Abstract
In recent years, due to the production and use of per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFASs), the research on the pollution characteristics and sources of PFASs in surface water and precipitation in China has attracted increasing attention. In this study, the related published articles with sampling years from 2010 to 2020 were reviewed, and the concentration levels, composition characteristics and possible sources of PFASs in surface water (rivers and lakes) and precipitation in China were summarized, including those in the Tibetan Plateau region. The results show that the concentrations of PFASs in surface water in different areas of China vary greatly, ranging from 0.775 to 1.06 × 106 ng/L. The production processes of fluorinated manufacturing facilities (FMFs) and sewage discharge from wastewater treatment plants (WWTPS) were the main sources of PFASs in surface water in China, and the concentrations of PFASs in water flowing through cities with high urbanization increased significantly compared with those before water flowed through cities with high urbanization. The compositions of PFASs in surface water gradually changed from long-chain PFASs, such as per-fluoro-octanoic acid (PFOA) and per-fluoro-octanesulfonic acid (PFOS) to short-chain PFASs, such as per-fluorobutanoic acid (PFBA), per-fluorobutanesulfonic acid (PFBS), perfluorohexanoic acid (PFHxA) and per-fluoropentanoic acid (PFPeA). The concentrations of PFASs in precipitation in China ranged from 4.2 to 191 ng/L, which were lower than those of surface water. The precipitation concentrations were relatively high around a fluorination factory and in areas with high urbanization levels. PFASs were detected in the surface water and precipitation in the Tibetan Plateau (TP), which is the global “roof of the world”, but the concentrations were low (0.115–6.34 ng/L and 0.115–1.24 ng/L, respectively). Local human activities and surface runoff were the main sources of PFASs in the surface water of the Tibetan Plateau. In addition, under the influence of the Southeast Asian monsoon in summers, marine aerosols from the Indian Ocean and air pollutants from human activities in Southeast Asia and South Asia will also enter the water bodies through dry and wet depositions. With the melting of glaciers caused by global warming, the concentration of PFASs in the surface water of the TP was higher than that before the melting of glaciers flowed into the surface water of the TP. Generally, this study summarized the existing research progress of PFAS studies on surface water and precipitation in China and identified the research gaps, which deepened the researchers’ understanding of this field and provided scientific support for related research in the future. The concentrations of PFASs in the water bodies after flowing through FMFs were significantly higher than those before water flowed through FMFs, so the discharge of the FMF production process was one of the main sources of PFASs in surface water.
1. Introduction
Per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) refer to a class of compounds in which all or part of the hydrogen atoms linked to carbon atoms in alkane molecules are replaced by fluorine atoms [1]. Because of the strong polarity of the C-F bond, PFASs have more stable and more excellent properties than other hydrocarbons (such as a remarkably high chemical stability and excellent hydrophobicity and oleophobicity), so they have been used in various fields of production, such as plastic wrap, paper, coatings, poly-tetrafluoroethylene products and foam fire-extinguishing agents [2]. According to different functional groups and physicochemical properties, PFASs can be divided into (1) ionic PFASs (i-PFASs), such as per-fluoroalkyl carboxylic acids (PFCAs) and per-fluoroalkane sulfonic acids (PFSAs), and (2) neutral PFASs (n-PFASs), such as fluorotelomer alcohols (FTOHs) and per-fluoro-octane sulfo-namidoethanols (FOSEs) [3]. The PFASs referred to in this paper are i-PFASs. Due to the mass production and use of some PFASs, PFASs have been widely detected in various environmental media, animals and plants in recent years [4,5,6], and have also been found in the human body [7,8]. With intensive studies, the persistence, bioaccumulation, long-distance transportation and biohazard of some long-chain PFASs (long-chain PFASs refer to PFCAs with seven or more perfluorinated carbons and PFSAs with six or more perfluorinated carbons) have been gradually confirmed [9]. Subsequently, some countries and organizations have successively issued series of rules and regulations to restrict the use of such substances [10], and PFOS, PFOA and their salts were listed under Annex B and Annex A of the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants in 2009 and 2019, respectively [11,12]. Meanwhile, in 2019, the Persistent Organic Pollutants Review Committee (POPRC) recommended that per-fluorohexane sulfonate acid (PFHxS) and its salts be listed in Annex A of the Convention [13]. In addition, at the 17th meeting of the POPRC, held in January 2022, it was suggested that long-chain PFCA (involving carbon-chain lengths from 9 to 21), its salts and related compounds should be listed in Annexes A, B and/or C of the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants [14]. With the restricted use of PFOS, PFOA (Table S2) and other substances, some short-chain per-fluoroalkyl acids and new polyfluoride substitutes [such as 6:2 chlorinated polyfluorinated ether sulphonic acid (F-53B)] are becoming research focuses [15,16]. The international community is paying increasing attention to PFASs.
