Abstract
In times of climate change, periods of drought will occur more frequently. This causes challenges for water use, ranging from limitations on the navigability of water courses, limited availability of water for irrigation and drinking water supply, reduced hydropower production, increasing concentrations of pollutants, deteriorating water quality, and ecosystem degradation. Dealing with droughts, however, is a complex puzzle due to the multi-level governance characteristics of international river basins and the need to meet the freshwater demands of all sectors involved. This increases the need to address drought issues in a coordinated way, along all levels of decision making. Thus far, the way this must be executed has been under-researched. This paper addresses this knowledge gap as it aims to provide design principles for good multi-level drought risk governance in international river basins. In order to meet our aim, we first reviewed literature on multi-level and good governance and established an assessment framework. This framework was applied in a case study on drought risk governance in the international Rhine basin. Policy documents were analyzed and key informants interviewed. We found that although the governance practice in the basin meets most of our framework criteria, differences between the international level, the Netherlands, Germany, and Switzerland also occurred. We have synthesized our findings into a list of 10 design principles for good multi-level drought risk governance, which could function as a starting point for the analysis and improvement of other multi-level drought risk governance practices.
1. Introduction
Water governance in northwestern Europe has traditionally focused on flood risk prevention and management and on improving water quality [1]. However, three consecutive dry summers (2018, 2019, and 2020) also showed that governance not only has to deal with too much water, but also with too little. IPCC studies indicate that we have to deal with a future of more weather extremes shaped by anthropocentric climate change [2].
Different definitions of drought can be found in the literature. A distinction can be made between meteorological, hydrological, agricultural and socio-economic drought. Meteorological drought is also known as the precipitation deficit: the quantitative difference between precipitation and evaporation in a given relatively short time. Compared to meteorological drought, hydrological drought is a longer-term process. It refers to the period during which too little water is replenished in groundwater levels and river discharges. Agricultural drought is defined as a lack of soil moisture for a particular crop at a particular time during the growing season. Lastly, socio-economic drought can incorporate all the previous definitions and is used to refer to the difference between the supply and demand of water as an economic good [3,4].
Drought issues negatively impact a variety of societal sectors, ranging from agriculture, industry, transport, public water supply, hydropower, and ecology [5,6]. As a result, societies may develop several strategies to deal with droughts (see Table 1). First, they can try to prevent droughts by influencing the availability, supply, and demand of water. However, mitigation and adaptation strategies will be necessary because droughts cannot be prevented entirely. This is also the case for the recovery measures that will be taken after the occurrence of a drought event in order to cope with the harm people may have suffered.

Table 1.
An overview of three different drought risk management strategies.
Drought risk management and governance are highly complex. First of all, different governance levels, different actors, and different interests are involved in decision making on the (re)allocation of water before and during periods of drought. Actors operate on fluvial, national, regional, and local levels on which they have a certain autonomy that cannot be reversed by another level without triggering a political, institutional, or constitutional crisis [8].
In transboundary river basin communication, coordination and cooperation between different jurisdictional areas is required [9]. Moreover, the impacts of droughts may not be evenly spread over interest groups but may be highly heterogeneous, as differences in soil characteristics, topography, demography, and land usage will make one area more vulnerable to droughts than another [2]. Impacts may differ within a particular region but also between regions, and tele-coupling may occur between upstream and downstream areas. Therefore, good multi-level drought risk governance is needed. Good drought risk governance should incorporate different levels of decision making and ensure good and reliable agreements in order to mitigate the potential impacts of water scarcity on people, nature, and assets. Good governance is essential in increasing the resilience of nations and populations against the effects of climate change [10]. The establishment and endurance of good governance in a multi-level context is vital as good governance ensures the acceptability and effectiveness of drought risk management strategies. The parties concerned must be willing to engage in collective decision making [11].
However, so far, the issue of good drought risk governance and good multi-level drought risk governance has been under-researched in journal papers. A framework for assessing and designing good multi-level drought risk governance is lacking. This paper therefore addresses this knowledge gap as it aims to produce such a framework. The framework is not only relevant for future academic research but may also be helpful in assisting policy makers aiming to prepare for, manage, and adapt to future droughts.
In order to meet our research aim, we first develop an assessment framework. We will apply this framework to a critical case study on multi-level drought risk governance of the Rhine river. The Rhine basin has been chosen since international cooperation on water issues in the basin has a long history [12], and the area has received several prizes for its outstanding and integrated river basin management. Before presenting our results, we will clarify our research methods. Next we will discuss our findings and will present 10 design principles for good multi-level drought risk governance that result from our analysis.
2. A Framework for Assessing Good Multi-Level Drought Risk Governance
Our framework aims to assess to what extent governance is well implemented [13]. The framework (Figure 1) is based on papers on multi-level governance [14] and good governance [15,16].

Figure 1.
A framework for assessing good multi-level drought risk governance.
The OECD [14] developed a framework for assessing blocking mechanisms in the context of multi-level water governance. The OECD [14] identifies seven gaps that prevent effective governance in complex and interdependent situations. Water governance is a typical example of such a context because of its interlinkages with other sectors like agriculture, spatial planning and transportation. It is multi-level governance that relates to the sharing of policy making authority, responsibility, development, and implementation at different administrative and territorial levels. Within this framework, seven essential dimensions of effective multi-level drought risk governance are distilled. The dimension administration refers to the match between hydrological and administrative scales and boundaries. Since upstream measures may have an impact on downstream water availability, ideally, decision making must be harmonized on the basin level. The policy dimension addresses the separation and allocation of roles and responsibilities between different policy fields relevant for water governance. Information deals with knowledge generation and sharing between the different stakeholders involved in decision making. Capacity is about the sufficiency of technical knowledge, staff, time, expertise, and infrastructure, while funding deals with the availability of enough revenue for sub-level governments who can effectively implement water policies. The objective dimension concerns agreement and cooperation between relevant ministries. Lastly, accountability deals with public participation and involvement in water policy making, as well as the monitoring and the reporting and sharing of information on water policy performance.
