Abstract
Irrigation water quality is important to sustain agricultural productivity. The primary irrigation water sources in Al-Ahsa Oasis, KSA, are groundwater wells, mixed with treated wastewater and agricultural drainage. This study sought to evaluate irrigation water quality in Al-Ahsa Oasis with the aid of using irrigation water quality indices (IWQIs). One hundred and forty-eight different water samples were collected from various irrigation water resources throughout Al-Ahsa Oasis. The investigated physiochemical characteristics include pH, temperature, TDS, EC, turbidity, free chlorine, total hardness, cations (Na, K, Ca, Mg), anions (Cl, CO3, HCO3, SO4), organic matter indices (DO, BOD, COD), and nutrients (NH4, NO3, PO4). The IWQIs used in this study include salinity hazard, sodium adsorption ratio (SAR), Kelly’s ratio (KR), soluble sodium percentage (SSP), Permeability index (PI), residual sodium carbonate (RSC), and magnesium hazard (MH). The results indicated that treated wastewater mixed with groundwater is acceptable for irrigation. Spatial variations in irrigation water quality throughout Al-Ahsa are associated with water resources. For instance, groundwater mixed with agricultural drainage has the highest values of TDS, cations, and anions, whereas the lowest values were reported for treated wastewater, reflecting the good efficiency of wastewater treatment plants. The IWQI results revealed that 4.1% and 62.1% of the investigated irrigation water samples were considered good (class III) and satisfactory (class IV) for irrigation, respectively, whereas 33.8% of the collected water samples fall within the severe irrigation restrictions. Moreover, 79.7% of the investigated water samples were classified to have high to very high salinity hazards (C3, C4) and medium to high sodium hazards (S2, S3). Regular monitoring and assessment of treated water quality and wastewater treatment plant efficiency are important factors in achieving the sustainability of treated wastewater reuse in irrigation and consequently food security.
1. Introduction
All known living forms, including plants, animals, and people, depend on water for their survival [1]. In many regions throughout the world today, competition for scarce water resources is fierce, especially in arid and semiarid countries such as Saudi Arabia [2,3]. Moreover, increased human activity has resulted in dramatically increased anthropogenic discharges of pollutants into the surrounding water environment, resulting in deteriorating water resources and impairing their potential uses [3,4,5,6]. For instance, agricultural expansion is leading to the extensive use of fertilizers and chemical pesticides, resulting in water contamination [7,8]. Hence, surface and groundwater might become contaminated through various human activities, including urbanization, industrialization, landfilling, and agricultural developments [9,10,11]. Thus, sustainable management of the available water resources, in terms of quantity and quality, is critical to any society to preserve water security [12].
Irrigation water should be available in an appropriate amount and conform to irrigation water quality standards to sustain agricultural production [8,13]. In Saudi Arabia, the agricultural sector consumes up to 87% of water resources, which derive from groundwater wells, little rainfall harvest, treated wastewater, and partially agricultural drainage [14,15]. Recent agricultural expansion and the related extensive abstraction of groundwater wells along with dried climate conditions has resulted in high salinity problems and led to the urgent reuse of treated wastewater mixed with groundwater for irrigation purposes [16,17]. Many scholars consider treated wastewater as a vital asset for agriculture and a trustworthy, stable, and reliable source of water and nutrients for plant growth [6,14,17,18].
The use of renewable treated wastewater in irrigation has many advantages and environmental/economic benefits. These include the provision of an alternative option to increase the available water resources, meeting water demand, addressing water shortages, conserving freshwater, coping with dried climatic conditions, and resolving the untreated sewage water indiscriminate disposal issues [6,18,19]. Moreover, the reuse of treated wastewater in irrigation leads to enhancing the soil and plants with organic matter and nutrients, reducing the use of soil chemical fertilizers, increasing agricultural production along with decreasing costs, and adapting to climate change [6,20,21].
On the other hand, there are some concerns associated with the prolonged reuse of treated wastewater and agricultural drainage in irrigation, such as health hazards, soil deterioration, and toxicity issues [19,22,23]. The prolonged reuse of irrigation water may result in high salinity and medium sodicity issues in some agricultural areas of Saudi Arabia [16,24]. The accumulation of heavy metals in soil might result from the prolonged reuse of treated wastewater in irrigation [11]. The WHO has issued guidelines for the safe reuse of treated wastewater in irrigation to reduce the possible risks on human health [25]. Moreover, any negative impacts associated with the use of treated wastewater can be mitigated using efficient sewage treatment technologies, the controlled reuse of treated wastewater, an appropriate irrigation system, along with an effective governing monitoring plan [18,19,25].
Al-Ahsa Oasis (also called Al-Hassa) is considered one of the largest agricultural zones in Saudi Arabia. There are no detailed recent comprehensive studies regarding the impacts of the reuse of treated wastewater and partially agricultural drainage on irrigation water quality after mixing with groundwater in Al-Ahsa Oasis. The quality of irrigation water sources is evaluated based on all kinds and quantities of dissolved salts, including major anions, cations, nutrients, and calculating irrigation water quality indices (IWQIs) [1,26]. A study on the characteristics evaluation of treated wastewater used for irrigation in Riyadh revealed that nitrate levels exceed the permissible limit for irrigation, and water salinity is high with a low sodium content (class C3–S1) [17]. An investigation of groundwater quality in Al-Ahsa Oasis revealed high salinity and nitrate values in groundwater wells [9]. Moreover, groundwater, used in irrigation in Al-Ahsa Oasis, is reported to be high in salinity and low/medium in sodicity (class C3–S1 and C4–S2), which might be the result of extensive abstraction from groundwater wells [27,28,29]. The investigation of irrigation water quality in other arid area such as Abu Dhabi (UAE) indicated that most of the water samples are high/very high in the salinity and sodicity category [3]. A study on water quality for irrigation in the Sultanate of Oman revealed that all samples fall within the range of high salinity and a low sodium content [30]. Hence, some researchers have studied irrigation water, with respect to the reuse of treated wastewater, to overcome water scarcity problems, salinity hazards, and increase agricultural productivity [8,11,16,28].
The current study aimed to assess spatial and seasonal variations in irrigation water quality within Al-Ahsa Oasis after mixing with both treated wastewater and agricultural drainage. The study also investigated the quality of irrigation water resources, including groundwater wells, treated wastewater, and reused agricultural drainage. The IWQIs were employed as an efficient management tool of water quality evaluation for irrigation purposes. This study is important in terms of evaluating the quality of irrigation water, which is closely associated with soil fertility/degradation and agricultural production. It also highlights the need for an ongoing monitoring/assessment program to further investigate the quality of renewable irrigated treated water, the performance of sewage treatment plants, and the probable benefits/risks of treated wastewater reuse.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Al-Ahsa Oasis is the largest oasis in the kingdom of Saudi Arabia and located in the eastern region. The oasis covers a total area of 200 km2, of which more than 80 km2 is under agricultural farming [31]. Al-Ahsa has a hot–dry climate, with summer temperatures reaching 46 °C, an evaporation rate of 2600 mm/year, and an annual rainfall rate of 80 mm [14,32]. For a long period, Al-Ahsa Oasis was dependent mainly on groundwater wells and natural springs for irrigation purposes. Since the 1980s, Al-Ahsa Irrigation and Drainage Authority (HIDA) has investigated the use of unconventional sources of irrigation water, such as the reuse of agricultural drainage, and then the reuse of treated wastewater started in 2000. Hence, the main sources of irrigation water in Al-Ahsa Oasis are currently groundwater wells mixed with both treated wastewater and partially agricultural drainage water. Approximately 200,000 m3/day of treated wastewater used in irrigation derives from main sewage treatment plants (STPs) in Al-Ahsa, namely Hofuf STP, Umran STP, Oyun STP, and Aramco STP [20]. These sewage treatment plants use both primary, secondary, and tertiary treatment processes along with the use of an aerobic activated sludge method. The Saudi Irrigation Organization (SIO) (previously called HIDA) follows a continuous water quality monitoring program, especially for treated wastewater along with the continuous assessment of STPs performances, to be conducted by the Saudi National Water Company (NWC).
