Abstract
The Maurepas swamp is the second largest contiguous coastal forest in Louisiana but it is highly degraded due to subsidence, near permanent flooding, nutrient starvation, nutria herbivory, and saltwater intrusion. Observed tree mortality rates at study sites in the Maurepas swamp are very high (up to 100% tree mortality in 11 years) and basal area decreased with average salinities of <1 ppt. Habitat classification, vegetation productivity and mortality, and surface elevation changes show a clear trajectory from stagnant, nearly permanently flooded forests with broken canopy to degraded forests with sparse baldcypress and dominated by herbaceous species and open water to open water habitat for most of the Maurepas swamp without introduction of fresh water to combat saltwater intrusion and stimulate productivity and accretion. Healthy forests in the Maurepas are receiving fresh water containing nutrients and sediments from urban areas, high quality river water, or secondarily treated municipal effluent. Currently, two proposed diversions into the swamp are via Hope Canal (57 m3·s−1) and Blind River (142 m3·s−1). These diversions would greatly benefit their immediate area but they are too small to influence the entire Maurepas sub-basin, especially in terms of accretion. A large diversion (>1422 m3·s−1) is needed to deliver the adequate sediments to achieve high accretion rates and stimulate organic soil formation.
1. Introduction
The lower Mississippi Delta, defined herein as the area south of the confluence of the Atchafalaya and Mississippi Rivers, is one of the most important coastal ecosystems, both ecologically and economically, in North America. However, it is severely degraded and is threatened with collapse unless wide-scale restoration efforts are undertaken [1]. During the 20th century, about 25% of the coastal wetlands in the Delta, approximately 4800 km2, were lost through conversion to open water [2,3,4,5]. A variety of factors led to this wetland loss including pervasive hydrological alteration, enhanced subsidence due to petroleum extraction, saltwater intrusion, and barrier island deterioration, but perhaps the most important was the almost complete elimination of riverine input to the deltaic plain due to flood control levee construction and closure of distributaries that connected the Mississippi River to the surrounding Delta prior to the 19th century [1,6,7].
The State of Louisiana has embarked on an ambitious $50 billion, 50-year restoration master plan of the Delta that focuses primarily on restoration of marshes and barrier islands [8]. There are, however, about 324,000 hectares of freshwater forested wetlands in the coastal zone. Despite the fact that almost all of these forested wetlands are degraded and non-regenerative [9,10,11,12], little of the Master Plan addresses forested wetlands. Freshwater forests are an important component of the Mississippi Delta. Dominated by baldcypress-water tupelo (Taxodium distichum-Nyssa aquatica) swamps and bottomland hardwood wetlands, these forests reduce nutrients and sediments in surface water that ultimately flows into the Gulf, provide wildlife habitat, protect coastal urban areas from storm damage by reducing storm surge and eliminating waves atop the surge, retain stormwater, recharge groundwater, support timber, fish, fur, and alligator harvests, offer opportunities for recreation, and sequester carbon [9,10,11,13,14]. Costanza et al. [15] estimated the value of ecosystem services worldwide and determined that swamps and floodplains had the second highest economic value ($7927 per acre per year), second only to coastal estuaries ($9248 per acre per year). Batker et al. [14] estimated that the value of ecosystem services of coastal forested wetlands in the Mississippi Delta was between $3.3 and $13.3 billion per year.
The Maurepas swamp is the second largest contiguous coastal forest in Louisiana, containing 776 km2 of freshwater forested wetlands, and about 52 km2 of fresh and oligohaline marshes [16]. This swamp is highly degraded due to subsidence, permanent flooding, lack of mineral sediment and nutrient input, nutria herbivory, and saltwater intrusion from Lake Pontchartrain during severe storms and drought. Observed tree mortality rates at study sites in the Maurepas swamp are very high (up to 100% tree mortality in 11 years for some plots), and at these rates the trees will be largely gone by mid century [10].
The Maurepas swamp is located in the Pontchartrain Basin, a 12,000-km2 watershed encompassing 16 Louisiana parishes that is the most densely populated region in Louisiana and includes both metro New Orleans and Baton Rouge (Figure 1). About 2.1 million people live in the Basin or over a third of the total Louisiana population [17]. Historically, the upper Pontchartrain Basin was 90% baldcypress-water tupelo (Taxodium distichum-Nyssa aquatica) swamp [18], but within the last several decades there has been a significant transition from forested to emergent wetlands due to increased salinities and saltwater intrusion events associated with leveeing of the Mississippi River and cessation of riverine inputs of fresh water [6,7,11,12].
Figure 1.
General location of the Maurepas swamp (yellow circle) within the Pontchartrain Basin, southeastern Louisiana. Figure modified from Lake Pontchartrain Basin Foundation 2015 Water Quality Brief.
Construction of deep navigation and access canals, such as the Mississippi River Gulf Outlet (MRGO) [11], combined with sea level rise, has exacerbated the frequency and intensity of saltwater intrusion events. Periodic droughts can raise salinity in western Lake Pontchartrain and parts of Lake Maurepas above 10 ppt for extended periods [12]. As a result of these impacts, tree mortality rates are high and much of the swamp is transitioning to marsh and open water [10]. There is very little closed canopy left and most of the trees in the swamp will not naturally regenerate due to semi-permanent to permanent flooding [9,10,11,19,20,21,22,23,24]. The vegetation under the swamp canopy is mostly weakly rooted marsh and shrub species or open water [10]. Without the forest in place, the understory vegetation is very susceptible to hurricane disturbance [25,26].
If current trends continue, most of the forested wetlands in the Maurepas sub-basin will have transitioned to emergent wetlands or open water by mid-century, exposing the developed natural levee ridge between Baton Rouge and New Orleans to much greater hurricane threat. Freshwater discharge into the Maurepas swamp will help lower salinity to historic concentrations, introduce nutrients, and enhance productivity, net sediment accretion, carbon sequestration, and biodiversity [14,27]. Preserving the remaining baldcypress—water tupelo trees and increasing the area of freshwater forested wetlands will improve several of the “multiple lines of defense” proposed by Lopez [28], including a decreased potential for storm damage.
Hydrologic alterations to the Maurepas swamp are characteristic of most coastal forested wetlands in the U.S. and elsewhere. Similarly, the trend of increasing saltwater intrusion into coastal forested wetlands, due to sea level rise, is occurring worldwide. So the trajectories of degradation described herein, and mechanisms to reverse them, are broadly applicable. Our objectives in this paper are to (1) review the current state of the Maurepas swamp; (2) introduce four new years of data and review its implications; and (3) address threats to the swamp and approaches to its restoration.
2. Methods
2.1. Study Sites
The swamps of Lake Maurepas are located in the upper Lake Pontchartrain Basin of southeastern Louisiana (Figure 1). Shaffer et al. [10] initiated a study in 2000 in which 20 sites in the Maurepas swamp were established with paired 625-m2 stations to capture three habitat types characterized by different hydrological regimes: (1) Relict—stagnant, nearly permanently flooded interior sites, characterized by trees with broken canopies, few mid-story species, a well-defined herbaceous community, and a complete lack of natural regeneration; (2) Degraded—sites near Lake Pontchartrain or the margin of Lake Maurepas that are prone to severe saltwater intrusion events characterized by dead trees, sparsely dotted with baldcypress, and dominated by herbaceous species and open water; and (3) Throughput—sites receiving reliable nonpoint sources of freshwater runoff, characterized by mature overstory and midstory stands and little herbaceous cover (Figure 2). The Relict, Degraded, and Throughput sites characterize an area roughly 828 km2 and were replicated to reflect the relative proportion of each habitat type. Four additional sites with paired 625-m2 stations were installed in 2004 to provide baseline conditions for a planned levee-gapping project on the Amite River Diversion Canal (Figure 2).
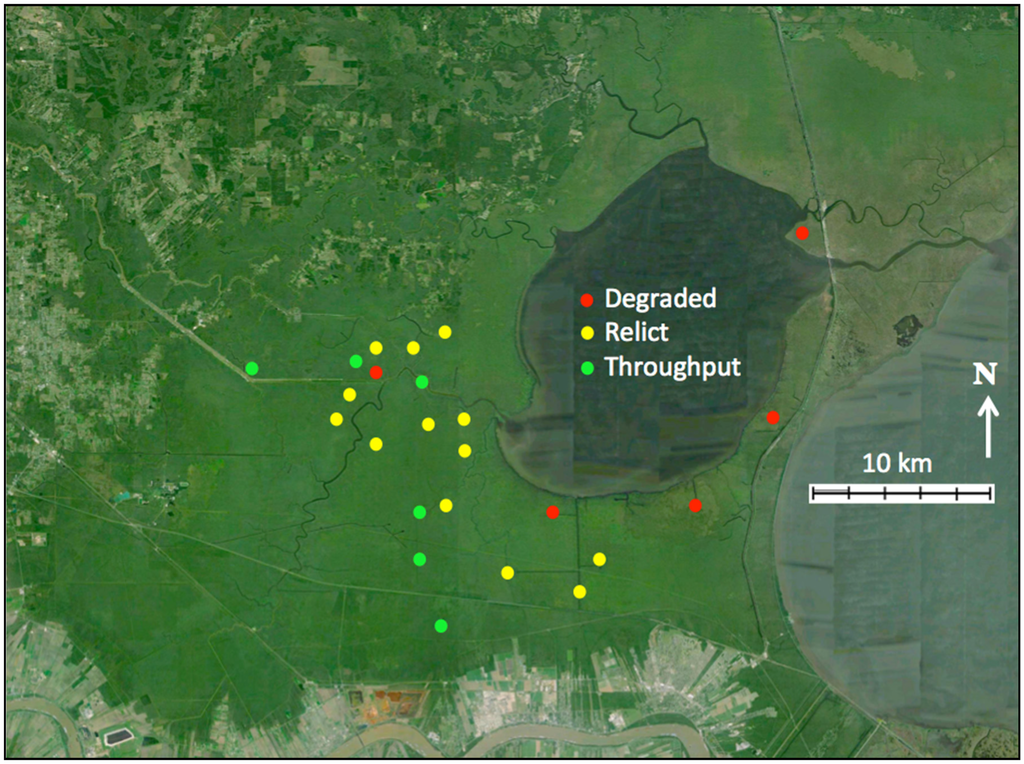
Figure 2.
Twenty four sites, each with two 625 m2 stations were selected to represent the three major habitat types: Throughput (green), Relict (yellow), and Degraded sites (red).
2.2. Environmental Variables
Annually, from 2000 through 2010, a number of abiotic variables were measured, with soil bulk density, interstitial soil salinity, and light penetration being the most important predictors of herbaceous and tree production so we will limit description to these.
To measure pore-water salinity, two 1-m by 6-cm diameter PVC wells were inserted 0.75 m into the ground at each of the 40 stations. Wells were capped at both ends. Horizontal slits were cut into the wells every 2 cm from a depth of 5 cm to a depth of 70 cm below the soil surface to enable ground water to enter. Well-water salinity was measured during most site visits and averaged to yield a measure of yearly mean salinity at each study plot.
Soil cores for bulk density analysis were collected during the fall sampling period in 2001 and 2002, using an aluminum soil corer with a 1.6 cm inner diameter. Samples were collected by coring to a depth of 10 cm. To minimize the influence of micro-scale heterogeneity of soil properties, five replicate cores were taken at two locations within each study plot. The five replicate cores were combined into a single sample in the field, while the two pooled samples from different locations within the same study plot were processed independently.
Light penetration was measured in the center of each of four 16 m2 herbaceous plots within each station, using a spherical crown microdensiometer. Tree height was measured with a Suunto Altimeter.
2.3. Herbaceous Vegetation
Within each of the 48 permanent stations, four 4 m × 4 m (16 m2) permanent herbaceous plots were established 5 m in from the diagonal corners of each station. A 4-m2 plot was established in the center of each 16-m2 plot for cover value estimates and biomass clip plots. Each year cover values were obtained by two independent estimates during summer and fall. Each year understory primary production was estimated within each herbaceous plot by clipping two randomly chosen (non-repeating) replicate subplots (of 0.25 m2 area) twice during the growing season. The pseudoreplicate subplots were pooled on site during May–June (summer) sampling and again during late September–early October (fall). Plant material was clipped at the soil surface, placed in a labeled bag, and transported to the lab, where it remained in cold storage until it could be oven-dried and weighed. Annual aboveground herbaceous production was estimated by summing the summer and fall biomass estimates [10].
2.4. Forest Vegetation
All trees greater than 5 cm diameter within each of the two 625 m2 plots at each of the 24 study sites in the Maurepas swamp were tagged using 8-penny galvanized nails and pre-numbered 5-cm metal ID tags in February and March of 2000. Trees were tagged at breast height, unless the fluting bases of baldcypress (Taxodium distichum) and water tupelo (Nyssa aquatica) or the complex branching structure of shrubs such as wax myrtle (Morella cerifera) required the tags to be somewhat higher. Using fiberglass metric diameter tapes, initial tree diameters of 1860 tagged trees were measured during February and March of 2000 at the bottom of the freely hanging metal tags. During late fall, 2000–2010, diameter measures were taken of all tagged trees. Throughout the study many trees suffered mortality and many saplings grew to the 5 cm tagging size such that a total of 2219 trees were tagged in all.
Tree primary production was measured through the collection of annual litter-fall and the measurement of annual tree diameter growth at the 48 stations. Five litter-fall traps were installed at approximately even spacing at each of the two stations at 24 study sites to yield a total of 240 litter traps deployed. Each of these traps was 0.25 m2 in area and was constructed to catch biomass in a fine (1 mm) mesh approximately 1 meter above the ground to prevent loss from flooding events. The litter was collected frequently during site visits, which occurred as often as once every two weeks or as infrequent as once every two months during periods of the growing season when few leaves were falling (i.e., spring, summer). During or after collection, the litter from each of the five pseudoreplicate litter traps at each plot was combined to yield one total sample of litter per plot. For this study, we use the term litter for leaves, flowers, fruits, and seeds. Collected litter was then dried to constant mass at 65 °C. After drying, the litter was sorted into T. distichum, N. aquatica and “Other” litter. This enabled us to monitor production effects at the species level for at least the two most dominant tree species in the swamp. The vast majority of “Other” stems were midstory swamp red maple (Acer rubrum (var. drummondii)) and ash (Fraxinus pennsylvanica and F. profunda).
