Abstract
Evolution and influencing factors of manufacturing production spaces in the global city regions of China are diverse from the West, attracting attention to accurately identify and analyze the real and continuous distribution of manufacturing production spaces on the basis of the actual situation of the region. The 18th National Congress of the Communist Party of China proposed that the production spaces should be intensive and efficient, but the existing studies focus less attention on the manufacturing entity spaces in city regions. Taking the Pearl River Delta as an instance, combined with the POI data of manufacturing enterprises, this study interprets the spatial information of manufacturing production spaces in 1987, 1997, 2007 and 2017 by means of high-resolution remote sensing images. Using various models to quantitatively explore the distribution pattern and evolution characteristics of manufacturing production spaces in the Pearl River Delta in dissimilar periods, and then providing policy guidance for the accurate planning and regulation of manufacturing production spaces in China’s global city regions, on the basis of comparing the evolution mechanism of manufacturing space in Western countries’ global city regions. The results show that: Under the coupling effect of the stage of time series and the heterogeneity of spatial distribution, the manufacturing production spaces in the Pearl River Delta has evolved from the scattered distribution of the core area to the complex and diversified spatial pattern. The hot spots of manufacturing production space expansion in distinct stages also exhibit stage differences. At the current stage, the factors of globalization, technological innovation and policy are becoming increasingly significant. The evolution characteristics of manufacturing production spaces in global city regions in China and Western countries are dissimilar, but the driving factors are similar, which involves the level of urbanization and industrialization, the local government-level infrastructure investment, etc. Instead of simply promoting or restraining the optimization control of manufacturing production spaces, the local governments conduct precise regulation in line with the actual space distribution and development mechanism of manufacturing production spaces in diverse cities. In this process, we can learn from but not copy the experience of the Western countries.
1. Introduction
Since the 1980s, economic globalization has increasingly become a crucial factor affecting urban regional development [1]. With the global diffusion of the manufacturing industries, the globalization elements dominated by high-end producer services are concentrated in global cities [2,3]. By virtue of advanced transportation and communication technology, the manufacturing sector spreads to the surrounding wider areas, and gathers near diverse nodes within the region to form a professional cluster space with flexible organization [4]. It has gradually formed a highly integrated multi-center and multi-level global city region with an international metropolis as the core [5,6]. In simple geographic terms, a global city region can be said to comprise any major metropolitan area or any contiguous set of metropolitan areas together with a surrounding hinterland of variable extent—itself a locus of scattered urban settlements—whose internal economic and political affairs are bound up in intricate ways in intensifying and far-flung extra-national relationships [7,8]. Meanwhile, the core area in the global city region is the cosmopolitan metropolis as a command post for the operations of multinational corporations, as a center of advanced services and information-processing activities, and as a deeply segmented social space marked by extremes of poverty and wealth [7]. Scott put forth the concept of global city region, which aimed to establish the association between world economic development and urban regional spatial reconstruction, but did not further clarify the mechanism of regional spatial structure [9].
Under the background of the rise of the knowledge economy, the industrial space within the global city regions in Western countries has entered the post-industrialization stage, and the principal economic activities, such as advanced producer services (APSs), knowledge-intensive industries, and innovative industries are reshaping the regional spatial structure [10,11,12,13]. As a result of the unique political, economic and social system, the path of global city region formation and spatial development in China differs from that in Western countries, the industrialization and deindustrialization are going on simultaneously in the global city regions of China [14,15]. Scholars primarily fix their attention on the fact that APSs, foreign direct investment (FDI), or foreign-funded manufacturing industries, as the leading industries, can exert a pivotal influence on regional spatial structure [16,17,18,19,20,21]. The spatial reconstruction of the manufacturing industries still plays a leading and guiding role for shaping the spatial structure of the global city regions in China [22], while the existing studies focus less attention on other types of manufacturing industries besides foreign-funded manufacturing industries. It is very necessary to study the spatial reconstruction of manufacturing industries in global city region of China, not only foreign-funded manufacturing industries, but also other types of manufacturing industries. The first aim is to better understand the evolution law of manufacturing production spaces (including all types of manufacturing) and its influencing factors in China’s global city regions through comparison with Western countries, enrich the practical content of global city regions applied to global Southern countries/regions, and guide regional spatial development policies.
Currently, the studies on the spatial reconstruction characteristics of manufacturing industries predominantly concentrate on collecting economic census data, manufacturing industry data in the industrial sector, or data on the employment of the manufacturing industries to construct the industrial space of manufacturing industries with the urban [23,24,25,26] or urban internal streets or districts [27,28,29,30,31,32] as the statistical unit. Nevertheless, these studies are primarily on the basis of the economic statistics and enterprise attribute data to construct the manufacturing industry space that is not the space of physical entities. The spatial characteristics of manufacturing industry space is not precise enough, and the spatial continuity of manufacturing industry space is not good enough, either. It could not precisely and appropriately provide a decision-making direction for industrial policy and urban spatial planning of the real local economy [33,34,35]. Although cadastral survey data can represent the real economy space of manufacturing theoretically, these data are not allowed to be released to the public in China. So far, only a few scholars characterize the manufacturing space by obtaining the land use number of individual cities [36,37]. However, it is still impossible to obtain the data of manufacturing physical entity space of all cities in global city regions in a long time series.
With the speedy development of remote sensing (RS) and geographic information system (GIS) technology, it is possible to obtain large-scale urban spatial information accurately and continuously. A few scholars have also made use of RS and GIS technology to obtain large-scale industrial production spaces and conduct relevant explorations on the spatial characteristics of industrial production spaces [38,39], the spatial and temporal evolution of industrial production spaces and their driving mechanisms [40,41,42]. Significantly, industrial production spaces include mining, electricity, heat, gas, water production and other production spaces, which cannot accurately characterize the spatial state of regional real economic production activities. In recent years, with the development of information technology and location acquisition technology, a sequence of geospatial data, such as point of interest (POI) data, a large area of urban ground objects can be accurately extracted, which provides a new approach to reveal the finer spatial structure and human activity patterns within a city [43,44,45]. As a result, it is essential to exert more intensified efforts to strengthen multiple facets with regard to using RS and GIS technology to interpret spatial information of industrial production spaces through manual visual interpretation [39], and combining the POI data of manufacturing enterprises to obtain attribute information of manufacturing enterprises, then separating the manufacturing production spaces from the industrial production spaces [46], and exploring the evolution characteristics, and influencing factors of manufacturing production spaces in city regions needs to be strengthened. The second aim is to strengthen the exploration of the spatial pattern and evolution characteristics of manufacturing physical entity space in global city regions, and further establish a global city region policy guidance system based on the precise identification of manufacturing production spaces.
The manufacturing production spaces are the representation of manufacturing activities and manufacturing sectors in the geographical space. The evolution of the spatial pattern of manufacturing production spaces not only reflects development characteristics of production activities in manufacturing in the historical period, but also influences the future direction of regional real economic space [47]. On the one hand, from a global perspective, the global city regions are the predominant space carriers for countries or regions to participate in global competition in the era of globalization, and manufacturing industries carry the function of local advanced production platform for international and domestic industrial development of global city regions [1,2]. The Pearl River Delta (PRD) global city region is an advanced territorial platform for China to integrate into economic globalization, and there are many studies on the spatial evolution characteristics of manufacturing space in the PRD [17,18,19,20,21,48]. Some scholars use the statistical data of enterprises to depict the manufacturing industry space in the Pearl River Delta global city region [20,21]. However, the types of manufacturing enterprises are not comprehensive enough, and the data time is short (only in the last decade), so it is impossible to comprehensively describe the evolution law of the long time series of manufacturing production activities. For this reason, it’s essential to strengthen the evolution characteristics of the entire spatial structure of regional manufacturing production spaces, and the interaction mechanism with the internal factors of city regions.
