Abstract
Vegetation coverage is important in global landscape change patterns, but research on temporal and spatial dynamic changes and analysis of vegetation landscape pattern is relatively lacking. The present study aimed to investigate the dynamic changes of vegetation coverage in the arid desert region of Northwest China and analyze the characteristics of its center of gravity migration. The normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) and pixel binary model were used to calculate the vegetation coverage to analyze the vegetation distribution characteristics and vegetation migration in the arid desert area in Northwest China in 1990, 1995, 2000, 2005, 2015 and 2020. The results showed that from 1990 to 2020, the proportion of light and severe vegetation coverage in the arid desert region of Northwest China increased, while the proportion of medium vegetation coverage decreased. The distribution types of medium- and high-grade vegetation generally migrate to the southeast and south, which may be mainly due to the humid climate conditions and higher population density in this direction. The vegetation center of gravity migration is mainly concentrated in the southeast-south direction. Vegetation degradation occurs in the northwest region, and vegetation improvement is the main trend in the southeast and south region. The direction of vegetation migration may be affected by precipitation and soil humidity. This study provides a theoretical basis and has certain guiding significance for desertification control, ecological sustainable management, ecological restoration, and protection in the arid desert region of Northwest China.
1. Introduction
As a comprehensive indicator for environmental changes [1], changing of vegetation coverage is closely related to the global material energy, material biochemical cycles and landscape patterns [2,3,4,5]. Using remote sensing technology to study the dynamic changes of vegetation coverage on a large scale can reveal its spatial distribution, which is helpful for protecting the ecosystem [6,7,8]. Vegetation in arid areas is an important part of terrestrial ecosystems, and its changes play an important role in improving the living conditions of organisms in this area and controlling desertification [9]. Therefore, elucidating the temporal and spatial changes of vegetation coverage in arid areas and analyzing the influencing factors of vegetation migration have important theoretical and ecological significance for evaluating the quality of habitats in arid areas [10].
The arid desert region of Northwest China is located in the hinterland of Eurasia in the mid-latitude zone, and its geographical location is extremely important and plays a central role in the national ecological security barrier [11]. Shortened by NDVI, normalized difference vegetation index is generally used to anticipate the vegetation dynamics in space and time scales [12]. Studies demonstrated that the NDVI has a positive relationship with annual mean precipitation and temperature [13]. The arid desert region of Northwest China particularly lacks water and is sensitive to global climate change (e.g., increasing temperature) and human activities (e.g., coal mining). It was demonstrated that the arid desert region of Northwest China is under increasing temperature and precipitation [14]. Previous research and analysis on the arid desert region of Northwest China mainly focused on the plants, animals, climate, deserts, and driving factors of desertification in the region [15,16,17,18,19,20]. Until now, research on temporal and spatial dynamic changes and analysis of vegetation landscape pattern is relatively lacking. Therefore, it is particularly important to study the changes of vegetation coverage and perform landscape pattern analysis in the arid desert regions of Northwest China.
Taking the arid desert region of Northwest China and based on a dataset of seven periods in 1990 to 2020, we carried out analysis using normalized vegetation index and pixel binary model. By calculating the vegetation coverage in different periods, this study aimed to reveal the dynamic characteristics of the temporal and spatial pattern of vegetation in the past 30 years and understand the regularity of vegetation restoration from the perspective of landscape pattern changes to provide certain guidance for desertification control, ecological restoration and protection, and ecological sustainable management.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The arid desert area of Northwest China is located in the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, the Hexi Corridor of Gansu, the northwest of Qinghai and Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, and the entire Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region and the Altay Mountains and national borders (Figure 1) [15,20]. The water resources in this area are extremely scarce and the average annual precipitation is below 200.00 mm, but the annual average potential evapotranspiration is as high as 1216.39 mm. The vegetation is dominated by grasslands, with a small amount of arbor and shrub forests sporadically scattered [21]. The living environment is extremely harsh, the ecology is fragile, wind erosion is serious, vegetation is sparse and of single type, and vegetation coverage is low; thus, suitable conditions are needed for vegetation restoration [22].