Each year, tree diameter was used to calculate tree wood biomass using published regression formulas [29,30,31]. Wood production was calculated as the difference in wood biomass per year. Wood production per tree was then summed by species category per plot and then converted to total wood production per square meter per year (g·m−2·year−1).
2.5. Sediment Elevation Change
In 2003, at a relatively healthy site located at the confluence of Bayou Lil’ Chen Blanc and Blind River, 12 surface elevation tables (SET) [32] were installed, each approximately 3 m from the bole of a mature baldcypress. Each SET was outfitted with a 3 m × 3 m platform for taking undisturbed measurements [32]. The area within the bench received one of three treatments: four plots received no treatment, four received 11.25 g·N·m−2·year−1 of 18-6-12 time-released fertilizer to simulate the loading rate of a 42.5 m3·s−1 Maurepas diversion [33] during the spring, and four received 11.25 g·N·m−2·year−1 fertilizer plus 1-cm of Bonnet Carré River silt to simulate sites located more proximal to a river diversion. The treatments were applied annually through 2008. SET measurements were taken in 2003 and again in 2008.
The nearest long-term NOAA tide gauge to the Maurepas swamp is located at New Canal in the southern Pontchartrain. That gauge registered a relative sea level rise (RSLR) trend of 4.5 mm·yeat−1 (1.38 mm·year−1, 95% CI) over the past 33 years (1982–2015). We also use the Grand Isle, Louisiana gauge (approximately 120 km away), because it is the standard used in coastal Louisiana; it registered a RSLR trend of 9.07 mm·year−1 (0.47 mm·year−1, 95% CI) over the past 60 plus years [34].
2.6. Mapping Habitat Types
Habitat classes were generated from the change between twelve historic images (1992, 1995, 1998, 2001, 2003, 2004, 2005, 2006, 2007, 2008, 2009 and 2010) via Google Earth and LSU Atlas DOQQ’s using a 2010 base map via ArcMap 9.3.1. The overall spatial area was broken down into 15 separate subunits that were independently assigned categorical values based on temporal change between images by creating a shape file over an ArcMap base layer. The separate subunit shape files were then ground-truthed and compared to our habitat map generated in 2006 (Figure 13 in [10]), along with many site-specific field inquiries where habitat class determination inconsistences were rectified. Final class assignment areas were computer generated using the ArcMap spatial analyst tool that generated acreages of habitat type present which was then converted into percentages.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using SYSTAT 10.2 [35] and SAS 9.1.2 for Windows [36]. Primary production data that included tree species (baldcypress, water tupelo, and “Other” (mostly swamp red maple and ash)) were subjected to a repeated measures analysis of covariance design with experimental (sites) and sampling (stations within sites) error terms. Interaction terms and higher order nested terms were pooled with the appropriate error term when non-significant F values were <1.70. Comparisons of herbaceous production with tree production required summing over tree species categories. Potential covariables included light penetration, bulk density, pore-water salinity, and woody basal area. Bonferroni-adjusted LSDs were used to determine significant mean differences. Linear contrasts were used to address specific a priori hypotheses. In addition, wood and litter production also were analyzed as total (all species) wood and litter production per m2 per year, again with bulk density, interstitial salinity, light penetration, and basal area as potential covariables. Finally, herbaceous, wood, and litter production were combined for total primary production and analyzed for site grouping differences. Unless otherwise noted, all statistical findings were significant at a Bonferroni-protected α = 0.05 level [37].
Non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMS) [38,39] using Bray-Curtis similarity, 50 iterations, and 10000 permutations was used to determine the nature of the temporal trajectory of the tree and herbaceous vegetation of the Maurepas swamp and to determine the crispness in habitat separation of the three habitat types (Degraded, Relict, and Throughput) over the study period. The ANOSIM test in Primer 6 [39] revealed a significant difference among habitat types (ANOSIM Global R = 0.42), therefore we used NMS in Primer 6 to describe these differences. We used the BEST procedure with the BVSTEP option to determine the most influential factors in our classification.
3. Results
3.1. Environmental Variables
Overall, salinity was highest at Degraded sites located near the Lake margin and lowest at Throughput sites which were all interior sites located near reliable sources of non-point freshwater input (Figure 3). Salinity spikes occurred at all sites during the droughts of 2000 and 2006.
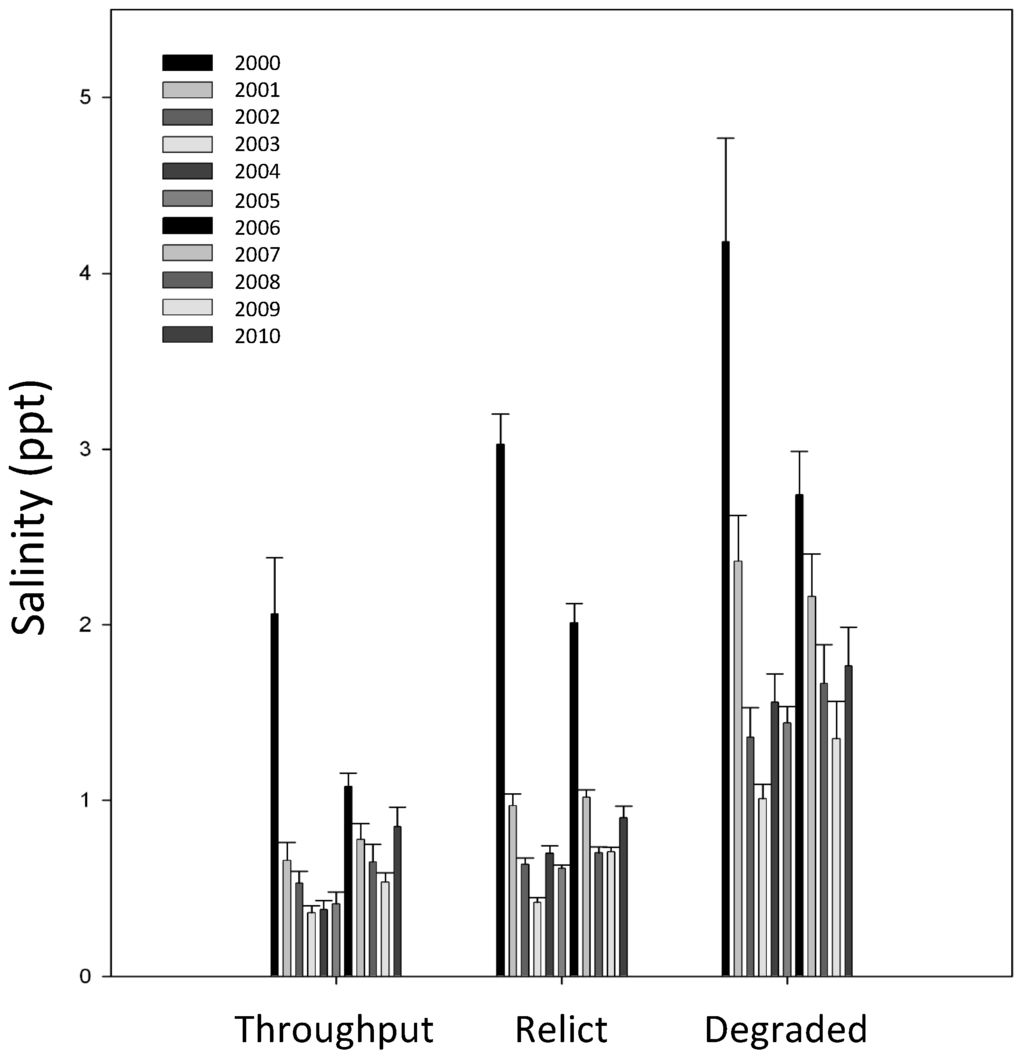
Figure 3.
The average observed interstitial soil salinity in the Maurepas swamp from 2000 through 2010.
Soil bulk density, light penetration, canopy tree height, stand density index [32], and basal area all differed widely across the three habitat types (Figure 4). The highest bulk densities were found at the Throughput sites (mean = 0.16 ± 0.03 g·cm−3 S.E.; Figure 4a) and the lowest at Degraded sites (mean = 0.06 ± 0.005 g·cm−3). Relict sites had intermediate bulk densities (mean = 0.08 ± 0.01 g·cm−3).
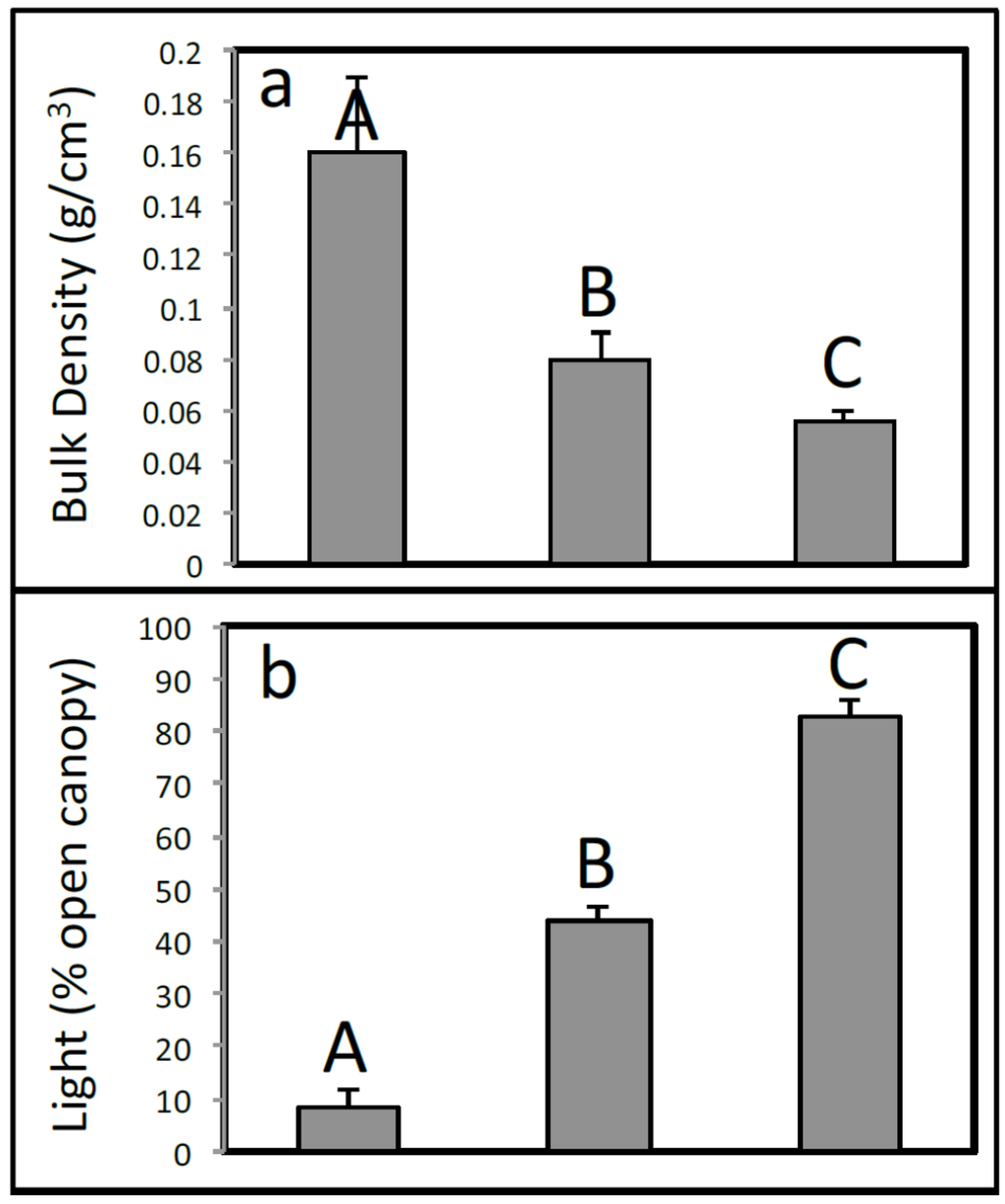
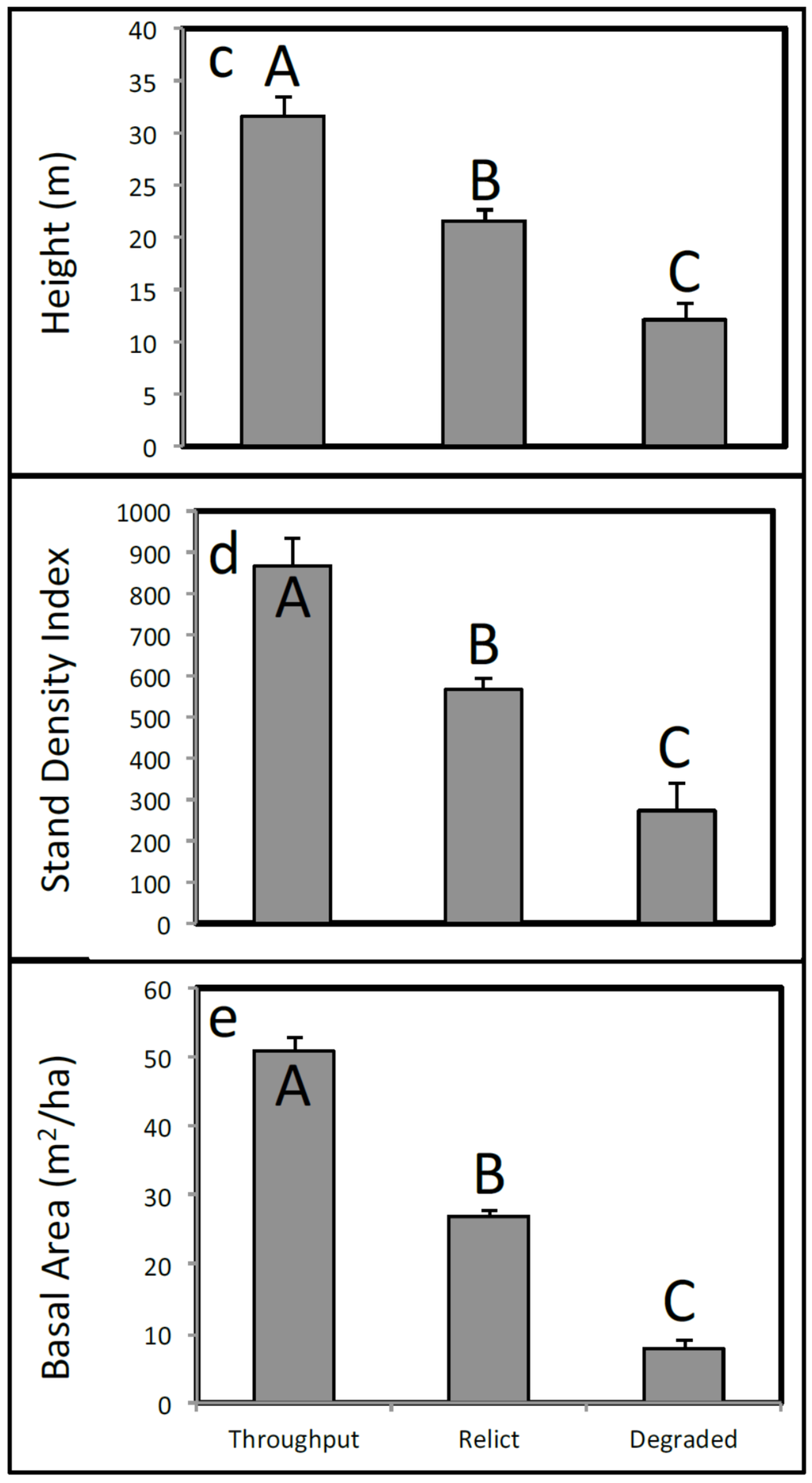
Figure 4.