On the other hand, from a local perspective, China’s global city regions have begun high-speed industrialization and urbanization by receiving the manufacturing industries of Western countries, in the past 40 years. In this process, the expansion of manufacturing production spaces is the predominant force in the development of urban production spaces, while it also gives rise to a range of sustainable development problems of urban production spaces to be solved urgently [49,50,51]. What is more, the contradiction between production and living ecological spaces is becoming increasingly prominent in global city regions [52]. With the deficiency of land resources and the weakening of the environmental carrying capacity, an increasing number of scholars are aware of the need to change the pattern of extensive land development used in the past [41], accordingly, an augmenting number of central and local governments have come up with policies for intensive and optimized development of production spaces. In some sense, accurately identifying and analyzing the real and continuous distribution of manufacturing production spaces in city regions, and exploring the evolution characteristics and the driving mechanism of manufacturing production spaces, then comparing the spatial characteristics and driving mechanism of manufacturing production spaces with those in the West, lay the solid basis for optimizing the regulation and promoting intensive, efficient and sustainable development [46,49]. Based on these, this paper first selects the PRD global city region as a case study to explore the evolution characteristics and influencing factors of manufacturing production spaces since the mid-1980s. Subsequently, this paper provides policy guidance for the accurate planning and regulation of manufacturing production spaces in China’s global city regions by comparing the evolution mechanism with the West.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The PRD has become one of China’s most representative global city regions [17,53], which is located on the south coast of mainland China with an area of 54,764.6 km2, comprising nine cities: Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Foshan, Dongguan, Huizhou, Zhongshan, Zhuhai, Zhaoqing and Jiangmen (Figure 1). Since the high development of economic globalization, the output value of the secondary industry in the PRD has kept a conspicuous upward trend, and its proportion in gross domestic product (GDP) has been maintained at more than 41% (Table 1) [54] (Guangdong Bureau of Statistics, 2021).
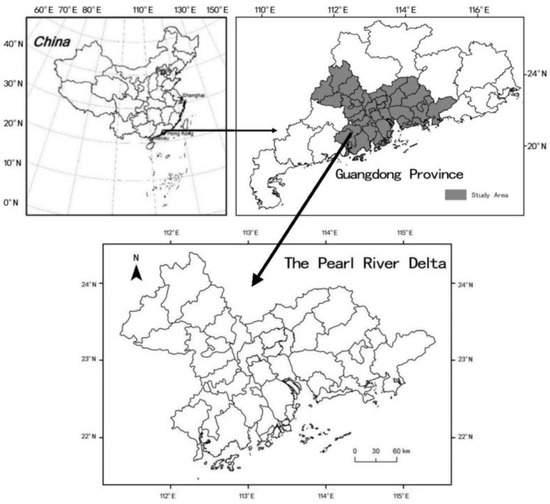
Figure 1.
Location of the PRD.

Table 1.
The economic profile of secondary industries in the PRD from 1990 to 2020.
2.2. Data Sources and Data Processing
- (1)
- Data Sources
Using Google Satellite Maps Downloader to obtain high-resolution maps: 2017 and 2007 high-resolution Google Earth image data, 16th grade 4.78 m; 1997 high-resolution Google Earth image data, 15th grade 9.55 m; 1987 medium-resolution TM image data, 30 m.
The POI data were obtained from the Gaode Map API interface by using Web crawler technology in May 2017. The POI data include diversified types, such as education, entertainment, industrial, etc. We selected the manufacturing enterprises’ POI data from the industrial type, including 60,114 records in total, and each manufacturing enterprises’ POI records have six attribute values: city code, enterprise name, address, telephone number, x-coordinates and y-coordinates.
- (2)
- Data Processing
Step1: 2017 high-resolution Google Earth image data, administrative division vector map of PRD and the POI data of manufacturing enterprises are corrected through ENVI software to control the image correction error within half a pixel. Using RS and GIS technology to interpret the spatial information of industrial production spaces through manual visual interpretation [39], combining the POI data of manufacturing enterprises to obtain attribute information of manufacturing enterprises, then separating the manufacturing production spaces from the industrial production spaces [46] (Figure 2). For the areas that were difficult to identify or difficult to determine, they could be corrected and supplemented by the planning information from the government. The ground objects extracted presented the texture and spectral characteristics of a typical manufacturing production spaces, and most of them could be clearly identified on remote sensing images.
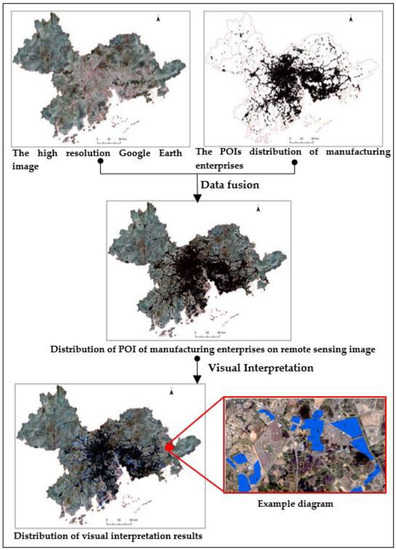
Figure 2.
Technique flowchart of the interpretation of manufacturing production spaces in 2017.
Step 2: in the historical period (2007 high-resolution Google Earth image data), taking the manufacturing production spaces vectorization data in 2017 as the benchmark data and superimpose it on the remote sensing image, so as to identify the increased or decreased manufacturing production spaces (Figure 3). Vectorize the manufacturing production spaces in 2007 high-resolution Google Earth image data through manual interpretation and visual interpretation, so as to accurately extract the manufacturing production spaces in 2007.
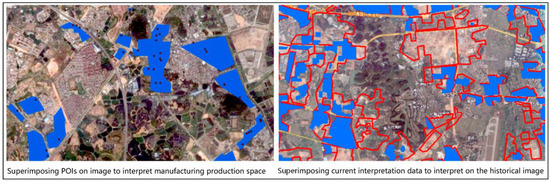
Figure 3.
Interpretation of manufacturing production spaces vector in the historical period.
Step 3: finally, by analogy, vectorize the manufacturing production spaces in 1997 and 1987, that is, obtain the manufacturing production spaces vector data of four time nodes in the PRD (1987, 1997, 2007 and 2017).
Combined with the POI data of the manufacturing enterprises, the vector information from the manufacturing production spaces in the historical periods can be accurately extracted through remote sensing manual visual interpretation. Despite the fact that the method was time-consuming, the accuracy was much better than that of the general automatic computer interpretation.
2.3. Methodology
- (1)
- Expansion Speed and Expansion Strength
The expansion speed indicates the increasing situation of manufacturing production spaces from the base period to the end period. Expansion strength indicates the proportion of the annual newly added industrial production space of each space unit in its total area. In essence, it is to standardize the annual expansion speed of the industrial production space of each space unit to make it longitudinally comparable [55,56]. The calculation formula is displayed as follows:
where LV is the expansion speed index and LS is the expansion intensity index; St and S0 are the area of the industrial production spaces at the end of the study period and the base period, respectively; t is the study period; A0 is the area of each research unit.
- (2)
- Incremental Variation Coefficient
For the sake of describing the comprehensive change state of industrial production spaces, this study constructs a comprehensive index reflecting the change degree of manufacturing production spaces, namely a comprehensive change coefficient, from three aspects of speed, intensity and spatial aggregation [57].
