Abstract
The presence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria (ARB) in receiving water can severely threaten the aquatic environment and human health. The treated effluent containing ARB in some livestock wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) is returned to the municipal WWTP to reduce the residual ammonia and phosphorus concentrations. ARBs are widespread through wastewater treatment processes and are discharged into river and lake. This study highlights that the isolated lytic phage could reduce ARB isolated from livestock WWTPs and apply phage-based biocontrol in mixed cultures. ARB and lytic phages were isolated from livestock wastewater and used in a batch reactor with diverse cultures. The isolated bacterium was from the Aeromonas species and was resistant to various antibiotics (penicillin, tetracycline, colistin, and kanamycin), indicating multi-drug resistance and biofilm formation. The isolated lytic phage successfully infected Aeromonas species in pure culture and was relatively stable in terms of pH, temperature, and toxic chemicals. The multiplicity of infection (MOI) was examined to determine the proper phage number to kill the host bacterium. The optimal number to control the isolated ARB was a 1:100 phage-to-host ratio. Scanning electron microscopy showed that lytic phages reduced bacterial growth and biofilm formation. Phage-mediated biocontrol was applied in a batch reactor with mixed cultures. Pyrosequencing data from the batch reactor indicated that lytic phages reduced the proportion of the isolated ARB from 65.7 to 20% in 24 h. This study provides evidence for the possible application of lytic phages to control ARB in treated wastewater and an alternative method to prevent the widespread exposure of ARB without producing chemical byproducts.
1. Introduction
Antimicrobial drug resistance is a major global threat to society and health care. The World Health Organization (WHO) has identified elevated levels of drug-resistant bacteria in the environment and recommended intensive monitoring surveillance to reduce antibiotic resistance [1,2]. Antibiotics are medicines to fight bacterial infection in humans and animals, but antibiotic misuse causes nutritional deficiency concerning side effects. Uncontrolled consumption leads to the rise and spread of antimicrobial resistance, which is a concerning problem worldwide. Drug-resistant bacteria are becoming a severe hazard to the living world. Various reasons for the emergence of drug-resistant bacteria include the overconsumption of antibiotics in animal farming, wastewater from the livestock industry, natural selection pressure, and resistant plasmids. Wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) are primary reservoirs of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and genes (ARB/ARG) [3]. Finally, antimicrobials and drug-resistant bacteria reach wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) through sewage collection systems [4,5].
WWTPs have contributed to the spread of antibiotic resistance genes among bacteria. Most studies have demonstrated that WWTPs are hotspots of multidrug resistance and spread antibiotic resistant genes (ARG) into the environment [6,7,8]. Notably, livestock WWTPs can be another hotspot for ARB growth and spread because a large amount of antibiotics by injection is used in livestock industries, especially in piggeries. In some cases of S. Korea, the treated effluent of livestock WWTPs containing high organics, ammonium and phosphorus is returned to increase C/N ratio in municipal WWTPs and mixed with municipal wastewater in the plant inlets to meet the discharge limit of the treated effluent of livestock WWTP. During this process, antibiotic-resistant bacteria and genes can be disseminated to other bacteria through horizontal gene transfer, including conjugation, transformation, and transduction. Effluents potentially containing ARB or ARG could provide a source of antibiotic resistance in receiving water basins. Chlorine can be used as a disinfectant to control antibiotic-resistant bacteria in WWTPs. However, chemical disinfection may also affect other bacteria and organisms that are essential for removing nutrients from WWTPs. Ultra-violet (UV) and Chlorine disinfection has been shown to increase both intracellular and extracellular antibiotic-resistance genes in full-scale WWTP [9,10]. Although various doses of chlorine were used to inactivate antibiotic-resistant bacteria, approximately 40% of erythromycin-resistant and 80% of tetracycline-resistant genes could not be treated by chlorine disinfection [11]. Therefore, an alternative method of targeting unwanted bacteria in WWTPs is required.
Recently, phage-based biocontrol has been used in wastewater-related studies to reduce biomass bulking [12], membrane biofouling [13], and antibiotic-resistant bacteria [14]. Phages, also called bacteriophages, are viruses that infect and lyse bacteria. Phage biocontrol termed phage therapy has been applied in the medical and food industries to infect the target bacteria to treat disease and disinfect meat, respectively [12,15]. Pure cultures have been used to control bacterial hosts in most previous studies. Although phage-mediated biocontrol has been used to reduce antibiotic-resistant bacteria and membrane biofouling in wastewater treatment processes [13], to our knowledge, few studies have been conducted using mixed cultures, including activated sludge.