Environmental variables include (a) soil bulk density (g·cm−3); (b) light penetration (%); (c) canopy tree height (m); (d) stand density index; and (e) basal area for each habitat type. Letters above bars indicate Bonferroni-adjusted significant differences.
3.2. Tree Mortality
Tree mortality has been remarkably steady over the 11-year study (Figure 5). To date, over 32% of the monitored trees have suffered mortality, with mortality as high as 100% at several Degraded sites. Recruitment of baldcypress and water tupelo is extremely rare. Early in the study most of the mortality occurred at Degraded sites. However, because these trees died, the highest rate of mortality now occurs at Relict sites. By far the highest mortality is for the “other” grouping, nearly all of which is swamp red maple, pumpkin and green ash midstory species (Figure 5).
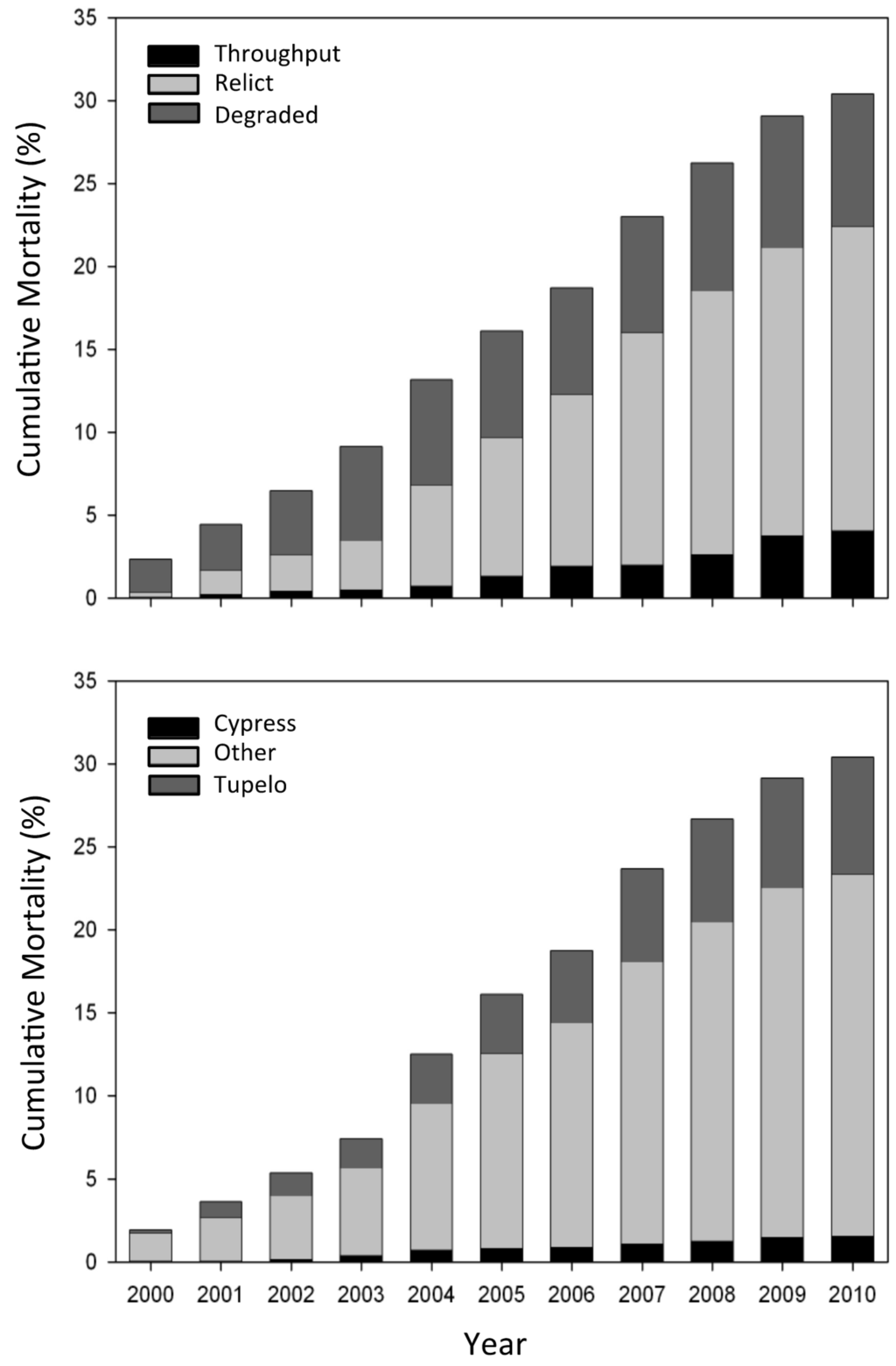
Figure 5.
Cumulative percentage mortality for the three habitat types and species—baldcypress, water tupelo, and “other” (predominantly swamp red maple and ash).
3.3. Herbaceous Vegetation
There were four dominant herbaceous species found in the study sites, including Sagittaria lancifolia, Eleocharis macrostchya, Eleocharis vivipara, and Alternanthera philoxeroides. S. lancifolia was present at all sites but most abundant at Relict sites (Figure 6A). E. macrostchya was found in the Throughput and Relict sites but not at Degraded sites (Figure 6B) and E. vivipara was in high abundance at the Degraded sites, intermediate abundance at the Relict sites, and was almost completely absent at Throughput sites (Figure 6C). Alternanthera philoxeroides was ubiquitous among all three habitat types, though more abundant at Throughput and Relict sites than at Degraded sites (Figure 6D).

Figure 6.
3-D nonmetric multidimensional scaling (NMS) ordination based on percent cover of all herbaceous species at the three different habitat types per year (2000–2010; red = degraded, brown = relict, and green = throughput). (A) Sagittaria lancifolia; (B) Eleocharis macrostachya; (C) Eleocharis vivipara; and (D) Alternanthera philoxeroides. Size of bubble reflects relative cover; missing bubble reflects no cover.
During hurricane years (2002, 2005 and 2008) extreme prolonged flooding during the fall killed much of the herbaceous ground cover. The year following hurricanes (2003, 2006, 2009) there was a strong trend of increased vegetative cover of annual species, such as Polygonum punctatum (Figure 7). The pattern of cover of P. punctatum during high salinity years was consistently different from other years (Figure 7).
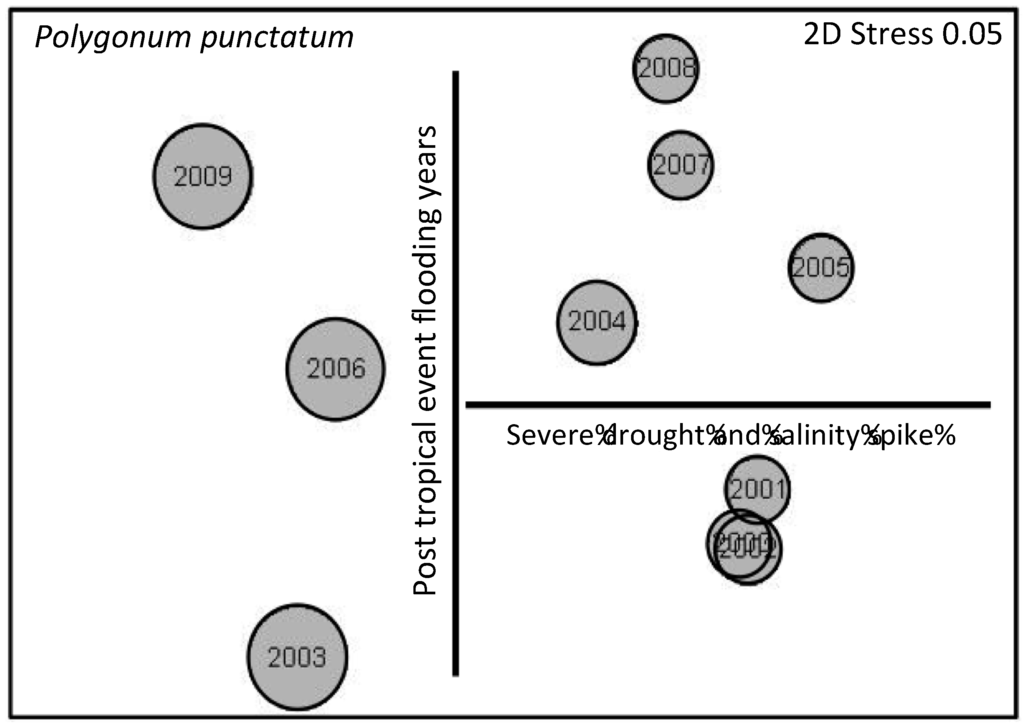
Figure 7.
Nonmetric multidimensional scaling (NMS) ordination based on percent cover of all herbaceous species from 2000–2010. Bubble plot is for Polygonum punctatum, where size of bubble reflects relative cover.
3.4. Herbaceous Vegetation Production
Net aboveground primary production of herbaceous species was consistently highest at Degraded sites and lowest at Throughput sites (Figure 8). Despite this overall trend, the three habitat types had remarkably similar patterns of herbaceous NPP over time (Figure 8). Herbaceous production peaked during 2006 and has subsequently declined as marsh continues to degrade to open water.
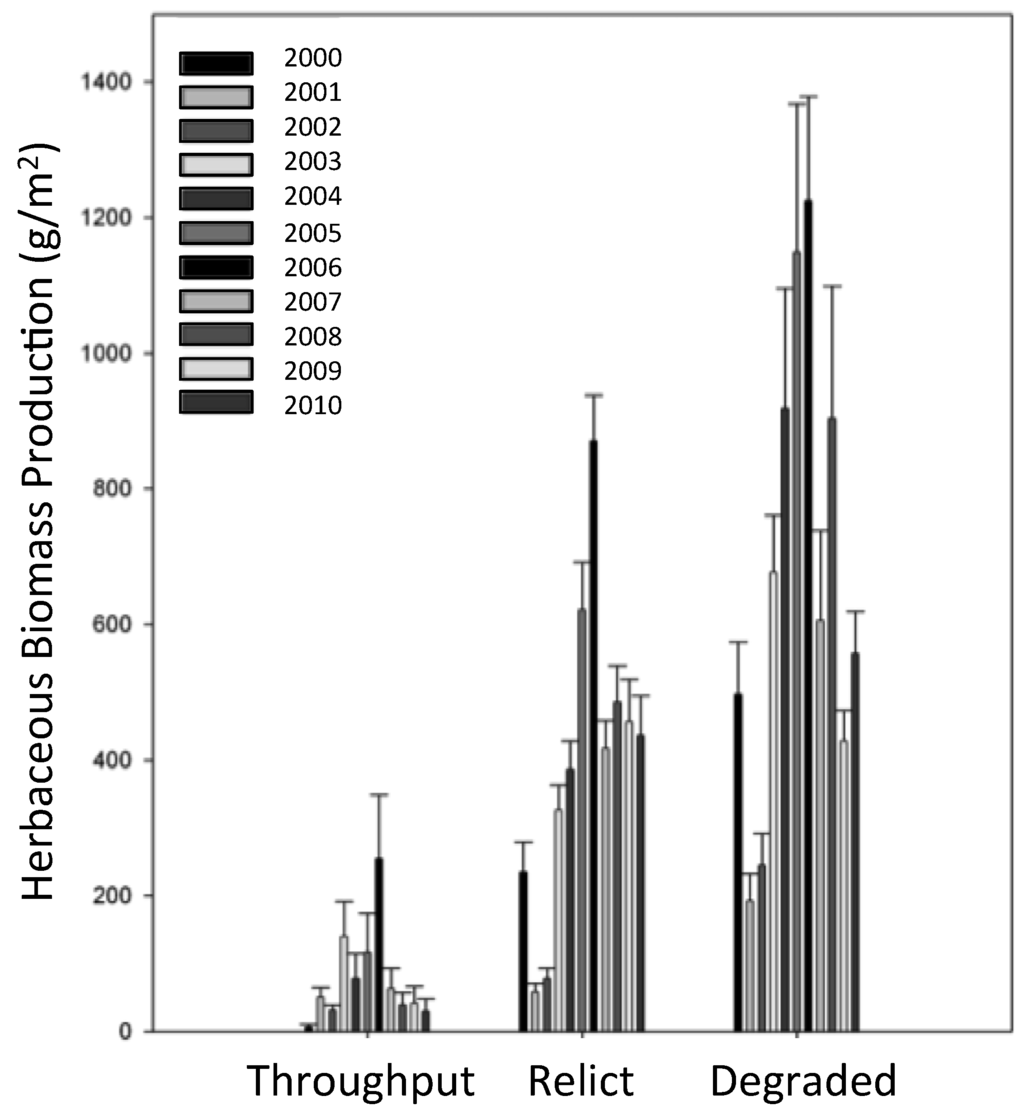
Figure 8.