Lockwood et al. [17] and de Bruijn and Dieperink [16] identify five good governance principles. First of all, transparency deals with the right of stakeholders to gain access to the information that is necessary for them. Accountability implies that stakeholders must have access to information to be able to hold governance actors accountable, while inclusiveness is about the opportunity for all stakeholders to participate in and (partly) steer decision-making processes. Connectivity deals with effective horizontal and vertical coordination in the multi-level system. Lastly, government effectiveness is about the quality of public services and policy formulation and implementation. De Bruijn and Dieperink [16] specify the five good governance principles using seventeen indicators.
Our assessment framework synthesizes the above papers using the dimensions of multi-level governance as a basis. The dimensions of policy and objective were combined, since they show considerable overlap. The five good governance principles and indicators were added to this base. The resulting framework, however, is rather general; we therefore added elements from the drought risk management strategies mentioned in Table 1 in order to tailor the framework a bit more towards this issue.
3. Materials and Methods
In order to find out to what extent and in what way the selected principles are present in multi-level drought risk governance praxis, we conducted a case study on the drought risk governance of the Rhine basin. In length (1233 km), the Rhine ranks 12th in Europe. The Rhine originates in the Swiss alps (2341 m above sea level) and has a basin size of 185,000 km2. The basin is located in 9 states, of which Switzerland (26,800 km2), Germany (105,000 km2), France, and the Netherlands (each 24,000 km2) are the key ones. The basin is home to 55 million people and offers drinking water to 30 million of them. However, agriculture and power plants are the biggest water consumers. Over the whole basin, the difference between high and low discharge is substantial. Rain is by far the most important source of water in the water balance of the Rhine basin. The Rhine and its tributaries contain 190 reservoirs with a total volume of 3.28 billion m3 [18]. The tributaries provide almost half of the annual discharge at the German–Dutch border. At this border, a normal discharge ranges from 1000 to 4450 m3/s, but in August 2022, it was as low as 660 m3/s [19,20].
The Rhine basin is considered to be a critical case study of governance due to its long experience and success in dealing with transboundary water quality and flooding issues. The Rhine’s cooperation has acted as a model for many other river basins in recent decades. We therefore expect good cooperation on drought issues between the riparian parties to be present. The empirical information found will be discussed and used to sharpen the framework and will ultimately lead to the development of design principles for good multi-level drought risk governance.
For feasibility reasons, we have restricted the scope of the study to governance at the international river basin level and the national levels of Switzerland, Germany, and the Netherlands. Most of the Rhine catchment is located in these three countries [21].
Data were collected from policy documents and interviews with key informants. Table 2 and Table 3 give an overview of the documents analyzed and the interviewees. Relevant policy documents and interviewees were found on the websites of the International Commission for the Protection of the Rhine (ICPR) and the three national governments. The indicators mentioned in Figure 1 were used to code (parts of) the documents. The document analysis gave us in particular insights in the development of drought policies, measures, and reporting, while the interviews revealed additional stakeholder views on the way the principles of multi-level drought risk governance are addressed in the basin. Snowballing was used to complete the set of documents and interviewees. Our key informants (see Table 3) represented relevant stakeholders and work as experts or policy advisors. The interviewees consented to the use of the interview data for scientific purposes. The interviews were carried out on Microsoft Teams and took about 1 h. The interviews were recorded, transcribed, and coded. Policy documents and interview transcripts were analyzed using NVivo14.

Table 2.
Analyzed policy documents regarding the basin (IRBD) and national levels with year of publication.

Table 3.
Affiliations of the interviewed experts and policy advisors.
We have combined the data from the analysis of the policy documents and the interviews in order to “score” the presence of our indicators in the multi-level drought risk governance praxis of the Rhine basin. Our qualitative interpretative analysis resulted in assigning traffic light scores to indicate whether the practice corresponds with the indicator (a green score), partly meets it (a yellow score), or needs urgent improvement (a red score).
4. Results
In Figure 2, we present an overview of the assessment of the presence of our good multi-level governance indicators on four decision making levels in the Rhine basin. As can be seen in the figure, overall drought risk governance performance is good, although room for improvement is identified as well. In the following, we will elaborate on the assessment of each principle.
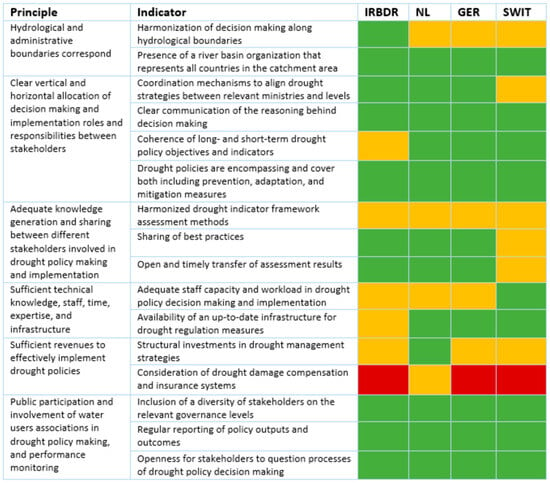
Figure 2.
The presence of good multi-level drought risk governance indicators on four levels of Rhine governance.
