Abstract
Previous studies of land degradation, topsoil erosion, and hydrologic alteration typically focus on these subjects individually, missing important interrelationships among these important aspects of the Earth’s system. However, an understanding of water–soil–vegetation dynamic interactions is needed to develop practical and effective solutions to sustain the globe’s eco-environment and grassland agriculture, which depends on grasses, legumes, and other fodder or soil-building crops. This special issue is intended to be a platform for a discussion of the relevant scientific findings based on experimental and/or modeling studies. Its 12 peer-reviewed articles present data, novel analysis/modeling approaches, and convincing results of water–soil–vegetation interactions under historical and future climates. Two of the articles examine how lake/pond water quality is related to human activity and climate. Overall, these articles can serve as important references for future studies to further advance our understanding of how water, soil, and vegetation interactively affect the health and productivity of the Earth’s ecosystem.
1. Introduction
Water, soil, and vegetation are key elements in the Earth’s system [1]. Their dynamic interactions affect, and are affected by, anthropogenic activities (e.g., grazing, farming, and/or urbanization) and climate change [2,3,4,5,6,7]. For a given area, inappropriate land management practices can result in soil and vegetation degradation [8,9], which in turn will inevitably alter natural hydrologic processes. The possible consequences are more severe flooding, drought, and pollution of lakes and streams. On the other hand, an altered hydrologic condition tends to prompt soil erosion through wind and water [9], which in turn can cause further vegetation degradation or even loss. Such interactions will likely become more interwoven in changing climate [10] because the non-stationary climate, superimposed on human interventions, can further deteriorate the already-altered hydrologic condition. Our understanding is very limited, with few algorithms and parameterization schemes that can be used to account for these dynamic interactions. Existing hydrologic models (e.g., Soil and Water Assessment Tool or SWAT) [11,12] and land–atmosphere models (e.g., Community Land Model or CLM) [13] do not represent such important dynamic interactions well [11,12,14].
Steppe grasslands occupy about 8% of the Earth’s terrestrial surface and are now considered the most altered and beleaguered ecosystem on the planet [15,16]. Over 40% of the globe’s grasslands have been somewhat altered from their indigenous state, including more than 70% of the Inner Mongolian steppe grasslands of China [17], which are part of the Earth’s largest and most characteristic grassland ecosystem, the Eurasian Steppe (or Great Steppe). Here, degradation has caused serious environmental and ecological problems including more frequent and damaging hydrologic extremes (i.e., flooding and/or drought), desertification, dust storms, which has led to shortage of agricultural commodities [9,10,18]. These problems are in turn likely to threaten the sustainability of “grassland agriculture,” a system of agriculture in which the major emphasis is on grasses, legumes, and other fodder or soil-building crops [19]. The main factors causing degradation are overgrazing, cultivation, overdevelopment, and climate change [16,20,21,22,23], which have altered the natural hydrology in the area [24] and led to the erosion of approximately 10 to 20 cm of calcic castanozem topsoil [25]. This topsoil is vital for efforts to sustain grasslands because it is loose and has a plentiful supply of humus/organic matter. Policy choices to reduce or reverse grassland degradation are often made with only a vague understanding of the causative complexity of the linkages between steppe hydrology, topsoil erosion, and grassland degradation, limiting efforts to manage, protect, and/or restore steppe grasslands.
Steppe grasslands across the world are suffering from moderate to severe degradation [26], which has become a key constraint limiting the sustainability of grassland agriculture. Peart [23] examined policies and economic systems that have contributed to grassland degradation, while Gőri et al. [27] assessed the impacts of grassland degradation on wildlife species. Christensen et al. [28] and Endo et al. [29] analyzed climate change and its effect on the vulnerability of steppe grasslands. Climate in the Inner Mongolia steppe, for instance, has been shown to be undergoing a significant spatiotemporal trend, with increasing air temperatures in winter and more frequent droughts in spring [3,30,31,32]. Other researchers (e.g., [24,28,33,34]) have investigated the ecological functions of steppe grasslands and how these functions are affected by grazing and overgrazing, demonstrating that a grazing intensity (i.e., the ratio of the biomass in a non-grazed area to the biomass in the same area if grazed) of 1.5 or below may not cause a sustainability problem for steppe grasslands. Only a few studies [24,35,36,37] have begun to assess the hydrologic processes of steppe grasslands. These studies largely focus on how evapotranspiration (ET) varies with precipitation and/or soil water content, revealing that ET is limited by the availability of soil water (i.e., atmospheric heat stress is weaker than soil water stress, and soil evaporation is the primary contributor to ET) and that ET has maximum daily values ranging from 3.0 to 6.2 mm d−1 in these grasslands. Daily ET rates tend to increase with increasing soil water content, which in turn is highly dependent upon the dry-wet fluctuations experienced by steppe grasslands. Overall, soil water content is higher when grass coverage is denser [38]. These studies also indicate that the aboveground biomass of grassland communities has a positive linear relationship with precipitation and that precipitation in the first half of the year (January to July) is the primary climatic factor causing fluctuations in community biomass production [2,4,10,26].
