Abstract
This study compared the effectiveness of the Sequencing Batch Biofilter Granular Reactor (SBBGR) plant with and without the integration of ozone (BIO-CHEM process) in the remediation of medium-aged landfill leachate. Special attention is given to the removal of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) as a group of bioaccumulative and persistent pollutants. The findings highlight the high SBBGR performance under biological process only for key wastewater contaminants, with 82% for chemical oxygen demand (COD), 86% for total nitrogen, and 98% for ammonia. Moderate removal was observed for total (TSS) and volatile (VSS) suspended solids (41% and 44%, respectively), while phosphorus and colour removal remained limited. Remarkably, the SBBGR process achieved complete removal of long-chain PFAS, while its performance declined for shorter-chain PFAS. BIO-CHEM process significantly improved COD (87.7%), TSS (84.6%), VSS (86.7%), and colour (92–96%) removal. Conversely, ozonation led to an unexpected increase in the concentrations of several PFAS in the effluent, suggesting ozone-induced desorption from the biomass. SBBGR treatment was characterised by a low specific sludge production (SSP) value, i.e., 5–6 times less than that of conventional biological processes. SSP was further reduced during the application of the BIO-CHEM process. A key finding of this study is a critical challenge for PFAS removal in this combined treatment approach, different from other ozone-based methods.
1. Introduction
Sanitary landfilling remains the most common method of disposing of municipal solid waste worldwide [1]. A major environmental issue associated with this method is the production of leachate, a highly polluted liquid generated when water percolates through deposited waste [2]. The composition of leachate is influenced by multiple variables, including rainfall patterns, the age of the landfill, and soil characteristics [3,4]. Leachate is typically enriched with high levels of organic matter, xenobiotic compounds, inorganic salts, ammonia, heavy metals, and various toxicants [5,6]. To date, over 200 organic substances have been detected in landfill leachate, of which more than 35 are recognised as having the potential to adversely affect environmental quality and public health [7]. Recent studies have revealed that landfill leachate is a major source of emerging contaminants, including per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), thereby contributing to their widespread dissemination in the environment [8].
The persistent contamination caused by PFAS is a significant environmental challenge, as they are exceptionally stable due to the strength of their C–F bonds. This stability enables them to persist and bioaccumulate in diverse environmental matrices, like soil, water, sediments, crops, and living organisms [9]. The polarity and strength of the C–F bond render PFAS compounds remarkably stable and resistant to chemical reactions such as reduction, oxidation, and hydrolysis [10]. PFAS are a broad class of synthetic chemicals commonly used in commercial and consumer products thanks to their unique properties, such as oleophobicity, chemical stability, and hydrophobicity. At life cycle termination, PFAS-containing products are often disposed of in landfills. The degradation of these materials can result in fluorinated compounds being released into leachate [11,12]. Generally, the total PFAS concentrations in landfill leachate typically range from a few hundred to several thousand nanograms per litre (ng/L). For instance, a study of six municipal landfills in western China reported total PFAS levels ranging from 1805 to 43,310 ng/L. These levels were predominantly composed of short-chain sulfonates, such as perfluorobutanesulfonic (PFBS) and perfluorobutanoic (PFBA) [13]. While in some European countries, the total concentration of PFAS in landfill leachate ranges from 1100 to 14,000 ng/L in Bulgaria, from 31 to 12,922 ng/L in Germany, and from 639 to 1379 ng/L in Spain [14,15,16,17,18]. A U.S. study analyzing leachate discharges to municipal wastewater treatment found total PFAS concentrations reaching 93,100 ng/L, over ten times higher than levels in influent (~6950 ng/L) and effluent (~3730 ng/L) from WWTPs [19]. Broad reviews estimate that the concentration of ∑PFAS in municipal solid waste (MSW) leachate worldwide ranges from non-detectable levels to 125,000 ng/L, with an average of around 10,500 ng/L [20]. This contaminated leachate has the potential to migrate into groundwater and surface waters, thereby impacting nearby ecological receptors and human communities [21], by disrupting microbial communities in soils and leachate-impacted zones; for instance, research has documented inhibition of Proteobacteria by PFBS, indicating ecological toxicity even at the microbial scale. Moreover, landfills can act as sources of PFAS volatilisation, where gas and condensate may further distribute PFAS off-site, expanding exposure pathways [22]. Leachate-derived PFAS pose a long-term health risk due to groundwater contamination, which may be used for irrigation or livestock, resulting in indirect human exposure. Chronic exposure to these substances has been linked to immunotoxic, developmental, and carcinogenic effects [23]. In addition, the environmental persistence of PFASs increases their risk potential due to their ability to bioaccumulate within the food chain, resulting in sustained human exposure. Consumption of PFAS-contaminated drinking water has notably been associated with significant adverse health outcomes, including hepatotoxicity, carcinogenicity, reproductive impairments, endocrine disruption, liver damage, cancer, hormone disruption, fertility issues, thyroid disease, and thyroid dysfunction [24]. Furthermore, landfill workers and nearby communities may be at risk of health problems due to indirect exposure, such as inhaling contaminated air or dust or coming into contact with PFAS-contaminated water, which can lead to airborne exposure [25].
The treatment of landfill leachate has therefore become a crucial concern in order to reduce PFAS levels before it is disposed of at municipal wastewater treatment plants, which are not designed to eliminate PFAS compounds. Various technologies have been tested for PFAS removal during landfill leachate treatment, including constructed wetlands [26,27], membranes [28], plasma reactors [29], ozone foam fractionation [30], continuous foam fractionation [31], photo/electrocatalysts [32,33], and electrochemical oxidation [34]. Most of these technologies demonstrated moderate removal efficiency for these compounds, particularly short-chain PFASs, due to their high chemical stability and matrix complexity (e.g., heterogeneous composition, high salinity, high levels of contamination, the occurrence of biorefractory compounds, colour, and turbidity) [35]. In addition, those approaches have certain drawbacks, like high costs and/or high energy demand. Therefore, it is necessary to explore an integrated approach that combines biological degradation with chemical oxidation. For instance, Singh et al. [29] evaluated plasma reactor technology, which showed promising results for the degradation of long-chain PFASs; however, this approach remains immature for large-scale application and is associated with relatively high energy consumption. Another approach proposed by Hegedus et al. [36] is based on the dehalogenation of persistent halogenated organic contaminants, including PFAS, exploring a high reduction in the concentrations of selected contaminants from water. Nevertheless, the cost of its large-scale application could not be ignored due to the price of the Raney alloy and the cost of regenerating it.