Annual aboveground net primary production of herbaceous ground cover from 2000–2010.
3.5. Tree Production
Across the 11 years of this study, litter production of trees generally exceeded woody production (Figure 9). Average woody production fell to a low of less than 200 g·C·m−2·year−1 in 2003 to a high of 560 g·C·m−2·year−1 in 2007, 2 years after Hurricanes Katrina and Rita. Total tree NPP was highest at Throughput sites, averaging about 800 g·C·m−2·year−1 for all species combined (Figure 10). Although baldcypress was the least common of the primary tree species, which included water tupelo, swamp red maple, and pumpkin and green ash, it had the highest rates of total NPP (Figure 10).

Figure 9.
Litter and wood net primary production of all tree species from 2000–2010. See Methods for details.

Figure 10.
Average net primary production of baldcypress, water tupelo, and “other” (predominantly swamp red maple and ash) for the three habitat types across eleven years.
The three habitat types differed widely in both herbaceous and tree net primary production (NPP), with Throughput NPP almost completely dominated by tree production and Degraded sites dominated by herbaceous production (Figure 11). In terms of total NPP, Relict sites had significantly lower NPP than the other two habitat types, which did not differ. When the study began in 2000, total NPP was dominated by trees (Figure 12). Midway through the study herbaceous species had considerably higher NPP than trees. By the end of the study NPP was about even and lower as portions of herbaceous marsh at several Degraded sites had converted to open water.
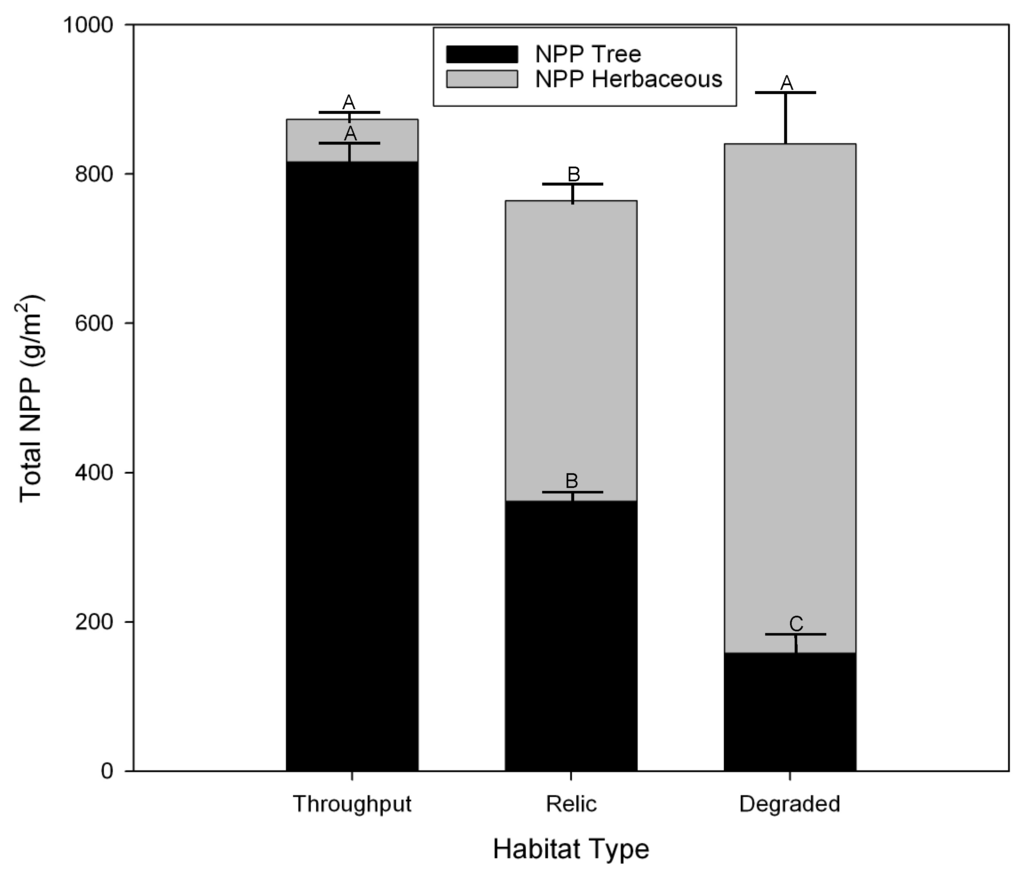
Figure 11.
Average net primary production of herbaceous vegetation and trees across the 11-year study by habitat type.
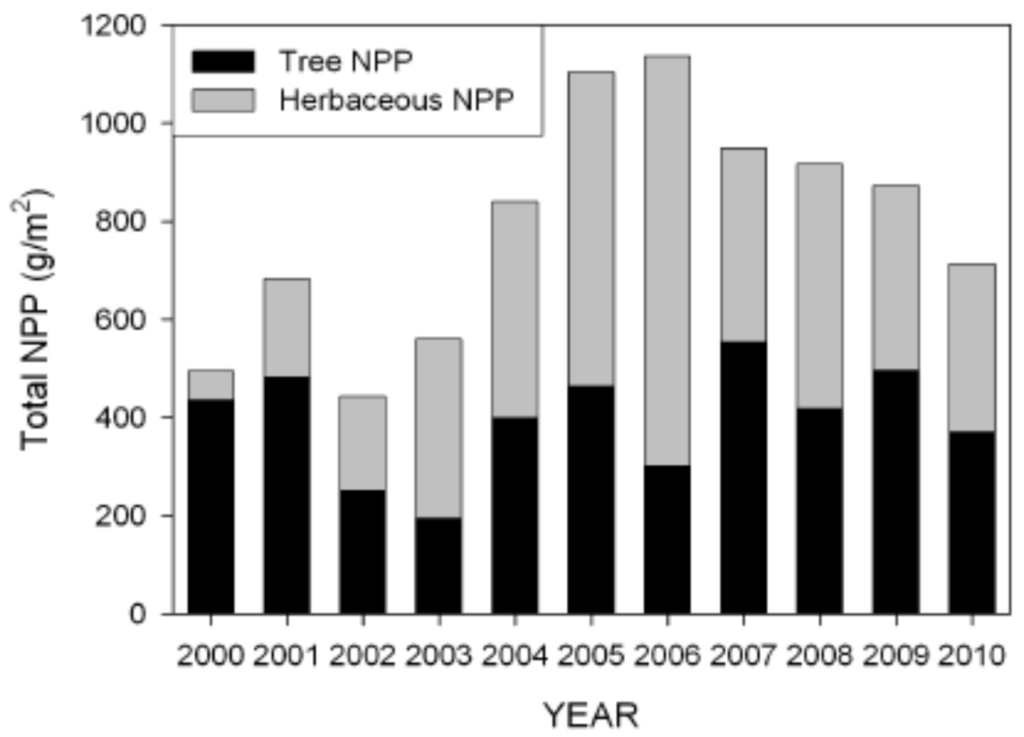
Figure 12.
Total net primary production of herbaceous vegetation and trees from 2000–2010.
Non-metric multidimensional scaling of wood NPP, litterfall NPP, and herbaceous NPP reveals Throughput sites to be the most stable and distinct habitat type and Degraded the least stable (Figure 13a). All three habitat types displayed strong cyclicity (Throughput Rho = 0.716, p < 0.001; Relict Rho = 0.553, p < 0.001; Degraded Rho = 0.611, p < 0.001). Inverse trajectories across habitat types exist for herbaceous (Figure 13b) and tree (Figure 13c) net primary production.
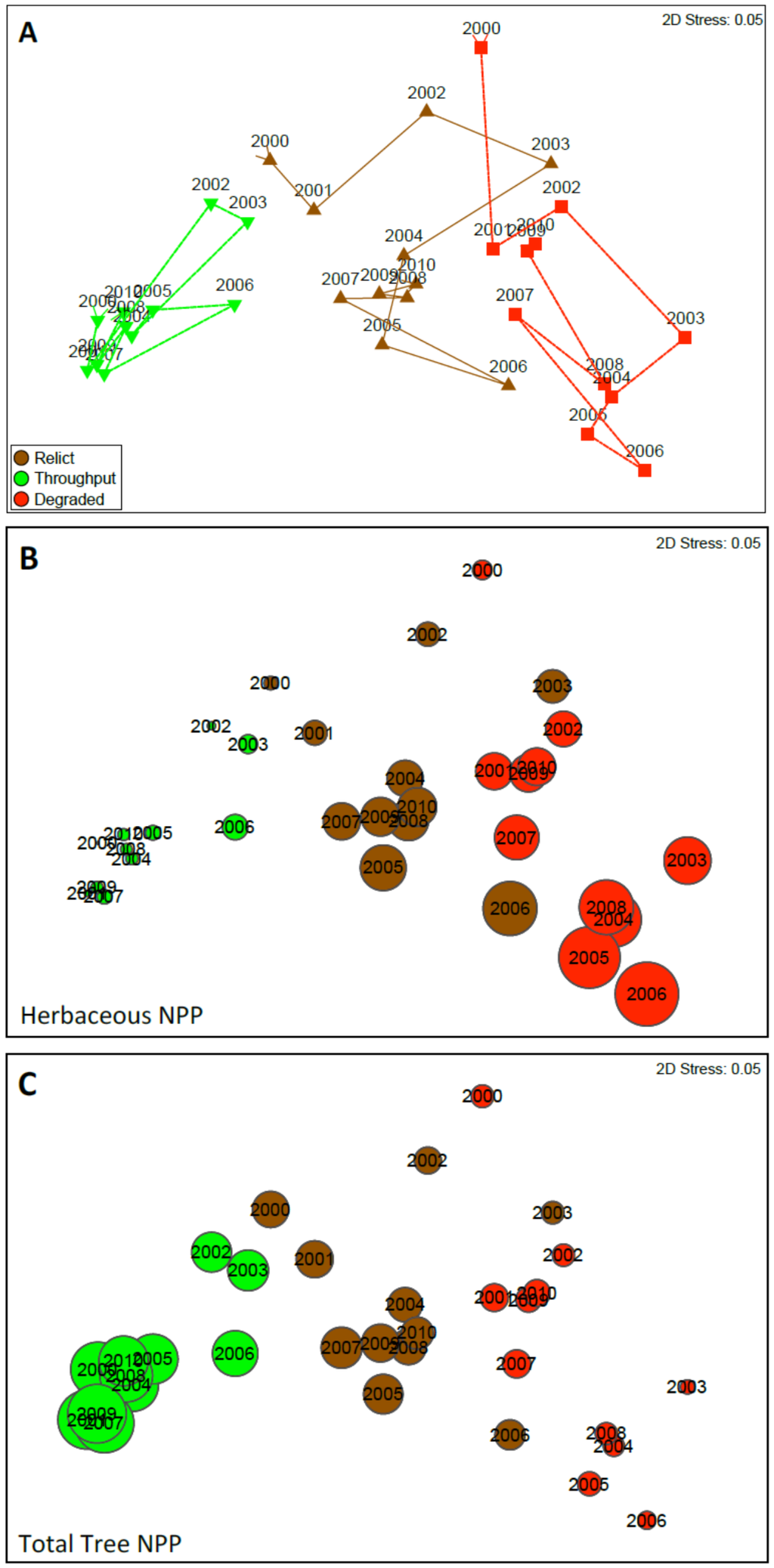
Figure 13.
Nonmetric multidimensional scaling (NMS) ordination of net primary productivity (NPP—grams dry weight per meters squared per year) based on wood production, litter fall, and total herbaceous biomass production, for all years (2000–2010). (A) represents all three habitat types and their trajectories over the 11-year study; The closer points are, the more similar their overall NPP; (B,C) are the same NMS as (A); however, instead of showing a trajectory for each habitat type, bubbles represent NPP for herbaceous biomass (B) and total tree NPP(C); The larger the bubble, the greater the NPP. Colors are consistent with habitat types in (A).
3.6. Basal Area and Salinity
To determine the relationship between basal area and long-term salinity average, we averaged both over the 11-year period for baldcypress, water tupelo, “other” midstory species (e.g., ash and maple) and the entire forest (Figure 14). Surprisingly, all species followed an exponential decay trend beginning at very low salinities. The 11-year salinity average for Degraded sites was 1.93 ppt (S.E. ± 0.15 ppt) and these sites have few to no trees remaining. Relict sites, with an average salinity of 1.05 ppt (S.E. ± 0.02 ppt) all have dead and dying water tupelo, ash, and swamp red maple and are completely lacking in natural regeneration. The healthy Throughput sites had an average salinity of 0.76 ppt (S.E. ± 0.07 ppt).