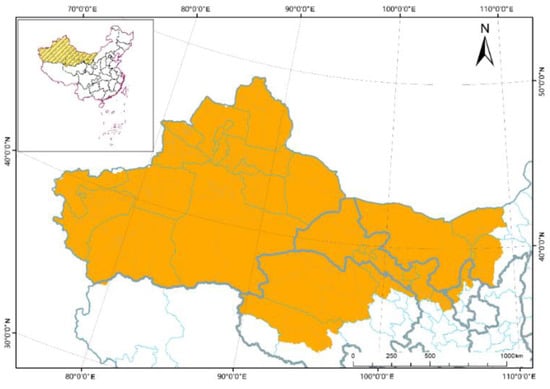
Figure 1.
Map of arid desert areas in Northwest China.
2.2. Data Source
This study uses the latest v1 global-scale data of the GIMMS NDVI 3g dataset released by NASA’s Global Monitoring and Modeling Study Group (GIMMS), with a time span from 1990 to 2020, a temporal resolution of 15 days, and a spatial resolution of 8 km. These data are widely used in the study of regional large-scale vegetation changes. In order to further reduce the influence of factors such as atmospheric, cloud, and solar altitude angle changes, the maximum value composite method was used to obtain the annual normalized vegetation index NDVI raster dataset, and the ArcGIS 10.3 was used based on the arid desert area of Northwest China. Boundary batch extraction was used to obtain the annual NDVI dataset from 1990 to 2020 in the study area.
2.3. Data Analysis
- Vegetation coverage calculation and classification
The normalized vegetation index (NDVI) is one of the important criteria to test the quality of vegetation growth [23,24]. Studies have found that NDVI has a significant positive correlation with vegetation coverage. Therefore, NDVI is combined with the pixel binary model to estimate vegetation coverage [6,25,26]. The calculation formula is as follows [27,28]:
In Equation (1), FVC is the vegetation coverage; NDVI is the vegetation index; NDVIsoil is the vegetation index of bare soil or no vegetation coverage; NDVIveg is the vegetation index of pure vegetation pixels; NDVIveg and NDVIsoil take the maximum and minimum values within the confidence interval of the given confidence; and the values of NDVIveg and NDVIsoil take the corresponding values when the cumulative frequency is 95.00% and 5.00%, respectively.
According to the “National Technical Regulations on Desertification and Sandification Monitoring” (revised in 2019) in combination with the specific conditions of the arid desert region of Northwest China, the vegetation coverage is divided into four levels: light coverage (≤10%), moderate coverage (10–25%), high coverage (25–40%), and severe coverage (40–100%) (Table 1).

Table 1.
Classification of vegetation coverage in arid desert regions of Northwest China.
- Analysis of dynamic change of vegetation coverage
The interpolation method is used to interpolate the vegetation coverage in different periods, and the calculation formula is as follows [29]:
In Equation (2), Fc is the vegetation coverage at the previous time point; Fc−1 is the vegetation coverage at the later time point; the difference ΔF can be classified into six grades: severe degraded as −1 ≤ ΔF ≤ −0.15, moderate degraded as −0.15 ≤ ΔF ≤ −0.05, mild degradation is −0.05 < ΔF ≤ 0, mild recovery is 0 < ΔF ≤ 0.05, moderate recovery is 0.05 < ΔF ≤ 0.15, and high recovery is 0.15 < ΔF ≤ 1.
- Vegetation center of gravity migration model
The vegetation center of gravity migration model is the regional weighted average center. By comparing the change in trajectories of the center of gravity of vegetation, temperature, and precipitation, the spatial distribution pattern of each element is found, and the relationship between the three changes is revealed [30]. Many scholars use the center of gravity migration model to calculate the changes of vegetation, land use, soil erosion, and other factors and to analyze the vegetation change trend in the spatial range [31]. The calculation formula for the migration of a certain vegetation type in the t year is as follows:
In Equation (3), Xt and Yt are the longitude and latitude coordinates of the barycenter of a certain vegetation type in year t; n is the number of patches of this vegetation type in year t; Cti is the area of the ith patch of this vegetation type in year t; Xti and Yti are the ith patch of this vegetation type in year t; and the geometric center coordinates of the ith patch of the vegetation type in year t.
