Abstract
Rivers across the globe experience and respond to changes within the riparian corridor. Disturbance of the riparian corridor can affect warmwater, intermediate, and coldwater streams, which can negatively influence instream physical structure and biological communities. This study focused on assessing the influence of the riparian habitat on instream structure within the Whitewater River, a coldwater stream system within an agricultural watershed in southeastern Minnesota, USA. To understand the influence of the riparian zone on the physical instream habitat, twenty variables (riparian, n = 9; instream, n = 11) were measured at 57 sites across three forks of the Whitewater using a transect method every 10 m across a 150 m reach. We used a modified Wentworth scale approach to assess coarse and fine substrates to describe habitat conditions. Canonical correlation detected significant associations between riparian and instream variables across the river forks, and indicated that wider riparian buffers, more bank grass and shrubs, longer overhanging vegetation, limited bare soil, and more rocks on banks were significantly associated with increased instream cover, high levels of coarse substrates with reduced embeddedness, increased pool habitats, and reduced fine sediments. In contrast, excessive fine sediments, lack of riffle habitat, reduced coarse substrates, and high width to depth ratios indicative of an impaired instream habitat were associated with narrow riparian buffers and high percentages of bare soil on banks. Riparian corridors have the capacity to enhance and protect physical instream habitats and overall ecosystem health when managed properly. Wide, grassy riparian corridors with stable banks, overhanging vegetation, and limited shade from trees should protect and/or enhance the instream physical habitat, providing the structural diversity favored by aquatic communities. We recommend revising the current Best Management Practices to include monitoring for impairments in the riparia, while promoting and developing good land stewardship with private landowners which can be effective in improving river ecosystems in agricultural settings.
1. Introduction
Freshwater streams and rivers provide a variety of ecosystem services (i.e., nutrient cycling, provisioning, and cultural) important for both aquatic communities and the riverscape [1], and human activities that alter landscapes can affect those ecosystem services. Human alterations often begin in land cover outside the river corridor, which change river processes and morphology [1]. Historic stratigraphic records show that humans altered riverscapes as far back as 7000 years ago in both China [2] and southeastern Europe [3], but less than 200 years ago in the United States for intense, large-scale agricultural practices [4]. Activities such as improper forest management in northwestern Europe [5], agriculture in East Africa [6], cattle grazing in the United States [7], and road construction everywhere all have the potential to increase sediment yield, alter hydrology, and restructure the physical instream habitat [8,9,10]. Human activities can be pervasive and damaging, and frequently encroach upon the riparian zones of rivers and streams [7,11]. Land alterations and the degradation of riparian zones can influence water quality, but certain characteristics of the riparian corridor can help buffer both instream processes and the lotic structure [7].
Riparian zones are transitional areas between terrestrial and aquatic environments that allow for biological, physical, and chemical interactions between floodplains and the plants, animals, water, and substrates within river channels [12]. Influenced by water table levels, flooding regimes, and the water retention of soils, the diverse vegetative structure and composition of riparian zones regulate a range of environmental processes vital for healthy ecosystem functioning [13]. The degree of influence of a riparian zone on its river channel will vary according to stream size and channel planform, landscape context and history, and the hydrological regime [14]. For example, riparian zones are an integral part of riverine systems through their functional role as an energy source in riverine food webs [15,16], nutrient regulation and management of non-point source pollution [17,18], thermal buffering [19], bank stabilization [20], and creation of a diverse instream habitat and refugia that enhances aquatic biodiversity [21,22].
In the context of ecological functionality and biodiversity, desirable characteristics of riparian zones are connectivity [23], heterogeneity [24], and resilience [23]. Connectivity within riparian zones is three-fold: lateral connectivity refers to the exchanges from a river channel across to its floodplain and broader river basin, vertical connectivity extends from the riparian canopy to underlying groundwater systems, and longitudinal connectivity follows the length of a river channel [7]. Riparian zones should be heterogeneous, in floral and faunal biodiversity and structure, as heterogeneity enhances productivity, species redundancy, and resilience [25,26]. Healthy riparian zones should, in turn, protect riverbanks from erosion, increase groundwater and instream water depths, and reduce instream sedimentation and associated nutrient loading [27]. Maintaining a healthy riparian zone in agricultural settings can include the creation of wide buffers [27] and/or excluding livestock by fencing the corridor [28]. Ideal instream conditions such as reduced temperatures [28], reduced fine-sediment inputs [29], suitable instream habitat and cover for aquatic life [12], and narrower, deeper channels with stable banks [30] may be achieved via well-vegetated banks and mixed deciduous trees [31].
Undesirable characteristics of riparian zones include fragmentation, homogenization, or simplification, and excessive modification of natural processes (e.g., the acceleration of erosional processes and sedimentation or modification of flow regimes after dam construction), which may accompany land alterations such as improper forest management [30], intensive agricultural practices, urbanization, and industrialization [32,33]. Undesirable characteristics of riparian zones may include bare soil, patchy vegetation, highly eroded banks, incised river channels, and high proportions of non-native and/or invasive vegetation, which have been shown to reduce riparian and instream biodiversity and habitat [34,35], exacerbate sedimentation and nutrient loading within the river channel [36,37], and alter aquatic food webs [38] or instream productivity [39].
Landscape alterations are well known to have negative impacts in the structure (ideal instream habitat and biological structure (i.e., sensitive taxa)) and functioning (e.g., food webs) of lotic ecosystems [40]. Due to such extensive and pervasive human activity, the functionality, biodiversity, and resilience of riparian zones are frequently compromised [41]. In the present study, we examined the physical characteristics in both the riparian zones and instream habitats within a catchment that has been subject to a long history of forest removal and agricultural activities [42]. Specifically, we examined the possible influences of riparian zones on a physical instream habitat within a network of highly valued trout streams [43] in southeastern Minnesota, USA. We expected that there would be important correlations between riparian and instream physical characteristics, both positive and negative. We hypothesized that grassy, wide riparian zones would benefit physical instream structures, and poor riparian conditions would correlate with negative instream impacts.
2. Methodology
2.1. Study Area
The Whitewater River, a catchment in southeastern Minnesota, USA, drains 829.6 km2 of agricultural land across three counties (Olmsted, Winona, and Wabasha). This catchment contains >189 km of fishable, coldwater, trout streams comprising the mainstem, three forks (North, Middle, South), and smaller tributaries (Figure 1a). This river system is known for its fisheries that include self-sustaining populations of native brook trout (Salvelinus fontinalis) and introduced brown trout (Salmo trutta), plus regularly stocked rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss).
