Abstract
This study investigates the densification/granulation of activated sludge with poor settleability, treating real industrial wastewater from a tank truck cleaning company. The wastewater is low in nutrients, acidic in nature, and high and variable in chemical oxygen demand (COD, ranging from 2770 mg·L−1 to 14,050 mg·L−1). A microbial selection strategy was applied to promote slow-growing glycogen-accumulating microorganisms (GAO) by the implementation of an anaerobic feast/aerobic famine strategy in a sequencing batch reactor (SBR). After 60 to 70 days, the uptake of carbon during the anaerobic phase exceeded 80%, the sludge morphology improved, and the sludge volume index (SVI) dropped below 50 mL·g−1. 16S rRNA gene sequencing showed the enrichment of the GAOs Defluviicoccus and Candidatus Competibacter. Stable sludge densification was maintained when using a constant organic loading rate (OLR) of 0.85 ± 0.05 gCOD·(L·d)−1, but the sludge quality deteriorated when switching to a variable OLR. In view of the integration of densified/granular sludge in a membrane bioreactor configuration, the filtration properties of the densified SBR sludge were compared to the seed sludge from the full-scale plant. The densified sludge showed a significantly lower resistance due to pore blockage and a significantly higher sustainable flux (45 vs. 15 L·(m2·h)−1).
1. Introduction
The activated sludge (AS) process is widely used in the biological treatment of domestic and industrial wastewater for the removal of organic matter (C) and nutrients (mainly, nitrogen (N) and phosphorous (P)) [1]. The AS process consists of two tanks, namely the aeration tank, where the biological reactions take place, followed by the secondary settling tank, where sludge is separated from the effluent by sedimentation. After settling, the effluent is discharged, and sludge is recycled back into aeration tank. Sludge separation from the effluent represents a significant challenge in AS processes and affects about 50% of biological wastewater treatment plants worldwide [2]. In Flanders (Belgium), one-third of biological wastewater treatment plants are facing problems due to sludge bulking [3]. The reasons for sludge bulking are nutrient deficiency, limited oxygen supply, low organic load rate (OLR), and low pH (<6.5). Besides these, the slow feeding of readily biodegradable COD (rbCOD) under aerobic conditions also negatively impacts sludge settling [4].
To control sludge bulking, both unspecific (curative) and specific (selector-based) preventive strategies are applied. Unspecific methods involve chemicals such as chlorine (Cl2), ozone (O3), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), iron, or aluminum salts to eliminate filamentous microorganisms extending from the flocs [5]. However, they have drawbacks like being temporary solutions and often negatively affecting nitrifiers, denitrifiers, and polyphosphate-accumulating organisms (PAOs) [6,7]. A selector is a small tank placed upstream from the main aeration tank that receives recycled sludge and influent wastewater, resulting in a high substrate concentration. The principle of aerobic selectors is based on the premise that creating a high food-to-microorganism ratio (F/M) to low F/M ratio gradient generates a ‘feast’-to-‘famine’ regime. The high substrate availability during the feast phase promotes preferential growth and simultaneous substrate storage by floc-forming microorganisms. The stored substrate is then used for growth in the famine phase when the F/M ratio decreases, granting these organisms a competitive advantage [8]. Aerobic selectors need to be operated at high F/M ratios of 3–12 gCOD·(gVSS·d)−1 [9]. The quality of the organic matter also plays a role in the effectiveness of aerobic selectors, and the presence of high amounts of particulate organic matter (POM) can be harmful to its performance. Anaerobic selectors select for floc-forming bacteria that store rbCOD and use the stored substrate for growth in the subsequent aerobic phase. Filamentous bacteria lacking substrate storage capacity under anaerobic conditions are then outcompeted [10].
The anaerobic feast and aerobic famine regimes favor the selection of slow-growing microorganisms such as PAOs and glycogen-accumulating organisms (GAOs), which are the main contributors to granulation [11,12,13]. The growth of PAOs and GAOs is enhanced by the availability of rbCOD in the influent [14]. In the anaerobic selector, the sludge in suspension contacts the influent, where rbCOD is fully utilized and converted to polyhydroxyalkoate (PHA). In the subsequent aerobic phase, these PHAs are oxidized for microbial growth [15]. The densification of the sludge is not only based on the anaerobic uptake of rbCOD, but it should also be concentrated on the best settling fraction of the sludge. In the bottom feeding strategy, both conditions are fulfilled, as there is a higher probability that the best-settling sludge will remain on the sludge bed. This process design results in well-settling dense sludge, which is further improved by selective discharge of the worst-settling sludge. The leakage of rbCOD into the aerobic phase, either directly or through the hydrolysis of POM, favors the growth of ordinary heterotrophic organisms (OHOs), which is detrimental to granulation. According to one study, a 20% leakage of rbCOD into the aerobic phase has no detrimental effect on the settling of granular sludge [16].
Aerobic granular sludge (AGS) is an innovative technology for industrial and domestic wastewater treatment. AGS has a dense, compact, and spherical structure and high biomass retention as compared to conventional floccular AS [17]. Also, AGS has easy dewaterability, which improves the quality of the effluent. These properties give a higher settling velocity (18–40 mph), which eliminates the requirement of a secondary clarifier tank [18]. Due to the compact size, the AGS reactor needs 25–30% less energy and 50–75% lower land footprint. These microenvironments help diverse microbial communities to coexist in a single granule, which makes a granule a hub of mini-ecosystems. This diversity of microorganisms leads to the removal of organic matter, nitrogen, and phosphorus in a single AGS reactor [19]. In AS, the COD is oxidized directly, while, in AGS, the COD is first converted to storage polymers and then oxidized. In addition, due to the large granule size, aerobic and anoxic zones coexist, which allows for simultaneous nitrification and denitrification.
There are many factors that affect the cultivation of AGS, such as the feeding strategy, the type of substrate, and the organic loading rate (OLR). The OLR, which depends on the strength of wastewater, ranges from 0.6 to 24 gCOD·(L·d)−1 for AGS cultivation [20]. A high OLR results quickly in large but unstable granules, while a low OLR slowly forms small and compact granules, sometimes failing too [21]. When the OLR is changed during a reactor operation, an imbalance between the feast and the famine phase may occur, which gives an opportunity to filamentous microorganisms to proliferate at the cost of slow-growing microorganisms, leading to worsening of the sludge structure [22]. The change in the microbial community thus influences the granule stability, as well as the performance of the reactor. In a previous study by Adav et al. [23], the stepwise increase of the OLR from 9 gCOD·(L·d)−1 to 12 gCOD·(L·d)−1 led to a loss of microbial diversity, and a high OLR functional microbial community was selected.