Figure 14.
The relationship between basal area of (a) baldcypress; (b) water tupelo; (c) midstory (mostly ash and maple); and (d) all tree species combined and salinity averaged over the 11-year study for each 625 m2 station.
3.7. Surface Elevation Change
The control plots averaged 8.1 mm·year−1 of elevation gain, the fertilized plots averaged 7.8 mm·year−1 gain, and the fertilizer plus sediment addition averaged 13.4 mm·year−1 of elevation gain. Considering the average RSLR of 4.50 mm year−1 for the New Canal tide gauge and 9.07 mm·year−1 for the Grand Isle tide gauge, the control and fertilizer treatments range between a 3.6 mm·year−1 surplus to a 1.27 mm·year−1 elevation deficit, whereas the fertilizer plus sediment addition treatment had an elevation surplus ranging between 4.3 and 8.9 mm·year−1.
3.8. Habitat Classification
The percentages of each habitat type in the 2010 habitat classification map (Figure 15) differed substantially from the 2006 map of Shaffer et al. ([10]; Figure 13). Mapped areas that classified as Degraded habitat increased from 16% to 28.2% (23,337 ha) and almost all of these are either close to Lake Pontchartrain or along the margins of Lake Maurepas (Figure 15), both of which are exposed to frequent events of saltwater intrusion. Throughput habitat occupied 26.9% (22,294 ha) of the classified area and was largely isolated from saltwater intrusion events and contiguous with sources of freshwater input, mostly nonpoint source runoff from developed areas. Relict swamp accounted for 44.8% (37,114 ha) of the classified area.
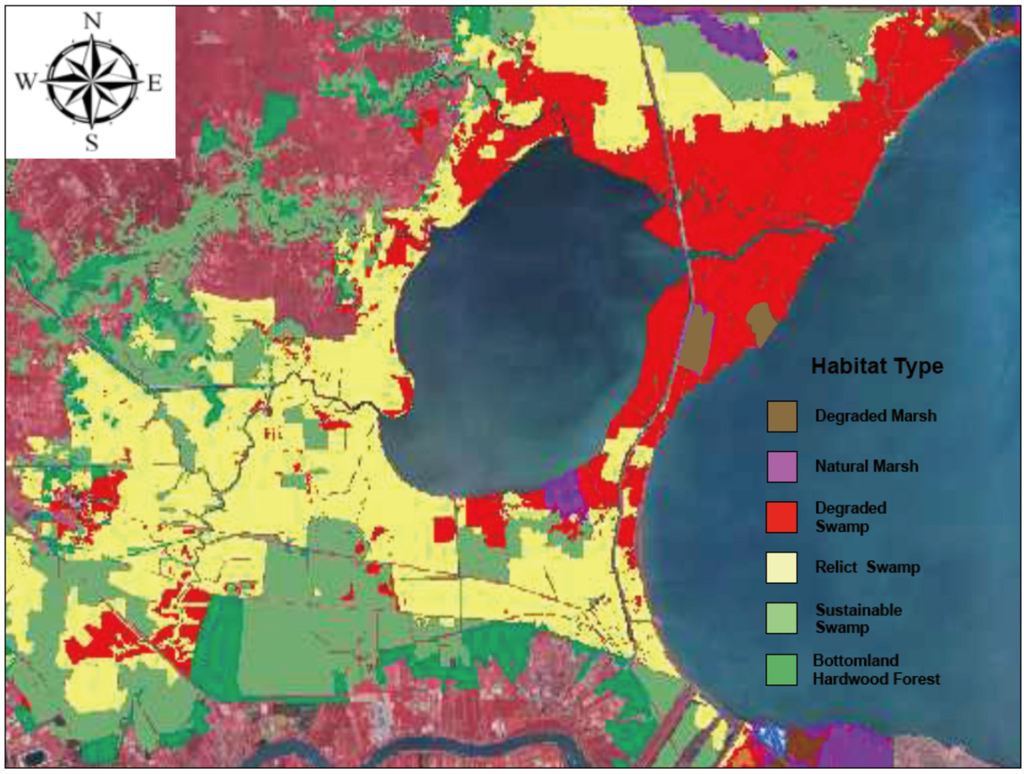
Figure 15.
Habitat type classification of the wetlands in the upper Lake Pontchartrain Basin, Louisiana. Habitats include natural marsh (purple), degraded marsh (brown), Degraded swamp that has converted to marsh over the past 60 years (red), Relict swamp (yellow), potentially sustainable Throughput swamp (light green), and bottomland hardwood forest (dark green).
4. Discussion
The dominant causes of coastal forested wetland degradation in the Lake Maurepas sub-basin are the same as many other coastal forests in the US and elsewhere, namely saltwater intrusion, altered hydrology, and nutrient limitation. The vast majority of the Maurepas swamp (73%) is characterized as either Relict or Degraded habitat. Surface water inundation has doubled in the Maurepas swamp since 1955 because of sea-level rise and subsidence [40]. Currently, the soil surface of most of the swamp is as low or lower than the surface elevation of the Lake, resulting in near permanent flooding (Figure 16). Furthermore, flood control levees, road embankments, and abandoned raised railroad tracks used for logging have impounded much of the remaining swamp, disconnecting surface water exchange and cutting off sustaining spring floods of the Mississippi River for over a century. Mean tree height, basal area (Figure 4) and tree net primary production (Figure 10) were highest at the sites receiving point and nonpoint sources of fresh water (Throughput sites), intermediate at those with stagnant, permanently flooded soils (Relict sites), and lowest at Degraded sites prone to saltwater intrusion.
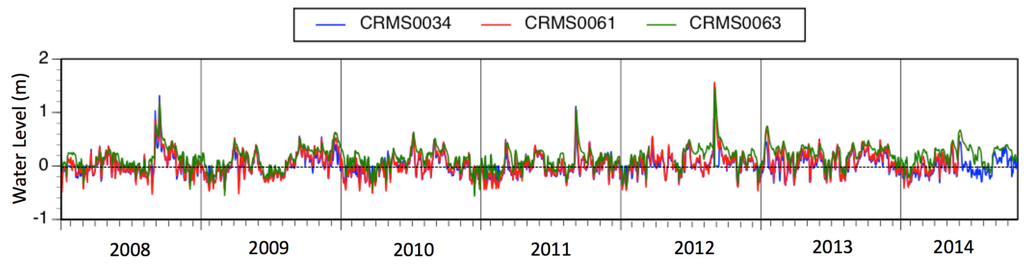
Figure 16.
Hydrograph data from three baldcypress—water tupelo Coastwide Reference Monitoring Sites (CRMS sites) in the Maurepas from 2008–2014. Note trend of increased flooding in more recent years.
For the relationship between forested basal area and long-term salinity we expected to find a threshold relationship for baldcypress and water tupleo with decreased basal area beginning at about 2 ppt and 1 ppt, respectively [22,41,42,43]. Instead, all species experienced exponential decline in basal area beginning at a chronic salinity as low as 0.5 ppt (Figure 14). As expected, basal area of baldcypress had the weakest relationship with increased salinity, as it is the most salt tolerant of these swamp tree species [44,45,46,47] These results indicate when baldcypress—water tupelo swamps are stressed by other factors such as permanent flooding, stagnant conditions, and nutrient limitation, they appear to be more sensitive to salinity than indicated by past greenhouse experiments [9,23,44,45,46,47] and field studies [9,22,41,42,43].
Baldcypress—water tupelo forests can be analyzed for their competitive status using the stand density index (SDI) [48] developed by Reineke [49]. In general, trees in stands with SDI > 660 are competing with each other for resources sufficiently to cause periodic mortality by self-thinning. Conversely, stands with SDI < 360 do not have enough trees to fully occupy site resources, indicating strong limitations on regeneration and/or growth, or mortality of trees by stressors not related to competition. For the 12 Throughput stations in the Maurepas swamp, nearly every station is above the self-thinning threshold of 660 (Figure 4d), indicating vigorous tree growth and no substantial mortality from non-competition stressors such as nutrient limitation, prolonged flooding, and saltwater intrusion. In contrast, Degraded stands generally have SDIs well below the site occupancy threshold, which indicates severe environmental stressors and lack of regeneration. Water tupelo, ash, and swamp red maple cannot tolerate the periodic salinity conditions during drought of 2–4 ppt found at these sites [10,24]. Likewise, the relatively low stem densities observed at the Relict swamp sites are primarily the result of the decreased abundance of ash and swamp red maple in the impounded and stagnant hydrologic regimes characteristic of these sites [22]. To date > 32% of the > 2000 trees monitored during this study have died, with some Degraded sites experiencing complete tree mortality.
In this study, nutrient addition simulating the planned 42.5 m3·s−1 Maurepas diversion did not stimulate elevation gain compared to the control, and both had slight elevation surpluses or deficits compared to RSLR at New Canal or the standard for coastal Louisiana located at Grand Isle. However, Rybczyk et al. [50] and Brantley et al. [51] found that waters diverted from municipal wastewater treatment facilities stimulated vertical accretion in coastal swamps of Louisiana. Hunter et al. [52] found that the Mandeville assimilation wetland, also located in coastal Louisiana, had average TN and TP loading rates of 56.5 and 13.9 g·m−2·year−1 from 2006–2013, respectively, which resulted in average swamp aboveground net primary production of an impressive 1250 g·m−2·year−1.
Shaffer et al. [53] found that baldcypress seedling aboveground production followed a remarkably similar pattern as that of inorganic nutrient concentration from the outfall pipe of the Hammond Assimilation Wetland to 700 m away. Growth was greatest at the outfall pipe and followed a linear decrease to 700 m from discharge, as did nutrient concentrations. Shaffer et al. [53] also reported that the diameter increase of mature baldcypress located along the outfall pipe was five times greater than that of the Maurepas swamp as a whole and 10-fold greater than trees at the nearby Joyce Wildlife Management Area. Similarly, baldcypress seedlings planted within 20 m of the outfall system in 2008 averaged 8-m tall in 2015 and grew about 2 cm·year−1 in diameter [53]. There have been numerous studies showing either increased growth or no effect on baldcypress that are exposed to high nutrient concentrations. Effler et al. [54] found increased growth rates in the Maurepas sub-basin for trees given nutrient amendments. Similar growth increases also have been reported for other wetlands [55,56,57]. Hunter et al. [13] found slightly higher, but not significant, baldcypress growth at the Breaux Bridge assimilation wetland. Total NPP was highest at the treatment sites for the assimilation wetlands in the town of Amelia, LA [58]. Finally, Hillmann [59] found a linear increase in above- and belowground NPP in baldcypress and water tupelo for loading rates ranging from 0 to 100 g·N·m−2·year−1. In this study an elevation surplus occurred at plots with both nutrient and sediment addition, suggesting sites most proximal to a River diversion would experience the greatest benefits. Since we have 11 years of baseline data covering various weather conditions, continued monitoring of our network of sites after the diversion is operational should provide clear demarcation of the degree of NPP stimulation and habitat recovery to the Throughput habitat type, depending on distance from outfall.
Tree biomass production rates at the Throughput sites were comparable to those found at periodically flooded baldcypress-water tupelo swamps in the southeast USA [19,56,60,61,62]. Relict and Degraded sites range in production between swamps that have been identified as either nutrient-poor and stagnant [63], just stagnant [64,65], or near-continuously flooded [62]. In contrast, the Throughput habitats show no overlap with other habitat types, although they do vary over time, especially with respect to hurricane years. During hurricane years, prolonged flooding during the fall causes high levels of mortality of herbaceous vegetation. The year following hurricanes, annuals from the soil seedbank respond immediately (e.g., Polygonum punctatum; Figure 7) with relatively high levels of NPP. Several herbaceous species display clear patterns across the three habitat types, especially Eleocharis vivipara, which is abundant at Degraded sites, intermediate at Relict sites, and nearly absent at Throughput sites (Figure 6c). Eleocharis macrostachya displays the opposite pattern (Figure 6b).
Extended periods of high salinity occur during droughts, like those experienced during the drought of 1999–2000 where levels in Lake Maurepas reached about 6–9 ppt for extended periods, and lead to substantial tree mortality. In the LaBranche wetlands adjacent to Lake Pontchartrain, salinity levels reached 10–12 ppt during the 1999–2000 drought (Figure 17) and caused extensive mortality to baldcypress in that system. During frontal setups, Lake Pontchartrain brings brackish water into Lake Maurepas and the mean salinity of surface water measured at Pass Manchac (the natural channel that connects Lakes Pontchartrain and Maurepas) has increased gradually over time, beginning in the early 1960s with the opening of the MRGO [11,41]. In addition, tropical storms introduce higher-salinity storm surge waters into impounded areas that are not drained during seasonal low-flow events or flushed by seasonal riverbank overflow events that, in turn, increase salinity of impounded waters and soils [66].
