Effects of Riparian Zone Width and Soil Depth: Soil Environmental Factors Drive Changes in Soil Enzyme Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
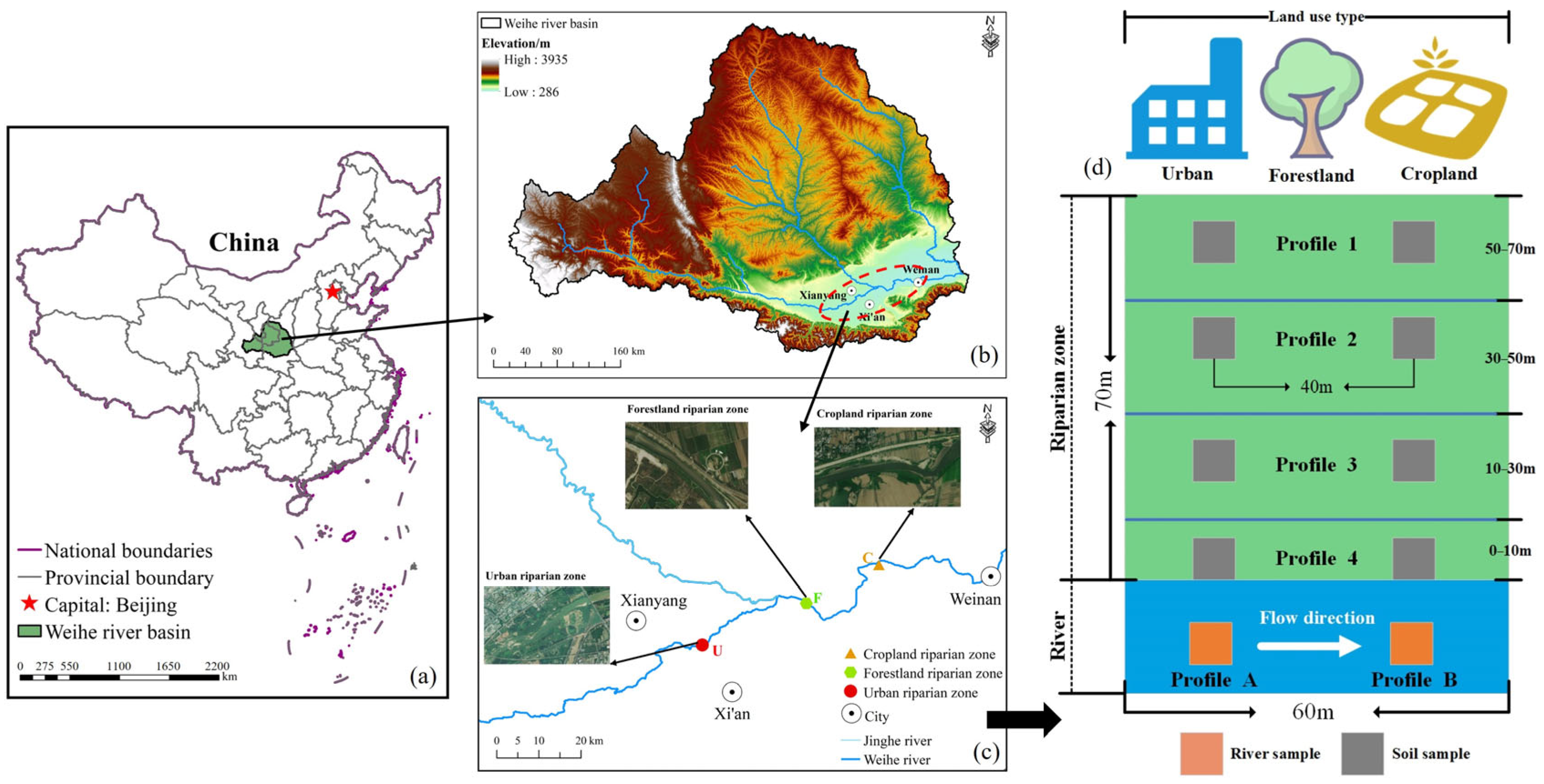
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Laboratory Analysis
2.3.1. Physical and Chemical Properties of River
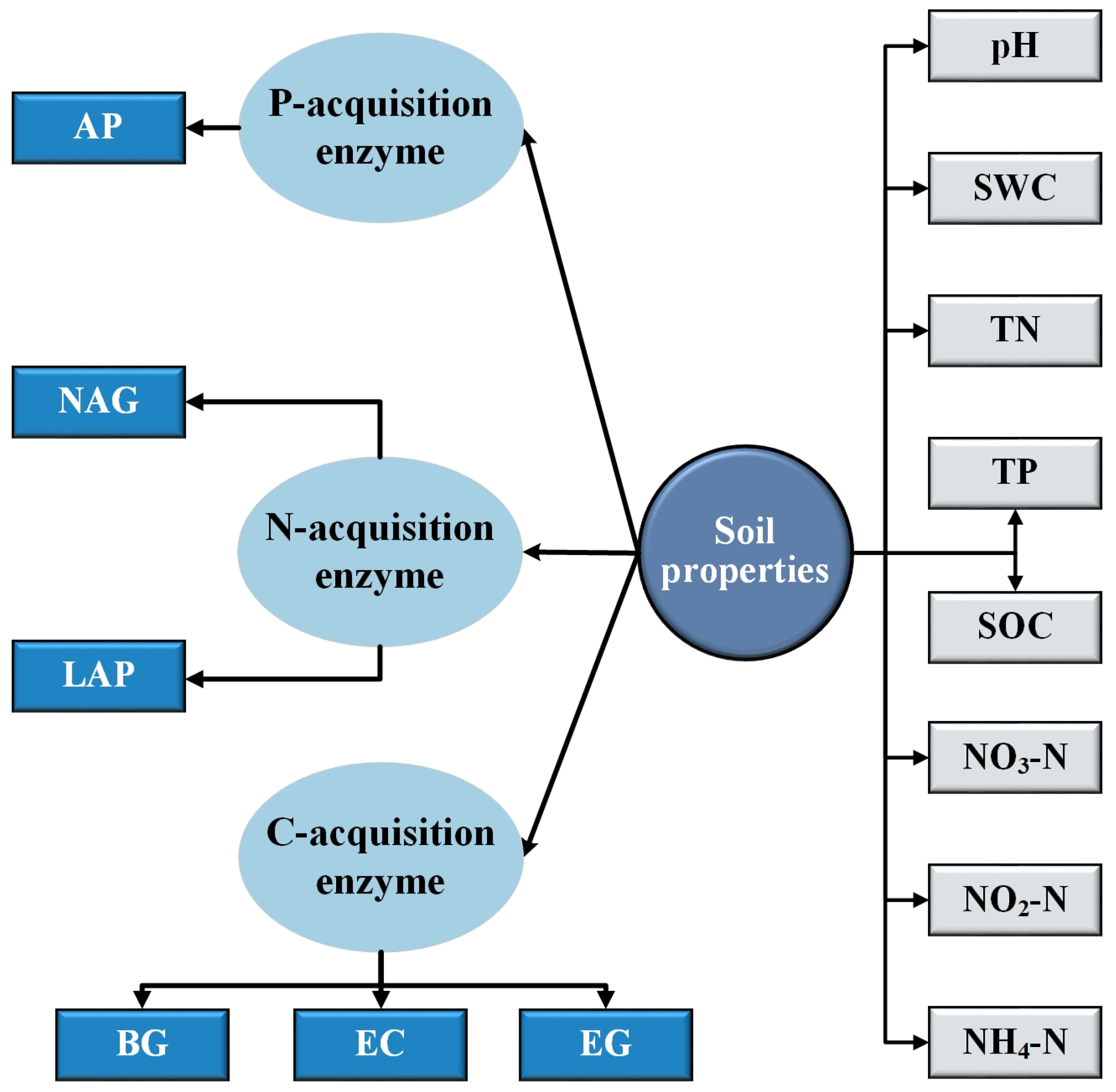
2.3.2. Physical and Chemical Properties of Soil
2.3.3. Soil Enzyme Activity
- F: Corrected fluorescence;
- q: Quenching coefficient;
- e: Fluorescence release coefficient;
- V: Total sediment suspension volume = 125 mL;
- V1: Sample suspension volume per well = 0.2 mL;
- t: Dark incubation time = 4 h;
- m: Dry mass of sediment (equivalent to 1 g fresh sample);
- f, fb: Fluorescence of sample and blank wells;
- fs, fr: Fluorescence of negative control and reference standard wells;
- Cs, V2: Concentration (10 μmol·L−1) and volume (0.00005 L) of reference standard;
2.4. Data Analysis and Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Physical-Chemical Properties of River in Different Riparian Zones
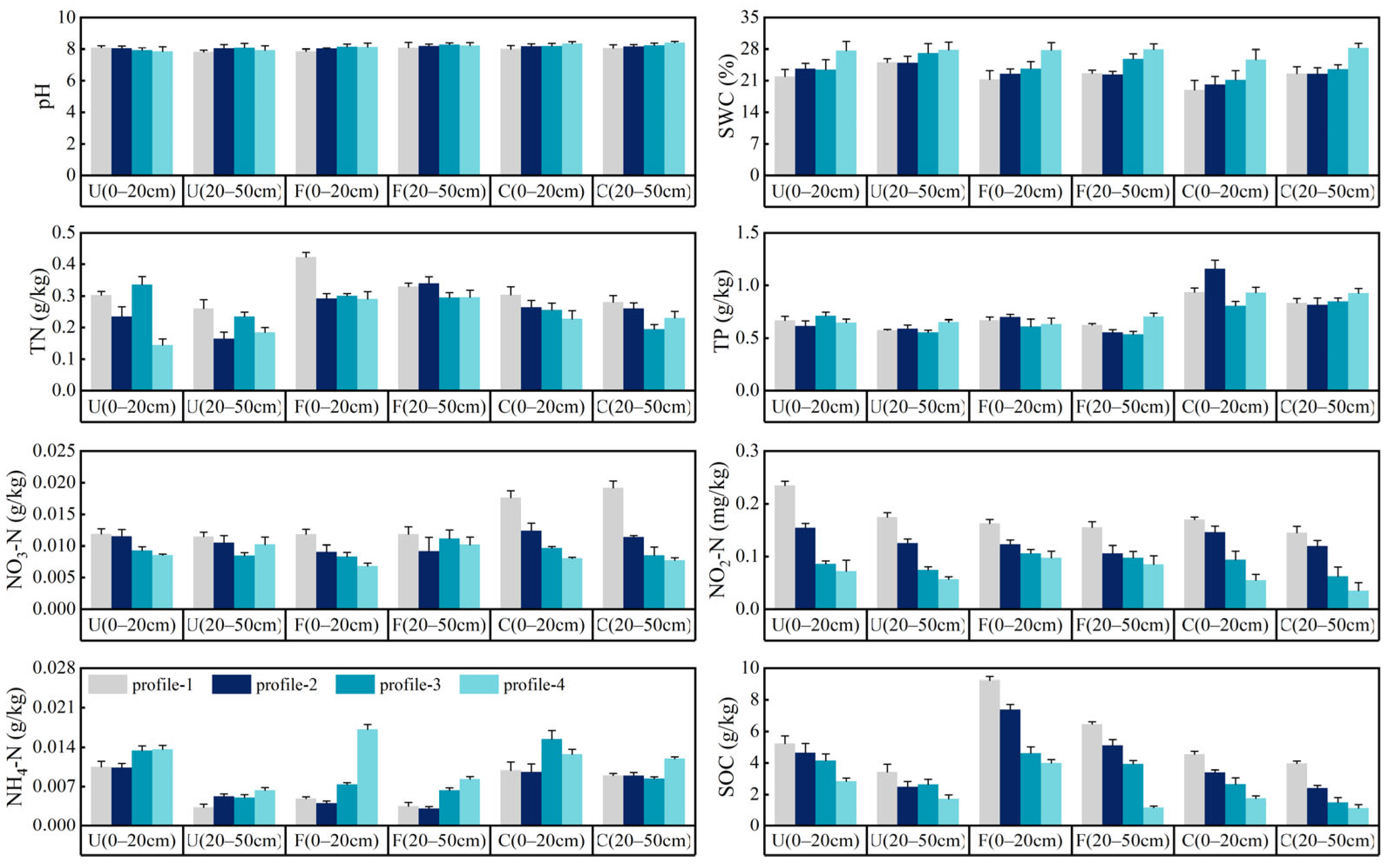
3.2. Physical-Chemical Properties of Soil in Different Riparian Zones
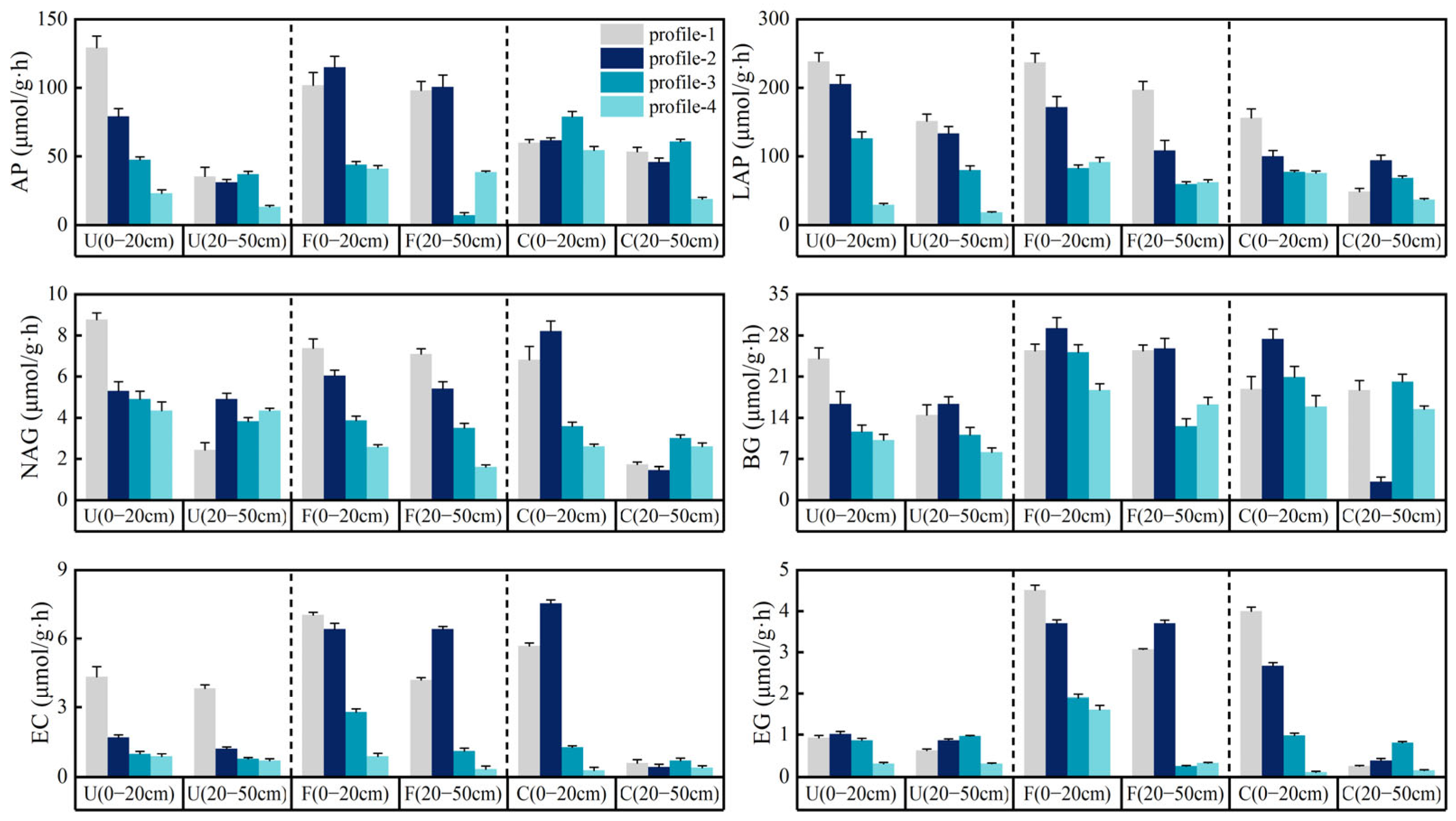
3.3. Soil Enzyme Activities in Different Riparian Zones
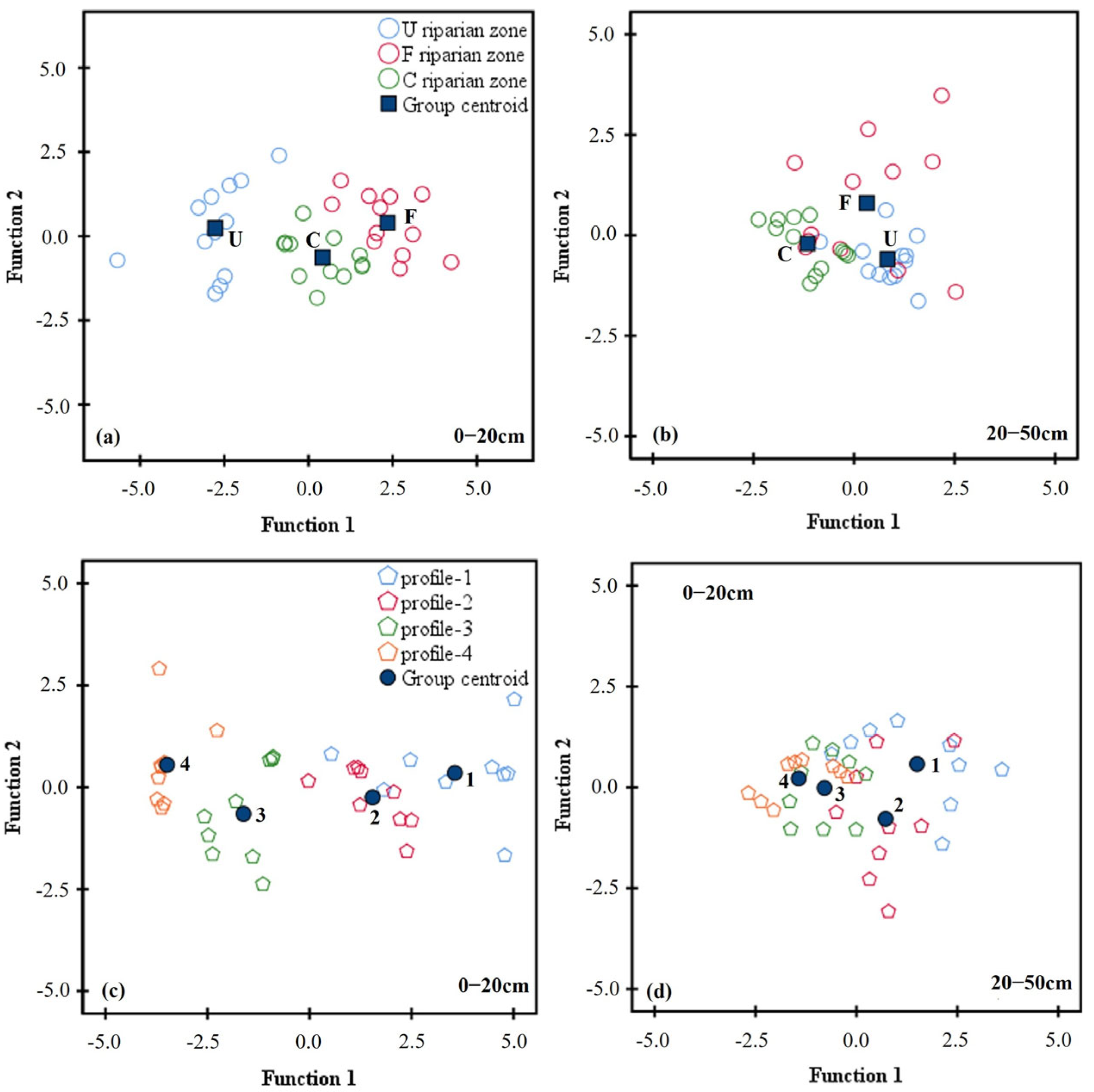
3.4. DFA and PCA Analyses of Soil Enzyme Activities
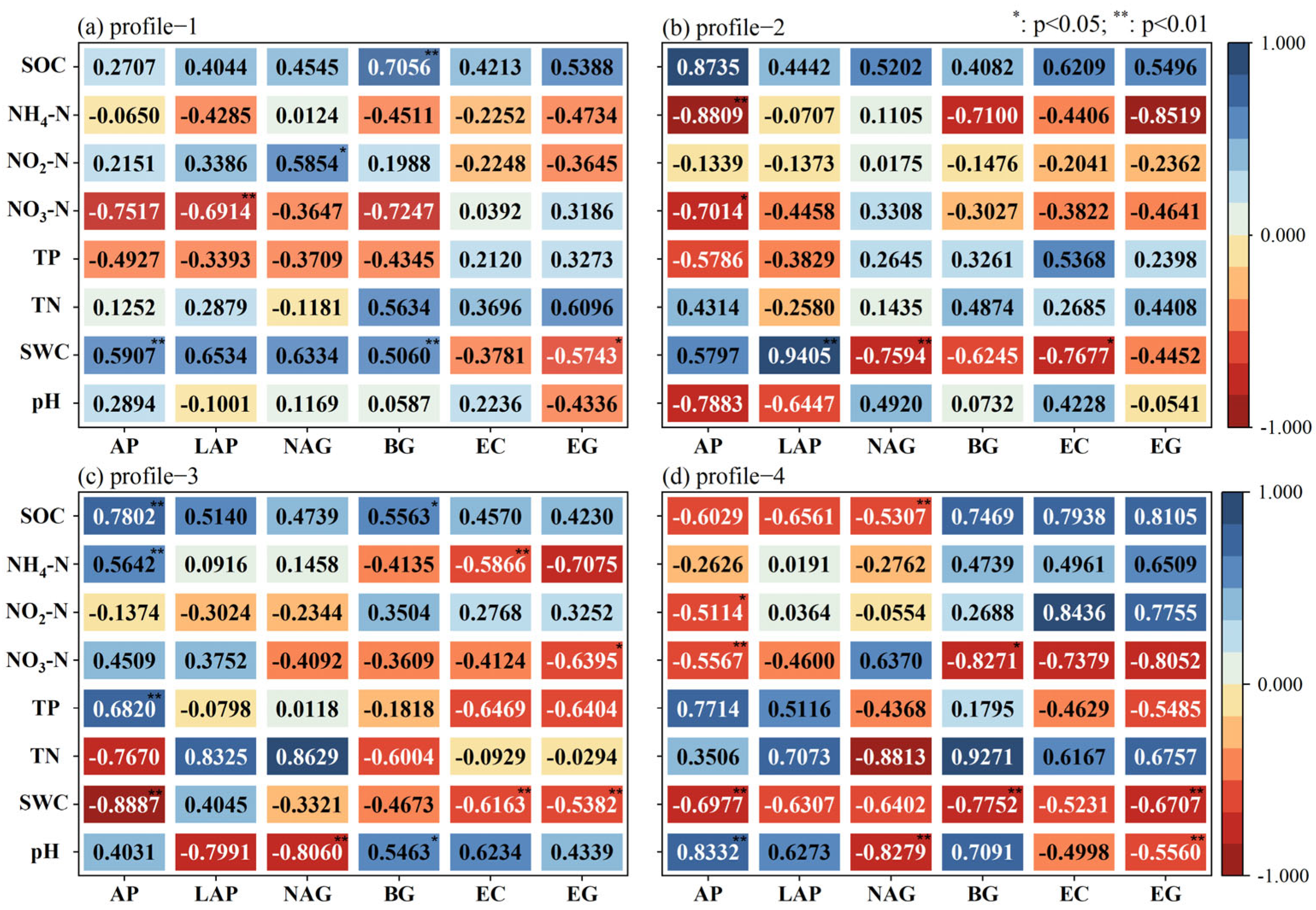
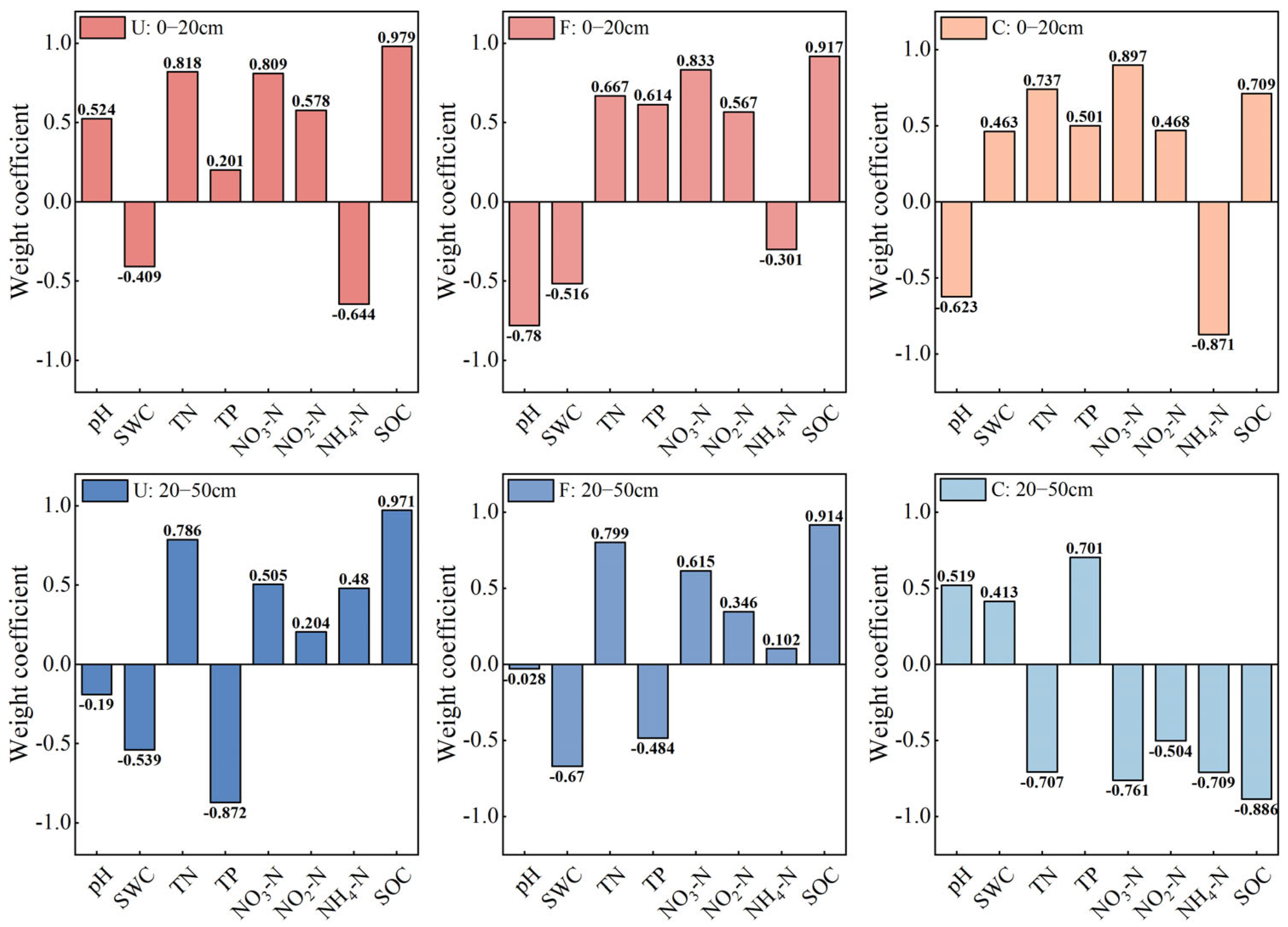
3.5. Analysis of Drivers of Riparian Zone Width Affecting Soil Enzyme Activity
3.6. Analysis of the Effect of Soil Depth on Soil Enzyme Activity in Riparian Zones
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Riparian Zone Width on Soil Enzyme Activities
4.2. Effect of Soil Depth on Soil Enzyme Activity in Riparian Zones
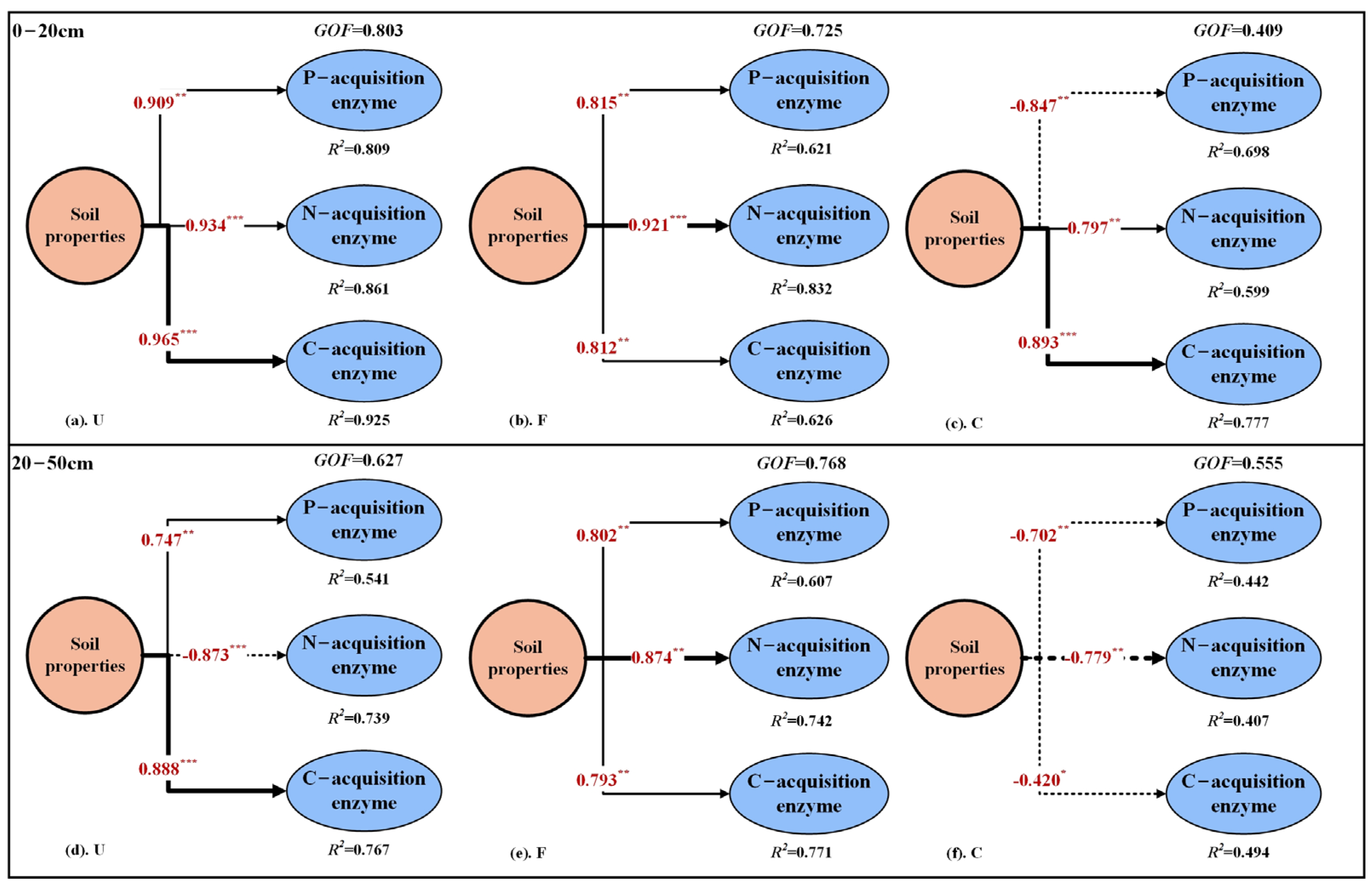
4.3. Mechanisms Driving Changes in Soil Enzyme Activity in Riparian Zones
4.4. Prospect and Follow-Up Studies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ye, M.M.; Hu, H.Z.; Wu, P.L.; Xie, Z.Y.; Hu, Y.C.; Lu, X.X. Ecological responses to hydrological connectivity in grassland riparian zones: Insights from vegetation and ground-dwelling arthropods. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 922, 171196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, T.J.Y.; Sargent, R.; Henry, R.; Fletcher, T.D.; Coleman, R.A.; Mccarthy, D.T.; Lintern, A. Riparian buffers: Disrupting the transport of e coli from rural catchments to streams. Water Res. 2022, 222, 118897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yorlano, M.; Demetrio, P.; Rimoldi, F. Riparian strips as attenuation zones for the toxicity of pesticides in agricultural surface runoff: Relative influence of herbaceous vegetation and terrain slope on toxicity attenuation of 2,4-d. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Hoang, D.T.T.; Luu, A.T.; Mostafa, T.; Razavi, B.S. Environmental memory of microbes regulates the response of soil enzyme kinetics to extreme water events: Drought-rewetting-flooding. Geoderma 2023, 437, 116593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Zhu, Y.; Jia, X.; Shao, M. Multifractal characteristics of particle size distributions (50–200 m) in soils in the vadose zone on the Loess Plateau, China. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 205, 104786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wei, T.; Sha, G.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, Z.; Ren, K.; Yang, C. Soil enzyme activities of typical plant communities after vegetation restoration on the loess plateau, China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 170, 104292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Qu, Q.; Lu, B.; Li, P.; Xue, S.; Liu, G. Response of soil specific enzyme activity to vegetation restoration in the loess hilly region of China. CATENA 2020, 191, 104564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtright, A.J.; Tiemann, L.K. Intercropping increases soil extracellular enzyme activity: A meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 319, 107489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margalef, O.; Sardans, J.; Fernández-Martínez, M.; Molowny-Horas, R.; Janssens, I.A.; Ciais, P.; Goll, D.; Richter, A.; Obersteiner, M.; Asensio, D.; et al. Global patterns of phosphatase activity in natural soils. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Qu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Liu, G.; Xue, S. Responses of soil enzyme activity and soil organic carbon stability over time after cropland abandonment in different vegetation zones of the Loess Plateau of China. CATENA 2021, 196, 104812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Sun, Q.; Yuan, J.; Fu, S.F.; Lan, Y.; Jiang, X.M.; Meng, J.; Han, X.R.; Chen, W.F. Successive corn stover and biochar applications mitigate N2O emissions by altering soil physicochemical properties and N-cycling-related enzyme activities: A five-year field study in Northeast China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 340, 108183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stutter, M.; Costa, F.B.; Ó’hUallacháin, D. The interactions of site-specific factors on riparian buffer effectiveness across multiple pollutants: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 798, 149238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brumberg, H.; Beirne, C.; Broadbent, E.N.; Zambrano, A.M.A.; Zambrano, S.L.A.; Gil, C.A.Q.; Gutierrez, B.L.; Eplee, R.; Whitworth, A. Riparian buffer length is more influential than width on river water quality: A case study in southern Costa Rica. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 286, 112132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.L.; Henry, H.A.L.; Miao, X.Z.; Shi, B.K.; Song, Y.Y.; Liang, Q.; Sun, W. Seasonal variation modifies the spatial patterns of soil microbial community structure and enzyme activity in a meadow steppe. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 182, 104686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.Y.; O’Connor, P.J.; Zhang, J.J.; Ye, X.X. Linking soil nutrient cycling and microbial community with vegetation cover in riparian zone. Geoderma 2021, 384, 114801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.T.; Huang, P.; Zhu, K.; Gao, X.; Chen, Q.; Chen, J.L.; Ran, Y.G.; Chen, S.S.; Ma, M.H.; Wu, S.J. Zonation of bulk and rhizosphere soil bacterial communities and their covariation patterns along the elevation gradient in riparian zones of three Gorges reservoir, China. Environ. Res. 2024, 249, 118383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Chen, X.; Fang, J.Y.; Ji, C.J.; Shen, H.H.; Zheng, C.Y.; Zhu, B. Soil microbial carbon and nutrient constraints are driven more by climate and soil physicochemical properties than by nutrient addition in forest ecosystems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 141, 107667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Długosz, J.; Piotrowska-Długosz, A. Changes in carbon-degrading enzyme activities and microbial biomass content–The effect of soil depth and soil-forming processes. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 180, 104629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinari, S.; Marabottini, R.; Falsone, G.; Vianello, G.; Antisari, L.V.; Agnelli, A.; Massaccesi, L.; Cocco, S.; Cardelli, V.; Serrani, D.; et al. Mineral weathering and lessivage affect microbial community and enzyme activity in mountain soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 167, 104024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, B.J.; Sun, X.H.; Yang, L.M. Hot spots and hot moments of nitrogen removal from hyporheic and riparian zones: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 144168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.Q.; Wang, D.M.; Yang, W.B. Effects of different inundation periods on soil enzyme activity in riparian