Abstract
National parks are key tools for safeguarding ecosystem health, yet their conservation performance remains unclear. Comprehensive evaluations are crucial for guiding targeted and effective conservation strategies. This study employed the Vigor–Service–Resilience (VSR) framework together with causal inference models to assess the role of Huangshan National Park (HNP) in promoting ecosystem health and to examine the heterogeneity of its ecological outcomes from 2010 to 2020. The results indicate that (1) ecosystem health improved significantly across the region, with 69.5% of pixels showing positive change, particularly in ecosystem services and vigor; (2) compared with matched unprotected sites, HNP enhanced EH by 5.7% in 2010, 3.4% in 2015, and 6.5% in 2020, and also generating positive spillover effects within 30 km of its boundaries; (3) conservation impacts differed notably across socio-ecological conditions, with greater benefits observed in areas of lower elevation, gentle slopes, and reduced precipitation. These findings provide robust causal evidence of the protective value of HNP and underscore the importance of targeted and cost-efficient management strategies to optimize conservation outcomes and support sustainable regional development.
1. Introduction
Under the 2030 Agenda, protected areas are regarded as essential for achieving multiple Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), playing a positive role in sustaining biodiversity [1] and enhancing ecosystem services [2]. Over the past 40 years, China has experienced a rapid expansion of its protected area network, now covering over 17% of its land and 3.5% of its marine territory—meeting the Aichi Target of 17% by 2020 [3,4]. To better protect the core natural landscape and respond to the “eco-civilization” initiative, China launched a series of pilot national parks [5], aiming to protect ecosystem integrity while also supporting community development and human well-being [6]. Yet, simply enlarging these sites does not guarantee effective ecosystem protection [3]. Many protected areas have been labeled as “paper parks” due to inadequate management resources, while others face mounting threats from local development and urbanization pressures [7,8]. These challenges highlight the need for systematic and scientific evaluations to determine whether protected areas are truly achieving their intended conservation goals.
The concept of ecosystem health has been introduced as a central solution to address ecological problems and is now widely recognized and applied around the world [9,10]. A healthy ecosystem reflects its ability to remain stable and provide essential services at specific spatial and temporal scales [10], which is vital for ensuring access to natural resources and for supporting public health, economic stability, and social well-being [11]. Many studies have adopted biological indicators or comprehensive indicator frameworks to assess ecosystem health [12], which are important for ecosystem conservation and monitoring. Previous bio-centric evaluations used species indicators such as microcystins [13], butterflies [14], or birds [15] to represent ecosystem health, while overlooking the impact of widespread human activities, especially in China’s protected areas. Severe human–land conflicts make the traditional “fortress conservation” approach both ecologically inappropriate and practically unfeasible [16]. On the other hand, many studies have developed multi-dimensional frameworks to evaluate ecosystem health. Examples include the hierarchical analysis method [17], the Pressure–State–Response (PSR) framework [18], the Drivers–Pressures–State–Impact–Response–Management (DPSIRM) framework [19], and the Vigor–Organization–Resilience (VOR) framework [20]. However, these approaches often overlook ecosystem services linked to human well-being, as national parks are expected not only to maintain the integrity of natural ecosystems but also to improve local livelihoods and provide opportunities for research, education, and tourism [21]. To address this gap, scholars proposed the vigor–services–resilience (VSR) framework based on the unique and sensitive human–nature relationship in national parks [16,22]. It is gaining recognition as an effective methodology, emphasizing the importance of biodiversity conservation, the role of ecosystem services in improving community well-being, and the resilience needed to maintain stability and ensure sustainability under disturbance [23].
Assessing conservation effectiveness is essential to determine whether protected areas achieve their intended goals. Previous studies have examined this topic from perspectives such as funding inputs or reductions in human and environmental threats [24,25], but these approaches fail to show a clear causal link between ecosystem health and management actions. Since many protected areas are in remote regions with little human disturbance and low social costs, ecosystems there may stay healthy even without formal protection, which can make evaluations misleading [7,26]. To reduce the bias from non-random site selection [27], researchers increasingly recognize the importance of using causal inference models to identify matched unprotected areas as counterfactuals [28]. Moreover, although growing attention has been given to the outcomes of conservation policies, few studies have connected this evidence to spatially explicit protection priorities that can inform region-based planning [29]. Even fewer have explored how spatial differences in conservation outcomes can be used to create suitability maps for guiding such priorities [30]. Examining the heterogeneity of national park effectiveness and applying this knowledge is crucial for setting more efficient future conservation strategies. Such evaluations are also vital for optimizing the quality of China’s national park system and for contributing to global conservation goals such as the United Nations 30×30 target.
To address the identified limitations, this study conducts an empirical analysis of Huangshan National Park (HNP) to examine its conservation effectiveness on ecosystem health. As a World Biosphere Reserve and a UNESCO World Cultural and Natural Heritage Site, the park is a model for sustainable management [31]. By combining rigorous counterfactual analysis with remote sensing data, this study aims to: (1) measure the spatial distribution and temporal changes in ecosystem health in HNP from 2010 to 2020; (2) evaluate the effects of HNP on enhancing ecosystem health using propensity score matching to build comparison groups from nearby unprotected areas; and (3) identify the heterogeneity in conservation outcomes across different social and environmental settings to determine priority areas for protection.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The study area is located in northern Huangshan City, Anhui Province, southeastern China (Figure 1). Its spatial range includes Huangshan Scenic Area, Jiulongfeng Nature Reserve, Wuxishan Nature Reserve, Tianhu Nature Reserve, and the ecological corridors connecting these protected areas, covering a total area of approximately 330.3 km2 [32]. As one of the candidate areas for China’s priority national park construction [33,34], Huangshan is world-famous for its granite geology and spectacular landforms [32]. It also serves as the core zone of the World Biosphere Reserve [31], and is home to 1805 native plant species and 323 wildlife species, including 28 under national protection such as the Chinese merganser and the clouded leopard [35,36].
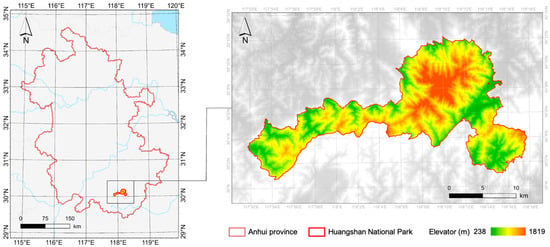
Figure 1.
Geographic location of the study area. This map is based on the standard map of the Map Technical Review Center of the Ministry of Natural Resources (Review No. GS (2020) 4619), without any modifications to the boundaries of the base map.
Historically, Huangshan was relatively underdeveloped until modern tourism began in 1979 [31,37]. Since then, tourism has grown rapidly, and most residents have become involved in the industry [38]. By 2024, the park received 5.57 million visitors and generated 3.45 billion RMB in revenue [39]. Green practices such as “clean supplies go up, waste comes down” and the “closed rotation” management system have helped restore forests while keeping balance with use [40]. These efforts earned Huangshan a place on the IUCN Green List for its achievements in ecosystem management and cultural landscape protection [41].
The existence of protected areas can have a spatial spillover effect or a leakage effect on the unprotected areas around them [7,42], which may compromise the accuracy of co-conservation effectiveness evaluations [43]. Particularly, as critical transition zones between national parks and surrounding urban areas, gateway communities exhibit a symbiotic relationship with parks through transportation hubs, sustainable agriculture, environmental education, and eco-recreation [44,45]. As a result, we generated a series of 10 km concentric buffers within a 50 km zone surrounding the park boundary (Figure 2). This approach enables a clear determination of whether conservation effects exist in HNP, and to what extent spillover or leakage effects occur.
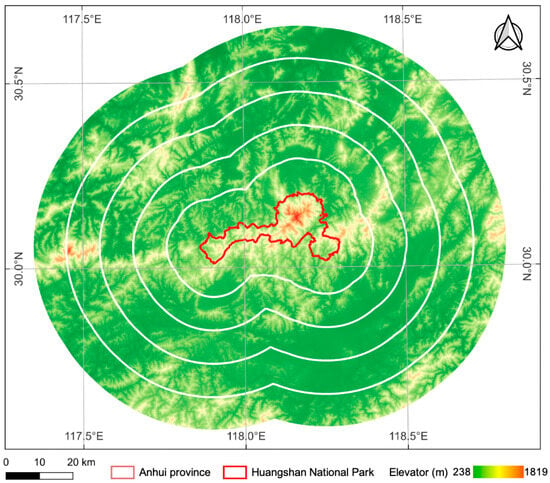
Figure 2.
Buffer zones of the study area.
2.2. Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
Table 1 provides the datasets used in this study. This study incorporated several types of data to quantify the ecosystem health of HNP and its surrounding zones, and applied causal inference models for counterfactual analysis. Specifically, land use, vegetation, and yearbook data were used to calculate ecosystem health, while meteorological, topographic, and transportation data supported the counterfactual evaluation. To ensure consistency across sources, all raster data were reprojected to the WGS 1984 coordinate system. A 30 × 30 m fishnet was generated using the Fishnet tool in ArcGIS 10.8 for data resampling and spatial joining.

Table 1.
Data sources.