As we do not yet know how the erosion of approximately 10 to 20 cm of the calcic castanozem topsoil will affect, and is affected by, degradation of the grasses covering it. Steppe grasslands’ vulnerability and resilience depend not only on the phenomena linking hydrologic cycle and topsoil properties but also their interactions. Understanding perturbations in the cycle that trigger unwanted changes in the spatiotemporal characteristics of steppe grasslands remains a challenge because developing such an understanding generally transcends disciplinary and geographical boundaries; it is, however, the key to developing adaptive measures for mitigating the degradation of grasslands. Most previous studies have focused on grassland degradation, topsoil erosion, or hydrologic alteration individually and were thus unable to examine the important interrelationships between them. Consequently, the results from these studies are of only limited utility for those seeking to develop practical and effective solutions to sustain grassland agriculture. In this regard, an ecohydrologic approach, which uses a systematic framework that seamlessly integrates three core components (Figure 1), namely field and laboratory measurement, remote sensing analysis, and modeling, should be adopted to develop effective tools for future steppe-related practice, research, education, training, and learning.
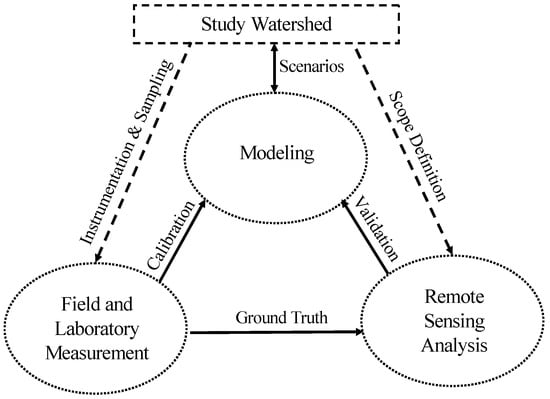
Figure 1.
Schematic showing the ecohydrologic approach.
The objective of this special issue is to provide a forum for original articles on experimental and modeling studies that address: (1) interrelations between hydrologic alteration and soil and/or vegetation degradation with climate change as a possible additional factor; (2) consequences from the alteration of natural hydrology in rural and urban environment; and (3) fate and transport of contaminants (e.g., nutrients) in streams and lakes from altered hydrology.
2. Overview of this Special Issue
This special issue consists of 12 papers that cover a wide range of research topics related to water, soil, and vegetation under the influence of changing climate and human activities. The specific topics include steppe vegetation affected by climate change [39,40], interactions of climate, anthropogenic activities, and watershed hydrology [41,42,43], SWAT modeling for quantifying topography-controlled hydrologic processes and sediment yield [44,45], snow cover and frozen soil dynamics in cold regions [46], quantification of plant transpiration in arid/semiarid environment [47], coupled infiltration-runoff modeling for slope stability analysis [48], and assessment of nutrients in aquatic systems [49,50]. In terms of methodologies, these studies involve both field/laboratory experiments and mathematical modeling across different scales.
Wang et al. [40] proposed a new method that utilized remote sensing images and a total Net Primary Production (NPP) model to predict grazing removal rate of grasses under different climate conditions at a watershed scale. The authors applied their method to evaluate the potential risk of steppe grassland degradation in a semiarid watershed in the Eurasian Steppe, demonstrating the advantages of the new method over the conventional approach that is over reliant upon detailed animal survey data. Particularly, the application of such a new methodology to precisely predict grazing removal rate is of importance to protect the vulnerable steppe ecosystem and effectively mitigate the adverse environmental and ecological consequences (e.g., desertification). In a case study for a desert steppe in China, Song et al. [39] analyzed micro-scale, pixel-level dynamics of Vegetation Fractional Coverage (VFC) and examined the correlations of VFC and its influential factors associated with climatic conditions, hydrologic processes, and human activities. The identified dominant factors were further used for evaluating the distribution of vegetation in the selected desert steppe. The quantitative information on vegetation variations in a desert steppe is useful for assessing the impacts of climate change and human activities and further facilitating ecological restoration.
