Abstract
Landfills, old and abandoned mines, industrial sites, heaps, sludge ponds and other sources of pollution represent environmental threats and are characterized as chemical time bombs. This work is focused on the evaluation of soil contamination by risk elements using various indices (geoaccumulation index—Igeo, enrichment factor—EF, contamination factor—Cif and degree of contamination—Cd). These selected agrarian problem areas are located in Slovakia, especially in the air pollution field of landfills consisting of power plant fly ash, tannery and footwear wastes, leachate (lúženec), iron ore slag, waste from metallurgy and sludge ponds in which coal sludge waste is deposited and waste from ore treatment. Nine research sites in the agrarian region of Slovak Republic were monitored. Ten risk elements (Fe, Mn, Zn, Cu, Co, Ni, Cr, Pb, Cd and Hg) and pH/H2O were included in this study and were determined in surface soils (of 0.05 m to 0.15 m) using atomic absorption spectrometry (AAS). Our study showed the highest exceedance of the limit values of risk elements in the order Ni (51.85 times) > Co (25.47 times) > Cd (13.70 times) > Cu (12.78 times) > Cr (8.37 times) > Fe (8.26 times) > Hg (7.94 times) > Zn (5.71 times) > Pb (4.63 times). The content of risk elements increased based on the average values of Igeo in the order of Cr < Hg < Zn < Pb < Ni < Cu < Cd. Igeo values for cadmium indicated mild-to-extreme contamination at all sites. We found the most significant enrichment in the order of Cd > Cu > Pb > Ni > Zn > Hg > Cr. EF values for cadmium indicated extremely high enrichment; the Cif and Cd values indicated a very high degree of soil contamination near the nickel smelter landfill, an industrial metallurgical plant and old but active mines. The studied areas pose a serious danger not only to the soil but also to groundwater and biota due to the prevailing low soil reaction, which increases the mobility of toxic elements. The study provides important results for the development of effective strategies for the control and remediation of endangered areas.
1. Introduction
Risk elements are considered to be one of the main sources of environmental pollution and their impact on the ecological quality of the environment has been identified and found to be significant [1,2]. They can cause primary damage with a direct impact on the environment or cause secondary damage and disruption of the biological balance of the food chain [3]. Hazardous substances are difficult to degrade in nature, have a high persistence and often have toxic effects on the environment. The impact of risk elements on the environment is accentuated by their non-degradability [4]. Human activities have become an important phenomenon for the redistribution of chemical elements in environmental components, significantly accelerating the release and accumulation of risk elements in soil, water and air [5,6,7]. Increasing concentrations of risk elements, especially in mobile form, can cause serious environmental problems to soil, water and biota [8,9]. An increase in the concentration of chemical elements creates unfavorable conditions, especially for living organisms. Even at very low levels of exposure, these chemicals can be toxic to living organisms [4,10], as is reflected in the weakening of their population, which decreases biodiversity and ultimately has a negative impact on human health and life expectancy [11,12]. Contamination by risk elements of the environment is a global concern due to the toxicity of metals and their potential threat to human health [13]. Additionally, it is becoming a globally recognized environmental problem [14]. Excessive intake of risk elements by soil has attracted the attention of scientists and experts worldwide as these elements are toxic, durable and negatively influence biological enrichment [15]. Risk elements are associated with soil components in different ways, and these connections indicate their mobility in soils and their bioavailability [16]. The soil system is a very specific component, and, to some extent, it can effectively eliminate various foreign substances naturally (natural attenuation) [17]. At the same time, soils have a natural content of risk elements released from the parent rock in the process of pedogenesis [18]. The input of risk elements to soil due to anthropogenic activity is much greater than the supply of risk elements from natural sources [19]. Anthropogenic sources of soil contamination in the form of risk elements include atmospheric deposition, metallurgy, fossil fuel combustion, motoring [20], organic and mineral fertilizers, liming, pesticides, sewage sludge and household as well as industrial waste [21]. Extensive mining and industrial activities have led to excessive anthropogenic pressures on the country in the past, resulting in landfills, old as well as abandoned mines, industrial sites, heaps, sludge ponds and other sources of pollution that represent environmental pressures and are characterized as chemical time bombs. Old environmental burdens can be a significant source of pollution of environmental components, including biota, posing a threat to human health and upsetting the stability of the landscape [22].
The area of agricultural land in the Slovak Republic represents 2,376,712 ha (48.5% of the total area of the Slovak Republic), of which no more than 20,000 ha are contaminated with at least one risk element. Soil pollution comes from natural and anthropogenic sources, mainly from industrial production and mining activities [17]. In the Slovak Republic, mining and the use of minerals date back to the Early Stone Age. In the past centuries, mining sites were located in the vicinity of mining towns. In the Slovak Ore Mountains, the problem of liquidating old mining works and removing their impact on the landscape and the environment persists in places. The negative impact of mining on the environment has manifested itself, for example, in the mining of antimony ores, mercury ores, asbestos, salt and copper ores. It is also apparent in the mining of iron, silver and magnesite. Metallurgy and metal treatment are also related to ore mining with significant interventions in the environment and its components. Post-treatment, the amount of waste left from the extracted volume of the raw material varies from 10 to 99%. Several areas of Slovakia are affected by the mining of mineral deposits and the processing of extracted or imported minerals. In these areas, there is a characteristic presence of emissions of ash, arsenic, cadmium and contamination of alluvial sediments (Horná Nitra Basin); mining and processing of ores with emissions of mercury, copper, arsenic, sulfur and nitrogen (Hornád basin); mining and processing of magnesite ores with emissions of magnesium, iron, manganese and chromium (Revúca Mountains, Lovinobaňa, Košice Basin); emissions of fluorine, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxide, arsenic compounds, tar and solid pollutants in the processing of imported minerals and in the disposal of their waste (Žiar Basin); waste with a high content of chromium oxide from the processing of iron–nickel ore (the area of town Sereď); and solid pollutants of chromium and manganese generated from the production of ferroalloys (the area of Istebné and Široká municipalities) [23].