Over the last decade, membrane bioreactors (MBRs) have gained attention due to their small footprint, excellent effluent properties, the ability to withstand high OLR, and the application of a high sludge concentration [24]. In MBRs, activated sludge processes are combined with membrane filtration to separate the effluent from sludge. However, membrane biofouling is the main barrier for the wide application of MBR technology, as this increases its operational and maintenance costs [25,26]. The sludge properties that cause biofouling are the mixed liquor suspended solids (MLSSs) concentration, the particle size of flocs, the soluble microbial products (SMPs), and the extracellular polymers substances (EPSs) [27].
To mitigate the fouling problem of conventional MBRs, the aerobic granular sludge membrane bioreactor (AGMBR) concept has been proposed as an alternative. AGMBR combines AGS and MBR for municipal and industrial wastewater treatment [28]. Due to its granular and larger structure, AGS is believed to reduce pore blockage and to form a loose cake layer, ultimately leading to increased permeability [29]. One study showed that, under the same conditions, conventional MBRs have 27-times higher fouling rates than AGMBRs [30]. The reason for the better filtration properties of AGS is due to its higher hydrophobicity than conventional AS [28]. In addition, AGMBR can be operated at higher sludge concentrations (up to 20 g·L−1) [31].
Using anaerobic feast/aerobic famine conditions, AGS have been cultured in SBR for the treatment of different industrial WW, such as the tank truck cleaning industry [32], dyeing industry [33], potato processing industry [34], and brewery industry [35]. However, to the best of our knowledge, there is no study available that shows aerobic granulation with the application of a microbial selection strategy only when treating high strength and variable industrial WW and how this strategy impacts the sludge filtration properties in a MBR.
This study investigates the densification of sludge with poor settleability, originating from a full-scale tank truck cleaning company (TTC) usually transporting chocolates and beverages. The wastewater originating from the TTC is low in nutrients, acidic in nature, and high and variable in COD. In addition, the evolution of the filterability of the sludge was determined to study the effect of the densification strategy on the filtration properties.
2. Methods
2.1. Laboratory-Scale SBR Reactor Set Up
A lab-scale SBR with a working volume of 10 L and height-to-diameter ratio = 1 was operated for 165 days at room temperature (20 ± 3 °C). The SBR reactor was equipped with a mechanical stirrer (RZR2020, Heidolph Instruments, Schwabach, Germany) to keep the sludge in suspension, and its speed was 120 revolutions per minute (rpm). A feeding pump (ES-B16VC-3, IWAKI, Tokyo, Japan), a discharge valve (Eriks RX10.X33.S00, ERIKS, Berchem, Belgium), a 13-cm diameter aeration disc (Aquadistri), and an aeration pump (Super Fish Koi Flow 60, Aquadistri, Klundert, The Netherlands) were also used for the stable operation of the reactor. Process operation was controlled by a Siemens PLC and a custom-built LABVIEW™ program (National instruments, Austin, TX, USA). A luminescent dissolved oxygen (LDO) sensor (Hach, Loveland, CO, USA) was used, and the DO level was kept between 1 and 4 mgO2·L−1 during the aerobic phase.
The seed-activated sludge for the SBR reactor was taken from a full-scale TTC plant. At the start of the experiment, when the sludge properties such as settling, dewaterability, and filterability were not good, the anaerobic feeding step (of 300 min) was followed by an (unfed) anaerobic reaction step (of 180 min) and an aerobic reaction step (of 860 min). The hydraulic retention time (HRT) varied between 4 and 9 days, depending upon the COD of the influent. After day 55, when the sludge properties improved, the anaerobic reaction was reduced to 60 min, while the aerobic reaction was increased to 1020 min. From days 69 to 130, a constant OLR was applied. The OLR was kept constant at a value of approximately 0.85 ± 0.05 gCOD·(L·d)−1 by adjusting the volume fed to the reactor. The volume of wastewater fed varied between 1.1 L·d−1 and 2.4 L·d−1, depending on the influent COD. From day 130 onward, a variable OLR was applied to investigate its effect on the sludge characteristics and the reactor performance. At this stage, a fixed volume of wastewater was fed (2 L·d−1). The 24-h SBR reactor cycle ended with settling (55 min) and discharge (4 min). The sludge retention time (SRT) was held constant at approximately 30 days by wasting mixed sludge daily from the reactor. The reactor was fed with the real TTC wastewater.
2.2. Set Up of Membrane Filtration Unit
A lab-scale membrane microfiltration unit was used to quantify the sludge filtration properties. A Kubota A4 size membrane (Type 510 cartridge, Osaka, Japan, with a surface area of 1040 cm2 and average pore size of 0.2 µm) was used in a submerged design inside a Plexiglas cascade. An air pump (Aqua Forte V-30, SIBO BV, Doornhoek, The Netherlands) was used to supply air through a bubble aerator at the bottom of the reactor. To recycle the filtered effluent, a peristaltic pump (Heidolph 5101, Schwabach, Germany) was used. To control the filtration process, a custom-built LABVIEW™ program (National Instruments) was used. Different fluxes were applied stepwise for sludge filtration, ranging from 5 L·(m2·h)−1 to 55 L·(m2·h)−1 with an air flowrate between 3.5 and 4 m·s−1. The flux of each magnitude was run twice with equal time intervals to check for irreversible fouling. The average transmembrane pressure (TMPavg), permeability, fouling rate (FR), and sustainable flux were calculated as mentioned by Tsertou et al. [36]. FR is an increase in the TMP as a function of time. It is calculated as the slope of TMP to time in minutes.
A clean water filtration test was carried out before (CW1) and after (CW2) the sludge filtration test. The CW filtration tests were carried out at a single flux rate of 55 L·(m2·h)−1 for 10 min, while the sludge filtration test was carried out at different flux ranges from 5 to 55 L·(m2·h)−1 (Figure 1). During the sludge filtration test, the flux was increased in steps of 10 min each. After each step, a relaxation time of 5 min was allowed to remove the reversible cake layer by air flushing. At the end of the sludge filtration test, the membrane was gently washed with demineralized water to remove the cake layer. By manually removing the cake layer, the cake layer resistance is assumed to be 0. In our experiment, variable flux was used to investigate its effect on TMP change. The sludge filtration allows the estimation of the different contributors to the total membrane resistance, based on the clean water tests CW1 and CW2.