In this manuscript, we reported the findings on new phage isolation to solve the problem of ARB spread in the environment and the approach to apply it in mixed culture systems. In this study, ARB was isolated from the effluent of a livestock WWTP and used for phage isolation. The isolated lytic phage was used to demonstrate phage therapy and control ARB in a mixed-culture batch reactor.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Isolation of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria
The treated effluent was collected from the livestock WWTP, Chungju, Republic of Korea. Duplicate samples (10 mL) were inoculated into 250 mL of Erlenmeyer flask containing (30 μg/mL tetracycline) 100 mL Luria-Bertani (LB) broth (BD Difco, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The flasks were incubated at 37 ± 2 °C for 24 h under shaking conditions (80× g. Subsequently, 10-fold serial dilution was plated in duplicate on the 30 μg/mL tetracycline (typically used as tetracycline soluble powder in piggery industries) Bacto agar (BD Difco, Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA) from each flask and incubated at 35 ± 2 °C for 24 to 48 h. Well-isolated colonies were subcultured on the same medium. The identified single isolate was subjected to a BacLight bacterial viability test (Invitrogen, Thermo Fisher, USA) using an Olympus BX53 microscope. The well-isolated bacterial genome was purified using a DNeasy power soil kit (Qiagen, Germantown, MD, USA), subjected to molecular confirmation using the 16S rDNA sequencing method, and then submitted to the NCBI database, as previously described [14]. PCR amplification of the 16S rRNA gene was performed using 2x GoTaq Mastermix with universal primers of 27f (AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCCAG) and 1492r (GGTTACCTTGTTTACGACTT) with an initial denaturation at 95 °C for 3 min, followed by 35 cycles of 20 s denaturation at 95 °C, 40 s of annealing at 56 °C, and 1.5 min of extension at 72 °C with a final 3 min extension at 72 °C. The amplicons were confirmed on 1.5% agarose gel, purified using a gel extraction method and sequenced on an ABI automated DNA sequencer (Applied Biosystems, Waltham, MA, USA). The DNA sequences were analyzed for homology against the NCBI database using BLAST. A phylogenetic tree was constructed using the MEGA4 algorithm [16,17].
2.2. Antibiotic Sensitivity
The identified tetracycline-resistant bacteria were tested for antibiotic susceptibility to other antibiotics. The antibiotics used in this study were penicillin (inhibitor of cell wall synthesis), tetracycline (inhibitor of cellular metabolic processes), colistin (inhibitor of cell wall synthesis), and kanamycin (protein synthesis inhibitor) at various concentrations (16, 32, 64, 200, and 500 µg/mL). Antibiotic sensitivity was performed in triplicate in small test tubes. Negative controls without antibiotics and positive controls with antibiotics were incubated at 35 ± 2 °C with shaking at 70× g for 20 h. Subsequently, bacterial growth in the test tubes was recorded by measuring the absorbance at 660 nm every 2 h. Graphs showing each antibiotic resistance profile was represented by the average absorbance value.
2.3. Isolation and Characterization of Bacteriophage
Sewage samples from WWTP were collected, and the double agar plate method was used to isolate lytic bacteriophages. The collected sewage samples were centrifuged at 21,840× g for 10 min. The supernatant was collected and filtered through 0.45 µm syringe-driven filters. Then, approximately 0.5 mL of chloroform was added to 50 mL of the filtrate and incubated for 20 min. Subsequently, 5 mL of the corresponding bacterial culture (in early log phase, optical density at 0.4–0.7) and 20 mL of 2X LB broth were added and incubated at 37 ± 2 °C. After 24 h, broth cultures demonstrating visible lysis were pelleted by centrifugation at 4 °C at 7600× g for 20 min and filtered through 0.45 µm syringe-driven filters. The filtrate obtained was then tested for lytic phage using the Adams double-layer agar method with minor modifications (5% glycerol) [18].
The bacterial culture (100 µL, 108 CFU/mL) and 100 µL of purified phage filtrate (108 PFU/mL) were mixed and incubated at room temperature for 3–5 min for phage adsorption. Afterward, this bacteria-phage filtrate was placed in a sterile tube mixed with 5 mL of soft agar (0.7% agar) poured onto the bottom agar and swirled to produce a uniform top layer. Plates in duplicates were incubated at 37 ± 2 °C for 24 h for plaque formation. After 24 h, the appearance of clear zones (plaques) suggested the presence of lytic phages. The plaques were collected and re-suspended in SM buffer (salt of magnesium: 100 mM NaCl, 8 mM MgSO4, 50 mM Tris-Cl (pH 7.5), and 0.01% gelatin). This phage lysate was used to test the lytic efficacy of the bacteriophages in vitro [19].
2.4. Biological Features of Bacteriophages
2.4.1. One-Step Growth Curve of the Isolated Phage
A one-step growth curve experiment was performed to determine the latent period and the phage burst size. The one-step growth curve was tested as previously described [20,21]. In brief, 50 mL of Aeromonas spp. (the isolated ARB) was incubated in LB medium and cells were harvested by centrifugation at 11,850× g for 30 s at 4 °C. The pellets were re-suspended in LB medium (0.5 mL of LB medium and mixed with 0.5 mL of the phage solution (108 PFU/mL)). This mixture was allowed to stand for 3–5 min at 37 ± 2 °C for phage adsorption onto the host cells. The mixture was centrifuged at 20,000× g for 2 min to remove free phage particles. The pellet was re-suspended in 100 mL of LB medium, and the culture was incubated at 37 ± 2 °C with agitation at 70× g. Duplicate samples were used to calculate the total plaque-forming unit with and without chloroform, respectively [12]. The assay was performed in triplicate. The latent period was defined as the time interval difference between adsorption and the beginning of the initial increase in phage count. The burst size of the respective phages was calculated as the ratio of the final phage titer to the initial count of the infected bacterial cells during the latent period.
2.4.2. Effect of Temperature, pH, and Toxic Substances on Phage
Thermal, pH, and toxic substance stability tests were performed according to the methods previously described [22,23]. Phage filtrates (108 PFU/mL) were acquired in microcentrifuge tubes and treated under different temperatures at 37 °C (control), –70, –20, and 40 °C for a storage period of (10, 9, 2, and 1 month), pH (3, 5, 7, 9, and 11) for 1, 5, and 10 h incubation in SM buffer, and toxic substances (Chromium and Cyanide at concentrations of 0.1, 0.5, and 1 mg/L) immediately and after seven days of incubation were tested. After incubation, the double-layer agar method was performed for each treated sample to evaluate the lytic ability of phages relative to their controls (37 °C). All assays were performed in triplicate to demonstrate the stability of the phage.