Agricultural farms in Al-Ahsa Oasis can be classified according to the source of irrigation water into four categories. First, agricultural farms using treated wastewater (TWW) only in irrigation. Second, agricultural farms using private groundwater wells (GW). Third, agricultural farms using groundwater mixed with agricultural drainage (GW + AD). Fourth, agricultural farms using mixed irrigation water (mixed of treated wastewater, groundwater, and agricultural drainage “TWW + GW + AD”).
The current study focused on irrigation water quality criteria, including physiochemical parameters such as pH, temperature, total dissolved solids (TDS), electrical conductivity (EC), turbidity, free chlorine, total hardness (TH), cations (sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium), anions (chloride, carbonate, bicarbonate, sulphate), nutrients (ammonium, nitrate, phosphate), and organic matter indices (dissolved oxygen “DO”, biochemical oxygen demand “BOD”, chemical oxygen demand “COD”).
2.2. Sample Collection
Irrigation water samples were collected from various agricultural areas of Al-Ahsa Oasis to represent all categories of the above mentioned agricultural farms (Figure 1). Hence, thirty-seven water samples were taken from various irrigation water canals and irrigation water resources, including groundwater wells, treated wastewater, and reused agricultural drainage. This study was conducted for over one year during October 2016 and January, May, and September 2017 to investigate any seasonal variations in irrigation water quality. Hence, a total number of 148 irrigation water samples was collected, representing all sorts of irrigation water (TWW, GW, GW + AD, mixed) in Al-Ahsa Oasis.
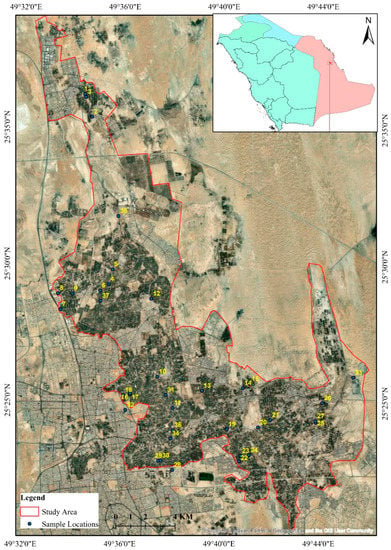
Figure 1.
Geographic map of the Al-Ahsa Oasis boundary, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), indicating the 37 sampling sites for collecting irrigation water samples.
2.3. Irrigation Water Analysis
Master water parameters such as temperature, pH, TDS/EC, and free chlorine were measured directly in the field during sample collection [5]. Portable pH (Hanna Instruments, HI-9124, Vöhringen, Germany) and conductivity (Jenway, EC-470, UK) meters were used to in situ measure pH/temperature, TDS (mg/L), and EC (µ-Siemens/cm), respectively. A portable colorimeter (Oakton, C-301, Singapore) was used to measure free chlorine (mg/L) based on the DPD colorimetric method. Turbidity (NTU) was measured using a Turbidity meter (Hanna Instruments, HI-88703, Germany) [33].
The American Standards for Water and Wastewater Examination Manual was followed for conducting the laboratory analysis of all irrigation water samples [34]. Nitrate, phosphate, and sulphate were analyzed in irrigation water using a UV-Visible Spectrophotometer (Shimadzu, UV-1650, Japan) by using a direct UV absorbance method, ascorbic acid/ammonium molybdate method, and turbidmetric method, respectively [33,34,35]. Ions such as Cl, CO3, HCO3, Ca, and Mg and organic matter indicators (DO, BOD, and COD) were analyzed using scientific well-known trimetric methods [33]. Ammonium was measured using the Kjeldahl method (Buchi Distillation, B-32, Switzerland). The flame emission photometric (Flame Photometer, Jenway, UK) was used for the analysis of sodium and potassium in irrigation water [34].
The quality control of analytical data was assured by implementing standard operating protocols, such as triplicate water sample analysis, calibration using high-purity standards, and the determination of analytical blank. The precision of water sample analysis, known as the coefficient of variation (CV), was normally below 3–5%. Additionally, the accuracy of the chemical analysis for water samples was confirmed by determining the ion balance error (up to 3–5% error) using the following formula (Equation (1)) [26,36]. The results of the measured parameters of collected water samples were compared with the irrigation standards limits of the Food and Agricultural Organization (FAO) [13] and the KSA irrigation water standards according to Saudi’s Water Law [37].
The IBM SPSS software (Version 26) was used to conduct the statistical analysis for the results of the water analysis data. The calculated data descriptive statistics include the average, minimum, maximum, median, standard deviation, and variance. Pearson’s correlation matrix was computed between pairs of irrigation water analysis parameters to explore any statistically significant correlations (p < 0.01 “the 99% confidence level”, n = 148). Additionally, the variance between the collected irrigation water samples from various agricultural areas (37 sampling sites) of Al-Ahsa Oasis and over one year (4 sampling campaigns) were investigated by calculating the one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) at a significant level of p < 0.01. An ANOVA was also used to examine any significant variance among irrigation water samples from various water resources (TWW, GW, GW + AD, mixed of all sources).
2.4. Irrigation Water Quality Indices (IWQIs)
Irrigation water contains various concentrations and kinds of dissolved salts. The salt contents of soil could be greatly affected by the salt contents of irrigation water, which would control plant growth and primary production [38]. Therefore, the assessment of irrigation water suitability is dependent on the calculation of some hydro-chemical water indices. The computed irrigation water quality indices in this study include salinity hazard (EC, TDS), total hardness (TH), sodium adsorption ratio (SAR), Kelly’s ratio (KR), soluble sodium percentage (SSP), permeability index (PI%), residual sodium carbonate (RSC), and magnesium hazard (MH%), which are widely used in the literature [1,3,12,39,40,41]. These IWQ indices provide crucial assistance for identifying problems that may arise in soil and crops due to the quality of irrigation waters used [3]. The selection of these irrigations indices is based on some agronomic issues related to water/soil salinity, soil permeability, crops toxicity, and, consequently, agricultural production [1,3,26]. Equations for calculating these irrigation water quality indices are outlined in Table 1.

Table 1.
Irrigation water quality suitability indices used in the current research [1,12,39].
The concentrations of all dissolved ions (Cl, HCO3, SO4, Na, K, Ca, Mg) used in calculations of the above irrigation water quality indices should be in milliequivalents per liter (meq/L). The evaluation of collected water samples for irrigation suitability was performed based on comparison with USA salinity laboratory diagrams [42] and irrigation water quality standards [13,37]. For instance, sodium hazard (SAR) is calculated as the ratio of sodium content to both calcium and magnesium contents in irrigation water. The sodium adsorption ratio is used to assess soil propensity to adsorb Na ions as well as the propensity of dissolved cations to enter the soil cation exchange zones [12]. High levels of sodium could lead to the adsorption of sodium ions onto soil cation exchange sites, causing soil to disaggregate and consequently reducing water flow [30,39]. Salinity hazards to soil and sensitive crops are related to high levels of EC, sodium, chloride, and calculated SAR in irrigation water [3,12].
Kelly’s ratio represents alkali hazards, as sodium concentration is measured against both calcium and magnesium, with a value below one indicating water suitable for irrigation [12]. A soluble sodium percentage reflects irrigation water adequacy and is calculated as the concentration of sodium against the concentration of all cations (Ca, Mg, Na, K) [44]. The permeability index is used to reflect soil permeability for water movement and, consequently, its suitability for irrigation [3]. Residual sodium carbonate is calculated to assess the risk of excessive carbonate/bicarbonate on suitability for irrigation [22]. The magnesium hazard highlights the significance of magnesium ion for soil and crops health.
The overall IWQI can be utilized to evaluate the suitability of water for irrigation through the conversion of large analytical data into a single numeric score to be used by decision makers for the improved explanation of water quality [3,47,48]. The water quality parameters used in the IWQI calculation includes EC, SAR, Na, Cl, and HCO3, which are also related to the calculation of the above hydro-chemical indices used for irrigation water rating [12].