4.1. Hydrological and Administrative Boundaries Correspond
On the basin level, decision making is harmonized along hydrological boundaries. A harmonized approach to deal with droughts is pursued in the Rhine 2040 program, which for the first time includes the management of low water levels as a pillar on its own [24]. The program aims for a common understanding of low water levels on the basin level as well as the development of common assessment and solutions by 2040. On the three national levels we studied, points for improvement were found. In the Netherlands, harmonization of decision making is found in short-term approaches like the Smart Water Management Program, which aims to steer water to the areas that need it most [32]. The Dutch interviewees voiced that connections in time and space between drought risk management strategies on the international and national system levels need more emphasis and improvement, as well as the connection between national and international drought risk management actions and the actual implementation of structural drought risk management plans (Interviewees 2, 6, and 10). The German federal structure—in which public water management tasks are distributed among the federal government, states, districts, and municipalities [38]—hinders a drought approach that is primarily defined by hydrological boundaries. The basin community of German federal states, however, tries to overcome fragmented decision making (Interviewee 13). Swiss national policy documents also acknowledge that cooperation between the federal and cantonal levels could be improved, and stress that integral water transboundary management is not enshrined in federal law [49]. Despite this, both the federal government and the cantons, however, have been promoting a more integrated drought risk management approach for years [47]. In the Rhine catchment, the ICPR acts as the basin organization in which the Netherlands, Germany, Luxemburg, France, and Switzerland cooperate as official member states. Countries like Belgium, Austria, and Liechtenstein (and several NGOs) have observer status and cooperate on a more ad hoc basis [24].
4.2. Separation and Explicit Allocation of Roles and Responsibilities in Decision Making and Implementation between Stakeholders Both Vertically and Horizontally
Figure 2 shows that overall decision making and implementation roles are well separated and allocated. Our analysis only identified two points for improvement. On the basin level, three commissions operate. The ICPR deals with integrated river basin management, while the Central Commission for the Navigation of the Rhine (CCNR) focuses on navigation issues and the International Commission for the Hydrology of the Rhine basin (CHR) acts as a provider of hydrological knowledge. These roles are clearly discerned. Coordination is achieved on an ad hoc basis, for instance, by the jointly organized coordination symposium on low flows in the Rhine catchment [30]. The ICPR itself offers a platform for the basin states to discuss potential cross-border problems and joint strategy making. These discussions can take place in expert groups and in plenary assemblies. The interviewees (1, 2 and 4) mentioned the existence of a close network of experts consisting of persons that play a bridging role by connecting knowledge as well as people operating on different levels in the basin. On the national level, roles are assigned and coordination is achieved in national water plans. The Dutch National Water Program 2022–2027 explicitly states the responsibilities of all actors involved and provides a national roadmap for water distribution [32]. The roles and responsibilities of German actors are described in the German national water and climate change adaptation strategy [38]. Furthermore, water scarcity guidelines and multi-stakeholder Water Advisory Councils are being established, which will function as coordination mechanisms [38]. Overall, the Swiss constitution clearly specifies the roles of the federal and cantonal levels in water management. Furthermore, the BG Bund Wasser Schweiz is being set up as the platform on which relevant ministries—including the Bundesamt für Umwelt (BAFU), Bundesamt für Energie (BFE), Bundesamt für Landwirtschaft (BLW), MeteoSwiss, and Bundesamt für Raumentwicklung (ARE)—cooperate [49]. Our interviewees (16, 17), however, argued that channels for knowledge sharing on drought issues between the federal and cantonal levels could be improved.
The experts also revealed that the reasoning behind the decisions on drought issues are clearly communicated. Our analysis of reports and policy documents confirm this. Important policy documents like the German National Water Strategy (NWS) and the German Climate Change Adaptation Strategy (DAS) are clearly structured, which makes the decision-making processes in drought situations easy to follow. Both documents include sections that outline current challenges and strategies to overcome them. This also applies to the Netherlands, where all programs have a clear argumentation and structure. For example, in the national water program, decision making is supported by providing a roadmap and elaborate explanations of the situation and necessary measures [32].
On the basis level, a long-term vision is specified in the drought goals of the Rhine 2040 program. These goals, however, are not translated into measurable objectives with an explicit short-term horizon. National programs are more specific in this respect. In the Netherlands, for instance, a long-term vision is established in the Deltaplan Freshwater [34]. Existing drought policy goals focus on prevention, adaptation, and mitigation. The German National Water Strategy, for example, identifies a variety of different goals leading to a more robust water management in periods of drought [38] and includes drought prevention and adaptation measures. It is foreseen that forecasting will be improved by better monitoring of water balance and groundwater levels. This will allow for a more adequate short-term management of water withdrawals and an early response to long-term changes in water resources; it will also help to avoid overexploitation of available water resources.