The calculation method is as follows:
Velocity variation index:
Strength variation index:
Aggregation index:
where I is the comprehensive variation coefficient of the industrial production spaces. The greater the I, the stronger the variation of the industrial production space; I1 is the speed variation index; I2 is the intensity change index, reflecting the relative expansion rate of manufacturing production space on each unit area space unit; I3 is the change index of the polymerization degree, reflecting the change degree of polymerization degree.
- (3)
- Spatial Autocorrelation
Spatial autocorrelation measures the correlation between the values of various variables in accordance with the spatial assignment status, which can be adopted to reveal the spatial pattern and structural characteristics of the expansion of manufacturing production spaces. Getis-OrdGi* (hot spot index) is introduced to measure the local spatial characteristics, respectively, and identify the spatial distribution of local hot spots and cold spots at dissimilar spatial locations [58]. The formula is exhibited as follows:
In an effort to facilitate interpretation and comparison, the above formula is standardized [57].
where E(Gi*) and Var(Gi*) are the mathematical expectation and variance of Gi*, respectively. If Z(Gi*) is noticeably positive, it indicates that region i belongs to high-value spatial agglomeration area, i.e., the hot spot area. On the contrary, if Z(Gi*) is strikingly negative, it indicates that region i belongs to the low value spatial agglomeration area, i.e., the cold spot area. In this paper, the spatial weight Wij adopts the spatial search radius method and selects 5 km as the correlation distance to construct the spatial weight matrix.
- (4)
- Stability Index
Fractal theory is universally employed to probe deep into the spatial structure of the city region, fractal characteristics of urban land use, Batty and Longley [59]. With the purpose of studying the morphological characteristics of manufacturing production spaces quantitatively, this paper introduces the stability index and fractal dimension. Fractal dimension can, not only reflect the complexity of land boundary shape, but also reflect the fragmentation degree of land and the spatial filling capacity of the graphics [60]. The calculation formula is described as follows [61]:
In the Equation (9): A is the patch area of manufacturing production space; P is the perimeter of the plaque; C is a constant (intercept); and D is the fractal dimension. The theoretical value of the D value is 1.0–2.0. The larger the D value, the more complex the shape of vector patches and the more irregular the boundary, and vice versa. When D = 1.5, it means that the vector plaque is in the Brownian random motion state. The closer it is to this value, the worse its stability will be. Based on this, the stability index SK of the manufacturing production space can be defined as follows [62]:
In the Equation (10): the theoretical value of SK is 0–0.5. The larger the value of SK, the more stable the manufacturing production space, and vice versa.
2.4. Research Steps
The first step is the data sources and processing. Combined with the POI data of manufacturing enterprises, this study interprets the spatial information of manufacturing production spaces in 1987, 1997, 2007 and 2017 by means of high-resolution remote sensing images. The second step is the data analysis. Using various models to quantitatively explore the distribution pattern and evolution characteristics of manufacturing production spaces in the PRD in dissimilar periods. The third step is the discussion and conclusions. Providing the policy guidance for the accurate planning and regulation of manufacturing production spaces in China’s global city regions, on basis of comparing the evolution mechanism of manufacturing spaces in Western countries’ global city regions (Figure 4).
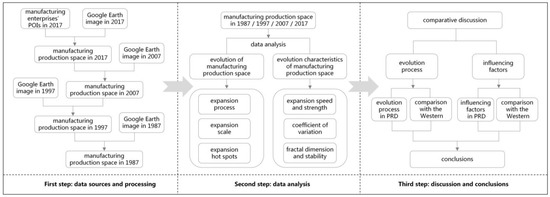
Figure 4.
Workflow schema.
3. Results
3.1. The Evolution of Manufacturing Production Spaces in the PRD
3.1.1. Expansion Process of Manufacturing Production Space Evolution
Through the visual interpretation of Google Earth remote sensing images of the PRD in 1987, 1997, 2007 and 2017, the manufacturing production spatial data of the PRD from 1987 to 2017 are obtained. The expansion process and spatial pattern are exhibited in Figure 5 below.
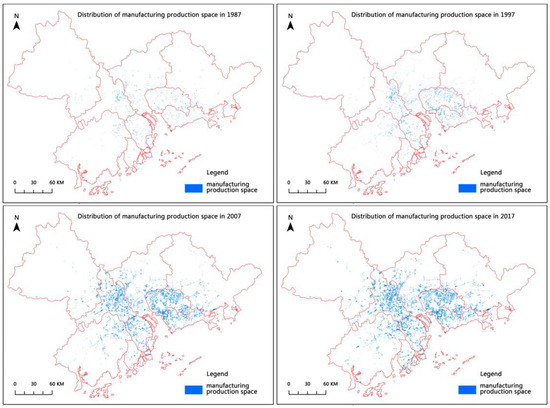
Figure 5.
Spatial distribution of manufacturing production spaces in PRD in 1987–2017.
3.1.2. Expansion Scale of Manufacturing Production Space Evolution
The spatial statistics and analysis of the manufacturing production space scale are conducted by adopting ArcGIS 10.2. The statistical results of the manufacturing production spaces in each city are exhibited in Figure 6 below.
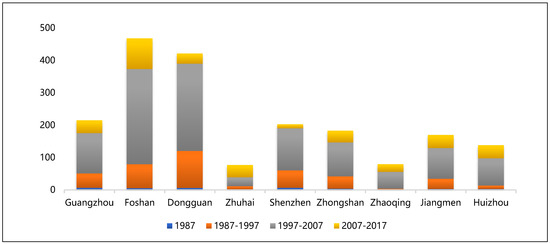
Figure 6.
Statistics of manufacturing production space areas in each city.
From the standpoint of expansion scale, from 1987 to 2017, the scale of manufacturing production spaces in the PRD continued to expand, and the expansion scale and speed of each city were markedly dissimilar. In 1987, 1997, 2007 and 2017, the total area of manufacturing production spaces in the PRD was 37.57 km2, 417.20 km2, 1599.00 km2 and 1953.84 km2, respectively. Among these three stages, the largest growth in the scale of manufacturing production spaces was the second stage. In the decade from 1997 to 2007 (reaching 1181.80 km2), the growth scale of the first stage was similar to that of the third stage. Overall, from 1987 to 2017, the scale of manufacturing production spaces expanded by nearly 51 times within 30 years. In terms of prefecture level cities, Foshan, Dongguan, Guangzhou and Shenzhen were the core growth poles of the expansion of manufacturing production spaces in the PRD, with contribution rates of 24.14%, 21.67%, 10.87% and 10.23%, respectively, totaling 66.91%, while the other five prefecture level cities contributed only 33.09%.
From the standpoint of the density index (that is, the ratio of the manufacturing production space areas to the administrative areas of the city) in each city (Figure 7), the cities in the central core area of the PRD were much higher than those in the marginal area. Especially in 2017, Dongguan’s manufacturing production spaces accounted for the highest proportion, nearly 18%, followed by Foshan, Shenzhen and Zhongshan. Meanwhile, at the current stage, these four cities are also urban areas with a high land development intensity in the PRD. Evaluated by development intensity (that is, the ratio of manufacturing production space areas to the total area of urban built-up areas reflects the development intensity of manufacturing production spaces), Dongguan, Foshan and Zhongshan have exceeded the international warning line (30%) [46]. Consequently, in the future development of urban regional land space, these prefecture level cities should control more the development intensity of manufacturing production spaces and concentrate on ameliorating intensive and efficient development of manufacturing production spaces.
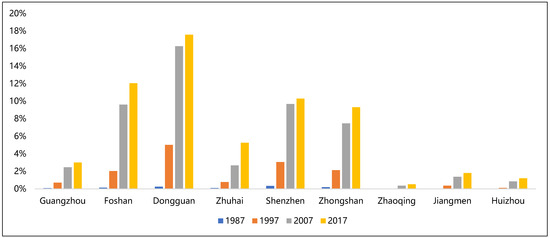
Figure 7.