Various pollution indices are used to document pollution and assess the environmental risk posed by large-scale mining and industrial activities. These indices provide a comprehensive geochemical assessment of the state of the soil environment, thereby performing environmental risk assessments and calculating the degree of soil degradation, in addition to helping determine whether the accumulation of risk elements has been caused by natural processes or is the result of anthropogenic activities [24]. Currently, the most commonly used are the index of geoacumulation, contamination factor, ecological risk factor, ecological risk index, degree of contamination, pollution load index, potential ecological risk index and metal enrichment factor, as shown in numerous studies [24,25,26,27,28,29,30]. A detailed review of the pollution indices is given by Kowalska et al. [31].
The aim of this study is to evaluate the contamination of soil with risk elements using various indices (geoaccumulation index, enrichment factor, contamination factor and degree of contamination). The study is conducted in selected agrarian areas of Slovakia located in the emission field of landfills consisting of power plant fly ash, iron ore slag, waste from copper metallurgy and sludge ponds where waste from coal sludge and ore treatment are also deposited. The assessment of soil contamination will provide important information on the environmental risks of old environmental burdens in relation to the agricultural landscape.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Nine research sites in the agrarian problem areas of the Slovak Republic were monitored (Figure 1).
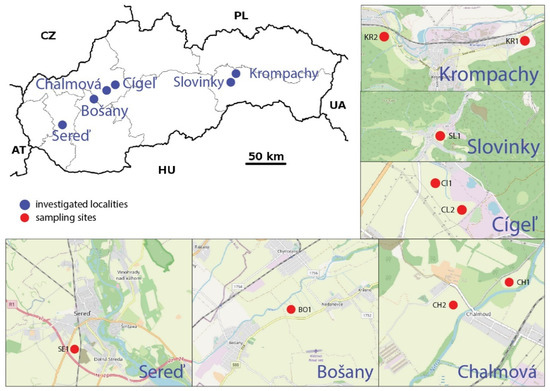
Figure 1.
Location of research sites in the investigated areas (Slovakia).
Chalmová landfill (CH1, CH2, GPS 48°40′26.6″ N; 18°29′47.3″ E, 48°39′45.9″ N; 18°28′45.5″ E). The investigated area of reclaimed landfill consisting of power plant fly ash, Chalmová, is located in the Horná Nitra region, and it represents an area of the 3rd environmental quality of the environment, that is, a region with a severely disturbed environment [32]. Since the establishment of the mines and the beginning of the production of energy from brown coal, industrial activities are the economic mainstay of the Horná Nitra region. Mining, coal burning, chemical and heavy industries have significantly affected the environment in this region [33]. According to the climatic division of Slovakia [34], the area is a warm, slightly humid area with a mild winter. The average annual temperature here is around 8.7 °C; the annual total precipitation reaches up to 700 mm. The predominant soil types are Rendzic Leptosol, Eutric Fluvisols and Dystric Planosols, with medium-to-heavy, without skeleton to slightly skeletal deep soils [35].
Cígeľ tailings pond (CI1, CI2, GPS 48°44′19.8″ N; 18°37′54.5″ E, 48°44′15.2″ N; 18°37′49.5″ E). According to the environmental regionalization of the Slovak Republic [32], the investigated area of the Cígeľ mine tailings pond is located in the Horná Nitra region and represents an area of the 3rd environmental quality of the environment, that is, a region with a severely disturbed environment. The territory of the burdened area is mainly affected by the mining of brown coal, which was also mined in this locality. The area of the Old Sludge pond is 8 ha, and it is estimated that there are about 545,000 tonnes of coal sludge stored in the form of dry matter. The area of the New Sludge pond is 3.46 ha, and the expected amount of coal sludge is about 235,000 tonnes. The capacity of the pond is exhausted; its functionality is ensured by measures of a technical nature [36]. The investigated area belongs to a warm and slightly humid region characterized by a mild winter, an average annual temperature of 8.6 °C and an average annual precipitation of 770 mm [34]. Eutric Cambisols, Dystric Planosols, Rendzic Leptosol and Skaletic Leptosols are found here [35].
Bošany landfill (BO1, GPS 48°35′24.8″ N; 18°16′16.6″ E). The investigated area of the reclaimed landfill, fed by the Babica tannery in Bošany, is located in the Horná Nitra region. It represents the area of the 3rd environmental quality, which is a region with a severely disturbed environment. The landfill was established in 1970 in the dead arm of the River Nitra resulting from some water management modifications. The waste, coming from leather and shoe production, was deposited directly into the water [37]. Waste disposal was completed in 1992. Currently, the landfill is spread over concrete panels on an area of approximately 2800 m2. The area around the landfill is used for agriculture. From the geomorphological point of view, the wider surroundings of the investigated locality belong to the central part of the Nitra loess hill [38]. The area belongs to the climatic area and is warm and dry with a mild winter. The average annual temperature is 9.6 °C, and the average annual precipitation is 600 mm. There are Eutric Fluvisols and Eutric Cambisols, which are moderately difficult.
Landfill Sereď (SE1, GPS 48°16′13.1″ N; 17°43′54.8″ E). According to the environmental regionalization of the Slovak Republic [32], the investigated area of Sereď, with its Luska landfill fed by a nickel smelter, is located in the Galanta region. It is a region with a severely disturbed environment, representing an area of the 3rd environmental quality. Production at the nickel smelter (1963–1993) was stopped after 30 years for economic and environmental reasons. The leachate landfill area is 35 ha and, together with the area of the former nickel smelter, is a serious environmental problem. Disposal by mining is slow with the risk of air pollution by polymetallic toxic dust. From a geomorphological point of view, Sereď is located in the northernmost outcrop of the Danube plain. The locality belongs to a warm climatic region and is very dry with a mild winter. The average annual temperature of the locality reaches 9.9 °C, with an annual precipitation of up to 540 mm. The soil cover at the landfill consists of Urbi-anthropic Regosolon substrates of technogenic origin [39]. The territory of the examined region is dominated by Haplic Chernozems and Eutric Fluvisols with their subtypes.