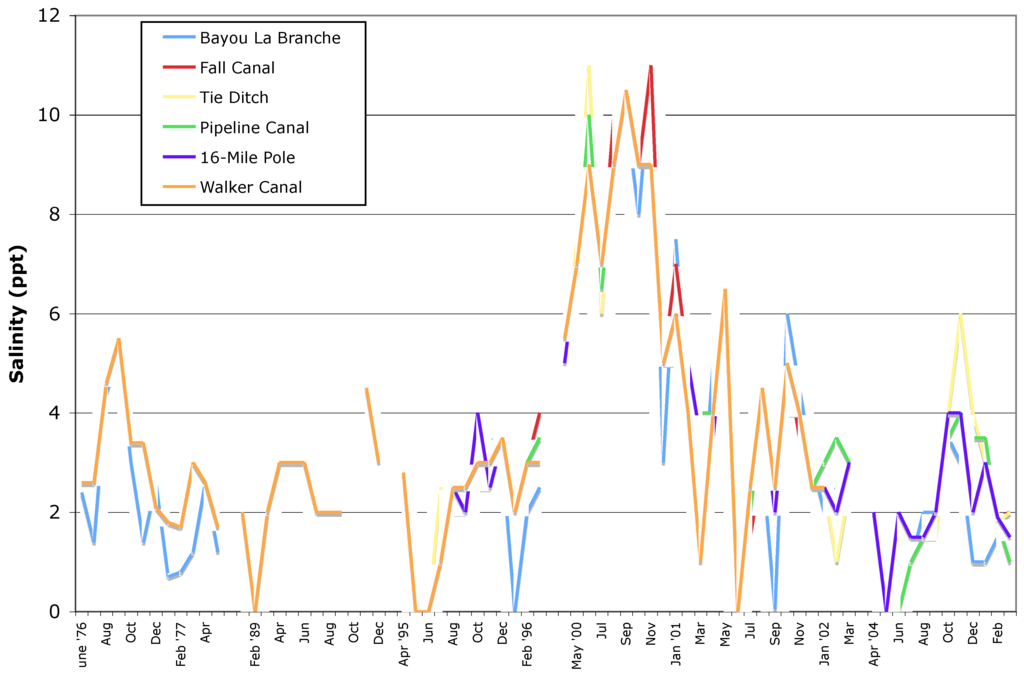
Figure 17.
Surface water salinity in the LaBranche wetlands from June 1976 through February 2005. Gaps in figure denote gaps in data.
Net primary productivity (NPP) for each of the forty eight 625 m2 stations was calculated as the sum of tree and herbaceous plant production. Contribution of tree productivity to NPP was highest at the Throughput sites while herbaceous productivity was highest at the Degraded sites (Figure 11 and Figure 13). Although it appears that the relationship between herbaceous NPP and tree NPP is compensatory, Degraded habitats are transitioning to open water and Relict habitats are in transition to Degraded. This shows a clear trajectory for most of the Maurepas swamp without restoration of Relict to Degraded to open water. Conner et al. [61] documented a similar long-term deterioration of a forested wetland in the Terrebonne Basin of the Mississippi Delta.
5. Restoration of the Maurepas Swamp
5.1. Approaches to Restoration
Healthy coastal baldcypress-water tupelo swamps require a reliable source of fresh water for system flushing following tropical storm events and during droughts to decrease soil salinity, and optimally to supply nutrients and sediments. Despite the degraded condition of the majority of the baldcypress-water tupelo swamps of the upper Lake Pontchartrain Basin, healthy areas of swamp (i.e., Throughput areas) still exist (Figure 15) because these swamps receive some form of reliable, nutrient-rich fresh water, often with suspended sediments. These healthy forests are either receiving nonpoint sources of fresh water from urban areas (e.g., forests of Hope Canal and Alligator Island in the Maurepas, forests near the Gore pump station in the Central Wetlands), high quality river water (e.g., forests of Pearl and Atchafalaya Rivers and in the Bonnet Carré Spillway), or secondarily treated municipal effluent (e.g., forests of Bayou Chinchuba, Tchefuncte marsh, Breaux Bridge, and Hammond Assimilation Wetland [12,51,53,67]). Without consistent freshwater input, most forested wetlands in coastal Louisiana will not survive. For example, after surviving for nearly a decade post-planting, 10,000 baldcypress trees on the Manchac land bridge and 70,000 on Jones Island suffered almost 100% mortality due to a single drought in 1999–2000.
Even if saltwater impacts can be reduced, forested wetland soils need to accrete vertically if they are to survive in the long-term because regeneration cannot occur with permanent or semi-permanent flooding. Accretion can take place through the introduction of mineral sediment input or in situ organic soil formation or a combination of both. Projects that input sediments to the swamp also stimulate organic soil formation [12]. If sufficient sediments are not introduced into the Maurepas swamp, it will die out within a few decades because of lack of regeneration, blow down during hurricanes, and increased salinity as has been documented for this basin and others in the Mississippi Delta [10,12,61]. Thus, even if salinity is controlled, the swamp will mostly die out by mid century unless the restoration projects described below are implemented.
Currently, many sources of fresh water exist within the Pontchartrain Basin, such as secondarily treated municipal effluent, nonpoint source stormwater runoff, stormwater pumps, and river water (e.g., Amite River, Tangipahoa River, Bonnet Carré Spillway). However, most of these sources are currently engineered to maximize drainage efficiency via ditches and canals that discharge directly to lakes and rivers, bypassing surrounding wetlands without any substantial contact (e.g., Amite River Diversion Canal with 40 foot wide levees, I-55 canal that bisects the Joyce wetlands between Lakes Pontchartrain and Maurepas). This creates a “lose-lose” situation because potential for eutrophication in Lake Pontchartrain and other water bodies is maximized while the wetlands are deprived of nutrients, sediments and fresh water. In contrast, rerouting the water to maximize sheet flow over wetlands would reduce nutrient input to surface waters and thus improve water quality and increase wetland NPP, while decreasing impacts of saltwater intrusion, sea level rise and subsidence [12,68].
Several restoration projects have been proposed to combat swamp loss, including diversion of Mississippi River water [69,70,71] and expansion of forested assimilation wetlands [13,53,58,67]. Lee Wilson and Associates [72] estimated that a 45 m3·s−1 (1600 ft3·s−1) diversion could deliver approximately 1098 g·m−2·year−1 of sediment to the swamp. Increased elevations would then create conditions amenable to seed germination and subsequent tree regeneration. But this would happen over a very small area. Lane et al. [33] modeled increases in productivity with increases in nitrate loading rates (0.1 to 0.28 g·m−2·day−1). Vegetation also would benefit, since the increased freshwater inflow would reduce the number of incidents and severity of saltwater intrusion events.
Currently, the two proposed diversions into the Maurepas swamp are a 57 m3·s−1 (2000 ft3·s−1) diversion via Hope Canal [24,33] and a 142 m3·s−1 (5000 ft3·s−1) diversion via Blind River. The Hope Canal diversion has been approved as part of the restoration program. These diversions would greatly benefit their immediate area but they are too small to influence the entire Maurepas sub-basin, especially in terms of accretion. They may be highly beneficial during times of severe drought (e.g., 2000–2001 drought) [10], except during fall when river stages are often too low for operation. A large (at least 1400 m3·s−1 but as high as 5000 m3·s−1) intermittently opened diversion, comparable to natural crevasses that occurred frequently before the existing levee system, would benefit the entire sub-basin.
There have been numerous natural crevasses and minor distributaries as well as seasonal overbank flooding along the lower Mississippi River prior to major human manipulation, that had peak flows ranging from 5000–10,000 m3·s−1 for several months [12,73,74,75]. Two examples of crevasses are the 1927 crevasse at Caernarvon and the Bonnet Carré Spillway. In 1927, the Mississippi River experienced a 100-year flood event with a peak discharge of about 70,000 m3·s−1 and a man-made crevasse was created at Caernarvon. Geochronological dating and a systematic survey of sediment deposition in the wetland receiving river water demonstrated unequivocally the presence of a thick 1927 sediment flood layer [76] and accretion rate during this time was more than two orders of magnitude greater than rates before and after the levee breech.
The Bonnet Carré Spillway was constructed in 1931 in response to the great Mississippi River flood of 1927 (See Day et al. [12] and Nittrouer [77] for detailed descriptions of the spillway), and since this time the spillway has been opened eleven times during high water events of the Mississippi River, with flows ranging from 3100 to 9000 m3·s−1. Day et al. [12] compared wetlands in the spillway to wetlands in the adjacent impounded and isolated LaBranche Basin (LB). The Bonnet Carré (BC) wetlands contain healthy baldcypress-water tupelo swamp while the LB wetlands are severely degraded due to saltwater intrusion, subsidence, and hydrologic alterations. 137Cs accretion rates in the BC wetlands were about 2.5 cm·year−1, compared to 0.43 cm·year−1 in the LB wetlands and baldcypress growth in BC averaged about 2.3 mm ring width year−1 compared to 1.4 mm·year−1 in LB [12]. Tree height, an indicator of site quality, was about 20% less at the LB sites compared to BC, even though the trees are approximately the same ages. In addition, regular tree recruitment is occurring in BC wetlands but not in LB due to semi-permanent flooding. It is interesting to note that when the Bonnet Carré crevasse functioned in the second half of the 19th century, up to 2 m of sediments were deposited in open water along the western shore of Lake Pontchartrain [18].
Both the 1927 crevasse and the Bonnet Carré Spillway, as well as historical crevasses, demonstrate that infrequent but large diversions of water can achieve substantial sediment accretion and enhance productivity of coastal wetlands. Infrequent diversion openings also minimize the effect on fisheries as demonstrated by increased fisheries after Bonnet Carré openings. Thus, we believe that a large diversion must be implemented if the Maurepas swamp is to be made sustainable in the long term. The ideal location for this diversion is near the juncture of I-10 and U.S.-61 at Sorrento, with the River diverted near Burnside, Louisiana (Figure 18).

Figure 18.
Existing assimilation wetlands (red), proposed assimilation wetland (purple), proposed river diversions into Hope Canal and Blind River (orange), and large river diversion at Sorrento (yellow) proposed herein. For the Sorrento diversion, the indicated area is similar to the 1927 Caernarvon diversion where visible accretion occurred with rates as high as 60 cm. Inset shows extent and amount of sediment deposited in 1927 Caernarvon diversion. The Hope Canal and Blind River diversions would take about 2 to 3 decades to generate enough accretion to allow baldcypress and water tupelo to regenerate naturally.
One goal of any restoration project in the Maurepas swamp should be to reverse the trajectory of Relict to Degraded habitat disassembly to Relict to Throughput reassembly. Ideally, the river diversion into the Hope Canal area will lead to both reduced salinity threat and enhanced accretion. But the small size of this diversion will positively impact a relatively small area in terms of enhanced accretion. Only further study will enable us to determine where the tipping point is for potential recovery or further degradation. Fortunately, the baseline data summarized herein will enable 48 station-specific comparisons of pre- and post-restoration measures under three primary climatic conditions (i.e., drought, hurricane, normal) to determine variance in ecosystem benefits within habitats and degree of reassembly (or the lack thereof) over time. It also will be possible to pinpoint where projected benefits are not occurring because of hydrologic short circuits, enabling operation and maintenance funds to be directed at correcting deficiencies to maximize ecosystem benefits.
5.2. Impediments to Restoration
5.2.1. Saltwater Intrusion and Sea Level Rise.
The greatest threat to restoration and sustainability of the Maurepas swamp, and coastal wetlands worldwide, is accelerating sea level rise. Along with rising tides, salt water will encroach further landward. Recent studies show that CO2 levels are tracking the highest IPCC scenarios and that emissions are likely to continue to increase by 2.5% per year through 2020, likely exceeding the international quota within 30 years [78]. Because Louisiana has a surplus of fresh water, it is possible to prevent saltwater intrusion, but only if fresh water that currently bypasses wetlands is utilized. In addition, as sea level rises in coastal Louisiana, periods of flooding increase as well, decreasing already low natural regeneration. For the Maurepas swamp to survive, a large river diversion is absolutely necessary to enhance accretion and vegetation productivity. In many areas, planting of tree seedlings will be necessary as well.
5.2.2. Hydrologic Isolation
Proposed hurricane protection levees in the Maurepas sub-basin have the potential to severely impact the effectiveness of large-scale restoration. One example is a proposed levee that would run along I-10, which would make protection and restoration of the Maurepas swamp extremely difficult. This alignment not only impounds and isolates a large area of swamp, but it also would make a large diversion difficult, if not impossible. The selected alternative is shorter and isolates a smaller area of wetland. Any levee project in the Maurepas sub-basin needs to accommodate a large diversion. If not, loss of the swamp will lead to increased hurricane surge and waves that will threaten the levee as occurred for the MRGO levees during Hurricane Katrina [11].
5.2.3. Nutrient Limitation
Waters of interior wetlands surrounding Lake Maurepas have extremely low levels of nitrogen, about 100 times less than nitrogen concentrations in the River [33]. Fertilizer studies have consistently demonstrated greatly increased rates of growth of both baldcypress [53,79,80,81,82] and herbaceous vegetation [10]. Based on past studies, it is anticipated that a Maurepas diversion will greatly stimulate above- and belowground net primary production, the extent of which depends largely upon the degree of nutrient uptake and rates of denitrification and the size of the diversion.
5.2.4. Herbivory
Nutria. Animal herbivory is a problem that has long existed in wetlands. In Louisiana, nutria (Myocaster coypus) were first imported and released beginning in 1933, and by 1959, the nutria population in Louisiana was over 20-million animals [83]. Nutria often clip or uproot newly planted baldcypress and water tupelo seedlings, thus destroying the whole seedling. Many plantings of hundreds of thousands of baldcypress seedlings have failed in coastal Louisiana because of nutria herbivory [55,84]. Several alternatives have been proposed to prevent nutria from killing newly planted seedlings. For the past decade, the CWPPRA-supported bounty program has been a great success; this incentive program resulted in the reduction of over 439,000 nutria in 2009. An additional and complimentary method of baldcypress-water tupelo restoration involves protecting seedlings from nutria with plastic sleeves called nutria exclusion devices until the seedlings obtain a “refuge in size” [79].
Canopy Insects. Forested wetlands in the coastal zone of Louisiana are often affected by insect herbivory during spring months, depending on location and year. Though there are no known consistent populations of tree-killing beetles, borers, or diseases, both baldcypress and water tupelo are defoliated frequently by caterpillars. For decades, baldcypress was renowned for its lack of serious insect and disease problems [55]. However, since the first recorded outbreak of the baldcypress leafroller (BCLR; Archips goyerana) in 1983, baldcypress has experienced significant, often repeated, springtime defoliation [85,86]. Impact caused by BCLR defoliation is of two main types—diameter growth reduction and dieback of canopy (followed in isolated cases by mortality). Although all sizes and maturity levels of trees are affected, pole-size trees, trees growing along edges of open water, and understory saplings appear most heavily and frequently defoliated by the immature stages of this insect.