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Ecosystem Health Assessment
Ecosystem health was evaluated through three main dimensions: Ecosystem Vigor (EV), Ecosystem Services (ES), and Ecosystem Resilience (ER). Traditional methods of ecosystem health assessment often overlook either the stability and integrity of internal structures or the impacts of human disturbance [10,46]. Considering that national parks should take into account both natural ecosystems protection while also providing essential services [21], this study integrated both biophysical and human factors [23], and adopted the Vigor–Services–Resilience (VSR) framework for assessing ecosystem health and tracking its variations. According to [10], the model is expressed as:
represents ecosystem health, while , , and correspond to ecosystem vigor, services, and resilience. Because the evaluation indicators differ in both units and magnitudes, data from different years are not directly comparable. To resolve this issue, the study applied a global normalization approach, standardizing the indicators across multiple time periods and adjusting all components to a uniform scale of [0, 1].
- (1)
- Ecosystem Vigor (EV)
Ecosystem vigor refers to the productivity of an ecosystem and shows how active and resilient it is [10]. It captures vegetation performance under nutrient supply, water availability, and broader environmental settings. Greater vigor suggests stronger growth and higher stability. In this study, NPP was adopted as the measure of EV because it reliably reflects photosynthetic efficiency and the ability to store carbon [47,48].
- (2)
- Ecosystem Services (ES)
Ecosystem services were assessed using the value transfer method developed by Xie et al. (2017) [49]. This approach is widely applied in studies to estimate the spatial and temporal distribution of ecosystem service values. Under this framework, ecosystems are grouped into six main categories: farmland, forest, grassland, wetland, barren land, and water bodies. Their services are further classified into four types: provisioning, regulating, habitat, and cultural or amenity services. Each ecosystem service was assigned an economic value by multiplying an equivalence coefficient with a standard equivalence factor (RMB/ha) [49]. The coefficient is dimensionless, while the factor provides a monetary reference. The factor is defined as the value of natural grain yield per hectare of farmland, based on the national average production. The standard equivalence factor for food production services can be calculated according to [49] as follows:
denotes the equivalent factor for food production services per unit area (RMB/ha), refers to the main crops in the study area, indicates the average market price of these crops (RMB/kg), while represents their yield per unit area (kg/ha). The value of ecosystem services was then estimated with the following formula [50]:
represents the total ecosystem service value across all ecosystem types. For each ecosystem type , is the land area (ha), and is the value coefficient (RMB/ha·year) for the ecosystem type , which indicates the average service value per hectare per year.
- (3)
- Ecosystem Resilience (ER)
Ecosystem resilience refers to the capacity of an ecosystem to endure external disturbances. It also reflects its ability to reduce damage through self-regulation and to keep both structure and function stable [10]. The idea of resilience covers two aspects: resistance to stress and the ability to recover afterward. This study applied the equation according to previous research for resilience evaluation [10,51]:
represents ecosystem resilience, is the area of land type , and is the total number of land types, indicates the resistance coefficient of land type , stands for its resilience coefficient. The weights of resistance and resilience depend on whether external pressures exceed the ecosystem’s self-regulation capacity [52]. Resistance should be emphasized when external disturbances are weaker than the ecosystem’s self-adjustment ability, while resilience becomes more important when pressures are stronger [53]. Unlike urban areas that experience more intensive human activities, Huangshan National Park (HNP) has largely preserved its natural state. Therefore, we assigned a higher weight of 0.6 () to the resistance coefficient (), while the resilience coefficient () was given a lower weight of 0.4 () according to previous studies [54,55].
In addition, diverse land use types show different resistance and resilience coefficients. In this study, the values for Huangshan National Park and the surrounding areas were taken from the literature [51] (Table 2).

Table 2.
The ecosystem resilience coefficient of each landscape type.
2.3.2. Propensity Score Matching for Conservation Effectiveness Assessment
Propensity score matching (PSM) is a widely accepted approach for evaluating the conservation outcomes of protected areas [56]. This approach establishes a robust counterfactual framework to address concerns that observed improvements in ecosystem health may simply result from the protected areas’ location in less disturbed landscapes, rather than from the actual effects of conservation policies. In this study, we applied PSM to identify comparable unprotected pixels that exhibit similar environmental features to protected pixels within the national park (treatment group). Drawing on previous studies [10,57], we controlled for key confounding variables, including altitude, slope, precipitation, population density, and distance to roads. We created a 30 × 30 m fishnet to extract pixel values and confined control pixels to a 50 km buffer around the park boundaries to ensure spatial comparability.
In selecting the matching method, we first tested several matching approaches, including one-to-one nearest neighbor, optimal, full, and subclassification matching. Balance was then tested using standardized mean differences (SMDs) of individual covariates. After adjustment, SMDs for most variables were below 0.25 (Table A1), confirming that these methods effectively reduced imbalance [57]. Based on these results, we finally selected 1:2 nearest-neighbor matching without replacement and set a caliper width of 0.2 in this study, which achieved relatively low SMDs while retaining as many samples as possible, and thus demonstrated the most robust performance [30]. Estimation was conducted using the MatchIt package (version 4.7.2) in R (version 4.5.0), with propensity scores generated through a logistic regression model. We also divided the buffer zone into five 10 km bands extending from the park boundary to further assess variations in conservation effects (Table A2).
We defined the causal effects of conservation based on the “potential outcomes model” [58]. In this article, we evaluated the average treatment effect on the treated group (ATT) to reflect the conservation effectiveness with the following equations [57]:
represents the conditional average treatment effect, represents the dummy variable, represents the treated group (inside the national park), and represents the confounding variables.
2.3.3. Stratification-Multilevel Method for Heterogeneity Analysis
Individuals differ in their background and in how they react to interventions. Treatment results can also change depending on the chance of receiving treatment [59]. Recent research in conservation planning increasingly highlights the importance of considering economic constraints and prioritizing ecological objectives within a limited financial budget [60]. Investigating treatment effect heterogeneity offers critical insights into how conservation resources can be optimally allocated across protected areas, especially in diverse ecological and socio-economic contexts. This study employed a stratified multilevel approach to assess heterogeneity in treatment effects. The process involved three steps: (1) calculate propensity scores for all units using logistic regression on observed covariates (see Section 2.3.2); (2) divide the sample into five balanced strata of propensity scores, ensuring no meaningful differences in covariates or scores between treated and control groups; and (3) estimate treatment effects within each stratum based on its matched scores.
3. Results
3.1. Spatial-Temporal Patterns of Ecosystem Health
According to the results (Figure 3), the most notable growth was found in ES, particularly within the national park and the area directly to its north. By 2020, 59.2% of the study area had attained high levels of ES, and over 66% of the pixels exhibited positive growth, which correlated strongly with the expansion of eco-tourism in HNP and surrounding regions, as well as the implementation of the ‘closed rotation’ management system [16].
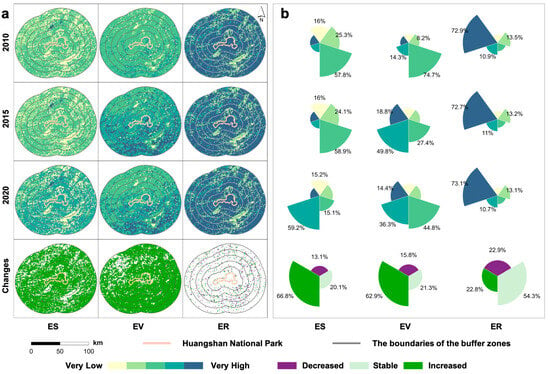
Figure 3.
Distribution characteristics of EV, ES, and ER during the period from 2010 to 2020. The ES, EV, and ER levels were classified into five categories using the natural breaks method. For each grid cell, we calculated the standard deviation. If the value increased by more than one standard deviation, it was marked as a significant improvement. If it decreased by more than one standard deviation, it was marked as a decline. Values that fell between these ranges were considered stable. (a) Spatial distributions and changes in EV, ES, and ER. (b) Proportions of different grades of EV, ES, and ER.
In terms of EV, the median values in 2010, 2015, and 2020 were 0.593, 0.678, and 0.655, respectively, showing an inverted “U-shaped” trend. Since 2013, Huangshan’s Degraded Forest Restoration Project has facilitated the transition of young forests into a rapid growth period, contributing to a 62.9% enhancement in EV. In 2020, EV remained close to the previous level but showed a slight decline. This was mainly due to the unprecedented heavy rainfall in July, which triggered severe flooding in the region and further reduced the total EV [61,62].
The study area exhibited a remarkably stable state (54.3%) of ER, with more than 70% of the pixels remaining at high resilience levels throughout the observation period. The mean ER values remained stable at 0.897, 0.895, and 0.896 during the study period, showing no statistically significant temporal variation. A total of 15.8% of the grid cells exhibited a declining trend, primarily observed in the basin area south of the national park, which could be largely attributed to anthropogenic activities from the urban areas.
From 2010 to 2020, the ecosystem health of HNP and its surrounding areas showed a gradual improvement, with the median increasing from 0.402 in 2010 to 0.439 in 2015 and then to 0.482 in 2020 (Figure 4a). The predominant EH grade shifted from moderate to high, and 69.5% of pixels showed significant enhancement over the decade-long study period. Overall, the spatial distribution of EH demonstrates superior conditions inside the national park compared to surrounding areas, with low-value zones predominantly occurring in urban regions of the northwest and southeast sectors.