Slovinky tailings pond (SL1, GPS 48°55′48.9″ N; 20°53′51.0″ E). The investigated area is located in the Spiš region, which represents an area of the 2nd environmental quality, which is a region with a slightly disturbed environment. It is partly located in the Rudňany district with a significantly disturbed environment [32]. Slovinky and its surrounding area are characterized by a significant number of deposits of silver, copper and iron ores. Mining activities in Slovinky were terminated in 1993. The persistent surface consequences of mining activities are mainly heaps and sludge ponds. The Slovinky tailings pond is the highest of such a pond in Slovakia. It sits on 15 ha, and the height of the tailings pond dam is 113 m. Flotation sludge, which was waste from ore treatment in Slovinky mines, was weighed through the pipeline. Its activity was terminated after an accident in 1999, in which the drainage pipe had ruptured. At present, 4.8 million cubic meters of sludge of solid consistency are stored here. The area belongs to a moderately warm, slightly humid, hilly-to-highland climate region. It has an average annual temperature of 6.7 °C, with an average annual rainfall of 837 mm. The predominant soil type is Eutric Cambisols on crystalline rocks and is medium heavy.
Landfill Halňa Krompachy (KR1, KR2, GPS 48°55′23.3″ N; 20°51′32.3″ E, 48°55′19.4″ N; 20°53′58.1″ E). The investigated area is located in the Spiš region and belongs to an area of the 2nd environmental quality, thus indicating a region with a slightly disturbed environment. It is partly located in the Rudňany district with a significantly disturbed environment [32]. Mining and industrial activities carried out in the area caused a high degree of pollution of the natural environment. The area is rich in copper and iron ores, which have been mined and processed here since the Middle Ages. One of the largest and most dangerous landfills is the Halňa landfill, to which iron ore slag and copper metallurgical waste was exported until the mid-1960s. Later, it received sludge from the production of copper as well as other metals; it also received highly hazardous cyanides. The Halňa landfill is not isolated from the subsoil, and it occupies an area of 10 ha. It was closed in 1999 because rainwater washed out toxic substances, especially risk elements, which subsequently contaminated the soil and groundwater. The area belongs to a moderately warm, slightly humid, hilly-to-highland climate region. It has an average annual temperature of 7.1 °C, with an average annual rainfall of 728 to 737 mm. The predominant soil types are Eutric Cambisols at a shallow deep on crystalline rocks, and they are medium heavy, mostly acidic.
2.2. Soil Assays and Data Analyses
In 2018–2019, soil samples were collected from the permanent research sites covering the A horizon to a depth of 0.05–0.15 m. These sites are used as permanent grasslands and are located in the air pollution field of dumps and tailing ponds. The nearest available localities were selected for the investigation, while the distance ranged from 0.5–2 km. The composite soil sampling method (5 random sampling) was used to collect soil samples weighing approximately 1000 g from one test site. The procedures were in accordance with state standards [40,41].
After homogenization, the soil samples were manually crumbled, dried at room temperature, sieved (< 2 mm) and stored in polyethylene bags until the analysis. The soil reaction (pH/H2O, 20 g of soil mixed with 50 mL of redistilled water) was studied and evaluated on the pH-meter Metrohm 691 (Metrohm AG Company, Herisau, Switzerland). Ten risk elements (Fe, Mn, Zn, Cu, Co, Ni, Cr, Pb, Cd and Hg) were included in this study, and they constituted priority pollutants of the studied areas. The total content of Fe, Mn, Zn, Cu, Co, Ni, Cr, Pb and Cd was determined by Atomic Absorption Spectrometry (AAS) on a VARIAN AA 240 FS machine (Varian, Melbourne, Australia). The soil samples were extracted in the solution of 2.5 mL of concentrated HNO3 and 7.5 mL of concentrated HCl. The process of mineralization lasts 30 min at a temperature of 160 °C, and the process of cooling lasts 20 min. Hg was determined by the AAS mercury AMA 254 analyzer (Altec, Czech Republic) following the methodology devised by Kobza et al. [42]. The assessed values of heavy metals in soils were compared to the limit values of Slovak soils [43].
The environmental indices, namely the geoaccumulation index (Igeo), the enrichment factor (EF), the contamination factor (CF) and the degree of contamination (Cd), were calculated.
The geoaccumulation index (Igeo) allows the assessment of heavy soil metal contamination on the base metal concentrations in the soil sample (topsoils) and the geochemical background of the metal as the reference level. The geoaccumulation index (Igeo) was calculated using the equation proposed by Müller [44]. Igeo = log2(Cn/1.5Bn), where Cn is the metal (n) concentration recorded in the sediments of the study area, Bn is the background value of the corresponding metal (n) and factor 1.5 is the background matrix correction due to lithogenic effects [45]. The Igeo classification proposed by Müller [44] was used to determine the level of contamination. The seven classes in this classification are: uncontaminated (Igeo ≤ 0; Class 0), uncontaminated to moderately contaminated (Igeo 0–1; Class 1), moderately contaminated (Igeo 1–2; Class 2), moderately to highly contaminated (Igeo 2–3; Class 3), highly contaminated (Igeo 3–4; Class 4), highly to very highly contaminated (Igeo 4–5; Class 5) and very highly contaminated (Igeo ≥ 5; Class 6) [44].
The enrichment factor (EF) allows the assessment of the degree of intensity of anthropogenic activities, and EF is based on the standardization of a tested element against a reference one. The most common reference elements are Sc, Mn, Ti, Al and Fe [46]. This work uses Mn as a reference element. The value of the enrichment factor was calculated using the modified formula based on the equation suggested by Buat-Menard and Chesselet [47]:
where cn (sample) is the content of the examined element in the examined environment, cref (sample) is the content of the reference element in the examined environment, Bn (back-ground) is the content of the examined element in the reference environment and Bref (background) is the content of the reference element in the reference environment. Five contamination categories are recognized on the basis of the enrichment factor [48]: EF < 2 is deficiency to minimal enrichment, EF = 2–5 is moderate enrichment, EF = 5–20 is significant enrichment, EF = 20–40 is very high enrichment and EF > 40 is extremely high enrichment.