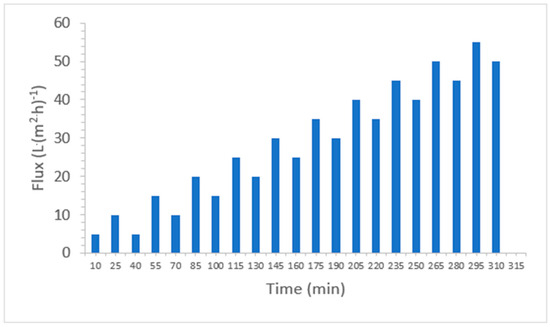
Figure 1.
Flux profile for sludge filtration.
To determine the membrane resistance, Darcy’s Law [37] was used:
where Rt is the total resistance, Rm is the membrane resistance, Rf is the fouling resistance, Rp is the resistance by pore blocking, Rc is the cake layer resistance, and µ is the viscosity of the demineralized water (µ = 0.001 Pa·s). As the cake layer was removed manually, Rc is assumed to be 0.
Rt = Rm + Rf = Rm + Rp + Rc = Rm +Rp + 0
Rt = Rm + Rp
Rp = Rt − Rm
2.3. Analytical Techniques
For the measurement of the influent and effluent parameters in the low range (Test 0-36 COD LR 150) for soluble COD (sCOD) and high range (Test 0-38 COD HR 1500) for total COD, a volatile fatty acid (VFA) test kit (Test-050 Ref: 985050), total nitrogen (Test-083 Ref: 985083), and total phosphorus (Test-080 Ref: 985080) test kits from Macherey-Nagel (Duren, Germany) were used. A Sievers InnovOx laboratory total carbon analyzer (Veolia, Aubervilliers, France) was used to measure the DOC. Nutrients were measured using an AQ300 discrete analyzer (SEAL Analytical, Inc., Southampton, UK). A pH meter of Hanna Instruments (HI 991003, Temse, Belgium) was used for pH measurement and a turbidimeter (Hach, Germany) for turbidity. All samples (except total COD) were filtered on 1.2-µm microfiber glass filters (VWR International, Leuven, Belgium) prior to analyses.
For the sludge analyses, biomass concentrations such as mixed liquor (volatile) suspended solids (ML(V)SSs) and the (diluted) sludge volume index ((D)SVI) were measured according to the standard method (APHA 1998). For the DSVI, the dilution factor was 2 times with the effluent. Sludge morphology was analyzed using an Olympus microscope (CX 43, Tokyo, Japan) with a bright field and phase contrast. The capillary suction time (CST) of the sludge was determined using a type 304B (Essex, UK).
2.4. In Situ DOC Substrate Removal
In situ DOC removal experiments were carried out regularly to determine the DOC removal during the anaerobic feeding and reaction step. Samples were taken at the start of the anaerobic feeding step and just before the end of the anaerobic phase. All sludge samples were filtered by fiberglass filter before analysis. The following formula was used to calculate the DOC removal during the anaerobic step:
DOCs is DOC right after feeding, DOCe is the DOCs at the end of the anaerobic step, and DOCc is the DOCs at the end of the SBR cycle.
2.5. DNA Extraction and Bacteria 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
To extract DNA from the nine activated sludge samples, 0.50 mL of each sample was processed using the FastDNA Spin Kit for Soil (MP Biomedicals, Santa Ana, CA, USA), following the manufacturer’s instructions. The frozen samples were then shipped to DNAsense ApS (Aalborg, Denmark) for library preparation, sequencing, and bioinformatics processing. The gene amplicon sequencing targeted the bacterial 16S rRNA gene variable regions 1–8 (bV18-A); after which, a taxonomic classification was conducted against the MiDAS 5.2 database. A custom DNAsense ApS (Aalbor, Denmark) protocol was used to prepare amplicon libraries for the 16S rRNA gene variable regions 1–8 (bV18-A) sequencing. Up to 25 ng of extracted DNA served as the basis for PCR amplification, each sample receiving custom 24 nt barcode sequence forward and reverse primers. The resulting amplicon libraries were purified using the standard protocol for CleanNGS SPRI beads (CleanNA, Waddinxveen, The Netherlands) and then prepared using the SQK-LSK114 kit (Oxford Nanopore Technologies, Oxford, UK), according to the manufacturer’s instructions, in addition to a few modifications. Next, the sequencing library was loaded onto a PromethION R10.4.1 flow cell and sequenced using MinKNOW 23.11.4 software (Oxford Nanopore Technologies, UK). Reads were base-called and demultiplexed with MinKNOW Dorado 7.2.13. The project also utilized DNASense’s custom bioinformatics workflow (version MGA_ONT_DS240221) for bioinformatics processing. The sequencing reads in the fastq files were first filtered for length and quality and then mapped to the QIIME-formatted MiDAS version 5.2 database. Further bioinformatics processing was conducted using RStudio IDE (2023.12.1.402), running R version 4.3.2 (2023-10-31) and employing R packages such as ampvis2 (2.8.7).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of the Industrial Wastewater
The TTC deals with the cleaning of tanks that transport various types of brewery and chocolate, generating highly variable wastewater. The lab-scale SBR was fed with 18 different batches of influent wastewater with COD values ranging from 14,050 mg·L−1 to 2770 mg·L−1 (Figure 2). The average total COD was 5967 mg·L−1 (standard deviation (SD) = 2437 mg·L−1, %CV = 42%), and the average soluble COD (sCOD) was 5135 mg·L−1 (SD = 2122 mg·L−1, %CV = 42%). On average, the sCOD was 86% of the total COD. The average ratio of COD to dissolved organic carbon (DOC) was 3.2. The influent wastewater was acidic, with an average pH of 3.22. Therefore, the pH was adjusted to 7 by using 1 M NaOH. A COD:N:P ratio of 100:3:0.5 was applied to provide nutrients by adding NH4Cl and K2HPO2.
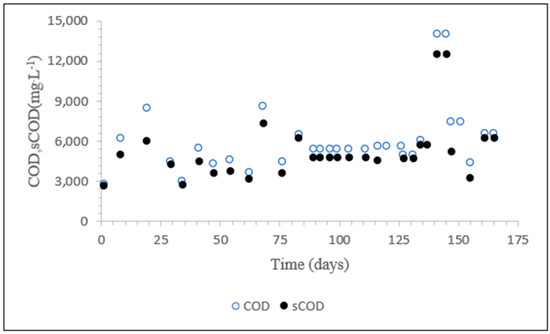
Figure 2.
COD values of all batches of influent wastewater collected from the full-scale TTC company.
Figure 3 shows the evolution of the OLR values. The OLR was not constant when the reactor was started with the seed sludge. The initial MLSS values of the sludge were high, and sludge washout was observed due to poor sludge settling. When the sludge settling improved on day 69 (SVI30 = 113 mL·g−1), a constant OLR of 0.85 ± 0.05 gCOD·(L·d)−1 was applied by varying the volume of the influent feed. After day 130, a variable OLR was applied by a constant daily feed of 2 L influent into the reactor.