2.4.3. Morphological Study of Phage Using the Transmission Electron Microscope
A transmission electron microscope (TEM) was used to characterize the phage morphology. The phage filtrate was filtered through 0.45 µm filters and concentrated using centrifugation at 45,000× g for 60 min. The pellet was mixed with 5 mL of SM buffer. Five microliters of phage filtrate was placed on formvar coated 200 × 200 copper grids; excess phage solution was removed with pieces of filter paper from the edges of the grid and left for 3 min. Subsequently, 2 μL of 1% uranyl acetate was added to the grid. The excess solution was immediately removed, and the grids were air-dried. Samples were viewed with an FEI Tecnai G2 S-Twin transmission electron microscope at an operating voltage of 80 kV.
2.4.4. Analysis of Phage-Host Ratio of Bacteriolysis In Vitro
The plaque from the agar plate was diluted in SM buffer. Subsequently, 1% chloroform was added to remove bacteria from the buffer. The phage lysate was centrifuged, and the supernatant was used to test the lytic activity of Aeromonas spp. at various concentrations of phage–host ratio (that is, 0.01:100, 0.1:100, 1:100, 10:100, and 100:100) with the blank containing only bacteria (108 CFU/mL). One milliliter of Aeromonas spp. was inoculated into two flasks containing 150 mL of LB broth. To evaluate the in vitro lytic efficacy of the phage, 500 μL phage filtrate with a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 0.01 to 100 was transferred into a test flask containing 150 mL of LB broth containing Aeromonas spp. Test and control flasks were incubated in a shaking incubator at 37 °C and 70× g for 24 h. Optical density (OD) at 600 nm was recorded after 24 h using a UV spectrophotometer (UV-1800, Shimadzu, Japan).
2.4.5. Phage Action on Biofilm of Aeromonas spp.
The lytic activity of the isolated phage on the biofilm of Aeromonas spp. was demonstrated using a scanning electron microscope. For this experiment, only the coverslip was placed in 1 mL of phosphate-buffered saline as a negative control; other sets with and without phage treatment were used to determine phage lytic activity on Aeromonas spp. (108 CFU/mL) were grown on borosilicate glass coverslips for 10 h, followed by the addition of 100 µL of the isolated phage at an MOI of 10 and placed in a sterilized Petri plate for 4 h. After treatment, the coverslips were washed twice with PBS and dried for 20 h at 37 °C. The biofilms coated on glass slides were fixed with glutaraldehyde (2.5%) and dehydrated using a series of graded ethanol (30–100%) for 5 min. The glass slides were sputtered with gold after critical point drying, and the aggregated biofilms were examined using a scanning electron microscope (FEI, Tecnai G-2S Twin) [24,25].
2.5. Feasibility Test of Phage-Based Biocontrol in Mixed Cultures
The activated sludge samples (200 mL) for batch reactors were divided into two separate Erlenmeyer conical flasks (500 mL) with aeration. One set was added to 150 mL of Aeromonas spp. (108 CFU/mL grown with 0.25x LB medium) as a control. The other flask contained 150 mL of Aeromonas spp. (108 CFU/mL) and 15 mL of lytic aerophage (108 PFU/mL) to determine the efficacy of lytic phage in mixed cultures and demonstrate the bacteriolytic activity of lytic phage on Aeromonas spp. The experiment was performed in duplicate at different time points (6, 12, and 24 h). The samples were then performed for water quality tests (COD, ammonia, and phosphorus) [26] and DNA extraction (Bioneer, Republic of Korea). The amplicons were sequenced according to the manufacturer’s instruction (Illumina, CA, USA). Oligomers containing the Illumina overhang adapter sequence, and the following sequences specific to the 16S rDNA region were used as amplicon primers for the V3-4 region of bacteria, 518F (5′-CCAGCAGCCGCGGTAATACG-3′) and 805R (5′-GACTACCAGGGTATCTAATCC -3′) [27]. The DNA samples were amplified at 58 °C. Purified amplicons were PCR-indexed using the Illumina Nextera XT index kit. A Taq DNA Polymerase Kit (Solgent, Republic of Korea) was used for library construction. The purified library was quantified, pooled, and combined with the PhiX control (Illumina). The library was paired-end (151 × 2) sequenced on the iSeq 100 platform. Paired reads were merged and processed to remove short- or low-quality sequences. More than 86,000 filtered reads were obtained from each sample. Operational taxonomic units (OTUs) were defined at 97% sequence-identity cutoff using the VSEARCH algorithm [28,29]. Taxonomic assignment was conducted using an online ribosomal database project (RDP) classifier (https://rdp.cme.msu.edu/classifier/, accessed on 1 June 2021).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the Isolated Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria from Livestock WWTP Effluent
Tetracyclines are applied routinely in livestock rearing and the largest amounts of antimicrobials were utilized for treating the respiratory organs of fattening pigs [30]. The isolated bacterium (01 Tet-2-1-2-27F D08) showed almost 99.9% similarities with A. hydrophilia strain and A. caviae strain (Figure 1). A. hydrophila is a heterotrophic, Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium found in brackish water. This microbe is resistant to most common antibiotics and cold temperatures [31]. The isolated bacterium named Aeromonas spp. showed optimum growth at a temperature of approximately 35 °C and a pH of 7–7.5.