Soil contamination was evaluated using the contamination factor and the degree of pollution according to Hakanson [49]: , where Ci is the average concentration of risk elements and is the background concentration of risk elements for soils of the Slovak Republic (Table 1) [50]. The following terminology may be used in this risk index approach in order to uniformly describe the contamination factor, as suggested by Hakanson [49]: < 1 is a low contamination factor (indicating low sediment contamination of the substance in question); 1 ≤ < 3 is a moderate contamination factor; 3 ≤ < 6 is a considerable contamination factor; ≥ 6 is a very high contamination factor.

Table 1.
Background values of risk elements (mg/kg) of the investigated localities for the soils of the Slovak Republic [50] and pH/H2O.
The degree of total environmental contamination Cd is defined as the sum of all :. The Cd is a measure of the degree of overall contamination in a particular sampling site and was defined as the sum of all . The following terminology may be used to describe the degree of contamination: Cd < 8 is a low degree of contamination; 8 ≤ Cd < 16 is a moderate degree of contamination; 16 ≤ Cd < 32 is a considerable degree of contamination; Cd ≥ 32 is a very high degree of contamination, indicating serious anthropogenic pollution.
The obtained data were processed statistically by means of the Statistica software (Ver. 13, 2015) and PAST 4.0. The data were log-transformed before the analysis.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Soil Reaction and the Total Concentration of Risk Elements in Soil
The tested soils in the vicinity of the Cígeľ tailings pond (CI1, CI2) were strongly acidic (pH below 3.5) and weakly acidic to neutral (pH 6.08–6.67) in the vicinities of the Halňa landfill (KR1, KR2) and the Slovinky tailings pond (SL1). The research also revealed the existence of weakly-alkaline-to-alkaline soils (pH 7.36–8.24) in the vicinities of the Chalmová (CH1), Bošany (BO1) and Sereď (SE1) landfills (Table 1).
The total concentrations of risk elements in soils (Zn, Cu, Co, Ni, Cr, Pb, Cd, Hg, Fe and Mn) from the investigated sites, which include various sources of pollution mainly from industrial activity, coal combustion and mining and processing activities, are summarized in Table 2. Extensive emissions of industrial dust containing hazardous elements come from landfills consisting of power plant ash, tanning and shoemaking waste, leachate, iron ore slag, and copper as well as other metallurgical sludge wastes on which coal sludge and ore waste are deposited.

Table 2.
Content of risk elements (mg/kg) in the soils of the studied localities expressed by descriptive statistics.
The average Zn content of soils worldwide ranges between 60 and 89 mg/kg [51]. The average content of Zn in agricultural soils in Slovakia fluctuates in the range of 40–120 mg/kg [52]. The relatively high content of Zn, up to 14,925 mg/kg (on average 61 mg/kg), is reported for some upper horizons of soils of the Slovak Republic [50]. Zn’s content is closely related to soil texture and is usually lowest in light sandy soils. Its increased concentration is often observed in calcareous and organic soils [51]. In the examined areas, we found its variability in the range of 35.8–856.0 mg/kg. In addition, we found above-limit values of Zn in the area of Krompachy (KR1, KR2), which exceeded the limit values by 5.71 times. Its variability, which also results from its mobility, is also mentioned in the work of Loska et al. [46].
The average Cu content of soils of different groups around the world ranges between 14 and 109 mg/kg [51]. According to the results of soil monitoring in Slovakia, the average Cu content is 24.48 mg/kg [52]. Copper leaching occurs in acidic soils, and the solubility of copper compounds is lowest in the pH range of 7 to 8 [51,53]. The copper content in the examined localities was in the range of 16–749 mg/kg, and above-limit values were found in the areas of Slovinky (SL1) and Krompachy (KR1, KR2), showing values up to 12.78 times the limit values. A common characteristic of Cu distribution in soil profiles is its accumulation in the upper horizons. This phenomenon is the effect of various factors, but above all, the concentration of Cu in surface soils reflects its bioaccumulation and also its anthropogenic sources [51].
The Co content of soils mainly comes from the parent rocks. The worldwide average value of Co in surface soils is calculated at 10 g/kg. Higher levels of Co are mainly found in heavy clay soils (Cambisols) and sometimes in organic soil (Histosols) [51]. The results of monitoring the soils of Slovakia show that the average Co content of agricultural soils is 8.8 mg/kg. In our research, Co content exceeding the limit values by 25.47 times was found in the localities of Chalmová (CH1, CH2) and Sereď (SE1). Co in the soil is often generated from anthropogenic sources and is found in the metallurgical industry, cement plants and power plants, which is confirmed in our research. There is evidence of Co enrichment in surface horizons of soils near the metalwork industry with the Co content reaching up to 154 mg/kg [54,55,56]. Co becomes mobile mainly in acidic oxidizing environments. It shows a high affinity with iron and manganese. The amounts of Co are always higher in the B-horizons of the soil, where Fe is concentrated [50,51].
The average Ni content of soil is 20 mg/kg, and it depends on the Ni content of soil in its soil-forming substrates. The highest Ni content is present in ultrabasic rocks (up to 2000 mg/kg) [51]. The average Ni content of agricultural soils is 29.43 mg/kg [52]. Nickel contamination of the investigated sites is not a problem, with the exception of the area around the nickel smelter in Sereď (SE1), where a content of 2592.7 mg/kg was found, which exceeded the limits by 51.85 times. In our research, an alkaline soil reaction (pH 8.7) was also found at the investigated locality. According to Kabata-Pendias [51], Ni is easily available, especially at pH < 6.
The average Cr content for the world’s surface soil horizons averages 80 to 100 mg/kg [51]. The average Cr content of agricultural soils in Slovakia is 42 mg/kg [52]. In small amounts, it is an important essential element in the form of Cr3+, in contrast to the hexavalent cation Cr6+, which is classified as a strong toxic substance. It is characterized by low mobility and low bioaccumulation. This is mainly influenced by soil reaction, content of clay parts, redox potential and the content of humus. Anthropogenic Cr contamination occurs mainly in the vicinities of ferroalloy, leather and metal chromium plating plants. Chromium contamination of the investigated sites is not a problem, with the exception of the area around the nickel smelter in Sereď (SE1), where the Cr content of 1254.8 mg/kg was found to exceed the limit values by 8.37 times.