4.3. Knowledge Generation and Sharing between Different Stakeholders Involved in Drought Policy Making and Implementation
Our assessment reveals that the generation and sharing of knowledge between different stakeholders involved in drought policy making and implementation overall have some room for improvement. The development of a harmonized indicator framework for assessing drought and low water on the basin level was addressed by the Rhine Ministers’ Conference, and in the Rhine 2040 program, it was stated that ‘to be better prepared for periods of low water, joint assessment criteria and solution approaches are being developed. A joint approach for dealing with the effects of low water events in the entire Rhine catchment area is sought’ [6] (p. 7). Currently, the basin’s countries use different models to predict future discharges. In the Dutch National Water Program, it has also been recognized that the water quantity data from all parties involved in the Netherlands should be standardized and exchanged in an additional national information system [32] (p. 149). In Germany, data harmonization and exchange between the federal and the state level could also be improved as the Umwelt Bundesamt, the responsible national authority mentioned in the German National Water Strategy [38,40]. In Switzerland, all cantons tend to measure water availability in their own way, using different indicators or not measuring some indicators at all (Interviewee 16). Switzerland also scores lower on the sharing of best practices. In the Netherlands, best practices like the ‘Smart Water Management approach’ to preventing drought-induced salinization were also adopted in the national strategy for climate-resilient freshwater supply in main water systems [35]. In Switzerland, knowledge on drought indicators and assessment results are generated by the cantons as they are actors responsible for water management in their region. Communication between the cantons and the federal level, however, does not take place on a structural basis. In the National Report on Water Supply Security and Management, the Swiss Federal Government therefore recommends that the cantons be more proactive in the sharing of their (good) practices and assessment results [47]. In order to fulfill its constitutional mandate to ensure economical use of water, the federal government needs more information from the cantons on the methods they initiated during dry periods. In order to achieve this, the federal government wants to make cantonal reporting mandatory [47]. In the Netherlands and Germany, sharing of assessment results seems to be better. In Germany, assessment results are effectively transferred through the LAWA, a group of German basin states (Interviewees 13 and 14). The results from pilot projects like the Bavarian low water management plan are elaborated upon by this body [44].
4.4. Sufficient Technical Knowledge, Staff, Time, Expertise, and Infrastructure
The assessment of documents and interviews reveals that overall improvements in staff capacity and workload are possible within drought policy decision making and implementation. This is the case for all levels, except for in Switzerland. Dutch interviewees revealed that a shortage of time and personnel has had a negative impact on decision making and the implementation of drought measures. The available capacity is currently spread over several multi-actor projects within which the interests of different sectors need to be accommodated (Interviewees 8 and 12). In the German National Water Strategy, it is stated that a lack of capacity is currently leading to incapability or heavy delays in the implementation of necessary measures [38]. Swiss documents state that in general, enough personnel and expertise are available, but that considerable additional efforts have to be made to acquire a relevant database and to develop and implement integral water management plans in the cantons [47]. This was also confirmed by the interviewees (16). During several symposia on low-water issues, the need to keep more water in the system and to increase the buffering capacity along the Rhine was stressed. An overall picture of the infrastructural options for buffering water on the basin level, however, is currently not available; however, ongoing research commissioned by the German BfG (the federal institute for hydrology) aims to create one. On the national level, insights into the possibilities of steering and buffering water flows are better. Steering possibilities and the regulation of water levels, however, depend on geographical characteristics. Most experts indicate that in the upstream High Rhine and Alpine Rhine regions, sufficient buffering capacity in the form of dams is available and can provide a continuous supply of water in dry periods [47]. In the Netherlands, it being the most downstream country, there is also enough up-to-date infrastructure to implement buffering measures, in particular in Lake IJssel and the Hollands Diep. These buffers are used to prevent salinization and to meet increasing demands in times of low water and droughts [35].
4.5. Sufficient Revenues to Effectively Implement Drought Policies
At the basin level, most infrastructural investments aim to accommodate navigation and trading and water drainage during floods. The focus is not on water storage. Furthermore, transboundary investments, like the Netherlands investing in storing freshwater in upstream Germany, currently do not occur. So far, this has only been talked about in informal discussions (Interviewee 2). In Switzerland, federal and cantonal levels co-fund the implementation of drought measures. The federal government, however, fears that climate change will put more pressure on federal budgets for drought risk management [48]. A comparable structure can be found in Germany, where there are structural funds available from the national water strategy and funds on the level of the federal states that are responsible for implementing and partly funding drought measures in their respective areas [38,50].
In the Netherlands, the Delta Fund provides for structural funding drought measures mentioned in the Deltaplan Freshwater. In this plan, a clear overview of investments in drought measures is given for the national, regional and local governments [34].
We found that the development of drought damage compensation mechanisms is in an urgent need of improvement. These measures are not considered on the basin level. An appeal to discuss these was made in the CCNR’s 2020 ‘Act Now’ report [23], but so far, nothing has been implemented. Neither documents nor interviewees revealed the existence of drought damage compensation schemes in Germany and in Switzerland. In the Dutch Deltaplan Freshwater, it is stated that despite several prevention and mitigation measures, (residual) damage may still occur [34] and society should therefore prepare for this. Specific measures so far are limited to the development of (costly) drought insurance policies for farmers, which are offered by agricultural insurance companies.
4.6. Public Participation and Involvement of Water Users’ Associations in Drought Policy Making as well as the Monitoring, Reporting, Sharing, and Distribution of Drought Policy Performance
On all levels, a diverse group of stakeholders are included in drought policy development. Several NGOs have an observer status in the ICPR, and in addition to this, the international Rhine 2040 program aims to work with water user interest groups, including the shipping, industry, agriculture, hydropower, and drinking water sectors [24]. In the Netherlands, stakeholders are actively incorporated in national-level drought decision making, as in Deltaplan Freshwater. According to the interviewees, the stakeholders are satisfied with how they were involved (Interviewee 1). Active public and stakeholder involvement can also be found in Germany, where, for instance, the national water strategy was built in response to a two-year-long public national water dialogue. Apart from experts, randomly selected citizens from different regions were invited to participate in this process [38].
On all levels, we found regular reporting of outputs and outcomes. For example, in the Netherlands, the current, second phase, of the Delta Freshwater Plan is a continuation and recalibration of the previous (first) phase, and an evaluation of its outputs has taken place [34]. This is also the case for Switzerland, where the Federal Department for the Environment reports every two years on the progress of plans for climate change adaptation [48]. Furthermore, one of the measures proposed by the Swiss central government is a cantonal that is obliged to report on measures taken during drought events. These reports are to include cantonal considerations of potential adjustments to water management which have been envisaged for future events [47] (p. 17).