zones in Lijiang. Catena 2017, 149, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.J.; Mo, Q.; Tang, J.Y.; Liu, W.H.; Batyrbek, M.; Liu, T.N.; Zhang, X.D.; Han, Q.F. Shaping the succession patterns of different soil nutrients, enzyme stoichiometry, and microbial communities through rotation systems. Catena 2024, 236, 107740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.X.; Liu, Y.L.; Yan, Z.X. Effects of land-use change on carbon emission and its driving factors in Shaanxi province from 2000 to 2020. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 68313–68326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.X.; Li, P.; Li, Z.B.; Xu, Y.T.; Zhao, C.X.; Cui, Z.W. Effects of land use and slope on water quality at multi-spatial scales: A case study of the Weihe River Basin. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 57599–57616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, S. Using multiparameter meters to monitor estuarine water quality. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargrizan, S.; Smernik, R.J.; Mosley, L.M. Spectrophotometric measurement of the pH of soil extracts using a multiple indicator dye mixture. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2018, 70, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lin, C.Y.; Han, Z.M.; Fu, C.B.; Huang, D.; Cheng, H.G. Dissolved nitrogen in salt-affected soils reclaimed by planting rice: How is it influenced by soil physicochemical properties? Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 824, 153863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kool, D.; Agam, N. Multi-spectral surface emissivity as an indicator of soil water content and soil water content changes in arid soils. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 305, 114064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Shah, J.J.F. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry and ecological theory. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2012, 43, 313–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waring, B.G.; Weintraub, S.R.; Sinsabaugh, R.L. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry of microbial nutrient acquisition in tropical soils. Biogeochemistry 2014, 117, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Lauber, C.L.; Weintraub, M.N.; Ahmed, B.; Allison, S.D.; Crenshaw, C.; Contosta, A.R.; Cusack, D.; Frey, S.; Gallo, M.E.; et al. Stoichiometry of soil enzyme activity at global scale. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abay, P.; Gong, L.; Luo, Y.; Zhu, H.Q.; Ding, Z.L. Soil extracellular enzyme stoichiometry reveals the nutrient limitations in soil microbial metabolism under different carbon input manipulations. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 913, 169793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.H.; Jin, G.Q.; Tang, H.W.; Xu, J.Z.; Jiang, M.M. Ammonium (NH4+) transport processes in the riverbank under varying hydrologic conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 826, 154097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, F.; Wang, X.; Chan, N.W.; Rahman, H.A.; Yang, S.; Tan, M.L. Assessing the factors influencing water quality using environment water quality index and partial least squares structural equation model in the Ebinur Lake watershed, Xinjiang, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 29033–29048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M.; Sinkovics, N.; Sinkovics, R.R. A perspective on using partial least squares structural equation modelling in data articles. Data Brief 2023, 48, 109074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, M.; Liu, X.P.; Tong, Z.J.; Sudu, B.; Zhang, J.Q.; Wang, R. Analysis of water quality influencing factors under multi-source data fusion based on PLS-SEM model: An example of East-Liao River in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 168126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.X.; Liu, Y.L.; Yan, Z.X.; Zhao, W.B.; Sun, J.Y. Ecological impacts of vermiculite and submerged macrophytes on sediment enzyme activity in lake restoration: Insights from the mesocosm study. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 67, 106222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, C.J.; Li, X.J.; Yu, H.B.; Song, Y.H.; Gao, H.J.; Yuan, P. Insight into the microbial nitrogen cycle in riparian soils in an agricultural region. Environ. Res. 2023, 231, 116100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, K.Y.; Ouyang, W.; Lin, C.Y.; He, M.C.; Liu, X.T. Eco-hydrological processes regulate lake riparian soil organic matter under dryness stress. Water Res. 2024, 260, 121938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacon, N.; Dezzeo, N.; Flores, S. Effect of particle-size distribution, soil organic carbon content and organo-mineral aluminium complexes on acid phosphatases of seasonally flooded forest soils. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2005, 41, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladwig, L.M.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Collins, S.L.; Thomey, M.L. Soil enzyme responses to varying rainfall regimes in Chihuahuan Desert soils. Ecosphere 2015, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa-Hueso, R.; Collins, S.L.