The average value of Pb content for different soils is estimated at 27 mg/kg [51]. Its content in different groups of soils is in the range of 3–90 mg/kg; the highest amount of Pb is found in Cambisols and Histosols. The average lead content of agricultural topsoil in Slovakia is in the wide range of 7.7–54.3 mg/kg [52]. Slightly above-limit soil contamination was found in our research in the vicinity of the nickel smelter in Sereď (SE1), but more significant soil contamination was found in the vicinity of the iron ore landfill and copper metallurgical waste (KR1, KR2), where an above-limit Pb content of 117–324 mg/kg was found to exceed the limits by 4.63 times.
The average content of Cd in soils ranged from 0.2 and 1.1 mg/kg [51]. Its occurrence in the soil is conditioned by sedimentation due to weathering from geochemical anomalies, emissions from industrial and energy heating plants to fossil fuels, application of phosphorus fertilizers or emissions from transport. It is significantly present in the so-called geochemical anomalies that are numerous in Slovakia. Cadmium is a risk element; its mobility is mainly influenced by soil reaction, humus content as well as quality, chemical composition of the soil solution and the sorption complex [51,52,57]. In our research, above-limit Cd content was found and measured at all investigated localities. An exceedance up to 13.70 times of the Cd limit values—among the highest—was found in the vicinity of the nickel smelter (SE1).
The average Hg content of soils of different groups around the world is between 0.58 and 1.8 mg/kg, and the global average content is estimated at 1.1 mg/kg [51]. Higher concentrations of Hg are found in Histosols and Cambisols. The results of soil monitoring in Slovakia show that the average amount Hg present in agricultural soils is 0.09 mg/kg [52]. Sources of anthropogenic contamination are hazardous substances of waste in sludge ponds and heaps from metallurgical and mining–processing complexes, which are also confirmed in our research. Exceedance of the limit values was found at localities that were in the immediate vicinity of the sludge pond (SL1) and the heap (KR1, KR2). The highest concentrations of this element exceeded the limit values by 7.94 times.
The average Mn content of the Slovak Republic soil ranges from 0.85 to 112.90 mg/kg, which indicates a significant spatial heterogeneity of the element. Kabata-Pendias [51] reported a value of 1500 mg/kg, which indicates manganese toxicity. However, the average Mn content of the soil mostly prevails. In our research, manganese content in the range of 166.20–2723.2 mg/kg was found. The toxic level of Mn content was found in the vicinity of the nickel smelter in Sereď (SE1).
The amount of Fe present in the soil is, on average, 3.5% and is likely to increase in heavy clay soils and some organic soils [51]. Background values of Fe content of soils of the Slovak Republic are 2.64 (%). Our research shows that the highest Fe values are found in the vicinity of the nickel smelter in Sereď (SE1), exceeding the average Fe content by up to 8.26 times. Iron has many biochemical functions, but excess intake can be toxic [50].
3.2. Assessment of Soil Pollution
Based on the determination of risk element concentrations in the soil, soil pollution was assessed using indices that indicated pollution. The geoaccumulation index (Igeo) for Zn, Cu, Ni, Cr, Pb, Cd and Hg varied. In the case of Hg and Zn, Igeo values lower than 1 were recorded in most of the examined localities, which indicated minimal anthropogenic effects rated as uncontaminated to slightly contaminated [44]. In the case of Cu, Cr and Pb, there was a slight-to-high contamination (Igeo = 2–3) at sites KR1, KR2 and SE1. High-to–very-high contamination (Igeo = 4–5) was found for Ni at the SE1 site. Igeo values for Cd ranged from 1.24–5.22, indicating that there was mild-to-extreme contamination at all sites. The content of risk elements increased based on the average values of Igeo in the following order Cr < Hg < Zn < Pb < Ni < Cu < Cd. Minimal enrichment of risk elements in the soil was attributed to the natural origin and fluctuation of risk elements if the EF values were lower than 2 [30]. The mean EF values ranged from 1.26 to 19.55. We found the most significant enrichment in the order of Cd > Cu > Pb > Ni > Zn > Hg > Cr. EF values > 40 were found in the Cd content of the soil at the KR1 site, indicating extremely high enrichment (Table 3). The increase in Cd content in the environment of the investigated localities was significantly affected by large-scale emissions of industrial dust containing hazardous elements from landfills, tannery and footwear, leachate, iron ore slag, copper metallurgical waste and sludge ponds. At the same time, a significant factor influencing the mobility of Cd, and thus its bioavailability, was the presence of highly acidic soils [58,59]. In our research, we found strongly acidic soils in the vicinity of the Cígeľ coal sludge tailings pond (CI1, CI2) and weakly acidic ones in the vicinity of the Halňa landfill, where iron ore slag and waste from copper metallurgy (KR1, KR2) were deposited. Highly acidic soils were also found in the environment of Slovinky tailings pond due to the presence of flotation sludge from copper and iron ores. High Igeo and EF correspond to the information obtained from Wang et al. [60] and Doležalová Weissmannová et al. [30] about the industrial area.

Table 3.
The index of geoaccumulation (Igeo) and enrichment factor (EF) for risk elements in the soil of the investigated localities (Slovakia).
3.3. Assessment of Soil Contamination
The contamination factor (Cif) and degree of contamination (Cd) were used in this study to assess soil contamination by risk elements (Table 4). The contamination factor (Cif ≥ 6) was very high for the investigated area KR1 in the order of Cd > Cu > Pb > Zn > Ni; for KR2, it was in the order of Cd > Pb > Cu > Zn; for SE1, in the order of Cd > Ni > Cr; for SL1, in the order Cd > Ni > Pb > Cu > Zn; and for site SE1, the contamination factor was in the following order: Cd > Ni > Cr. At the same time, a very high contamination factor in Cd was present in all monitored localities. The degree of contamination (Cd≥ 32) was very high for sites SE1, KR1 and KR2. The maximum value for Cd was at SE1 (106.30). The calculated values, which indicate the state of pollution according to the classifications, belong to soil samples from places near the landfill of the Sereď nickel smelter (SE1) and near the industrial metallurgical plant and long-term active mines (KR1, KR2). Similar to Cd, Ni increases its mobility and bioavailability under acidic and neutral conditions [51], which have been confirmed in our research at most of the sites examined. Research has shown that Igeo for Cr in all sites except SE1 falls into the uncontaminated-to-moderately-contaminated class: Igeo < 1; Igeo moderately-to-highly contaminated and EF moderately enriched were found at the SE1 site where Cif and Cd were very high. Contamination factors confirmed the results obtained by using the Igeo and EF indices. Our findings were in line with the Loska study [46], which pointed to the contamination of the Cd industrial region in the emission area of coal mines, coke ovens, steelworks and power plants.