Density index of manufacturing production spaces in each city from 1987 to 2017.
3.1.3. Expansion Hot Spots of Manufacturing Production Space Evolution
ArcGIS 10.2 is adopted to conduct geostatistical hot spot detection simulations for the expansion scale of manufacturing production spaces in three periods of the PRD, as illustrated in Figure 8. On the whole, from 1987 to 2017, the expansion hot spots of manufacturing production spaces in the PRD were predominantly concentrated in the core areas on both sides of the Pearl River Estuary. Apart from that, its peripheral areas were the main expansion cold spots. In general, its spatial expansion exhibited a distribution pattern of “core hot spots/peripheral cold spots”. Among them, the uppermost core of the expansion of manufacturing production spaces are distributed in the Nanhai District of Foshan, Shunde District and in most areas of Dongguan.
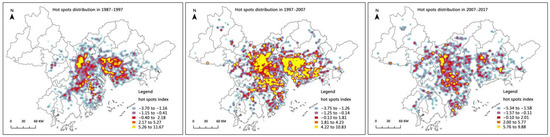
Figure 8.
Hot spots distribution of manufacturing production space expansion in 1987–2017.
We analyze the spatial expansion hot spots in diverse stages. From 1987 to 1997, the polarization characteristics of the expansion of manufacturing production spaces in the PRD were comparatively noticeable. The most vital expansion hot spots were chiefly distributed in the following areas: Guangzhou development zone, Baiyun district, Nanhai district of Foshan, Northwest Zhongshan, most areas of Dongguan, the border area between Shenzhen and Dongguan, etc. Weak expansion hot spots are prevalently distributed in the periphery of the PRD, which demonstrates the expansion scale of manufacturing production spaces in the core area as “indomitable”, and the expansion scale of manufacturing production spaces in the periphery area as “blooming everywhere”. From 1997 to 2007, the polarization characteristics of manufacturing production space expansion were not conspicuous. The expansion hot spots in the central area of the PRD were very high, forming a continuous expansion hot spot. This stage is the fastest development period of manufacturing production spaces in the past three decades. The hot spot, high value, scope and quantity of manufacturing production space expansion have reached the highest level. From 2007 to 2017, the polarization effect of the expansion of manufacturing production spaces in the PRD had markedly weakened, and the scope of the expansion hot spots was strikingly reduced. Compared with the previous two stages, the expansion hot spots of manufacturing production spaces in the core areas of Pearl River Delta decreased the most, and many areas even became cold spots, such as the western region of Dongguan, The core area of Shenzhen and Guangzhou. At this stage, the expansion hot spot high-value areas are mostly distributed in the periphery of the core city, especially in the east of Nanhai District of Foshan City, the periphery of Guangzhou City and most areas at the junction of Jiangmen City and Zhongshan City. Simultaneously, the peripheral prefecture level cities of the Pearl River Delta, such as Zhaoqing City as well as a few counties and cities of Hezhou City, are also expansion hot spot high-value areas.
3.2. Evolution Characteristics of Manufacturing Production Spaces in the PRD
3.2.1. Expansion Speed and Expansion Strength
In accordance with Formulas (1) and (2), we calculate the expansion speed and expansion strength (Table 2). Since 1987, the overall expansion speed of manufacturing production spaces in the PRD has displayed the following characteristics: the slow rise in the first stage, the speedy development in the second stage and the gradual slowdown in the third stage. The average annual expansion rate of the first two stages exceeded 10%, while the expansion rate of manufacturing production spaces decreased remarkably after 2007. As further combined with the expansion scale of manufacturing production spaces in various cities in the PRD in Figure 6, the cities with the highest expansion scale in the three stages are basically the cities in the core area of the PRD, such as Shenzhen, Foshan and Dongguan. The cities with the fastest expansion speed are those in the marginal areas of the PRD, such as Zhaoqing, Jiangmen and Huizhou. For instance, from 1997 to 2007, the expansion speed of manufacturing production spaces in Zhaoqing reached 31.25%, which is the highest among the cities in the same period.

Table 2.
Expansion speed and intensity of manufacturing production spaces in PRD in 1987–2017.
Since 1987, the expansion strength of manufacturing production spaces in the PRD has increased first and then decreased. Cities at all levels were comparatively stable from 1987 to 1997. Then, with the exception of Zhuhai, the expansion intensity continued to increase, other cities increased sharply from 1997 to 2007, when they reached the peak of their expansion strength, and then gradually decreased, from 2007 to 2017.
3.2.2. Coefficient of Variation
The results are displayed in Table 3. Since 1987, the total change index of manufacturing production spaces in the PRD has exhibited a trend of speedy development in the first stage and the second stage, and gradually slowing down in the third stage. With reference to the values of the speed change index, intensity change index and aggregation change index, and in line with the comprehensive change coefficient of manufacturing production spaces in various cities in the PRD, it can be divided into three types. Type 1 is the “dramatic change type”, and its comprehensive variation coefficient I is greater than or equal to 1000; Type 2 is the “slow change type”, and its comprehensive variation coefficient I is greater than 100 and less than 1000; Type 3 is the “stable type” and its comprehensive variation coefficient I is less than or equal to 100.

Table 3.
Comprehensive change coefficient and change type of the manufacturing production space increments in the PRD in 1987–2017.
From the viewpoint of the three stages as a whole, most cities in the first stage and the second stage are of the “dramatic change type” and “slow change type”, while all cities in the third stage are of the “stable type”. As a result, by concentrating on the changes of cities from 1987 to 2007, it is found that Foshan and Dongguan are the prefecture level cities with the most drastic changes, and Shenzhen changed sharply from 1987 to 1997. Most of the other cities are of the “slow change type”, except for Huizhou and Zhaoqing, which were of the “stable type” from 1987 to 1997.
3.2.3. Fractal Dimension and Stability
Through ArcGIS 10.2, the attribute values of patch area (A) and perimeter (P) of the manufacturing production spaces in four years of the cities in the PRD are extracted, the double logarithm relationship scatter map of perimeter area (P-A) of the manufacturing production space patch is established (as described in Figure 9), and the linear regression analysis is carried out. Then, we calculate the form compactness index and stability index of the manufacturing production spaces on the basis of Formulas (9) and (10) (Table 4).
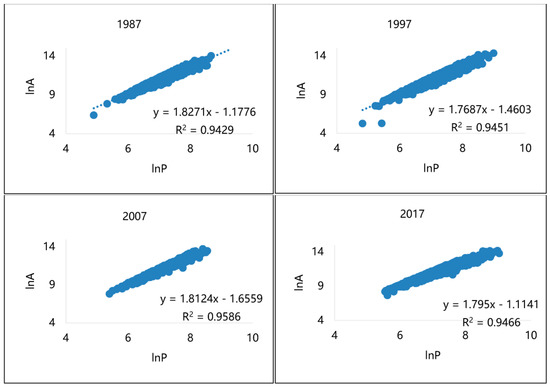
Figure 9.
P-A diagram of the manufacturing production spaces in the PRD in 1987–2017.

Table 4.
Fractal dimension and stability index of the manufacturing production spaces in 1987–2017.
In accordance with the P-A relationship model of the patch spatial form of manufacturing production spaces in Figure 9, the overall manufacturing production spaces in the PRD passed the significance test from 1987 to 2017, and has strong fractal characteristics. As further revealed by Table 3, that the fractal characteristics of each stage are dissimilar. From 1987 to 1997, the fractal dimension of the manufacturing production spaces in the PRD gradually increased, then decreased from 1997 to 2007, and continued to decrease from 2007 to 2017. From 1987 to 1997, the stability index of the manufacturing production spaces in the PRD decreased, then tended to increase from 1997 to 2007, and also maintained a high level from 2007 to 2017.