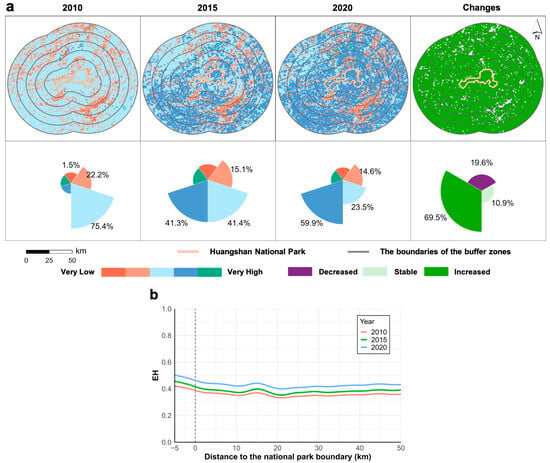
Figure 4.
Distribution characteristics of EH from 2010 to 2020. The EH levels were classified into five categories using the natural breaks method. For each grid cell, we calculated the standard deviation. If the value increased by more than one standard deviation, it was marked as a significant improvement. If it decreased by more than one standard deviation, it was marked as a decline. Values that fell between these ranges were considered stable. (a) Spatial patterns and proportions of different grades of EH; (b) spatial variation in EH along the distance from the national park boundary.
Moreover, we identified a significant negative correlation between EH and the distance to the national park boundary (Figure 4b). From 2010 to 2020, interior park areas furthest from the boundaries maintained the highest EH status. EH decreased sharply from core protected areas to park boundaries, with the trend persisting in the 10 km buffer outside the national park. These findings provide clear evidence that national parks effectively preserve ecosystem health while generating positive spillover effects to surrounding landscapes.
3.2. Effectiveness of the National Park on Promoting EH
There was a mismatch in covariates between the national park and nearby unprotected lands. Compared to surrounding areas, the national park had a lower initial population density, as well as a higher initial elevation, slope, and annual precipitation (Table A3). These factors show that baseline gaps existed in ecosystem health across the treatment and control groups (Table A4). To address this, we applied propensity score matching to choose nearby sites with comparable conditions to the park, which served as control samples. This approach effectively reduced covariate differences between the park and the surrounding areas.
According to the propensity score matching model, the ATT results for EH were significantly positive for three years, indicating that the national park had a positive conservation impact on improving EH (Figure 5). In 2010, 2015, and 2020, the average treatment effects on the treated group were 0.022, 0.014, and 0.029. Therefore, in comparison to the unprotected situation, the overall EH values were promoted by 5.7%, 3.4%, and 6.5%, respectively.
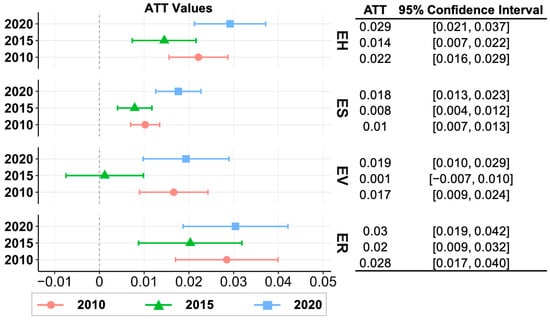
Figure 5.
Effects of the national park on promoting EH. ATT is the “average treatment effect on the treated,” namely, the estimated average effect of the national park on improving EH, ES, EV, and ER in 2010, 2015, and 2020. The error bars for each figure denote 95% confidence intervals of treatment effects. The exact p-values can be found in Table A5.
Specifically, the national park performed best in enhancing ES. From 2010 to 2020, conservation effects promoted ES in the national park by 10%, 7%, and 11.8% through better water restoration, soil conservation, air quality, and cultural or recreational services. Similarly, the national park contributed steadily to ER improvement, with ATT values exceeding those of non-protected areas by over 0.02 in all three years. However, EV is a notable exception. In 2015, the region’s overall EV peaked, with both inside and outside the park showing high vigor, which made the park’s conservation advantage less apparent. Yet, the gap widened again in 2020 (0.018), mainly because flooding reduced EV across the region, with low-altitude areas outside the park suffering the most. In contrast, the ecosystems inside the park were more resilient, which increased the difference between inside and outside, as shown by the higher ATT values.
We also found that the spillover effects of the national park vary with distance. By comparing samples from each 10 km buffer zone with those in the national park (Figure 6), we discovered that most of the ATT values of ES, ER, and EH within 30 km buffer zones showed a gradual upward trend with the increasing distance from the park border. Since ATT reflects the difference between treated and control groups, increasing ATT values indicate that ecological conditions in buffer zones diverge more from the park as distance grows [43], showing the typical characteristics of a positive spillover effect.
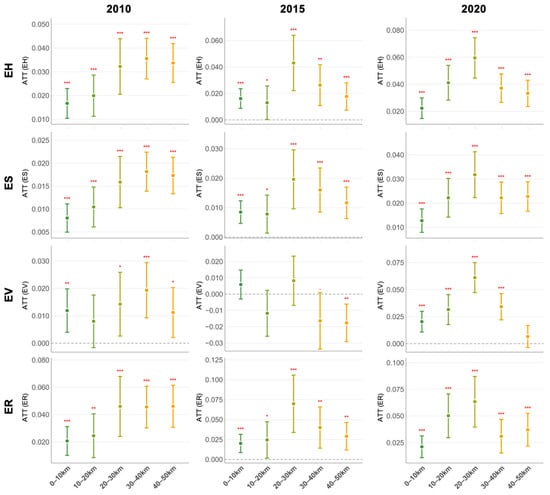
Figure 6.
Variation in conservation effects on buffer zones. 0–10 km, 10–20 km, 20–30 km, 30–40 km, and 40–50 km denote the matched samples within the buffer zones at the corresponding distances. Asterisks represent significance levels: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001. The exact p-values can be found in Table A5. The absence of an asterisk indicates statistical non-significance. Significant positive values indicate that the national park has a higher value of EH, ES, EV, or ER than the matched buffer areas, while negative values indicate the opposite.
To be specific, in terms of ER, the 20–30 km buffer zone maintained a relatively high ATT value (0.046, 0.070, 0.063) over the past decade, while the ATT value of the 0–10 km buffer zone remained stable at 0.020–0.021, always lower than other areas, highlighting that the conservation measures of the national park had provided continuous support for ecosystem resilience in neighboring areas. As for ES, the impact of the national park also showed an obvious distance attenuation pattern within the 0–30 km buffer zone, which means that gateway communities closer to the national park will have better access to natural resources and ecotourism development opportunities. Regarding the EV, both 2010 and 2015 witnessed a slight leakage effect, as areas closer to the park boundary showed higher ATT values. It suggested that protection inside the park limited disturbances but also shifted some human pressures, such as logging or farming [63,64], to areas just outside the boundary. As a result, vegetation vigor near the park edge declined, even though overall EV in the region, especially in 2015, remained high. By 2020, however, the pattern changed. Extreme weather reduced EV outside the park more severely, while ecosystems inside remained more resilient, leading ATT values to follow the broader trend of ecosystem health.
3.3. Heterogeneity in the Conservation Effects of the National Park
Although our results confirm that the national park contributes to enhancing ecosystem health, the extent of these benefits may differ depending on the starting ecological conditions. To examine this variation, we used a stratification–multilevel method to evaluate how the impacts of treatment shift across different propensity score groups and covariate patterns.
For areas with better initial ecosystem health conditions, the ATT estimates suggest that the national park substantially enhances ecosystem health. As shown by the right side of Figure 7a, the ATT values steadily increased as the propensity score rose above 0.6, indicating stronger positive effects in these regions. Areas with low propensity scores (<0.2) also showed relatively high and statistically significant treatment effects. However, as ecological conditions improved, the conservation effect declined. We summarize this pattern as evidence of diminishing marginal returns in conservation effectiveness, meaning degraded areas bring higher gains from extra measures. For regions with a medium level of initial ecological condition (propensity scores between 0.2 and 0.6), the impact of the national park appears to be more complex. As shown in the middle range of Figure 7a, ATT values exhibited a declining trend and became statistically non-significant. This pattern reflected a transitional space where conservation impacts may be mediated by factors such as mixed land use, fragmented habitats, or competing socioeconomic pressures. These results highlighted the importance of considering ecological and social context when evaluating the effectiveness of protected areas across a spectrum of baseline conditions.
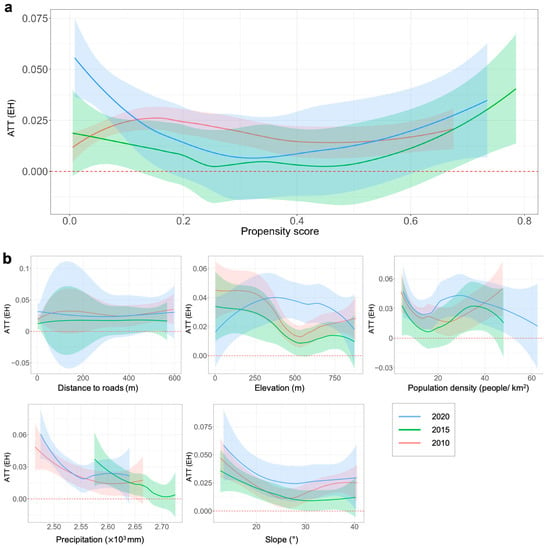
Figure 7.
Stratification-multilevel heterogeneous effects of the national park on promoting ecosystem health. (a) The variation in ATT with propensity score. The x-axis represents the continuous propensity score, indicating the probability of each sample unit being protected by the national park, while the y-axis shows the estimated ATT values. Units with higher propensity scores exhibited superior baseline ecosystem health status. (b) The variation in treatment effects with major covariates. The x-axis presents values of the covariates, and the y-axis displays the estimated ATT values. The color bands represent the 95% confidence interval.