Table 4.
Ranking order of soil contamination of the investigated localities according to Cd –value and sequence of the contamination factors (Cif).
The dendrogram of the hierarchical cluster analysis of environmental parameters at the investigated localities of problem areas in Slovakia is shown in Figure 2. HCA is identified in accordance with the monitored environmental parameters in relation to the area and common source of pollution by three groups of risk elements: Group I includes CH1–CH2 and SL1, and this group includes problem areas located in the emission field of landfills originating from power plant fly ash and waste from copper metallurgy and after the treatment of iron ores. In these localities, above-limit content was found, especially of Co and Cd. Group II consists of CL1–CL2 together with KR1, KR2 and BO1, and this group consists of areas in the emission field of coal sludge, iron ore slag and copper metallurgical waste and waste from leather and shoe production, where the limit values, in particular Cd, have been exceeded. Group III is formed by SE1 and includes the surroundings of the area of the former nickel smelter where the lusher landfill is located. The investigated area is contaminated mainly by Ni and Cr.
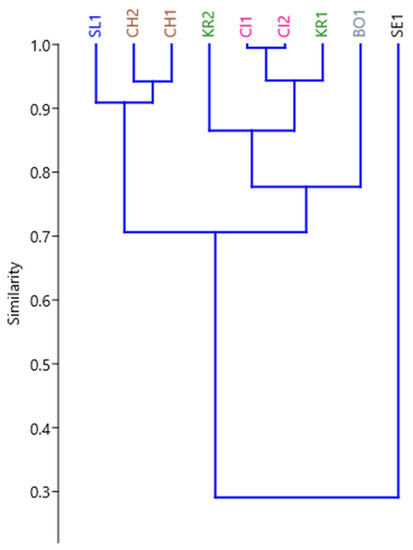
Figure 2.
Dendrogram derived from hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA) of the environmental parameters in the agrarian problem areas of Slovakia.
4. Conclusions
In this study, soil contamination with risk elements was assessed using various indices (geoaccumulation index—Igeo, enrichment factor—EF, contamination factor— Cif and degree of contamination—Cd) in selected problem areas of Slovakia’s agrarian regions. The areas included the emission pollution field of landfills originating from power plant fly ash, tannery and footwear production waste, leachate, iron ore slag, and waste from copper metallurgy, as well as sludge ponds in which waste from coal sludge and ore treatment was deposited. Based on the achieved results, it can be stated that:
- The average Igeo values ranged from −1.21 to 3.04, and the content of risk elements increased based on the average Igeo values in the following order Cr < Hg < Zn < Pb < Ni < Cu < Cd. Igeo values for Cd ranged from 1.24 to 5.22, indicating that there was mild-to-extreme contamination at all sites;
- The average of the EF values ranged from 1.26 to 19.55; we found the most significant enrichment in the order of Cd > Cu > Pb > Ni > Zn > Hg > Cr; EF values > 40 were found at Cd in the vicinity of the landfill and sludge pond, where iron ore slag and copper metallurgical waste were deposited, indicating extremely high enrichment;
- The calculated Cif and Cd values indicated a very high degree of soil contamination near the nickel smelter landfill, an industrial metallurgical plant and long-term active mines;
- HCA was identified in accordance with the monitored environmental parameters in relation to the area and common source of pollution by three groups of risk elements;
- The study areas pose a serious risk not only to the soil but also to groundwater and biota due to the prevailing low soil reaction, which increases the mobility of toxic elements;
- The study provides important results that can support the development of effective strategies for the management, control and remediation of endangered areas at regional and national levels.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.F. and F.P.; methodology, D.F., F.P. and J.F.; formal analysis, J.F., L.Š., I.B., F.T. and T.T.; investigation, D.F., F.P., J.F., L.Š., I.B., F.T. and T.T.; data analysis, J.F. and L.Š.; resources, D.F. and L.Š.; writing—original draft preparation, D.F., F.P., J.F. and L.Š.; writing—review and editing, D.F. and L.Š. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by VEGA grant number 1/0313/19, by KEGA grant number 011PU-4/2019 and by APVV-20-0140.