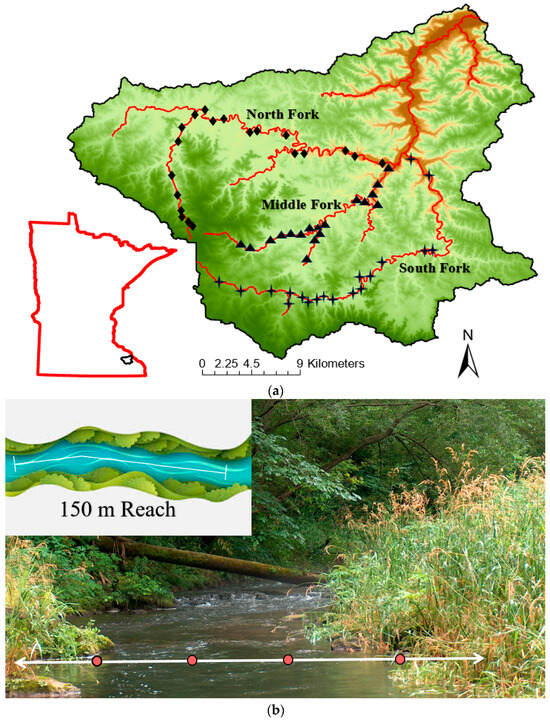
Figure 1.
(a). This map is of the Whitewater River catchment located in southeastern Minnesota, USA. Displayed are the North, Middle, and South Forks along with main tributaries. Diamond, triangle, and four-point star shapes are study sites along each fork, respectively. (b). Upper left shows an illustrated 150 m reach. Flow is not shown, however, sampling occurs in the upstream direction. The picture provided is a coldwater trout stream of the North Fork Whitewater River in southeastern Minnesota, USA. The picture shows one transect that is 5.5 m wide with four equidistant points (solid red circles). At these points along the transect, water depth (cm), current velocity (cm/s), dominant substrate, and embeddedness were assessed. See methods section-habitat surveys for specifics on dominant substrate and embeddedness.
The Whitewater River catchment is one of several in southeastern Minnesota located within the Driftless Area ecoregion, a geographic area missed by recent glaciation which has been described previously [27,44,45,46]. The coldwater stream fisheries within the Driftless Area are credited with generating an estimated US$1.6 billion annually in economic gain for the region [43]. Revenue generated from these recreational fisheries (i.e., spending by anglers and associated tourism) helps sustain local economies.
In the mid-1800’s, the landscape surrounding the Whitewater River catchment, along with other catchments, began to change post-settlement due to human alterations. A long history of intense forest removal (logging), along with agricultural practices (steep slope plowing, hillside grazing, and planting of crops), reshaped physical instream habitat and covered much of the landscape under meters of eroded soils [42]. Affected by the aftermath of intense landscaping, the catchment experienced changes not only to instream structure, but to fish and other aquatic communities. Riparian conditions were altered, landscapes converted for agriculture, and the effects of poor land-use habits induced conservation measures around the mid-1900’s to ameliorate the effects of land abuse past.
Following decades of conservation practices, many streams within the Whitewater basin began to recover [27]. However, the drainage remains heavily impacted by agricultural practices, with >70% of the surrounding forested land converted for agriculture (i.e., crops and pastureland) [27,44]. This catchment, like many others in southeastern Minnesota, is classified as at-risk/impaired due to current physical (high turbidity), chemical (high nitrates), and biological (high bacteria counts, poor macroinvertebrate, and fish assemblages) conditions [47]. To aid in reducing overland erosion and protecting instream habitats, a buffer law requiring new and/or expanded riparian buffers along streams was passed in 2014 by the State of Minnesota (Minnesota Statutes 2014, section 103B.101, subdivision 12, as amended in 2016 and 2020; https://www.revisor.mn.gov/statutes/cite/103F.48, accessed on 30 December 2023). The buffer law mandated the presence of a continuous, vegetative buffer (perennially rooted vegetation, 15 m average width, 9 m minimum width) between all public waters and cultivated lands. A recent study [27] examined instream conditions before and after the buffer law, concluding that more than 5 years may be needed before the positive effects of streamside buffers on instream habitats are observed.
2.2. Stream Surveys
During summer and early autumn (May–October) in 2018 and 2019, we surveyed stream habitats (riparian and instream) at 57 sites within the three forks of the Whitewater River catchment (North = 20 sites, Middle = 18, South = 19). Surveys were conducted at sites along each of the three river forks and within the larger tributaries to each fork. Sites included locations both on private lands (with landowner consent) and public lands (e.g., state parks and wildlife management areas). We attempted to select study sites located approximately every 1.5 km along each fork and larger tributaries. However, there were areas within all forks that were inaccessible due to terrain and lack of roadways, causing some spatial gaps among sites, especially along the lower reaches of the North and South forks.
Habitat surveys. At each study site, instream and riparian variables were assessed along a representative 150 m stream reach with transects every 10 m (15 transects/site; Figure 1b) at baseflow conditions. For each transect spanning the width of the stream, four variables each were assessed at four equidistant points along the transect: water depth (cm), current velocity (CV) at 0.6-depth (cm/sec), dominant substrate composition (estimated visually according to a modified Wentworth scale: <2 mm (clay, silt, and sand), gravel (2–52 mm), cobble (53–254 mm), boulder (>254 mm), plus muck, vegetation, and detritus) [46], and embeddedness (the percent of large substrates such as cobbles covered by fine materials, estimated visually on a five-category scale: 1 = <5%, 2 = 5–25%, 3 = 25–50%, 4 = 50–75%, and 5 = >75% [high score indicates high embeddedness]) [48]. The percentage of fines (estimated as an aggregate of sand, silt, clay, muck, vegetation, and detritus) was determined on a site-wide basis and presented as a percent of all substrates assessed. Similarly, width-to-depth ratios were determined for each site using mean depth and mean width measurements.
Additional instream features were estimated visually. Percentage of the channel shaded by the riparian canopy at noon, the percentage of riffle, pool, and run, and the percentage of channel with instream fish cover were estimated to the nearest 5%. Fish cover included all overhanging bank vegetation (AOV), woody structures, aquatic macrophytes, boulders, and water >60 cm in depth (contributions by specific cover types were not recorded).