According to the heterogeneity analysis of the covariates (Figure 7b), we discovered that conservation effects on EH were more obvious in areas with lower elevation, less annual precipitation, and smaller slopes. This also reflects the principle of diminishing marginal benefits, as these areas face greater human pressure [57] and therefore have more room for ecological improvement. The correlation between population density and ATT exhibits a nonlinear pattern. In natural areas with low population density, the effectiveness of protecting EH decreases sharply or even becomes ineffective, suggesting that the area should be strictly preserved in its natural state because the environment is extremely sensitive to even the smallest human activity. As population density increased, ATT values rebounded briefly but then showed a downward trend, indicating that there was a “threshold” for management measures, excessive tourism activities and population aggregation in local communities had a negative impact on conservation efforts. The ATT values did not change significantly with the distance from the road, but the confidence interval is wider in the area close to the road, indicating that the estimation of ATT is interfered by complex human factors such as fluctuations in the number of tourists and high uncertainty.
4. Discussion
4.1. Characteristics of Ecosystem Health Changes in HNP and Its Surrounding Areas
Based on the VSR (Vigor–Service–Resilience) framework, this study comprehensively considered the intrinsic health of ecosystems while innovatively incorporating human well-being into the evaluation criteria [23]. The overall ecosystem health in Huangshan National Park and its surrounding areas showed a positive trend between 2010 and 2020. This outcome is consistent with the conclusions reported by Ma et al. (2024) [16]. The past decade has witnessed a significant improvement in ecosystem health in the region, driven by the implementation of ecological compensation policies and the expansion of the leisure and education industries [32,65]. In addition, as a dynamic indicator of ecosystem productivity, ecosystem vigor is particularly sensitive to disruptions [48]. Our results align with previous findings showing that extreme rainfall in the southern Anhui mountainous region reduces photosynthetic activity [62], and the flooding in the summer of 2020 further suppressed productivity [61], underscoring the importance of timely and appropriate forest management.
4.2. The Remarkable Contributions of the HNP on Promoting Ecosystem Health
Causal inference analysis confirms the effectiveness of the national park in enhancing ecosystem health. By using the PSM model, this study overcomes the shortcomings of previous spatiotemporal analyses based on GIS and remote sensing, minimizing errors and baseline bias caused by confounding environmental factors [7,57]. It is worth noting that the national park performed best in enhancing ecosystem services. The results support existing literature that national parks generate economic benefits by enhancing local habitat quality and attracting ecotourism, recreation, and environmental education opportunities [43], thereby creating a positive feedback loop for conservation investments [66].
To better explore the spatial spread of conservation effects in surrounding areas, five 10 km wide buffer zones outside the HNP were generated. The majority of conservation efforts on ES, ER, and the overall EH within 30 km buffer zones showed a gradual downward trend with the increasing distance from the park border. This pattern supports the view of Ament and Cumming (2016) [67] that national parks generate positive spillover effects by encouraging nearby land users to maintain the ecological environment for nature-based ecotourism. However, both 2010 and 2015 witnessed a slight leakage effect in EV, suggesting that resource demands may have shifted to nearby areas and caused deforestation and vegetation loss [63,68]. This speculative interpretation needs to be verified in future studies using more detailed in situ data. It is also important to note that spatial spillover effects are scale-dependent [68]. Previous studies constantly applied a single buffer radius of 10 or 20 km [64,69], ignoring that the extent of spillover possibly varied with sizes and distance from the protected areas [63]. Our findings confirm that the influence of national parks on ecosystem health can reach 30 km or more beyond their borders. This suggests that areas closest to national parks, especially gateway communities, should make use of their stronger ecological resilience and better access to natural resources and ecotourism opportunities to improve local well-being [70,71].
4.3. Heterogeneous Conservation Effects Across Ecological Baselines
Protected areas need to balance protection efficiency, costs, and benefits [72]. Although more studies are now paying attention to the outcomes of conservation policies, few have linked this evidence to spatially explicit protection priorities that could guide region-based conservation planning [30]. In order to develop more equitable and precise zoning management strategies, this study innovatively employed a stratification–multilevel method to analyze the effectiveness of conservation measures across different socio-ecological conditions. This method addresses a key research gap by moving beyond single-dimension ecosystem indicators and helps ensure that limited resources are allocated for the greatest ecological gains [60]. The heterogeneity analysis showed that conservation benefits were most pronounced in areas with lower elevations, gentler slopes, and less precipitation, a pattern consistent with previous research [30,73]. At the same time, some scholars argue that rigorous management measures enhance the performance of protected areas [74], while others present contrary findings [75]. Our results support the conclusions in the literature that areas with better ecological conditions experience stronger conservation effects and should be prioritized for protection [76]. In addition, we also observed a pattern of diminishing marginal returns that regions with poorer ecological baselines often showed greater improvements after protection, but these gains decreased as conditions improved [30]. This can be explained by the weaker capacity of degraded areas to provide ecosystem services and self-regulate, which makes the benefits of protection more evident. To maximize the effectiveness of conservation interventions, management should integrate both area-based and outcome-based approaches [24]. This is especially important in regions where strict protection is difficult to enforce [77]. Overall, these findings offer planners and decision-makers a spatially explicit, results-based approach to account for heterogeneity in conservation effectiveness, which is especially valuable when facing trade-offs or budget constraints [78].
4.4. Managerial Implications
Based on the previously mentioned analysis, the following management suggestions are provided to improve ecosystem health conservation in national parks: (1) Incorporating an ecosystem services approach can strengthen the synergy between biodiversity conservation and ecosystem service provision in planning [21,79]. It is recommended that the management committee strengthen ecological compensation mechanisms while enhancing disaster-prevention and forest-maintenance measures. This should include sustainable logging regulations, reforestation programs, and continuous ecological monitoring. Such an integrated approach can sustain long-term improvements in ecosystem services and resilience while reducing the vulnerability of ecosystem vigor to climate disturbances. (2) Given the heterogeneity of conservation costs and benefits across different landscape types, it is necessary to implement a zoning management strategy. For wilderness areas with better ecological conditions, strict protection should be maintained. At the same time, it is important to recognize the diminishing marginal benefits of protection and give priority to areas with lower elevation, less rainfall, and gentler slopes, where conservation gains are higher. Such targeted interventions not only safeguard ecosystems, but also ensure efficient resource allocation and maximize conservation effectiveness [8]. (3) Recognizing the significant spillover effects of the national park on surrounding buffer zones, future management should prioritize conserving and restoring critical connectivity areas [80]. At the same time, conservation efforts need to be integrated with local economic development in ways that align with both community interests and park objectives [81]. In particular, promoting eco-friendly enterprises such as ecotourism in buffer zones can strengthen ecosystem conservation, support species protection, and improve local livelihoods.
4.5. Limitations and Future Research
It is important to acknowledge certain limitations and uncertainties of this study. Due to data availability, the analysis relied on information from a specific period. Future work should aim to compile more comprehensive datasets, including extended hydrological and meteorological records, detailed land use change data, and long-term, high-resolution remote sensing images. Such data would allow for deeper, multi-scale analyses of ecosystem health dynamics and patterns [10]. In addition, although this study used counterfactual analysis to identify both positive spillover and slight leakage effects in areas surrounding the national park, future research should qualify the heterogeneity of these effects across regions and explore the natural and social factors driving them. This would provide more nuanced insights for the sustainable use of areas adjacent to national parks, especially for the gateway communities. Despite these limitations, the study offers a useful framework for evaluating ecosystem health and developing cost-effective spatial conservation strategies. Future research could apply this framework to other national parks in China for comparison and validation, or conduct scenario simulations to explore how ecosystem health might change under different management or land use interventions, thereby maximizing the benefits of conservation measures [79,82].
5. Conclusions
This study examined the conservation effectiveness of Huangshan National Park (HNP) in promoting ecosystem health between 2010 and 2020 by integrating the Vigor–Service–Resilience (VSR) framework with causal inference models. Results showed that ecosystem health improved significantly across the park and its surrounding areas, with 69.5% of the study area experiencing positive changes. Compared with matched unprotected sites, HNP enhanced overall ecosystem health by 5.7%, 3.4%, and 6.5% in 2010, 2015, and 2020, respectively. Positive spillover effects were detected up to 30 km beyond park boundaries, underscoring the broader regional benefits of conservation. Heterogeneity analysis revealed that conservation outcomes were not uniform. Areas with lower elevation, gentler slopes, and less precipitation benefited most, while diminishing marginal returns were observed as ecological conditions improved. These findings highlight the need for precision-oriented conservation strategies that balance strict protection in ecologically intact areas with outcome-based interventions where ecological gains are greatest. This study advances previous work by applying a robust counterfactual framework to establish clear causal links between national park policies and ecosystem health outcomes, offering valuable insights for achieving the 30 × 30 conservation target. In future work, greater attention should be given to long-term data monitoring, zoning strategies, and gateway community management to maximize the effectiveness of conservation interventions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.W. and J.Z.; methodology, T.W. and X.M.; software, T.W.; validation, Z.Q. and Y.D.; formal analysis, T.W., Z.Q. and Y.D.; investigation, J.Z.; resources, X.M.; data curation, X.M.; writing—original draft preparation, T.W., Z.Q. and Y.D.; writing—review and editing, J.Z. and X.M.; visualization, T.W.; supervision, J.Z.; project administration, J.Z.; funding acquisition, J.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Social Science Foundation of China, grant number 42271251.