This suggests that during the period from 1987 to 2007, the manufacturing production spaces were mostly external expansions, and the expansions demonstrate the characteristics of disorder. During this period, as analyzed by the indicators in Table 4, the shape of the manufacturing production spaces tends to be more unstable, and the degree of irregularity and fragmentation are increasing. While from 2007 to 2017, the expansion of the manufacturing production spaces in the PRD were primarily filled with marginal areas. During this period, as revealed by the indicators in Table 4, the patch spatial form of manufacturing production spaces generally tended to be simple, regular and neat, and the spatial shape was more stable. The increase of the manufacturing production space areas were predominantly filled by marginal areas, which also reflected that the expansion of manufacturing production spaces in the PRD global city region began to be progressively controlled by planning, which was more standardized and orderly.
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison of the Manufacturing Production Space Evolution of Global City Region between China and the Western Countries
4.1.1. Evolution Pattern of the Manufacturing Production Spaces in the PRD Global City Region
Previous studies on the spatial evolution of the manufacturing industries in the Pearl River Delta were mainly based on economic statistical data and they used cities as statistical units to build manufacturing spaces [63,64,65]. These studies could not explore the spatial patterns and evolution characteristics of manufacturing physical entity spaces. The spatial continuity of manufacturing industries is not good enough, and cannot accurately depict the spatial evolution characteristics of manufacturing industries on the micro-scale. In addition, some previous studies on the spatial evolution of manufacturing industries in the Pearl River Delta paid more attention on the industrial characteristics with few discussions on the underlying spatial relationships. The spatial evolution of manufacturing industries was not linked to the spatial development of different cities, just from the perspective of industries discussing the agglomeration characteristics of manufacturing industries in the Pearl River Delta, as a whole [66], or discussing the overall industrial structure adjustment of the Pearl River Delta from the perspective of industry [67]. This study summarizes the evolution pattern of manufacturing production spaces in the PRD global city region from three aspects: the expansion speed and intensity, the expansion hot spot pattern and the morphological agglomeration.
① Since 1987, the expansion speed and intensity of manufacturing production spaces in the Pearl River Delta region has presented distinct patterns in three stages: a trend of slow development in the first stage, a speedy development in the second stage, and a trend of gradual slowdown in the third stage. From 1987 to 1997, Foshan and Dongguan, as prefecture-level cities, have developed most speedily, and Shenzhen has also developed speedily with great changes from 1987 and 2007. By contrast, most of the other cities have developed slowly. Only Huizhou and Zhaoqing have developed moderately without much change from 1987 to 1997. ② The expansion hot spot pattern of manufacturing production spaces in the PRD has continued to evolve, and evolution patterns of the three stages are noticeably dissimilar in times and space. Above all, the expansion hot spots of manufacturing production spaces are primarily distributed in the core area of the Pearl River Delta, and most of the “less hot” spots and the cold spots are distributed in the periphery. Thus, the pattern can be characterized as “hot spots at the core and cold spots in the periphery”. Under this pattern, the most essential core area refers to the Nanhai district, Shunde district and most areas of Dongguan in Foshan with the highest development intensity and development level of manufacturing production in the PRD. In terms of spatial expansion, the hot spots in the three time stages are conspicuously distinct. The centralization of expansion hot spot areas of manufacturing production spaces is tremendously noticeable in the early stage, while the centralization becomes weaker gradually in the later stage. Initially, there are hot spots in the periphery of the PRD, but a few areas have changed from hot spots in the early stage to cold spots later. In the third stage, the number and scope of hot spots in the periphery areas of the PRD have increased, but most of them are actually weak hot spots. ③ Since 1987, the morphological agglomeration of manufacturing production spaces in the PRD has exhibited conspicuous differences, in terms of the stages and the spatial heterogeneity. The manufacturing production spaces tend to be fragmented and complicated in the first two stages, while the patched pattern tends to be stable in the third stage, and it is predominantly concentrated in the periphery area. That is to say, the manufacturing production spaces in the global city region of the PRD is controlled in a better way through planning that results in a more standardized and orderly pattern.
4.1.2. Comparison of the Evolution Pattern of the Manufacturing Production Spaces in the City Region between China and Western Countries
The evolution characteristics of manufacturing production spaces in city regions are different between China and Western countries (see Figure 10).
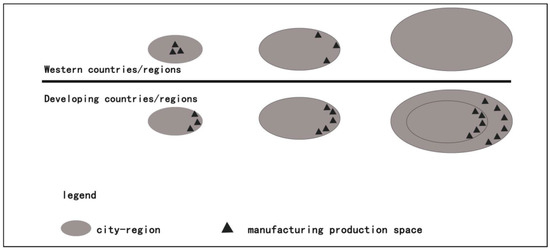
Figure 10.
Comparison diagram of the evolution patterns of manufacturing production spaces in city regions between China and Western countries.
In the early stage, the manufacturing production spaces in Western countries are largely distributed in the core cities, and then gradually move to the peripheral areas of the cities, and then further move to the developing countries. As revealed by the study, the manufacturing production spaces of the developing countries have expanded speedily in the past three decades. Prior to the reform and opening up, some core cities, such as Guangzhou, have experienced the transfer of manufacturing industries from the core cities to the periphery, and then to other cities in the PRD. It is noteworthy that the evolution process of manufacturing production spaces in most other cities in the PRD differs from that in Western countries. In the initial stage, there is not much manufacturing production space in the core cities of the PRD, during which the manufacturing production spaces were largely distributed in the peripheral areas of the core cities, some typical manufacturing cities and marginal township areas. Unlike in Western countries, the manufacturing production spaces at this stage are chiefly distributed in the internal areas of the core cities. In the phase of high-speed development, the manufacturing production spaces are further expanded at a higher density and speed in the PRD, on the basis of its original pattern. Unlike in Western countries that began to experience the process of deindustrialization in this period, the periphery of the world’s cities in developing countries at this stage were still high-value areas for the expansion of manufacturing production spaces. In the phase of slowdown and transformation, although the manufacturing production spaces in the PRD global city regions gradually approached a state of saturation, a large part of the region still maintained expansion hot spots of manufacturing production spaces. This demonstrates that most businesses in the process of production and processing are still in the global city region of the PRD. The distribution of manufacturing production spaces differs from that in Western countries, which have finished the process of deindustrialization and moved their manufacturing production spaces to developing countries. It has cost about one hundred years for Western countries to complete the process of industrialization and deindustrialization. Nevertheless, the developing countries have basically completed the process of industrialization within only 20 to 30 years since the new international division of labor was introduced. This illustrates that the new round of capital cycle has not only accelerated the process of the evolution of manufacturing production spaces, but has also enlarged the regional differences.
There are similarities, in terms of the spatial evolution of manufacturing production spaces in city regions between China and Western countries in diverse historical periods. As pointed out by Hall [68], a host of important business activities occurred in a few top cities (called “world cities”) in Europe in the mid-20th century before the launch of the new global division of labor. In the inner space of world cities, the industrial system was completed, the division of labor in the region was clear, and a lot of manufacturing production spaces were distributed in their surrounding areas. Nevertheless, with the development of the new international division of labor, the manufacturing production spaces were decentralized and started to move to the developing countries. In our study, since the mid-1980s, the process of economic globalization has accelerated, and manufacturing production activities around the world began to gather in the PRD. The function of controlling and serving manufacturing production activities began to gather in the international metropolis at the core of the PRD. With the speedy development of the knowledge economy, the technology of transportation and communication has ameliorated quickly, which gives rises to the compression of geographical distance and time spending. Hence, the controlling and serving functions in the core areas of PRD have begun to spread to the global city region, and a new spatial agglomeration node has formed. Near the new spatial agglomeration node, an augmenting number of manufacturing production spaces with close industrial ties have gathered, which have the function of the post-Ford regional production platform of global market competition. As a consequence, driven by the new round of global capital after the new international division of labor, the global city region of the developing countries is actually the upgraded version of the scale of world cities before the new international division of labor, such as the PRD global city region.