We also found that decision making on all levels is open to stakeholder questioning. Stakeholders can actively participate in discussions in ICPRs. They are not only allowed to participate in discussions in all expert and working groups; they also participate in the general assembly (Interviewee 6). However, they have no voting rights in the latter. Additionally, an annual meeting between NGOs and the ICPR president is scheduled in order to exchange ideas about their needs and stakes. Stakeholders are satisfied with the opportunities they have to voice their ideas and/or criticize decision making (Interviewee 1).
5. Discussion
The starting point of this paper was that multi-level drought risk governance has been under-researched. In order to address this knowledge gap, we therefore reviewed the literature, which we synthesized into a framework to assess multi-level drought risk governance praxis in the Rhine basin. Our analysis revealed that our framework is useful for first identifying strengths and weaknesses in drought risk governance in the Rhine catchment. Overall governance praxis in the Rhine basin meets our criteria for good multi-level drought risk governance.
We have to admit that our empirical approach has some limitations. First of all, we limited our scope to the basin level and to the national governance levels of the three largest countries in the basin. The other basin countries also play a role in governing droughts in the basin but for practical reasons have to be left out of this paper. Apart from this, we have not focused on the more general role the EU plays in governing droughts, and we left the Water Framework Directive (with its focus on groundwater sufficiency), the EU Green Deal and Strategy on Climate Adaptation, and European platforms like the European Drought Observatory out of our analysis. Apart from this, the governing roles of sub-national-level actors like regions, municipalities, and regional water authorities have not been addressed. It also has to be noted that there is a slight off-balance in our data collection since in the number of interviewees and documents analyzed, the river basin level and the Netherlands were slightly overrepresented.
Our framework is useful for gaining some initial insight into the quality of a given multi-level drought risk governance case. Our case study also made clear that some criteria tend to overlap a bit and that some further specification of the framework is possible. Figure 3 shows the 10 design principles for good multi-level drought risk governance that resulted from this study.

Figure 3.
Ten design principles for good multi-level drought risk governance in international river basins.
Our 10 design principles are open to further scrutinization. The principles are based on a review of papers concerning multi-level and good governance and a single case study. However, the Rhine basin is a highly temperate, stable, wealthy zone in which, from a global perspective, drought problems so far are rather limited. The vulnerability of basins in other parts of the world like the Mediterranean is much higher, and this may result in governance practices that could be guided by other governance principles. The latter does not seem to be the case.
An additional review of the literature on drought risk management first indicated that our principles cover the Guidelines for National Drought Management Policies issued by the World Meteorological Organization and the Global Water Partnership [51] and also that they address the key challenges in drought management identified by Kampragou et al. [52].
Moreover, Australia and Brazil show convergence in the development of their water (scarcity) governance systems, which is in line with our principles. Both countries have significantly reformed their water policies and practices by introducing a legal foundation for more integrated and participatory basin governance based on the best information available [53].
The literature on integrated drought risk management, however, also indicates that our design principles could be further refined. Wilhite, for instance, advocates for shifting the focus from reactive to proactive risk management strategies [54]. Our third design principle might be refined accordingly. In-depth analyses of drought risk governance practices in other basins may also give insights that allow for further refinement of principle 5. A challenging issue, for instance, is how we might give a voice to local stakeholders in cases in which highly professionalized stakeholders also participate, as was the case in the Room for the River projects in the Netherlands. [55].
Our 10 design principles can also be criticized from a normative point of view, as they mainly refer to the governance process, while one could argue that good drought risk governance should also deal with the fair sharing of limited available water resources. In cases of water scarcity, available water has to be divided over different functions and users. In these cases, priorities have to be set. In the Netherlands, priority setting is based on the so-called Priority Chain, according to which certain water functions are prioritized over others in times of droughts. Too-dry peat dikes, for instance, lose their stability and water supply; wetting such dikes is therefore prioritized over functions like drinking water provision and navigation. On the Rhine basin level, however, such a prioritization scheme is lacking. Moreover, a water sharing agreement between the Rhine basin countries is also lacking. In such an agreement, fair sharing and minimum flows to downstream countries should be guaranteed. Fair water sharing could be based on criteria like the relative catchment sizes and/or the number of people per basin country. Treaties dealing with more water scarcity-prone basins like the Indus [56], the Jordan [57], and the Colorado [58] contain such sharing principles. Upper-basin states in the Colorado basin, for instance, are obliged to explore the feasibility of demand management programs [59]. Fair sharing principles may also be found in case law produced by international arbitration or adjudication.
Additional (legal) research could result in a more encompassing and further refined list of principles for a good multi-level drought governance. An enrichment of our design principles could also result from on additional review of papers on governance themes like connectivity or policy integration [60,61].