Apart from the properties of the soil itself, rainfall–runoff processes are controlled by climate variations and affected by human activities in a hydrologic system. Li et al. [42] utilized hydrologic modeling and sensitivity analysis, and the climate elasticity method, to evaluate the impacts of climate and human activities on runoff changes in the upper Red River watershed in China. They found that runoff reduction could be primarily attributed to climate variability in the watershed. The modeling results can be used for sustainable water resources planning and management. In another study, Li et al. [41] analyzed the decreased streamflow in the Yellow River basin in China and examined the potential impacts of climate and human activities based on the observed flow data over a period of more than half a century. The results from their improved Budyko framework and hydrologic modeling indicated that instead of the climatic factors, human activities (e.g., land use and land cover changes, operation of reservoirs, and population) had the greatest impacts on the streamflow in the Yellow River basin. This case study provides analysis approaches to demonstrate the dominant impact of human activities on streamflow. Lu et al. [43] applied the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 5 (CMIP5) dataset and a large-scale Variable Infiltration Capacity (VIC) hydrologic model to assess the impact of climate change on droughts in the upstream Yangtze River region in China. Their predictions revealed that regional drought could be more severe by the 2030s, in terms of duration, frequency, areal extent, and intensity, demonstrating that coupled climatic and hydrologic modeling can be effectively applied to address the hydrologic extreme issues.
Tahmasebi Nasab et al. [45] developed the PD-SWAT model that coupled the widely used SWAT with Puddle Delineation (PD) algorithm for hydrologic modeling in depression-dominated areas. The model incorporated topographic characteristics from the PD into SWAT at the hydrologic response unit (HRU) scale. They tested their new PD-SWAT model for a large watershed in North Dakota and demonstrated the important role of topographic depressions in runoff generation and the related threshold behavior. Implications of the modeling method developed in this study would improve the simulation of the effects of surface depressions on overland flow dynamics, especially for depression-dominated areas such as the Prairie Pothole Region (PPR) in North America. Moon and Kang [44] conducted SWAT modeling to predict basin-scale long-term runoff and sediment yield by using bias-corrected and downscaled Regional Climate Model (RCM) datasets. Their simulation results suggested that sediment yield was closely related to high-intensity and high-frequency rainfall events and the changes in sediment runoff rate mainly depended on climate scenarios and spatiotemporal scales. This study demonstrated the application of combined hydroclimatic modeling and stochastic analysis for terrestrial sediment yield projection.
Two studies on snow cover and frozen soil, and plant transpiration in Northeast China are included. To better understand the dynamic changes and distributions of soil water and heat in a black soil area of Songnen Plain in Northeast China, Fu et al. [46] analyzed the soil freeze–thaw process under different snow cover conditions, and further identified the critical freeze–thaw soil depth using field observed data. Their study helps determine the critical level of soil water and heat dynamics in cold regions with seasonally frozen soils. The findings from this study can be potentially used for soil–water management, soil salinity control, and integrated crop management. Duan et al. [47] measured sap flow of individual stems of two selected plants and then estimated the community-level transpiration using an upscaling function for a site in the Horqin Sandy Land in Northeast China. Their study emphasized the important role of the plant community in stabilizing fixed and semi-fixed sandy dunes. The upscaling function can be utilized for managing and restoring sand-fixing vegetation in arid/semiarid environments.
Johnson and Loáiciga [48] proposed a new method that coupled numerical modeling of runoff and infiltration under variable rainfall conditions for analyzing the translational stability of long slopes associated with the advancing depth of infiltration. Particularly, their slope stability analysis accounted for the effect of the infiltration-induced reduction in apparent cohesion and the increased soil unit weight caused by a moving wetting front. In addition to the basic slope stability analysis, the new modeling method can also be used to improve landslide hazard assessment.