First, the water quality measurement value () was computed for each of the selected water quality parameters using the following formula (Equation (2)) [1,12,48] and according to Table 2.
- where is the maximum value of for the corresponding class (for instance of first q class 85–100);
- is the laboratory-measured value for the water quality parameter;
- is the corresponding value to the lower limit of the class to which the measured parameter belongs (for example in the case of first class of EC);
- is class amplitude (for instance of first q class 85–100);
- is the class amplitude to which the measured water parameter belongs (for example in the case of first X class of EC);
- In order to calculate the of the final class of each water parameter, the maximum laboratory-measured value of water quality parameters was used as the upper limit (for example in the case of final X class of EC).

Table 2.
Parameter limiting values for the water quality measurement (qi) and the relative weight (wi) for each IWQI parameter [1,12,48].
Table 2.
Parameter limiting values for the water quality measurement (qi) and the relative weight (wi) for each IWQI parameter [1,12,48].
| qi | EC (µs/cm) | SAR | Na (meq/L) | Cl (meq/L) | HCO3 (meq/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 85–100 | 200 ≤ EC < 750 | 2 ≤ SAR < 3 | 2 ≤ Na < 3 | 1 ≤ Cl < 4 | 1 ≤ HCO3 < 1.5 |
| 60–85 | 750 ≤ EC < 1500 | 3 ≤ SAR < 6 | 3 ≤ Na < 6 | 4 ≤ C l< 7 | 1.5 ≤ HCO3 < 4.5 |
| 35–60 | 1500 ≤ EC < 3000 | 6 ≤ SAR < 12 | 6 ≤ Na < 9 | 7 ≤ Cl < 10 | 4.5 ≤ HCO3 < 8.5 |
| 0–35 | EC < 200 or EC ≥ 3000 | SAR < 2 or SAR ≥ 12 | Na < 2 or Na ≥ 9 | Cl < 1 or Cl ≥ 10 | HCO3 < 1 or HCO3 ≥ 8.5 |
| Wi (Sum = 1) | 0.211 | 0.189 | 0.204 | 0.194 | 0.202 |
Second, the IWQI was computed for each of the collected water samples using the following formula (Equation (3)) [1,12,48].
where is the above-calculated water quality value and is the relative weight of each water quality parameter (Table 2), as illustrated in the literature [1,48]. The calculated IWQI is a dimensionless parameter with five categories: (i) excellent (85–100), (ii) very good (70–85), (iii) good (55–70), (iv) satisfactory (40–55), and (v) unsuitable (0–40), according to a range from 0 to 100 [49].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physio-Chemical Properties
Table 3 and Supplementary Materials provide descriptive statistical data for the overall measured irrigation water quality variables. The average water temperature was 27.9 ± 4.97 °C, with a range of 16.1 to 38.0 °C. The average temperature values of irrigation water samples collected during September 2017 (33.2 ± 2.43 °C) were found to be higher than that of irrigation water samples collected during January 2017 (21.9 ± 3.44 °C), as supported by the ANOVA F-time significance value (F = 106, p < 0.01, Table 3). The collected irrigation water samples had an average pH value of 7.72 ± 0.45, with the range of 6.09 to 8.83. pH is a crucial indicator of the quality of irrigation water and the suitability of soil for plant growth. The pH results indicated that higher values were recorded during January 2017 compared to lower values of those collected during October 2016 (F = 13.9, p < 0.01, Table 3). The majority of the measured pH values (94.6%) are within the range of 6.5 to 8.4, which is compliant with the FAO and Saudi irrigation standards [13,37].

Table 3.
Average ± standard deviation of the measured parameters in irrigation water samples collected during the four surveys from Al-Ahsa Oasis, KSA, including ANOVA (F ratio) for sites, time, and water resources.
The average TDS concentration in the collected irrigation water samples was 2275 ± 1127 mg/L and ranged 860–5950 mg/L, whereas EC values ranged between 1430 and 9820 µS/cm, with an average of 3789 ± 1873 µS/cm. Approximately half of the measured water samples (49.3%) have TDS values greater than the maximum permissible limit of 2000 mg/L for irrigation purposes [13,37]. As shown in Figure 2, higher values of TDS (and EC) were found in water samples collected during October 2016 relative to those collected during January 2017. Lower values of TDS (and EC) were reported in treated wastewater, relative to higher values measured in irrigation water mixed of groundwater with agricultural drainage, which increase water corrosivity [1]. This revealed that significant variations in the salinity levels of irrigation waters are associated with their water resources and sample collection sites, as supported by ANOVA F-resources and site significance values (F = 21.2, 19.3 p < 0.01, Table 3). Higher salinity values in irrigation water reported in the current study, which agree with previous similar studies, might result from extensive groundwater abstraction, the reuse of agricultural drainage, hot/dried climatic conditions, sea water intrusion, and soil weathering [3,9,11,17,50].
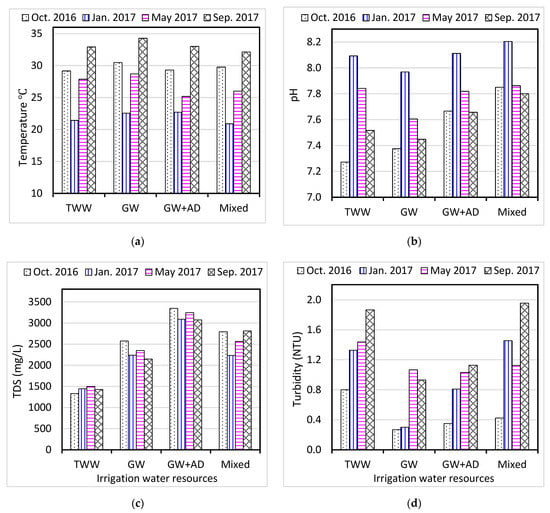
Figure 2.
Average concentrations of (a) temperature, (b) pH, (c) TDS (mg/L), and (d) turbidity (NTU) in irrigation water resources collected from Al-Ahsa Oasis, Saudi Arabia. TWW stands for treated wastewater, GW for groundwater, GW + AD for groundwater combined with agriculture drainage, and mixed for TWW + GW + AD (the same for Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5).
The turbidity levels of the collected irrigation water samples ranged from 0.11 to 2.81 NTU. Almost all of the measured irrigation water samples have turbidity values lower than the maximum allowance limit of 5 NTU [37]. The results revealed that higher values of turbidity were recorded during May and September 2017 compared to the lower turbidity values of those collected during October 2016 as supported by ANOVA F-time significance value (F = 22.2, p < 0.01) (Figure 2). Moreover, lower turbidity values were measured in groundwater samples compared to other resources of irrigation water (F = 13.9, p < 0.01, Table 3). Groundwater samples recorded the lowest turbidity values due to a low suspended solids content in groundwater wells. Concentrations of free chlorine (Cl2) measured in irrigation waters ranged 0.02–0.98 mg/L. Lower levels of chlorine (<0.5 mg/L) present in irrigation water at agricultural farmers (especially TWW) are required to prevent any microbial contamination along with irrigation canals transport [37].
3.2. Water Anions and Cations
Table 3 and Figure 3 show the results of anions (Cl, HCO3, and SO4) measured in the irrigation water samples of the current study. The concentrations of chloride (Cl) ranged from 268 to 2500 mg/L, with significant variations among irrigation water resources and sampling sites. The chloride concentrations measured in irrigation water samples collected during January 2017 were lower in value compared to those water samples collected during October 2016 (Table 3). As shown in Figure 3, lower values of chlorides were measured in irrigation-treated water compared to the higher values of chlorides observed in mixed irrigation water (groundwater wells and agricultural drainage) (F = 18.4, p < 0.01). A high level of chloride in irrigation water is considered toxic to soil and plants as it is not adsorbed by soil particles and accumulates in plant leaves [22].