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Vegetation Coverage Changes
Based on pixels with a resolution of 8 km, a time series change analysis of the change in trend of vegetation coverage from 1990 to 2020 was carried out through the pixel binary model, and different levels were divided to obtain the distribution of vegetation coverage in the arid desert region of Northwest China in different periods (Table 2, Figure 2). This study selects seven periods of vegetation coverage data analysis in 1990, 1995, 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2020. The results show that from 1990 to 2020, the grade I vegetation coverage first increased and then decreased, with the largest area in 2005 of 1,646,998 km2, which accounted for 54.45%; the vegetation coverage of grade II was opposite to that of grade I and exhibited a trend of first decreasing and then increasing (Table 2). The vegetation coverage area reached the maximum in 1990, which was 407,997 km2, and then continuously decreased to the lowest level in 2000 and then began to rise; the overall vegetation coverage of grade IV did not change much. Compared with 1990, the area increased to 525,175 km2 after 30 years, thereby accounting for 17.12%. Overall, the proportion of vegetation coverage of grades I and IV in the arid desert region of Northwest China increased from 1990 to 2020, while the proportion of vegetation coverage of grades II and III decreased, thereby indicating that the difference in vegetation coverage increased.

Table 2.
Vegetation coverage area and changing rate from 1990 to 2020.
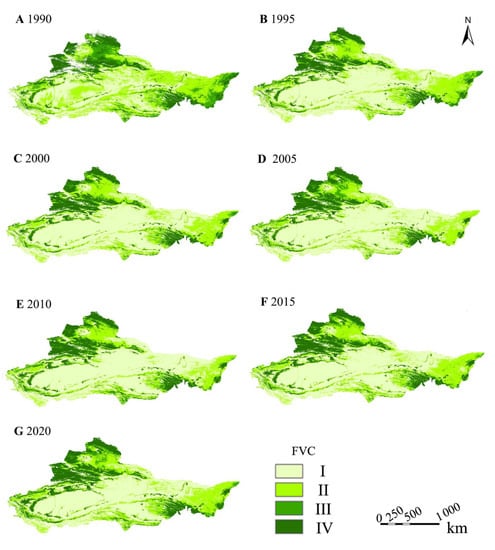
Figure 2.
Classification map of vegetation coverage from 1990 to 2020.
The vegetation coverage under different degradation degrees changed during the targeted years for different patterns (Figure 3). During 1990–1995, the vegetation under severe degradation was dominant, but from 1995 to 2010, the vegetation under mild degradation, mild, moderate, and high recovery was dominant. Particularly, the vegetation under moderate and severe degradation was mainly located at the border of the arid desert region of Northwest China during 1995–2005 but was mainly located in the northern and southern regions during 2005–2010 and in the southern part during 2010–2015, respectively.
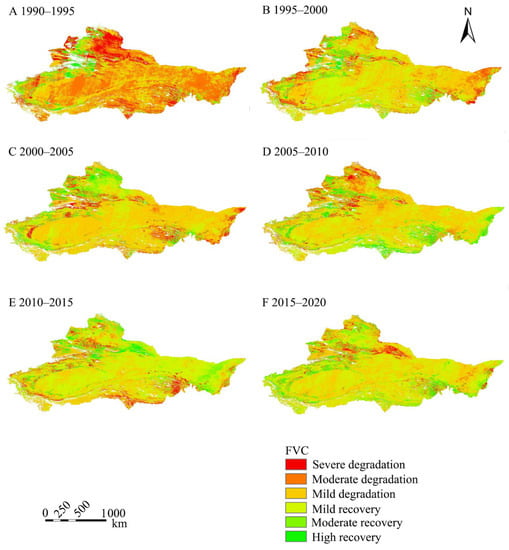
Figure 3.