4.2. Comparison of the Manufacturing Production Spaces Influencing Factors of Global CityRegions between China and Western Countries
4.2.1. The Factors Affecting the Evolution of the Manufacturing Production Spaces in the PRD
The evolution of manufacturing production spaces in the PRD have been driven by the production factors, such as capital, labor force, land and systems under the control of nations, local governments, enterprises, individual and other principal bodies, and the pivotal degree of each factor varies in diverse stages. Hence, at distinct stages, the primary factors affecting the evolution of manufacturing production spaces are dissimilar, as exhibited in Figure 11.
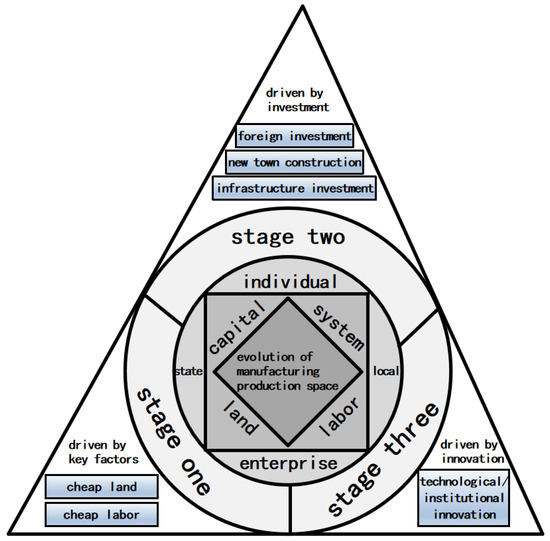
Figure 11.
Analysis of the driving mechanism of manufacturing production space evolution.
The initial stage was driven by the key production factors (1987–1997). With the rural industrialization and the establishment of market economy system, it has promoted the agglomeration and expansion of manufacturing production spaces in the PRD from 1987 to 1997 [69]. Relying on the geographical advantages of being next to Hong Kong and Macao, as well as the comparative advantages of low costs on land and labor force, the PRD actively undertakes the transfer of labor-intensive companies and factories enterprises in Hong Kong and Macao. Through the development mode of “front store and back factory”, a multitude of townships have led industrial parks with the “OEM production” concept, as the predominant mode [53,70]. During the high-speed development stage driven by investment (1997–2007), large amounts of cheap land and low-cost of labor forces were no longer advantageous and could not adapt to the new development demands. As a consequence, a new mode of ameliorating inputs of capital, infrastructure and talent cultivation, were created, which could be further divided into two phases [71]. In the first period, the development zones and foreign direct investment were the primary factors for the spatial manufacturing production spaces in the PRD from 1997 to 2001 [72]. In the second period, the establishment of new towns and areas, the construction of transportation infrastructure and the implementation of industrial transfer policies boosted the manufacturing production spaces in the PRD from 2002 to 2007 [71]. The slowdown and transformation stage were driven by innovation (2007–2017). Under the influence of the global financial crisis in 2008, the manufacturing enterprises in global city regions in the PRD started to seek new opportunities. The innovative development model focused its attention on planning, talent, innovation, knowledge and other factors that have become the trend of development for the PRD global city region [21]. The manufacturing industries in the PRD global city region have entered into a period of slowing down and transforming, which suggests that the manufacturing production spaces tend to be developed in a more compacted and intensive way. Moreover, industrial planning tends to follow the direction of the sustainable development of the industrial ecosystem.
4.2.2. Comparison of the Influencing Factors of Manufacturing Production Space Evolution in City Regions between China and Western Countries
In the middle of the 20th century, the new international division of labor had not begun. Thus, the industrial system of the world cities and their surrounding regions in Western countries was complete and had a wide range of manufacturing production spaces [68]. As the new international division of labor deepened, the PRD attracted global manufacturing businesses. Furthermore, the improvement of transportation and information technology has given rise to the compression of geographical distance and time spending. Hence, the manufacturing production spaces with close industrial ties that are closely connected gather in the polycentric spatial nodes of urban areas in the PRD [5], which has become a competitive global production platform in the post-Ford era [7,8]. Consequently, under the new round of global capital circulation, the evolution pattern of manufacturing production spaces in global city regions of developing countries has a scaled-up version of that in Western countries before the new international division of labor, from the standpoint of evolutionary economic geography. While there were some similarities and differences in the driving factors of manufacturing production spaces.
In the speedy development stage of industrialization, no matter in which developing country [72] or in Western countries [73], the degree of industrialization and urbanization of the region greatly affected the development of manufacturing production spaces. Especially the level of urban infrastructure, such as highways and railways, which conduct a positive role in pushing urban economy and manufacturing enterprises ahead. The differences in driving factors of the manufacturing production spaces are expounded as follows. The manufacturing production spaces in world cities and the surrounding areas in Western countries have predominantly been driven by domestic internal capital before the launch of the new international division of labor. On account of the underdeveloped computer information and transportation logistics, the activities of manufacturing enterprises were primarily limited to regional internal contacts. Nowadays, with the speedy development of information technology and internet of things technology, a global production network has formed. The development of manufacturing production spaces in the global city regions of developing countries have been driven by both domestic investment and foreign investment, as well as with the close connection of other global city regions in the world with transnational manufacturing enterprises as the carrier.
4.3. Some Policy Implications and Limitations of the Study
In accordance with the analysis on the spatial distribution and evolution characteristics of manufacturing production spaces at dissimilar scales in the actual situation, it can provide policy reference for intensive and optimal regulation of manufacturing production spaces. The main policy suggestions are summarized as follows: ① For the intensive and optimal regulation of manufacturing production spaces, instead of simply promoting or restraining the optimization control of manufacturing production spaces, the local governments conduct precise regulation in line with the actual space distribution and development mechanism of manufacturing production spaces in diverse cities, the development characteristics of manufacturing industries in Western countries can be referred to in policy formulation as well; ② The cities from the PRD global city region can refer to the development experience of global cities in Western countries: The arrangement of APS with high industrial added value and control functions should be promoted while the “three high” manufacturing enterprises (i.e., high pollution, high energy consumption and high emissions) need to be restricted; ③ For the typical manufacturing cities of the PRD global city region, it is essential to strictly control the areas with an intensity of manufacturing development of over 30%, to actively apply the stock space of manufacturing production spaces in this region, and lessen the extensive utilization mode; ④ For the peripheral cities of the PRD global city region, the local government should not only effectively control the development intensity of manufacturing production spaces, but also forcefully encourage the enterprises to ameliorate the technology and seek for innovation-driven development. In consideration of our findings, it is paramount that we spell out the limitations. Above all, this paper makes nothing more than a qualitative analysis of the influencing factors of manufacturing production spaces in the PRD. In the future, relevant index systems and models can be constructed to give a quantitative explanation, so as to explore the driving mechanism of manufacturing production spatial evolution in the PRD. Apart from that, the internal connection between manufacturing production spaces and industrial transformation and upgrading, the interactive coupling between manufacturing production spaces and globalization, as well as the optimization and regulation path of manufacturing production spaces are also topics that need further exploration in the future.
