Abstract
Saltwater intrusion is one of the most significant groundwater challenges in the southern Laizhou Bay. Previous studies have predominantly focused on regional scales, leaving the vertical saltwater intrusion pattern relatively underexplored. This knowledge gap hinders the effective prevention and control of saltwater intrusion. This study utilized hydrochemical and stable isotopic methods combined with hydrochemical facies evolution diagrams to investigate the groundwater evolution and the processes of saltwater intrusion in a typical profile and saline–fresh groundwater transition zones. The results showed that the groundwater types in the study area were complex and diverse, with fresh groundwater, saline groundwater, and brine. Stable isotope and hydrochemical analyses indicated that mixing and evaporation of seawater were the predominant processes governing the evolution and salinity of groundwater. In the south of the typical profile, carbonate dissolution played a significant role, and the silicate dissolution may represent the primary water–rock interaction in the saline–fresh groundwater transition zones. Groundwater samples from various locations within the study area exhibited different stages of hydrochemical facies evolution, and the majority of the typical profile samples were in the salinization phase during the mixing process. The saltwater intrusion in the saline–fresh groundwater transition zone primarily occurred between −20 and −30 m, exhibiting a wedge-shaped saltwater intrusion pattern. This study enhanced the understanding of vertical saltwater intrusion.
1. Introduction
Groundwater serves as a critical natural resource that plays an indispensable role in regional economic and social development. Due to its attributes of easy accessibility, stable reserves, and superior water quality, it has been extensively exploited and utilized. However, the groundwater environment is vulnerable to influences from local geological conditions, weather patterns, and human activities [1,2]. Currently, coastal regions are characterized by high population density, resulting in substantial water demands for daily life, industry, and agriculture. Intensive groundwater extraction stands out as a primary method to fulfill these production and living requirements [3]. However, long-term overexploitation of groundwater can result in the formation of groundwater depression cones, disrupt the dynamic equilibrium of the salt–freshwater system in coastal aquifers, cause the salt–freshwater interface to shift inland, and consequently trigger seawater intrusion [4,5]. Seawater intrusion can directly result in the degradation of regional groundwater quality, accelerating the corrosion and aging of industrial pipelines and equipment, as well as leading to soil salinization and other associated issues [6,7].
In coastal aquifers, significant quantities of saltwater are commonly present, likely originating from ancient marine transgression and regression events that took place over geological periods spanning thousands of years or more [8]. The ancient transgression–regression cycles are typically associated with factors such as tectonic uplift of the oceanic and continental crusts, as well as paleoclimate changes [9,10]. The aforementioned factors can cause the paleo-seawater intrusions in the pore water, which was previously in equilibrium with both seawater and fresh groundwater, to extend further inland. In low-permeability coastal areas and island regions, the distribution of saline groundwater associated with the mixing of paleo-seawater within geological structures has been observed, particularly in arid regions. Following the geological tectonic event, the isolated seawater became sealed off, and over time, atmospheric precipitation or other water sources gradually reduced the salinity through leaching or dilution. However, in arid regions, this process may occur at an extremely slow rate [11,12,13,14,15]. The above phenomena are found in the low-permeability strata of volcanoes, the low-permeability strata of islands, and typical muddy coastal plains. In recent years, intensive human activities, particularly excessive groundwater extraction, has disrupted the hydrodynamic balance. This disruption has led to the movement of saline groundwater and subsequently caused saltwater intrusion [8].
The formation of many coastal plain areas is usually closely related to the terrigenous sediments transported by rivers. This is evident in the presence of multiple strata containing paleochannel in numerous coastal plains. These strata, primarily composed of medium to coarse sands, not only offer an excellent aquifer for groundwater storage but also serve as significant conduits for saltwater intrusion in coastal regions [16,17]. Since the Late Pleistocene, multiple transgressive and regressive events have occurred in southern Laizhou Bay. Consequently, alternating marine–terrestrial transitional sedimentary strata have developed, leading to the accumulation of substantial amounts of seawater within these strata, forming brine deposits [14]. Under the background of groundwater overexploitation that began at the end of the last century, the brine in different marine sedimentary layers on the southern Laizhou Bay has invaded inland [18].
The paleochannels present in the coastal plain of southern Laizhou Bay exhibit characteristics of high abundance and extensive distribution [8]. This unique hydrogeological condition facilitates longitudinal saltwater intrusion, a factor that has been underappreciated in previous studies. At present, most of the research on saltwater intrusion focuses on regional assessment, ignoring the vertical spatial differences, which is not conducive to identifying the current situation and proposing scientific governance measures. Yang et al. (2021) [9] conducted a comprehensive analysis of groundwater in the entire southern coastal region of Laizhou Bay. They separately examined shallow groundwater (depth < 30 m) and deep groundwater (depth > 30 m), delineated the boundaries of different groundwater functional zones, and assessed the spatial pattern of saltwater intrusion across the study area. This study focused on a large-scale regional investigation. While the evolution process of groundwater at varying depths has been taken into account, the specific mechanisms and pathways of saltwater intrusion in local areas remain unidentified. Liu et al. (2017) [8] carried out long-term monitoring of a representative profile of the Bailang River along the southern Laizhou Bay. They investigated the origins of groundwater and salt in both the Holocene (shallow layer) and the Late Pleistocene (deep layer) aquifers and further identified the wedge-shaped pattern of saltwater intrusion. However, whether this pattern of saltwater intrusion is similarly observed in profiles at different locations remains to be validated through further monitoring and investigation. Currently, research in this field predominantly centers on regional assessments of saltwater intrusion while overlooking the vertical characteristics of such phenomena. This oversight may result in inadequate investigation and an inability to accurately reflect the true situation.