Variation map of vegetation coverage in the arid desert region of Northwest China.
Vegetation coverage under different grades in the arid desert region of Northwest China showed varying change during 1990–2020 (Figure 4). In 1990, the area of grade II was the highest, followed by grades I, III, and IV. Since 1995–2020, the area of grade I is the highest, followed by grades II, III, and IV. For grades I and III, the area of vegetation coverage increased with time. Meanwhile, the area of vegetation coverage decreased during 1990–2020 for grades II and IV.
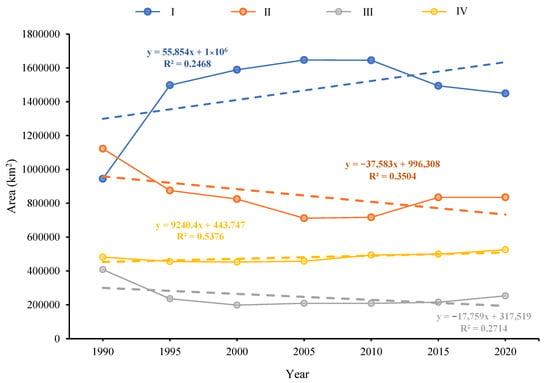
Figure 4.
Variation curve of vegetation coverage area of different grades in the arid desert region of Northwest China from 1990 to 2020.
3.2. Shifting Law of Vegetation Coverage Gravity Center
Using the vegetation center of gravity migration model, the changes of the center of gravity coordinates of the five types of vegetation cover in different periods in the arid desert region of Northwest China were calculated, and the spatial changes of each center of gravity in the study area from 1982 to 2015 were plotted according to the results. The results are shown in Figure 5. The low vegetation coverage area migrated from the central region to the northwest and southeast. Specifically, the vegetation center of gravity migrated to the southeast from 1982 to 2005, and the migration distance was approximately 25.34 km; from 2005 to 2015, it migrated to the northwest with migration distance of approximately 17.13 km (Appendix A Table A1). The areas with medium and low vegetation coverage mainly migrated to the southeast, and the migration distances in the two periods from 1982 to 1994 and 1994 to 2015 were approximately 99.37 and 222.60 km, respectively. The areas with medium vegetation coverage mainly migrated to the southwest and south. The vegetation coverage migrated approximately 66.34 km to the southwest during 1982–2005, and approximately 29.50 km to the south from 2005 to 2015. The area of medium and high vegetation coverage mainly migrated to the south, southwest, and southeast, and the migration distances to each direction were approximately 34.09, 38.97, and 25.89 km, respectively. The areas with high vegetation coverage mainly migrated to the north and southeast, of which approximately 31.60 km was northward from 1982 to 1994, and approximately 140.58 km was to the southeast from 1994 to 2015. In general, except for areas with low vegetation coverage, the rest of the vegetation distribution types generally migrated to the southeast and south (Appendix A Table A2). This may be attributed to the relatively humid climate conditions and higher population density in this direction.
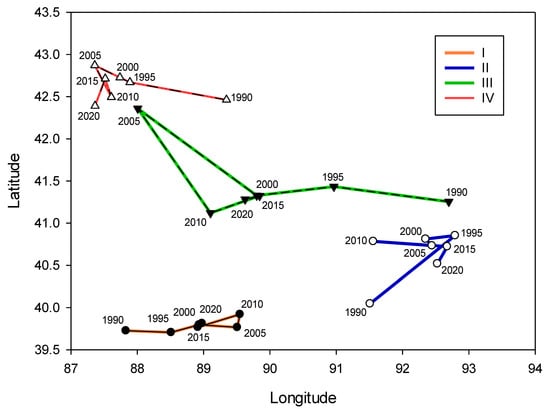
Figure 5.
Migration of center of gravity of vegetation coverage in the arid desert region of Northwest China.