Riparian habitat measures were recorded on one stream bank per transect, alternating the side measured with each transect. The width of the riparian buffer (WRB) was measured to the nearest meter with a rangefinder or meter tape. The average length of vegetation overhanging the stream was measured to the nearest 0.1 meter. The percentages of bank area as grass, forb, tree, shrub, bare soil, and rock were estimated visually to the nearest 5% for each category. Data collected from all transects were averaged to determine the overall site values. All visually estimated data collected in situ, were estimated independently by trained ecologists (2), averaged to obtain one value for each measurement, analyzed, and reported.
2.3. Data Analyses
Data were analyzed using Program R version 3.5.1 (R Core Team 2018), and Microsoft Excel. Basic descriptive statistics were used to describe riparian and instream habitat data (i.e., means, and standard deviation). Inferential statistical methods following [49] (e.g., analysis of variance [ANOVA], Chi-square goodness of fit analysis, two-sample t-test) were used as appropriate to test for differences across riparian and instream habitats among study reaches.
Canonical Correlation analysis (CanCorr) [50] was used to explore multivariate relationships among riparian and instream measures. In contrast to multiple regression analysis, which finds the linear combination of the multivariate set of explanatory variables that is most correlated to a single response variable, CanCorr finds separate linear combinations for the riparian and stream multivariate data sets that have the maximum correlation with each other; these are denoted as the first canonical variate pair. Subsequent pairs of canonical variates (i.e., second, third, etc.) are independent of all previous canonical variates and show relationships among variables after accounting for factors driving all previous canonical variates; however, correlation strength decreases for subsequent canonical variates so approximate F-tests [50] were used to test for non-zero correlations between canonical variate pairs. Heliographs [51] of the correlations between all significant canonical variates and the riparian and instream measures were used to portray multivariate relationships among stream characteristics. Prior to the analysis, all percentage data were arcsine transformed as required to meet normality assumptions.
3. Results
3.1. Riparian and Instream Variables: General Assessment
Riparian (n = 9) and instream (n = 11) variables were assessed across 57 sites in the Whitewater River catchment. Observations allowed us to describe typical conditions across all forks. In general, coarse substrates like rubble and gravel were present throughout the study area but embedded by fines, while lacking boulders, width/depth ratios averaged 7 across all forks, with few riffles and pools and more run habitat. Riparian conditions throughout the study area were similar with a range of buffer widths of 98–127 m and transitioned from forests to grasslands to grazed pasturelands (buffer type was not a measured component of this study but anecdotally noted). Bank structure within the riparian corridor consisted of more bare soil and grasses than forbs, shrubs, and trees collectively and a lack of overhanging vegetation.
Following initial analysis, we ultimately decided to omit several variables. The first variable omitted was temperature due to its lack of contribution or influence on the study’s overall outcome. Width and depth were omitted and replaced with width/depth ratio as it has been used in recent studies as an effective variable describing physical instream conditions. Lastly, bedrock was omitted due to rarity (only two sites were observed with bedrock but are used in the figures below). After omissions, we analyzed the data with the new modifications with outcomes reported below.
Data were analyzed using ANOVA single factor to test for differences in variables across all forks (North, Middle, and South) within the study area. Seven variables showed significant differences among the forks (Table 1): percent fines, percent gravel, embeddedness, percent riffle, percent run, percent pool, and percent cover. Riparian corridors generally were wide and vegetated for all forks; however, there was also high percentages of bare soil in riparian areas with instream areas showing high proportions of fines (Figure 2), embeddedness of coarse substrates (Figure 3), and run habitats.

Table 1.
Riparian (n = 9) and instream (n = 11) variables measured in this study. Means are represented followed by (+/−) one standard deviation parenthetically, ANOVA results with the F value and probability statistic. Data were collected during summer in 2018 and 2019 across three forks (North, Middle, and South) of the Whitewater River in southeastern Minnesota, USA. Abbreviations are as follows: AOV = average overhanging-bank vegetation, WRB = width of the riparian buffer, CV = current velocity. Asterisks denote significant differences for a specific variable.
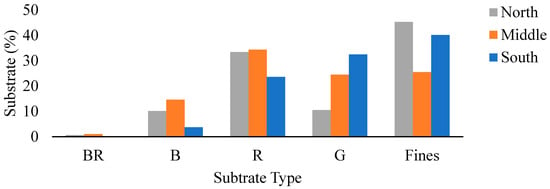
Figure 2.
A bar graph displaying substrate types. Data were gathered during summer in 2018 and 2019 across three forks (North, Middle, and South) and across main tributaries of the Whitewater River located in southeastern Minnesota, USA. A mean percentage is presented with standard deviation error bars. From left to right, are coarse substrates with bedrock (BR), boulder (B), rubble (R), gravel (G), and Fines. Fines is an aggregate of sand, silt, clay, muck, vegetation, and detritus.
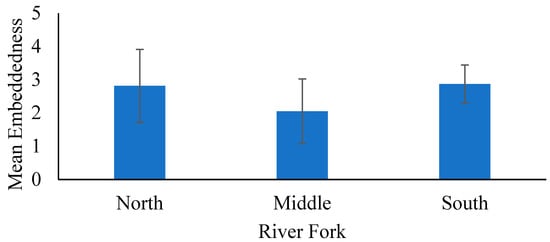
Figure 3.
Displayed in the bar graph are mean embeddedness values (+/− on standard deviation error bars) from a scale of 1–5. Data were collected during summer in 2018 and 2019 across three forks (North, Middle, and South) of the Whitewater River in southeastern, Minnesota, USA.
3.2. Canonical Correlations Modeling: Riparian Influence on Instream Habitat
CanCorr modeling was used to further investigate the correlation structure between riparian variables (n = 9) and instream habitat variables (n = 11) to determine whether riparian conditions can have an influence on the physical instream habitat structure. The model produced a total of nine canonical variate pairs, of which the first three showed correlation strength significantly (p < 0.05) different from zero (Table 2). Heliographs revealed several variables with strong correlations in describing both desirable and undesirable conditions (Figure 4). The first canonical variates of riparian and instream data sets had a 90% correlation and showed that high percentages of bare soil and trees on stream banks, along with narrow riparian buffers and a lack of forbs and rock on stream banks, were associated with high percentages of fines and run/pool habitat, high embeddedness, few riffles, a reduced width–depth ratio, and a lack of boulder and rubble substrates. The second canonical variates of the riparian and instream data sets had a correlation of 79%, in which greater percentages of grass, and AOV along with a lack of bare soil, forbs, trees, and shrubs, were associated with increased cover, pool, and rubble/gravel substrates along with low width/depth ratio, fines, run, and boulder habitats. The third canonical variates of the riparian and instream had a 72% correlation showing wide riparian buffers, more bank rock, and shrubs, along with a lack of grass, forbs, and shrubs along the stream bank, were correlated with more rubble, high width/depth ratios, faster flow, and high embeddedness.