Based on this, groundwater samples were collected from a typical profile (TP) along the direction of saltwater intrusion and at various depths within the salt–fresh groundwater transition zone (SFZ) in the southern Laizhou Bay. Through the analysis of hydrochemical and isotopic characteristics, we evaluated the hydrochemical properties of regional groundwater, analyzed the origin and evolution processes of groundwater, and assessed the vertical patterns of saltwater intrusion in the SFZ.
2. Study Area
The plain area on the southern Laizhou Bay in eastern China represents a typical silty–muddy coastal plain (Figure 1). The Quaternary exhibits variable thicknesses with a maximum of 400 m. The strata in the upper alluvial fan in the south predominantly consist of gravel and grit, gradually transitioning to fine sand, silt, sandy clay, and silty clay as they approach the coast, and its distribution is evidently influenced by both structural and geomorphological factors. The strata in the area can be divided into two main periods from bottom to top: the Pleistocene and the Holocene, comprising approximately nine distinct units. Vertically, the groundwater quality exhibits a two-layer structure. The upper layer is characterized by brackish groundwater, with the TDS ranging from 2 to 50 mg/L. In the northern brine region, the TDS exceeds 50 g/L. The lower layer consists of fresh groundwater, typically having a TDS below 2 g/L.
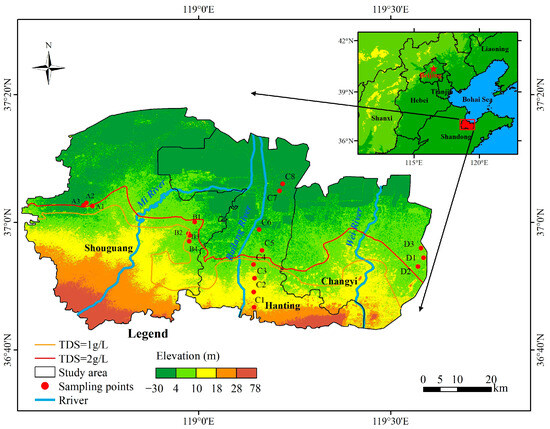
Figure 1.
Location of the study area.
In the southern mountainous region of Laizhou Bay, the bedrock is exposed at the surface, as shown in Figure 2. The sedimentary facies of aquifer sediments transition from south to north, starting with alluvial layers in the south, followed by proluvial layers, and finally, marine sediments in the coastal plain. The coastal plain consists of typical silty–clayey coastal sediments commonly found in China [19]. The aquifer consists of Quaternary sediments, with a thickness ranging from 30 to 50 m in the southern region and approximately 360 m in the northern area. Near the mountain front, both shallow and deep groundwater occur as unconfined aquifers. In contrast, towards the coastline, the increasing presence of upper sandy clay layers causes deep groundwater to transition into confined aquifers [20]. The aquifer exhibits a complex multi-layered structure (Figure 2), typically transitioning gradually from coarse grains in the lower part to finer materials in the upper layers. The study area contains several ancient buried river channels, which are filled with coarse-grained sediments that facilitate substantial groundwater flow. Under natural conditions, the groundwater flows from the south (mountain area) towards the north (sea area). Shallow groundwater is primarily recharged through atmospheric precipitation and lateral inflow from rivers, while its discharge mainly occurs via atmospheric evaporation and groundwater extraction. In contrast, deep groundwater aquifers are predominantly recharged by groundwater from other aquifers, with their discharge largely occurring through artificial exploitation. Near the coastline, groundwater dynamics are influenced by tidal fluctuations and wave actions [8].
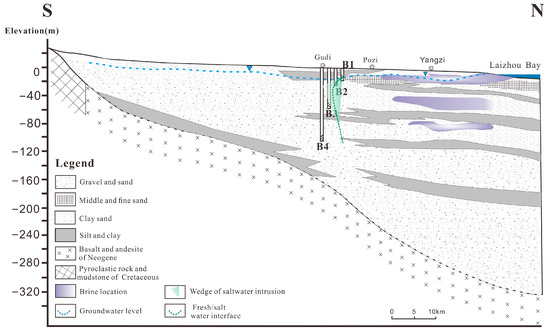
Figure 2.
The geological section of the study area modified from Liu et al. (2017) and Yang et al. (2021) [8,9].
The overall terrain in the region slopes from higher elevations in the south to lower elevations in the north. Major rivers, including the Mi River, the Bailang River, and the Wei River, traverse the area before eventually discharging into the sea. The extensive region experienced the formation of strata enriched with ancient seawater (saline groundwater-brine) during the marine transgression, and these strata are hydraulically connected to the freshwater aquifer [19]. The development of multiple groundwater depression cones in the region has altered the original flow direction of groundwater. Driven by the regional hydraulic gradient, saline groundwater from the north migrates towards the south. The alluvial layer downstream of the river is the main channel for saltwater intrusion, mainly occurring in the area with a burial depth exceeding 80 to 100 m [8].
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Groundwater Sampling
Samples in this study were collected in 2020 from two distinct sets of sampling points. The first set consisted of eight sampling points (C1–C8) along a transect extending from the inland to the sea along the southern Laizhou Bay (Figure 1). The second set comprised sampling points at different depths within three locations (A1–A3, B1–B4, and D1–D3) in the SFZ. The aforementioned samples were utilized to analyze the hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater and to investigate the origins of both groundwater and salinity. Furthermore, in 2022, seven samples (A1′–A3′ and B1′–B4′) were repeatedly collected and analyzed in the SFZ to assess the evolution processes of groundwater at varying depths within this zone.