Since 2000, some major manufacturers have phased out the production of PFOS, PFOA and their salts [17]. The production of these substances has gradually shifted from developed countries, such as North America and Europe, to developing countries, especially China [18]. China has become the largest manufacturer and supplier of PFOS and PFOA in the world since 2004 [3]. Some studies have estimated the emissions of PFOA and its salts in China from 2004 to 2012. The results show that the cumulative emissions reached 250 tons, and China became the largest PFOA emission site at that time [19]. Therefore, the environmental monitoring of and risk research on PFASs in China have attracted international attention. Studies have shown that PFASs can exist stably in water environments [20], and the ocean is the final sink for PFASs [21]. Therefore, it is necessary to explore the pollution characteristics and possible sources of PFASs in China’s waters. Most of the related studies have been carried out for a single water body [22,23], but there were a few comprehensive literature reviews. In this study, the related published articles with sampling years from 2010 to 2020 were reviewed, and the concentration levels, composition characteristics and possible sources of PFASs in surface water (rivers and lakes) and precipitation in China were summarized (Table S1 shows the PFASs involved in the paper). The research area also covered the Tibetan Plateau. The purpose is to summarize the existing research progress, identify the existing research gaps and provide scientific support for future research in this field.
2. PFASs in Surface Water
This study summarized the concentration data from monitoring studies of PFASs in surface water in China over the past 10 years, as shown in Figure 1 and Table 1 for details. It was revealed that the concentrations of PFASs in surface water varied greatly in different areas in China (from 0.775 to 1.06 × 106 ng/L). The average concentrations in the Daling River, tested in 2018, and Xiaoqing River, tested in 2013, were highest (2.31 × 103 ng/L and 2.14 × 103 ng/L, respectively) [24,25], followed by that in the Daling River in 2011 (1.04 × 103 ng/L) [26]. The concentrations in other rivers were relatively low. It was found that the concentrations and composition characteristics of PFASs were mainly related to the emissions of fluorinated manufacturing facilities (FMFs), wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) and urbanization development. The concentrations of PFASs in the water bodies after they flowed through FMFs were significantly higher than those before they flowed through FMFs, so the discharge from the FMF production process was one of the main sources of PFASs in surface water. For example, the concentration of PFASs in the Daling River flowing through the Fluorochemical Industrial Zone in Fuxin City was significantly higher than the concentration in other watersheds by an order of magnitude. With the development of the fluorochemical industry, the PFASs from manufacturing processes caused more pollution to enter the Daling River, and the concentrations detected in 2018 increased by 50% compared to 2011 [25,26]. Liaohe River was also affected by the Fluorochemical Industrial Zone in Fuxin City with the maximum concentration of 781 ng/L [27]. Similarly, Xiaoqing River was influenced by FMFs, such as metallurgy, electronics, and firefighting, with the maximum concentration of 1.06 × 106 ng/L detected in 2013 [24]. The north of Taihu Lake was close to FMFs, such as the manufacturing of paint and plastic products, with concentrations of 56.1–120 ng/L, while concentrations in other parts of the study area ranged from 10.0 to 79.4 ng/L [28]. The concentration in Guanlan River during the abundant water period was six times higher than that in the dry water period, probably due to the large amount of surface runoff and rainwater flushing during the abundant water period that carried pollutants from the periphery of the industrial area into the water body [29]. East China was also a concentrated area for FMFs, and the PFAS concentration in Huangpu River flowing through this region increased (from about 300 to 380 ng/L) [30]. Moreover, the variation tendencies of PFAS concentrations in different water bodies were also different; for example, the concentration of PFASs in the Daling River increased from 2011 (average of 1.04 × 103 ng/L [26]) to 2018 (average of 2.31 × 103 ng/L [25]), and that in Xiaoqing River decreased from 2013 (average of 2.14 × 103 ng/L) [24] to 2014 (average of 457 ng/L) [31].