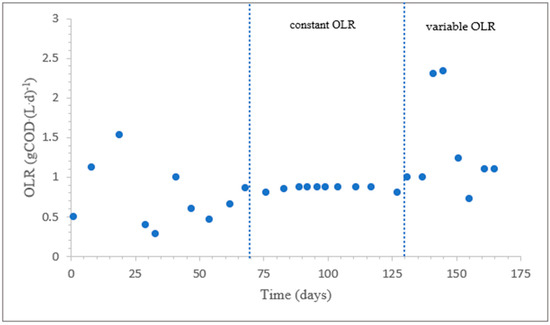
Figure 3.
Evolution of the OLR values.
3.2. In Situ DOC Removal
The purpose of the anaerobic feeding and reaction step is to allow uptake of the readily biodegradable organic carbon by the substrate storing organism. During feeding, the high concentration of substrate in the feed penetrates the entire depth of the sludge. Under anaerobic conditions, this readily biodegradable COD is converted into storage polymers such as PHA and glycogen by PAOs and GAOs [38]. When oxygen is supplied to the microorganisms in the subsequent aerobic phase, the internally stored polymers are slowly consumed for the production of a new biomass. As the growth of heterotrophic microorganisms on storage polymers is low compared to their growth rate on readily biodegradable carbon substrate, stable and dense granulation is possible. If the readily biodegradable substrate would not be converted to storage polymers in the anaerobic phase, the granule structure will be fluffy, and filamentous bacteria may be stimulated [21].
At the beginning of the experiment, the total anaerobic phase lasted 480 min, and the anaerobic DOC removal was 47% (Figure 4), which means more than half of the biodegradable substrate entered the aerobic phase. At this stage, the sludge was highly flocculated, and its sedimentation was poor (SVI30 = 155 mL·g−1). After a few days, the anaerobic DOC uptake decreased to 30% and then further to 24%. During this period, a decrease in MLSS was observed due to sludge washout. On day 35, the anaerobic DOC removal increased to 63%. On day 42, the DOC removal decreased slightly to 54%. However, the DOC removal efficiency soon reached 73% and then increased steadily to 94% on day 69. At this time, the filamentous microorganisms were almost gone from the sludge, the floc size increased, and the settling characteristics improved (see below). From day 69 to the end, the DOC removal efficiency during the anaerobic phase was over 84%. A constant OLR of 0.85 ± 0.05 gCOD·(L·d)−1 was applied from day 69 until day 130. During the constant OLR period, an average of 7.71 mg·L−1 of DOC leaked into the aerobic phase. After day 130, when a variable OLR was applied, an average of 11.45 mg·L−1 of DOC leaked into the anaerobic phase.
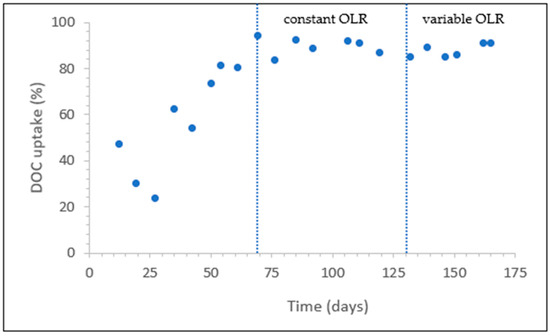
Figure 4.
Anaerobic DOC uptake.
3.3. Sludge Properties
3.3.1. Sludge Concentration ML(V)SS
The MLSS of the seed sludge was 11.7 g·L−1 and MLVSS was 9.6 g·L−1 (Figure 5). On day 4, the MLSS decreased to 6.65 g·L−1. The sudden decrease in the MLSS is attributed to washout of loose sludge flocs due to bad settling. The decline in MLSS continued until day 44, when it became stable. At this point, a SRT of 30 days was applied. From day 44 to day 98, the MLSS values were between 6 g·L−1 and 8.6 g·L−1. On day 140, the MLSS reached 10.4 g·L−1 when a high COD of 14,050 mg·L−1 was fed [39]. From day 145, the SRT was lowered to 25 days to reduce the sludge concentration for proper aeration. In Figure 5 the evolution of the ML(V)SS is given.
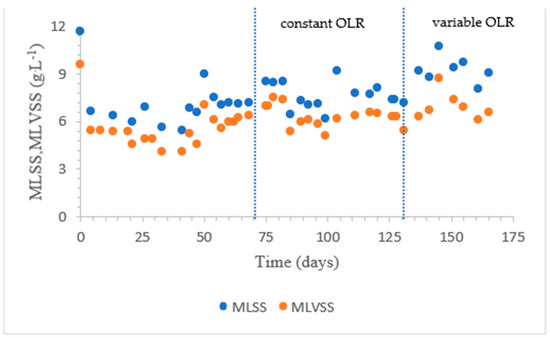
Figure 5.
Evolution of the ML(V)SS values.
3.3.2. Settleability
The change in settleability of the sludge is shown in Figure 6. The SVI30 of the seed sludge was 147 mL·g−1, but due to the high sludge concentration, this means it did not settle at all. The DSVI was 295 mL·g−1. From day 40, the sludge settleability improved gradually until day 70. On day 89, the SVI30 reached the value of 26 mL·g−1. The sludge settleability was stable until day 130 but then deteriorated when the reactor operation switched to the application of a variable OLR. Bad settling was caused by filamentous bulking, which continued to increase until day 166, as evidenced from microscopic analyses. Filamentous bulking resulted in poor settleability of the sludge (SVI30 values above 120 mL·g−1) [40].
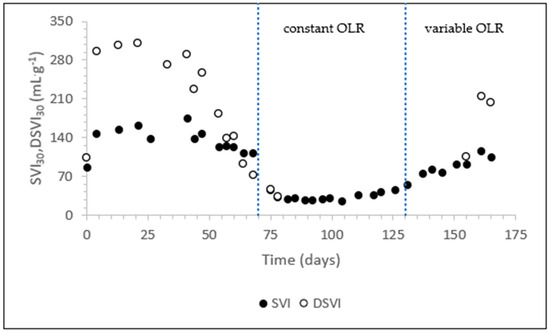
Figure 6.
The (D)SVI of the sludge.
3.3.3. CST
The CST of the sludge was measured regularly to characterize its dewaterability. The CST of the seed sludge was infinite. On day 4, the CST dropped to 543 s, and it decreased further to 48 s on day 13 and to 10 s on day 57. Afterwards, the CST value was almost stable at 11 s until the end of the study. A study by Wang et al. [41] showed that a larger floc size and lower amount of SMP are the main reasons for a low CST. It should be noted that a high CST is correlated to poor filtration properties and could result in elevated membrane fouling [42].