Data Availability Statement
Dataset is available upon request from the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| HNP | Huangshan National Park |
| EH | Ecosystem health |
| ES | Ecosystem service |
| EV | Ecosystem vigor |
| ER | Ecosystem resilience |
| NPP | Net Primary Productivity |
| PSM | Propensity score matching |
| ATT | Average treatment effect on the treated group |
Appendix A

Table A1.
Standardized mean differences (SMDs) of covariates before and after alternative matching approaches.
Table A1.
Standardized mean differences (SMDs) of covariates before and after alternative matching approaches.
| a. 2010 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1:1 Nearest Matching | 1:2 Nearest Matching | Optimal Matching | Full Matching | Subclassification Matching | ||||||
| Covariate | Before | After | Before | After | Before | After | Before | After | Before | After |
| Distance to road (m) | −0.8182 | −0.1277 | −0.8192 | −0.0706 | −0.8182 | −0.1244 | −0.8182 | −0.0818 | −0.8182 | −0.2399 |
| Population density (people/km2) | −0.3273 | −0.0814 | −0.3286 | 0.1197 | −0.3273 | 0.0445 | −0.3273 | 0.0778 | −0.3273 | 0.034 |
| Elevation (m) | 1.5725 | 0.1623 | 1.575 | −0.0233 | 1.5725 | 0.1465 | 1.5725 | −0.007 | 1.5725 | 0.1448 |
| Slope (°) | 0.8536 | 0.076 | 0.8564 | 0.0364 | 0.8536 | 0.0809 | 0.8536 | 0.0894 | 0.8536 | 0.2056 |
| Precipitation (mm) | 1.7338 | 0.0913 | 1.7341 | −0.0007 | 1.7338 | 0.1693 | 1.7338 | 0.012 | 1.7338 | 0.1603 |
| b. 2015 | ||||||||||
| 1:1 Nearest Matching | 1:2 Nearest Matching | Optimal Matching | Full Matching | Subclassification Matching | ||||||
| Covariate | Before | After | Before | After | Before | After | Before | After | Before | After |
| Distance to road (m) | −0.8182 | −0.1077 | −0.8192 | −0.0766 | −0.8182 | −0.0513 | −0.8182 | 0.0169 | −0.8182 | −0.1899 |
| Population density (people/km2) | −0.3568 | −0.0299 | −0.3581 | 0.0999 | −0.3568 | −0.0331 | −0.3568 | 0.0519 | −0.3568 | 0.03 |
| Elevation (m) | 1.5725 | 0.2525 | 1.575 | −0.0089 | 1.5725 | 0.2583 | 1.5725 | 0.0635 | 1.5725 | 0.166 |
| Slope (°) | 0.8536 | 0.0243 | 0.8564 | 0.0043 | 0.8536 | 0.0367 | 0.8536 | 0.075 | 0.8536 | 0.1972 |
| Precipitation (mm) | 1.9335 | 0.2925 | 1.9363 | −0.0125 | 1.9335 | 0.3171 | 1.9335 | 0.0624 | 1.9335 | 0.2203 |
| c. 2020 | ||||||||||
| 1:1 Nearest Matching | 1:2 Nearest Matching | Optimal Matching | Full Matching | Subclassification Matching | ||||||
| Covariate | Before | After | Before | After | Before | After | Before | After | Before | After |
| Distance to road (m) | 0.2891 | −0.1289 | 0.2902 | −0.0849 | 0.2891 | −0.1367 | 0.2891 | −0.2731 | 0.2891 | −0.1395 |
| Population density (people/km2) | −0.3486 | 0.0862 | −0.3499 | 0.083 | −0.3486 | 0.1304 | −0.3486 | 0.0761 | −0.3486 | 0.0313 |
| Elevation (m) | 1.6004 | 0.0846 | 1.6029 | −0.0117 | 1.6004 | 0.1058 | 1.6004 | −0.0645 | 1.6004 | 0.1503 |
| Slope (°) | 0.9046 | −0.0244 | 0.9075 | 0.0375 | 0.9046 | −0.0379 | 0.9046 | −0.0204 | 0.9046 | 0.0849 |
| Precipitation (mm) | 2.0914 | 0.1039 | 2.0942 | −0.0038 | 2.0914 | 0.104 | 2.0914 | −0.031 | 2.0914 | 0.2519 |

Table A2.
Standard mean difference (SMD) of covariates before and after 1:2 nearest-neighbor matching.
Table A2.
Standard mean difference (SMD) of covariates before and after 1:2 nearest-neighbor matching.
| a. 2010 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Sample | 0–10 km | 10–20 km | 20–30 km | 30–40 km | 40–50 km | |||||||
| Covariate | Before | After | Before | After | Before | After | Before | After | Before | After | Before | After |
| Distance to road (m) | −0.8192 | −0.0706 | −0.2759 | −0.0357 | −0.9789 | −0.3123 | −0.632 | −0.5859 | −0.6758 | −0.4166 | −1.1445 | −0.271 |
| Population density (people/km2) | −0.3286 | 0.1197 | −0.1706 | 0.147 | −0.3839 | 0.184 | 0.261 | 0.11 | −0.9123 | 0.1974 | −0.2728 | 0.1023 |
| Elevation (m) | 1.575 | −0.0233 | 1.2523 | 0.0541 | 1.5938 | −0.0257 | 1.7322 | −0.1192 | 1.6958 | −0.1004 | 1.4876 | −0.064 |
| Slope (°) | 0.8564 | 0.0364 | 0.703 | 0.0069 | 0.9053 | 0.1549 | 1.1079 | −0.0835 | 0.9671 | −0.0308 | 0.6415 | −0.031 |
| Precipitation (mm) | 1.7341 | −0.0007 | 1.2808 | 0.052 | 1.6407 | −0.1203 | 1.8138 | −0.0508 | 1.8653 | −0.1461 | 1.7898 | −0.2317 |
| b. 2015 | ||||||||||||
| Total Sample | 0–10 km | 10–20 km | 20–30 km | 30–40 km | 40–50 km | |||||||
| Covariate | Before | After | Before | After | Before | After | Before | After | Before | After | Before | After |
| Distance to road (m) | −0.8192 | −0.0766 | −0.2759 | −0.0875 | −0.9789 | −0.5116 | −0.632 | −0.8694 | −0.6758 | −0.8904 | −1.1445 | −0.2963 |
| Population density (people/km2) | −0.3581 | 0.0999 | −0.2083 | 0.1141 | −0.4176 | 0.0648 | 0.2536 | 0.111 | −0.9543 | 0.3587 | −0.3019 | 0.0935 |
| Elevation (m) | 1.575 | −0.0089 | 1.2523 | 0.0618 | 1.5938 | −0.0294 | 1.7322 | −0.2968 | 1.6958 | −0.206 | 1.4876 | −0.087 |
| Slope (°) | 0.8564 | 0.0043 | 0.703 | 0.0452 | 0.9053 | 0.0368 | 1.1079 | −0.1367 | 0.9671 | −0.1526 | 0.6415 | −0.0494 |
| Precipitation (mm) | 1.9363 | −0.0125 | 1.3983 | 0.0567 | 1.8383 | −0.062 | 2.0502 | −0.1853 | 2.1026 | −0.1024 | 1.9702 | −0.1242 |
| c. 2020 | ||||||||||||
| Total Sample | 0–10 km | 10–20 km | 20–30 km | 30–40 km | 40–50 km | |||||||
| Covariate | Before | After | Before | After | Before | After | Before | After | Before | After | Before | After |
| Distance to road (m) | 0.2902 | −0.0849 | 0.4482 | −0.1012 | 0.4011 | −0.2829 | 0.2751 | −0.4227 | 0.1592 | −0.3439 | 0.2018 | −0.0886 |
| Population density (people/km2) | −0.3499 | 0.083 | −0.2156 | 0.0907 | −0.4199 | 0.1196 | 0.2606 | 0.0905 | −0.9669 | 0.1948 | −0.3076 | 0.0507 |
| Elevation (m) | 1.6029 | −0.0117 | 1.2523 | 0.0428 | 1.5938 | 0.0842 | 1.7322 | −0.0222 | 1.6958 | 0.0551 | 1.4877 | 0.0249 |
| Slope (°) | 0.9075 | 0.0375 | 0.703 | 0.0646 | 0.9053 | −0.108 | 1.1079 | −0.1433 | 0.9671 | 0.0075 | 0.6417 | 0.0168 |
| Precipitation (mm) | 2.0942 | −0.0038 | 1.3732 | 0.0508 | 1.7769 | 0.1037 | 1.9426 | −0.0349 | 1.9558 | 0.087 | 1.8057 | 0.0357 |

Table A3.
Mean covariate values of treated and control groups.
Table A3.