5. Conclusions
Evolution and the influencing factors of manufacturing production spaces in the global city regions of China are influenced from the West, attracting attention to accurately identify and analyze the real and continuous distribution of manufacturing production spaces, on basis of the actual situation of the region. It is necessary to provide policy guidance for the accurate planning and regulation of manufacturing production spaces in China’s global city regions. This paper principally studies the evolutionary characteristics and relevant influencing factors of manufacturing production spaces in the global city region in the PRD since the mid-1980s. Subsequently, it compares the similarities and differences of evolutionary characteristics as well as influencing factors of manufacturing production spaces in global city regions between Western countries and China. From the perspective of global to local, by summing up the evolution mechanism of manufacturing production spaces in China’s global city regions, we have enriched the application practice of the global city region theory in the global Southern countries, and revealed the local characteristics of manufacturing shaping the regional spatial structure.
The evolutionary characteristics of manufacturing production spaces in global city regions in China are strikingly different from those in Western countries. Given the further advancement of transportation and communication, the manufacturing production spaces in the developing countries are principally distributed in secondary cities in global city regions (i.e., the typical manufacturing cities), and then spread to the peripheral cities. This thoroughly differs from the pattern of Western countries in 1950s, during which the manufacturing production spaces in Western countries are predominantly distributed in the core cities, and gradually spread to the peripheral areas, and then move to the developing countries.
The evolution of manufacturing production spaces in the global city region of PRD and the mechanism of its interaction with urban regional factors are the dynamic processes, which are affected by the market environment globally, the policies of local government and the regional comprehensive factors. It presents dissimilar feathers in diverse stages. The influential factors have been changed from production factors driven in initial the stage to investment factors driven in the high-speed development stage and then to innovation factors in the slowdown and transformation stage.
The factors affecting the spatial distribution of manufacturing production in city regions of China and Western countries are similar in distinct historical periods and regions, which involve the level of urbanization and industrialization, the local government-level infrastructure investment, etc. Aside from that, in the global city regions of China, the export-oriented globalization still has a paramount role in regional spatial development. Hence, the regulation and future development planning of manufacturing production spaces in the global city regions of China cannot copy the Western experience. The past experience of Western countries can help us to understand and study the mechanism of the spatial evolution of manufacturing production spaces in global city regions of developing countries.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.L. and D.X.; methodology, B.L. and D.X.; software, B.L.; formal analysis, B.L.; writing—original draft preparation, B.L.; writing—review & editing, D.X. and S.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41930646), the Social development science and technology project of Shanghai Science and Technology Commission (No.22dz1202600) and the Scientific Research Program of Shanghai Science and Technology Commission (No.19DZ1203300).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dicken, P. Global Shift: Mapping the Changing Contours of the World Economy; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, R.B. The new international division of labour, multi-national corporations and urban hierarchy. In Urbanization and Urban Planning in Capitalist Society; Dear, M., Scott, A.J., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 1981; pp. 287–315. [Google Scholar]
- Sassen, S. Dispersal and new forms of centralization. In The Global City: New York, London and Tokyo; Princeton University: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1991; pp. 22–35. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, A.J. Regions and the World Economy: The Coming Shape of Global Production, Competition and Political Order; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, P.G. Global City-Regions in the Twenty-first Century. In Global City-Regions: Trends, Theory, Policy; Scott, A.J., Ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2001; pp. 59–77. [Google Scholar]
- Daniels, P.W. Book review: Global city regions: Their emerging forms. Prog. Hum. Geog. 2002, 26, 714–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A.J. Global City-Regions: Trends, Theory, Policy; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, A.J. Globalization and the Rise of City-regions. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2001, 9, 813–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.G.; Hooper, A. Book Review. Urban. Stud. 2003, 40, 631–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pain, K. Examining ‘core-periphery’ relationships in a global city-region: The case of London and South East England. Reg. Stud. 2008, 42, 1161–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Pose, A.; Fitjar, R.D. Buzz, Archipelago Economies and the Future of Intermediate and Peripheral Areas in a Spiky World. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2013, 21, 355–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varis, M.; Tohmo, T.; Littunen, H. Arriving at the Dawn of the New Economy: Is Knowledge-Based Industrial Renewal Possible in a Peripheral Region? Eur. Plan. Stud. 2014, 22, 101–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, V.; Solís, E.; De Ureña, J.M. Beyond the metropolis: New employment centers and historic administrative cities in the Madrid global city region. Urban. Geogr. 2014, 35, 889–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.C.S. Toward a post-socialist city? Economic tertiarization and urban transformation in the Guangzhou metropolis, China. Eurasian Geogr. Econ. 2004, 45, 18–44. [Google Scholar]
- Daniels, P.W.; Ho, K.C.; Hutton, T. Service industries and Asia-Pacific cities: Introduction and overview. In Service Industries and Asia-Pacific Cities: New Development Trajectories; Routledge: London, UK, 2005; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.D. Restructuring for growth in urban China: Transitional institutions, urban development, and spatial transformation. Habitat Int. 2012, 36, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bie, J.B.; Jong, M.; Derudder, B. Greater Pearl River Delta: Historical Evolution towards a Global City-Region. J. Urban. Technol. 2015, 22, 103–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, A.G.O.; Yang, F.F.; Wang, J.J. Producer service linkages and city connectivity in the mega- city region of China: A case study of the Pearl River Delta. Urban. Stud. 2015, 52, 2458–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Kloosterman, R.C. Connecting the ‘Workshop of the World’: Intra-and Extra-Service Networks of the Pearl River Delta City-Region. Reg. Stud. 2016, 50, 1069–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.X.; Derudder, B.; Huang, J.H. Examining the transition processes in the Pearl River Delta polycentric mega-city region through the lens of corporate networks. Cities 2017, 60, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.Y.; Wu, K.M.; Xie, Y.C.; Huang, G.Z.; Wang, C.J.; Chen, J. How firm heterogeneity affects foreign direct investment location choice: Micro-evidence from new foreign manufacturing firms in the Pearl River Delta. Appl. Geogr. 2019, 106, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.X.B.; Zhang, L. Foreign direct investment and the formation of global city-regions in China. Reg. Stud. 2007, 41, 979–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.F.; Dennis Wei, Y.H.; Pan, F.H. Geographical concentration of manufacturing industries in China: The importance of spatial and industrial scales. Eurasian Geogr. Econ. 2007, 48, 603–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.Y.; Liu, W.D.; Michael, D. State land policy, land markets and geographies of manufacturing: The case of Beijing, China. Land Use Policy 2014, 36, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, J.J.; Xu, W.; Ning, Y.M. Dynamic regional manufacturing agglomeration in the Yangtze River Delta region. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2021, 41, 1773–1782. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.T.; Song, Y.; Qian, S.T.; Zhang, Y. Spatial pattern of manufacturing industry and its impact on air pollution in Northeast China based on enterprise data. Geogr. Res. 2022, 41, 193–209. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.P.; Huang, P.T.; Sun, L.; Wang, Z.H. Spatial evolution and locational determinants of high-tech industries in Beijing. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2013, 23, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.H.; Song, Y.Q.; Zhu, S.Q.; Cheng, X.F. The spatial pattern of Shanghai urban industry based on point data. Geogr. Res. 2015, 34, 1708–1720. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.L.; Yuan, F.; Chen, W. Economic transition and restructuring of manufacturing spaces in urban China: The evidence from Nanjing. Geogr. Res. 2017, 36, 1014–1028. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.B. Spatial Distribution Evolvement Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Automobile Manufacturing Industry under the Guidance of Foreign Investment: A Case Study of Guangzhou. Econ. Geogr. 2019, 39, 119–128. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L.; Zheng, Z.H.; Luo, J.; Jia, Y.Q.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Y.F.; Sun, J. Spatial Agglomeration of Manufacturing in the Wuhan Metropolitan Area: An Analysis of Sectoral Patterns and Determinants. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L. Research on Spatial Evolution Pattern of Advanced Manufacturing under the Effect of Local Policies in Guangzhou City. Areal Res. Dev. 2022, 41, 38–43. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, A.G.O.; Li, X. An integrated remote sensing and GIS approach in the monitoring and evaluation of rapid urban growth for sustainable development in the Pearl River Delta, China. Int. Plan. Stud. 1997, 2, 193–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yeh, A.G.O. A planning support model for sustainable land development using remote sensing and GIS: A case study in the Pearl River Delta. J. Remote Sens. 1999, 3, 215–219. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Yao, D.; Zhen, Y.; Li, W.; Li, K. Mismatched Relationship between Urban Industrial Land Consumption and Growth of Manufacturing: Evidence from the Yangtze River Delta. Land 2022, 11, 1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.H.; Luo, C. volution and Optimization Strategy of Manufacturing Space in Changsha Metropolitan Area since 1990. Econ. Geogr. 2020, 40, 155–163. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.; Yuan, M.; Huang, Y.; Lin, K. Effects of Institutions on Spatial Patterns of Manufacturing Industries and Policy Implications in Metropolitan Areas: A Case Study of Wuhan, China. Land 2021, 10, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deligeer; Yuan, J.D.; Li, Y.Y. The spatial-temporal evolution characteristics of the industrial spatial in Changchun. Econ. Geogr. 2014, 34, 81–86. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.; Wang, K.Y. Spatial pattern and morphological characteristics of industrial production space and influential factors in the Pearl River Delta urban agglomeration. Prog. Geogr. 2016, 35, 610–621. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, F.Y.; Chen, C.; Liu, J.S. Research on the extension characteristics and driving forces of industrial space in Changchun since 1990. Hum. Geogr. 2014, 29, 88–94. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.; Wang, K.Y. Spatio-temporal evolution of industrial production space and its driving mechanisms in Pearl River Delta urban agglomeration. Geogr. Res. 2018, 37, 53–66. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.L.; Yue, W.Z.; Liu, Y.; Fan, P.L.; Wei, Y.H. Suburban industrial land development in transitional China: Spatial restructuring and determinants. Cities 2018, 78, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, C.; Chen, X.; Rong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, B.; Bai, L.; Chen, Q.; Su, Y.; et al. Spatial Identification and Interactive Analysis of Urban Production—Living—Ecological Spaces Using Point of Interest Data and a Two-Level Scoring Evaluation Model. Land 2022, 11, 1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Shen, P.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Feng, Y. Spatial Distribution Changes in Nature-Based Recreation Service Supply from 2008 to 2018 in Shanghai, China. Land 2022, 11, 1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, J. Extracting Network Patterns of Tourist Flows in an Urban Agglomeration Through Digital Footprints: The Case of Greater Bay Area. IEEE Access. 2022, 10, 16644–16654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Xue, D.S.; Tan, Y.M. Deciphering the Manufacturing Production Space in Global City-Regions of Developing Countries—A Case of Pearl River Delta, China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.C. Modern Industrial Geography; China Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 1994. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sit, V.F.S.; Yang, C. Foreign-investment-induced Exo-urbanisation in the Pearl River Delta, China. Urban Stud. 1997, 34, 647–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.D.; Fang, C.L. Quantitative function identification and analysis of urban ecological-production-living spaces. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2016, 71, 49–65. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.F.; Sun, B.D. The spatial pattern of urban production-living-ecological space quality and its related factors in China. Geogr. Res. 2020, 39, 13–24. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Li, S.; Wei, B.; Zhou, X. Characterizing Production–Living–Ecological Space Evolution and Its Driving Factors: A Case Study of the Chaohu Lake Basin in China from 2000 to 2020. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liang, Y.; Ma, S.; Huang, K.; Liu, Y.; Liang, Y.; Ma, S.; Huang, K. Divergent developmental trajectories and strategic coupling in the pearl river delta: Where is a sustainable way of regional economic growth? Sustainability 2017, 9, 1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C. Cross-boundary integration of the Pearl River Delta and Hong Kong—An emerging global city-region in China. In Globalization and the Chinese City; Wu, F.L., Ed.; Routledge Press: London, UK, 2006; pp. 125–147. [Google Scholar]
- Guangdong Burenu of Statistics. Guangdong Statistical Yearbook 2021; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2021. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.H.; Wu, C.J.; Shen, H.Q. A GIS based model of urban land use growth in Beijing. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2000, 55, 407–416. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.Y.; Ge, J.F.; Shen, Y.J.; Chang, C.P.; Liang, Y.Q. Analysis on urban land use sprawl by using GIS: The case of Shijiazhuang city, China. Geogr. Res. 2003, 22, 789–798. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Duan, X.J. The expansion of urbanization area in Yangtze River Detla. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2010, 30, 702–709. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.D.; Zhu, C.G.; Ma, R.H.; Pu, Y.X. Urban spatial growth pattern and its evolution in Suzhou. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2008, 63, 405–416. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Batty, M.; Longley, P. Fractal Cities: A Geometry of Form. and Function; Academic Press: London, UK, 1994; pp. 42–49. [Google Scholar]
- Benguigui, L.; Czamanski, D.; Marinov, M.; Portugali, Y. When and where is a city fractal? Environ. Plan. B 2000, 27, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.G.; Jiang, S.G. Modeling fractal structure of systems of cities using spatial correlation function. Int. J. Artif. Life Res. IJALR 2010, 1, 12–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.H. Mathematical Methods in Contemporary Geography, 2nd ed.; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2002. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.Q.; Yuan, W.; Ma, M.Q.; Yuan, W. Manufacturing industry agglomeration characteristics in the Pearl River Delta and evolution based on growth data. Prog. Geogr. 2018, 37, 1291–1302. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.C.; Fan, J.; Zhang, H.P.; Wang, P.Y. Dynamics of manufacturing industry and change of its spatial pattern in the Pearl River Delta urban agglomeration. Prog. Geogr. 2020, 39, 195–206. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tan, Y.; Xue, D. From World Factory to Global City-Region: The Dynamics of Manufacturing in the Pearl River Delta and Its Spatial Pattern in the 21st Century. Land 2022, 11, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.B.; Li, X.W. Evolution of spatial pattern and influencing factors of manufacturing industries in Guangdong Province. Hum. Geogr. 2017, 32, 95–102. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C. The transformation of foreign investment-induced ‘exo(genous)-urbanisation’ amidst industrial restructuring in the Pearl River Delta, China. Urban Stud. 2020, 57, 618–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, P.G. The World Cities; Heinemann: London, UK, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, D.S.; Xu, X.Q.; Chen, H.G. Xiangzhen industrial development and its local economic influence in the Pearl River Delta–Taking Beijiao in Shunde City as an Example. Hum. Geogr. 1998, 13, 35–39. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, A.G.O.; Yang, F.; Xu, Z.H. Will rural urbanization produce a new producer service space in China? Habitat Int. 2017, 67, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.S.; Jin, W.F.; Shi, C.Y. Development strategy of the Pearl River Delta Urban Agglomeration under the current socioeconomic situation. Prog. Geogr. 2015, 34, 302–312. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.Q.; Li, X. Review and preview of the urbanization in Pearl River Delta in the past 30 years of reform and opening up. Econ. Geogr. 2009, 29, 13–18. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lampard, E.E. The history of cities in the economically advanced areas. In Regional Development and Planning; Friedmann, J., Alonso, W., Eds.; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).