Group A was situated within the alluvial layer of the Mi River in the western region, with three sampling points (A1 to A3) at depths of 18 m, 55 m, and 8 m, respectively. Group B was located in the alluvial layer of the Bailang River in the central region, with four sampling points (B1 to B4) set at depths of 10 m, 23 m, 55 m, and 100 m, respectively. Group C was situated within the alluvial layer of the Wei River in the eastern region, with three sampling points (C1 to C3) established at depths of 8 m, 30 m, and 61 m, respectively.
Prior to collecting groundwater samples, the sampling wells were purged for a minimum of 30 min to ensure that the collected samples accurately reflected the in situ conditions.
3.2. Sample Analysis
At the field site, all groundwater samples were collected from a depth of 0.5 m below the groundwater level and immediately filtered using 0.45 μm filter membranes. The multi-parameter measuring instrument was used to measure the pH values on site. Samples for cation analysis were stored in polyethylene bottles that were washed with HNO3 and preserved with 1:1 HNO3 to ensure a pH < 2. In contrast, samples intended for anion analysis were collected in centrifuge tubes without acidification. For isotopic analysis, groundwater samples were filtered through 0.45 μm membranes and stored in pre-cleaned borosilicate glass vials (20 mL capacity, without rubber septa). The bottles underwent sequential pretreatment: soaking in 10% HCl solution followed by thorough rinsing with ultrapure water. All samples were stored at 4 °C in light-proof containers during transportation and preservation, with analyses completed within one week of collection.
Hydrochemical analyses were entirely conducted at the Water Quality Analysis Laboratory within the Institute of Hydrogeology and Environmental Geology, CAGS. Concentrations of major cations (Na+, K+, Ca2+, and Mg2+) were performed using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Concentrations of anions (Cl−, SO42−, and NO3−) were quantified using ion chromatography. The TDS was quantified using gravimetric analysis. The HCO3− was determined by acid–base titration. The stable isotopes of water were analyzed using an isotope mass spectrometer, MAT 253. Before analyzing, 10 mL aliquots were transferred to pre-baked bottles for δ18O determination, while 5 mL subsamples for δD analysis were stored in bottles pre-treated with 1% HCl (24 h immersion) and triple-rinsed with ultrapure water. The CO2–H2O equilibrium method was employed for δ18O measurements, whereas δD values were determined using the metallic zinc reduction method. The δ values are presented in the subsequent sections, expressed in ‰ relative to Vienna Standard Mean Ocean Water (VSMOW). The analytical precision errors of inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry and ion chromatography were less than 5%. The analytical precisions for δD and δ18O were ±1 and ±0.1‰, respectively. Table 1 presents the descriptive statistics of the chemical constituents in the groundwater samples.

Table 1.
Statistics of hydrochemical variables in groundwater samples.
4. Results
4.1. Hydrogeochemical Properties
The TDS values of TP groundwater in the study area ranged from 907.1 mg/L to 177,947 mg/L, with an average value of 37,199 mg/L and a median value of 3570 mg/L. The groundwater types were classified as follows: fresh groundwater (TDS ≤ 1 g/L, denoted as C1), brackish groundwater (1 g/L < TDS ≤ 3 g/L, denoted as C2, C3, and C5), and saline groundwater (TDS > 3 g/L, denoted as C4, C6, C7, and C8). The TDS values of SFZ groundwater ranged from 706.7 to 13,285 mg/L, with an average of 3530 mg/L and a median of 2,456.5 mg/L. Based on these TDS values, the groundwater quality can be classified into three categories: fresh groundwater (TDS ≤ 1 g/L, A1), brackish groundwater (1 g/L < TDS ≤ 3 g/L, A3, B2, B3, B4, D2, and D3), and saline groundwater (TDS > 3 g/L, A2, D1, and D2). In 2022, the TDS value range of SFZ groundwater was 343–6352 mg/L, and the average and median values were 2316.57 mg/L and 1694 mg/L, respectively. The groundwater quality types were classified as fresh groundwater (TDS ≤ 1 g/L, A2′ and B4′), brackish groundwater (1 g/L < TDS ≤ 3 g/L, A1′, B1′, and B3′), and saline groundwater (TDS > 3 g/L, A3′ and B2′). The TDS in TP exceeded the World Health Organization (WHO) guideline value (1000 mg/L) by 90%, while those in the SFZ exceeded it by 87.5%. These findings suggest that the majority of water samples from both regions are unsuitable for drinking purposes.
In the TP groundwater, Na+ was the predominant cation, with concentrations ranging from 63.54 mg/L to 53,800 mg/L and an average concentration of 10,932 mg/L. Meanwhile, Cl− was the predominant anion, with concentrations ranging from 170.8 mg/L to 99,546 mg/L and an average concentration of 20,101 mg/L. In the SFZ groundwater, Na+ was the predominant cation, with concentrations ranging from 96.46 mg/L to 3014 mg/L and an average concentration of 763 mg/L. Similarly, Cl− was the predominant anion, with concentrations varying from 56.02 mg/L to 6933 mg/L and an average concentration of 1215 mg/L.