3.3.4. Microscopy
Microscopic analysis (Figure 7) was carried out to monitor the development of the sludge morphology. The structure of the flocs is an indicator of undesirable sludge characteristics. The seed sludge came from a plant where carbohydrate-rich influent is treated. The seed sludge on day 0 was free of filamentous microorganisms but had very small flocs. The complete absence of filamentous bacteria results in small, weak, and dispersed flocs [43]. On day 27, some filamentous growth appeared, which may aid in the granulation process [44]. On day 54, the flocs increased in size with the presence of a few filaments. On day 78, the filaments disappeared completely, and the flocs increased in size and were more compact in shape. During this period, the anaerobic DOC removal increased to 94% (Figure 4), indicating that the substrate had completely penetrated the flocs, resulting in smooth flocs. In addition, the settling characteristics of the sludge greatly improved during this time (SVI30 = 26 mL·g−1), as compact flocs have a high settling velocity. On day 117, some filaments reappeared on the flocs, and the size of the flocs also increased with the improved settling. On day 127, the OLR was changed from constant to variable mode. On day 151, after switching to a variable OLR operation, filaments dominated the sludge, and the settling capability deteriorated again [25]. The reason for the dominance of filamentous organisms during the variable OLR period was probably the availability of rbCOD and hydrolyzed products in the aerobic phase, as a higher amount of DOC (11.45 mg·L−1) leakage was observed in this period. The increased DOC leakage into the aerobic phase has harmful effects on densification [45,46].
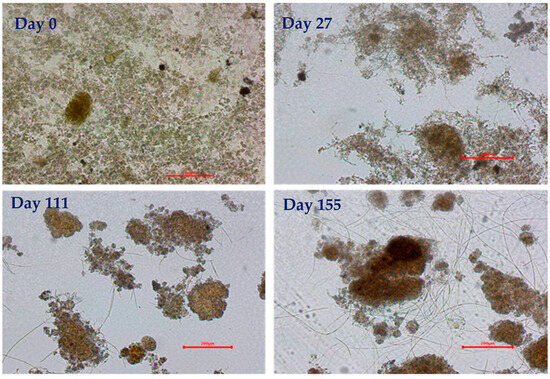
Figure 7.
Microscopic evaluation of the sludge for floc size and filamentous bacteria (scale bar = 200 µm).
3.3.5. Microbial Community
Microorganisms from the phylum Bacteriodota and Patescibacter were in abundance in the seed sludge. The most abundant genus was Ca. Epiflobacter from Bacteriodota and midas_g_8390 from Patescibacteria, with an abundance of 16.26%. The role of midas_g_8390 is still unclear, while Ca. Epiflobacter degrades proteins, polysaccharides, and complex molecules [47]. At the start, the flocs were small, and the sludge was facing a viscous bulking problem with no settling and infinite CST. On day 19, microorganisms from the phylum Bacteriodota were still predominant, with the OHO Terrimonas high in abundance, reaching 37.5%. The values of the CST, SVI, and anaerobic uptake were not good at this time. From day 60, the sludge morphology showed significant densification, the anaerobic DOC uptake was high, and the CST reached low values. During this time, the GAO Candidatus Competibacter became the most abundant GAO, followed by the genus Defluviicoccus. Candidatus Competibacter secretes EPS to form compact AGS [48,49]. The substrate of the second-most abundant GAO Defluviicoccus is propionate and butyrate, and the formation of alginate-like extracellular polymers are linked to Defluviicoccus [50,51]. The overall abundance of GAOs reached 8% on day 82. The flocs become denser and larger in size without any filaments. The overall abundance of the PAOs and GAOs reached 12% on day 117. The PAO Candidatus Accumulibacter appeared during the variable OLR phase and reached a maximum value of 0.23% on day 161. A study conducted by Caluwe et al. [52] to form hybrid granular sludge using microbial selection found that the PAO abundance was never more than 1%, and Defluviicoccous and Candidatus Competibacter were the common genera of the GAOs. These GAOs can store VFA and convert them into PHA under anaerobic conditions. The storage by GAOs of rbCOD under anaerobic conditions and preventing its leakage to the aerobic phase hinders filamentous organism growth. Another study conducted by Tsertou et al. [11] also found that Defluviicoccus and Candidatus Competibacter were the most common GAOs. A study carried out by Burzio et al. [53] found that Candidatus Competibacter was more dominant in AGS while treating complex synthetic water. Li et al. [51] found that the Defluviicoccus and Candidatus Competibacter abundance ranged from 16.88% to 39.31% in a successful AGS cultivation. A study by Begum et al. [54] showed that a high abundance of Defluviicoccus resulted in the deterioration of P-removal in the enhanced biological phosphorous removal (EBPR) system. The abundance of filamentous organisms was low until variable OLR was applied from day 130 onwards. The filamentous organisms Thiothrix and Leptothrix from the phylum proteobacteria appeared in the sludge and also affected the sludge morphology (Figure 6). Thiothrix is a common filamentous organism in WWTPs and its presence negatively correlates with settling. On day 161, the abundance of filamentous organisms reached 11%. The increase in abundance of filamentous MOs was related to the increase in SVI values, but the CST and the anaerobic DOC uptake values were not affected. In Table 1a–c, the abundances of GAOs, PAOs, and filamentous microorganisms are listed.

Table 1.
(a) Abundance of genera of the GAOs found in the SBR (%). (b) Abundance of genera of the PAOs found in the SBR (%). (c) Abundance of genera of the filamentous microorganisms found in the SBR (%).