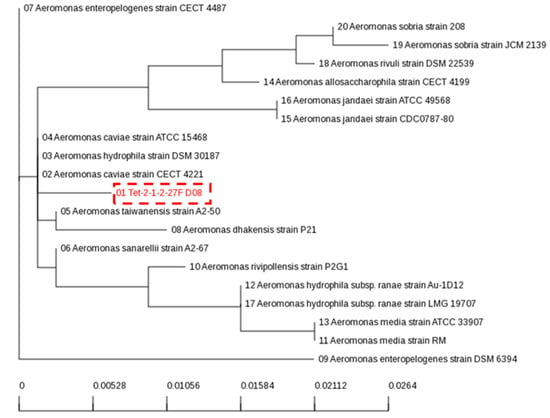

Figure 1.
Phylogenetic analysis of 16S rRNA gene sequencing of isolated MDR-bacteria and interspecies relationship with genus of Aeromonas spp.
Bacteria isolated from environmental sources have less drug resistance than clinical samples because resistance mechanisms are acquired from clinical strains. In general, drug resistance is observed in Proteobacteria and is associated with a rich source of multiple resistance plasmids. Confirmed using molecular analysis, Aeromonas spp. were subjected to an antibiotic sensitivity test using penicillin, tetracycline, colistin, and kanamycin (Figure 2). Sensitivity was defined as the absence of growth on solid media containing any of the antibiotics. The presence of bacterial growth indicated that Aeromonas spp. were resistant to penicillin, tetracycline, and colistin. However, the sensitivity was observed under all kanamycin concentrations. The maximum extent of drug resistance was recorded for tetracycline and penicillin (16, 32, 64, and 200 µg/mL). In both cases, resistance was reduced to 45% at 500 µg/mL. Reduced resistance (70%) was observed with colistin (16, 32, 64, 200, and 500 µg/mL) at all concentrations, whereas Aeromonas spp. showed 100% sensitivity to kanamycin at all applied concentrations. In general, the growth of Aeromonas spp. is inhibited by most antibiotics [32]. Isolated bacteria showed resistance to tetracycline at all applied concentrations, consistent with previous reports from Asia (49%) but contradicted the studies from the USA and Australia, where the sensitivity was high (94.3%) [33].
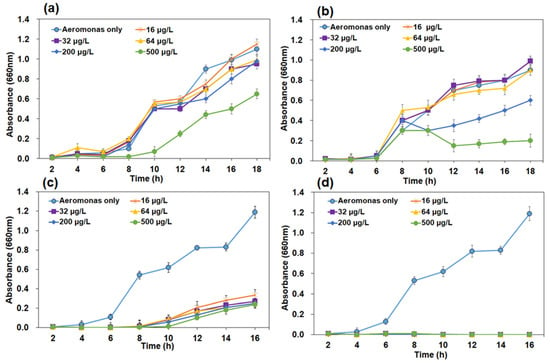
Figure 2.
Antibiotic susceptibility pattern of Aeromonas (01Tet-2-1-2-27FD08) at 16, 32, 64, 200, and 500 µg/mL concentrations, OD values at 660 nm. (a) Tetracycline, (b) Penicillin, (c) Colistin and (d) Kanamycin, respectively.
3.2. Isolation and Characterization of Lytic Bacteriophage
Influent samples from wastewater treatment plants were used for the isolation of bacteriophages against the isolated Aeromonas spp. using the double-layer agar method. In general, sewage contains an abundant number and variety of phages, and the high lytic activity of the phage cycle can be used to infect unwanted bacterial growth. The characterized bacteria were inoculated into the LB media, and filtered sewage samples were mixed with soft agar and layered over it, and then incubated at 37 °C for 24 h. After the incubation period, clear zones were formed on soft agar. The developed clear zones were considered plaques, as shown in Figure 3b. Precise plaque formation on double-layer agar confirmed the presence of a specific lytic phage against the isolated Aeromonas spp. The formed plaques were irregular, small in size, and had a clear area on the agar plate. The phage titer value was determined using log dilutions of phage lysate, and the titer value was recorded as 4 × 108 PFU/mL. Bacteriophages are generally isolated from sewage, hospital waste, and environmental sources. Bacteriophages are preferentially host-specific, for example, phages that attach to the bacterium Pseudomonas are called Pseudophages, Staphylococcus is called Staphylophages, and phages that attack Escherichia coli are called coliphages. For this study, we used Aeromonas spp., and the isolated phages were termed phage vB_AenM_AeKnut 1 or Aerophage. Isolation and characterization of bacteriophages from the natural environment should be performed to determine their evolutionary perspectives, ecological significance, and development of therapeutics. The continued emergence of multidrug-resistant bacteria and the application of traditional antibiotics have been challenged. Therefore, these natural parasites of bacteria, that is, bacteriophages, are reconsidered in conjunction with antibiotics for treating super- or multidrug-resistant bacteria.
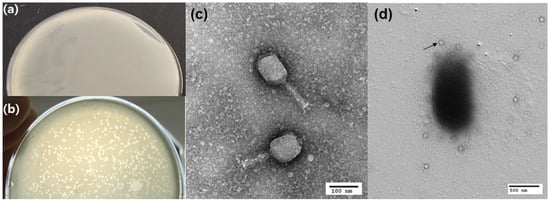
Figure 3.
Double-layer agar plates and images of transmission electron microscope (TEM), (a) Control (no plaque), (b) plaque formation (phage infection), (c) TEM image of bacteriophage under 100 nm. (d) TEM image of phage–bacterial interaction under 500 nm. Arrow represents phages.