The Piper diagram was extensively utilized in the classification of groundwater hydrochemical types [21]. In the cation triangle shown in Figure 3, TP was predominantly located in Areas B and D, whereas the SFZ was distributed across the boundary between Areas B and D, as well as within Area D. In the anion triangle, TP was predominantly located in area G, whereas the SFZ was distributed across areas E, B, and G. In the rhombic region of the Piper diagram, TP was predominantly found in areas ① and ④, with hydrochemical compositions classified as the SO4·Cl-Ca·Mg type (C1–C4) and the SO4·Cl-Mg type (C5–C7). The SFZ groundwater was distributed not only in Area ① and Area ④ but also in Areas ② and ③, exhibiting a diverse range of hydrochemical types.
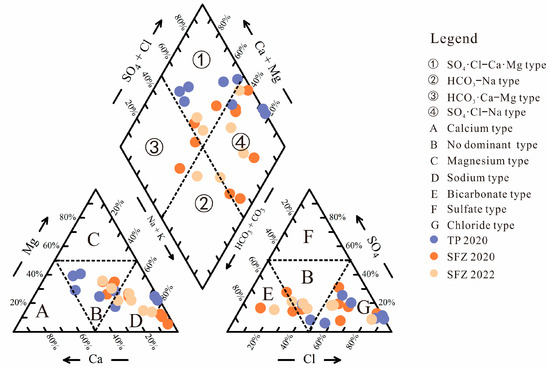
Figure 3.
Piper diagram showing the hydrochemical classification of water samples based on the relative concentrations of major cations (Ca2+, Mg2+, and Na++K+) and anions (HCO3−, SO42−, and Cl−). The trilinear plots and central diamond field represent ion dominance and water types (e.g., Ca-HCO3 and Na-Cl).
4.2. Origin of Groundwater and Salinity
Figure 4 illustrates the relationship between δ2H and δ18O in the groundwater of the study area. The δ2H of TP groundwater ranged from −77‰ to −45‰, with an average of −61‰, and the δ18O ranged from −10.4‰ to −5.2‰, with an average of −7.62‰. For SFZ groundwater, the δ2H ranged from −72‰ to −36‰, with an average of −54.25‰, and the δ18O ranged from −9.4‰ to −3.4‰, with an average of −6.99‰. The isotopic values of the aforementioned samples were all lower than those of the seawater samples (δ2H = −18‰ and δ18O = −1.8‰ in Bohai Bay, from [22]). The distribution of groundwater samples deviated from both the Global Meteoric Water Line (GMWL: δ2H = 8 × δ18O + 10, as defined by [23]) and the Local Meteoric Water Line (LMWL: δ2H = 6.29 × δ18O − 3.63, as reported by [24]). Several groundwater samples, including B1, B3, B4, C1, C3, D1, and D3, were closely aligned with the LMWL, suggesting that these samples predominantly received recharge from atmospheric precipitation. Seawater had the highest δ18O and δ2H isotope values, and the isotopic values of saline groundwater were enriched and had a relatively high Cl− concentration at the same time (A2, C4, C5, C7, C8, and D2 in Figure 4b). Both TP and SFZ samples were located to the right of the LMWL, indicating that seawater mixing and evaporation processes may significantly influence the salinity and isotopic composition (δ2H, δ18O) in the study area [25]).
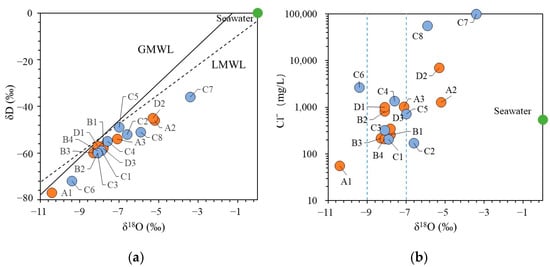
Figure 4.
(a) Groundwater δD versus δ18O relationship; (b) Cl− versus δ18O relationship.
As shown in Figure 4, certain samples (e.g., C7, C8) exhibited a characteristic where the TDS was higher than that of seawater, yet the δ2H and δ18O values were depleted relative to seawater. These samples were distributed within the brine occurrence zones in the study area. The brine in the study area was a type of saltwater characterized by low isotope values and high TDS. It originated from the continuous evaporation and concentration of ancient seawater and has been subject to ongoing dilution and mixing due to rainfall [26,27].
The diagram of water chemical composition can elucidate the relationships among various ions and serves as a tool for identifying the sources of groundwater composition. As shown in Figure 5a,b, the TP groundwater samples were distributed below the mixing line of seawater, whereas most of the SFZ samples were located above this line. This distribution suggests that the sources of SFZ and TP groundwater differ significantly.
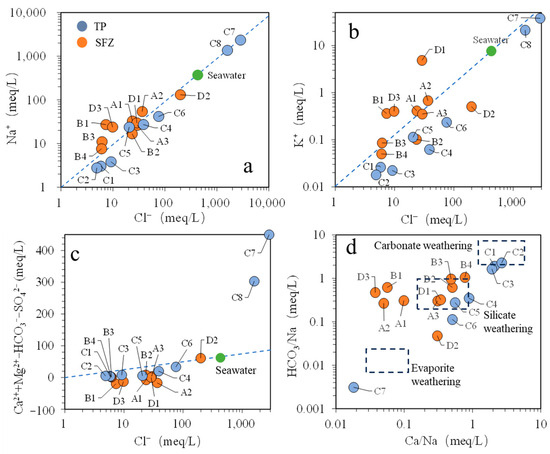
Figure 5.
Scatter plots of dissolved substance tracer (a) Cl− versus Na+, (b) Cl− versus K+, (c) Cl− versus Ca2++ Mg2++ HCO3− − SO42+, and (d) Ca/Na versus HCO3/Na.