To improve treatment efficiency, a hybrid bio-chemical (BIO-CHEM) process integrating a Sequencing Batch Biofilter Granular Reactor (SBBGR) with ozonation treatment represents a promising approach for the remediation of landfill leachate. The discontinuous operation of the SBBGR system enables the targeted application of ozone in a controlled and sequential manner. Implementing ozonation post-biological treatment facilitates the selective oxidation of biologically recalcitrant compounds. Controlled ozone dosing allows partial oxidation of persistent contaminants, enhancing their subsequent biodegradability by the microbial community. While limited, existing studies have demonstrated the potential of ozone-enhanced SBBGR systems in effectively removing conventional pollutants from landfill leachate and wastewater. For example, Lotito et al. [37] tested the efficacy of the BIO-CHEM process in treating printing textile wastewater. This process allowed for the removal of >99% of total and volatile suspended solids (TSS and VSS, respectively), 80% of chemical oxygen demand (COD), >85% of total Kjeldahl nitrogen (TKN), >95% of surfactants, and >90% of colour, with an ozone dose of 135 mg O3/L influent. Di Iaconi et al. [38] used the BIO-CHEM process for treating tannery wastewater, showing a high removal performance exceeding 99% for COD, 98% for dissolved organic carbon (DOC), 99% for TSS, 90% for ammonia (NH3), 99% for surfactants, and 98% for colour under an ozone dose of 300 mg O3/Linfluent. In another study, Di Iaconi et al. [39] used the BIO-CHEM process after a pre-treatment stage for nitrogen recovery as struvite from mature municipal landfill leachate. The authors obtained a removal of 98% for COD, 94% for DOC, 99% for 5-day bio-chemical oxygen demand (BOD5), 94% for TSS, 98% for surfactants, and 98% for colour under an ozone dose of 100 mg O3/Linfluent. A similar process has been used by Di Iaconi et al. [40] for the treatment of a medium-age landfill leachate, achieving compliance with current sewer discharge limits by applying a targeted ozone dose of 600 mg O3/Linfluent, confirming the great effectiveness improvement of the BIO-CHEM process. Nevertheless, this process has never been tested for the treatment of contaminants of emerging concern, such as PFAS compounds from landfill leachate.
Based on the aforementioned considerations, the present study aimed to assess the effectiveness of the BIO-CHEM process in removing PFAS compounds from medium-age landfill leachates, and to compare it with a biological process by SBBGR only, to investigate the impact of ozonation on treatment performance.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Set-Up
The experimental laboratory-scale plant combined a biological unit with an ozonation unit (Figure 1). The biological unit was based on the SBBGR system comprising
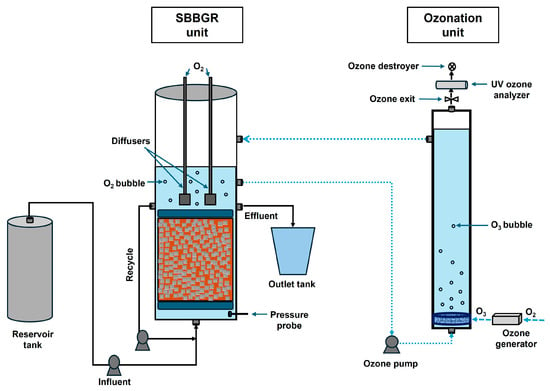
Figure 1.
Sketch of SBBGR and ozonation unit.
- -
- A plexiglass cylindrical reactor of 19 cm in diameter, 100 cm in height, and a total volume of 28 L, which was partially packed with 13 L of Kaldness-type plastic carriers. These wheel-shaped elements (7 mm in height, 8 mm in diameter) offer a specific surface area of 690 m2/m3, a density of 0.95 g/cm3, and a porosity of 0.75. The media were secured between two perforated plates to maintain a fixed bed structure.
- -
- A volumetric pump was used to recirculate liquid through the bed at a rate of 90 L/h.
- -
- Two peristaltic pumps are used to supply leachate and acetate, the latter acting as an external substrate to facilitate nitrogen elimination.
- -
- Two diffusers positioned atop the bed supply pure oxygen to the process.
- -
- A motorised valve is required for the gravity drainage of effluent.
- -
- A head loss measuring probe with an associated display.
- -
- A programme logic control (PLC) for automation of the system.
In this study, the SBBGR had a total geometric working volume of 20 L, with 13 L filled by plastic support material.
The ozonation unit consisted of (Figure 1)
- -
- A peristaltic pump operating at a flow rate of 70 L/h, which was used to withdraw liquid from the SBBGR system;
- -
- A cylindrical glass reactor with a diameter of 85 mm, a height of 90 cm, and a total volume of 5 L;
- -
- An ozone generator (WEDECO Modular 8HC, Herford, Germany), operating with pure oxygen and providing an output of 0.5 to 8 gO3/h;
- -
- A thermocatalytic residual ozone destructor;
- -
- A UV ozone analyser (BMT 964, WEDECO, Herford, Germany) was used to measure the ozone concentration in the gas stream at the inlet and outlet of the ozone reactor.
2.2. Operational Schedule
The experimental monitoring was divided into three periods (A, B, and C). Period A lasted around 103 days and was addressed to the SBBGR start-up. SBBGR bed was inoculated with a mixed biomass comprising 30%:70% (v/v) of leachate treatment plant activated sludge and municipal wastewater treatment facility. This mixed inoculum strategy aimed to provide both leachate-adapted species and a broad microbial diversity to enhance biomass acclimatisation and growth. During period A, a gradual feeding plan was used involving the dilution of the leachate with tap water at gradually decreasing ratios to acclimatise the inoculated biomass to the high salinity of the leachate (from 1.5 mS cm−1 to 22 mS cm−1) and simultaneously enhance microbial activity. During this period, SBBGR operated in batch mode by 8 h treatment cycles, each consisting of three consecutive phases of filling, biodegradation, and emptying. In the first phase (filling), which lasted about 0.5 h, a defined volume of leachate was introduced from the bottom of the reactor into the liquid retained from the previous treatment cycle. Throughout the second phase of biological degradation, lasting about 7 h, the liquid was continuously recycled and oxygenated within the reactor bed. Ultimately, during the drawing phase (0.5 h), a volume of liquid equal to that loaded was discharged from the gravity-fed reactor via a motorised valve. A pressure probe installed at the SBBGR unit bottom continuously measured online head losses caused by biomass development and influent suspended solids retained by the bed during reactor operation. Once the head loss reached 300 cm, a washing phase using compressed oxygen was carried out until it decreased to 100 cm. The solids expelled from the bed were carefully collected and measured to determine the specific sludge production (SSP) of the process.
Period B (2 months) was aimed at determining the efficiency of SBBGR fed with undiluted leachate, in terms of traditional pollutants and PFAS removal.
During period C (3 months), the ozonation unit was activated to enhance SBBGR treatment (BIO-CHEM process). During this period, a fourth phase (i.e., “chemical + biological oxidation” phase) lasting 1 h was added in the SBBGR treatment cycle after the “biological degradation” phase, whose duration was then shortened by 1 h. During the “chemical + biological oxidation” phase, the liquid was circulated simultaneously between the SBBGR and ozonation unit and through the SBBGR bed. An ozone dose of 5 gO3/L was converted to the leachate, with a feeding flow rate of 3 L/d used throughout the experimental period. Leachate from a non-hazardous waste landfill in the Lombardy region of northern Italy was used.
2.3. Evaluation of Treatment Performance
SBBGR and BIO-CHEM process performances were evaluated in terms of conventional macro-pollutants and PFAS removal.