3.4. Membrane Filtration Experiments
The membrane filtration process operates in two modes: the constant flux and the constant TMP modes. In the constant flux mode, the TMP rises as fouling occurs to maintain a constant flux. In the constant TMP mode, the permeability declines as a result of fouling to maintain a constant TMP. In our experiments, the constant flux mode is used for the filtration tests. For SBR sludge, the TMPavg increased with the increasing flux as the fouling potential increased. The minimum TMPavg of 0.9 mbar was observed at a flux of 5 L·(m2·h)−1, and the maximum TMPavg was observed at a flux of 55 L·(m2·h)−1, which was 29.4 mbar. The permeability first decreased and then increased at a flux rate of 15 L·(m2·h)−1. After the flux of 15 L·(m2·h)−1 was reached, the permeability decreased continuously and reached a minimum value at the flux of 55 L·(m2·h)−1. The permeability decreased as the flux rate increased and as the chances of fouling increased. When fouling occurs, the available pores for permeation become limited, which reduces the overall permeability [55]. For SBR sludge, the contribution of irreversible fouling to the initial permeability loss was almost 20%. During the relaxation step, a fraction of the cake layer was removed, which helped in regaining the permeability. At higher flux rates, the cake layers were probably too difficult to be removed completely during relaxation, leading to continuous permeability losses [56]. The sustainable flux (SF0.5) is the flux at which the fouling rate (FR) remains below the value of 0.5 mbar·min−1, as shown by Stes et al. [57]. The concept of sustainable flux is suitable to determine the practical and economic feasibility of the filtration processes. In SBR sludge filtration, the FR crossed the value of 0.5 mbar·min−1 at the flux of 50 L·(m2·h)−1. The SF0.5 value for the lab-scale SBR sludge was therefore 45 L·(m2·h)−1. The flocculent sludge from the full-scale TTC treatment plant showed very high values of TMPavg and FR and low values for permeability as compared to the lab-scale SBR cultivated sludge. First, the TMPavg increased steadily up to 10.1 mbar until a flux of 20 L·(m2·h)−1. The FR value at a flux of 20 L·(m2·h)−1 was 0.52 mbar·min−1, which showed that the SF0.5 for the full-scale sludge was 15 L·(m2·h)−1 [58]. For the TTC sludge, the contribution of irreversible fouling was 40% after the initial permeability loss. In SBR sludge filtration, the average membrane resistance due to pore blockage (Rp) was 5.3 × 1010 m−1, which was 2.1 times lower than the Rp of the TTC sludge. During the filtration of the full-scale sludge, the main reason for fouling was the cake layer with the contribution of pore blocking, while, during filtration of the lab-scale SBR sludge, pore blocking was the sole factor for fouling [59]. The comparison of TMPavg, permeability and FR of the seed sludge from full-scale and SBR cultivated sludge are shown in Figure 8a,b.
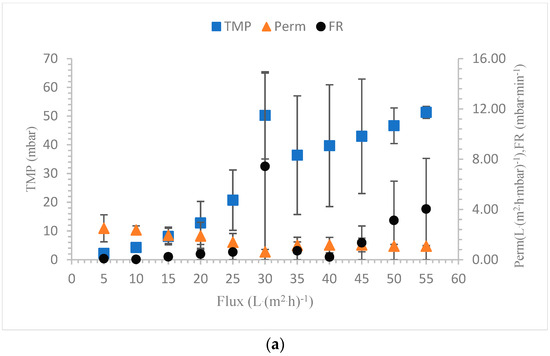
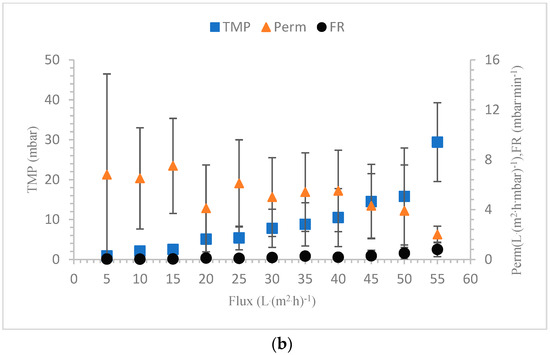
Figure 8.
(a) TTC sludge filtration characteristics. (b) SBR sludge filtration characteristics.
The findings of Tsertou et al. [36] confirm our results. Their study was to check the performance of AGS and conventional AS in membrane filtration, and it was shown that the SF0.5 value for AGS was higher than for activated sludge. For AGS, the FR never exceeded 0.1 mbar·min−1 at a maximum flux of 55 L·(m2·h)−1, while the SF0.5 for conventional sludge was less than 35 L·(m2·h)−1. The permeability of AGS was also more than twice that of conventional AS. The high SF0.5 value indicates less fouling problems.
Truong et al. [60] also carried out a comparative study of AGS and AS. They found that the Rc of AS was 4–13 times higher than AGMBR, resulting in two to three-times higher Rt for AS than AGMBR. Iorhemen et al. [29] also compared the filtration results of AGS and AS. They observed that the TMP increased more rapidly in AS than in AGS. The reasons for the rapid increase in TMP for AS were that AS was easily deposited on the membrane surface, resulting in a dense cake layer and pore blockage. For AGS, the large and rigid structure of AGS causes shear on the membrane surface, which mitigates the fouling. Wang et al. [37] conducted filtration experiments on AGS and AS. They found that fouling was higher in AS than in AGS because of the larger AGS particle size. In a study by Zhang et al. [24], it was concluded that pore blocking was the main form of the fouling in the AGMBR.
3.5. Unsuccessful Granulation
The objective of this study was to form AGS starting from floccular sludge using microbial selection only. The results showed that the applied strategy resulted in a more densified sludge as compared to the initial full-scale sludge, but full granulation was not achieved. AGS has some unique features, like a SVI30 of less than 50 mL·g−1, SVI10/SVI30 value of approximately 1, and a minimum size of 200 μm. In our experiment, the lowest SVI30 value was 26 mL·g−1, the SVI10/SVI30 was 1.16, and the DV50 of the flocs reached 254 μm, but its shape was never spherical. There are two possible reasons for the incomplete granulation in our experiment. These reasons are:
- High settling time: The settling of the reactor in our experiment was 55 min. For AGS, the settling time should be less, so the loose flocs are washed out, and the best settling flocs remains in the reactor. In AGS formation, typically, a short settling of 2–10 min is applied [20].
- High particulate COD (pCOD): A high amount of pCOD in the influent is not good for granulation. In our experiment, the average pCOD value was 832 mg·L−1. In pCOD, the most challenging part is the slowly biodegradable fraction, which is hydrolyzed to rbCOD in the reactor. The leakage of rbCOD to the aerobic phase favors OHO, and it is detrimental to granulation [48].
4. Conclusions
The aim of this study was to improve the settleability and filterability of a seed sludge originating from a TTC company treating highly variable influent wastewater. A slow anaerobic feeding strategy was adopted to improve the sludge characteristics and pollutant removal by the microbial selection of slow-growing organisms such as GAOs. Slow anaerobic feeding, sludge densification, improved settling, and better membrane filtration properties were achieved when applying a constant OLR. The application of variable OLR was detrimental to sludge settling, as filamentous organisms appeared. For the densification of the sludge, a stable OLR is required. The strategy of microbial selection to form aerobic granules can be further improved by implementing an adequate influent pretreatment to remove particulates in the influent.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.A. and J.D.; methodology, D.G.; software, D.G.; validation, M.A., D.G. and J.D.; formal analysis, C.V.; investigation, M.A.; resources, K.G.; data curation, M.A.; writing—original draft preparation, M.A.; writing—review and editing, M.A.; visualization, M.A.; supervision, J.D.; project administration, J.D.; funding acquisition, M.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Higher Education Commission (HEC) of Pakistan.