On the other hand, bicarbonate concentrations ranged from 78 to 552 mg/L, whereas carbonate ion was not detected in all irrigation water samples. Concentrations of sulphates in the collected irrigation water ranged between 219 and 1489 mg/L. As illustrated in Figure 3, higher concentrations of bicarbonate and sulphate were measured in groundwater combined with agricultural drainage (GW + AD) and mixed irrigation water compared to lower values observed in irrigation-treated water (F = 20.5, 29.5, respectively; p < 0.01). Bicarbonate and sulphate are also crucial parameters in determining irrigation water suitability [1].
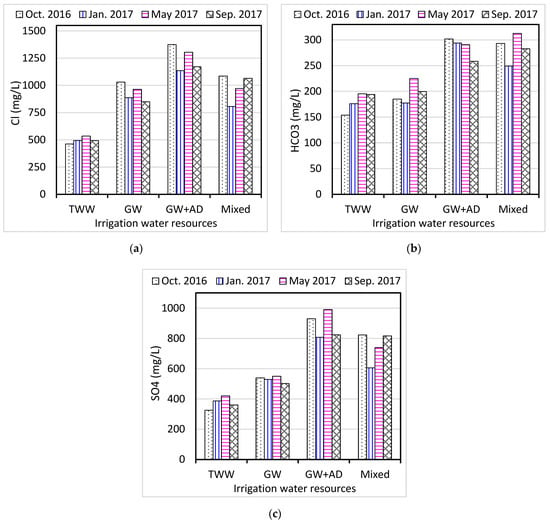
Figure 3.
Average anions concentrations in irrigation water resources collected from Al-Ahsa Oasis, Saudi Arabia: (a) Cl, (b) HCO3, (c) SO4 (mg/L).
A summary of the results of the cations (Na, K, Ca, and Mg) analysis in the irrigation water samples is shown in Table 3 and Figure 4. The average concentration of sodium was 593 ± 318 mg/L, with the range of 144–1541 mg/L, whereas the potassium values ranged from 4.64 to 185 mg/L. In comparison to higher values of sodium reported in water samples taken in October 2016, irrigation water samples taken in January 2017 had lower sodium values. Lower values of sodium and potassium were reported in irrigation-treated water relative to higher values measured in mixed irrigation water (groundwater and agricultural drainage) as supported by ANOVA F-resources significance values (F = 18.4, 14, respectively; p < 0.01). Sodium concentration is a crucial parameter in assessing irrigation water suitability. A high level of sodium causes the formation of an alkaline soil, which might result in decreasing soil permeability and impact soil structure [22,26].
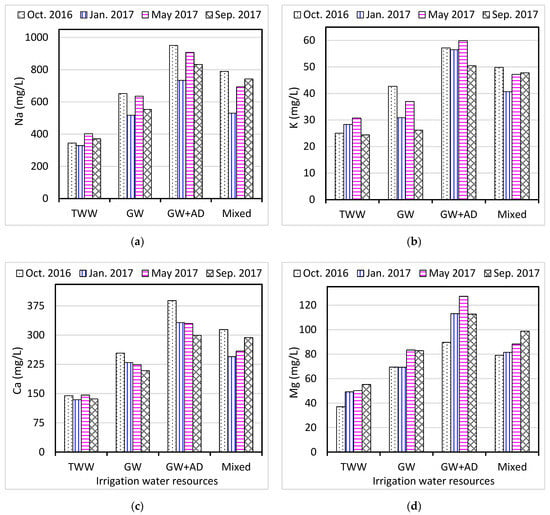
Figure 4.
Average cations concentrations in irrigation water resources collected from Al-Ahsa Oasis, Saudi Arabia: (a) Na, (b) K, (c) Ca, (d) Mg (mg/L).
The average calcium value measured in the irrigation water samples was 233 ± 122 mg/L, with a range of 80.1–673 mg/L. Magnesium concentrations ranged from 24.7 to 221 mg/L, with an average of 76.5 ± 42.4 mg/L. In comparison to lower values of calcium reported in irrigation water samples taken in September 2017, higher calcium levels were found in samples taken in October 2016. As illustrated in Figure 4, higher concentrations of calcium and magnesium were measured in mixed irrigation groundwater with agricultural drainage, whereas lower values were reported in irrigation-treated water (F = 22.7, 17.9, respectively; p < 0.01). Total hardness of the irrigation water samples was determined as CaCO3 and ranged from 315 to 2368 mg/L. the presence of dissolved cations in water such as calcium and magnesium, and anions such as carbonate and bicarbonate, contribute to total hardness [1]. These results demonstrated that the Al-Ahsa Oasis irrigation water was very hard, with almost 83% of the analyzed water samples exceeding the 500 mg/L acceptable criteria [51]. Very hard water is not suitable for irrigation, causes scale formation, and consumes more soap detergent [5].
3.3. Organic Matter Indices and Nutrients
DO, BOD, and COD are considered the main organic matter indicators and are used widely to assess water quality in terms of organic pollution [52]. When the water environment is freshly polluted with organic matter, aerobic microorganisms consume dissolved oxygen in the biodegradation process and, consequently, the amount of biologically adsorbed oxygen increases [53]. The results of the organic matter indices (DO, BOD, COD) and nutrients (NH4, NO3, PO4) measured in the collected irrigation water are shown in Table 3 and Figure 5. The average dissolved oxygen values measured in the irrigation water samples was 7.98 ± 1.85 mg/L, with a range of 1.47–10.9 mg/L. Slightly lower DO concentrations were reported in May 2017 compared to higher values reported in January 2017, where DO levels increase in winter with a decreasing temperature. The solubility of oxygen in water decreases with increasing temperature and salinity values [52].
The BOD values ranged from 0.10 to 8.89 mg/L. Irrigation water samples taken in October 2016 had higher BOD levels. As illustrated in Figure 5, lower concentrations of BOD were measured in groundwater wells, compared to higher values of BOD observed in irrigation-treated water and mixed irrigation water (F = 17.6, p < 0.01). The average value of COD determined in the irrigation water samples was 18.5 ± 12.5 mg/L, with a range of 1–51 mg/L. Higher COD levels were measured in irrigation water samples collected during May 2017. Also, higher values of COD were measured in mixed irrigation water (groundwater wells, agricultural drainage, and treated water) compared to lower values observed in groundwater wells. Both BOD and COD levels in the irrigation water samples were below the maximum allowable value of 10 mg/L and 90 mg/L, respectively [37]. The results of the current study revealed that relatively high levels of organic matter were observed in irrigation-treated water and agricultural drainage. Recent agricultural expansion resulted in the excessive use of fertilizers and pesticides with the consequence of a high concentration of organic matter in agricultural drainage [8]. Treated wastewater is characterized by relatively high levels of biodegradable organic matter which can be used to improve soil fertility [18,19].
The range of ammonium content in the irrigation water samples was 0.11–1.59 mg-N/l. Ammonium is mostly present in treated wastewater as a result of organic matter decomposition, whereas a lower ammonium concentration would be found in groundwater [11]. As shown in Figure 5, relatively higher values of ammonium were measured in irrigation-treated water compared to lower values observed in groundwater wells (F = 7.24, p < 0.01). In comparison to lower ammonium levels reported in irrigation water samples taken in October 2016, higher ammonium concentrations were found in water samples taken in September 2017 (F = 10.9, p < 0.01). Almost all the irrigation water samples have ammonium values that are below the acceptable limit of 5 mg-N/L [13,37]
The average Nitrate content of the irrigation water samples was 4.87 ± 3.07 mg-N/L and ranged from 0.46 to 15.1 mg-N/L. Higher concentrations of nitrate were measured in irrigation water samples taken in October 2016 relative to lower values determined in water samples taken in May 2017 (F = 8.22, p < 0.01). Higher values of nitrate were measured in both groundwater wells and irrigation-treated water (F = 4.69, p < 0.01). Nitrate is negatively correlated with ammonium (Table 4) as nitrate is the last stable oxidation form of organic nitrogen decomposition. Previous similar studies in Al-Ahsa and Riyadh have reported high levels of nitrate in groundwater and treated irrigation water [9,17].