Table 2.
Canonical variates produced using Canonical Correlation modeling along with the correlation strength (Corr) between the variate pair, approximate F-test statistics (F), and p-values for tests of non-zero correlations. Data for the model were collected during summer in 2018 and 2019 across three forks (North, Middle, and South) of the Whitewater River in southeastern Minnesota, USA. Asterisks–presence denotes significant correlation of the variate and number of asterisks denote strength of correlation.

Figure 4.
Heliographs of the first three canonical variates from Canonical Correlation modeling displaying the correlation between canonical variates and associated riparian (X) and instream (Y) variables. Length of bars are proportional to the absolute strength of the correlation; solid black bars are positive correlations, while clear bars show negative correlations plotted on polar coordinates. Data were collected during summer in 2018 and 2019 across three forks (North, Middle, and South) of the Whitewater River in southeastern Minnesota, USA.
3.3. Important Riparian and Instream Characteristics
In general, we noted the typical characteristics of the riparian corridor which may have influenced the physical instream habitat (Table 3). For example, the Middle Fork displayed more favorable riparian conditions such as wide riparian corridors, a mix of bank conditions favoring grasses, moderate shade, low embeddedness, and more riffles. The North Fork was in a less favorable condition with lots of shade, wide riparian corridors, bare soil, high fines, and high embeddedness. Conversely, the South Fork displayed poor conditions in comparison to the North and Middle Forks. The riparian corridor was narrow with more bare soil and high fines, embeddedness, and more runs. Based on our findings, we can speculate that with narrow riparian buffers and poor bank conditions, the physical instream habitat can be adversely affected.

Table 3.
This table displays the physical characteristics that best describe which riparian conditions influence instream conditions. Data were collected during summer in 2018 and 2019 across three forks (North, Middle, and South) of the Whitewater River in southeastern Minnesota, USA.
4. Discussion
4.1. Major Findings
Riparian zones are physical features within the riverscape that promote the health and proper functioning of riverine ecosystems by providing protection from landscape processes. This study focused on investigating riparian conditions in a watershed with a long history (>150 years) of land alterations for agricultural activities (i.e., row crops, livestock grazing, forest removal). We sought to determine which riparian characteristics influenced desirable instream conditions, and which riparian characteristics were associated with unfavorable instream conditions. First, we found that wider riparian buffers, more bank grass and shrubs, longer overhanging vegetation, and limited bare soil and more rocks on banks were significantly associated with increased instream cover, high levels of coarse substrates with reduced embeddedness, increased pool habitats, and reduced fine sediments. Second, we observed that excessive fine sediments, lack of riffle habitat, reduced coarse substrates, and high width-to-depth ratios indicative of impaired instream habitat were associated with narrow riparian buffers and high percentages of bare soil on banks.
Lotic systems in agricultural settings can be impacted negatively by surface runoff and nutrients [52]. However, vegetated riparian zones can insulate lotic systems from land-use effects [53]. Wide intact continuous forest and grass buffers can intercept eroded soils before they enter streams, reducing instream fines and nutrient concentrations [54]. By comparison, forested buffers can provide woody structures important for physical instream habitat [55] and organic carbon inputs for food webs [13], while also reducing water temperatures and filtering out nutrients [56]. Grass and forb buffers are known to perform better in filtering than forested buffers [57], increasing suitable habitat for aquatic organisms [30], reducing overland flow of nutrients and increasing infiltration [54], and increasing stream velocity that flushes out fines and reduces embeddedness of coarse substrates [27,53]. Based on our findings, we suggest that certain physical conditions in the riparian zone can either protect suitable physical instream habitat from deteriorating or may help to restore previously damaged habitat. We observed mostly intact (continuity of buffer was not a measure, but visually noted) riparian buffers throughout the study area, with many being very wide (>90 m).
Within the study area, there were well-vegetated grassy buffers, a few restored prairies, and some forested areas, likely due to good land stewardship and compliance with the state mandated buffer law (Minnesota Statutes 2014, section 103B.101, subdivision 12, as amended in 2016 and 2020; https://www.revisor.mn.gov/statutes/cite/103F.48, accessed on 30 December 2023). Studies suggest that there may be a significant time lag between the establishment of new buffers and observable improvement in instream habitats; although, it may be possible to observe some improvements soon after buffer establishment [58]. We observed several “good” characteristics typically associated with ideal riparian zones, including long overhanging vegetation [31], minimal bare soil [27], bank reinforcement with natural rocks, and scattered shrubs and trees on and/or along the banks [12]. These features were correlated with better instream cover, more coarse substrates, reduced embeddedness, more pool habitat, and reduced fine sediments. Each of these “good” instream features likely can be correlated to wide, grassy expanses of the riparian zone across the study area [12,27,58]. We understand that seasonality can be a limitation, as physical changes can be easily tracked with varying seasons; however, due to logistics (short season, flashiness of streams, limited personnel), we were limited to mostly summer months.
Lotic systems have been subject to human activities for centuries and will continue to be subject to negative changes caused by the alterations of their floodplains, riparian ecosystems, and instream structure. Attempts have been made to enhance or restore degraded river ecosystems [59] with expectations to return stream functions to a desirable condition (i.e., better water quality, better physical habitat) [60,61]. However, results may vary, with both positive- and no-effect outcomes being possible [59]. We documented the physical characteristics that were assessed as negative or negatively influencing certain physical instream habitat features. Overall, undesirable riparian characteristics included narrow riparian buffers with mostly bare soil (i.e., lack of vegetation cover). Modeling determined that these characteristics correlated significantly to instream impairments such as excessive fine sediments, lack of proper riffle structure, lack of coarse substrates, and high width-to-depth ratios. Although most study sites were buffered, we did observe riparian areas that were minimally in compliance with the buffer law (i.e., mean width of 15 m, minimum width of 9 m). Narrow riparian zones are less effective in protecting streams and capturing eroding soils [62]; this likely explains our observations across many study sites and we also noted grazing livestock across many sites.