3.2.1. Phage Morphology
The isolated phage, aerophage (vB_AenM_AeKnut 1), against the isolated Aeromonas spp. belongs to the Myoviridae family because it has a short contractile tail with an icosahedral head (Figure 3c). Myoviruses are typically virulent bacteriophages in lytic cycle, meaning they usually infect their host bacteria and they do not integrate their genetic material with host cells [12]. The length and width of the phage were measured as follows: the size of the tail was approximately 130 nm, the head was 90 nm, and the width was 70 nm. Figure 3d shows that phage adsorbed (attacked) on the respective Aeromonas spp. Many aerophages are attached to the surface of the bacteria. Bacteria–bacteriophage interactions are mediated through receptor sites present on the cell wall of the host bacterium. Phage–host interactions are essential for bacteriolytic activity, irrespective of multidrug resistance. This is the principle behind the application of phages as therapeutic agents in phage therapy. A previous study reported that phages (N21, W3, and G65) isolated from Aeromonas hydrophilia belong to the Myoviridae family and have a broad host range and high thermal and pH stability [22]. Phages 2 and 5 isolated from sewage against A. hydrophilia belong to the Myoviridae family and show excellent bacteriolytic activity at MOI 1 [34].
3.2.2. Phage Stability
Stability is an essential criterion for the use of phages as bacteriolytic agents. The isolated phage was thermally stable at various temperatures. There was not much difference in the rate of infectivity when stored at temperatures −70 and −20 °C, compared with control at 25 °C (room temperature). However, a marginal reduction in infectivity was observed at 40 °C, which indicates a negative effect on the phage infectivity, suggesting possible denaturation of capsid proteins and nucleic acids at higher temperatures [12]. Considering the storage period, recently stored or prepared phage filtrate (1–2 months old) showed a higher rate of infectivity than 9–10-month-old preserved phages. pH is a critical external factor that affects phage stability. The aerophage showed maximum activity at pH 5, 7, and 9 for 1, 5, and 10 h incubation periods, respectively, but no phage infectivity was observed at pH 3 and 11 for all tested periods. In this study, a pH ranging from 5 to 9 was ideal for stabilizing aerophage infectivity. These results suggest that extreme temperature and pH conditions affect the stability of the aerophage. The effect of toxic substances on phage was determined within 1 h and after 7 days of incubation with chromium and cyanide at different concentrations (0.1, 0.5, and 1 mg/L). Notably, there was not much difference in phage infectivity after 1 h or 7 days of incubation. Depending on the results obtained from all tested parameters, such as temperature, pH, and toxic chemicals (chromium and cyanide), the phage exhibited efficient lytic activity against MDR-Aeromonas spp. This is consistent with previous study done on phages of P. aeruginosa, S. aureus, E. coli, and K. pneumoniae [24].
3.2.3. One-Step Growth Curve
One- or single-step growth curves of the aerophage, including the eclipsed period, latent period, and burst size, are shown in Figure 4b. The results showed that the aerophage had an eclipsed period of approximately 10 min and a latent period of 20 min. An average burst size of 250 phages per infected bacterial cell was observed after 50 min of incubation at 37 °C. The latent and eclipse periods are crucial for phage growth when bacteriophages are used to control the process. The latent period refers to the point from phage adsorption to the point at which host lysis occurs. The eclipse period spans from phage adsorption to the point at which the first phage matures in the infected cell.
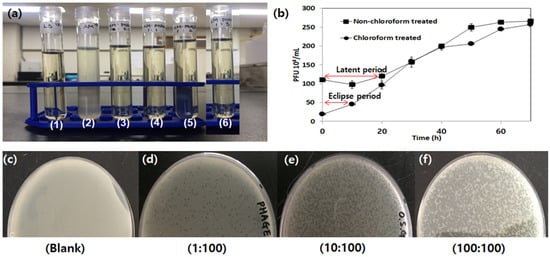
Figure 4.
(a) Invitro bacteriolytic activity of phage 1. Negative control (LB broth), 2. LB broth with Aeromonas (108 CFU/mL) 3. (0.5:1), 4. (1:100), 5. (10:100), 6. (100:100) phage–host ratio respectively. (b) Single- or one-step growth curve of Aerophage. (c–f) Multiplicity of infection (MOI) of lytic phage; where (c)—Blank, (d)—MOI at 1, (e)—MOI at 10, and (f)—MOI at 100, plaque formation on double layer agar method.
3.2.4. Effect of Phage-to-Host Ratio on Bacteriolysis
The phage-to-host bacteriolysis ratio was observed in vitro. The blank showed 96.9% bacteria compared with others (Table 1). The 10:100 and 100:100 phage–host ratios presented a lower bacterial ratio, 0.9%, with optical density from 0.004 to 0.002. Even a 1:100 phage-to-host ratio (5.9%) presented an OD of 0.06. Hence, in vitro bacteriolytic studies have shown that a single virion is efficient to lyse 100 bacteria in vitro. The in vitro bacteriolytic activity is shown in Figure 4a at various multiplicity of infections (MOI), and phage-to-host ratios at 1:100, 10:100, and 100:100 are illustrated in Figure 4c–f. MOI is an important factor in the utilization of phage as part of targeted host control. This number provides the number of bacteriophage particles in the host cell [35]. The number of plaques increased with MOI, indicating that aerophages are extremely efficient in eradicating MDR bacteria under laboratory conditions, even at a 1:100 ratio. Compared with the blank, phage infection produced a substantial reduction in optical density values at an MOI of 1:100.