Conventional macro-pollutants included pH, electrical conductivity (EC), total and soluble COD, 5-day bio-chemical oxygen demand (BOD5), TSS, VSS, NH3, TN, NO2−, N-NO3−, total phosphorus (TP), and colour removal. The latter was evaluated at three different wavelengths (i.e., 426, 558, and 660 nm).
Regarding PFAS, 13 substances were detected: 9 perfluorocarboxylic acids containing 4 to 10 carbon atoms [perfluorobutanoic (PFBA), perfluorohexanoic (PFHxA), perfluoropentanoic (PFPeA), perfluoroheptanoic (PFHpA), perfluorononanoic (PFNA), perfluorooctanoic (PFOA), perfluoroundecanoic acid (PFUdA), perfluorodecanoic (PFDA), and perfluorodecanoic acid (PFDoDA)], 4 perfluorosulfonic acids [perfluorobutanesulfonic (PFBS), perfluorohexanesulfonic (PFHxS), perfluorooctanesulfonic (PFOS), and 6:2-fluorotelomersulfonic acid (6:2 FTSA)].
2.4. Analytical Methods
Influent and effluent samples were collected weekly and analysed promptly after each sampling during the entire experimental period.
Macro-pollutants were analysed through a combination of selective probes and standardised testing procedures. EC and pH were continuously monitored using selective probes. BOD5, COD, TN, NH3, NO3−, and NO2− concentrations were determined using DR Lange test kits. The soluble COD (sCOD) concentration was assessed following filtration of the samples using a 0.45 μm nylon filter. VSS and TSS were determined according to standard protocols [41]. The methods and reagents used for analysis of the mentioned parameters are described in full in the Supplementary Materials.
To assess colour elimination, sample absorbance was measured using quartz cuvettes (1 cm path length) at 424, 558, and 660 nm, corresponding to the leachate’s colour range from yellowish to brown. The decolourisation percentage was subsequently calculated.
Sample preparation before analysis involved an initial centrifugation at 5000 rpm for 5 min. The supernatant was then recovered and subjected to three dilutions: 1:10, 1:100, and 1:1000. This dilution procedure was necessary due to the wide variation in the concentrations of individual PFAS compounds within the samples. Performing multiple dilutions ensured accurate quantification of each compound by placing their concentration within the range of the calibration curve. PFAS analysis was performed using liquid chromatography coupled with high-resolution tandem mass spectrometry (LC-HRMS/MS). The chromatographic system (Ultimate 3000, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) was connected to a TripleTOF 5600+ mass spectrometer (AB Sciex, Framingham, MA, USA), operated in negative electrospray ionisation (ESI) mode. A 100 µL aliquot of each sample was injected into the LC-MS system using a ZORBAX Eclipse Plus C18 column (150 × 2.1 mm, 1.8 µm), Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA, maintained at 40 °C, with a 0.300 mL/min flow rate. Chromatographic separation was performed using a mobile phase composed of 10 mM C2H7NO2 (A) and CH3OH (B), under the following gradient conditions:
- -
- 0–2 min: 5% B;
- -
- 2–4 min: linear gradient to 70% B;
- -
- 4–9 min: linear gradient to 100% B;
- -
- 9–14 min: 100% B;
- -
- 14–14.5 min: return to 5% B;
- -
- 14.5–20 min: column reconditioning.
The mass spectrometry detection was made by a TOF-MS scan analysis between m/z 70 and m/z 900 (Table S1). The analytical method also included an IDA (Information Dependent Acquisition) analysis from m/z 70 to m/z 900 in order to obtain MS-MS data of the investigated PFAS.
PFAS quantification was performed using a calibration curve ranging from 1 to 200 ng/L (1, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100 and 200 ng/L). Before analysis, an internal standard mixture containing 13C8-PFOA and 13C8-PFOS at a concentration of 100 ng/L was added to all samples and calibration standards. The integration of the chromatographic peak was made by extracting the ion current of analytical interest with a width equal to m/z 0.02. The LOQ value for each analyte was determined using 10 times the value associated with the standard deviation on linear regression residuals as the reference response.
The specific sludge production (SSP), expressed as g TSS/g COD removed, was calculated from the COD and TSS balance by dividing the total TSS that exit the system (including TSS in the effluent and TSS removed during washing) by the COD eliminated between two consecutive washing operations.
The ozone dose transferred per unit volume of leachate fed to the plant, referred to as the Transferred Ozone Dose (TOD), was used in preference to the applied ozone dose to eliminate the influence of scale-related factors in the experiment. It was determined using the equation below:
where
Fgas (L/min)—gas flow rate entering the ozone reactor (set at 70 L/h), regulated by the ozone generator flowmeter;
CO3IN (mg O3/L of gas)—ozone concentration in the inlet, regulated by acting on the generator power;
CO3OUT (mg O3/L of gas)—ozone concentration in outlet during the “chemical + biological oxidation” phase, measured by BMT 964 UV analyzer (WEDECO, Herford, Germany);
Vinf (L)—leachate volume fed per treatment cycle (i.e., 1 L).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. SBBGR Start-Up
Figure 2 illustrates the kinetic evolution of the conventional parameters during the start-up period (period A). The start-up phase of the SBBGR system highlighted the vital importance of acclimation in achieving stable and efficient biological treatment of landfill leachate. This phase enabled the microbial community to progressively adapt to the specific operational conditions, reducing the risk of cellular shock that could impair metabolic functions and overall treatment efficiency. The inoculum biomass consisted of a blend of 30% activated sludge from a landfill leachate treatment facility and 70% from a municipal wastewater treatment plant. Over 103 days, the leachate was gradually diluted with tap water in seven incremental steps, each designed to slowly increase salinity and prevent abrupt environmental shifts that could stress the microbial population.
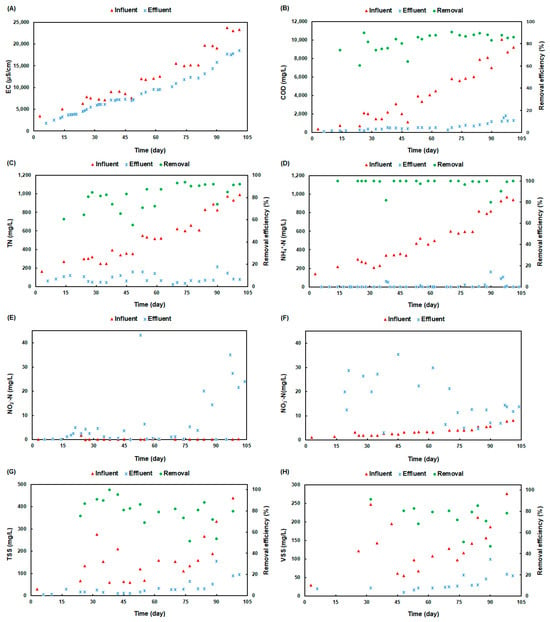
Figure 2.
Evolution of conventional parameters in the influent and effluent samples of the SBBGR system through the start-up phase. (A): EC, (B): COD, (C): TN, (D): NH4+-N, (E): NO2−-N, (F): NO3−-N, (G): TSS, and (H): VSS.