As illustrated in Figure 5c, C7 and C8 exhibited marked differences compared to the other groundwater samples, with notably higher concentrations of Ca2+ and Mg2+ relative to the remaining samples. As indicated in Figure 5d, C7 and C8 likely experienced significant evaporation, consistent with the previously described intense evaporation process involved in brine formation [24]. In Figure 5d, C1–C3 were predominantly found in areas influenced by carbonate weathering, whereas the samples (C4–C6) from the saline–fresh groundwater transition zone and SFZ groundwater primarily stemmed from silicate weathering.
5. Discussion
5.1. Saltwater Intrusion Processes
The Gibbs diagram can be used to identify the hydrochemical processes that control groundwater [28]. Figure 6 illustrates the distribution of TP and SFZ groundwater as plotted on the Gibbs diagram.
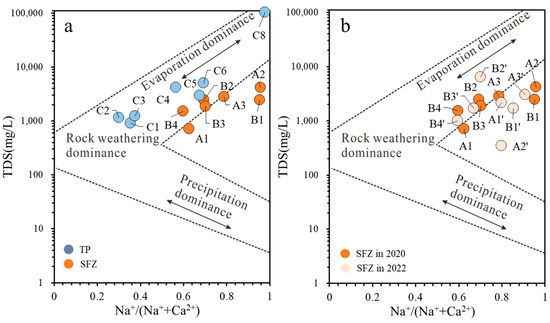
Figure 6.
Gibbs diagram illustrating the mechanisms controlling water chemistry (e.g., evaporation, rock weathering, or precipitation dominance) in the study area. The plot compares the ratio of major ions (Na+/(Na++Ca2+) vs. Cl−/(Cl− + HCO3−)) to identify dominant hydrogeochemical processes. (a) shows the relationship between TP and SFZ (b) shows the relationship between TP in 2020 and TP in 2022.
It can be seen from Figure 6a that the formation of several samples, C1–C3 of TP, in the study area near the south was in the process of water–rock interaction. For the other samples, as the location kept moving northward (towards the sea), they gradually tended to move towards the evaporation control area, indicating that the formation of C4–C6 may be in the stage dominated by the mixture of saline groundwater and fresh groundwater. The SFZ groundwater was situated within the transitional zone between the region primarily influenced by water–rock interactions and the region dominated by evaporation. This positioning highlighted its characteristics during the mixing process of saline and fresh groundwater. Figure 6b illustrates the distribution and variation of SFZ groundwater in the Gibbs diagram for both 2020 and 2022. It is evident that the SFZ groundwater in 2022 continued to display characteristics of a mixture of saline and fresh groundwater. Notably, the changes in A1, A2, and B2 were particularly pronounced, suggesting that the mixing process at these locations underwent significant transitions.
The hydrochemical facies evolution diagram (HFE-D) provided a convenient method for identifying the groundwater evolution process in coastal aquifers, exploring the hydrogeochemical variations that occurred over time by groundwater freshening and salinization processes [29]. The temporal progression of intrusion or freshening stages can be characterized by the distribution of anion and cation percentages in the HFE-D [29,30].
The X-axis represents the evolutionary trend with two endpoints (%Ca and %Na, respectively), reflecting the progression of Na/Ca and Ca/Na exchanges as calcium-rich and sodium-rich waters mixed. When seawater intrudes into the aquifer, the groundwater can evolve from the Ca–HCO3 facies to the Na–Cl facies, passing through an intermediate Ca–Cl facies that is characteristic of this process (intrusion phase). The Ca–Cl facies is recognized as the clearest indicator of the saline wedge encroachment, while the Na–HCO3 facies characterizes the full development of the freshening phase. During the freshening phase, the initial Na–Cl water gradually transitions to Ca–HCO3 water, mediated by an intermediate Na–HCO3 facies or one of the other isopycnic facies [31]. Figure 7 illustrates the detailed characterization of the facies evolution sequence for both TP groundwater and SFZ groundwater in the study area during freshening and intrusion events.
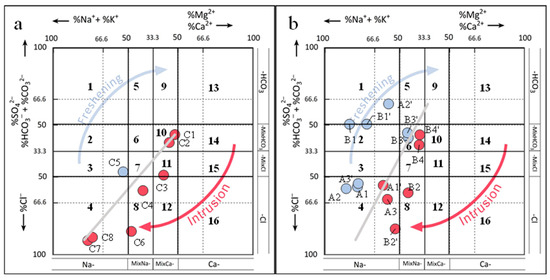
Figure 7.
Hydrochemical facies evolution diagram (HFE-Diagram): 1: Na–HCO3, 2: Na–MixHCO3/MixSO4, 3: Na–MixCl, 4: Na–Cl, 5: MixNa–MixHCO3/SO4, 6: MixNa–MixHCO3/MixSO4, 7: MixNa–MixCl, 8: MixNa–Cl, 9: MixCa/MixMg–HCO3/SO4, 10: MixCa/MixMg–MixHCO3/MixSO4, 11: MixCa/MixMg–MixCl,12:MixCa/MixMg–Cl, 13: Ca/Mg–Cl, 14: Ca/Mg–MixHCO3/MixSO4, 15: Ca/Mg–MixCl, and 16: Ca/Mg–Cl. (a) TP; (b) SFZ in 2020 and SFZ in 2022.