6. Conclusions
In this paper, we have developed and applied a framework for the assessment of multi-level drought risk governance. Based on our assessment, we have defined 10 principles for good multi-level drought risk governance. We have shown that our framework is useful for gaining a first insight into strengths and weaknesses but also learned that the design principles we derived from our application can be refined and need further elaboration and specification. This can be achieved both by practitioners involved in actual drought risk governance practices (in which they have to specify our 10 principles) but also by researchers that could carry out more in-depth (comparative) analyses of the drought risk governance practices of different international basins. Such comparisons may provide more robust insight into the key characteristics of good multi-level drought risk governance. The latter is needed, since climate change will continue and will affect water availability and scarcity in the years to come.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.J. and C.D.; methodology, H.J. and C.D.; validation, H.J. and C.D.; formal analysis, H.J.; investigation, H.J.; data curation, H.J.; writing—original draft preparation, H.J. and C.D.; writing—review and editing, H.J. and C.D.; visualization, H.J.; supervision, C.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for the respondents who participated in this study. We would also like to thank the reviewers for their feedback on an earlier draft of the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Brockhoff, R.C.; Biesbroek, R.; Van der Bolt, B. Drought Governance in Transition: A Case Study of the Meuse River Basin in the Netherlands. Water Resour. Manag. 2022, 36, 2623–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Wiel, K.; Batelaan, T.J.; Wanders, N. Large increases of multi-year droughts in north-western Europe in a warmer climate. Clim. Dyn. 2022, 60, 1781–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieperink, C.; van Helden, L.; Triyanti, A.; Stijnen, C. Dealing with droughts in Deltas towards a Framework for Comparative Governance Assessments; Hub Water Climate and Future Deltas, Utrecht University: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- KNMI. Achtergrondinformatie Neerslagindexen SPI en SPEI. 2021. Available online: https://www.knmi.nl/kennis-en-datacentrum/achtergrond/achtergrondinformatie-neerslagindex-spi (accessed on 25 June 2023).
- Blauhut, V.; Stoelzle, M.; Ahopelto, L.; Brunner, M.I.; Teutschbein, C.; Wendt, D.E.; Akstinas, V.; Bakke, S.J.; Barker, L.J.; Bartošová, L.; et al. Lessons from the 2018–2019 European droughts: A collective need for unifying drought risk management. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 22, 2201–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICPR. Internationaal Gecoördineerd Stroomgebiedbeheerplan 2022–2027 van het Internationaal Stroomgebieddistrict Rijn. 2022. Available online: https://www.iksr.org/fileadmin/user_upload/DKDM/Dokumente/BWP-HWRMP/NL/bwp_Nl_SGBP_2021.pdf (accessed on 18 April 2023).
- Gerats, K. Towards Good Drought Governance in High Sandy Areas; Drawing Lessons from Three Dutch Case Studies. Master Thesis, Utrecht University, Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zürn, M.; Wälti, S.; Enderlein, H. Introduction. In Handbook on Multi-Level Governance; Edward Elgar Publishing Limited: Cheltenham, UK, 2010; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Garrick, D.E.; Schlager, E.; De Stefano, L.; Villamayor-Tomas, S. Managing the Cascading Risks of Droughts: Institutional Adaptation in Transboundary River Basins. Earth’s Future 2018, 6, 809–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachbauer, J.; Feygina, I.; Lipkowitz, E.; Karwat, D. Climate Change Resilience: Governance and Reforms. Consortium for Science, Policy & Outcomes. 2017. Available online: https://cspo.org/research/climate-change-resilience-governance-and-reforms/ (accessed on 10 March 2023).
- Jiménez, A.; Saikia, P.; Gine, R.; Avello, P.; Leten, J.; Lymer, B.L.; Schneider, K.; Ward, R.A. Unpacking Water Governance: A Framework for Practitioners. Water 2020, 12, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieperink, C. From open sewer to salmon Run: Lessons from the Rhine Water Quality regime. Water Policy 1998, 1, 471–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julio, N.; Figueroa, R.; Oliva, R.D.P. Water Resources and Governance Approaches: Insights for Achieving Water Security. Water 2021, 13, 3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Water Governance in OECD Countries: A Multi-Level Approach. In OECD Studies on Water; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockwood, M. Good governance for terrestrial protected areas: A framework, principles and performance outcomes. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 754–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Bruijn, E.; Dieperink, C. A Framework for Assessing Climate Adaptation Governance on the Caribbean Island of Curaçao. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockwood, M.; Davidson, J.; Curtis, A.; Stratford, E.; Griffith, R. Governance Principles for Natural Resource Management. Soc. Nat. Resour. 2010, 23, 986–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Rhine in Facts & Figures. Available online: https://www.chr-khr.org/sites/default/files/chrpublications/leporello%20ENGELS_def.pdf (accessed on 5 March 2024).
- Debiet in m3/s. Available online: https://waterinfo.rws.nl/#/details/publiek/waterafvoer/Lobith%28LOBI%29/Debiet___20Oppervlaktewater___20m3___2Fs (accessed on 5 March 2024).
- Waterafvoer Rijn Nadert Laagste Debiet Ooit. Available online: https://www.h2owaternetwerk.nl/h2o-actueel/waterafvoer-rijn-nadert-laagste-afvoer-ooit (accessed on 5 March 2024).
- IAWR. Der Rhein. 2023. Available online: https://www.iawr.org/der-rhein/ (accessed on 22 June 2023).
- Van Der Krogt, W.; Passchier, R.; Hegnauer, M. RIBASIM River Basin Simulation Model of the Rhine—Volume 1 Main Report. Deltares. 2017. Available online: https://www.chr-khr.org/sites/default/files/RIBASIM%20River%20basin%20simulation%20model%20of%20the%20Rhine%20-%20Volume%201%20Main%20Report%20%281%29.pdf (accessed on 26 May 2023).
- CCNR. Act Now! On Low Water and Effects on the Rhine Navigation. 2021. Available online: https://www.ccr-zkr.org/files/documents/workshops/wrshp261119/ien20_06en.pdf (accessed on 24 May 2023).
- ICPR. Rijn 2040: De Rijn en Zijn Stroomgebied: Duurzaam Beheerd en Klimaatbestendig. 2020. Available online: https://www.iksr.org/fileadmin/user_upload/DKDM/Dokumente/Broschueren/NL/bro_Nl_2040_lang.pdf (accessed on 18 April 2023).