The profiles shown in Figure 2 indicate that the system followed a carefully structured feeding strategy to acclimate the biomass to the high leachate salinity. This process required a long period of 103 days due to the significant difference in EC between the leachate under study (approximately 23 mS/cm) and the biomass inoculum sample used (approximately 1.5 mS/cm). Throughout the start-up phase, the profiles of the TN, NH3, and COD concentrations in the influent and effluent samples of the plant change in a parallel way, showing a gradual increase in inlet concentrations and stable low effluent concentrations (Figure 2B–D). These three parameters, therefore, demonstrated high removal efficiency, alongside high NO3− release and slight NO2− release (Figure 2E,F). This indicates that this phase enabled the growth of a specialised microbial community capable of efficiently removing pollutants like organic matter and ammonia (COD and NH3), despite the challenges posed by high salinity and complex leachate characteristics. However, the trend concentrations of TSS and VSS showed regressive behaviour in the influent sample. Consequently, the effluent showed a slight progressive increase, resulting in fluctuating TSS and VSS removal efficiencies, which depended on the influent concentrations.
3.2. SBBGR and BIO-CHEM Process Performance
3.2.1. Conventional Pollutants Removal
Table 1 summarises the average concentrations of conventional pollutants measured at the inlet and outlet of the plant fed with the undiluted leachate during periods B (under SBBGR only) and C (under BIO-CHEM process), along with their corresponding removal efficiencies.

Table 1.
Performance of the plant during periods B and C, under the biological (BIO) and bio-chemical (BIO-CHEM) processes, respectively, based on conventional parameters and removal efficiencies (mean ± standard deviation).
During the period B under biological process only, the data indicate a slight increase in pH values following treatment from 8.2 to 8.6, which can be attributed to biological oxidation processes, as reported by Gomes [42]. Conversely, EC exhibits a great decrease from 28.3 to 23.4 mS/cm after biological treatment, probably due to the high decline in total nitrogen concentration, particularly ammoniacal nitrogen. The integration of the chemical process together with the SBBGR (BIO-CHEM process) during period C showed a negligible effect on both pH and EC.
Regarding organic matter, the findings showed a high reduction in both total and soluble COD concentrations after treatment during periods B and C, resulting in a high removal efficiency of COD (82–88%) due to the high content of biodegradable external carbon added (i.e., 5.5–6.5 g/L). Nevertheless, the residual concentrations of COD in the effluent are still high enough and should be minimised before being disposed of at municipal wastewater treatment plants. The persistence of high residual COD concentrations can be attributed to the presence of a recalcitrant pollutant fraction in the leachate, as indicated by the complete elimination of biodegradable matter (5–7 mg/L of BOD5). It should also be stated that when BOD5/COD is less than 0.5, the residual COD of non-biodegradable substances is present in the influent, as shown by Del Moro et al. [43], which is confirmed by nearly complete removal efficiency of BOD5 (99.8%). Similar phenomena were observed by Di Iaconi et al. [40] through the SBBGR treatment of medium-age sanitary landfill leachates, reaching a limited removal efficiency of 54% for COD due to the high fraction of recalcitrant pollutants. Furthermore, Saxena et al. [44] reported that treating a diluted real leachate with municipal wastewater at a 20:80 (v/v) ratio using an aerobic granular reactor (AGR) provides moderate COD removal efficiency (62–65%). The granules became destabilised when real leachate containing toxic pollutants was supplied to the AGR, resulting in reduced AGR performance. The increase in COD removal efficiency recorded by the BIO-CHEM process (i.e., from 81.8% to 88%) must be attributed to the ozone effect, which, as is known, is able to mineralise or make recalcitrant pollutants biodegradable. This finding is consistent with previous research and confirms that this process is suitable for effectively degrading COD. For instance, Di Iaconi et al. [38] pointed out that the BIO-CHEM process enhanced the removal efficiency of COD to 97–99%, compared with the biological process only (91%) during the tannery wastewater treatment. In another study, Di Iaconi et al. [39] evaluated the ozonation effect on the treatment of stabilised municipal landfill leachates. The authors achieved a significant enhancement in COD removal efficiency using the BIO-CHEM process, achieving 91–98% removal, compared to only 48% with the biological treatment alone. The improvements observed in previous studies can be attributed to the use of ozone primarily for converting recalcitrant compounds into biodegradable forms, which were subsequently removed through biological processes [38].
As far as TSS and VSS are concerned, Table 1 shows that the SBBGR performed moderately in removing both parameters, exceeding 41% and 44%, respectively. This demonstrates the limited effectiveness of biomass in filtering particles and breaking down organic pollutants due to its low microbial activity. In general, the removal of suspended solids is greatly influenced by gravity separation [45], as well as by the biomass contained within fixed filling material, which functions as a filter for particulate matter. Initially, suspended particles were physically trapped in the reactor bed and then decomposed enzymatically into soluble compounds by lytic enzymes produced by the biomass. Ultimately, these compounds were either mineralised or used for microbial growth [46]. However, the plant exhibits a significant improvement in TSS and VSS removal performance during period C under the BIO-CHEM process, exceeding 85% and 87%, respectively, compared to period B under the biological process only. The observed improvement could be due to the increased concentration of dissolved oxygen in the plant during the BIO-CHEM process, resulting from the purer oxygen supplied to the ozone generator [38]. The results obtained are consistent with those of previous studies employing the BIO-CHEM process, which reported removal efficiencies of up to 99% for TSS and VSS from textile printing wastewater [37], 94–99% of TSS from industrial recalcitrant wastewater [38], 88–94% of TSS from stabilised municipal landfill leachate [39], and 86–88% of TSS from medium-aged sanitary landfill leachate [40].
As regards nitrogen species, including TN, NH3, NO2−, and NO3−, the data in Table 1 indicate a higher performance of the SBBGR system during period B, reaching an excellent removal efficiency of 86% for TN and 98% for NH3. The removal trend of ammoniacal nitrogen is due to the nitrification process, extending to the denitrification process, whereby oxidised nitrogen is reduced to molecular nitrogen gas, resulting in a significant decrease in the total nitrogen concentration (from 1498 mg/L in the influent to 198 mg/L in the effluent), affecting the nitrogen cycle [47]. Nitrification is a two-stage reaction in which ammonia is first converted to nitrite, and then to nitrate. However, the effective nitrification process results in a high concentration of nitrous nitrogen (25 mg/L) and nitric nitrogen (25 mg/L), which should be minimised as much as possible to avoid their high toxicity on the fauna of water bodies. Nevertheless, the landfill leachate treatment using SBBGR is an initial step in minimising macro- and micropollutants. Conversely, many studies reported that the treatment of the landfill leachate based on a biological process was characterised by a moderate removal of nitrogen species, especially ammonia, due to the inhibitory effect of the high toxicity of PFAS and bacterial ammonification [48,49]. The addition of chemical oxidation, such as ozonation, together with a biological process, allowed for approximately a complete removal of ammonia, reaching 99.9%, indicating that the nitrification process has been completed, resulting in a very low residual level of ammoniacal nitrogen (1 mg/L). This high nitrification of ammonia leads to a very high release of NO3−-N (305 mg/L). The sharp rise in the effluent’s nitrate concentration during the BIO-CHEM process must be attributed to the increase in dissolved oxygen concentration generated by the ozone unit, which led to incomplete denitrification with consequent doubling of the effluent’s TN concentration from 198 mg/L to 399 mg/L and reduction in the treatment’s effectiveness by 16%. However, the integration of the chemical process showed no significant effect on the residual nitrite concentration, suggesting that ozone does not notably influence nitrite levels as an intermediate in the nitrification process.