In Figure 7, four heterotopic facies were identified: Na–Cl (seawater), Ca–HCO3 (natural freshwater), Ca–Cl (salinized water with reverse exchange), and Na–HCO3 (salinized water with direct exchange). Facies types positioned above and to the left of the conservative mixing line represented the freshening phase, whereas those located below and to the right of the line corresponded to the seawater intrusion stage. The freshwater was characterized by the Ca–HCO3/SO4 facies (13), while the saltwater exhibited the Na-Cl facies (4). The results indicated that the majority of TP groundwater samples fell below or on the mixing line, suggesting that TP groundwater was undergoing saltwater intrusion. Furthermore, it demonstrated that TP groundwater fully evolved from the MixCa/MixMg-MixHCO3/MixSO4 (10) type to the Na–Cl (4) type. In the groundwater samples of SFZ, it can be found that individual samples underwent relatively obvious freshening or salinization processes. A2 had a freshening process from the Na–Cl (4) type to the Na–HCO3 (1) type, B2 had a salinization process from the MixNa–Cl (8) type to the Na–Cl (4) type, and others, such as changes within the same phase, such as the salinization of A1 within Na–Cl (4) and the freshening of A3 within Na–Cl (4). Overall, the TP groundwater continued to exhibit a general trend of salinization. The processes of freshening and salinization in SFZ groundwater varied with depth and location.
The TDS, Cl− concentrations, and sampling depths were plotted in Figure 8 to derive the TDS concentration depth and Cl− concentration depth relationship for the SFZ. As illustrated in Figure 8, the response changes of TDS and Cl−, with respect to depth, exhibited a similar trend. At monitoring point A of the SFZ (Figure 8a,b), from 2020 to 2022, we observed a significant decrease in the concentrations of TDS and Cl− in deep-layer groundwater samples (A2–A2′), while there was a notable increase in TDS and Cl− concentrations in shallow-layer samples (A1–A1′) at a burial depth of approximately 20 m. In HFE-D, A1–A1′ was undergoing a salinization process. These observations collectively suggest that saltwater intrusion occurred in the middle layer at this location.
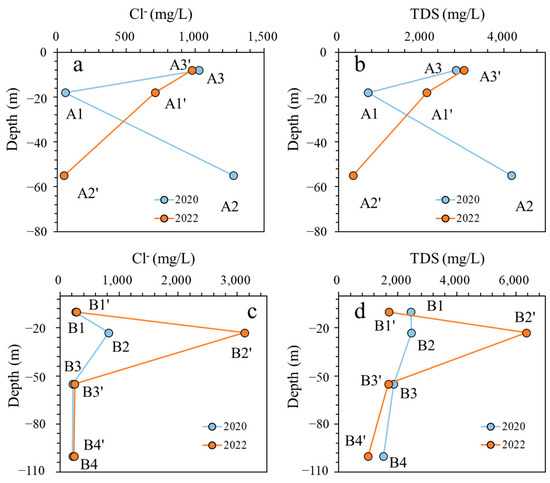
Figure 8.
The relationships between burial depth versus TDS (a) and Cl− (b) in A. The relationships between burial depth versus TDS (c) and Cl− (d) in B.
At monitoring point B of the SFZ, we observed a significant increase in TDS and Cl− concentrations in the middle layer (approximately 20 m deep, B2–B2′), while samples from other depths showed no substantial changes. These findings aligned closely with the hydrochemical facies analysis presented in Figure 7, which indicates that B2–B2′ experienced a salinization process, transitioning from the MixNa–Cl (8) to the Na–Cl (4) type. This suggests that saltwater intrusion at this location also exhibited a typical wedge-shaped pattern, and the intrusion area in the north was wider than that in the south, as shown in Figure 2. In the areas of saline water intrusion, Cl− and Na+ concentrations increased significantly from fresh groundwater and brackish groundwater to saline groundwater. The pattern of saltwater intrusion identified in this study is consistent with the findings reported by Liu et al. (2017) [8]. This phenomenon where saltwater intrusion predominantly affects the middle layer is primarily governed by the permeability of the aquifer [8]. In this region, due to historical sedimentation factors, the permeability of aquifers at varying depths differs, leading to variations in the extent of vertical saltwater intrusion.
5.2. Environmental Management Implications
Groundwater salinization due to seawater intrusion has become a significant global resource and environmental concern. This phenomenon is primarily driven by two factors: the rise in sea level attributed to climate warming and the overexploitation of groundwater resources to satisfy the growing water demand [32,33,34]. Measures to address seawater intrusion in coastal areas focus on management strategies comprising groundwater extraction prohibitions/restrictions, coupled with engineering solutions, including tide barrier installation, subsurface dam construction, and artificial recharge projects [35,36]. Their effectiveness in controlling seawater intrusion and influence on associated groundwater quality variations have undergone a systematic evaluation. However, measure selection requires integrated consideration of regional geological features and site-specific seawater intrusion conditions [32,33]. Based on the aforementioned findings, it is evident that diverse control measures should be implemented in response to the distinct regional characteristics and specific groundwater environmental issues. In light of the escalating trend of saltwater intrusion, it is imperative to implement rational planning and management of regional water resources while augmenting the supply of alternative water sources in order to mitigate groundwater extraction. Given that saltwater intrusion exhibits spatial variability across different locations and depths, it is imperative to enhance the monitoring of groundwater quality and increase the frequency of monitoring. Particular emphasis should be placed on monitoring at various depths, an aspect that has historically received less attention. This approach facilitates the rational utilization of regional water resources and enhances the accuracy of water environment assessment.