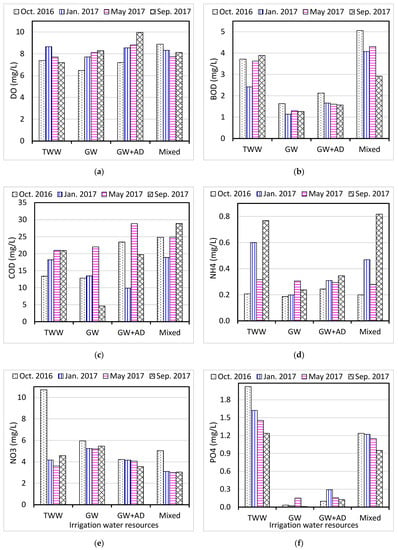
Figure 5.
Average concentrations of organic matter: (a) DO, (b) BOD, (c) COD and nutrients: (d) NH4, (e) NO3, (f) PO4 (mg/L) in irrigation water resources collected from Al-Ahsa Oasis, Saudi Arabia.
In the present study, phosphate values ranged from 0.01 to 3.25 mg/L, with significant variations among irrigation water resources. As shown in Figure 5, relatively higher levels of phosphate were measured in irrigation-treated water and mixed irrigation water compared to lower values observed in groundwater wells, as supported by the ANOVA F significance value (F = 84.5, p < 0.01). Higher values of phosphate were present in treated wastewater because of the domestic use of detergents [18]. Lower concentrations of phosphate were measured in irrigation water samples collected during September 2017. Approximately 6.75% and 11.5% of the collected irrigation water from Al-Ahsa Oasis has nitrate and phosphate values higher than the permitted irrigation limits of 10 mg-N/L and 2 mg/L, respectively [13]. High concentrations of phosphate and nitrate in treated wastewater can cause eutrophication problems of the receiving water body. However, the controlled use of treated water in irrigation improves soil and plant health with nutrients and consequently increases agricultural production, especially in arid/semiarid areas [6,20,21].
3.4. Correlation between Irrigation Water Quality Variables
To examine the connections between various irrigation water quality variables, Pearson correlation analysis was employed (Table 4). The results revealed strong positive significance correlations (p < 0.01) between TDS and other measured water quality ions as follows: chloride, bicarbonate, sulphates, sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and total hardness with a correlation coefficients range of r = 0.70–0.99. These substantial associations reflect the importance of these ions in the mineralization of irrigation water. Additionally, all the above mentioned water quality ions were strongly correlated with each other. The Mg and Cl substantial positive correlation (r = 0.89) revealed that water hardness was permanent in nature [36].

Table 4.
Water quality parameter correlations coefficient matrix for irrigation water samples taken from Al-Ahsa Oasis, Saudi Arabia.
Table 4.
Water quality parameter correlations coefficient matrix for irrigation water samples taken from Al-Ahsa Oasis, Saudi Arabia.
| pH | TDS | Turb. | Cl2 | Cl | HCO3 | SO4 | Na | K | Ca | Mg | TH | DO | BOD | COD | NH4 | NO3 | PO4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| TDS | 0.05 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| Turb. | 0.18 | −0.08 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| Cl2 | −0.01 | −0.06 | 0.08 | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| Cl | 0.03 | 0.99 | −0.10 | −0.06 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| HCO3 | 0.04 | 0.71 | 0.10 | −0.01 | 0.65 | 1 | ||||||||||||
| SO4 | 0.08 | 0.90 | −0.03 | −0.05 | 0.86 | 0.82 | 1 | |||||||||||
| Na | −0.01 | 0.98 | −0.08 | −0.04 | 0.98 | 0.68 | 0.86 | 1 | ||||||||||
| K | 0.07 | 0.90 | −0.02 | −0.05 | 0.89 | 0.64 | 0.77 | 0.91 | 1 | |||||||||
| Ca | 0.04 | 0.93 | −0.12 | −0.08 | 0.90 | 0.80 | 0.94 | 0.90 | 0.79 | 1 | ||||||||
| Mg | 0.08 | 0.83 | 0.06 | −0.05 | 0.81 | 0.65 | 0.79 | 0.77 | 0.66 | 0.74 | 1 | |||||||
| TH | 0.06 | 0.95 | −0.06 | −0.07 | 0.93 | 0.79 | 0.95 | 0.91 | 0.79 | 0.97 | 0.88 | 1 | ||||||
| DO | 0.26 | −0.04 | 0.21 | 0.05 | −0.04 | −0.05 | −0.03 | −0.05 | −0.04 | −0.08 | 0.00 | −0.06 | 1 | |||||
| BOD | 0.06 | −0.11 | 0.31 | −0.02 | −0.12 | 0.05 | −0.08 | −0.08 | −0.03 | −0.07 | −0.10 | −0.09 | 0.19 | 1 | ||||
| COD | 0.12 | 0.32 | 0.20 | −0.15 | 0.30 | 0.35 | 0.40 | 0.33 | 0.36 | 0.31 | 0.23 | 0.30 | −0.03 | 0.03 | 1 | |||
| NH4 | 0.15 | −0.18 | 0.62 | 0.12 | −0.19 | −0.04 | −0.12 | −0.18 | −0.15 | −0.19 | −0.08 | −0.16 | 0.16 | 0.22 | 0.02 | 1 | ||
| NO3 | −0.23 | −0.13 | −0.29 | −0.11 | −0.10 | −0.38 | −0.22 | −0.12 | −0.15 | −0.17 | −0.16 | −0.18 | −0.12 | −0.06 | −0.11 | −0.28 | 1 | |
| PO4 | −0.01 | −0.43 | 0.21 | 0.10 | −0.44 | −0.31 | −0.38 | −0.42 | −0.26 | −0.43 | −0.38 | −0.44 | −0.12 | 0.24 | 0.05 | 0.13 | 0.30 | 1 |
Note: Bold correlation is significant at the 0.01 level, Italic and underline correlation is significant at the 0.05 level, (n = 148).
Furthermore, phosphate and TDS showed a weak negative significant association (p < 0.01) with a correlation coefficient of r = 0.43. High phosphate concentrations were associated with low TDS values, as observed in irrigation-treated wastewater samples. Phosphate and nitrate were positively correlated (p < 0.01) with correlation coefficients of r = 0.30. The current study revealed relatively higher values of phosphate and nitrate measured in treated wastewater used in irrigation, which could improve the soil fertility of semiarid land [20]. Nitrate and ammonium had a weak, but significant, negative correlation (r = 0.28, p < 0.01). As the ammonium concentration in water decreases, the nitrate value increases as nitrate is the final stable oxidation state of nitrogenous organic compound [52].
Significantly positive relationships (p < 0.01) were found between BOD (organic matter) and turbidity, ammonium, and phosphate, with correlation coefficients of r = 0.31, 0.22, and 0.24, respectively. This significant positive correlation revealed that higher concentrations of organic matter (BOD) are associated with concentration increases in ammonium, phosphate, and water turbidity. A weak positive significance correlation (p < 0.01) was observed between COD and TDS (and related ions), with a correlation coefficients range of r = 0.30–0.39. Higher COD values were associated with higher TDS, as reported in irrigation water mixed with agricultural drainage. Agricultural drainage contains chemical residues of pesticides and chemical fertilizers which could increase the value of COD.
3.5. Irrigation Water Quality Indices (IWQIs)
The following discussed hydro-chemical water indices were used to assess the suitability of irrigation water from various sources within the study area (Table 5). Regarding EC values, approximately half of the measured water samples (52.7%) are considered unsuitable for irrigation, whereas 16% and 31% are in the “permissible” and the “doubtful” category, respectively. Furthermore, nearly all the measured water samples (97.3%) were classified as brackish water due to the higher levels of TDS (>1000 mg/L). All total hardness (TH) values determined in the collected irrigation water samples are higher than 300 mg/L, which were in the “very hard” category. These observations assure the elevated salinity levels in irrigation water sources (especially groundwater and agricultural drainage) within the study area.