Cheng et al. [49] conducted a series of laboratory experiments to examine the mechanisms of nutrient release from aquaculture sediments influenced by hydrodynamic and dissolved oxygen conditions. They found that hydrodynamics (e.g., flow rate) significantly affected the release of nitrogen (NH3-N, NO3-N, and NO2-N), while the adsorption–desorption processes dominated the phosphorus release from the sediments. The results and findings from these laboratory-scale experiments provide valuable data and information for larger-scale water quality studies. Based on the analyses of long-term field data, Zhang et al. [50] evaluated the wind effects on spatiotemporal variations of total nitrogen, total phosphorus, and Chl-a in Lake Tai in East China. Two critical wind speeds were identified and used to characterize the eutrophication of the lake. It was highlighted in their study that a combination of reduced wind speed and the ongoing anthropogenic activities tended to worsen the eutrophication problem and further led to the deterioration of the entire aquatic ecosystem of the lake. This case study concerning lake eutrophication affected by human activities and climate can be useful for other lake monitoring and assessment research.
3. Conclusions
The 12 articles of this special issue advanced our understanding of water–soil–vegetation interactions as three key components of the Earth’s system under various climatic conditions and anthropogenic activities. The new algorithms presented in four articles [39,40,44,45,48] provide necessary tools for better modeling effects of grazing on steppe grassland degradation, future climates on sedimentation at watershed scale, micro-topographic features (e.g., puddles) on hydrologic processes, and infiltration on the translational stability of long slopes. In addition, two articles [41,43] found that human activities were the primary reason for runoff reduction, whereas, another article [42] showed that climate variability was the dominant driver for decreasing trend of streamflow. Such an apparent difference between these studies can be attributed to the fact that the basins of the former study areas (i.e., Yellow River and Yangtze River basins) are much more populated than watershed of the latter study area (i.e., upper Red River watershed). For an area of interest, the impacts of climate variability and anthropogenic activities tend to affect runoff interactively, while their relative individual impact usually depends on the population. Further, two articles [46,47] examined evaporation from freezing soils and transpiration from sparse-vegetation environments, where the ecosystems are vulnerable and sensitive to water–soil–vegetation interactions. Given that such ecosystems are common across the world, the results presented in these two articles can be insightful for how to protect the global eco-environment. Moreover, two articles [49,50] studied pond/lake water quality and eutrophication as influenced by land management, water hydrodynamics, and climate, demonstrating the linkages between terrestrial and aquatic systems.
The articles cover a wide range of geographic regions across China [39,40,41,42,43,44,46,47,49,50] and the United States of America (USA) [45,48] with contrasting hydro-climate, soil, and vegetation conditions. Thus, the results presented in these articles can have global inferences: the data, analysis/modeling approaches, results, and findings will lay a solid foundation to further our scientific understanding of water–soil–vegetation interactions, ultimately leading to the development of practically effective solutions to sustaining the globe’s ecosystem health and productivity.
Acknowledgments
This special issue is partially supported by the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) International Research Experience for Students (IRES) program (Project # 100653-010), NSF Established Program to Stimulate Competitive Research (EPSCoR # IIA-1355466), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project # 51139002, 51369016, 51469019, 51579106, and 51620105003), the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (Project # 2015RA4013), and the Ministry of Education of China Innovative Research Team (Project # IRT13069). The authors highly appreciate the editor and anonymous reviewers for their invaluable comments as well as the publication team of Water for their tireless efforts.