6. Conclusions
This paper investigated the hydrochemistry and evolutionary processes during saltwater intrusion in the saline–fresh groundwater transition zone in southern Laizhou Bay. The study area is characterized by complex geological conditions, intense human interference, and a deteriorated groundwater environment. By sampling typical profiles and the salt–fresh groundwater transition zone, we examined the hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater, identified the sources of water and salts in both TP and the SFZ, analyzed the evolutionary processes of groundwater at various depths within the SFZ, and elucidated the characteristics and patterns of saltwater intrusion. Furthermore, we also offered a range of management strategies for various environmental problems. The conclusions and policy recommendations are as follows:
The groundwater types within the entire study area exhibited a complex and diverse distribution, comprising fresh groundwater, brackish groundwater, and saline groundwater. The TDS in groundwater exhibited significant variation, ranging from 706.7 mg/L to 177,947 mg/L. The hydrochemical types of groundwater varied from the SO4·Cl-Ca·Mg type through the HCO3–Na type and to the SO4·Cl–Mg type. The stable isotope composition of groundwater suggests that the mixing and evaporation of seawater were the predominant processes governing the formation and salinity of groundwater in this region. In the southern part of the typical section, carbonate weathering predominated, whereas silicate weathering appeared to be the primary process influencing groundwater at the SFZ.
The TP groundwater samples exhibited varying stages of hydrochemical facies evolution. The majority of the groundwater samples were in the salinization stage during the mixing process, whereas the C5 sample was at the desalination stage. The processes of freshening and salinization in the SFZ groundwater varied with depth and location. Saltwater intrusion in the SFZ displayed a characteristic wedge-shaped distribution, primarily impacting the middle layer.
Based on the aforementioned findings, it is evident that diverse control measures should be implemented in response to the distinct regional characteristics and specific groundwater environmental issues. In light of the escalating trend of saltwater intrusion, it is imperative to implement rational planning and management of regional water resources while augmenting the supply of alternative water sources in order to mitigate groundwater extraction. Given that saltwater intrusion exhibits spatial variability across different locations and depths, it is imperative to enhance the monitoring of groundwater quality and increase the frequency of monitoring. Particular emphasis should be placed on monitoring at various depths, an aspect that has historically received less attention. This approach facilitates the rational utilization of regional water resources and enhances the accuracy of water environment assessment.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.W., Y.Z. and Y.Y.; methodology, X.W. and G.W.; software, X.D.; formal analysis, Y.Y.; investigation, X.W. and G.W.; writing—original draft preparation, X.W. and Y.Z.; writing—review and editing, F.Y., X.H. and Y.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Fundamental Water Resources Investigation Project of Shandong Province and the project of Jinan Science and Technology Bureau (2021GXRC070).
Data Availability Statement
Data are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kumar, M.; Rao, M.S.; Deka, J.P.; Ramanathan, A.; Kumar, B. Integrated Hydrogeochemical, Isotopic and Geomorphological Depiction of the Groundwater Salinization in the Aquifer System of Delhi, India. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 111, 936–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wu, M.; Duan, Z.; Zha, Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, L.; Zou, L.; Zheng, M.; Chen, P.; Cao, W.; et al. Forecasting the Human and Climate Impacts on Groundwater Resources in the Irrigated Agricultural Region of North China Plain. Hydrol. Process. 2023, 37, e14853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, X.; Liu, J.; Scanlon, B.R.; Jiao, J.J.; Jasechko, S.; Lancia, M.; Biskaborn, B.K.; Wada, Y.; Li, H.; Zeng, Z.; et al. The Changing Nature of Groundwater in the Global Water Cycle. Science 2024, 383, eadf0630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Lu, C.; Ye, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, L.; Luo, J. Assessment of the Impact of Sea-Level Rise on Steady-State Seawater Intrusion in a Layered Coastal Aquifer. J. Hydrol. 2018, 563, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.W.; Clement, T.P.; Simpson, M.J.; Lee, K.-K. Does Sea-Level Rise Have an Impact on Saltwater Intrusion? Adv. Water Resour. 2011, 34, 1283–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chala, D.C.; Quiñones-Bolaños, E.; Mehrvar, M. An Integrated Framework to Model Salinity Intrusion in Coastal Unconfined Aquifers Considering Intrinsic Vulnerability Factors, Driving Forces, and Land Subsidence. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 106873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Gao, M.; Wen, Z.; Guo, F.; Hou, G.; Liu, Z.; Cai, Z.; Chang, X.; Zheng, T.; Zhao, G. Reactive Transport Modeling for the Effect of Pumping Activities on the Groundwater Environment in Muddy Coasts. J. Hydrol. 2023, 621, 129614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Tang, Z.; Gao, M.; Hou, G. Evolutionary Process of Saline-Water Intrusion in Holocene and Late Pleistocene Groundwater in Southern Laizhou Bay. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 586–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Liu, S.; Jia, C.; Gao, M.; Chang, W.; Wang, Y. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Functions of Groundwater in Southern Laizhou Bay Based on the Multivariate Statistical Analysis Approach. Estuarine. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 250, 107153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, C.; Godfrey, L.; Urrutia, J.; Custodio, E.; Gamboa, C.; Jódar, J.; Lam, E.; Fuentes, J. Origin of Old Saline Groundwater in the Deep Coastal Formations of the Atacama Desert Region: Consideration of Lithium, Boron, Strontium and Uranium Isotopes Contents. J. Hydrol. 