Table 5.
Classification of irrigation water sources samples (collected during the four field campaigns from Al-Ahsa Oasis, Saudi Arabia) based on the standard value intervals for irrigation water quality standards [1,13,42,48].
The average values of SAR calculated for the collected water samples are 8.29 ± 2.62. The SAR values showed that 20.9% of the collected water samples are in the “good” category, 43.9% in the “doubtful” category, and 35.2% in the “unsuitable” category. The sodium adsorption ratio is used to assess the suitability of irrigated water to sodium hazards. SAR reflects the tendency of sodium ion to be adsorbed into the soil, affecting soil permeability and soil structure [1,30].
Kelly’s ratio (KR) represents the ratio of the measured sodium against both calcium and magnesium. The KR values in the current study ranged from 0.84 to 2.31. Approximately 93.9% of the measured water samples are in the “unsuitable” class for irrigation, with KR values > 1. The percentage of sodium content (SSP) against other cations in the measured irrigation water samples ranged from 44.7% to 66.4%. The SSP results indicated that 81.8% of the measured water samples are in the “permissible” category, and 18.2% are in the “doubtful” category. The above mentioned values of SAR, KR, and SSP reflect the elevated sodium concentrations (averaged 593 ± 318 mg/L) measured in the collected irrigation water. High sodium levels in irrigation water might result in a reduction in soil permeability, weak drainage, and toxicity to some crops [1,13].
On the other hand, the permeability index (PI), residual sodium carbonate (RSC), and magnesium hazard (MH%) were computed as important parameters to assess the suitability of water for irrigation within the study area. The percentage values of the permeability index ranged from 53.8% to 75.8%, showing that all the measured water samples (99.3%) were in the “suitable” category for irrigation. Values of RSC indicated that all measured water samples were in the “good” category, which is <1.25 meq/L, indicating minimal alkalinity hazards. Higher values of residual sodium carbonate reflect high levels of water alkalinity, which shows a harmful influence on irrigation [26]. Magnesium hazard values ranged from 14.4% to 49.2% in the measured water samples. MH% values revealed that 100% of the collected water sample were in the “suitable” category for irrigation, indicating appropriate levels of magnesium for soil and plant health.
The results of the overall IWQI calculations are outlined in Table 6. The IWQI values revealed that only 4.1% of the collected water samples are classified as good (class III) for irrigation uses with moderate restriction (MR), which can be used for moderate to high permeable soil and irrigate moderate salinity tolerance crops, whereas 62.1% of the collected water samples were considered satisfactory (class IV) for irrigation with high restriction (HR), which can be used to irrigate crops with a moderate to high salinity tolerance in soil with a high permeability without compact layers and at a certain irrigation frequency. Approximately, 33.8% of the collected water samples were classified in the severe restriction (SR) range (class V), which can be used to irrigate high-salt-tolerance plants only [1]. The average IWQI value in irrigation-treated water was 48.9 ± 4.51%, whereas a lower average value of 34.7 ± 6.82% was reported in groundwater mixed with agricultural drainage (as indicated in Supplementary Materials). This emphasizes the suitability of treated wastewater for irrigation.

Table 6.
IWQI characteristics of irrigation water samples (n = 148) collected from Al-Ahsa Oasis, Saudi Arabia [1,48,49].
In similar studies, 45% of the investigated groundwater wells in Makkah (KSA) were classified under high to severe restrictions for irrigations (HR and SR) [26]. Moreover, assessing groundwater for irrigation in Abu Dhabi (UAE) revealed that 44% and 52% of water samples were classified also in the high and severe irrigation restrictions (HR and SR) [3]. The above findings concluded that the majority of irrigation water resources in Al-Ahsa Oasis are considered high/very high in salinity and medium/high in sodicity, which might result from the extensive abstraction of groundwater, as reported by previous similar studies [27,28,29]. Hence, the IWQI can be utilized as an efficient water management tool to aid in the evaluation of irrigation water quality and enhance decision making [39,47].
3.6. Irrigation Water Overall Quality
Generally, as indicated in Supplementary Materials, the average measured values of TDS, EC, anions (Cl, HCO3, SO4), cations (Na, K, Ca, Mg), and total hardness were low in irrigation-treated wastewater (TWW) relative to higher values measured in mixed irrigation water (groundwater and agricultural drainage), as supported by the ANOVA F-water resources significance value (Table 3). A similar study on the evaluation of groundwater quality used for irrigation in Riyadh concluded that as the demand for water increases due to agricultural expansion, irrigation water became of low quality with a high salinity content [8].
In contrast, lower values of turbidity, BOD, COD, ammonium, and phosphate were observed in groundwater wells compared with higher values of those measured in both treated wastewater (TWW) and mixed irrigation water, as supported by the ANOVA F significance value (Table 3). Average higher values of nitrate were measured in both irrigation-treated water (TWW) and groundwater (GW). A relatively higher value of BOD, nitrate, and phosphate in irrigation-treated water could improve soil fertility and plant production, especially in arid and semiarid soil [6,19]. It is reported in the literature that the prolonged use of treated wastewater in irrigation could adversely impact soil and plant properties [21,22]. However, there are inconsistencies in the reported effects of using treated wastewater for irrigation on soil and plants, which could be due to wastewater characteristics, soil structure and types, plant species, the irrigation system used, and the ability to thrive in a nutrient-deficient environment [18,23,25].
The results revealed that relatively higher average values of water temperature were observed in irrigation water samples collected during October 2016 and September 2017 compared to lower values of those collected during January 2017. On the other hand, higher values of pH were recorded during January 2017 compared to lower values of those collected during October 2016 and September 2017. Higher values of turbidity and ammonium were recorded during September 2017 compared to lower values of those collected during October 2016. The above observed seasonal variations were supported by significance values ANOVA F-time, as shown in Table 3.
Almost half of the collected irrigation water samples of the current study have TDS (and related dissolved anions and cations) values greater than the maximum acceptable limit of 2000 mg/L for irrigation [13,37]. In contrast, almost all the collected water samples have turbidity, ammonium, BOD, and COD values lower than the permissible limits for irrigation [37]. The majority of pH, nitrate, and phosphate values (94.6%, 93.3%, and 88.5%; respectively) measured in the irrigation water samples are within the range of FAO irrigation standards [13]. The current study (as shown in Table 3) revealed the following chemical abundance order of the analyzed ions Cl− > SO42− > HCO3− > NO3− for anions and Na+ > Ca2+ > Mg2+ > K+ for cations. This chemical abundance order is similar to what has been reported for irrigation water assessment in Makkah, KSA [26]. This indicated that the investigated irrigation water samples in Al-Ahsa Oasis had sodium as the dominant cation and chloride as the dominant anion, as also reported in a similar study [54].
Classification of irrigation water samples based on the USSL diagram (Figure 6 and Table 7) indicated that most of the irrigation water resources in Al-Ahsa Oasis were categorized as high to very high salinity hazards (C3, C4) and medium to high sodium hazards (S2, S3). Approximately, 79.7% of the collected irrigation water samples were high to very high salinity and medium to high sodium hazards (C3–S2, C4–S2, C4–S3), whereas only 16.9% of water samples were categorized as very high salinity and very high sodium hazards (C4–S4), and 3.4% were classified as high salinity and low sodium hazards (C3–S1). Higher values of salinity within the study area might result from the extensive exploitation of groundwater, reuse of agricultural drainage, along with a high evaporation rate, as reported in similar studies [26,54,55].
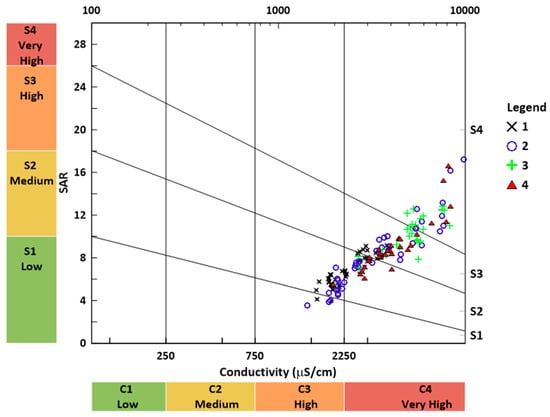
Figure 6.