Water tupelo, the other dominant swamp canopy species, has been defoliated regularly by the forest tent caterpillar (FTC; Malacosoma disstria) for decades, with regular outbreaks recorded since 1948 [87]. In Louisiana, widespread, complete canopy defoliation by this insect has occurred over as much as 200,000 hectares during a single season [88].
Often, defoliation of water tupelo and baldcypress co-exists, and swamps take on an appearance of winter-like dormancy prior to refoliation in late spring or early summer. Because wetlands often are stressed by both abiotic and biotic factors, determining the precise impact due to insect defoliation is difficult. Nevertheless, a strong negative relationship between the degree of defoliation of baldcypress and mean annual growth has been measured [86]. Growth reduction caused by defoliation is often exacerbated by duration and depth of flooding and/or saltwater intrusion [86,89,90].
6. Conclusions
Forested wetlands in the Maurepas swamp have a high mortality rate and most will be gone within the next few decades if landscape-scale restoration does not take place. Once the swamp and marsh vegetation is gone, the flood protection levees along the natural levee ridge between New Orleans and Baton Rouge will be exposed to the full force of hurricane surge and waves atop the surge. This exposure will make it more likely that the flood control levees will be compromised by overtopping and levee failure. However, there are both short-term and long-term approaches to preventing wetland loss in the Maurepas swamp.
In the short-term, there should be optimum use of all freshwater resources including small river diversions, stormwater runoff, and treated municipal effluent. These activities will help prevent saltwater intrusion and improve swamp health; however, they will not solve the permanent flooding conditions causing low tree recruitment. Use of freshwater resources should be augmented with major plantings of baldcypress, water tupelo, and nutria-resistant marsh species (e.g., arrow arum (Peltandra virginica), giant bullwhip (Schoenoplectus californicus)). The planned Hope Canal diversion can help with preventing salinity intrusion, but is much too small to deliver adequate sediments to enhance accretion in a wide area. However, it is likely that the influences of freshening would impact wetlands as distant as those between Lake Pontchartrain and Lake Maurepas because the smallest proposed diversion of 42.5 m3·s−1 could replace all of the water in Lake Maurepas twice each year, all of which has to exit Lake Maurepas through Pass Manchac and North Pass.
In the longer term, a large diversion (>1422 m3·s−1·−50,000 ft3·s−1, and up to 5000 m3·s−1) is needed. This would deliver the needed quantity of sediments to achieve high accretion rates and stimulate organic soil formation. Such a diversion would not need to operate every year at a high discharge. Both Bonnet Carré and the 1927 Caernarvon crevasse demonstrate that high accretion rates can be achieved with infrequent openings (i.e., decadal). It is critical that a large diversion plan for the Maurepas sub-basin is incorporated into the Louisiana Coastal Master Plan of 2017. If this is not done, then the flood protection levees will need to be made stronger because without a large diversion, most of the baldcypress—water tupelo forests in the Maurepas will die off. The understory vegetation in these swamps is weakly rooted or floating. Thus, when the forests die out, the herbaceous wetlands will be mostly destroyed by hurricane winds, waves, and surge resulting in greater hurricane surge against the levees. And more important, the levees will be subject to wave attack atop the surge. High waves during hurricane Katrina were a significant factor leading to the failure of the levees along the Mississippi River Gulf Outlet [11]. If a large diversion is not constructed, flood control levees will have to be much stronger and thus much more expensive. And in the end, the great majority of the Maurepas swamp will be lost.
For at least seven reasons, river diversions should be located as far north in the lower Delta as is possible, such as the Sorrento area proposed herein (Figure 18): (1) With respect to hurricane protection, baldcypress—water tupelo swamps are far superior to other wetland habitat types [10,91,92,93,94,95]. They stand strong during hurricanes and serve as major matrix levees. All river diversions have a freshwater zone, which is maximized to the north, and swamps should be created in all of these freshwater zones. Swamps also sequester more carbon than other habitat types and are self sustaining/maintaining for many centuries; (2) Subsidence decreases to the north; (3) Sediment retention increases to the north; (4) The estuarine gradient is maximized; (5) Public support is much higher to the north, because diversions are placing fresh water onto existing freshwater habitat, minimizing habitat shifts; (6) There is more head due to the higher elevation gradient and therefore greater operational flexibility further north; (7) The land to the north is far more likely to be in the public domain; for example, much of the Maurepas and Manchac swamp is owned by LDWF as part of the Maurepas and Joyce Wildlife Management Areas.
Acknowledgments
Over the 11-year period, this study was funded by EPA contract 68D60067, NOAA-PRP contracts NA16FZ2719 and NA04NOS4630255, EPA-PBRP contracts R-82898001-2 and X-83262201-1, and NOAA-CREST contracts 674139-04-6A and 674139-07-6. We are tremendously grateful that these agencies value the importance of detailed longitudinal ecological studies and worked together to keep this study alive and gap free for over a decade. We also acknowledge the Coastal Protection and Restoration Authority of Louisiana for funding data management and analysis. Funding was provided to CPRA through the Gulf Environmental Benefit Fund, established by the National Fish and Wildlife Foundation. We thank Glen Martin and Louisiana Department of Wildlife and Fisheries for allowing us access to their land. We thank Jacko Robinson and tens of undergraduate and graduate students for their tenacious help in the field.
Author Contributions
Gary Shaffer was the primary writer of the manuscript and also was extensively involved in all aspects of field work, data management, and statistical analysis. John Day, Rachael Hunter, and Rob Lane helped write the manuscript. Demetra Kandalepas and Bern Wood were involved with data management, statistical analysis, and production of figures. Eva Hillmann was involved in field work, lab work, and data management.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Day, J.W.; Kemp, G.P.; Freemen, A.M.; Muth, D.P. Perspectives on the Restoration of the Mississippi Delta; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; p. 194. [Google Scholar]
- Barras, J.A.; Bourgeois, P.E.; Handley, L.R. Land Loss in Coastal Louisiana, 1956–1990; National Wetlands Research Center Open File Report 94-01; National Biological Survey: Lafayette, LA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Barras, J.A.; Bernier, J.C.; Morton, R.A. Land Area Change in Coastal Louisiana—A Multidecadal Perspective (from 1956 to 2006); U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Map 3019, scale 1:250,000; US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey: Lafayette, LA, USA, 2008; p. 14.
- Britsch, L.D.; Dunbar, J.B. Land loss rates: Louisiana Coastal Plain. J. Coast. Res. 1993, 9, 324–338. [Google Scholar]
- Couvillion, B.R.; Barras, J.A.; Steyer, G.D.; Sleavin, W.; Fischer, M.; Beck, H.; Trahan, N.; Griffin, B.; Heckman, D. Land Area Change in Coastal Louisiana from 1932 to 2010; US Geological Survey Scientific Investigation Map 3164, scale 1:265,000; US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2011; p. 12.
- Day, J.W.; Shaffer, G.P., Jr.; Britsch, L.D.; Hawes, S.R.; Reed, D.J.; Cahoon, D. Pattern and process of land loss in the Mississippi delta: A spatial and temporal analysis of wetland habitat change. Estuaries 2000, 23, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, J.W., Jr.; Boesch, D.F.; Clairain, E.F.; Kemp, G.P.; Laska, S.B.; Mitsch, W.J.; Orth, K.; Mashriqui, H.; Reed, D.R.; Shabman, L.; et al. Restoration of the Mississippi Delta: Lessons from Hurricanes Katrina and Rita. Science 2007, 315, 1679–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CPRA. Louisiana’s Comprehensive Master Plan for a Sustainable Coast; Coastal Protection and Restoration Authority: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chambers, J.L.; Conner, W.H.; Day, J.W., Jr.; Faulkner, S.P.; Gardiner, E.S.; Hughes, M.S.; Keim, R.F.; King, S.L.; Miller, C.A.; Nyman, J.A.; et al. Conservation, Protection, and Utilization of Louisiana’s Coastal Wetland Forests; Final report to the Governor of Louisiana from the Coast Wetland Forest Conservation and Use Science Working Group: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2005; p. 121. [Google Scholar]
- Shaffer, G.P.; Wood, W.B.; Hoeppner, S.S.; Perkins, T.E.; Zoller, J.A.; Kandalepas, D. Degradation of baldcypress-water tupelo swamp to marsh and open water in southeastern Louisiana, USA: An irreversible trajectory? J. Coast. Res. 2009, 54, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, G.P.; Day, J.W.; Mack, S.; Kemp, G.P.; van Heerden, I.; Poirrier, M.A.; Westpahl, K.A.; FitzGerald, D.; Milanes, A.; Morris, C.; et al. The MRGO navigation project: A massive human-induced environmental, economic, and storm disaster. J. Coast. Res. 2009, 54, 206–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, J.W.; Hunter, R.; Keim, R.; DeLaune, R.; Shaffer, G.; Evers, E.; Reed, D.; Brantley, C.; Kemp, P.; Day, J.; et al. Ecological response of forested wetlands with and without large-scale Mississippi River input: Implications for management. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 46, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, R.G.; Day, J.W., Jr.; Lane, R.R.; Lindsey, J.; Day, J.N.; Hunter, M.G. Impacts of secondarily treated municipal effluent on a freshwater forested wetland after 60 years of discharge. Wetlands 2009, 29, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batker, D.; de la Torre, I.; Costanza, R.; Swedeen, P.; Day, J.; Boumans, R.; Bagstad, K. Gaining Ground: Wetlands, Hurricanes and the Economy: The Value of Restoring the Mississippi River Delta; Earth Economics, Inc.: Tacoma, WA, USA, 2010; p. 98. [Google Scholar]
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; de Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LDNR. Coast 2050: Toward a Sustainable Coastal Louisiana; Louisiana Coastal Wetlands Conservation and Restoration Task Force and the Wetlands Conservation and Restoration Authority. Louisiana Department of Natural Resources: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 1998; p. 161. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez, J.A. The Environmental History of human-induced impacts to the Lake Pontchartrain Basin in Southeastern Louisiana since European settlement-1718 to 2002. J. Coast. Res. 2009, 54, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saucier, R.T. Recent Geomorphic History of the Ponchartrain Basin; Louisiana State University, Coastal Studies Series 9: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 1963; p. 114. [Google Scholar]
- Conner, W.H.; Day, J.W. Productivity and composition of a baldcypress-water tupelo site and a bottomland hardwood site in a Louisiana swamp. Am. J. Bot. 1976, 63, 1354–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conner, W.H.; Day, J.W. Diameter growth of Taxodium distichum (L.) Rich. and Nyssa aquatica L. from 1979–1985 in four Louisiana swamp stands. Am. Mid. Nat. 1992, 127, 209–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeppner, S.S. Feasibility and Project Benefits of a Diversion into the Degraded Cypress–Tupelo Swamp in the Southern Lake Maurepas Wetlands, Lake Pontchartrain Basin, Louisiana. Master’s Thesis, Southeastern Louisiana University, Hammond, LA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hoeppner, S.S.; Shaffer, G.P.; Perkins, T.E. Through droughts and hurricanes: Tree mortality, forest structure, and biomass production in a coastal swamp targeted for restoration in the Mississippi River Deltaic. For. Ecol. Manag. 2008, 256, 937–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezeshki, S.R.; DeLaune, R.D.; Patrick, W.H.J. Flooding and saltwater intrusion: Potential effects on survival and productivity of wetland forests along the U.S. Gulf Coast. For. Ecol. Manag. 1990, 33/34, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, G.P.; Perkins, T.E.; Hoeppner, S.S.; Howell, S.; Benard, T.H.; Parsons, A.C. Ecosystem Health of the Maurepas Swamp: Feasibility and Projected Benefits of a Freshwater Diversion; Final Report; Environmental Protection Agency, Region 6: Dallas, TX, USA, 2003; p. 95. [Google Scholar]
- Morton, R.; Barras, J. Hurricane impacts on coastal wetlands: A half-century record of storm-generated features from southern Louisiana. J. Coast. Res. 2011, 27, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howes, N.C.; FitzGerald, D.M.; Hughes, Z.J.; Georgiou, I.Y.; Kulp, M.A.; Miner, M.D.; Smith, J.M.; Barras, J.A. Hurricane-induced failure of low salinity wetlands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14014–14019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trettin, C.C.; Jorgensen, M.F. Carbon Cycling in Wetland Forest Soils. In The Potential of U.S. Forest Soils to Sequester Carbon and Mitigate the Greenhouse Effect; Kimble, J.M., Heath, L., Birdsey, R.A., Lai, R., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; pp. 311–331. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez, J.A. The multiple lines of defense strategy to sustain coastal Louisiana. J. Coast. Res. 2009, 54, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A.; Phillips, D.R.; Frederick, D.J. Weight, Volume, and Physical Properties of Major Hardwood Species in the Gulf and Atlantic Coastal Plains; USDA Forest Service Research Paper SE-250; Southeastern Forest Experimental Station: Asheville, NC, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Muzika, R.M.; Gladden, J.B.; Haddock, J.D. Structural and Functional Aspects of Succession in South-eastern Floodplain Forests Following a Major Disturbance. Am. Midl. Nat. 1987, 117, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, M.L.; Sharitz, R.R.; Lee, L.C. Disturbance in a Cypress-Tupelo Wetland: An interaction between thermal loading and hydrology. Wetlands 1985, 5, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahoon, D.R.; Marin, P.E.; Black, B.K.; Lynch, J.C. A method for measuring vertical accretion, elevation, and compaction of soft, shallow-water sediments. J. Sed. Res. 2000, 70, 1250–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, R.R.; Day, J.W.; Kemp, G.P.; Mashriqui, H.S.; Day, J.N.; Hamilton, A. Potential Nitrate Removal from a Mississippi River Diversion into the Maurepas Swamps. Ecol. Eng. 2003, 20, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOAA. Tides & Currents, Mean Sea Level Trend, Grand Isle, Louisiana: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, On-line Material. Available online: http://tidesandcurrents.noaa.gov/sltrends/sltrends_station.shtml?id=8761724 (accessed on 23 March 2015).