2023, 624, 129919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christofi, C.; Bruggeman, A.; Kuells, C.; Constantinou, C. Isotope Hydrology and Hydrogeochemical Modeling of Troodos Fractured Aquifer, Cyprus: The Development of Hydrogeological Descriptions of Observed Water Types. Appl. Geochem. 2020, 123, 104780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, C.; Custodio, E. Groundwater Flow in a Relatively Old Oceanic Volcanic Island: The Betancuria Area, Fuerteventura Island, Canary Islands, Spain. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 496, 531–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Currell, M.; Cendón, D.I. Marine Water from Mid-Holocene Sea Level Highstand Trapped in a Coastal Aquifer: Evidence from Groundwater Isotopes, and Environmental Significance. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 544, 995–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Q.; Yu, Y.; Chen, M.; Fu, T.; Lyu, W.; Liu, W. Exploration of the Formation Mechanism of Underground Brine Based on Hydrodynamic Environment Analysis Using Grain-Size Data of One Drilling Core. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Gao, M.; Wen, Z.; Hou, G.; Dang, X.; Liu, S.; Zhao, G. Hydrochemical Evolution Processes of Multiple-Water Quality Interfaces (Fresh/Saline Water, Saline Water/Brine) on Muddy Coast under Pumping Conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 857, 159297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Kong, K.; Yao, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, D.; Shao, S. Combining Multi-Source Data to Identify the Paleochannel System in the Saltwater Intrusion Area. Mar. Georesources Geotechnol. 2024, 42, 562–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulligan, A.E.; Evans, R.L.; Lizarralde, D. The Role of Paleochannels in Groundwater/Seawater Exchange. J. Hydrol. 2007, 335, 313–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Hu, B.X.; Xu, Z.; Li, X.; Tong, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Miao, J.; Liu, H.; Ma, Z. Numerical Simulation of Seawater Intrusion to Coastal Aquifers and Brine Water/Freshwater Interaction in South Coast of Laizhou Bay, China. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2018, 215, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.M.; Song, X.F.; Currell, M.J.; Yang, J.L.; Xiao, G.Q. Chemical and Isotopic Constraints on Evolution of Groundwater Salinization in the Coastal Plain Aquifer of Laizhou Bay, China. J. Hydrol. 2014, 508, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Ma, T.; Chen, L.; Shan, H.; Xiao, C.; Lu, Y.; Liu, C.; Cai, H. Genesis of Salinized Groundwater in Quaternary Aquifer System of Coastal Plain, Laizhou Bay, China: Geochemical Evidences, Especially from Bromine Stable Isotope. Applied Geochemistry 2015, 59, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, A.M. A Graphic Procedure in the Geochemical Interpretation of Water-analyses. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1944, 25, 914–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, C.; Hu, X.; Yang, F.; Huang, X.; Chen, H.; Chen, L.; Chen, G.; Wu, Z.; Wang, S. Unraveling Microbial Community Variation along a Salinity Gradient and Indicative Significance to Groundwater Salinization in the Coastal Aquifer. J. Hydrol. 2024, 642, 131893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, H. Isotopic Variations in Meteoric Waters. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, G.; Yang, P.; Chen, J. Recognition and Vertical Spatiotemporal Distribution of Brine Intrusion in the Weibei Plain. Coast. Eng. 2024, 43, 24–37. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Pang, Z.; Kong, Y.; Li, J.; Tian, J. An Isotopic Geoindicator in the Hydrological Cycle. Procedia Earth Planet. Sci. 2017, 17, 534–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Kohfahl, C.; Song, X.; Xiao, G.; Yang, J. Geochemical and Isotopic Evidence for Palaeo-Seawater Intrusion into the South Coast Aquifer of Laizhou Bay, China. Appl. Geochem. 2011, 26, 863–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Ma, C.; He, Z.; Hu, X.; Gao, L. Lithium and Its Isotopes as Tracers of Groundwater Salinization: A Study in the Southern Coastal Plain of Laizhou Bay, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 878–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, R.J. Mechanisms Controlling World Water Chemistry. Science 1970, 17, 1088–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez-Forcada, E. Dynamic of Sea Water Interface Using Hydrochemical Facies Evolution Diagram. Groundwater 2010, 48, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, V.; Nakhaei, M.; Lak, R.; Kholghi, M. Assessment of Seasonal Groundwater Quality and Potential Saltwater Intrusion: A Study Case in Urmia Coastal Aquifer (NW Iran) Using the Groundwater Quality Index (GQI) and Hydrochemical Facies Evolution Diagram (HFE-D). Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2016, 30, 1473–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez-Forcada, E. Space/Time Development of Seawater Intrusion: A Study Case in Vinaroz Coastal Plain (Eastern Spain) Using HFE-Diagram, and Spatial Distribution of Hydrochemical Facies. J. Hydrol. 2014, 517, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Currell, M.J. Review of Drivers and Threats to Coastal Groundwater Quality in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, A.D.; Bakker, M.; Post, V.E.A.; Vandenbohede, A.; Lu, C.; Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Simmons, C.T.; Barry, D.A. Seawater Intrusion Processes, Investigation and Management: Recent Advances and Future Challenges. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 51, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, A.H.; David, C.H.; Famiglietti, J.S. Continental Patterns of Submarine Groundwater Discharge Reveal Coastal Vulnerabilities. Science 2016, 353, 705–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Zheng, X.; Chang, Q.; Zhan, H.; Walther, M. Timescale and Effectiveness of Residual Saltwater Desalinization Behind Subsurface Dams in an Unconfined Aquifer. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2020WR028493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Wang, S.; Kong, X.; Zheng, W.; Feng, W.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, R.; Song, X.; Sprenger, M. Interaction of Surface Water and Groundwater Influenced by Groundwater Over-Extraction, Waste Water Discharge and Water Transfer in Xiong’an New Area, China. Water 2019, 11, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).