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Suni, T.; Guenther, A.; Hansson, H.C.; Kulmala, M.; Andreae, M.O.; Arneth, A.; Artaxo, P.; Blyth, E.; Brus, M.; Ganzeveld, L.; et al. The significance of land-atmosphere interactions in the Earth system—iLEAPS achievements and perspectives. Anthropocene 2015, 12, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, F.; Gao, R.; Duan, L.; Liu, T. Responses of grass production to precipitation in a mid-latitude typical steppe watershed. Trans. ASABE 2014, 57, 1595–1610. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, T.; Li, F.; Gao, R.; Duan, L.; Luo, Y. Trend and extreme occurrence of precipitation in a midlatitude Eurasian steppe watershed at various time scales. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 28, 5547–5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, F.; Gao, R.; Luo, Y.; Liu, T. Predicted NPP spatiotemporal variations in a semiarid steppe watershed for historical and trending climates. J. Arid Environ. 2014, 104, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesmeier, M.; Steffens, M.; Kölbl, A.; Kögel-Knabner, I. Degradation and small-scale spatial homogenization of topsoils in intensively-grazed steppes of Northern China. Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 104, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Li, F.; Wang, X.; Liu, T.; Du, D. Temporal variations of runoff in a rapidly urbanizing semi-arid watershed. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2016, 7, 578–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. Advances in separating effects of climate variability and human activity on stream discharge: An overview. Adv. Water Resour. 2014, 71, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.; Wub, J.; Yonga, S.; Yangd, J.; Yonga, W. A landscape-scale assessment of steppe degradation in the Xilin River Basin, Inner Mongolia, China. J. Arid Environ. 2004, 59, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, T.; Li, F.; Gao, R.; Yang, X.; Duan, L.; Luo, Y.; Li, R. Simulated soil erosion from a semiarid typical steppe watershed using an integrated aeolian and fluvial prediction model. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X. Hydro-Climate Temporal Variations and Their Influences on Net Primary Production in a Eurasian Steppe Watershed. Master’s Thesis, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Old Dominion University, Norfolk, VA, USA, 2014; p. 100. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Shang, S.; Yang, W.; Melesse, A.M. Simulation of an agricultural watershed using an improved curve number method in SWAT. Trans. ASABE 2008, 51, 1323–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, W.; Melesse, A.M. Using hydrologic equivalent wetland concept within SWAT to estimate streamflow in watersheds with numerous wetlands. Trans. ASABE 2008, 51, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunke, M.; Broxton, P.; Pelletier, J.; Gochis, D.; Hazenberg, P.; Lawrence, D.M.; Leung, L.R.; Niu, G.; Troch, P.A.; Zeng, X. Implementing and evaluating variable soil thickness in the Community Land Model, Version 4.5 (CLM4.5). Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 29, 3441–3461. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Bagen, C.; Zhu, Z. Revision of the Basal crop coefficients of planted grassland as the source for the sandstorm in Beijing and Inner Mongolia. J. Water Resour. Water Eng. 2006, 15, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Henwood, W. The world’s temperate grasslands: A beleaguered biome. Parks 1998, 8, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- White, R.P.; Murray, S.; Rohweder, M. Pilot Analysis of Global Ecosystems: Grassland Ecosystems; World Resource Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2000; Volume 4, p. 275. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z. Strategic considerations for the protection of grassland ecosystems in China. Grassl. China 2005, 27, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Luo, Y.; Liu, T.; Gao, R.; Li, F.; Duan, L. Estimated grazing removal rate of grasses in a semiarid Eurasian steppe watershed as influenced by climate. In Proceedings of the 18th CIGR World Congress, Session I Land and Water Engineering, 2nd Inter-Regional Conference on Land and water Challenges Ecohydrological Process and Pasture Management Issues, Hohhot, China, 12 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, R.F.; Nelson, C.J.; Collins, M.; Moore, K.J. Forages: An Introduction to Grassland Agriculture; Iowa State Press: Ames, IA, USA, 2003; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Chepil, W.S. Dynamics of wind erosion: V. cumulative intensity of soil drifting across eroding fields. Soil Sci. 1946, 61, 257. [Google Scholar]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Climate Change: The Scientific Basis, in Contribution of Working Group 1 to Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Houghton, J., Ding, Y., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001; p. 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Shi, P.J.; Lin, X.Q. Development of a Chinese grassland-livestock balance dynamic monitoring system. Grassl. Sci. 1995, 3, 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Peart, B. Lift in a Working Landscape: Towards a Conservation Strategy for the World’s Temperate Grasslands; The World Temperate Grasslands Conservation Initiative Workshop: Hohhot, China, 2008; Volume 1, p. 25. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Asanuma, J.; Kotani, A.; Davaa, G.; Oyunbaatar, D. Evapotranspiration from a Mongolian steppe under grazing and its environmental constraints. J. Hydrol. 