4. Discussion
The vegetation distribution, spatial variation characteristics, and vegetation migration trends in the arid desert region of Northwest China in 1990, 1995, 2000, 2005, 2015, and 2020 were analyzed using the NDVI and pixel binary model. The results show that from 1990 to 2020, the proportion of slight and severe vegetation coverage in the arid desert region of Northwest China increased, while the proportion of moderate vegetation coverage decreased. The distribution types of moderate- and high-grade vegetation generally migrate to the southeast and south. It is apparent that the migration of vegetation center of gravity is mainly concentrated in the southeast-south direction. Vegetation degradation occurs in the northwest region, and vegetation improvement is the main trend in the southeast and south. The direction of vegetation migration may be affected by precipitation and transpiration of the arid desert region of Northwest China.
As one of the most sensitive areas to climate changes and anthropogenic activities [14,32], the arid desert region of Northwest China was characterized by increasing slight and severe vegetation coverage but decreasing in moderate vegetation in this study (Table 2, Figure 2). This indicates that changing vegetation coverage started to polarize, i.e., the vegetation coverage became either slight or severe grade. The growth of vegetation is tightly controlled by climate change including precipitation and temperature. The precipitation of the arid desert region of Northwest China was demonstrated to have an increasing trend from southeast to northwest [14]. Meanwhile, the temperature in the arid desert region of Northwest China increased by approximately 0.3 °C per decade in the past 50 years [33]. The polarized vegetation change could have resulted from the fast-increasing precipitation and temperature [34,35]. Moreover, vegetation degradation was severe in the northwest, and vegetation improvement was mainly centered to the south and southeast. Studies showed that the annual average of precipitation and humidity index in the arid desert region of Northwest China turned to the southeast during 2010–2019 [31], which is the same as the trend of vegetation improvement. Thus, the vegetation improvement in southeast and south could result from the improvement of precipitation and humidity [14,21]. The south and southeast (Inner Mongolia and Qinghai province) have greater population and subsequent anthropogenic activities, which could also lead to higher vegetation improvement by farming, planting trees and grasses for a better living environment.
In this study, 30 years’ data from 1990 to 2020 were analyzed to accurately grasp the changes in vegetation coverage and the migration of the center of gravity at different times in the study area. Currently, most scholars’ data for landscape pattern analysis come from the interpretation of remote sensing images [36,37,38]. Although the accuracy of remote sensing image interpretation can be guaranteed to a certain extent by calculating the interpretation accuracy, there are still errors [39]. Therefore, in future research, remote sensing images with longer research time span, shorter time interval, higher resolution, and higher-precision vegetation index model should be selected to carry out corresponding research to analyze the changes more accurately in vegetation coverage and migration in the arid desert region in Northwest China.
Research on the regional landscape pattern and vegetation structure can also be carried out on a smaller scale. The research area is divided into smaller suitable cells for analysis, which can compensate for the shortcomings of rough analysis of the entire area, and more accurately explore the landscape distribution pattern and vegetation cover dynamics [39,40,41]. In addition, the evolution of the vegetation distribution landscape pattern is the result of the combined effect of natural, socio-economic, and policy factors. Factors affecting vegetation including policy (such as “returning farmland to forests” and “Three-North Shelter Forest Project”), climate (such as global climate change), terrain (such as altitude, slope, and slope aspect), and population should be considered while conducting research [42,43,44,45,46,47,48]. In this study, the increasing of vegetation coverage in southeast and south of the arid desert region of Northwest China is helpful to formulate long-term effective desertification control, ecological restoration and protection, and ecological sustainable management.
5. Conclusions
From 1990 to 2020, the proportion of light and severe vegetation coverage in the arid desert region of Northwest China increased, while the proportion of moderate vegetation coverage decreased. The distribution types of moderate- and high-grade vegetation generally migrated to the southeast and south. Our study also found that vegetation degradation occurs in the northwest region, with vegetation improvement being the main trend in the southeast and south.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.L. and H.Z.; methodology, X.L.; software, D.W.; validation, X.L., W.X. and T.Z.; formal analysis, X.L.; investigation, X.L.; resources, X.L.; data curation, H.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, X.L.; writing—review and editing, X.L.; visualization, T.Z.; supervision, T.Z.; project administration, T.Z.; funding acquisition, T.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National key research and development program, grant number 2017YFC0504400.