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by VEGA 1/0313/19 Ecosystem approach as a parameter of the modern environmental research of contaminated areas, KEGA 011PU-4/2019 Implementation of environmental education and research into the teaching of management courses in the study program management and APVV-20-0140 Possibilities of critical raw materials recovery by advanced methods of mining wastes processing.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sastre, J.; Sahuquillo, A.; Vidal, M.; Rauret, G. Determination of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn in environmental samples: Microwave-assisted total digestion versus aqua regia and nitric acid extraction. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 462, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaishankar, M.; Tseten, T.; Anbalagan, N.; Mathew, B.B.; Beeregowda, K.N. Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2014, 7, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Naggar, A.; Shaheen, S.M.; Ok, Y.S.; Rinklebe, J. Biochar affects the dissolved and colloidal concentrations of Cd, Cu, Ni, and Zn and their phytoavailability and potential mobility in a mining soil under dynamic redox-conditions. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 624, 1059–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RoyChowdhury, A.; Datta, R.; Sarkar, D. Heavy Metal Pollution and Remediation. Green Chem. 2018, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.-Y.; Peng, X.-T.; Pan, J.-M. Distribution, source and enrichment of some chemical elements in sediments of the Pearl River Estuary, China. Cont. Shelf Res. 2004, 24, 1857–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimann, C.; de Caritat, P. Distinguishing between natural and anthropogenic sources for elements in the environment: Regional geochemical surveys versus enrichment factors. Sci. Total. Environ. 2005, 337, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gu, A.Z.; Cen, T.; Li, X.; He, M.; Li, D.; Chen, J. Sub-inhibitory concentrations of heavy metals facilitate the horizontal transfer of plasmid-mediated antibiotic resistance genes in water environment. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, B.A.; Ellis, N.; Kim, C.S.; Bi, X. The role of tailored biochar in increasing plant growth, and reducing bioavailability, phytotoxicity, and uptake of heavy metals in contaminated soil. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopin, E.I.B.; Alloway, B.J. Distribution and Mobility of Trace Elements in Soils and Vegetation around the Mining and Smelting Areas of Tharsis, Ríotinto and Huelva, Iberian Pyrite Belt, SW Spain. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2007, 182, 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdu, N.; Abdullahi, A.A.; Abdulkadir, A. Heavy metals and soil microbes. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2017, 15, 65–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, A.; Verma, A.; Jaiswal, P. Detrimental Effects of Heavy Metals in Soil, Plants, and Aquatic Ecosystems and in Humans. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 2018, 37, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noskovič, J.; Chlpík, J.; Jedlovská, L.; Lacko-Bartošová, M.; Nozdrovický, L.; Ondrišík, P.; Porhajašová, J.; Rakovská, A.; Sklenár, Š.; Streďanská, A.; et al. Ochrana a Tvorba Životného Prostredia/Environmental Protection And Creation; Slovenská poľnohospodárska univerzita v Nitre: Nitra, Slovakia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kashem, A.; Singh, B.R.; Kawai, S. Mobility and distribution of cadmium, nickel and zinc in contaminated soil profiles from Bangladesh. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2006, 77, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Zhang, J.; Ren, L.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, J.; Luo, L.; Yang, Y.; Peng, Q.; Huang, H.; Chen, A. Diagnosis of soil contamination using microbiological indices: A review on heavy metal pollution. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 242, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Parihar, R.; Sharma, A.; Bakshi, P.; Sidhu, G.P.S.; Bali, A.S.; Karaouzas, I.; Bhardwaj, R.; Thukral, A.; Gyasi-Agyei, Y.; et al. Global evaluation of heavy metal content in surface water bodies: A meta-analysis using heavy metal pollution indices and multivariate statistical analyses. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahumada, I.; Mendoza, J.; Escudero, P.; Ascar, L. Effect of acetate, citrate, and lactate incorporation on distribution of cadmium and copper chemical forms in soil. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2001, 32, 771–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazekašová, D.; Barančíková, G.; Torma, S.; Ivanová, M.; Manko, P. Chemické a Environmentálne Aspekty Zložiek Životného Prostredia a Krajiny/Chemical and Environmental Aspects of the Environment and Landscape; University of Prešov: Prešov, Slovakia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ďurža, O. Využitie Pôdnej Magnetometrie v Environmentálnej Geochémii Ťažkých Kovov/Use of Soil Magnetometry in Environmental Geochemistry of Heavy Metals. Acta Geol. Univ. Comen. 2003, 58, 29–55. [Google Scholar]
- Marrugo-Negrete, J.; Pinedo-Hernández, J.; Díez, S. Assessment of heavy metal pollution, spatial distribution and origin in agricultural soils along the Sinú River Basin, Colombia. Environ. Res. 2017, 154, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahurpawar, M. Effects of heavy metals on human health. Int. J. Res. Granthaalayah 2015, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafka, Z.; Punčochářová, J. Těžké kovy v přírodě a jejich toxicita/Heavy metals in nature and their toxicity. Chem. Listy 2002, 96, 611–617. [Google Scholar]
- Frankovská, J. Čiastkový monitorovací systém geologických faktorov/Partial monitoring system of geological factors. In Podsystém 03 Antropogénne Sedimenty Charakteru Environmentálnych Záťaží. Záverečná Správa za Rok 2008/Subsystem 03 Anthropogenic Sediments Character of Environmental Loads. Final Report for 2008; Štátny Geologický Ústav Dionýza Štúra: Bratislava, Slovakia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Michaeli, E.; Boltižiar, M. Environmentálne záťaže/Environmental Burdens. In Potraviny Špecifického Charakteru/Food Of A Specific Character; Dudríková, E., Michaeli, E., Eds.; Univerzita Veterinárneho Lekárstva a Farmácie v Košiciach: Košice, Slovakia, 2011; pp. 80–105. [Google Scholar]
- Wojciechowska, E.; Nawrot, N.; Walkusz-Miotk, J.; Matej-Łukowicz, K.; Pazdro, K. Heavy Metals in Sediments of Urban Streams: Contamination and Health Risk Assessment of Influencing Factors. Sustainability 2019, 11, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Shi, L.; Yang, G.; You, M.; Vasseur, L. Ecological Risk Assessment of Soil Heavy Metals and Pesticide Residues in Tea Plantations. Agriculture 2020, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugoša, B.; Đurović, D.; Nedović-Vuković, M.; Barjaktarović-Labović, S.; Vrvić, M. Assessment of Ecological Risk of Heavy Metal Contamination in Coastal Municipalities of Montenegro. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, M. The Importance of Enrichment Factor (EF) and Geoaccumulation Index (Igeo) to Evaluate the Soil Contamination. J. Geol. Geophys. 2016, 5, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.H.; Khanam, D.; Adyel, T.M.; Islam, M.S.; Ahsan, M.A.; Akbor, M.A. Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination of Agricultural Soil around Dhaka Export Processing Zone (DEPZ), Bangladesh: Implication of Seasonal Variation and Indices. Appl. Sci. 2012, 2, 584–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Huang, C.; Chen, Z.; Bao, K. Distribution, Ecological Risk Assessment, and Bioavailability of Cadmium in Soil from Nansha, Pearl River Delta, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolezalova Weissmannová, H.; Mihočová, S.; Chovanec, P.; Pavlovský, J. Potential Ecological Risk and Human Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution in Industrial Affected Soils by Coal Mining and Metallurgy in Ostrava, Czech Republic. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalska, J.B.; Mazurek, R.; Gąsiorek, M.; Zaleski, T. Pollution indices as useful tools for the comprehensive evaluation of the degree of soil contamination–A review. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 2395–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinda, J.; Mičík, T.; Némethová, M.; Slámková, M. Environmentálna Regionalizácia Slovenskej Republiky/Environmental Regionalization of the Slovak Republic; Ministerstvo Životného Prostredia: Bratislava, Slovakia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Šebáň, O.; Doležal, I.; Buzinkai, M.; Včelková, T.; Paulen, T. Transformácia Uhoľného Regiónu Horná Nitra/ Transformation of the Horná Nitra Coal Region. Available online: https://www.novaky.sk/download/1554464344Transformacia-Hornej-Nitry_Akcny-plan_Draft_v1.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2021).