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Hamonts, K.; Pockman, W.T.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Smith, M.D.; Knapp, A.K.; Power, S.A. Drought consistently alters the composition of soil fungal and bacterial communities in grasslands from two continents. Glob. Change Biol. 2018, 24, 2818–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogati, K.; Walczak, M. The impact of drought stress on soil microbial community, enzyme activities and plants. Agronomy 2022, 12, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuccarini, P.; Sardans, J.; Asensio, L.; Penuelas, J. Altered activities of extracellular soil enzymes by the interacting global environmental changes. Glob. Change Biol. 2023, 29, 2067–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asensio, D.; Zuccarini, P.; Sardans, J.; Marañón-Jiménez, S.; Mattana, S.; Ogaya, R.; Mu, Z.B.; Llusià, J.; Peñuelas, J. Soil biomass-related enzyme activity indicates minimal functional changes after 16 years of persistent drought treatment in a Mediterranean holm oak forest. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 189, 109281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szejgis, J.; Carrillo, Y.; Jeffries, T.; Dijkstra, F.A.; Chieppa, J.; Horn, S.; Bristol, D.; Maisnam, P.; Eldridge, D.; Nielsen, U.N. Altered rainfall greatly affects enzyme activity but has limited effect on microbial biomass in Australian dryland soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 189, 109277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.N.; Wang, H.W.; Guo, T.D.; Li, Z.L.; Mi, W.B.; Cao, Z. Response of soil C-, N-, and P-acquisition enzymes to moisture pulses in desert grassland to shrubland state transition. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 861, 160569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.R.; Xu, M.Z.; Li, W.T.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.N.; Moorhead, D.L.; Brangarí, A.C.; Liu, J.; Cui, Y.X.; Zeng, Y.; et al. Linking soil depth to aridity effects on soil microbial community composition, diversity and resource limitation. Catena 2023, 232, 107393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska-Długosz, A.; Długosz, J.; Gryta, A.; Frac, M. Responses of N-cycling enzyme activities and functional diversity of soil microorganisms to soil depth, pedogenic processes and cultivated plants. Agronomy 2022, 12, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poffenbarger, H.; Olk, D.C.; Cambardella, C.; Kersey, J.; Liebman, M.; Mallarino, A.P.; Six, J.; Castellano, M.J. Whole-profile soil organic matter content, composition, and stability under cropping systems that differ in belowground inputs. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 291, 106810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska-Długosz, A.; Kobierski, M.; Długosz, J. Enzymatic activity and physico chemical properties of soil profiles of Luvisols. Materials 2021, 14, 6364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumwimba, M.N.; Akter, S.; Li, X.Y.; Dzakpasu, M.; Ifon, B.E.; Manirakiza, B.; Muyembe, D.K.; Zhang, Y.F.; Huang, J.L.; Guadie, A. Nutrient and sediment retention by riparian vegetated buffer strips: Impacts of buffer length, vegetation type, and season. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 369, 109050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokol, N.W.; Slessarev, E.; Marschmann, G.L.; Nicolas, A.; Blazewicz, S.J.; Brodie, E.L.; Firestone, M.K.; Foley, M.M.; Hestrin, R.; Hungate, B.A.; et al. Life and death in the soil microbiome: How ecological processes influence biogeochemistry. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Gong, L.; Luo, Y.; Tang, J.; Ding, Z.; Li, X. Effects of litter and root manipulations on soil bacterial and fungal community structure and function in a Schrenk’s spruce (Picea schrenkiana) forest. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 849483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, L.; Wu, F.; Fan, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhu, J.; Ni, X. Different effects of litter and root inputs on soil enzyme activities in terrestrial ecosystems. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 183, 104764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Qu, Q.; Li, G.; Liu, G.; Geissen, V.; Ritsema, C.J.; Xue, S. Impact of nitrogen addition on plant-soil-enzyme C-N–P stoichiometry and microbial nutrient limitation. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 170, 108714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, G.; Dhaka, A.K.; Singh, B.; Kumar, A.; Choudhary, A.K.; Kumar, A.; Kamboj, N.K.; Hasanain, M.; Singh, S.; Bhupenchandra, I.; et al. Productivity, soil health, and carbon management index of soybean-wheat cropping system under double zero-tillage and natural-farming based organic nutrient management in north-Indian plains. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 917, 170418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.C.; Li, S.Y.; Wang, S.; Bian, Z.X.; Zhou, W.; Wang, C.Q. Effects of farmland landscape pattern on spatial distribution of soil organic carbon in Lower Liaohe Plain of northeastern China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Zeng, Q.; Mei, T.; Zhang, S.; Li, Q.; Wang, M.; Tan, W. Disentangling drivers of soil microbial nutrient limitation in intensive agricultural and natural ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Ju, W.; Chen, H.; Yue, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; et al. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry reveals microbial phosphorus limitation decreases the nitrogen cycling potential of soils in semi-arid agricultural ecosystems. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 197, 104463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.L.; Fan, J.W.; Lu, X. Soil specific enzyme stoichiometry reflects nitrogen limitation of microorganisms under different types of vegetation restoration in the karst areas. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 169, 104253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benitez, M.S.; Ewing, P.M.; Osborne, S.L.; Lehman, R.M. Rhizosphere microbial communities explain positive effects of diverse crop rotations on maize and soybean performance. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 159, 108309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Factor | AP | LAP | NAG | BG | EC | EG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Riparian zone width (Rzw) | 4.14 * | 10.03 *** | 3.73 * | 1.42 | 6.16 * | 2.83 |
| Soil depth (Sd) | 4.99 * | 6.96 ** | 8.37 * | 3.21 * | 4.46 * | 3.21 |
| Interaction (Rzw & Sd) | 0.13 | 0.53 | 1.68 * | 0.39 | 0.72 | 4.39 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, Z.; Li, P.; Feng, C.; Cao, Y.; Lu, K.; Zhao, C.; Li, Z. Effects of Riparian Zone Width and Soil Depth: Soil Environmental Factors Drive Changes in Soil Enzyme Activity. Land 2025, 14, 2056. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14102056
Yan Z, Li P, Feng C, Cao Y, Lu K, Zhao C, Li Z. Effects of Riparian Zone Width and Soil Depth: Soil Environmental Factors Drive Changes in Soil Enzyme Activity. Land. 2025; 14(10):2056. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14102056
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Zixuan, Peng Li, Chaohong Feng, Yongxiang Cao, Kunming Lu, Chenxu Zhao, and Zhanbin Li. 2025. "Effects of Riparian Zone Width and Soil Depth: Soil Environmental Factors Drive Changes in Soil Enzyme Activity" Land 14, no. 10: 2056. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14102056
APA StyleYan, Z., Li, P., Feng, C., Cao, Y., Lu, K., Zhao, C., & Li, Z. (2025). Effects of Riparian Zone Width and Soil Depth: Soil Environmental Factors Drive Changes in Soil Enzyme Activity. Land, 14(10), 2056. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14102056