Table 1.
Effect of phage to host ratio on bacteriolysis in invitro.
3.2.5. Biofilm Reduction by Lytic Aerophage
Scanning electron microscope (SEM) images represent biofilm behavior on a glass slide (negative control), only biofilm formed by Aeromonas spp., and aerophage-treated biofilm of Aeromonas spp. (Figure 5). The negative control exhibited an apparent field, indicating no bacterial contamination. Figure 5b,c show the effect on biofilm morphology and architecture before and after phage treatment. Little growth on the glass slide after 4 h of phage treatment was implied for phage (108 PFU/mL) lytic activity on the biofilm of Aeromonas spp. Previous studies have shown reduced bacterial load and biofilm formation of MDR E. coli by lytic phages on modified nanocomposite membranes by SEM analysis [14]. In addition, phages isolated from a sewage source belonging to Podoviridae presented excellent bacteriolytic activity on biofilms of Delftia tsuruhatensis isolated from WWTPs [13].
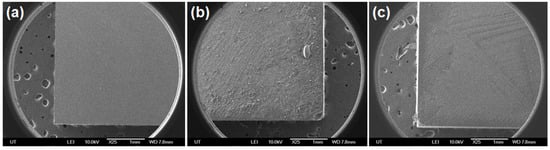
Figure 5.
Scanning electron microscopic images of biofilm on glass slide before and after phage treatment. Where (a) Cover slip, (b) Bacterial biofilm, (c) Surface with phage treatment, all are under 1 mm at 10 kV.
3.3. Bacterial Community Analysis in Lab-Scale Batch Reactors Controlled by Aerophage
The application of lytic bacteriophages in biological wastewater treatment has been limited to pure culture systems. Kotay et al. [12] studied phage-mediated biocontrol of biomass bulking in a pure culture of Haliscomenobacter hydrossis. Biofouling reduction was investigated by lytic phage application infecting isolated single bacteria on a modified nanocomposite membrane [14], but the effect of mixed culture has rarely been studied. Pure culture (single culture) is generally used when phage therapy is applied in the medical and food science fields. However, phage efficacy in mixed cultures is required if phage-based biocontrols are used for biological wastewater treatment processes. In mixed cultures, including activated sludge and biomass, the effectiveness of phage therapy is difficult to achieve with the conventional double agar plate method.
It is necessary to determine whether the efficiency of organics and nutrient removal from the original bioreactor is affected by phage addition when bacteriophages are used in mixed cultures of wastewater treatment systems. In a previous study [12], phage addition was investigated under sludge bulking, and no change in COD and ammonia removal was observed with the biomass bulking control. In this study, the isolated lytic bacteriophage did not affect organic and nutrient removal compared with the batch reactor without phage addition (Table 2). However, phosphorus was not removed as the batch reactor was performed only under aerobic conditions.

Table 2.
Water quality monitoring in batch reactors with and without Aerophage treatment.
Next-generation sequencing that provides a massively parallel sequencing is a powerful method for determining various phyla, classes, and genera in environmental or clinical samples. The results of the microbial analysis of bioreactors with and without phage treatment are shown in Figure 6. At the class level, Gammaproteobacteria, Deltaproteobacteria, and Betaproteobacteria were the major classes during the initial stage of reactor operation (Figure 6a). The distribution of the bacterial communities did not change when the lytic phage was not added to the bioreactor. However, an approximately 20% reduction was recorded in the distribution of Gammaproteobacteria between 12 and 24 h when the lytic phage was treated in the bioreactor. A relative increase in beta-proteobacteria was observed with a decrease in the Gammaproteobacteria distribution.
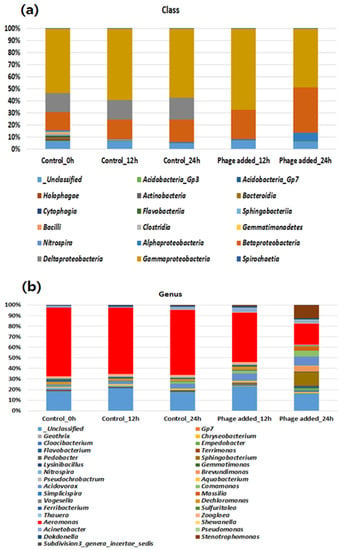
Figure 6.
Microbial analysis by employing next generation sequencing before and after aerophage treatment ((a) Class level and (b) Genus level).
At the genus level (Figure 6b), there were noticeable differences in the reaction tank of the bioreactor before and after Aerophage treatment. Initially, Aeromonas spp. (65.7%) was the most abundant species in the reaction tank, followed by unclassified bacteria (19.0%), Acidovorax (4.2%), Dechloromonas (3.4%), Dokdonella (2.5%), Ferribacterium (2.4%), and the remaining genera 2.8%. The phage exhibited bacteriolytic activity on the host cell, indicating that the level of Aeromonas spp. was reduced to 45 and 20% at 12 and 24 h, respectively. In this experiment, the Aeromonas genera were reduced to approximately 70% using the isolated bacteriophage. In recent years, phages have become the targeting agents for MDR bacteria present in the environment and have been proposed as anti-biofilm agents, antifoaming agents, and bacterial load reducers. A previous study reported that phages NOC1, NOC2, and NOC3 were used as antifoaming agents against Nocardia species [36].