Data Availability Statement
All relevant data are included in the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interests.
References
- Fan, N.; Wang, R.; Qi, R.; Gao, Y.; Rossetti, S.; Tandoi, V.; Yang, M. Control strategy for filamentous sludge bulking: Bench-scale test and full-scale application. Chemosphere 2018, 210, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tandoi, V.; Rossetti, S.; Wanner, J. (Eds.) Activated Sludge Separation Problems: Theory, Control Measures, Practical Experiences; IWA Publishing: Melbourne, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelissen, R.; Van Dyck, T.; Dries, J.; Ockier, P.; Smets, I.; Van den Broeck, R.; Van Hulle, S.; Feyaerts, M. Application of online instrumentation in industrial wastewater treatment plants—A survey in Flanders, Belgium. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 78, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Pot, M.A.; Heijnen, J.J. Importance of bacterial storage polymers in bioprocesses. Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 35, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Peng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Yang, X.; Wang, S. Control filamentous bulking caused by chlorine-resistant Type 021N bacteria through adding a biocide CTAB. Water Res. 2012, 46, 6531–6542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Yu, Z.; Qi, R.; Zhang, H. Detailed comparison of bacterial communities during seasonal sludge bulking in a municipal wastewater treatment plant. Water Res. 2016, 105, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerva, I.; Remmas, N.; Kagalou, I.; Melidis, P.; Ariantsi, M.; Sylaios, G.; Ntougias, S. Effect of Chlorination on Microbiological Quality of Effluent of a Full-Scale Wastewater Treatment Plant. Life 2021, 11, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, V.; Martins, C.; Pereira, M.O.; Nicolau, A. Use of an aerobic selector to overcome filamentous bulking in an activated sludge wastewater treatment plant. Environ. Technol. 2014, 35, 1525–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, D.; Richard, M.G.; Daigger, G.T. Manual on the Causes and Control of Activated Sludge Bulking, Foaming, and Other Solids Separation Problems; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.S.; Teo, K.H.; Yuen, W.A.; Long, W.Y.; Seah, B. Performance analysis of anoxic selector in upgrading activated sludge process in tropical climate. Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 52, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsertou, E.; Caluwé, M.; Goossens, K.; Dobbeleers, T.; Dockx, L.; Poelmans, S.; Suazo, K.S.; Dries, J. Is building up substrate during anaerobic feeding necessary for granulation? Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 86, 763–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caluwé, M.; Goossens, K.; Seguel Suazo, K.; Tsertou, E.; Dries, J. Granulation strategies applied to industrial wastewater treatment: From lab to full-scale. Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 85, 2761–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stes, H.; Aerts, S.; Caluwé, M.; Dobbeleers, T.; Wuyts, S.; Kiekens, F.; D’aes, J.; De Langhe, P.; Dries, J. Formation of aerobic granular sludge and the influence of the pH on sludge characteristics in a SBR fed with brewery/bottling plant wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 77, 2253–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.; Wang, Z.; Salam, K.W.; Hari, A.R.; Pronk, M.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Saikaly, P.E. Importance of Species Sorting and Immigration on the Bacterial Assembly of Different-Sized Aggregates in a Full-Scale Aerobic Granular Sludge Plant. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 8291–8301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.M.P.; Heijnen, J.J.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Bulking sludge in biological nutrient removal systems. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2004, 86, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haaksman, V.; Schouteren, M.; van Loosdrecht, M.; Pronk, M. Impact of the anaerobic feeding mode on substrate distribution in aerobic granular sludge. Water Res. 2023, 233, 119803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorhemen, O.T.; Hamza, R.A.; Zaghloul, M.S.; Tay, J.H. Simultaneous organics and nutrients removal in side-stream aerobic granular sludge membrane bioreactor (AGMBR). J. Water Process Eng. 2018, 21, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, B.-J.; Xie, W.-M.; Liu, S.-G.; Yu, H.-Q.; Wang, Y.-Z.; Wang, G.; Dai, X.-L. Granulation of activated sludge in a pilot-scale sequencing batch reactor for the treatment of low-strength municipal wastewater. Water Res. 2009, 43, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nancharaiah, Y.; Reddy, G.K.K. Aerobic granular sludge technology: Mechanisms of granulation and biotechnological applications. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 1128–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Show, K.-Y.; Lee, D.-J.; Tay, J.-H. Aerobic granulation: Advances and challenges. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 167, 1622–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kreuk, M.; van Loosdrecht, M. Selection of slow growing organisms as a means for improving aerobic granular sludge stability. Water Sci. Technol. 2004, 49, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsino, S.F.; Di Trapani, D.; Torregrossa, M.; Viviani, G. Aerobic granular sludge treating high strength citrus wastewater: Analysis of pH and organic loading rate effect on kinetics, performance and stability. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 214, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adav, S.S.; Lee, D.-J.; Lai, J.-Y. Functional consortium from aerobic granules under high organic loading rates. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 3465–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Jiang, F. Membrane fouling in aerobic granular sludge (AGS)-membrane bioreactor (MBR): Effect of AGS size. Water Res. 2019, 157, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurung, K.; Ncibi, M.C.; Fontmorin, J.-M.; Särkkä, H.; Sillanpää, M. Incorporating Submerged MBR in Conventional Activated Sludge Process for Municipal Wastewater Treatment: A Feasibility and Performance Assessment. J. Membr. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le-Clech, P. Membrane bioreactors and their uses in wastewater treatments. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 88, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Shi, Y.; Jegatheesan, V.; Haq, I.U. A Review on the Mechanism, Impacts and Control Methods of Membrane Fouling in MBR System. Membranes 2020, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Huang, D.; Shen, Y.; Yin, W.; Gao, X.; Zhang, B.; Shi, W. Treatment of municipal wastewater with aerobic granular sludge membrane bioreactor (AGMBR): Performance and membrane fouling. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 273, 123124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorhemen, O.T.; Hamza, R.A.; Zaghloul, M.S.; Tay, J.H. Aerobic granular sludge membrane bioreactor (AGMBR): Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) analysis. Water Res. 2019, 156, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, J.H.; Yang, P.; Zhuang, W.Q.; Tay, S.T.L.; Pan, Z.H. Reactor performance and membrane filtration in aerobic granular sludge membrane bioreactor. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 304, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, X.; Zhang, S.; Xu, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, J. Performance and fouling characteristics in a membrane sequence batch reactor (MSBR) system coupled with aerobic granular sludge. Desalination 2010, 261, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caluwé, M.; Dobbeleers, T.; Daens, D.; Geuens, L.; Blust, R.; Dries, J. SBR treatment of tank truck cleaning wastewater: Sludge characteristics, chemical and ecotoxicological effluent quality. Environ. Technol. 