Acknowledgments
The two anonymous reviewers are acknowledged for their useful comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Dynamic changes of landscape in arid desert region of Northwest China.
Table A1.
Dynamic changes of landscape in arid desert region of Northwest China.
| Vegetation Coverage Classification | 1990 | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Longitude (°) | Latitude (°) | Longitude (°) | Latitude (°) | Longitude (°) | Latitude (°) | Longitude (°) | Latitude (°) | Longitude (°) | Latitude (°) | Longitude (°) | Latitude (°) | Longitude (°) | Latitude (°) | |
| I | 87.89 | 39.73 | 88.70 | 39.71 | 89.23 | 39.79 | 89.90 | 39.76 | 89.97 | 39.92 | 89.18 | 39.77 | 89.27 | 39.81 |
| II | 91.51 | 40.05 | 92.79 | 40.85 | 92.34 | 40.81 | 92.45 | 40.73 | 91.55 | 40.79 | 92.68 | 40.73 | 92.53 | 40.53 |
| III | 92.67 | 41.28 | 90.92 | 41.44 | 89.79 | 41.35 | 87.97 | 42.38 | 89.09 | 41.13 | 89.82 | 41.35 | 89.61 | 41.30 |
| IV | 89.34 | 42.47 | 87.89 | 42.67 | 87.73 | 42.73 | 87.35 | 42.88 | 87.60 | 42.50 | 87.51 | 42.72 | 87.36 | 42.40 |

Table A2.
Changes in center of gravity of vegetation coverage of different grades in the arid desert region of Northwest China from 1990 to 2020.
Table A2.
Changes in center of gravity of vegetation coverage of different grades in the arid desert region of Northwest China from 1990 to 2020.
| Classification | 1990–1995 | 1995–2000 | 2000–2005 | 2005–2010 | 2010–2015 | 2015–2020 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Distance (km) | Direction | Distance (km) | Direction | Distance (km) | Direction | Distance (km) | Direction | Distance (km) | Direction | Distance (km) | Direction | |
| I | 70.05 | SE | 45.84 | NE | 58.15 | SE | 18.21 | NE | 69.48 | SW | 9.38 | NE |
| II | 140.68 | NE | 37.8 | SW | 12.81 | SE | 76.22 | NW | 96.03 | SE | 25.82 | SW |
| III | 148.18 | NW | 94.8 | SW | 188.98 | NW | 166.65 | SE | 65.92 | NE | 17.92 | SW |
| IV | 121.15 | NW | 14.72 | NW | 35.16 | NW | 46.83 | SE | 25.67 | NW | 37.98 | SW |
Notes: SE = southeast; NE = northeast; NW = northwest; SW = southwest.