As regards phosphorus removal, a slight decrease in concentration was achieved following treatment, regardless of the process used (SBBGR or BIO-CHEM), confirming that SBBGR with or without ozonation has a limited ability to remove phosphorus. It is also well known that the biological process has limited phosphorus elimination capabilities, which is related to the limited sludge production achieved in the SBBGR system (see below), where phosphorus is removed solely through biomass growth, and/or microbial uptake during assimilation for growth and development [50]. Nevertheless, the limited availability of biodegradable organic matter in aged leachate may further influence phosphorus removal, representing a key factor affecting the process [51]. Prendergast et al. [52] obtained a relatively moderate removal of phosphorus (39%) using an SBBGR system, attributing this outcome to the “luxury uptake” mechanism, where phosphorus is sequestered from the bulk fluid into the solid phase during the aerobic stage. Saxena et al. [44] attributed the low removal of phosphorus to the development of an anoxic zone in the inner parts of the aerobic granules.
UV-Vis absorbance analysis at 426, 556, and 660 nm is a common method for assessing the quality of treated wastewater. It is particularly useful for indicating the presence and removal of coloured pollutants, especially in dye-containing or industrial effluents. Different dye types or coloured compounds correspond to each wavelength: 426 nm for yellow-orange compounds, 556 nm for red or pink species, and 660 nm for blue dyes such as methylene blue, as shown by Lanzetta et al. [53]. Monitoring absorbance at these wavelengths helps to evaluate the efficiency of the biological treatment process, track the degradation of dyes, and ensure compliance with environmental discharge regulations.
The colour data mentioned in Table 1 demonstrate that the treatment performance of the plant using only the biological process is completely ineffective in decolourising the effluent, with colour removal rates of 1%, 1%, and 0% at 426, 556, and 660 nm, respectively. A similar finding was found by Lotito et al. [37], who reported a very low removal efficiency of colour at the three wavelengths (0.141%, 0.090%, and 0.064%, respectively) for textile wastewater treatment by SBBGR. The limited performance of SBBGR in removing the colour dyes from leachate wastewater could be due to a mixture of various coloured compounds, such as humic substances, complex aromatic structures, and synthetic dyes, which are recalcitrant and poorly biodegradable under typical biological conditions [54]. These compounds resist microbial degradation due to their stable chemical bonds, which may also inhibit microbial activity. Conversely, during the period C under the BIO-CHEM process, the plant showed a significant decolourisation reaching 92%, 96%, and 95% for the wavelengths 426, 556, and 660 nm, respectively, due the ozone action in BIO-CHEM process, which effectively targets a broad range of dyes, leading to significant decolourisation across the visible spectrum [55]. Furthermore, the biological treatment uses microorganisms and enzymes to degrade complex organic chromophores, while chemical treatment (e.g., oxidation) further destroys or removes the resulting intermediates [56]. In addition, colour removal from landfill leachate after ozonation is primarily attributed to the degradation of chromophoric structures such as humic and fulvic acids, aromatic compounds, and melanoidins. These substances, rich in conjugated double bonds and aromatic rings, are responsible for the dark colour of mature leachate [57]. Ozone, as a strong oxidising agent, effectively breaks down these complex structures, leading to a significant reduction in visible colour and improved biodegradability of the leachate [58]. The oxidation process disrupts light-absorbing systems, converting them into smaller, less coloured or colourless molecules [59].
Regarding specific sludge production, five washing operations were carried out during period B, with an average frequency of 2 weeks, after the first operation, which occurred approximately 100 days after the plant start-up. Therefore, according to what is reported in Section 2.4, four mass balances of COD and TSS were performed. SSP as low as 0.07 ± 0.01 g TSS/g COD removed was obtained. This value was consistent with that obtained by Di Iaconi et al. [40] when treating sanitary landfill leachate using the same system (i.e., approximately 0.06 g TSS/g COD was removed with a washing operation frequency of 2–3 weeks). The low SSP value is typical for the SBBGR system and can be ascribed to the very long sludge age (more than 1 year).
The SSP was further reduced to 0.014 ± 0.003 g TSS/g COD removed during period C, i.e., under the BIO-CHEM process. This decline should be attributed to the double action of ozone: on the one hand, it is able to mineralise organic pollutants without any production of solid residues and on the other, to cause the lysis of external layers of the biomass with consequent activation of lysis and cryptic processes that is one of the mechanisms used to reduce production of sludge in wastewater treatment plants.
3.2.2. PFAS Compounds Removal
Table 2 reports the average concentrations of PFAS compounds at the inlet and outlet of the plant over periods B and C, while Figure 3 illustrates their corresponding removal efficiencies. The results showed that, among PFAS compounds, PFBS, PFOA, and PFBA were the predominant compounds, achieving the highest average concentrations during periods B and C, reaching 67,525 and 44,370 ng/L, 10,595 and 8626 ng/L, and 8363 and 5189 ng/L (Table 2), representing 91% and 88% of 13 PFAS (Σ PFAS13) analysed, the sum in the effluents, respectively, and hence controlled the performance of the plant. Similarly, Huang et al. [13] pointed out that PFBS and PFBA have been identified as dominant compounds, often comprising over 40% of the total PFAS mass in leachate from municipal solid waste landfills. Moreover, the data highlights the presence of a high level of short-chain PFAS in the influent leachate samples during the operational periods B and C, representing 85% and 81%, respectively. The high levels of short-chain PFAS in influent landfill leachate are primarily due to the phase-out of long-chain PFAS (e.g., PFOS, PFOA) and their replacement with short-chain alternatives (e.g., PFBS, PFBA) in industrial and consumer products [60]. In addition, short-chain PFAS are more soluble and mobile in water, making them more likely to leach from waste into landfill leachate [61]. Additionally, the degradation of PFAS precursors under landfill conditions often leads to the formation of stable short-chain compounds [62]. Lang et al. [62] reported that the reason for the prevalence of short-chain PFASs remains unclear, but it may be indicative of a shift towards producing shorter-chain PFASs, variations in solubility, and/or microbial biodegradation differences.

Table 2.
Average concentrations (mean value ± standard deviation) of PFAS compounds at the inlet and outlet of the plant through periods B and C, under the biological (BIO) and bio-chemical (BIO-CHEM) processes, respectively.
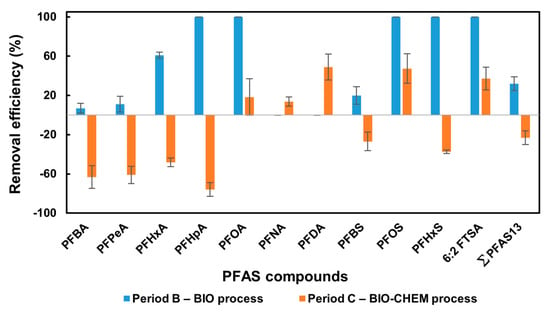
Figure 3.