The US Salinity Laboratory diagram for classification of irrigation water samples (n = 148) collected from Al-Ahsa Oasis, Saudi Arabia (1: TWW, 2: GW, 3: GW + AD, 4: mixed).

Table 7.
Classification of the collected irrigation water samples (n = 148) based on the USSL diagram regarding both salinity hazards (C1–C4) and sodium hazards (S1–S4) [42].
4. Conclusions and Recommendations
Water is essential to the persistence of all life forms. Irrigation water consumes up to 87% of water resources in Saudi Arabia. Supplying irrigation water of good quality and enough quantity is essential to sustain agricultural production and ensure food security. Modern urbanization, industrialization, and agricultural activities have resulted in contamination of the surrounding environment, including water resources. Water scarcity along with soil salinity and sodicity are becoming pressing problems in arid and semiarid areas, including KSA. The main sources of irrigation water in Al-Ahsa Oasis are groundwater wells, mixed with both treated wastewater and agricultural drainage water.
This study emphasized the evaluation of irrigation water quality from various resources in Al-Ahsa Oasis by analyzing the physiochemical characteristics of water, comparing with irrigation water standards, and with the aid of using irrigation water quality indices. The IWQI has been used as a management tool to evaluate water quality and judge its suitability for irrigation purposes. The results concluded that treated wastewater is suitable for irrigation, especially in arid/semiarid areas and is improving soil and plant with nutrients, whereas the reuse of agricultural drainage is not appropriate for irrigation due to the high levels of salinity and related dissolved ions.
The research findings contain a thorough assessment of the existing situation of the quality of irrigation water from various resources, including groundwater wells, treated wastewater, and agricultural drainage, to assist in achieving water conservation and the sustainability of agricultural developments in Al-Ahsa Oasis. The quality of irrigation water is mostly determined by the amount of total dissolved solids, major anions, and cations. The controlled used of treated wastewater in irrigation in Al-Ahsa can overcome water scarcity, reduce soil salinity hazards, improve soil fertility with nutrients (N, P), conserve conventional groundwater for domestic uses, increase vegetation cover (Saudi Green Initiative, SGI), and consequently assist in mitigating the effects of climate change. Finally, this study recommends that specific water management strategies be applied to improve irrigation water quality/quantity and consequently achieve water security:
- Improving the efficiency of sewage treatment plants by introducing advanced technologies such as nanofiltration, activated carbon adsorption, and UV disinfection along with continuous monitoring of their performance.
- Investigating the application of effective treatment and desalination techniques to treat agricultural drainage before reuse.
- Enhancing the coordinated collaboration between the Ministry of Environment, Water and Agriculture (MEWA), Saudi Irrigation Organization (SIO), relevant sectoral authorities, research centers, and universities for the irrigation water quality assessment, mitigation measures, and exchanges of water data.
- Proper monitoring and evaluation program of the available freshwater resources and their suitability for irrigation purposes.
- Applying efficient irrigation and drainage systems to reduce salinity hazards and achieve water security.
- Finally, further research is needed to investigate the consequences benefits/risks of long-term irrigation with renewable treated wastewater on soil fertility and plant productivity.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w15132488/s1, Table S1: Average ± standard deviation of the measured parameters in water samples collected from various irrigation water resources of Al-Ahsa Oasis, KSA (TWW: treated wastewater; GW: groundwater; GW + AD: groundwater mixed with agriculture drainage; Mixed: TWW + GW + AD).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.-S.A.B., R.T.T. and M.S.A.; methodology E.-S.A.B. and M.S.A.; software, E.-S.A.B. and R.T.T.; validation, E.-S.A.B. and R.T.T.; formal analysis, E.-S.A.B. and M.S.A.; investigation, E.-S.A.B. and M.S.A.; resources, E.-S.A.B. and R.T.T.; data curation, E.-S.A.B. and M.S.A.; writing—original draft preparation, E.-S.A.B.; writing—review and editing, E.-S.A.B. and R.T.T.; visualization, E.-S.A.B., R.T.T. and M.S.A.; supervision, E.-S.A.B.; project administration, E.-S.A.B.; funding acquisition, E.-S.A.B. and R.T.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research, King Faisal University, annual research grant number 180038.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the help of the Saudi Irrigation Organization (SIO) and agricultural farmers in Al-Ahsa Oasis in providing access to irrigation water samples. The authors are thankful to the Deanship of Scientific Research, KFU for funding the research. The authors appreciate the reviewers’ anonymous feedback.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Karakus, C.; Yıldız, S. Evaluation for Irrigation Water Purposes of Groundwater Quality in the Vicinity of Sivas City Centre (Turkey) by Using Gis and an Irrigation Water Quality Index. Irrig. Drain. 2020, 69, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, A.G.; Aly, A.A.; Aldhumri, S.A.; Al-Barakaha, F.N. Hydrochemical and Quality Assessment of Groundwater Resources in Al-Madinah City, Western Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batarseh, M.; Imreizeeq, E.; Tilev, S.; Al Alaween, M.; Suleiman, W.; Al Remeithi, A.M.; Al Tamimi, M.K.; Al Alawneh, M. Assessment of groundwater quality for irrigation in the arid regions using irrigation water quality index (IWQI) and GIS-Zoning maps: Case study from Abu Dhabi Emirate, UAE. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 14, 100611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robins, N.S. Groundwater quality in Scotland: Major ion chemistry of the key groundwater bodies. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 294, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badr, E.-S.A.; Al-Naeem, A.A. Assessment of Drinking Water Purification Plant Efficiency in Al-Hassa, Eastern Region of Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chojnacka, K.; Witek-Krowiak, A.; Moustakas, K.; Skrzypczak, D.; Mikula, K.; Loizidou, M. A transition from conventional irrigation to fertigation with reclaimed wastewater: Prospects and challenges. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 130, 109959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabdula’aly, A.I.; Al-Rehaili, A.M.; Al-Zarah, A.I.; Khan, M.A. Assessment of nitrate concentration in groundwater in Saudi Arabia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 161, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Omran, A.M.; Falatah, A.M.; Matrud, S.S. Evaluation of irrigation well water quality in Riyadh region, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. J. King Abdulaziz Univ. Meteorol. Environ. Arid Land Agric. Sci. 2005, 16, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Naeem, A.A.; Al-Barrak, K.M. Assessment and evaluation of hydro-chemical and elemental analysis for Ain Al-Khadoud, Al-Hassa Oasis, Eastern Province, Saudi Arabia. J. Soil Sci. Agric. Eng. Mansoura Univ. 2010, 1, 815–826. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.Z.; Ding, Z.Y.; Wei, G.X.; Zhao, H.; Huang, T.M. Sources of water pollution and evolution of water quality in the Wuwei basin of Shiyang river, Northwest China. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 1168–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Omran, A.M.; El Maghraby, S.E.; Nadeem, M.E.A.; El Eter, A.M.; Al Mohani, H. Long term effect of irrigation with the treated sewage effluent on some soil properties of Al-Hassa Governorate, Saudi Arabia. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2012, 11, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldız, S.; Karakuş, C.B. Estimation of irrigation water quality index with development of an optimum model: A case study. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 22, 4771–4786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, R.S.; Westcot, D.W. Water Quality for Agriculture; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1994; p. 174. [Google Scholar]