References
- Parmesan, C.; Yohe, G. A globally coherent fingerprint of climate change impacts across natural systems. Nature 2003, 421, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Yu, J.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J. Spatiotemporal evolution of ecosystem service values in an area dominated by vegetation restoration: Quantification and mechanisms. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 131, 108191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, D.R.; Belcher, R.N. Global changes in urban vegetation cover. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Tian, S.; Zheng, Z.; Zhan, Q.; He, Y. Human activity influences on vegetation cover changes in Beijing, China, from 2000 to 2015. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotton, J.A.; Wharton, G.; Bass, J.A.B.; Heppell, C.M.; Wotton, R.S. The effects of seasonal changes to in-stream vegetation cover on patterns of flow and accumulation of sediment. Geomorphology 2006, 77, 320–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Wang, X.; Johnson, B.A.; Tian, Q.; Wang, Y.; Verrelst, J.; Gu, X. Remote sensing algorithms for estimation of fractional vegetation cover using pure vegetation index values: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2020, 159, 364–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoshany, M.; Lavee, H.; Kutiel, P. Seasonal vegetation cover changes as indicators of soil types along a climatological gradient: A mutual study of environmental patterns and controls using remote sensing. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1995, 16, 2137–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Sha, Z.; Yu, M. Remote sensing imagery in vegetation mapping: A review. J. Plant Ecol. 2008, 1, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.Z.; Li, X.B.; He, C.Y. Research on comprehensive land cover classification in China: Based on NOAA/AVHRR and Holdridge PE index. Quaterary Sci. 2000, 20, 270–281. [Google Scholar]
- Gulzat, H.; Zhao, J.B. Changes of extreme temperature and precipitation in Altay region, Xinjiang in recent 50 years. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2011, 25, 112–116. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.N.; Chen, Y.P.; Zhu, C.G.; Li, W.H. The concept and mode of ecosystem sustainable management in arid desert areas in northwest China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 7410–7417. [Google Scholar]
- Pettorelli, N.; Ryan, S.; Mueller, T.; Bunnefeld, N.; Jędrzejewska, B.; Lima, M.; Kausrud, K. The Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI): Unforeseen successes in animal ecology. Clim. Res. 2011, 46, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, J. Vegetation dynamics of coal mining city in an arid desert region of Northwest China from 2000 to 2019. J. Arid Land 2021, 13, 534–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Qin, D.H. Influence of climate change and human activity on water resources in arid region of Northwest China: An overview. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2017, 8, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Xing, H. Spatiotemporal change and drivers analysis of desertification in the arid region of northwest China based on geographic detector. Environ. Chall. 2021, 4, 100082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amuti, T.; Luo, G. Analysis of land cover change and its driving forces in a desert oasis landscape of Xinjiang, northwest China. Solid Earth 2014, 5, 1071–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.H.; Gao, X.Y.; Huang, J.F.; Zhang, M.L. Plant phylogeography in arid Northwest China: Retrospectives and perspectives. J. Syst. Evol. 2015, 53, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Gang, C.; Zhou, F.; Li, J.; Dong, X.; Zhao, C. Quantitative assessment of the individual contribution of climate and human factors to desertification in northwest China using net primary productivity as an indicator. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, G.; Li, Z.; Wang, P.; Wang, Z. Comparative assessment of vegetation dynamics under the influence of climate change and human activities in five ecologically vulnerable regions of China from 2000 to 2015. Forests 2019, 10, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Eziz, A.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Tang, Z.; Fang, J. Responses of four dominant dryland plant species to climate change in the Junggar Basin, northwest China. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 13596–13607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulkar, H.; Zhao, T.N.; Jiang, Q.O. Boundary scope and change of arid desert area in northwest China. Arid Land Geogr. 2021, 44, 1635–1643. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Feng, Q.S.; Guo, N.; Sha, S.; Hu, D.; Wang, L.J. Dynamic monitoring of vegetation coverage based on long time-series NDVI data sets in northwest arid region of China. Pratacult. Sci. 2015, 32, 1969–1979. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, A.Y.; Chu, S.L.; Wang, Z.W.; Chen, Q. Analysis of vegetation coverage change based on NDVI—A case study in Ganzhou area, Zhangye city, Gansu. Pratacult. Sci. 2008, 25, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, H.M.; Li, X.; Dong, D.R. Estimation of desert vegetation coverage based on multisource remote sensing data. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2012, 23, 3331–3337. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Z.J.; Zeng, Z.Y.; Shi, X.Z.; Zheng, W.; Zhang, Z.L.; Hu, Z.F. A model calculating vegetation fractional coverage from ETM+ imagery. Ecol. Environ. 2008, 17, 771–776. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.J.; Li, X.G.; Yan, K.; Liu, B. Temporal and Spatial Variation Characteristics of Grassland Vegetation Coverage in Hejing of Xinjiang Based on Remote Sensing and Dimidiate Pixel Model. J. Northwest For. Univ. 2017, 32, 210–217. [Google Scholar]