2007, 333, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Liu, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, G.; Ma, L.; Luo, Y. Spatio-temporal variations in soil moisture and physicochemical properties of a typical semiarid sand-meadow-desert landscape as influenced by land use. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1865–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Han, X.; Wu, J.; Chen, Z.; Li, L. Ecosystem stability and compensatory effects in the Inner Mongolia grassland. Nature 2004, 431, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gőri, S.; Kapocsi, I.; Szilágyi, A.; Zsoldos, I.; Molnár, A.; Nagy, G.; Tamás, G. Restoration of Pannonic Steppes and Marshes. In LIFE-Nature Project in the Hortobágy National Park; HortobáNational Park Directorate: Debrecen, Hungary, 2005; Volume 1, p. 20. [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, L.; Coughenour, M.B.; Ellis, J.E.; Chen, Z. Vulnerability of the Asian typical steppe to grazing and climate change. Clim. Chang. 2004, 63, 351–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, N.; Kadota, T.; Matsumoto, J.; Ailikun, B.; Yasunari, T. Climatology and trends in summer precipitation characteristics in Mongolia for the period 1960–1998. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2006, 84, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Li, F.; Wang, X.; Liu, T.; Du, D.; Bai, Y. Spatiotemporal variations in precipitation across the Chinese Mongolian plateau over the past half century. Atmos. Res. 2017, 193, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.; Chen, J.; Li, L.; Xu, W.; Chen, S.; Gwen, T.; Xu, J.; Zhang, W. Spatial variability in soil heat flux at three Inner Mongolia steppe ecosystems. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2008, 148, 1433–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. Temporal variations of streamflow in a mid-latitude Eurasian steppe watershed in the past half century. Hydrol. Res. 2016, 47, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blank, B.; Breuer, L.; Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Frede, H.G. Indicators of grazing impact in Inner Mongolian steppe ecosystems. Geophys. Res. Abstr. 2009, 11, EUG2009-8683. [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, L.; Coughenour, M.B.; Ellis, J.E.; Chen, Z. Sustainability of Inner Mongolian grasslands: Application of the Savanna model. J. Range Manag. 2003, 56, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Mei, X.; Huang, X.; Cui, X.; Zhou, X.; Niu, H. CO2, H2O and energy exchange of an Inner Mongolia steppe ecosystem during a dry and wet year. Acta Oecol. 2008, 33, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Munkhtsetseg, E.; Kadota, T.; Ohata, T. An observational study of ecohydrology of a sparse grassland at the edge of the Eurasian cryosphere in Mongolia. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S. Responses of grassland ecosystems to precipitation and land use along the northeast China transect. J. Veg. Sci. 2002, 13, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Liu, X.; Yu, R. Field measurement of the water retention curves and simple estimation of the parameters for soils in the central region of Horqin sandy land. In Proceedings of the 2006 Western Pacific Geophysics Meeting, Beijing, China, 24–27 July 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Guo, Z.; Lu, Y.; Yan, D.; Liao, Z.; Liu, H.; Cui, Y. Pixel-level spatiotemporal analyses of vegetation fractional coverage variation and its influential factors in a desert steppe: A case study in Inner Mongolia, China. Water 2017, 9, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Pedram, S.; Liu, T.; Gao, R.; Li, F.; Luo, Y. Estimated grass grazing removal rate in a semiarid Eurasian steppe watershed as influenced by climate. Water 2017, 8, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Duan, L. Decreased streamflow in the Yellow River Basin, China: Climate change or human-induced? Water 2017, 9, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; He, D.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L. Contributions of climate variability and human activities to runoff changes in the upper catchment of the Red River Basin, China. Water 2017, 8, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Wu, H.; Xiao, H.; He, H.; Wu, Z. Impact of climate change on drought in the upstream Yangtze River Region. Water 2017, 8, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.; Kang, B. Terrestrial sediment yield projection under the bias-corrected nonstationary scenarios with hydrologic extremes. Water 2017, 8, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasebi Nasab, M.; Singh, V.; Chu, X. SWAT modeling for depression-dominated areas: How do depressions manipulate hydrologic modeling? Water 2017, 9, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Hou, R.; Li, T.; Yan, P.; Ma, Z. The critical depth of freeze-thaw soil under different types of snow cover. Water 2017, 9, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Lv, Y.; Yan, X.; Liu, T.; Wang, X. Upscaling stem to community-level transpiration for two sand-fixing plants: Salix gordejevii and Caragana microphylla. Water 2017, 9, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.M.; Loáiciga, H.A. Coupled infiltration and kinematic-wave runoff simulation in slopes: Implications for slope stability. Water 2017, 9, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Zhu, D.; Wang, X.; Yu, D.; Xie, J. Effects of nonaerated circulation water velocity on nutrient release from aquaculture pond sediments. Water 2017, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, Q.; Wang, X.; Hu, X.; Wang, C.; Pang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, X. Spatiotemporal distribution of eutrophication in Lake Tai as affected by wind. Water 2017, 9, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).