3.4. Potential Application and Limitation in Wastewater Treatment Systems
In the real wastewater treatment systems, phage-based biocontrol could be used in various methods, including the mitigation of membrane biofouling, sludge bulking and ARB growth. Published studies that control unwanted bacterial growth using lytic phage in water and wastewater engineering have been limited to use of single isolated phage [13,14,36]. However, future research on the use of a phage cocktail and the solution of lysogenic conversion in a real scenario is required to enhance stable application for removing residual antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the effluent of WWTPs.
In the case of potential use in real field-based plants, the dose location of the isolated phage should be determined to increase the efficacy and stability in WWTPs (Figure 7). In a conventional activated sludge process (Figure 7a), the location of phage dose should be prior to the secondary settling tank to avoid the death of beneficial microorganisms that remove organic matters and nutrients (N and P). In membrane bioreactor, phage can be directly added to remove biofouling-causing bacteria due to the lack of a settling tank. In activated sludge processes, the phage dose infecting ARB can be two different locations, where phage can be injected before and after of the secondary settling tank (Figure 7a,c). Installing an optional tank for phage therapy would provide a benefit on ARB removal with a proper retention time.
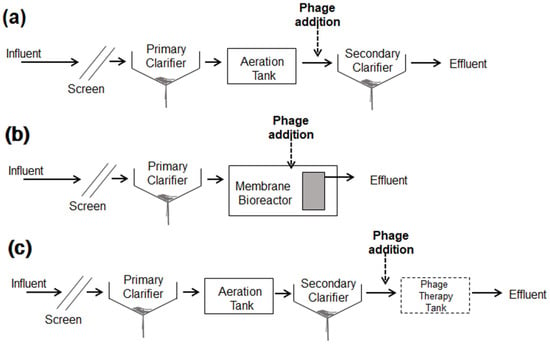
Figure 7.
Potential location of phage dose in wastewater treatment processes. (a) Conventional activated sludge process, (b) membrane bioreactor, and (c) conventional activated sludge process with optional reservoir of phage treatment.
Despite of advantages on phage-based biocontrol, the limitations are present during water and wastewater treatment processes. Antibiotic resistance gene (ARG) could be transferred to other bacteria by the transformation and transduction process. In addition, the stock for many phages termed phage cocktail is required to reduce certain antibiotic resistance bacteria. This process can be time-consuming and laborious.
4. Conclusions
The presence of ARB in treated wastewater is unavoidable because no effluent discharge limit for ARB exists in water reclamation facilities. The multidrug-resistant bacterium Aeromonas spp. and its lytic phage were isolated from livestock WWTP. Aeromonas spp. is the predominant antibiotic-resistant bacteria in WWTP with almost 65.7% of total bacterial species. Aerophage effectively reduced the bacterial population to 45% after 12 h of incubation and to 20% after 24 h of incubation. The isolated bacteria were resistant to different antibiotic concentrations. The dose of phage in mixed cultures could mitigate the population of a target bacterium, which can spread antibiotic traits to wastewater treatment processes and receiving water basins. Therefore, these results indicate that lytic phages can be an alternative method to reduce antibiotic resistance in wastewater without the presence of chemical byproducts. Further studies on the use of phage cocktails and accurate ARB monitoring of phage treatment will be required to enhance the efficacy and stability of ARB control in wastewater treatment systems.
Author Contributions
R.P.: methodology, analysis, writing; D.S.: methodology, analysis; J.C.: conceptualization, analysis, writing and editing, supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), grant number 2021R1A2C1007887.
Data Availability Statement
Data is available upon request.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MIST) (No.2021R1A2C1007887).
Conflicts of Interest
There are no conflict of interest to declare.
References
- Rohde, C.; Wittmann, J.; Kutter, E. Bacteriophages: A Therapy Concept against Multi-Drug-Resistant Bacteria. Surg. Infect. 2018, 19, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, D.; Mukherjee, R. Ameliorating the Antimicrobial Resistance Crisis: Phage Therapy. IUBMB Life 2019, 71, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Li, X.; Fan, X.Y.; Zhao, J.R.; Zhang, Z.X. Wastewater treatment plants as reservoirs and sources for antibiotic resistance genes: A review on occurrence, transmission and removal. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 46, 102539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauppinen, A.; Siponen, S.; Pitkanen, T.; Holmfeldt, K.; Pursiainen, A.; Torvinen, E.; Miettinen, I.T. Phage biocontrol of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa in water. Viruses 2021, 13, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.; Choi, J. Bacterial communities and antibiotic resistance communities in a full scale hospital wastewater treatment plant by high-throughput pyrosequencing. Water 2016, 8, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan Raj, J.R.; Karunasagar, I. Phages amid Antimicrobial Resistance. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 45, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, L.; Manaia, C.; Merlin, C.; Schwartz, T.; Dagot, C.; Ploy, M.C.; Michael, I.; Fatta-Kassinos, D. Urban wastewater treatment plants as hotspots for antibiotic resistant bacteria and genes spread into the environment: A review. Sci. Total. Environ. 2013, 447, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Li, J.; Chen, H.; Bond, P.L.; Yuan, Z. Metagenomic analysis reveals wastewater treatment plants as hotspots of antibiotic resistance genes and mobile genetic elements. Water Res. 2017, 123, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.S.; Qu, H.M.; Yang, D.; Hu, H. Chlorine disinfection increases both intracellular and extracellular antibiotic resistance genes in a full-scale wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2018, 136, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; LI, B.; Li, N.; Sardar, M.F.; Song, T.; Zhu, C.; Lv, X.; Li, H. Effects of UV disinfection on phenotypes and genotypes of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in secondary effluent from a municipal wastewater treatment plant. Water Res. 2019, 157, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.B.; Guo, M.T.; Yang, J. Fate of antibiotic resistant bacteria and genes during wastewater chlorination: Implication for antibiotic resistance control. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotay, S.M.; Datta, T.; Choi, J.; Goel, R. Biocontrol of biomass bulking caused by Haliscomenobacter hydrossis using a newly isolated lytic bacteriophage. Water Res. 2010, 45, 694–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharjee, A.S.; Choi, J.; Motlagh, A.M.; Mukherji, S.T.; Goel, R. Bacteriophage therapy for membrane biofouling in membrane bioreactors and antibiotic-resistant bacterial biofilms. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2015, 112, 1644–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayyaru, S.; Choi, J.; Ahn, Y.H. Biofouling reduction in a MBR by the application of a lytic phage on a modified nanocomposite membrane. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2018, 4, 1624–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withey, S.; Cartmell, E.; Avery, L.M.; Stephenson, T. Bacteriophages—Potential for application in wastewater treatment processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 339, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerbergen, K.; Willems, K.A.; Dewil, R.; Impe, J.V.; Appels, L.; Lievens, B. Isolation and screening of bacterial isolates from wastewater treatment plants to decolorize Azo dyes. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2018, 125, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numberger, D.; Ganzert, L.; Zoccarato, L.; Muhldorfer, K.; Sauer, S.; Grossart, H.S.; Greenwood, A.D. Characterization of bacterial communities in wastewater with enhanced taxonomic resolution by full-Length 16S rRNA sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallavali, R.R.; Degati, V.L.; Lomada, D.; Reddy, M.C.; Durbaka, V.R.P. Isolation and in vitro evaluation of bacteriophages against MDR-bacterial isolates from septic wound infections. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallavali, R.R.; Degati, V.L.; Reddy, N.V.R.; Durbaka, V.R.P. Isolation and Characterization of a lytic bacteriophage (VB_PAnP_PADP4) against MDR- Pseudomonas Aeruginosa isolated from septic wound infections. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2019, 18, 325–333. [Google Scholar]
- Kasurinen, J.; Spruit, C.M.; Wicklund, A.; Pajunen, M.I.; Skurnik, M. Screening of bacteriophage encoded toxic proteins with a next generation sequencing-based assay. Viruses 2021, 13, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skurnik, M.; Pajunen, M.; Kiljunen, S. Biotechnological challenges of phage therapy. Biotechnol. Lett. 2007, 29, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Dong, Y.; Lu, C.; Liu, Y. Isolation and characterization of bacteriophages against virulent Aeromonas hydrophila. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torabi, L.R.; Naghavi, N.S.; Doudi, M.; Monajemi, R. Efficacious antibacterial potency of novel bacteriophages against Esbl-producing Klebsiella Pneumoniae isolated from burn wound infections. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2021, 13, 678–690. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pallavali, R.R.; Degati, V.L.; Narala, V.R.; Velpula, K.K.; Yenuhu, S. Lytic bacteriophages against bacterial biofilms formed by multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Staphylococcus aureus isolated from burn wounds. Phage 2021, 2, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wintachai, P.; Surachat, K.; Singkhamanan, K. Isolation and characterization of a novel autographiviridae phage and its combined effect with tigecycline in controlling multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii-Associated skin and soft tissue infections. Viruses 2022, 14, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Rhee, C.; Park, S.G.; Kim, D.W.; Yu, S.I.; Shin, J.; Hwang, S.; Shin, S.G. Tracking microbial community shifts during recovery process in overloaded anaerobic digesters under biological and non-biological supplementation strategies. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 340, 125614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A Versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toya, R.; Sasaki, Y.; Uemura, R.; Sueyoshi, M. Indications and patterns of antimicrobial use in pig farms in the southern Kyushu, Japan: Large amount of tetracyclines used to treat respiratory disease in post-weaning and fattening pigs. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2021, 83, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, R.T. Leech Biology and Behaviour: Feeding, Biology, Ecology and Systematic; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1986; Volume II. [Google Scholar]
- Ghenghesh, K.S.; El-Mohammady, H.; Levin, S.Y.; Zorgani, A.; Tawil, K. Antimicrobial resistance profile of Aeromonas species isolated from Libya. Libyan J. Med. 2013, 8, 21320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravena-Roman, M.; Inglis, T.J.J.; Henderson, B.; Riley, T.V.; Chang, B.J. Antimicrobial susceptibilities of Aeromonas strains isolated from clinical and environmental sources to 26 antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 1110–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.S.; Nguyen, T.H.; Vo, H.P.; Doan, V.C.; Nguyen, H.L.; Tran, M.T.; Tran, T.T.; Southgate, P.C.; Kurtboke, D.I. Protective effects of bacteriophages against Aeromonas hydrophila species causing motile Aeromonas Septicemia (MAS) in striped catfish. Antibiotics 2018, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiha, S.; Grewal, R.K.; Roy, S. Modeling bacteria-phage interactions and its implications for phage therapy. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 103, 103–141. [Google Scholar]
- Khairnar, L.; Pal, P.; Chandekar, R.H.; Paunikar, W.N. Isolation and characterization of bacteriophages infecting Nocardioforms in wastewater treatment plant. Biotechnol. Res. Int. 2014, 4, 151952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Gill, J.J.; Young, R.; Summer, E.J. Bacteriophages of wastewater foaming-associated filamentous Gordonia reduce host levels in raw activated sludge. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).