Unprotected riparian zones left open for livestock to freely graze also have negative impacts on streams due to reduced vegetation volume [55], failing (collapsing and eroding) banks, and stream widening, allowing sediments to enter the water column [45]. On many occasions, we halted field measurements due to the presence of livestock grazing the banks and wading in the water to drink. Such livestock impacts can be reduced by fencing that would limit livestock stream access only to designated watering locations, while also protecting and enhancing stream processes [28]. In areas where livestock were grazing on and near banks, we often observed active channel widening (e.g., unstable collapsing banks). Wide streams often have higher width-to-depth ratios, which can create slower flows and reduced sediment transport, effectively embedding coarse substrates and altering physical habitat structure [44]. The lack of riffle structure likely can be explained by the lag time from the implementation of improved riparian conditions and the instream response to that improvement [63], with the desired conditions just not yet observable. We likely will continue to see physical instream habitat improvements over the next several years, with maximum effect potentially requiring one or more decades [63,64].
The Whitewater River catchment has a long history of undesirable forest management and agricultural practices beginning in 1853, the year farming practices began in the region [42]. Despite determining that the “healthiest” part of the catchment was the Middle Fork, fines dominated physical instream habitat throughout the Whitewater watershed. Due to its lengthy history of human alterations, the catchment, like many others in the region, suffers from the effects of generational trauma known as legacy sediments. In river science, legacy has been used in connection with diverse past events including natural processes (i.e., wildfires, floods) [1]; here, we use the term legacy sediments as it has been associated with human activities [65]. Land altering activities in the Whitewater catchment continue to negatively impact water quality, suffocate coarse substrates, and alter other physical habitat features. On land, the impact of land alterations is shown through meters thick accumulations of legacy sediments [27] that are then transported via floods during intense storm events [66]. The effects of land alterations are well known throughout the world (Sweden, [67]; Australia, [68]; Europe, [69]; U.S., [70]). To remediate such adverse impacts, revegetation, bank stabilization techniques, and protection of riparian corridors through fencing and livestock exclusion are all common river management activities [71]. River scientists often intervene to remediate negative impacts, but these efforts are not always successful due to insufficient river management knowledge and or appropriate target scale [40].
4.2. Management Implications
Over the last several decades, much has been learned about riparian zones, their importance, and their relationship with lotic systems. For example, riparian zones have the capacity to insulate streams from agricultural activities (i.e., capture soil runoff, retain nutrients) [27], provide subsidies for biological communities [55], cool-down stream temperature [72], support primary production [73], provide ideal habitats [74], provide cover [46], and support local communities (e.g., subsistence (fish), drinking water) [1]. Following decades of interdisciplinary research, scale and riparian zone width were identified as major factors in a healthy and functioning riparian ecosystem [71]. Rivers are arrayed in a hierarchical nature (i.e., different levels of organization with a top-down structure; upper levels affecting lower levels), which makes it difficult to manage rivers at different spatial scales [40]. Managing rivers at the proper scale can prevent undesired effects at lower organizational levels [40]. When managing riparian zones, acknowledging that their width and physical structure (e.g., grass and forest buffers) varies depending on river type, will aid in proper management approaches [7]; not all rivers and streams require the same buffer widths [75]. In the U.S., a minimum buffer width of 30 m is mandated around perennial rivers by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) and the National Forest Management Act (NFMA) [7] and increased from the prior 7.5 m minimum [75] to better capture nutrients and eroding soils. In New Zealand, a recent study [76] reviewed riparian management progress in perennial, low-order streams (second to fourth order) [28] and found that most streams had a variable buffer width of 2–5 m as a compromise with private landowners to maintain productive arable land near streams. A study in Australia [77] described different widths protecting against certain processes. For lowland floodplain perennial rivers, the minimum requirements are 28 m to moderate stream temperature and 29 m to improve water quality. However, for low-order, high-gradient streams, a 28 m minimum buffer width is required for temperature regulation and 38 m to improve water quality.
The importance of riparian zones to aquatic ecosystems is well studied [8,14,27,78,79], and the need to manage and protect these sensitive ecosystems is emphasized. In the mid-1990s, the need for guidelines to protect riparian zones (at a basic level) was initiated by several nations, including the United States, Australia, New Zealand, Canada, United Kingdom, Sweden, and South Africa [80,81]. To that end, strategies to protect riparian areas began initially with forested buffers (improved forest management) [75], later expanding to include grassy buffers [31,82]. Despite a deeper understanding (i.e., how to protect, issues with scale, determining necessary width, and so on), monitoring of important river features is often overlooked. Despite the relatively low cost of monitoring compared with ecosystem services’ (i.e., nutrient cycling, provisioning, cultural) benefits from environmental protection, monitoring often is neglected as it requires funding and long-term efforts by qualified researchers [83]. Protection of the riparian corridor must continue, which means allocating funding for protection, maintaining intact corridors with sufficient buffer widths relative to the landscape template [14], establishing riparian areas that are spatially heterogeneous in nature (combinations of native grasses, mixed forests, prairie meadows) [84,85] and installing exclusions for livestock [28,76].
To better manage riparian ecosystems, we need to acknowledge that there are basic (at times minimal) management standards that should be followed. Researchers proposed a framework of five activities to conserve and protect riparian corridors: education, inventory, protection, sustainable management, and restoration [86]. Still, management of riparian corridors is met with challenges and patterns to overcome. One trend regularly emerging is the myriad of national, regional, and local legislation affecting riparian corridors [87] often focused only on water quality while failing to include non-aquatic features of lotic systems (e.g., the European Water Framework Directive, and in the USA the Clean Water Act, National Environmental Protection Act, and Farm Bill). An exception to this trend was the U.S. National Wild and Scenic Rivers Act (WSR Act, 1968). The WSR Act has protected well over 20,000 km of streams and rivers across the U.S. that exhibit natural, cultural, or aesthetic qualities, to preserve water quality and other non-aquatic components vital to conservation. Trends in changing climate have demonstrated the magnitude of the effects of floods and droughts which alter the structure and functioning of riparian ecosystems, affecting the response and recovery trajectories of aquatic organisms to disturbances [88]. Climate trends coupled with human-influenced impacts have a compounding effect which makes the diagnosis of riparian conditions difficult due to lag-time of the onset of impacts and how rivers respond [89]. This is important to identify early on to better protect and conserve riparian ecosystems which can be heeded with regular monitoring. Although many of the tools needed to protect riparian and river ecosystems are utilized, they are not broadly applied together with the applicable standards needed to buffer lotic systems.