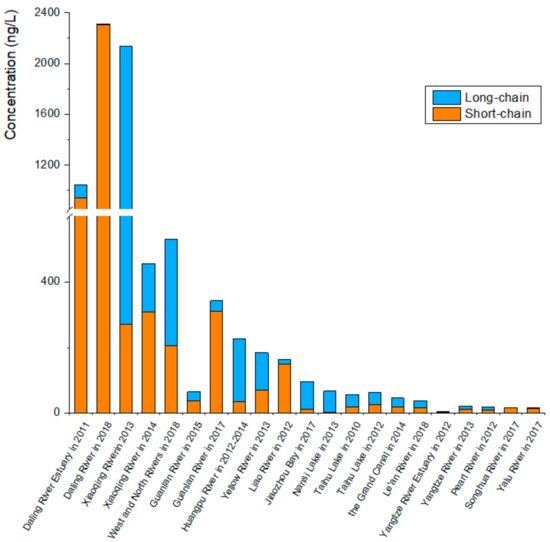
Figure 1.
Levels and compositions in surface water in China in past ten years.

Table 1.
PFAS concentrations in surface water in China in past ten years.
In addition, the concentrations of PFASs in the water bodies after flowing through WWTPs were obviously higher than those before the water flowed through WWTPs, so the sewage discharge of WWTPs was another main source of PFASs in surface water. For example, after flowing through WWTPs, the concentration of PFASs in Huangpu River, mentioned above, rose from ~200 to ~250 ng/L [30]. The peak concentration of the Yongding River occurred at 108 ng/L downstream of the WWTP in its watershed and 12.4 ng/L upstream [32]. Due to the sewage discharged by WWTPs entering into the north of Dianchi Lake directly, concentrations in the north (35.8–135.9 ng/L) were higher than those in the south (less than 25 ng/L) [33]. It was found that the concentrations of PFASs in water flowing through cities with high degrees of urbanization had significant rises because of traffic, commercial activities and so on. For example, the West and North Rivers flow through the cities of Shaoguan, Heze and Qingyuan, and rapid urban development had a remarkable impact on the PFASs in the water bodies with the concentrations up to 1.06 × 103 ng/L [34]. Yanghe River (one of the tributaries of the Yongding River) ran through the highly urbanized city of Zhangjiakou with a high concentration of 197 ng/L, and Sangan River, another tributary of the Yongding River, ran through less densely populated and less urbanized areas with relatively smaller concentrations ranging from 6.67 to 9.74 ng/L [32]. Likewise, the Songhua River and the Yalu River, which were relatively less densely populated, also had relatively low concentrations of PFASs, with a maximum of only 32 ng/L [35].
In the past, long-chain PFASs made the greatest contributions, especially PFOA and PFOS. In recent years, short-chain PFASs have gradually become the main compounds in water pollution, such as PFBA, PFBS, PFHxA and PFPeA. For instance, in the Daling River, the proportions of PFBS (35.9% in 2011 and 48% in 2018) and PFBA (32.8% in 2011 and 41% in 2018) have gradually increased [25,26]. On the contrary, PFOA (17.5% in 2011 and 2.3% in 2018) showed a decreasing trend [25,26]. In the main stem of the Pearl River, PFBS contributed 36% while PFOS contributed 21% [36], and the same phenomenon was found in the tributaries of the Pearl River (52% PFBA and 25% PFOA) [34]. Similarly, PFHxA accounted for 46% in spring and 53% in summer for PFPeA, with short-chain PFASs predominating in the Jiulongjiang estuary [37].
3. PFASs in Precipitation
The monitoring results of studies of PFASs in precipitation in China over the past 10 years were summarized as shown in Table 2. The monitored concentrations of PFASs in precipitation from the available studies in China, except for TFA (trifluoroacetic acid), ranged from 4.2 to 191 ng/L, which were higher than those in precipitation from developed countries, such as Germany (1.6–48.6 ng/L) [48], Japan (8.16–37.2 ng/L) [49] and France (2.59–3.76 ng/L) [50] during the same period, but lower than the concentrations in the United States (50–850 ng/L) [51].