2018, 39, 2524–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manavi, N.; Kazemi, A.S.; Bonakdarpour, B. The development of aerobic granules from conventional activated sludge under anaerobic-aerobic cycles and their adaptation for treatment of dyeing wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 312, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobbeleers, T.; Daens, D.; Miele, S.; D’aes, J.; Caluwé, M.; Geuens, L.; Dries, J. Performance of aerobic nitrite granules treating an anaerobic pre-treated wastewater originating from the potato industry. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 226, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsino, S.F.; di Biase, A.; Devlin, T.R.; Munz, G.; Torregrossa, M.; Oleszkiewicz, J.A. Effect of extended famine conditions on aerobic granular sludge stability in the treatment of brewery wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 226, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsertou, E.; Caluwé, M.; Goossens, K.; Seguel Suazo, K.; Dries, J. Performance of an aerobic granular sludge membrane filtration in a full-scale industrial plant. Water Sci. Technol. 2023, 87, 3002–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhong, C.; Huang, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J. The membrane fouling characteristics of MBRs with different aerobic granular sludges at high flux. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 136, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pronk, M.; Abbas, B.; Al-zuhairy, S.H.K.; Kraan, R.; Kleerebezem, R.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Effect and behaviour of different substrates in relation to the formation of aerobic granular sludge. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 5257–5268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toja Ortega, S.; Pronk, M.; de Kreuk, M.K. Effect of an Increased Particulate COD Load on the Aerobic Granular Sludge Process: A Full Scale Study. Processes 2021, 9, 1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, M.; Mirbagheri, S.A.; Bagheri, Z.; Kamarkhani, A.M. Modeling and optimization of activated sludge bulking for a real wastewater treatment plant using hybrid artificial neural networks-genetic algorithm approach. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2015, 95, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Han, X. Sludge reduction and process performance in a submerged membrane bioreactor with aquatic worms. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 172, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karczmarczyk, A.; Kowalik, W. Combination of Microscopic Tests of the Activated Sludge and Effluent Quality for More Efficient On-Site Treatment. Water 2022, 14, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layer, M.; Adler, A.; Reynaert, E.; Hernandez, A.; Pagni, M.; Morgenroth, E.; Holliger, C.; Derlon, N. Organic substrate diffusibility governs microbial community composition, nutrient removal performance and kinetics of granulation of aerobic granular sludge. Water Res. X 2019, 4, 100033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, E.; Lind, G.; Lemmer, H.; Wilderer, P.A. Population structure and chemical EPS analyses of activated sludge and scum. Acta Hydrochim. Hydrobiol. 2005, 33, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondrotaite, Z.; Valk, L.C.; Petriglieri, F.; Singleton, C.; Nierychlo, M.; Dueholm, M.K.D.; Nielsen, P.H. Diversity and Ecophysiology of the Genus OLB8 and Other Abundant Uncultured Saprospiraceae Genera in Global Wastewater Treatment Systems. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 917553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemaire, R.; Webb, R.I.; Yuan, Z. Micro-scale observations of the structure of aerobic microbial granules used for the treatment of nutrient-rich industrial wastewater. ISME J. 2008, 2, 528–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seviour, T.W.; Lambert, L.K.; Pijuan, M.; Yuan, Z. Selectively inducing the synthesis of a key structural exopolysaccharide in aerobic granules by enriching for Candidatus “Competibacter phosphatis”. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 92, 1297–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oehmen, A.; Yuan, Z.; Blackall, L.L.; Keller, J. Comparison of acetate and propionate uptake by polyphosphate accumulating organisms and glycogen accumulating organisms. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2005, 91, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begum, S.A.; Batista, J.R. Impact of butyrate on microbial selection in enhanced biological phosphorus removal systems. Environ. Technol. 2014, 35, 2961–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schambeck, C.M.; Magnus, B.S.; de Souza, L.C.R.; Leite, W.R.M.; Derlon, N.; Guimarães, L.B.; da Costa, R.H.R. Biopolymers recovery: Dynamics and characterization of alginate-like exopolymers in an aerobic granular sludge system treating municipal wastewater without sludge inoculum. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 263, 110394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J. Research on rapid cultivation of aerobic granular sludge (AGS) with different feast-famine strategies in continuous flow reactor and achieving high-level denitrification via utilization of soluble microbial product (SMP). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 786, 147237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caluwé, M.; Dobbeleers, T.; D’aes, J.; Miele, S.; Akkermans, V.; Daens, D.; Geuens, L.; Kiekens, F.; Blust, R.; Dries, J. Formation of aerobic granular sludge during the treatment of petrochemical wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 238, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burzio, C.; Ekholm, J.; Modin, O.; Falås, P.; Svahn, O.; Persson, F.; van Erp, T.; Gustavsson, D.J.I.; Wilén, B.-M. Removal of organic micropollutants from municipal wastewater by aerobic granular sludge and conventional activated sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 438, 129528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begum, S.A.; Batista, J.R. Microbial selection on enhanced biological phosphorus removal systems fed exclusively with glucose. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 28, 2181–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, C.S.; Bilad, M.R.; Nordin, N.A.H.M. Silica incorporated membrane for wastewater based filtration. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1891, 020041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vleeschauwer, F.; Caluwé, M.; Dobbeleers, T.; Stes, H.; Dockx, L.; Kiekens, F.; Copot, C.; Dries, J. A dynamically controlled anaerobic/aerobic granular sludge reactor efficiently treats brewery/bottling wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 84, 3515–3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stes, H.; Caluwé, M.; Dockx, L.; Cornelissen, R.; Langhe, P.; Smets, I.; Dries, J. Cultivation of aerobic granular sludge for the treatment of food-processing wastewater and the impact on membrane filtration properties. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 83, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-G.; Jang, H.-N.; Kim, H.-M.; Lee, D.-S.; Chung, T.-H. Effects of the sludge reduction system in MBR on the membrane permeability. Desalination 2010, 250, 601–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Cheng, F. Reactor performance and membrane fouling of a novel submerged aerobic granular sludge membrane bioreactor during long-term operation. J. Water Reuse Desalination 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, H.T.B.; Bui, H.M. Potential of aerobic granular sludge membrane bioreactor (AGMBR) in wastewater treatment. Bioengineered 2023, 14, 2260139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).