- Ghanim, A. Water-Resources-Crisis-in-Saudi-Arabia-Challenges-and-Possible-Management-Options-An-Analytic-Review. Int. J. Environ. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 13, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, G.; Alquwaizany, A.; Al-Zarah, A. Guidelines for Irrigation Water Quality and Water Management in The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia: An Overview. J. Appl. Sci. 2010, 10, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Naeem, A.A. Monitoring of Groundwater Salinity for Water Resources Management in Irrigated Areas of Al-Jouf Region, Saudi Arabia. Res. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 9, 256–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Garni, H.M.; Al Omran, A.M. Determination and evaluation of chemical compostion of sewage treated water in Riyadh Main Plant for irrigation. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2009, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Hashem, M.S.; Qi, X. Treated Wastewater Irrigation—A Review. Water 2021, 13, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.F.; Alvarenga, P.; Gando-Ferreira, L.M.; Quina, M.J. Urban Wastewater as a Source of Reclaimed Water for Irrigation: Barriers and Future Possibilities. Environments 2023, 10, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saikhan, M.S.; Badr, E.A.; Babeker, M.Y. Study of Sewage Sludge Use for the Cultivation of Plants and its Effects on Soil Properties in Al Ahsa. Sci. J. King Faisal Univ. 2020, 21, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Lyu, S.; Weiling, Z.; Lili, Y.; Wentao, J. Ecological risks and sustainable utilization of reclaimed water and wastewater irrigation. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakir, E.; Zahraw, Z.; Al-Obaidy, A.H.M.J. Environmental and health risks associated with reuse of wastewater for irrigation. Egypt. J. Pet. 2017, 26, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drechsel, P.; Scott, C.A.; Raschid-Sally, L.; Redwood, M.; Bahri, A. Wastewater Irrigation and Health: Assessing and Mitigating Risk in Low-Income Countries; Routledge: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Falatah, A.M.; Al Omron, A.M.; Nadeem, M.E.A.; Mursi, M.M. Chemical composition of irrigation groundwater used in some agricultural regions of Saudi Arabia. Emir. J. Agric. Sci. 1999, 11, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Drechsel, P.; Qadir, M.; Galibourg, D. The WHO Guidelines for Safe Wastewater Use in Agriculture: A Review of Implementation Challenges and Possible Solutions in the Global South. Water 2022, 14, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Osta, M.; Masoud, M.; Alqarawy, A.; Elsayed, S.; Gad, M. Groundwater Suitability for Drinking and Irrigation Using Water Quality Indices and Multivariate Modeling in Makkah Al-Mukarramah Province, Saudi Arabia. Water 2022, 14, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Gossaibi, A.M.; Almadini, A.M. The assessment of irrigation water quality and its agricultural uses at Al-Hassa Oasis, KSA. Sci. J. King Faisal Univ. Basic Appl. Sci. 2000, 1, 87–102. [Google Scholar]
- Almadini, A.M.; Al-Safarjalani, A.M.; Al-Naeem, A.A. Spatial variations in chemical properties of irrigation groundwater at Al-Hassa Oasis, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Arab Gluf J. Sci. Res. 2007, 25, 207–218. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, G.; Sadiq, M. Metal chemistry of irrigation and drainage waters of Al-Ahsa Oasis of Saudi Arabia and its effects on soil properties. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1991, 57, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.T. Water quality for irrigation and drinking water use of Aflaj in Oman. Water Supply 2014, 15, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.I.H.; Hassaballa, A.A.; Almadini, A.M.; Daffalla, S. Analyzing the Spatial Correspondence between Different Date Fruit Cultivars and Farms’ Cultivated Areas, Case Study: Al-Ahsa Oasis, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5728. [Google Scholar]
- Almuhanna, E.A. Atmospheric aerosol characterization and element composition at Al-Ahsa Oasis of Saudi Arabia. Sci. J. King Faisal Univ. Basic Appl. Sci. 2017, 18, 35–74. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, V.D. Water and Wastewater Examination Manual; Lewis Publishers: Chelsea, MI, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Waters and Wastewaters, 20th ed.; Franson, M.A.H., Eaton, A.D., Clesceri, L.S., Greenberg, A.E., Eds.; American Public Health Association (APHA): Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hanrahan, G.; Gardolinski, P.; Gledhill, M.; Worsfold, P. Environmental monitoring of nutrients. In Environmental Monitoring Handbook; Burden, F.R., Mckelvie, I.D., Forstner, U., Guenther, A., Eds.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 8.1–8.16. [Google Scholar]
- Aly, A.A.; Al Omran, A.M.; Alharby, M.M. The water quality index and hydrochemical characterization of groundwater resources in Hafar Albatin, Saudi Arabia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2015, 8, 4177–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MEWA. Standards and Specifications for Water Types; according to the water law and its implementing regulations; Ministry of Environment, Water and Agriculture (MEWA): Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 2021.
- Al-Hawas, I.A. Irrigation Water Quality Evaluation of Al-Hassa Springs and its Predictive Effects on Soil Properties. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2002, 5, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, M.; Shahid, S.A.; Heng, L. Irrigation Water Quality. In Guideline for Salinity Assessment, Mitigation and Adaptation Using Nuclear and Related Techniques; Zaman, M., Shahid, S.A., Heng, L., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 113–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, S.; Hussein, H.; Moghanm, F.S.; Khedher, K.M.; Eid, E.M.; Gad, M. Application of Irrigation Water Quality Indices and Multivariate Statistical Techniques for Surface Water Quality Assessments in the Northern Nile Delta, Egypt. Water 2020, 12, 3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasnia, A.; Radfard, M.; Mahvi, A.H.; Nabizadeh, R.; Yousefi, M.; Soleimani, H.; Alimohammadi, M. Groundwater quality assessment for irrigation purposes based on irrigation water quality index and its zoning with GIS in the villages of Chabahar, Sistan and Baluchistan, Iran. Data Brief 2018, 19, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, L.A. Diagnosis and Improvement of Saline and Alkali Soils; United States Department of Agriculture (USDA): Washington, DC, USA, 1954; Volume 60.
- Kelly, W.P. Adsorbed Sodium, cation exchange capacity and percentage sodium adsorption in alkali soils. Science 1957, 84, 473–477. [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox, L.V. Classification and Use of Irrigation Waters; United States Department of Agriculture (USDA): Washington, DC, USA, 1955; Volume 969.
- Doneen, L.D. Water Quality for Agriculture; Department of Irrigation, University of California: California, CA, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Paliwal, K.V. Irrigation with Saline Water; Water Technology Centre, Indian Agricultural Research Institute: New Delhi, India, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.; Ghosh, N.C.; Gurjar, S.; Krishan, G.; Kumar, S.; Berwal, P. Index-based assessment of suitability of water quality for irrigation purpose under Indian conditions. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meireles, A.; Andrade, E.; Chaves, L.C.; Frischkorn, H.; Crisóstomo, L. A new proposal of the classification of irrigation water. Rev. Ciência Agronômica 2010, 41, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedi, S. Modification of expected conflicts between Drinking Water Quality Index and Irrigation Water Quality Index in water quality ranking of shared extraction wells using Multi Criteria Decision Making techniques. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 83, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, F.K.; Mogren, S.; Mukhopadhyay, M.; Ibrahim, E. Evaluation of groundwater chemistry and its impact on drinking and irrigation water quality in the eastern part of the Central Arabian graben and trough system, Saudi Arabia. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2016, 120, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality, 4th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Badr, E.A. Spatio-temporal variability of dissolved organic nitrogen (DON), carbon (DOC), and nutrients in the Nile River, Egypt. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badr, E.A.; El-Sonbati, M.A.; Nassef, H.M. Water Quality Assessment in the Nile River, Damietta Branch, Egypt. Int. J. Environ. Sci. CATRINA 2013, 8, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar Aly, A.A. Mohamed Alwabel, Abdullah Almahaini, Mohammed Alamari. Hydrochemical and quality of water resources in Saudi Arabia groundwater: A comparative study of Riyadh and Al-Ahsa regions. Proc. Int. Acad. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2013, 3, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Al Omran, A.M. Long term effect of irrigation with the treated sewage effluent on some soil properties for date palms in Al-Hassa, Saudi Arabia. In Proceedings of the 19th Conference on Soil Science, Brisbane, Australia, 1–6 August 2010. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).