5. Conclusions
Understanding the importance of riparian zones and their role in river ecosystems is vital to water quality, conservation, and protection of riparia. To a much greater end, understanding how altering landscapes affect river ecosystems and all their components is equally important due to the hierarchical nature (top-down processes) of these ecosystems [40]. Recently, a study demonstrated the importance of riparian zones in improving water quality, and their buffering potential with increasing widths when attempting to improve the overall structure and functioning of riparian and lotic ecosystems [27]. At the reach scale, the present study demonstrated the type of riparian conditions needed to maintain a healthy functioning ecosystem. Although a broader scale riparian habitat type (i.e., forest, agriculture, pasture) was not a point of interest in this study, past studies have documented how the landscape surrounding the Whitewater River was converted and is now used [44,45,47,52]. Reducing or modifying the physical structure of the riparia at smaller scales can have undesired effects on the water column.
Growing trends in land alterations, either naturally or humanly influenced, have been widely known to alter community compositions and physical instream habitats [13,79]. Coldwater trout streams of the Driftless Area ecoregion are vastly important for the services they provide in the form of local economic gain and the sensitive biota that inhabit these coldwater systems [43]. However, due to decades of land abuse and legacy sediment accumulations, these sensitive ecosystems are impaired, negatively impacting their biota [52]. Maintaining good stream health in river ecosystems is thus important for small local economies to continue to thrive, locally, regionally, and globally. A revision of riparian Best Management Practices (BMPs) and setting minimum guidelines to better suit lotic systems in their current state is needed. Incorporating ecosystem monitoring to adapted BMPs and fostering land stewardship with private landowners can be an effective approach in improving river ecosystems in agricultural catchments. In addition, we recommend future studies investigate riparian conditions across seasons to better understand influences and indicators of change. We propose that by having well-vegetated, wide riparian corridors (>20 m), with rocks on banks, shrubs, and minimal bare soil on banks, and with continued monitoring for protection, improvements could be observed over time.
Author Contributions
W.L.V. and N.D.M. developed the concept for the paper. W.L.V., N.D.M., C.R.W. and J.C.-B. participated in field work consisting of stream surveys. W.L.V., D.F.S. and S.B. performed the analyses, and W.L.V. and R.H.G. led the writing of the paper. All authors will edit the manuscript and eventually accept the submitted version. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This project was funded by the Minnesota’s Environment and Natural Resources Trust Fund, as recommended by the Legislative-Citizen Commission on Minnesota Resources (M.L. 2017, Chp. 96, Sec. 2, Subd. 04d/Water Quality Monitoring in Southeastern Minnesota Trout Streams).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study did not require approval of an institutional review board.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available directly from the authors per reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We thank the private landowners who granted us permission to access the river for this study. T. Biederman, O. Graziano, and others that assisted with stream surveys. We also thank two anonymous reviewers for their commentary which ultimately improved the clarity, focus, and readability of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wohl, E. Forgotten Legacies: Understanding and Mitigating Historical Human Alterations of River Corridors. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 5181–5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, A.M. The impact of environmental change and human land use in alluvial valleys in the Loess Plateau of China during Middle Holocene. Geomorphology 2008, 101, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotterweich, M. The history of human-induced soil erosion: Geomorphic legacies, early descriptions and research, and the development of soil conservation-A global synopsis. Geomorphology 2013, 201, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimble, S.W. Historical Agriculture and Soil Erosion in the Upper Mississippi Valley Hill Country; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, A.G. Learning from the past: Palaeohydrology and palaecology. Freshw. Biol. 2002, 47, 817–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenfert Kroese, J.; Batista, P.V.G.; Jacobs, S.R.; Breuer, L.; Quinton, J.N.; Rufino, M.C. Agricultural land is the main sources of stream sediments after conversion of an African montane forest. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graziano, M.P.; Deguire, A.K.; Surasinghe, T.D. Riparian Buffers as a Critical Landscape Feature: Insights for Riverscape Conservation and Policy Renovations. Diversity 2022, 14, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimble, S.W., Jr.; Sartz, R.S. How far from a stream should a logging road be located? J. For. 1957, 55, 339–341. [Google Scholar]
- Froehlich, W. Sediment production from unmetalled road surfaces. In Sediment and Stream Water Quality in a Changing Environment: Trends and Explanations; IAHS Publication: Wallingford, UK, 1991; Volume 203, pp. 21–30. [Google Scholar]
- Wolter, A.; Ward, B.; Millard, T. Instability eight sub-basins of the Chilliwack River Valley, British Columbia, Canada; a comparison of natural and logging-related landslide. Geomorphology 2010, 120, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolman, M.G. A cycle of sedimentation and erosion in urban river channels. Geogr. Ann. Ser. A Phys Geogr. 1967, 49, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, S.V.; Swanson, F.J.; McKee, W.A.; Cummins, K.W. An ecosystem perspective of riparian zones. BioScience 1991, 41, 540–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusey, B.J.; Arthington, A.H. Importance of the riparian zone to the conservation and management of freshwater fish: A review. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2003, 54, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naiman, R.J.; Decamps, H. The ecology of interfaces: Riparian zones. Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1997, 28, 621–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannote, R.L.; Minshall, G.W.; Cummins, K.W.; Sedell, J.R.; Cushing, C.E. The river continuum concept. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1980, 37, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junk, W.J.; Bayley, P.B.; Sparks, R.E. The flood-pulse concept in river-floodplain systems. Can. Spec. Publ. Fish. Aqua. Sci. 1989, 106, 110–127. [Google Scholar]
- Anbumozhi, V.; Radhakrishnan, J.; Yamaji, E. Impact of riparian buffer zones on water quality and associated management considerations. Ecol. Eng. 2005, 24, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stutter, M.; Kronvang, B.; Huallachain, D.O.; Rozemeijer, J. Current insights into the effectiveness of riparian management, attainment of multiple benefits, and potential technical enhancements. J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, J.A.; Rishel, G.B.; Corbett, E.S. Thermal alteration of streams draining clearcut watersheds: Quantification and biological implications. Hydrobiologia 1984, 111, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakley, A.L.; Collins, J.; Everson, L.; Heller, D.; Howerton, J.; Vincent, R. Riparian zones and freshwater wetlands. In Management of Wildlife and Fish Habitats in Forest of Western Oregon and Washington; US Department of Agriculture, Forest Service: Portland, OR, USA, 1985; pp. 57–80. [Google Scholar]