- Wilkinson, L. SYSTAT 10.2 for Windows; SYSTAT Software, Inc.: Chicago, IL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- SAS Institute Inc. SAS 9.1.3 Help and Documentation; SAS Institute Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 2000–2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zar, J.H. Biostatistical Analysis, Fourth Edition; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1996; p. 662. [Google Scholar]
- Kruskal, J.B. Multidimensional scaling by optimizing goodness of fit to a nonmetric hypothesis. Psychometrika 1964, 29, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Warwick, R.M. Primer 6; PRIMER-E: Plymouth, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, D.A.; Shaffer, G.P.; McCorquodale, J.A. A potential interaction between sea-level rise and global warming: Implications for coastal stability in the Mississippi River deltaic plain. Glob. Plan. Chang. 2002, 32, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormier, N.; Krauss, K.W.; Conner, W.H. Periodicity in stem growth and litterfall in tidal freshwater forested wetlands: Influence of salinity and drought on nitrogen recycling. East Coasts 2013, 36, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackney, C.T.; Avery, G.B.; Leonard, L.A.; Posey, M.; Alpin, T. Biological, Chemical, and Physical Characteristics of Tidal Freshwater Swamp Forests of the Lower Cape Fear River/Estuary, North Carolina. In Ecology of Tidal Freshwater Forested Wetlands of the Southeastern United States; Conner, W.H., Doyle, T.W., Krauss, K.W., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 183–221. [Google Scholar]
- Krauss, K.W.; Duberstein, J.A.; Doyle, T.W.; Conner, W.H.; Day, R.H.; Inabinette, L.W. Site condition, stand structure, and growth of baldcypress along tidal/non-tidal salinity gradients. Wetlands 2009, 29, 505–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabreck, R.H. Vegetation, Water and Soil Characteristics of the Louisiana Coastal Region; Bulletin 664; Louisiana State University Agricultural Experimental Station: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 1972; p. 72. [Google Scholar]
- Penfound, W.T.; Hathaway, E.S. Plant communities in the marshlands of Southeastern Louisiana. Ecol. Mono. 1938, 8, 1–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conner, W.H.; McLeod, K.W.; McCarron, J.K. Flooding and salinity effects on growth and survival of four common forested wetland species. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 1997, 5, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezeshki, S.R.; DeLaune, R.D.; Patrick, W.H., Jr. Assessment of saltwater intrusion impact on gas exchange behavior of Louisiana Gulf Coast wetland species. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 1989, 1, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keim, R.F.; Dean, T.J.; Chambers, J.L.; Conner, W.H. Stand density relationships in baldcypress. For. Sci. 2010, 56, 336–343. [Google Scholar]
- Reineke, L.H. Perfecting a stand density index for even-aged forests. J. Agric. Res. 1933, 46, 627–638. [Google Scholar]
- Rybczyk, J.M.; Cahoon, D.R. Estimating the potential for submergence for two wetlands in the Mississippi River Delta. Estuaries 2002, 35, 985–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brantley, C.G.; Day, J.W.; Lane, R.R.; Hyfield, E.; Day, J.N.; Ko, J.Y. Primary production, nutrient dynamics, and accretion of a coastal freshwater forested wetland assimilation system in Louisiana. Ecol. Eng. 2008, 34, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, R.G.; Shaffer, G.P.; Lane, R.R.; Day, J.W. Analysis of Long-Term Productivity and Nutrient Removal at Assimilation Wetlands in Coastal Louisiana; LDEQ OC No. 855–400144: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2015; p. 98. [Google Scholar]
- Shaffer, G.; Day, J.; Hunter, R.; Lane, R.; Lundberg, C.; Wood, B.; Hillmann, E.; Day, J.; Strickland, E.; Kandalepas, D. System response, nutria herbivory, and vegetation recovery of a wetland receiving secondarily-treated effluent in coastal Louisiana. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 79, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effler, R.S.; Goyer, R.A.; Lenhard, G.J. Baldcypress and water tupelo responses to insect defoliation and nutrient augmentation in Maurepas Swamp, Louisiana, USA. For. Ecol. Manag. 2006, 236, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.A.; Montz, G.N. Baldcypress and the Tree Unique, the Wood Eternal; Claitor’s Publishing Division: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 1986; p. 139. [Google Scholar]
- Conner, W.H.; Gosselink, J.G.; Parrondo, R.T. Comparison of the vegetation of three Louisiana swamp sites with different flooding regimes. Am. J. Bot. 1981, 68, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesse, I.D.; Day, J.W.; Doyle, T.W. Long-term growth enhancement of baldcypress (Taxodium distichum) from municipal wastewater application. Environ. Manag. 1998, 22, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, J.; Ko, J.Y.; Rybczyk, J.; Sabins, D.; Bean, R.; Berthelot, G.; Brantley, C.; Breaux, A.; Cardoch, L.; Conner, W.; et al. The use of wetlands in the Mississippi Delta for wastewater assimilation: A review. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2004, 47, 671–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillmann, E.R. The Implications of Nutrient Loading on Deltaic Wetlands. Master’s Thesis, Southeastern Louisiana University, Hammond, LA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, M.R.; Burns, L.A.; Cavinder, T.R.; Dugger, K.R.; Fore, P.L.; Hicks, D.B.; Revills, H.L.; Schmidt, T.W. Ecosystems Analysis of the Big Cypress Swamp and Estuaries; USEPA Region IV, South Florida Ecological Study: Miami, FL, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Conner, W.H.; Duberstein, J.A.; Day, J.W., Jr.; Hutchinson, S. Forest community changes along a flooding/elevation gradient in a south Louisiana forested wetland from 1986–2009. Wetlands 2014, 34, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megonigal, J.P.; Conner, W.H.; Kroeger, S.; Sharitz, R.R. Aboveground production in southeastern floodplain forests: A test of the subsidy-stress hypothesis. Ecology 1997, 78, 370–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, W.H. Community structure, dyes, and nutrient ecology in the Okenfenokee cypress swamp-forest. Ecol. Mono. 1978, 48, 43–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsch, W.J.; Day, J.W., Jr.; Gilliam, J.W.; Groffman, P.M.; Hey, D.L.; Randall, G.W.; Wang, N. Reducing Nutrient Loads, Especially Nitrate–Nitrogen, to Surface Water, Groundwater, and the Gulf of Mexico; Topic 5 Report for the Integrated Assessment on Hypoxia in the Gulf of Mexico. NOAA Coastal Ocean Program Decision Analysis Series No. 19; NOAA Coastal Ocean Program: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 1999; p. 111. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, J.R. Community Structure and Primary Productivity of Forested Wetlands in Western Kentucky. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Louisville, Louisville, KY, USA, 1985; p. 139. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. Louisiana Coastal Protection and Restoration Final Technical Report; USACE: New Orleans, LA, USA, 2009; p. 94. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, R.G.; Day, J.W., Jr.; Lane, R.R.; Lindsey, J.; Day, J.N.; Hunter, M.G. Nutrient removal and loading rate analysis of Louisiana forested wetlands assimilating treated municipal effluent. Environ. Manag. 2009, 44, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaffer, G.P.; Day, J.W., Jr. Use of Freshwater Resources to Restore Baldcypress–Water Tupelo Swamps in the Upper Lake Pontchartrain Basin; White Paper; Louisiana Department of Wildlife and Fisheries: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2007; p. 44. [Google Scholar]
- Nyman, J. Integrating successional ecology and the delta lobe cycle in wetland research and restoration. East Coasts 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paola, C.; Twilley, R.R.; Edmonds, D.A.; Kim, W.; Mohrig, D.; Parker, G.; Viparelli, E.; Voller, V.R. Natural processes in delta restoration: Application to the Mississippi delta. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2010, 3, 67–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twilley, R.R.; Rivera-Monroy, R. Sediment and nutrient tradeoffs in restoring Mississippi river delta: Restoration vs. eutrophication. Cont. Water Resour. Ed. 2009, 141, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee Wilson and Associates, Inc. Diversion into the Maurepas Swamps. A complex project under the Coastal Wetlands Planning, Protection, and Restoration Act; Final report prepared for the U.S.; Environmental Protection Agency, Region 6: Dallas, TX, USA, 2001; p. 59, Contract No. 68-06-0067 WA#5-02. [Google Scholar]
- Condrey, R.E.; Hoffman, P.E.; Evers, D.E. The Last Naturally Active Delta Complexes of the Mississippi River (LNDM): Discovery and Implications. In Perspectives on the Restoration of the Mississippi Delta; Day, J.W., Kemp, G.P., Freemen, A.M., Muth, D.P., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 33–50. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, D.W. Crevasses on the lower course of the Mississippi River. CoastZone 1993, 1, 360–378. [Google Scholar]
- Welder, F.A. Processes of Deltaic Sedimentation in the Lower Mississippi River; Louisiana State University, Coastal Studies Institute Technical Report: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 1959; pp. 1–90. [Google Scholar]
- Bentley, S.J.; Freeman, A.M.; Wilson, C.S.; Cable, J.E.; Giosan, L. Using What We Have: Optimizing Sediment Management in Mississippi River Delta Restoration to Improve the Economic Viability of the Nation. In Perspectives on the Restoration of the Mississippi Delta; Day, J.W., Kemp, G.P., Freemen, A.M., Muth, D.P., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 85–97. [Google Scholar]
- Nittrouer, J.A.; Best, J.L.; Brantley, C.; Cash, R.W.; Czapiga, M.; Kumar, P.; Parker, G. Mitigating land loss in coastal Louisiana by controlled diversion of Mississippi River sand. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 534–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedlingstein, P.; Andrew, R.M.; Rogelj, J.; Peters, G.P.; Canadell, J.D.; Knutti, R.; Luderer, G.; Raupach, M.R.; Schaeffer, M.; van Vuuren, D.P.; et al. Persistent growth of CO2 emissions and implications for reaching climate targets. Nat. Geosci. 2014, 7, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, R.S.; Shaffer, G.P.; Llewellyn, D.W. Baldcypress (Taxodium distichum (L.) Rich.) restoration in southeast Louisiana: The relative effects of herbivory, flooding, competition, and macronutrients. Wetlands 1994, 15, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beville, S.L. The Efficacy of a Small-Scale Freshwater Diversion for Restoration of a Swamp in Southeastern Louisiana. Master’s Thesis, Southeastern Louisiana University, Hammond, LA, USA, 2002; p. 86. [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg, C.J. Using Secondarily Treated Sewage Effluent to Restore the Baldcypress-water Tupelo Swamps of the Lake Pontchartrain basin: A Demonstration Study. Master’s Thesis, Southeastern Louisiana University, Hammond, LA, USA, 2008; p. 85. [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg, C.J.; Shaffer, G.P.; Wood, W.B.; Day, J.W., Jr. Growth rates of baldcypress (Taxodium distichum) seedlings in a treated effluent assimilation marsh. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowery, G.H., Jr. The Mammals of Louisiana and its adjacent Waters; Louisiana State University Press: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Blair, R.M.; Langlinais, M.J. Nutria and swamp rabbits damage baldcypress seedlings. J. For. 1960, 58, 388–389. [Google Scholar]
- Goyer, R.A.; Lenhard, C.G. A new insect pest threatens baldcypress. Agricultura 1988, 31, 16–17. [Google Scholar]
- Goyer, R.A.; Chambers, J. Evolution of Insect Defoliation in Baldcypress and its Relationship to Flooding; USDI. N BS. Biological Sciences Report 8: Lafayette, LA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Nachod, L.H.; Kucera, D.R. Observations of the Forest Tent Caterpillar in South Louisiana; Insect and Disease Report; Louisiana Office of Forestry: Woodworth, LA, USA, 1971; p. 2. [Google Scholar]
- Nachod, L.H. Spring Defoliation by Forest Insects in Louisiana; Insect and disease Report; Louisiana Office of Forestry: Woodworth, LA, USA, 1977; p. 2. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, J.A.; Conner, W.H.; Goyer, R.A.; Chambers, J.L.; Krauss, K.W. Freshwater Forested Wetlands and Global Climate Change. In Vulnerability of Coastal Wetlands in the Southeastern United States; Biological Science Report USGS/BRD/BSR-1998–0002: Honolulu, HI, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Souther-Effler, R.F. Interactions of Insect Herbivory and Multiple Abiotic Stress Agents on Two Wetland Tree Species in Southeast Louisiana Swamps. Ph.D. Thesis, Louisiana State University and Agricultural and Mechanical College, Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Touliatos, P.; Roth, E. Hurricanes and trees—Ten lessons from Camille. J. For. 1971, 69, 285–289. [Google Scholar]
- Gresham, C.A.; Williams, T.M.; Lipscomb, D.J. Hurricane Hugo wind damage to southeastern U.S. Coastal forest tree species. Biotropica 1991, 23, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putz, F.E.; Sharitz, R.R. Hurricane damage to old-growth forest in Conaree Swamp National Monument. Can. J. For. Res. 1991, 21, 1765–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, T.W.; Keeland, B.D.; Gorman, L.E.; Johnson, D.J. Structural impact of Hurricane Andrew on forested wetlands of the Atchafalaya Basin in south Louisiana. JCR 1995, 21, 354–364. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, K.; Pinzon, Z.S.; Stumpf, R.P.; Raabe, E.A. Sea-Level Rise and Coastal Forests on the Gulf of Mexico; USGS-99-441; U.S. Department of the Interior: Washington, DC, USA, 1999; p. 63. [Google Scholar]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).