- Slovak Hydrometeorological Institute. Climate Atlas of Slovakia; SHI: Bratislava, Slovakia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sobocká, J. Morfogenetický Klasifikačný Systém Pôd Slovenska/Morphogenetic Classification System of Slovak Soils; Výskumný Ústav Pôdoznalectva a Ochrany Pôdy: Bratislava, Slovakia, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Hájková, V. Staré Environmentálne Záťaže/Old Environmental Burdens. Available online: http://www.prologno.sk/proenviro/view.php?cisloclanku=2006081601 (accessed on 20 August 2021).
- Auxt, A.; Minařik, M.; Hertlová, L.; Kamas, J.; Machala, A.; Polčan, I.; Filo, J.; Gretsch, J. Prieskum Pravdepodobnej Environmentálnej Záťaže PE(001) Bošany—Skládka Koželužní (SK/EZ/PE/637), PE (1874) Bošany—Skládka Koželužní ll (SK/EZ/PE/1874), Záverečná Správa Geologickej Úlohy s Analýzou Rizika, Názov Geologickej Úlohy: Prieskum Environmentálnych záťaží na Vybraných Lokalitách Slovenskej Republiky/Probable Environmental Burden Survey PE (001) Bošany — Tannery Landfill (SK/EZ/PE/637), PE (1874) Bošany — Tannery Landfill ll (SK / EZ / PE / 1874), Final Report of the Geological Task with Risk Analysis, Title Geological Task: Survey of Environmental Loads in Selected Localities of the Slovak Republic; HES-COMGEO: Bratislava, Slovakia; Cenvis: Bratislava, Slovakia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lapin, M.; Faško, P.; Melo, M.; Št’astný, P.; Tomlain, J. Climate Areas. In Atlas of the Slovak Republic; Ministry of Environment of the Slovak Republic: Bratislava, Slovakia, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Šály, R.; Bedrna, Z.; Bublinec, E.; Čurlík, J.; Fulajtár, E.; Gregor, J.; Hanes, J.; Juráni, B.; Kukla, J.; Račko, J.; et al. Morfogenetický Klasifikačný Systém Pôd Slovenska/ Morphogenetic Soil Classification System of Slovakia; VÚPOP: Bratislava, Slovakia, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Agriculture Decree No. 338/2005 Coll., Slovak Republic. Available online: https://www.slov-lex.sk/pravne-predpisy/SK/ZZ/2005/338/20060101.html (accessed on 20 August 2021).
- Slovak Technical Standard ISO 10381-6. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/43691.html (accessed on 20 August 2021).
- Kobza, J.; Barančíková, G.; Čumová, L.; Dodok, R.; Hrivňaková, K.; Makovníková, J. Methods of Determining Indicators of Agrochemical Soil Properties; SSCRI: Bratislava, Slovakia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Act of the National Council of the Slovak Republic No. 220/2004 Coll. Available online: https://www.mpsr.sk/zakon-c-220-2004-z-z/27-23-27-8366/ (accessed on 20 August 2021).
- Müller, G. The heavy metal pollution of the sediments of Neckars and its tributary: A stocktaking. Chem. Zeit. 1981, 105, 157–164. [Google Scholar]
- Salomons, W.; Förstner, U. Sediments and the transport of metals. In Metals in the Hydrocycle; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1984; pp. 63–98. [Google Scholar]
- Loska, K.; Wiechuła, D.; Korus, I. Metal contamination of farming soils affected by industry. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buat-Menard, P.; Chesselet, R. Variable influence of the atmospheric flux on the trace metal chemistry of oceanic suspended matter. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1979, 42, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, R.A. Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu, Hawaii. Environ. Geol. 2000, 39, 611–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håkanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čurlík, J.; Šefčík, P. Geochemický Atlas Slovenskej Republiky/Geochemical Atlas of the Slovak Republic; SSCRI: Bratislava, Slovakia, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Kabata-Pendias, A. Trace Elements in Soils and Plants, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kobza, J.; Barančíková, G.; Makovníková, J.; Pálka, B.; Styk, J.; Širáň, M. Current State and Development of Land Degradation Processes Based on Soil Monitoring in Slovakia. Agriculture 2017, 63, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Blaser, P.; Zimmermann, S.; Luster, J.; Shotyk, W. Critical examination of trace element enrichments and depletions in soils: As, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn in Swiss forest soils. Sci. Total. Environ. 2000, 249, 257–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, I.C.; Carson, B.L. Trace Metals in the Environment. Ann Arbor Sci. Publ. 1981, 6. Available online: https://catalogue.nla.gov.au/Record/913912 (accessed on 20 August 2021).
- Spahić, M.M.P.; Sakan, S.; Glavaš-Trbić, B.M.; Tančić, P.I.; Škrivanj, S.B.; Kovačević, J.R.; Manojlović, D.D. Natural and anthropogenic sources of chromium, nickel and cobalt in soils impacted by agricultural and industrial activity (Vojvodina, Serbia). J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2019, 54, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machender, G.; Dhakate, R.; Prasanna, L.; Govil, P.K. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in soils around Balanagar industrial area, Hyderabad, India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 63, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Zhao, Z.; Xing, Z.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Liu, Y. Comparison of Models for Spatial Distribution and Prediction of Cadmium in Subtropical Forest Soils, Guangdong, China. Land 2021, 10, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alloway, B.J. The origins of heavy metals in soils. In Heavy Metals in Soils; Blackie Academic and Professional: London, UK, 1995; pp. 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Adriano, D.C. Chromium. In Trace Elements in Terrestrial Environments; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 315–348. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Han, J.; Wei, Y.; Li, G.; Sun, Y. Potential Ecological Risk and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals and Metalloid in Soil around Xunyang Mining Areas. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).