- ICPR. 16th Rhine Ministerial Conference Communiqué. 2020. Available online: https://www.iksr.org/fileadmin/user_upload/DKDM/Dokumente/Kommuniques/EN/com_En_communiqu%C3%A9_EN.pdf (accessed on 18 April 2023).
- ICPR. Rapport over de Laagwatergebeurtenis van Juli–November 2018 (No. 263). 2020. Available online: https://www.iksr.org/nl/publieksvoorlichting/documenten/archief/rapporten/rapporten-en-brochures-afzonderlijk/263-rapport-over-de-laagwatergebeurtenis-van-juli-november-2018 (accessed on 18 April 2023).
- ICPR. Standpunt van de Ngo’s Met Waarnemersstatus Bij de ICBR op Het Gebied van Waterkwaliteit: Gepresenteerd Door de Heer Matthias Maier, IAWR. 2020. Available online: https://www.iksr.org/fileadmin/user_upload/DKDM/Dokumente/Sonstiges/NL/ot_Nl_NGO_waterkwaliteit.pdf (accessed on 18 April 2023).
- ICPR. ICPR Low Water Monitoring for the Rhine and Its Basin (No. 261). 2019. Available online: https://www.iksr.org/en/public-relations/documents/archive/technical-reports/reports-and-brochures-individual-presentation/261-icpr-low-water-monitoring-for-the-rhine-and-its-basin (accessed on 18 April 2023).
- ICPR. Inventory of the Low Water Conditions on the Rhine (No. 248). 2018. Available online: https://www.iksr.org/fileadmin/user_upload/DKDM/Dokumente/Fachberichte/EN/rp_En_0248.pdf (accessed on 18 April 2023).
- CHR. Low Flows in the Rhine Catchment”: Theme of the International-Scientific Symposium ‘Science Meets Practice’. 2017. Available online: https://www.chr-khr.org/sites/default/files/chreventdocuments/report_symposium_basel.pdf (accessed on 24 May 2023).
- ICPR. Strategy for the IRBD Rhine for Adapting to Climate Change (No. 219). 2015. Available online: https://www.iksr.org/fileadmin/user_upload/DKDM/Dokumente/Fachberichte/EN/rp_En_0219.pdf (accessed on 18 April 2023).
- Rijksoverheid. Nationaal Water Programma 2022–2027: Het Nationale Waterbeleid en de Uitvoering in de Rijkswateren. 2022. Available online: https://open.overheid.nl/documenten/ronl0c5086b3029ab6a4ab28d52838ce44d5e6285d1a/pdf (accessed on 29 May 2023).
- Kosters, A.; Asselman, N. Kennisontwikkeling Voor Het Nederlandse Rivierengebied: Inventarisatie Lopend Onderzoek (No. 11206796-001-ZWS-0027). Deltares. 2022. Available online: https://publications.deltares.nl/11206796_001_0027.pdf (accessed on 10 April 2023).
- Rijksoverheid. Deltaplan Zoetwater 2022–2027. 2021. Available online: https://www.deltaprogramma.nl/documenten/publicaties/2021/09/21/dp2022-d-deltaplan-zoetwater-2022-2027 (accessed on 22 June 2023).
- Rijksoverheid. Strategie Klimaatbestendige Zoetwatervoorziening Hoofdwatersysteem. 2020. Available online: https://www.slimwatermanagement.nl/nieuws/nieuwsberichten/nieuwe-strategie-zoetwater/ (accessed on 22 June 2023).
- Watermanagementcentrum Nederland. Handleiding Verdringingsreeks. 2020. Available online: https://www.helpdeskwater.nl/@212059/handleiding/ (accessed on 22 June 2023).
- Beleidstafel Droogte. Eindrapportage Beleidstafel Droogte: Nederland Beter Weerbaar Tegen Droogte. 2019. Available online: https://open.overheid.nl/documenten/ronl-749b44a3-8e4b-427b-ad23-9be64203a619/pdf (accessed on 28 June 2023).
- BMUV. Nationale Wasserstrategie: Kabinettsbeschluss Vom 15. Märy 2023. 2023. Available online: https://www.bmuv.de/fileadmin/Daten_BMU/Download_PDF/Binnengewaesser/nationale_wasserstrategie_2023_bf.pdf (accessed on 28 June 2023).
- LAWA. Umgang mit Zielkonflikten bei der Anpassung der Wasserwirtschaft an den Klimawandel. 2022. Available online: https://www.lawa.de/documents/lawa-zielkonflikte-endbericht_2_1667831150.pdf (accessed on 22 June 2023).
- Umweltbundesamt. Niedrigwasser, Dürre und Grundwasserneubildung—Bestandsaufnahme zur Gegenwärtigen Situation in Deutschland, den Klimaprojektionen und den Existierenden Maßnahmen und Strategien. 2021. Available online: https://www.umweltbundesamt.de/sites/default/files/medien/1410/publikationen/2022-01-17_texte_174-2021_niedrigwasser_duerre_und_grundwasserneubildung.pdf (accessed on 28 June 2023).
- BMUV. Zweiter Fortschrittsbericht zur Deutschen Anpassungsstrategie an den Klimawandel. 2020. Available online: https://www.bmuv.de/fileadmin/Daten_BMU/Download_PDF/Klimaschutz/klimawandel_das_2_fortschrittsbericht_bf.pdf (accessed on 22 June 2023).