- Long, H.Y.; Weng, B.S.; Huang, B.B.; Meng, L. Response of vegetation covarage to varying gydrological conditions in Honggze lake wetland, 1984–2017. J. Hydrogeol. 2020, 41, 98–106. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Z.; Ping, J.; Sun, L.; Dai, Y. Research on the change of vegetation loss and gain in Shenyang based on NDVI index. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1629, 012054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Dong, G.; Chen, J.L.; Cheng, W.X. Study on the cover and the change of vegetation in Ruoergai Plateau. Bull. Sci. Technol. 2021, 37, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.G.; Zhang, F. Spatial-temporal pattern and gravity center change of fractional vegetation cover in Xinjiang, China from 2000 to 2019. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 188–194. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.J.; Mu, X.M.; Tian, P.; Gao, P.; Sun, W.; Xu, W. Prediction of vegetation variation and vegetation restoration patential in the Loess Plateau. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 35, 205–212. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Krause, C.M.; Cobb, N.S. Climate change and human activities: A case study in Xinjiang, China. Clim. Change 2010, 99, 457–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Chen, Y.; Shi, X.; Chen, Z.; Li, W. Temperature and precipitation changes in different environments in the arid region of northwest China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2013, 112, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeppel, M.J.B.; Wilks, J.V.; Lewis, J.D. Impacts of extreme precipitation and seasonal changes in precipitation on plants. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 3083–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Chen, Y.; Shi, X. Why does the temperature rise faster in the arid region of northwest China? J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D16115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, G.; Wu, J. On the accuracy of landscape pattern analysis using remote sensing data. Landsc. Ecol. 2008, 23, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.S.; Wang, K.; Hong, Y.; Qi, J.G. Spatio-temporal dynamics and evolution of land use change and landscape pattern in response to rapid urbanization. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2009, 92, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’neill, R.V.; Riitters, K.H.; Wickham, J.D.; Jones, K.B. Landscape pattern metrics and regional assessment. Ecosyst. Health 1999, 5, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.Y.; Qin, F.C.; Wang, D.H.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y. Changes and driving force of landscape pattern in Yongshou County during 1998–2018. J. Northwest For. Univ. 2020, 35, 279–286. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Xie, X.P.; Chen, Z.C. Dynamic evolution of landscape spatial pattern in Taihu Lake basin, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 28, 3720–3730. [Google Scholar]
- Ramachandra, T.V.; Aithal, B.H.; Sanna, D.D. Insights to urban dynamics through landscape spatial pattern analysis. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2012, 18, 329–343. [Google Scholar]
- Trac, C.J.; Schmidt, A.H.; Harrell, S.; Hinckley, T.M. Environmental reviews and case studies: Is the returning farmland to forest program a success? Three case studies from Sichuan. Environ. Pract. 2013, 15, 350–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, R.; Shi, Z. Long-term impact of China’s returning farmland to forest program on rural economic development. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, R.; Yang, J. Temporal-spatial variations and influencing factors of vegetation cover in Xinjiang from 1982 to 2013 based on GIMMS-NDVI3g. Glob. Planet. Change 2018, 169, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aït-Mesbah, S.; Dufresne, J.; Cheruy, F.; Hourdin, F. The role of thermal inertia in the representation of mean and diurnal range of surface temperature in semiarid and arid regions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 7572–7580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamchin, M.; Wang, S.W.; Lim, C.H.; Ochir, A.; Pavel, U.; Gebru, B.M.; Choi, Y.; Jeon, S.W.; Lee, W.-K. Understanding global spatio-temporal trends and the relationship between vegetation greenness and climate factors by land cover during 1982–2014. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 24, e01299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, S.; Yang, H.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Gang, C.; Zhou, W.; Ju, W. Spatio-temporal dynamics of vegetation coverage and its relationship with climate factors in Inner Mongolia, China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2013, 23, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, T.; Dong, G.; Jiang, X.; Lei, Y. Spatio-temporal changes and driving forces of vegetation coverage on the loess plateau of Northern Shaanxi. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).