Table 2.
PFAS concentrations in precipitation in past ten years.
The PFAS concentrations in precipitation were generally lower than those in surface water in the same area. The average concentration in precipitation in Jiaozhou Bay was 22.0 ng/L [45], which was lower than that in surface water (60.5 ng/L) [45]. In the Nanchang section of Yangtze River, the average PFAS concentration in precipitation was 9.2 ng/L [52], which was lower than that in surface water (44.6 ng/L) [46]. Similarly, in the Xiamen section of Jiulong River, the average precipitation concentration of PFASs (22.0 ng/L) [52] was lower than that of surface water (38.2 ng/L) [37].
PFAS precipitation concentrations tended to be higher in areas with concentrated distribution of FMFs. High PFAS concentrations (80.6 ng/L) were found in urban areas in Northeast China (such as Fuxin, Dalian and Harbin) with a high distribution of FMFs [52]. Similarly, the PFAS precipitation concentration in Tianjin was also high (63.1 ng/L) [53]. Moreover, higher precipitation concentrations were found in inland and coastal cities with higher urbanization levels. The average concentration was 84.8 ng/L in more urbanized inland cities, such as Zhengzhou and Chengdu, with high traffic volumes and commercial activities [52]. In coastal cities, such as Shantou, Xiamen and Weifang, the average concentration of PFASs in precipitation reached 182 ng/L [53]. Ship maintenance in the port contributed greatly to PFAS pollution.
A precipitation monitoring study conducted by Chen et al. [52] in 28 cities in China found that TFA contributed the largest proportion, accounting for 78.1%, followed by PFOA, PFBA and PFOS, accounting for 5.08%, 3.16% and 3.12%, respectively. The proportions of short-chain PFASs (C4–C7) and long-chain PFASs (≥C8) were almost the same [52]. Han et al. [45] found that PFOA occupied 61.2% of the precipitation monitored in Jiaozhou Bay, followed by PFOS and PFHxA with 9.20% and 8.21%, respectively, and long-chain PFASs represented the largest proportion (87.3%).
4. PFASs in the Tibetan Plateau (TP)
Compared to the above studies, concentrations of PFASs in surface waters (including rivers and meltwater runoff) in the TP were relatively low (0.115–6.34 ng/L) as shown in Table 3. The hydrographic network in the Tibetan Plateau area were shown in Figure 2. A monitoring study of river water on the eastern edge of the TP found that pollutants in the upstream area entered the river water directly with snow melt, with the PFAS concentration at about 2 ng/L [54]. The midstream area was located in a high-altitude area with no surrounding inhabitants, and the highest PFAS concentration was 1.12 ng/L. The downstream area was densely populated, and the river water was greatly affected by the direct discharge of domestic garbage and sewage into the river, with the concentration of PFASs at about 1.8 ng/L [54]. Chen et al. [55] studied runoff from Nam Co Lake and its surroundings in the TP and found that PFAS concentrations in glacial runoff (0.892–1.94 ng/L) were generally higher than those in non-glacial runoff (0.443–1.12 ng/L), and the average PFAS concentration was generally higher in the southern part of Nam Co Lake (1.28 ng/L) than in the northern part (0.901 ng/L). There is more glacial runoff in the south of Nam Co Lake. Under the trend of global warming, glacial meltwater in the south flows into the lake along with the runoff, which makes PFAS-enriched glaciers release PFASs into the lake, raising the PFAS concentration of Nam Co Lake in the south. In terms of components, PFBA and PFOS were the major pollutants in lake water, with concentrations accounting for 19% and 17%, respectively. The proportion of PFBA was significantly higher in glacial runoff (61%) than in non-glacial runoff (10%). PFPeA was widely present in both glacial runoff (14%) and non-glacial runoff (23%) [55].

Table 3.
PFAS concentrations in surface water and precipitation in TP in past ten years.
Figure 2.
The hydrographic network in the Tibetan Plateau area.