Performance of the plant during periods B and C, under the biological (BIO) and bio-chemical (BIO-CHEM) processes, respectively, in removing PFAS compounds.
During period B, under the biological process only, the plant was able to eliminate 32% of the ΣPFAS13 content. Interestingly, an approximately complete removal efficiency was achieved for long-chain PFAS, including 6:2 FTSA, PFOA, PFHpA, PFHxS, and PFOS (Figure 3). The exceptional removal efficiency observed for most of the long-chain compounds is directly attributable to the SBBGR biomass featured by high hydrophobicity and long retention times, allowing hydrophobic substances (such as long-chain PFAS) to be adsorbed and degraded [63]. In contrast, short-chain PFAS (e.g., PFHxA, PFPeA, PFBA, PFBS), being less hydrophobic, showed a limited removal. This suggests that PFAS removal is strongly affected by the physicochemical properties and chemical structure of the individual compounds, particularly their carbon chain length. These findings are consistent with the literature. For instance, Gagliano et al. [64] reported that granular activated carbon (GAC) preferentially adsorbs long-chain PFAS, leading to near-complete removal of PFOA and PFOS, while short-chain compounds (e.g., PFBA, PFBS) breakthrough quickly due to lower hydrophobicity and competitive displacement by longer chains. Similarly, sorptive media comparisons indicate consistently lower affinities for short-chain PFAS, underscoring challenges in their retention. Meanwhile, Travar et al. [65] noted that constructed wetlands and biological systems exhibited enhanced retention of long-chain PFAS through sorption and plant uptake, though there was minimal degradation or elimination of short-chain species.
Activating the ozonation unit during period C (BIO-CHEM process) had a negative effect on treatment performance, leading to a high release of most PFAS compounds (Figure 3). In terms of overall impact, the mass balance of the parameter Σ PFAS13 clearly shows an increase of approximately 15,328 ng/L of PFAS in the effluent compared to the influent concentration (Table 2). This unexpected result must be attributed to a desorption process of PFAS from the biomass. It is possible that residual ozone in the SBBGR slightly lyses the surface layers of the biomass, resulting in the release of a high quantity of PFAS compounds into the liquid phase. This was accompanied by reduced biomass growth performance, further confirming the occurrence of cell lysis due to oxidative stress. Similar phenomena were observed by Xin et al. [66], who investigated pilot-scale O3/H2O2 oxidation of wastewater effluent and found that high ozone doses increased residual ozone in downstream biological systems, leading to biomass cell lysis and higher effluent PFAS concentrations, especially for cell-associated, long-chain PFAS due to surface release.
4. Conclusions and Future Directions
This study compared the effectiveness of the Sequencing Batch Biofilter Granular Reactor (SBBGR) plant with and without the integration of ozone (BIO-CHEM process) for the treatment of mature leachate. The biological process by SBBGR alone showed moderate effectiveness in reducing conventional pollutants, particularly in terms of organic matter (COD removal up to 81.7%) and nitrogen species (TN and NH3 removal of 86% and 98%, respectively). However, limitations remained due to the persistence of recalcitrant organic compounds, leading to high residual COD concentrations in the effluent. As well as for the removal of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), which achieved a 32% overall removal of Σ PFAS13 (sum of concentration of 13 PFAS analytes), with complete elimination of long-chain PFAS compounds (i.e., PFOA, PFHpA, PFOS, 6:2 FTSA, and PFHxS), likely due to the particular biomass features of SBBGR. The latter result is of great relevance if compared with conventional biological systems that are ineffective for PFAS removal. Nowadays, the efficient removal of long-chain PFAS compounds from landfill leachates can be achieved only by expensive physical and chemical processes, as reported in the detailed literature review [9,67]. However, the system was ineffective against short-chain PFAS (PFBA, PFPeA).
The integration of chemical oxidation by ozone (BIO-CHEM process) significantly improved the treatment outcomes. COD removal efficiency increased slightly (~6%), while suspended solids (TSS and VSS) removal exceeded 85%, likely due to improved biomass activity and oxygen availability. Ammonia was almost completely removed (99.9%), though the accompanying rise in NO3 (305 mg/L) highlighted incomplete denitrification, negatively impacting total nitrogen removal efficiency. Phosphorus removal remained limited under both treatment regimes, emphasising the need for complementary strategies for its effective elimination. Interestingly, the PFAS removal during BIO-CHEM treatment resulted in a paradoxical increase in effluent concentrations, particularly for several PFAS compounds. This was attributed to ozone-induced desorption of PFAS previously retained by the biomass, along with partial biomass lysis and reduced microbial activity, ultimately undermining the biological system’s PFAS retention capacity. Despite its potential for enhanced oxidation, the chemical unit appears to have compromised the stability and performance of the biomass reactor under the tested conditions.
Most notably, colour removal exhibited a dramatic enhancement under the BIO-CHEM process, achieving over 90% decolourisation across the UV-Vis spectrum. This confirmed the superior capability of the combined approach in targeting recalcitrant and coloured pollutants, which are largely resistant to biological degradation alone.
Furthermore, due to the very long biomass age, SBBGR treatment was characterised by a low specific sludge production (SSP) value, i.e., 5–6 times lower than that of conventional biological processes. SSP was further reduced when ozonation was integrated.
The findings confirm the SBBGR system’s potential for effectively removing organic pollutants, colour, and long-chain PFAS from stabilised landfill leachate. Integrating ozonation significantly improves the degradation of persistent organic and chromophoric compounds. However, integrating this process presents challenges, including the deterioration of long-chain PFAS removal, likely due to the oxidative disruption of the biofilm matrix. These results emphasise the need for careful process integration and further optimisation to improve treatment performance and ensure compliance with strict environmental discharge standards.
Future studies should focus on in-depth characterisation of the microbial community within the SBBGR system, employing high-throughput sequencing techniques. This will provide valuable insights into the microbial dynamics and functional roles that drive pollutant degradation and system stability. Furthermore, the implementation of non-targeted screening approaches for PFAS, using advanced analytical tools such as high-resolution mass spectrometry, will facilitate the identification of a wider array of PFAS compounds, including those that are unknown or emerging.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w17172501/s1, Table S1: 13 PFAS mass spectrometry detection parameters, including retention time, limit of detection, and collisional energy.
Author Contributions
S.E.B.: writing—original draft, methodology, data curation, and formal analysis. M.D.S.: investigation and data curation. S.M. (Subhoshmita Mondal): writing—original draft, methodology, data curation, and formal analysis. M.P.: investigation. S.M. (Sapia Murgolo): investigation. S.F.: data curation and validation. E.S.: project administration and funding acquisition. G.M.: data curation and validation. C.D.I.: writing—reviewing and editing, resources, conceptualisation, methodology, and supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to Rossella Annelio for her valuable support in monitoring the treatment processes of the SBBGR plant during her PhD thesis.
