.; Bekaert, D.; Spaans, K.; Arıkan, M. Recent advances in SAR interferometry time series analysis for measuring crustal deformation. Tectonophysics 2012, 514–517, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, C.; Yin, Y.; Tomás, R.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, Y.; Wang, M.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.M. Refined InSAR method for mapping and classification of active landslides in a high mountain region: Deqin County, southern Tibet Plateau, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 304, 114030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yu, Q.; Ma, J.; Yang, L.; Liu, W.; Li, J. Study and Prediction of Surface Deformation Characteristics of Different Vegetation Types in the Permafrost Zone of Linzhi, Tibet. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, T.; Tang, X.; Zhang, X.; Fan, H.; Wang, Y. Research on the Applicability of DInSAR, Stacking-InSAR and SBAS-InSAR for Mining Region Subsidence Detection in the Datong Coalfield. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebker, H.A.; Rosen, P.A.; Goldstein, R.M.; Gabriel, A.; Werner, C.L. On the derivation of coseismic displacement fields using differential radar interferometry: The Landers earthquake. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 99, 19617–19634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Li, Z.; Hu, J. InSAR deformation monitoring methods and research progress. J. Surv. Mapp. 2017, 46, 1717–1733. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, H.; Ding, Y.; Hu, J.; Geng, S.; Guan, P.; Xu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, M. Monitoring Analysis of Urban Subsidence in Northern Henan Province Based on TS-InSAR Technology. J. Sens. 2024, 2024, 1190407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Xie, C.; He, Y.; Zhu, M.; Huang, W.; Shao, T. Monitoring Potential Geological Hazards with Different InSAR Algorithms: The Case of Western Sichuan. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Tang, J.; Zhong, K.; Ying, L.; Leng, Q.; Ding, S.; Lin, B. Geology of the Jiama porphyry copper–polymetallic system, Lhasa Region, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 74, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, Z.; Ding, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Q. Resolving three-dimensional surface displacements from InSAR measurements: A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2014, 133, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, L.; Wang, C.; Tang, J.; Wang, D.; Qu, W.; Li, C. Re–Os systematics of sulfides (chalcopyrite, bornite, pyrite and pyrrhotite) from the Jiama Cu–Mo deposit of Tibet, China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2014, 79, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, D.L.; Burbey, T.J. Review: Regional land subsidence accompanying groundwater extraction. Hydrogeol. J. 2011, 19, 1459–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodell, M.; Famiglietti, J.S. Detectability of variations in continental water storage from satellite observations of the time dependent gravity field. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 2705–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dijk, A.I.J.M.; Renzullo, L.J.; Wada, Y.; Tregoning, P. A global water cycle reanalysis (2003–2012) merging satellite gravimetry and altimetry observations with a hydrological multi-model ensemble. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 2955–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Long, D.; Scanlon, B.R.; Mann, M.E.; Li, X.; Tian, F.; Sun, Z.; Wang, G. Climate change threatens terrestrial water storage over the Tibetan Plateau. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2022, 12, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, P.; England, P.; Martinod, J. Mantle dynamics, uplift of the Tibetan Plateau, and the Indian Monsoon. Rev. Geophys. 1993, 31, 357–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, D. An integrated approach to hydrologic data assimilation: Interpolation, smoothing, and filtering. Adv. Water Resour. 2002, 25, 1275–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, X.; Li, D.; Yang, S.; Xie, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, W. Landslide Hazard Assessment for Wanzhou Considering the Correlation of Rainfall and Surface Deformation. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Jing, C.; He, X.; He, Y.; Zhang, L. A TDFC-RNNs framework integrated temporal convolutional attention mechanism for InSAR surface deformation prediction: A case study in Beijing Plain. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinform. 2024, 134, 104199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gül, Y.; Hastaoğlu, K.Ö.; Poyraz, F. A new methodology for determining the long-term behavior of earth surface deformations from InSAR results. Adv. Space Res. 2025, 75, 3521–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).