In addition to pollution from local human activities and surface runoff, dry and wet depositions of atmospheric pollutants were also two of the main sources of PFASs in the water bodies of the TP. Influenced by the East Asian monsoon (from the east and southeast) and the Indian monsoon (from the south), PFAS pollutants in the atmosphere of the TP were increased [56]. It had been suggested that PFASs found in the waters of pristine areas in the eastern and central TP were greatly under the influence of the Southeast Asian monsoon in summers. Marine aerosols transported over long distances from the Indian Ocean and atmospheric pollutants from anthropogenic activities in Southeast and South Asia entered the water bodies through long-distance transportation and dry and wet depositions [55].
PFASs were also detected in precipitation in the TP, but at low concentrations (0.212–1.24 ng/L), with a 100-fold difference (0.212–190 ng/L) compared to precipitation concentrations from other regions. The average precipitation concentration of the Nam Co basin (0.616 ng/L) was higher than that of other areas of the TP (Motuo, Lulang, Lhasa and Muztagh Ata; 0.367 ng/L) [55,57]. The composition of PFASs in TP precipitation was similar to that of surface water with the main compounds PFOA and PFBA. Long- and short-chain PFASs in the Nam Co basin accounted for half of each, while short-chain PFASs were predominant in other regions of the TP (66%) [55]. One of the main sources of PFASs in precipitation in the TP may be atmospheric long-distance transportations from Northeast India, Southern Nepal and Northern Pakistan. Moreover, local emissions of PFAS-related manufacturing and the degradation of PFAS precursors in Eastern China also contributed to PFAS contaminations in precipitation [57].
5. Conclusions
The research on PFASs in surface water and precipitation in China has attracted in-creasing attention. Generally, the concentrations of PFASs in the surface water in different areas of China varied greatly, ranging from 0.775 ng/L in the West and North Rivers in 2018 to 1.06 × 106 ng/L in the Daling River in 2013. With the production and consumption of long-chain PFASs gradually changing to short-chain PFASs, the pollutant composition of PFASs in China’s surface water also gradually changed from long-chain PFASs (such as PFOS and PFOA) to short-chain PFASs (such as PFBA, PFBS and PFPeA). The emissions from FMFs and WWTPS were considered the main sources of PFASs in China’s surface water. It was also found that the concentrations of PFASs in water flowing through cities with high degrees of urbanization had significant rises. The concentration of PFASs in precipitation in China was lower than that in surface water, ranging from 4.2 ng/L in Jiaozhou Bay in 2017 to 191 ng/L in Weifang–Linqu County in 2016. PFAS concentrations were relatively high in precipitation around a fluorination plant and in areas with high urbanization levels. The release of PFASs from factories and human activities were assumed to be the main sources of PFASs in precipitation. Compared with other areas, the concentrations of PFASs in surface water and precipitation in the Tibetan Plateau were lower (0.115–6.34 ng/L and 0.115–1.24 ng/L, respectively). In addition to the emissions from local human activities, PFASs in the surface water of the Tibetan Plateau came from the inflow of surface runoff and dry and wet depositions of PFASs in the atmosphere. Under the general trend of global warming, the accelerated melting of glaciers will lead to further increases in PFAS concentrations. Moreover, influenced by the southeast monsoon in summers, PFASs can reach the Tibetan Plateau through long-distance transportation and finally enter the surface water of this area through depositions.
We find that there is a lack of continuous PFAS-monitoring research based on the PFASs in the same water body, and the research on novel PFAS substances (such as PFECAs and PFESAs) and their substitutes (such as HFPO-DA, ADONA and F-53B) in surface water is relatively limited. In addition, the research on PFASs in Tibetan Plateau surface water environments is extremely insufficient and needs further development. Overall, this study can supply researchers with a deeper understanding of the PFAS research progress on China’s surface water and precipitation and provide scientific support for researchers to further grasp the research direction in this field.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w14050812/s1, Table S1. Compound list of PFASs in the text. Table S2. Published administrative guidelines for PFOA and PFOS in water. References [34,58,59] are cited in the Supplementary Materials.