- BMDV. Gemeinsame Erklärung des Bundesministers für Verkehr und Digitale Infrastruktur und Vertretern der Stahl-, Chemie- und Mineralölindustrie, der Produzenten Mineralischer Massenrohstoffe und des Binnenschifffahrtsgewerbes zur Sicherstellung Zuverlässig Kalkulierbarer Transportbedingungen am Rhein („8-Punkte-Plan“). 2019. Available online: https://www.vci.de/langfassungen/langfassungen-pdf/2019-07-04-gemeinsamer-8-punkte-plan-bmvi-verbaende-niedrigwasser-rhein.pdf (accessed on 22 June 2023).
- Deutscher Bundestag. Bericht zur Risikoanalyse im Bevölkerungsschutz 2018. 2019. Available online: https://dserver.bundestag.de/btd/19/095/1909521.pdf (accessed on 22 June 2023).
- LAWA. Auswirkungen des Klimawandels auf die Wasserwirtschaft Bestandsaufnahme, Handlungsoptionen und Strategische Handlungsfelder. 2017. Available online: https://www.umweltministerkonferenz.de/documents/top_29_wasserwirtschaft_bericht_1532603521.pdf (accessed on 22 June 2023).
- BAFU. Gewässer in der Schweiz: Zustand und Massnahmen. 2022. Available online: https://www.bafu.admin.ch/bafu/de/home/themen/wasser/publikationen-studien/publikationen-wasser/gewaesserbericht.html (accessed on 22 June 2023).
- Bundesrat. Trockenheit: Bundesrat will Nationales System zur Früherkennung und Warnung. 2022. Available online: https://www.admin.ch/gov/de/start/dokumentation/medienmitteilungen.msg-id-88854.html (accessed on 22 June 2023).
- Bundesrat. Wasserversorgungssicherheit und Wassermanagement—Grundlagenbericht. 2021. Available online: https://www.newsd.admin.ch/newsd/message/attachments/71507.pdf (accessed on 22 June 2023).
- Schweizerische Eidgenossenschaft. Anpassung an den Klimawandel in der Schweiz: Aktionsplan 2020–2025. 2020. Available online: https://www.bafu.admin.ch/bafu/de/home/themen/klima/publikationen-studien/publikationen/anpassung-klimawandel-schweiz-aktionsplan-2020-2025.html (accessed on 19 June 2023).
- Schweizerische Eidgenossenschaft. Umgang Mit Lokaler Wasserknappheit in der Schweiz. 2012. Available online: https://www.blw.admin.ch/dam/blw/de/dokumente/Nachhaltige%20Produktion/Umwelt/Wasser/Umgang%20mit%20lokaler%20Wasserknappheit%20in%20der%20Schweiz.pdf.download.pdf/umgangmitlokalerwasserknappheitinderschweiz.pdf (accessed on 19 June 2023).
- FGG Rhein. Überblicksbericht der Flussgebietsgemeinschaft Rhein zur Bewirtschaftungsplanung nach Wasserrahmenrichtlinie für den 3. Bewirtschaftungszeitraum. 2021. Available online: https://fgg-rhein.de/servlet/is/4367/20211222_%C3%9C-Bericht_final.pdf?command=downloadContent&filename=20211222_%DC-Bericht_final.pdf (accessed on 28 June 2023).
- Pischke, F.; Stefanski, R. Drought management policies—From global collaboration to national action. Water Policy 2016, 18, 228–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampragou, E.; Apostolaki, S.; Manoli, E.; Froebrich, J.; Assimacopoulos, D. Towards the harmonization of water-related policies for managing drought risks across the EU. Environ. Sci. Policy 2011, 14, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa Junior, W.; Baldwin, C.; Camkin, J.; Fidelman, P.; Silva, O.; Neto, S.; Smith, T.F. Water: Drought, crisis and Governance in Australia and Brazil. Water 2016, 8, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhite, D.A. Integrated drought management: Moving from managing disasters to managing risk in the Mediterranean region. Euro-Mediterr. J. Environ. Integr. 2019, 4, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelenbos, J.; Roth, D.; Winnubst, M. Dealing with uncertainties in the Dutch Room for the river programme: A comparison between the Overdiep polder and Noordwaard. In Making Space for the River, Governance Experiences with Multifunctional River Flood Management in the US and Europe; Warner, J.F., van Buuren, A., Edelenbos, J., Eds.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kalair, A.R.; Abas, N.; Ul Hasan, Q.; Kalair, E.; Kalair, A.; Khan, N. Water, energy and food nexus of Indus Water Treaty: Water governance. Water-Energy Nexus 2019, 2, 10–24. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2588912518300262 (accessed on 4 March 2024). [CrossRef]
- Talozi, S.; Altz-Stamm, A.; Hussein, H.; Reich, P. What constitutes an equitable water share? A reassessment of equitable apportionment in the Jordan–Israel water agreement 25 years later. Water Policy 2019, 21, 911–933. Available online: https://iwaponline.com/wp/article/21/5/911/67699/What-constitutes-an-equitable-water-share-A (accessed on 5 March 2024). [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Torres, M.; Gerlak, A.K. Evolving together: Transboundary water governance in the Colorado River Basin. Int. Environ. Agreem. 2021, 21, 553–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spivak, S. The Colorado river drought contingency plan. Nat. Resour. J. 2021, 61, 173–204. [Google Scholar]
- Ingold, K.; Driessen, P.P.J.; Runhaar, H.; Widmer, A. On the necessity of connectivity: Linking key characteristics of environmental problems with governance modes. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2018, 62, 1821–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candel, J.J.L.; Biesbroek, R. Towards a processual understanding of policy integration. Policy Sci. 2016, 49, 211–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).