- Everett, R.A.; Ruiz, G.M. Coarse woody debris as a refuge from predation in aquatic communities. Oecologia 1993, 93, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedell, J.R.; Reeves, G.H.; Hauer, F.R.; Stanford, J.A.; Hawkins, C.P. Role of refugia in recovery from disturbance: Modern fragmented and disconnected river systems. Environ. Manag. 1990, 14, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fremier, A.K.; Kiparsky, M.; Gmur, S.; Aycrigg, J.; Craig, R.K.; Svancara, L.K.; Goble, D.D.; Cosens, B.; Davis, F.W.; Scott, J.M. A riparian conservation network for ecological resilience. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 191, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, J.R.; Fryirs, K.A.; Lenz, T.; Leishman, M.R. Heterogeneous flows foster heterogeneous assemblages: Relationships between functional diversity and hydrological heterogeneity in riparian plant communities. Freshw. Biol. 2015, 60, 2208–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellnitz, T.; Poff, N.L. Functional redundancy in heterogeneous environments: Implications for conservation. Ecol. Lett. 2001, 4, 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotschy, K.; Biggs, R.; Daw, T.; Folke, C.; West, P. Principle 1—Maintain diversity and redundancy. In Principles for Building Resilience: Sustaining Ecosystem Services in Social-Ecological Systems; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2015; pp. 50–75. [Google Scholar]
- Mundahl, N.D.; Varela, W.L.; Weaver, C.; Mundahl, E.D.; Cochran-Biederman, J.L. Stream habitats and aquatic communities in an agricultural watershed: Changes related to a mandatory riparian buffer law. Environ. Manag. 2023, 5, 945–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jowett, L.G.; Richardson, J.; Boubée, J.A.T. Effects of riparian manipulation on stream communities in small streams: Two case studies. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2009, 43, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.M. Riparian pasture retirement effects on sediment, phosphorous and nitrogen in channelised surface run-off from pastures. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1989, 23, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opperman, J.J.; Merenlender, A.M. The effectiveness of Riparian Restoration for Improving Fish Habitat in Four Hardwood-Dominated California Streams. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2004, 24, 822–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houston, W.A.; Black, R.L.; Wormington, K.R. Grasslands of cleared woodlands have lower invertebrate diversity and different assemblages to remnant woodlands in grazed landscapes of eastern Australia. J. Insect Conserv. 2023, 27, 999–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiens, J.A. Ecological heterogeneity: An ontogeny of concepts and approaches. In The Ecological Consequences of Environmental Heterogeneity; Blackwell Science: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Brierley, G.J. The socio-ecological river, Socio-economic, cultural and environmental relations to river systems. In Finding the Voice of the River: Beyond Restoration and Management; Springer International Publishing AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 29–60. [Google Scholar]
- Allan, J.D. Landscapes and riverscapes: The influence of land use on stream ecosystems. Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2004, 35, 257–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, L.J.; Peterson, G.D.; Bennet, E.M. Agricultural modifications of hydrological flows create ecological surprises. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2007, 23, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armour, C.L.; Duff, D.A.; Elmore, W. The effects of livestock grazing on riparian and stream ecosystems. Fisheries 1991, 16, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglin, W.; Fairchild, J. Potential toxicity of pesticides measured in midwestern streams to aquatic organisms. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 45, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, B. Water pollution by agriculture. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B 2008, 363, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McTammany, M.E.; Benfield, E.F.; Webster, J.R. Recovery of stream ecosystem metabolism from historical agriculture. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2007, 26, 532–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorp, J.H.; Thoms, M.C.; Delong, M.D. The Riverine Ecosystem Synthesis: Toward Conceptual Cohesiveness in River Science; Academic Press: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Matson, P.A.; Parton, W.J.; Power, A.J.; Swift, M.J. Agricultural intensification and ecosystem properties. Science 1997, 277, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitewater River Watershed Project. A History of the Whitewater Watershed in Minnesota; Whitewater River Watershed Project: Lewiston, MI, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Trout Unlimited. The Economic Impact of Trout Angling in the Driftless Area; Trout Unlimited: Denver, CO, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nerbonne, B.A.; Vondracek, B. Effects of local land use on physical habitat, benthic macroinvertebrates, and fish in the Whitewater River, Minnesota, USA. Environ. Manag. 2001, 28, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, M.A.; Vondracek, B. Spring distributions and relationships with land cover and hydrogeologic strata in a karst landscape in Winona County, Minnesota, USA. Carbonates Evaporites 2010, 25, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, W.L.; Mundahl, N.D.; Bergen, S.; Staples, D.F.; Cochran-Biederman, J.; Weaver, C.R. Physical and Biological Stream Health in an Agricultural Watershed after 30+ Years of Targeted Conservation Practices. Water 2023, 15, 3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnesota Pollution Control Agency. Mississippi River (Winona) Watershed Monitoring and Assessment Report; Minnesota Pollution Control Agency: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Platts, W.S.; Megahan, W.F.; Minshall, G.W. Methods for Evaluating Stream, Riparian, and Biotic Conditions; Intermountain Forest and Range Experiment Station Technical Report INT-138; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service: Portland, OR, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Zar, J.H. Biostatistical Analysis; Prentice Hall Inc.: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Rencher, A.C.; Christensen, W.F. Methods of Multivariate Analysis, 3rd ed.; Wiley Series in Probability Statistics; John Wiley and Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Degani, A.; Shafto, M.; Olson, L. Canonical correlation analysis: Use of composite heliographs for representing multiple patterns. In Diagrammatic Representation and Inference, Proceedings of the International Conference on Theory and Application of Diagrams, Stanford, CA, USA, 28–30 June 2006; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 93–97. [Google Scholar]