Conflicts of Interest
Author E. Slavik was employed by the company Erica. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Nanda, S.; Berruti, F. Municipal Solid Waste Management and Landfilling Technologies: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 1433–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassano, D.; Zapata, A.; Brunetti, G.; Del Moro, G.; Di Iaconi, C.; Oller, I.; Malato, S.; Mascolo, G. Comparison of Several Combined/Integrated Biological-AOPs Setups for the Treatment of Municipal Landfill Leachate: Minimization of Operating Costs and Effluent Toxicity. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 172, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.H. Assessment of Leachates from Sanitary Landfills: Impact of Age, Rainfall, and Treatment. Environ. Int. 1996, 22, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Choi, K.S.; Joe, K.S.; Kim, W.H.; Kim, H.S. Variations of Landfill Leachate’s Properties in Conjunction with the Treatment Process. Environ. Technol. 2001, 22, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, T.H.; Kjeldsen, P.; Bjerg, P.L.; Jensen, D.L.; Christensen, J.B.; Baun, A.; Albrechtsen, H.-J.; Heron, G. Biogeochemistry of Landfill Leachate Plumes. Appl. Geochem. 2001, 16, 659–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivato, A.; Gaspari, L. Acute Toxicity Test of Leachates from Traditional and Sustainable Landfills Using Luminescent Bacteria. Waste Manag. 2006, 26, 1148–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzbauer, J.; Heim, S.; Brinker, S.; Littke, R. Occurrence and Alteration of Organic Contaminants in Seepage and Leakage Water from a Waste Deposit Landfill. Water Res. 2002, 36, 2275–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, A.; Blaney, L.; Kao, J.; Tyagi, R.D.; Zhang, T.C.; Surampalli, R.Y. Emerging Contaminants in Landfill Leachate and Their Sustainable Management. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 1357–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Dikshit, A.K.; Dangi, M.B. Technological Advances in Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Removal from Landfill Leachate: Source Identification and Treatment Options. Emerg. Contam. 2025, 11, 100458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Xu, T.; Zhao, D. Treatment of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Landfill Leachate: Status, Chemistry and Prospects. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2019, 5, 1814–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallen, C.; Drage, D.; Eaglesham, G.; Grant, S.; Bowman, M.; Mueller, J.F. Australia-Wide Assessment of Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in Landfill Leachates. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 331, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, H.; Li, L.Y.; Grace, J.R. Review of the Fate and Transformation of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in Landfills. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Wei, X.; Liu, H.; Li, W.; Shi, D.; Qian, S.; Sun, W.; Yue, D.; Wang, X. Occurrence of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Municipal Solid Waste Landfill Leachates from Western China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 69588–69598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busch, J.; Ahrens, L.; Sturm, R.; Ebinghaus, R. Polyfluoroalkyl Compounds in Landfill Leachates. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1467–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuertes, I.; Gómez-Lavín, S.; Elizalde, M.P.; Urtiaga, A. Perfluorinated Alkyl Substances (PFASs) in Northern Spain Municipal Solid Waste Landfill Leachates. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoiber, T.; Evans, S.; Naidenko, O.V. Disposal of Products and Materials Containing Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS): A Cyclical Problem. Chemosphere 2020, 260, 127659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; McDonald, J.A.; Kuchel, R.P.; Khan, S.J.; Leslie, G.; Tang, C.Y.; Mansouri, J.; Fane, A.G. Surface Modification of Nanofiltration Membranes to Improve the Removal of Organic Micropollutants: Linking Membrane Characteristics to Solute Transmission. Water Res. 2021, 203, 117520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribarova, I.; Valchev, D.; Valentina, G.; Frugis, A. Presence of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Untreated Leachate from Regional Municipal Waste Landfills: A First Assessment for Bulgaria. J. Ecol. Eng. 2025, 26, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoner, J.R.; Kolpin, D.W.; Cozzarelli, I.M.; Smalling, K.L.; Bolyard, S.C.; Field, J.A.; Furlong, E.T.; Gray, J.L.; Lozinski, D.; Reinhart, D.; et al. Landfill Leachate Contributes Per-/Poly-Fluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) and Pharmaceuticals to Municipal Wastewater. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2020, 6, 1300–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolaymat, T.; Robey, N.; Krause, M.; Larson, J.; Weitz, K.; Parvathikar, S.; Phelps, L.; Linak, W.; Burden, S.; Speth, T.; et al. A Critical Review of Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Landfill Disposal in the United States. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvin, F.; Tareq, S.M. Impact of Landfill Leachate Contamination on Surface and Groundwater of Bangladesh: A Systematic Review and Possible Public Health Risks Assessment. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Titaley, I.A.; Kim-Fu, M.L.; Moll, A.R.; Field, J.A.; Barlaz, M.A. Release of Volatile Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances from Plant Fiber-Based Food Packaging and Municipal Solid Waste to Gas under Simulated Landfill Conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 21295–21304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunderland, E.M.; Hu, X.C.; Dassuncao, C.; Tokranov, A.K.; Wagner, C.C.; Allen, J.G. A Review of the Pathways of Human Exposure to Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) and Present Understanding of Health Effects. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2019, 29, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Montelius, M.; Carlsson, C. Life Cycle Assessment of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Remediation Technologies: A Literature Review. Environments 2024, 11, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqua, A.; Hahladakis, J.N.; Al-Attiya, W.A.K.A. An Overview of the Environmental Pollution and Health Effects Associated with Waste Landfilling and Open Dumping. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 58514–58536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lott, D.J.; Robey, N.M.; Fonseca, R.; Bowden, J.A.; Townsend, T.G. Behavior of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Pilot-Scale Vertical Flow Constructed Wetlands Treating Landfill Leachate. Waste Manag. 2023, 161, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, T.; Chen, H.; Reinhard, M.; Yi, X.; He, Y.; Gin, K.Y.-H. Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances Removal in a Full-Scale Tropical Constructed Wetland System Treating Landfill Leachate. Water Res. 2017, 125, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tow, E.W.; Ersan, M.S.; Kum, S.; Lee, T.; Speth, T.F.; Owen, C.; Bellona, C.; Nadagouda, M.N.; Mikelonis, A.M.; Westerhoff, P.; et al. Managing and Treating Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Membrane Concentrates. AWWA Water Sci. 2021, 3, e1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Brown, E.; Mededovic Thagard, S.; Holsen, T.M. Treatment of PFAS-Containing Landfill Leachate Using an Enhanced Contact Plasma Reactor. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 408, 124452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, P.H.N.; Nguyen, T.T.P.; Nguyen, H.T.M.; Baulch, J.; Dong, S.; Nguyen, C.V.; Thai, P.K.; Nguyen, A.V. PFAS Removal from Landfill Leachate by Ozone Foam Fractionation: System Optimization and Adsorption Quantification. Water Res. 2024, 253, 121300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.J.; Wiberg, K.; McCleaf, P.; Ahrens, L. Pilot-Scale Continuous Foam Fractionation for the Removal of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) from Landfill Leachate. ACS EST Water 2022, 2, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Xu, T.; Zhao, D. Metal-Doped Carbon-Supported/Modified Titanate Nanotubes for Perfluorooctane Sulfonate Degradation in Water: Effects of Preparation Conditions, Mechanisms, and Parameter Optimization. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 853, 158573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Yuan, T.; Yang, X.; Ding, S.; Ma, M. Insights into Photo/Electrocatalysts for the Degradation of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) by Advanced Oxidation Processes. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urtiaga, A.; Gómez-Lavín, S.; Soriano, A. Electrochemical Treatment of Municipal Landfill Leachates and Implications for Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annelio, R. Advanced Treatments for PFAS Removal from Landfill Leachate: Evaluating Biological and Ozone Based Chemical Approaches. Ph.D. Thesis, Politecnico di Bari, Bari, Italy, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Hegedus, M.; Lacina, P.; Plotěný, M.; Lev, J.; Kamenická, B.; Weidlich, T. Fast and Efficient Hydrodehalogenation of Chlorinated Benzenes in Real Wastewaters Using Raney Alloy. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 38, 101645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotito, A.M.; Fratino, U.; Bergna, G.; Di Iaconi, C. Integrated Biological and Ozone Treatment of Printing Textile Wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 195–196, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Iaconi, C.; Del Moro, G.; De Sanctis, M.; Rossetti, S. A Chemically Enhanced Biological Process for Lowering Operative Costs and Solid Residues of Industrial Recalcitrant Wastewater Treatment. Water Res. 2010, 44, 3635–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Iaconi, C.; Rossetti, S.; Lopez, A.; Ried, A. Effective Treatment of Stabilized Municipal Landfill Leachates. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 168, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Iaconi, C.; De Sanctis, M.; Rossetti, S.; Mancini, A. Bio-Chemical Treatment of Medium-Age Sanitary Landfill Leachates in a High Synergy System. Process Biochem. 2011, 46, 2322–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. APHA (2005) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Water Works Association/Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, I.d.E. Treatment Train for Mature Urban Landfill Leachate. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Porto, Porto, Portugal, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Del Moro, G.; Mancini, A.; Mascolo, G.; Di Iaconi, C. Comparison of UV/H2O2 Based AOP as an End Treatment or Integrated with Biological Degradation for Treating Landfill Leachates. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 218, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, V.; Padhi, S.K.; Pattanaik, L.; Bhatt, R. Simultaneous Removal of Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus from Landfill Leachate Using an Aerobic Granular Reactor. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 28, 102657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, Z.J.; Bashir, M.J.K.; Ng, C.A.; Sethupathi, S.; Lim, J.-W. A Sequential Treatment of Intermediate Tropical Landfill Leachate Using a Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR) and Coagulation. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 205, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Iaconi, C.; Del Moro, G.; Bertanza, G.; Canato, M.; Laera, G.; Heimersson, S.; Svanström, M. Upgrading Small Wastewater Treatment Plants with the Sequencing Batch Biofilter Granular Reactor Technology: Techno-Economic and Environmental Assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 148, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Chen, S.; Hou, Y.; Lei, L. Study on the Formation Process and Mechanism of Aerobic Granular Sludge in the Sequencing Batch Biofilter Granular Reactor. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 107661–107672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Zhang, W.; Liang, Y. Uptake of Individual and Mixed Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) by Soybean and Their Effects on Functional Genes Related to Nitrification, Denitrification, and Nitrogen Fixation. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alukkal, C.R.; Lee, L.S.; Staton, K. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances Behavior: Insights from Autothermal Thermophilic Aerobic Digestion—Storage Nitrification-Denitrification Reactors. Chemosphere 2024, 365, 143357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padhi, S.K.; Gokhale, S. Treatment of Gaseous Volatile Organic Compounds Using a Rotating Biological Filter. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 244, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Ferraz, F.M.; Yuan, Q. Landfill Leachate Treatment Using Aerobic Granular Sludge. J. Environ. Eng. 2017, 143, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prendergast, J.; Rodgers, M.; Healy, M.G. The Efficiency of a Sequencing Batch Biofilm Reactor in Organic Carbon and Phosphorus Removal. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2005, 40, 1619–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanzetta, A.; Papirio, S.; Oliva, A.; Cesaro, A.; Pucci, L.; Capasso, E.M.; Esposito, G.; Pirozzi, F. Ozonation Processes for Color Removal from Urban and Leather Tanning Wastewater. Water 2023, 15, 2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forgacs, E.; Cserháti, T.; Oros, G. Removal of Synthetic Dyes from Wastewaters: A Review. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 953–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotito, A.M.; De Sanctis, M.; Rossetti, S.; Lopez, A.; Di Iaconi, C. On-Site Treatment of Textile Yarn Dyeing Effluents Using an Integrated Biological–Chemical Oxidation Process. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 11, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, S.; Venkatesh, K.; Quaff, A.R. Dye Decomposition by Combined Ozonation and Anaerobic Treatment: Cost Effective Technology. J. Appl. Res. Technol. 2017, 15, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Gu, Z.; Wen, P.; Li, Q. Degradation of Refractory Organic Contaminants in Membrane Concentrates from Landfill Leachate by a Combined Coagulation-Ozonation Process. Chemosphere 2019, 217, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Morais, J.L.; Zamora, P.P. Use of Advanced Oxidation Processes to Improve the Biodegradability of Mature Landfill Leachates. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 123, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maroneze, M.M.; Zepka, L.Q.; Vieira, J.G.; Queiroz, M.I.; Jacob-Lopes, E. A Tecnologia de Remoção de Fósforo: Gerenciamento Do Elemento Em Resíduos Industriais. Rev. Ambient. E Agua 2014, 9, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; DeWitt, J.C.; Higgins, C.P.; Cousins, I.T. A Never-Ending Story of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs)? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2508–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahrens, L. Polyfluoroalkyl Compounds in the Aquatic Environment: A Review of Their Occurrence and Fate. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, J.R.; Allred, B.M.; Field, J.A.; Levis, J.W.; Barlaz, M.A. National Estimate of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance (PFAS) Release to U.S. Municipal Landfill Leachate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2197–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sanctis, M.; Murgolo, S.; Altieri, V.G.; De Gennaro, L.; Amodio, M.; Mascolo, G.; Di Iaconi, C. An Innovative Biofilter Technology for Reducing Environmental Spreading of Emerging Pollutants and Odour Emissions during Municipal Sewage Treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 149966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliano, E.; Sgroi, M.; Falciglia, P.P.; Vagliasindi, F.G.A.; Roccaro, P. Removal of Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) from Water by Adsorption: Role of PFAS Chain Length, Effect of Organic Matter and Challenges in Adsorbent Regeneration. Water Res. 2020, 171, 115381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travar, I.; Uwayezu, J.N.; Kumpiene, J.; Yeung, L.W.Y. Challenges in the PFAS Remediation of Soil and Landfill Leachate: A Review. Adv. Environ. Eng. Res. 2020, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.; Kim, J.; Weng, S.; Huang, C.-H. Pilot Assessment of Impacts of Ozone and Ozone/Hydrogen Peroxide Treatment on the Fate of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances and Precursors. ACS EST Water 2024, 4, 4545–4555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Lu, H.; Liang, D.; Feng, S.; Li, Y.; Li, J. A Review of the Occurrence, Monitoring, and Removal Technologies for the Remediation of per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) from Landfill Leachate. Chemosphere 2023, 332, 138824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).