Author Contributions
F.W.: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, writing—original draft, validation; Y.Z.: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, writing—original draft; B.D.: conceptualization, methodology, investigation; J.W.: conceptualization, methodology, supervision, writing—reviewing and editing, project administration, validation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Second Tibetan Plateau Scientific Expedition and Research Program (STEP, grant no. 2019QZKK0103) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, grant no. 21976053).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank all individuals involved in this work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Cui, Q.; Shen, N.; Yeung, L.W.Y.; Sun, Y.; Guo, Y.; Dai, J. Worldwide Distribution of Novel Perfluoroether Carboxylic and Sulfonic Acids in Surface Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 7621–7629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, J.M.; Guo, Y.; Zeng, L.; Liu, L.Y.; Lu, X.; Wang, F.; Zeng, E.Y. Global distribution of perfluorochemicals (PFCs) in potential human exposure source—A review. Environ. Int. 2017, 108, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Ruan, Y.; Lin, H.; Lam, P. Review on perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in the Chinese atmospheric environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 139804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Yao, Y.; Chang, S.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Yuan, X.; Wu, F.; Sun, H. Occurrence and Phase Distribution of Neutral and Ionizable Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in the Atmosphere and Plant Leaves around Landfills: A Case Study in Tianjin, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Sheng, N.; Wang, J.; Guo, Y.; Dai, J. Occurrence and Tissue Distribution of Novel Perfluoroether Carboxylic and Sulfonic Acids and Legacy Per/Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Black-Spotted Frog (Pelophylax nigromaculatus). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 982–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wang, C.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Khan, K.; Song, S.; Wang, P.; Wang, C. Occurrence, sources and health risk of polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in soil, water and sediment from a drinking water source area. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 174, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worley, R.R.; Moore, S.M.; Tierney, B.C.; Ye, X.; Calafat, A.M.; Campbell, S.; Woudneh, M.B.; Fisher, J. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in human serum and urine samples from a residentially exposed community. Environ. Int. 2017, 106, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Zhu, J.; Chen, Z.; Hong, Y.; Cai, Z. Occurrence and Partitioning of Bisphenol Analogues in Adults’ Blood from China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 812–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cousins, I.T.; Scheringer, M.; Hungerbuehler, K. Hazard assessment of fluorinated alternatives to long-chain perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs) and their precursors: Status quo, ongoing challenges and possible solutions. Environ. Int. 2015, 75, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockholm Convention. Available online: http://www.pops.int/TheConvention/POPsReviewCommittee/Meetings/POPRC3/POPRC3documents/tabid/77/Default.aspx (accessed on 1 March 2022).
- USEPA. Drinking Water Contaminant Candidate List 3 (CCL3)—Final. Fed. Regist. 2009, 74, 51850–51862. [Google Scholar]
- Stockholm Convention. Available online: http://www.pops.int/TheConvention/POPsReviewCommittee/Meetings/POPRC13/Overview/tabid/5965/Default.aspx (accessed on 1 March 2022).
- Stockholm Convention. Available online: http://www.pops.int/TheConvention/POPsReviewCommittee/Meetings/POPRC15/Overview/tabid/8052/Default.aspx (accessed on 1 March 2022).
- Stockholm Convention. Available online: http://www.pops.int/TheConvention/POPsReviewCommittee/Meetings/POPRC17/Overview/tabid/8900/Default.aspx (accessed on 1 March 2022).
- Chen, F.; Yin, S.; Kelly, B.; Liu, W. Isomer-specific transplacental transfer of perfluoroalkyl acids: Results from a survey of paired maternal, cord sera, and placentas. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 5756–5776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Lee, H.K.; Lim, J.E.; Moon, H.B. Legacy and emerging per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in the coastal environment of Korea: Occurrence, spatial distribution, and bioaccumulation potential. Chemosphere 2020, 251, 126633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buck, R.; Franklin, J.; Berger, U.; Conder, J.; Cousins, I.; De Voogt, P.; Jensen, A.; Kannan, K.; Mabury, S.; Van Leeuwen, S. Perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the environment: Terminology, classification, and origins. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2011, 7, 513–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Geng, J.; Wang, T.; Shi, Y.; Hu, W.; Li, J. A review of spatial and temporal assessment of PFOS and PFOA contamination in China. Chem. Ecol. 2009, 25, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhai, Z.; Liu, J.; Hu, J. Estimating industrial and domestic environmental releases of perfluorooctanoic acid and its salts in China from 2004 to 2012. Chemosphere 2015, 129, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remucal, C.K. Spatial and temporal variability of perfluoroalkyl substances in the Laurentian Great Lakes. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2019, 21, 1816–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prevedouros, K.; Cousins, I.; Buck, R.; Korzeniowski, S. Sources, fate and transport of perfluorocarboxylates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.; Ding, G.; Zhang, J.; Wei, L.; Xue, H.; Zhang, N.; Li, Y.; Chen, G.; Sun, Y. Occurrence and distribution of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in surface water and bottom water of the Shuangtaizi Estuary, China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 216, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Cheng, X.; Hua, X.; Jiang, B.; Tian, C.; Tang, J.; Li, Q.; Sun, H.; Lin, T.; Liao, Y.; et al. Emerging and legacy per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in water, sediment, and air of the Bohai Sea and its surrounding rivers. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Lu, Y.; Wang, T.; Meng, J.; Li, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Wang, R.; Giesy, J.P. Shifts in production of perfluoroalkyl acids affect emissions and concentrations in the environment of the Xiaoqing River Basin, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 307, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Liu, J.; Bao, K.; Chen, N.; Meng, B. Multicompartment occurrence and partitioning of alternative and legacy per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in an impacted river in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 138753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Lu, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhu, Z.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Giesy, J.P. Transport of short-chain perfluoroalkyl acids from concentrated fluoropolymer facilities to the Daling River estuary, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 9626–9636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Zhu, L.; Pan, X.; Fang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L. Isomeric specific partitioning behaviors of perfluoroalkyl substances in water dissolved phase, suspended particulate matters and sediments in Liao River Basin and Taihu Lake, China. Water Res. 2015, 80, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Du, P.; Liu, S.; Lv, J.; Xu, F.; Meng, W.; Xu, J. Distribution, source characterization and inventory of perfluoroalkyl substances in Taihu Lake, China. Chemosphere 2015, 127, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Liang, X.; Zhan, B.; Wu, J.; Gao, Y.; Xu, N. Pollution Characteristics and Ecological Risk of Perfluorinated Compounds in a Rapidly Urbanizing Catchment. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Pekin. 2019, 55, 543–552. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Zhang, C.; Yan, H.; Han, C.; Chen, L.; Meng, X.; Zhou, Q. Spatiotemporal distribution and potential sources of perfluoroalkyl acids in Huangpu River, Shanghai, China. Chemosphere 2017, 174, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Vestergren, R.; Xu, L.; Song, X.; Niu, X.; Zhang, C.; Cai, Y. Characterizing direct emissions of perfluoroalkyl substances from ongoing fluoropolymer production sources: A spatial trend study of Xiaoqing River, China. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 206, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, S.; Chen, S.; Wang, T. Increasing perfluoroalkyl substances and ecological process from the Yongding Watershed to the Guanting Reservoir in the Olympic host cities, China. Environ. Int. 2019, 133, 105224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Meng, W.; Guo, C.; Xu, J.; Yu, T.; Fan, W.; Li, L. Determination and partitioning behavior of perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acids and perfluorooctanesulfonate in water and sediment from Dianchi Lake, China. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 1292–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Y.; Hu, L.; Li, B.; Li, C.; Ying, G. Legacy and alternative per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in the West River and North River, south China: Occurrence, fate, spatio-temporal variations and potential sources. Chemosphere 2021, 283, 131301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hu, T.; Yang, L.; Guo, Z. The Investigation of Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Seasonal Freeze—Thaw Rivers During Spring Flood Period: A Case Study in Songhua River and Yalu River, China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2018, 101, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Lai, S.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, F.; Chen, H.; Zou, S.; Xie, Z.; Ebinghaus, R. Spatial distribution of perfluoroalkyl acids in the Pearl River of Southern China. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 1519–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cai, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Li, Y.; Ma, L.; Chen, C.; Huang, J.; Yu, G. Temporal trends and transport of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in a subtropical estuary: Jiulong River Estuary, Fujian, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Liang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Xu, L.; Cai, Y. Occurrence and Transport of Perfluoroalkyl Acids (PFAAs), Including Short-Chain PFAAs in Tangxun Lake, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 9249–9257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Tang, J.; Mi, L.; Tian, C.; Zhong, G.; Zhang, G.; Wang, S.; Li, Q.; Ebinghaus, R.; Xie, Z.; et al. Perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the lower atmosphere and surface waters of the Chinese Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea, and Yangtze River estuary. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599–600, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Cao, X.; Wang, H.; Wan, L.; Wang, S. Assessment on the distribution and partitioning of perfluorinated compounds in the water and sediment of Nansi Lake, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhang, H.; Xie, L.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, B. Spatial distribution and partition of perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs) in rivers of the Pearl River Delta, southern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 524–525, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Ying, G.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Y.; Jiag, Y.; Zhang, Q. Spatiotemporal distribution and mass loadings of perfluoroalkyl substances in the Yangtze River of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Xia, X.; Dong, J.; Xia, N.; Jiang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Y. Short- and long-chain perfluoroalkyl substances in the water, suspended particulate matter, and surface sediment of a turbid river. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 568, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piao, H.; Jiao, X.; Gai, N.; Chen, S.; Lu, G.; Yin, X.; Yamazaki, E.; Yamashita, N.; Tan, K.; Yang, Y.; et al. Perfluoroalkyl substances in waters along the Grand Canal, China. Chemosphere 2017, 179, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Gao, L.; Chen, J.; He, X.; Wang, B. Spatiotemporal variations, sources and health risk assessment of perfluoroalkyl substances in a temperate bay adjacent to metropolis, North China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 115011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, K.; Lu, G.; Yuan, X.; Zheng, Y.; Shao, P.; Cai, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, X.; Yang, Y. Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Water from the Yangtze River and Its Tributaries at the Dividing Point Between the Middle and Lower Reaches. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2018, 101, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Yu, Y. Concentrations of Typical Perfluoroalkyl Acids and Contributions of Their Precursors in the Water of the Le’an River in China. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 3204–3211. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dreyer, A.; Matthias, V.; Weinberg, I.; Ebinghaus, R. Wet deposition of poly- and perfluorinated compounds in Northern Germany. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniyasu, S.; Yamashita, N.; Moon, H.; Kwok, K.; Lam, P.; Horii, Y.; Petrick, G.; Kannan, K. Does wet precipitation represent local and regional atmospheric transportation by perfluorinated alkyl substances? Environ. Int. 2013, 55, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, K.; Taniyasu, S.; Yeung, L.; Murphy, M.; Lam, P.; Horii, Y.; Kannan, K.; Petrick, G.; Sinha, R.; Yamashita, N. Flux of Perfluorinated Chemicals through Wet Deposition in Japan, the United States, And Several Other Countries. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 7043–7049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pike, K.; Edmiston, P.; Morrison, J.; Faust, J. Correlation Analysis of Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Regional U.S. Precipitation Events. Water Res. 2021, 190, 116685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, M.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Munoz, G.; Sun, H. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in precipitation from mainland China: Contributions of unknown precursors and short-chain (C2-C3) perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acids. Water Res. 2019, 153, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, T.; Sun, H. Polyfluorinated and Perfluorinated Chemicals in Precipitation and Runoff from Cities Across Eastern and Central China. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2013, 64, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Lu, G.; Shao, P.; Gai, N.; Yang, Y.; Feng, J.; Zhao, Q. Level and distribution of perfluorinated compounds in snow and water samples from the transition zone in eastern Qinghai-Tibet. Environ. Chem. 2020, 39, 1192–1201. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Fu, J.; Gong, P.; Yan, J.; Yu, Z.; Yan, F.; Nawab, J. Release of Perfluoroalkyl Substances from Melting Glacier of the Tibetan Plateau: Insights into the Impact of Global Warming on the Cycling of Emerging Pollutants. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 8, 7442–7456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, E.; Falandysz, J.; Taniyasu, S.; Hui, G.; Jurkiewicz, G.; Yamashita, N.; Yang, Y.; Lam, P. Perfluorinated carboxylic and sulphonic acids in surface water media from the regions of Tibetan Plateau: Indirect evidence on photochemical degradation? J. Environ. Sci. Health A 2016, 51, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Wang, C.; Gao, K.; Wang, X.; Fu, J.; Gong, P.; Wang, Y. Perfluoroalkyl substances in precipitation from the Tibetan Plateau during monsoon season: Concentrations, source regions and mass fluxes. Chemosphere 2021, 282, 131105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barisci, S.; Suri, R. Occurrence and removal of poly/perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in municipal and industrial wastewater treatment plants. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 84, 3442–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, F. Emerging poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances in the aquatic environment: A review of current literature. Water Res. 2017, 124, 482–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).