- Mundahl, N.D.; Mundahl, E.D. Aquatic community structure and stream habitat in a karst agricultural landscape. Ecol. Process. 2022, 11, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, A.G.; Bailey, R.C.; Schwindt, J.A. Effectiveness of best management practices in improving stream ecosystem quality. Hydrobiologia 2007, 583, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, L.S.; Felton, Z.G.K.; Russek-Cohen, E. Use of Maryland biological stream survey data to determine effects of agricultural riparian buffers on measure of biological stream health. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2006, 117, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meleason, M.A.; Gregory, S.V.; Bolte, J.P. Implications of Riparian Management Strategies on Wood in Streams of the Pacific Northwest. Ecol. Appl. 2003, 13, 1212–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabacchi, E.; Correll, D.L.; Hauer, R.; Pinay, G.; Planty-Tabacchi, A.M.; Wissmar, R.C. Development, maintenance, and role of riparian vegetation in the river landscape. Freshw. Biol. 1998, 40, 497–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, K.W.; Schultz, R.C.; Mabry, C.M.; Isenhart, T.M. Ability of remnant riparian forests, with and without grass filters, to buffer concentrated surface runoff. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2010, 46, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duehr, J.P.; Siepker, M.J.; Pierce, C.L.; Isenhart, T.M. relation of riparian buffer strips to in-stream habitat, macroinvertebrates and fish in a small Iowa stream. J. IOWA Acad. Sci. 2006, 113, 101–107. [Google Scholar]
- Tapsell, S.M. River restoration: What are we restoring to? A case study of the Ravensbourne river, London. Landsc. Res. 1995, 20, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohl, E.; Lane, S.N.; Wilcox, A.C. The science and practice of river restoration. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 5974–5997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, M.A.; Menninger, H.; Bernhardt, S.E. River restoration, habitat heterogeneity and biodiversity: A failure of theory or practice? Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidon, P.G.; Welsh, M.K.; Hassanzadeh, Y.T. Twenty Years of Riparian Zone Research (1997–2017): Where to Next? J. Environ. Qual. 2018, 48, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroll, S.A.; Oakland, H.C. A review of studies documenting the effects of agricultural best management practices on physiochemical and biological measure of stream system integrity. Nat. Areas J. 2019, 39, 58–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, N.J.T.; Yates, A.G. Agricultural best management practices abundance and location does not influence stream ecosystem function of water quality in the summer season. Water 2015, 7, 6861–6876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, L.A. Legacy sediment: Definitions and processes of episodically produced anthropogenic sediment. Anthropocene 2013, 2, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, L. South Branch Whitewater River Unified Fish Kill Response; Minnesota Department of Agriculture: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2015; 367p. [Google Scholar]
- Tornlund, E.; Ostlund, L. Floating timber in northern Sweden: The construction of floatways and transformation of rivers. Environ. Hist. 2002, 8, 85–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brierley, G.J.; Brooks, A.P.; Fryirs, K.; Taylor, M.P. Did humid-temperate rivers in the Old and New Worlds respond differently to clearance of riparian vegetation and removal of woody debris? Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2005, 29, 27–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pišút, P. Channel evolution of the pre-channelized Danube River in Bratislava, Slovakia (1712–1886). Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2002, 27, 369–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.D.; Park, L. Forest blowdown impacts of Hurricane Rita on fluvial systems. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2009, 34, 1069–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, M.J.; Harding, J.S.; Niyogi, D.K.; McIntosh, A.R. Improving the effectiveness of riparian management for aquatic invertebrates in a degraded agricultural landscape: Stream size and land-use legacies. J. Appl. Ecol. 2012, 49, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, J.M.; Williamson, R.B.; Smith, R.K.; Vickers, M.V. Effects of riparian grazing and channelisation on streams in Southland, New Zealand. 2. Benthic Invertebrates. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1992, 26, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunn, S.E.; Davies, P.M.; Mosisch, T.D. Ecosystem measures of river health and their response to riparian and catchment clearing. Freshw. Biol. 1999, 41, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walser, C.A.; Bart, H.L., Jr. Influence of agriculture on instream habitat and fish community structure in Piedmont watersheds of the Chattahoochee River system. Ecol. Freshw. Fish. 1999, 8, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinn, C.R.; Kilgore, M.A. Riparian Management Practices: A summary of state guidelines. J. For. 2001, 99, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- McKergow, L.A.; Matheson, F.E.; Quinn, J.M. Riparian management: A restoration tool for New Zealand streams. Ecol. Manag. Restor. 2016, 17, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, B.; Reich, P.; Cavagnaro, T.; Lake, P.S. Challenges in applying scientific evidence to width recommendations for riparian management in agricultural Australia. Ecol. Manag. Restor. 2015, 16, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welcomme, R.L. Fisheries Ecology of Floodplain Rivers; Longman: London, UK, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Death, R.G.; Collier, K.J. Measuring stream macroinvertebrate responses to gradients of vegetation cover: When is enough enough? Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 1447–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, S.V. Riparian management in the 21st century. In Creating a Forestry for the 21st Century: The Science of Ecosystem Management; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; pp. 69–86. [Google Scholar]
- Boothroyd, I.K.G.; Langer, E.R. Forest Harvesting and Riparian Management Guidelines: A Review; Technical Report 56; National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research: Hamilton, New Zealand, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Majer, J.D.; De Sousa-Majer, M.J.; Heterick, B.E. Partial clearing of a road corridor leads to homogenisation of the invertebrate fauna. Pac. Conserv. Biol. 2021, 27, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovett, G.M.; Burns, D.A.; Driscoll, C.T.; Jenkins, J.C.; Mitchell, M.J.; Rustad, L.; Shanley, J.B.; Likens, G.E.; Haeuber, R. Who needs environmental monitoring? Front. Ecol. Environ. 2007, 5, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swartz, A.; Roon, D.; Reiter, M.; Warren, D. Stream temperature responses to experimental riparian canopy gaps along forested headwaters in western Oregon. For. Ecol. Manag. 2020, 474, 118354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuglerová, L.; Muotka, T.; Chellaiah, D.; Jyväsjärvi, J.; Richardson, J.S. Protecting our streams by defining measurable targets for riparian management in a forestry context. J. Appl. Ecol. 2024, 61, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, M.L.; Acuña, V.; Bauer, D.M.; Bell, K.P.; Calhoun, A.J.K.; Felipe-Lucia, M.R.; Fitzsimons, J.A.; González, E.; Kinnison, M.; Lindenmayer, D.; et al. Conserving small natural features with large ecological role: A synthetic overview. Biol. Conserv. 2017, 211, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, E.; Felipe-Lucia, M.R.; Bourgeois, B.; Boz, B.; Nilsson, C.; Palmer, G.; Sher, A.A. Integrative conservation of riparian zones. Biol. Conserv. 2017, 211, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garssen, A.G.; Verhoeven, J.T.A.; Soons, M.B. Effects of climate-induced increases in summer drought on riparian plant species: A meta-analysis. Freshw. Biol. 2014, 59, 1052–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, G.L.; Friedman, J.M.; Beatty, S.W. Delayed effects of flood control on a flood-dependent riparian forest. Ecol. Appl. 2005, 15, 1019–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).