Mean covariate values of treated and control groups.
| a. 2010 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Sample | 0–10 km | 10–20 km | 20–30 km | 30–40 km | 40–50 km | ||||||||
| Covariate | Treated | Control | Treated | Control | Treated | Control | Treated | Control | Treated | Control | Treated | Control | |
| Distance to road (m) | before | 2299.2998 | 3750.0526 | 2298.843 | 2788.2403 | 2298.843 | 4034.9366 | 2298.843 | 3419.8323 | 2298.843 | 3497.3887 | 2298.843 | 4328.7817 |
| after | 2296.8441 | 2421.7849 | 2304.6852 | 2367.9645 | 2353.2238 | 2907.049 | 2371.4306 | 3410.6341 | 2438.5972 | 3177.4503 | 2340.1089 | 2820.7544 | |
| Population density (people/km2) | before | 39.8905 | 75.6599 | 39.9759 | 58.5697 | 39.9759 | 81.8281 | 39.9759 | 11.5188 | 39.9759 | 139.4278 | 39.9759 | 69.7117 |
| after | 39.6203 | 26.5857 | 41.068 | 25.0437 | 46.4267 | 26.3709 | 39.2163 | 27.2241 | 48.2512 | 26.7321 | 43.1658 | 32.0079 | |
| Elevation (m) | before | 814.6774 | 344.6342 | 814.6798 | 440.3627 | 814.6798 | 338.3007 | 814.6798 | 296.9489 | 814.6798 | 307.821 | 814.6798 | 370.0524 |
| after | 722.9438 | 729.9082 | 715.0471 | 698.8864 | 561.4861 | 569.1784 | 534.8763 | 570.5133 | 623.261 | 653.2831 | 659.9815 | 679.1186 | |
| Slope (°) | before | 28.6589 | 20.4584 | 28.6397 | 21.9028 | 28.6397 | 19.9634 | 28.6397 | 18.0217 | 28.6397 | 19.3712 | 28.6397 | 22.492 |
| after | 27.7201 | 27.3711 | 27.1925 | 27.1263 | 26.5667 | 25.0825 | 25.0202 | 25.8207 | 26.4656 | 26.761 | 27.2732 | 27.5701 | |
| Precipitation (mm) | before | 2158.6183 | 1917.4703 | 2158.8503 | 1980.5435 | 2158.8503 | 1930.4489 | 2158.8503 | 1906.347 | 2158.8503 | 1899.1792 | 2158.8503 | 1909.682 |
| after | 2119.5538 | 2119.6498 | 2115.3079 | 2108.0651 | 2054.3095 | 2071.0627 | 2047.8952 | 2054.9657 | 2087.6172 | 2107.9552 | 2094.4999 | 2126.7496 | |
| b. 2015 | |||||||||||||
| Total Sample | 0–10 km | 10–20 km | 20–30 km | 30–40 km | 40–50 km | ||||||||
| Covariate | Treated | Control | Treated | Control | Treated | Control | Treated | Control | Treated | Control | Treated | Control | |
| Distance to road (m) | before | 2299.2998 | 3750.0526 | 2298.843 | 2788.2403 | 2298.843 | 4034.9366 | 2298.843 | 3419.8323 | 2298.843 | 3497.3887 | 2298.843 | 4328.7817 |
| after | 2343.6505 | 2479.3505 | 2260.8373 | 2415.9495 | 2460.4962 | 3367.8896 | 2727.1873 | 4269.2183 | 2949.3417 | 4528.5073 | 2494.007 | 3019.5325 | |
| Population density (people/km2) | before | 36.4278 | 75.0241 | 36.5066 | 58.9943 | 36.5066 | 81.576 | 36.5066 | 9.133 | 36.5066 | 139.5122 | 36.5066 | 69.0929 |
| after | 39.0544 | 28.2871 | 38.4965 | 26.1793 | 29.8832 | 22.8872 | 34.8755 | 22.8953 | 58.71 | 19.9926 | 46.2367 | 36.1451 | |
| Elevation (m) | before | 814.6774 | 344.6342 | 814.6798 | 440.3627 | 814.6798 | 338.3007 | 814.6798 | 296.9489 | 814.6798 | 307.821 | 814.6798 | 370.0524 |
| after | 726.5854 | 729.2512 | 723.4696 | 704.9945 | 559.0807 | 567.8628 | 511.4322 | 600.1312 | 630.3683 | 691.9307 | 603.027 | 629.0275 | |
| Slope (°) | before | 28.6589 | 20.4584 | 28.6397 | 21.9028 | 28.6397 | 19.9634 | 28.6397 | 18.0217 | 28.6397 | 19.3712 | 28.6397 | 22.492 |
| after | 27.3952 | 27.3541 | 27.6572 | 27.2243 | 26.3665 | 26.0135 | 25.0673 | 26.3775 | 25.2971 | 26.7592 | 26.3219 | 26.7954 | |
| Precipitation (mm) | before | 2429.0029 | 2125.386 | 2429.0371 | 2209.4455 | 2429.0371 | 2140.3498 | 2429.0371 | 2107.0823 | 2429.0371 | 2098.8471 | 2429.0371 | 2119.6327 |
| after | 2376.1734 | 2378.1334 | 2372.7792 | 2363.8683 | 2285.4191 | 2295.1616 | 2267.1484 | 2296.2406 | 2315.7657 | 2331.8468 | 2312.6804 | 2332.1895 | |
| c. 2020 | |||||||||||||
| Total Sample | 0–10 km | 10–20 km | 20–30 km | 30–40 km | 40–50 km | ||||||||
| Covariate | Treated | Control | Treated | Control | Treated | Control | Treated | Control | Treated | Control | Treated | Control | |
| Distance to road (m) | before | 2137.7774 | 1720.1455 | 2136.8252 | 1490.9546 | 2136.8252 | 1558.734 | 2136.8252 | 1740.3323 | 2136.8252 | 1907.4124 | 2136.8252 | 1846.01 |
| after | 2162.8421 | 2284.9909 | 2072.9991 | 2218.896 | 2173.1071 | 2580.8344 | 2338.7935 | 2948.025 | 2276.1901 | 2771.8036 | 2094.7608 | 2222.5002 | |
| Population density (people/km2) | before | 35.9829 | 73.0048 | 36.0603 | 58.9012 | 36.0603 | 80.5498 | 36.0603 | 8.4471 | 36.0603 | 138.518 | 36.0603 | 68.6497 |
| after | 36.7455 | 27.9584 | 35.2438 | 25.6339 | 33.2056 | 20.5373 | 31.8279 | 22.2396 | 38.2269 | 17.5804 | 40.6419 | 35.2743 | |
| Elevation (m) | before | 814.6774 | 336.3074 | 814.6798 | 440.3627 | 814.6798 | 338.3007 | 814.6798 | 296.9489 | 814.6798 | 307.821 | 814.6798 | 370.0258 |
| after | 757.3263 | 760.8066 | 717.398 | 704.5992 | 633.5675 | 608.3949 | 594.2765 | 600.8972 | 730.7725 | 714.2959 | 703.4744 | 696.0442 | |
| Slope (°) | before | 28.6589 | 19.969 | 28.6397 | 21.9028 | 28.6397 | 19.9634 | 28.6397 | 18.0217 | 28.6397 | 19.3712 | 28.6397 | 22.4898 |
| after | 28.2641 | 27.9047 | 27.4034 | 26.784 | 25.7991 | 26.8338 | 26.13 | 27.5036 | 27.8387 | 27.7665 | 27.7925 | 27.6312 | |
| Precipitation (mm) | before | 2120.3072 | 1827.7762 | 2120.3783 | 1928.273 | 2120.3783 | 1871.8062 | 2120.3783 | 1848.6164 | 2120.3783 | 1846.7676 | 2120.3783 | 1867.7727 |
| after | 2089.446 | 2089.9827 | 2068.3312 | 2061.2286 | 2028.807 | 2014.2997 | 2006.2251 | 2011.1011 | 2081.6965 | 2069.5315 | 2060.961 | 2055.9651 | |

Table A4.
Mean values of ecosystem health (EH), ecosystem service (ES), ecosystem resilience (ER), and ecosystem vigor (EV) for treated and control groups.
Table A4.
Mean values of ecosystem health (EH), ecosystem service (ES), ecosystem resilience (ER), and ecosystem vigor (EV) for treated and control groups.
| a. 2010 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EH | ES | ER | EV | |
| Treated | 0.4050037 | 0.10959544 | 0.9879207 | 0.6190458 |
| Control | 0.3819352 | 0.09890886 | 0.9581496 | 0.6017086 |
| b. 2015 | ||||
| EH | ES | ER | EV | |
| Treated | 0.4321984 | 0.1213692 | 0.9851929 | 0.6829016 |
| Control | 0.4171342 | 0.1131893 | 0.9644158 | 0.6810368 |
| c. 2020 | ||||
| EH | ES | ER | EV | |
| Treated | 0.4812389 | 0.1709042 | 0.9865474 | 0.6672542 |
| Control | 0.4508396 | 0.1525037 | 0.9549505 | 0.6468838 |

Table A5.
Results of average treatment effect on the treated (ATT) for ecosystem health (EH) across buffer zones.
Table A5.
Results of average treatment effect on the treated (ATT) for ecosystem health (EH) across buffer zones.
| a. 2010 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | ATT | SE | p-Value | CI_lower | CI_upper |
| Total sample | 0.022132 | 0.003349 | 7.33 × 10−11 | 0.015567 | 0.028697 |
| 0–10 km | 0.0167 | 0.003192 | 2.24 × 10−7 | 0.010443 | 2.30 × 10−2 |
| 10–20 km | 0.01993 | 0.004436 | 9.61 × 10−6 | 0.011235 | 2.86 × 10−2 |
| 20–30 km | 0.032232 | 0.00596 | 1.36 × 10−7 | 0.020551 | 0.043913 |
| 30–40 km | 0.035535 | 0.004354 | 3.90 × 10−15 | 0.027002 | 4.41 × 10−2 |
| 40–50 km | 0.033678 | 0.004171 | 4.00 × 10−15 | 0.025502 | 4.19 × 10−2 |
| b. 2015 | |||||
| Group | ATT | SE | p-Value | CI_lower | CI_upper |
| Total sample | 0.014491 | 0.003637 | 7.51 × 10−5 | 0.007362 | 0.02162 |
| 0–10 km | 0.01614 | 0.003801 | 2.49 × 10−5 | 0.00869 | 2.36 × 10−2 |
| 10–20 km | 0.013009 | 0.006464 | 4.52 × 10−2 | 0.000339 | 2.57 × 10−2 |
| 20–30 km | 0.043009 | 0.010665 | 8.09 × 10−5 | 0.022105 | 0.063913 |
| 30–40 km | 0.026267 | 0.007872 | 1.01 × 10−3 | 0.010837 | 4.17 × 10−2 |
| 40–50 km | 0.017708 | 0.005267 | 8.56 × 10−4 | 0.007383 | 2.80 × 10−2 |
| c. 2020 | |||||
| Group | ATT | SE | p-Value | CI_lower | CI_upper |
| Total sample | 0.029194 | 0.004068 | 1.63 × 10−12 | 0.02122 | 0.037167 |
| 0–10 km | 0.022292 | 0.003882 | 1.42 × 10−8 | 0.014683 | 2.99 × 10−2 |
| 10–20 km | 0.041111 | 0.006552 | 1.06 × 10−9 | 0.028269 | 5.40 × 10−2 |
| 20–30 km | 0.059526 | 0.007609 | 1.08 × 10−13 | 0.044613 | 0.074439 |
| 30–40 km | 0.037132 | 0.00536 | 1.55 × 10−11 | 0.026627 | 4.76 × 10−2 |
| 40–50 km | 0.033277 | 0.004954 | 4.21 × 10−11 | 0.023567 | 4.30 × 10−2 |
References
- Terraube, J.; Van Doninck, J.; Helle, P.; Cabeza, M. Assessing the Effectiveness of a National Protected Area Network for Carnivore Conservation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Jeppesen, E.; Gao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lu, Q.; Wang, C.; Sun, X. Assessment of the Effectiveness of China’s Protected Areas in Enhancing Ecosystem Services. Ecosyst. Serv. 2024, 65, 101588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Luo, Z.; Mallon, D.; Li, C.; Jiang, Z. Biodiversity Conservation Status in China’s Growing Protected Areas. Biol. Conserv. 2017, 210, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Su, S.; Gong, Z.; Lv, C.; Li, N.; Luo, Q.; Zhou, X.; Li, S. Effectiveness of Protected Areas in the Three-River Source Region of the Tibetan Plateau for Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.; Liu, X.; He, S. Establishing an Ecological Monitoring System for National Parks in China: A Theoretical Framework. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 143, 109414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Viña, A.; Kong, L.; Pimm, S.L.; Zhang, J.; Yang, W.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Liu, J.; et al. Reassessing the Conservation Status of the Giant Panda Using Remote Sensing. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 1635–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodie, J.F.; Mohd-Azlan, J.; Chen, C.; Wearn, O.R.; Deith, M.C.M.; Ball, J.G.C.; Slade, E.M.; Burslem, D.F.R.P.; Teoh, S.W.; Williams, P.J.; et al. Landscape-Scale Benefits of Protected Areas for Tropical Biodiversity. Nature 2023, 620, 807–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, W.; Zhang, L.; Hull, V.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Liu, J.; Polasky, S.; et al. Strengthening Protected Areas for Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 1601–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, X.; Shi, K.; Fu, Y.; Zhou, W.; Zhao, R.; Bao, H. Influence Mechanism of Natural Factors and Human Socio-Economic Activities on Ecosystem Health in Arid Regions of Central Asia: A Case Study of Fuyun Area, Northwest China. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 173, 113356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, J.; Xu, D.; Chen, D.; Tao, J.; Wang, J.; Ma, X. Study on Driving Factors of Island Ecosystem Health and Multi-Scenario Ecology Simulation Using Ecological Conservation and Eco-Friendly Tourism for Achieving Sustainability. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 373, 123480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-H.; Chen, F.; Tang, C.-J.; Lu, Y.; Feng, Y.-X. Integration of DPSIR Framework and TOPSIS Model Reveals Insight into the Coastal Zone Ecosystem Health. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2022, 226, 106285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhenqi, Z.; Tongyan, Z.; Hongrun, J. Assessment of Coastal Zone Ecosystem Health in the Context of Tourism Development: A Case Study of Jiaozhou Bay. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 169, 112874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, R.; Alcocer, J.; Oseguera, L.A. Microcystins Presence Threatens the Ecosystem Health of a Tropical National Park: Lagunas de Montebello, Chiapas. Braz. J. Bot. 2021, 44, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyer, J.; Sana, Y.; Samandoulgou, Y.; Cesar, J.; Guerrini, L.; Kabore-Zoungrana, C.; Dulieu, D. Identification of Ecological Indicators for Monitoring Ecosystem Health in the Trans-Boundary W Regional Park: A Pilot Study. Biol. Conserv. 2007, 138, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallory, M.L.; Gilchrist, H.G.; Braune, B.M.; Gaston, A.J. Marine Birds as Indicators of Arctic Marine Ecosystem Health: Linking the Northern Ecosystem Initiative to Long-Term Studies. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2006, 113, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, J.; Tao, J.; Wang, P.; Guo, L.; Yang, L. National Park Ecosystem Health Measurement Model Construction and Empirical Study in Huangshan National Park. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 5746–5760. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.; Zhang, F.; Li, J.; Zhao, C.; Jiang, Q.; Cheng, Z. Ecosystem Health Assessment Based on AHP-DPSR Model and Impacts of Climate Change and Human Disturbances: A Case Study of Liaohe River Basin in Jilin Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 142, 109171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, C.; Ge, C.; Yang, J.; Liang, Z.; Li, X.; Cao, X. Ecosystem Health Assessment Using PSR Model and Obstacle Factor Diagnosis for Haizhou Bay, China. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2024, 250, 107024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, J.; Wu, R.; Ma, Q.; Yang, J. Ecosystem Health Assessment Based on DPSIRM Framework and Health Distance Model in Nansi Lake, China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2016, 30, 1235–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, H.; Xiao, C.; Ma, T.; Sang, W. Ecological Health Assessment of Chinese National Parks Based on Landscape Pattern: A Case Study in Shennongjia National Park. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Su, Y.; Wang, L.; Gallagher, L.; Cheng, H. Taking an Ecosystem Services Approach for a New National Park System in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 137, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, L.; Lu, C.; Yang, X.; Chen, X. Spatio-Temporal Variation of the Ecosystem Service Value in Qilian Mountain National Park (Gansu Area) Based on Land Use. Land 2023, 12, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xue, H.; Li, A.; Ma, X.; Sun, A.; Zhang, J. Spatial-Temporal Differentiation and Influencing Factors of Ecosystem Health in Three-River-Source National Park. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 171, 113183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, S.L.; Cazalis, V.; Dudley, N.; Hoffmann, M.; Rodrigues, A.S.L.; Stolton, S.; Visconti, P.; Woodley, S.; Kingston, N.; Lewis, E.; et al. Area-Based Conservation in the Twenty-First Century. Nature 2020, 586, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.R.; Venter, O.; Fuller, R.A.; Allan, J.R.; Maxwell, S.L.; Negret, P.J.; Watson, J.E.M. One-Third of Global Protected Land Is under Intense Human Pressure. Science 2018, 360, 788–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joppa, L.N.; Loarie, S.R.; Pimm, S.L. On the Protection of “Protected Areas”. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 6673–6678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Wu, H.; Yang, B. Conserving Habitat and Ecosystem in Protected Areas amid Increasing Intensive Human Modification: A Case Study of China’s Pan-Pearl River Delta. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleicher, J.; Eklund, J.; Barnes, M.D.; Geldmann, J.; Oldekop, J.A.; Jones, J.P.G. Statistical Matching for Conservation Science. Conserv. Biol. 2020, 34, 538–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, P.J.; Hanauer, M.M.; Sims, K.R.E. Conditions Associated with Protected Area Success in Conservation and Poverty Reduction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 13913–13918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Li, H.; Prishchepov, A.V. Assessing Forest Conservation Outcomes of a Nature Reserve in a Subtropical Forest Ecosystem: Effectiveness, Spillover Effects, and Insights for Spatial Conservation Prioritization. Biol. Conserv. 2023, 285, 110254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Zhang, J.; Lu, L.; Tang, G.; Yan, B.; Xiao, X.; Han, Y. Eco-Efficiency and Its Determinants at a Tourism Destination: A Case Study of Huangshan National Park, China. Tour. Manag. 2017, 60, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H. Can Tourism Development Enhance Livelihood Capitals of Rural Households? Evidence from Huangshan National Park Adjacent Communities, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 748, 141099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xinhua News Agency, China Plans to Expand National Park System. Available online: https://english.www.gov.cn/statecouncil/ministries/202212/29/content_WS63ad525fc6d0a757729e4e36.html (accessed on 6 September 2025).
- National Forestry and Grassland Administration of China. Spatial Planning Scheme for National Parks; National Forestry and Grassland Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Huangshan Management Committee. Sustainable Development Policy of Huangshan Scenic Area; Huangshan Management Committee: Huangshan, China, 2019.
- Li, W.-B.; Yang, P.-P.; Xia, D.-P.; Huffman, M.A.; Li, M.; Li, J.-H. Ecotourism Disturbance on an Endemic Endangered Primate in the Huangshan Man and the Biosphere Reserve of China: A Way to Move Forward. Biology 2022, 11, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhu, D.; Bao, J. Sustainability and Nature-Based Mass Tourism: Lessons from China’s Approach to the Huangshan Scenic Park. J. Sustain. Tour. 2016, 24, 182–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; Sasaki, N.; Jourdain, D.; Kim, S.M.; Shivakoti, P. Local Livelihood under Different Governances of Tourism Development in China—A Case Study of Huangshan Mountain Area. Tour. Manag. 2017, 61, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huangshan Management Committee. Huangshan Scenic Area 2024 Work Summary and 2025 Work Arrangements; Huangshan Management Committee: Huangshan, China, 2025.
- Hu, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Yu, P.; Chu, G. What Influences Tourists’ Intention to Participate in the Zero Litter Initiative in Mountainous Tourism Areas: A Case Study of Huangshan National Park, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 1127–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, T.; Yu, C. Representation of Online Image of Tourist Destination: A Content Analysis of Huangshan. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2017, 22, 1063–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, R.; Long, Y.; Hu, J.; Yang, F.; Jin, T.; Wang, J.; Hu, P.; Wu, W.; Diao, Y.; et al. Individual-Level Performance of Nature Reserves in Forest Protection and the Effects of Management Level and Establishment Age. Biol. Conserv. 2019, 233, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhong, L.; Zhang, H. Using Propensity Score Matching Models to Assess the Protection Effectiveness in Pudacuo National Park, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 150, 110222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frauman, E.; Banks, S. Gateway Community Resident Perceptions of Tourism Development: Incorporating Importance-Performance Analysis into a Limits of Acceptable Change Framework. Tour. Manag. 2011, 32, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, N.; Lemelin, R.H.; Koster, R.; Budke, I. A Capital Assets Framework for Appraising and Building Capacity for Tourism Development in Aboriginal Protected Area Gateway Communities. Tour. Manag. 2012, 33, 752–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Xie, H.; Yue, W.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Z.; Chen, S. Urban Ecosystem Health Evaluation for Typical Chinese Cities along the Belt and Road. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 101, 572–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; He, B.-J.; Liu, Y.; Li, R. How Does Rapid Urban Construction Land Expansion Affect the Spatial Inequalities of Ecosystem Health in China? Evidence from the Country, Economic Regions and Urban Agglomerations. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2024, 106, 107533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Liao, L.; Fu, T.; Lan, S. Do Establishment of Protected Areas and Implementation of Regional Policies Both Promote the Forest NPP? Evidence from Wuyi Mountain in China Based on PSM-DID. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2024, 55, e03210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Zhang, C.; Zhen, L.; Zhang, L. Dynamic Changes in the Value of China’s Ecosystem Services. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 26, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sannigrahi, S.; Chakraborti, S.; Joshi, P.K.; Keesstra, S.; Sen, S.; Paul, S.K.; Kreuter, U.; Sutton, P.C.; Jha, S.; Dang, K.B. Ecosystem Service Value Assessment of a Natural Reserve Region for Strengthening Protection and Conservation. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 244, 208–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, R.; Liu, Y.; Fei, X.; Yu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Meng, Q. Ecosystem Health Assessment: A Comprehensive and Detailed Analysis of the Case Study in Coastal Metropolitan Region, Eastern China. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 98, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Wu, J. Regional Ecosystem Health Response to Rural Land Use Change: A Case Study in Lijiang City, China. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 72, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Xu, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Cui, J.; Meng, Q. Ecological Health Assessment of the Middle Route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project Using an Enhanced VORS Model. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 172, 113281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, T.; Zeng, C.; Lin, C.; Liu, W.; Cheng, Y.; Li, Y. Towards an Integrated Approach for Land Spatial Ecological Restoration Zoning Based on Ecosystem Health Assessment. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 147, 110016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; He, J.; Liu, D.; Wang, J. Predicting the Joint Effects of Future Climate and Land Use Change on Ecosystem Health in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Appl. Geogr. 2020, 124, 102293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Su, H.; Pan, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, J.; Fang, J.; Tang, Z. Assessing the Effectiveness of Global Protected Areas Based on the Difference in Differences Model. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 130, 108078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, L.; Shen, L.; Zhong, S.; Li, D.; Zhu, Y. Conservation Effects of Transboundary Protected Areas on Mitigating Anthropogenic Pressure across China’s Borders. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2025, 212, 107976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbens, G.W.; Rubin, D.B. Causal Inference in Statistics, Social, and Biomedical Sciences; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2015; ISBN 978-0-521-88588-1. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Brand, J.E.; Jann, B. Estimating Heterogeneous Treatment Effects with Observational Data—Yu Xie, Jennie E. Brand, Ben Jann, 2012. Sociol. Methodol. 2012, 42, 314–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drechsler, M.; Johst, K.; Ohl, C.; Wätzold, F. Designing Cost-Effective Payments for Conservation Measures to Generate Spatiotemporal Habitat Heterogeneity. Conserv. Biol. 2007, 21, 1475–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Xue, H.; Wang, J.; Li, A. Spatiotemporal Variations in Carbon Sources and Sinks in National Park Ecosystem and the Impact of Tourism. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Hu, D.; Xu, H.; Zhong, X. Assessing the Spatiotemporal Variation of NPP and Its Response to Driving Factors in Anhui Province, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 14915–14932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, C.; Ondei, S.; Brook, B.W.; Buettel, J.C. First, Do No Harm: A Systematic Review of Deforestation Spillovers from Protected Areas. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2019, 18, e00591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, S.A.; Jepsen, M.R.; Kingston, N.; Lewis, E.; Brooks, T.M.; MacSharry, B.; Mertz, O. Deforestation Leakage Undermines Conservation Value of Tropical and Subtropical Forest Protected Areas. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2020, 29, 2014–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Chen, C.; Shao, C. Spatial and Temporal Changes in Ecosystem Service Driven by Ecological Compensation in the Xin’an River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-H.Z. National Parks in China: Parks for People or for the Nation? Land Use Policy 2019, 81, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ament, J.M.; Cumming, G.S. Scale Dependency in Effectiveness, Isolation, and Social-ecological Spillover of Protected Areas. Conserv. Biol. 2016, 30, 846–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Liu, G.; Zhou, W.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, H.; Su, X. Protected Areas Have Remarkable Spillover Effects on Forest Conservation on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Divers. Distrib. 2022, 28, 2944–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, B.; Anthony, B.P. Counterfactual Assessment of Protected Area Avoided Deforestation in Cambodia: Trends in Effectiveness, Spillover Effects and the Influence of Establishment Date. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2022, 38, e02228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beunen, R.; Regnerus, H.D.; Jaarsma, C.F. Gateways as a Means of Visitor Management in National Parks and Protected Areas. Tour. Manag. 2008, 29, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Fan, S.; Knight, D.W. Household Livelihood Adaptive Strategies in Gateway Communities of New National Parks. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2025, 30, 1065–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Zhou, L.; Wu, T.; Yang, X.; Ren, M. Ecosystem Services in National Park of Hainan Tropical Rainforest of China: Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Conservation Implications. J. Nat. Conserv. 2024, 80, 126649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powlen, K.A.; Gavin, M.C.; Jones, K.W. Management Effectiveness Positively Influences Forest Conservation Outcomes in Protected Areas. Biol. Conserv. 2021, 260, 109192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geldmann, J.; Coad, L.; Barnes, M.D.; Craigie, I.D.; Woodley, S.; Balmford, A.; Brooks, T.M.; Hockings, M.; Knights, K.; Mascia, M.B.; et al. A Global Analysis of Management Capacity and Ecological Outcomes in Terrestrial Protected Areas. Conserv. Lett. 2018, 11, e12434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andam, K.S.; Ferraro, P.J.; Pfaff, A.; Sanchez-Azofeifa, G.A.; Robalino, J.A. Measuring the Effectiveness of Protected Area Networks in Reducing Deforestation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 16089–16094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Liang, Z.; Ye, J.; Li, J.; Yang, F.; Li, Z.; Cui, D.; Yan, L.; Li, B.; Hu, J. Conservation Implications of Climatically Heterogeneous Areas for Species Diversity in a Biodiversity Hotspot. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 371, 123275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Fang, C.; Watson, J.E.M.; Sun, S.; Qi, W.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J. Mixed Effectiveness of Global Protected Areas in Resisting Habitat Loss. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 8389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdoch, W.; Ranganathan, J.; Polasky, S.; Regetz, J. Using Return on Investment to Maximize Conservation Effectiveness in Argentine Grasslands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 20855–20862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.; Fang, Z.; Bai, Y.; Alatalo, J.M.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, F. The Next Step for China’s National Park Management: Integrating Ecosystem Services into Space Boundary Delimitation. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 329, 117086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan, A.; Naidoo, R.; Greenstreet, L.; Mehrabi, Z.; Ramankutty, N.; Kremen, C. Functional Connectivity of the World’s Protected Areas. Science 2022, 376, 1101–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldekop, J.A.; Holmes, G.; Harris, W.E.; Evans, K.L. A Global Assessment of the Social and Conservation Outcomes of Protected Areas. Conserv. Biol. 2015, 30, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, M.; Arnell, A.; de Lamo, X.; García-Rangel, S.; Lewis, M.; Mark, J.; Merow, C.; Miles, L.; Ondo, I.; Pironon, S.; et al. Areas of Global Importance for Conserving Terrestrial Biodiversity, Carbon and Water. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 5, 1499–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).