Abstract
The paleoclimatic and paleoenvironmental changes inferred from shifts in lake sediment geochemistry require reliable, efficient and cost-effective methods of analysis. The available geochemical techniques, however, suggest that different analytical approaches can influence data interpretation. X-ray fluorescence core scanner analyses (XRF-CS), field portable X-ray fluorescence (FPXRF) and inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES) were concurrently applied to provide a multi-method geochemical appraisal of a 6000-year-long karstic sediment record (Lake Ighiel, Romania). The comparison between techniques was based on a set of elements that are widely employed in environmental reconstructions (Ti, K, Fe, Ca). Descriptive and statistical approaches were used to assess the advantages and disadvantages of each method and assess their optimal use in karstic environments. Our data display similar downcore patterns, with strong to moderate correlations between the datasets. The discrepancies observed between method-specific downcore multi element behaviour are related to the preparation steps and sampling. To best capture the complexity of past environmental changes in karstic settings, a combination of quantitative and qualitative geochemical methods would be the most appropriate approach to reliable data acquisition and subsequent paleoenvironmental interpretation of lake sediment data.
1. Introduction
Lake sediments are among the most valuable records when unravelling local to regional environmental changes over time [1,2,3]. Karstic lakes are distributed worldwide, and their closed basins and direct connection with aquifers make the system very sensitive to changes in hydrological balances, expressed as fluctuations in lake level, changes in water chemistry and aquatic communities. Karstic lake sequences provide a large variety of depositional environments and sediment facies, but the strong connection with their aquifer can make sediment interpretation rather complex. Therefore, there are knowledge gaps in how to treat and interpret these data.
In recent decades, a proliferation in the availability of quantitative and qualitative geochemical analyses has resulted in a range of high-resolution research studies aiming to better understand long- and short-term lacustrine changes in relation to climate variability and human impacts. These studies focused on a variety of topics such as past climate variability [4], land-use changes [5,6], catchment dynamics, sediment delivery and lake responses [7,8,9,10,11,12], identifying rapid depositional events [13] and assessing the rate and amplitude of anthropogenic impacts [14,15,16,17].
From such studies, it is apparent that the reconstruction methods employed depend on the type of sediment, the scientific questions to be addressed and the available resources. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages. For example, the standard chemical treatment procedures employed in inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES) used to determine sediment chemical composition are time-consuming and costly but can deliver accurate quantitative data [18]. However, more recent developments in geochemical techniques have opened up new opportunities, which facilitate the rapid, high-resolution, continuous screening of sediment cores without the need for sub-sampling. Among these, the most widely used are X-ray fluorescence core scanners (XRF-CS).
XRF-CS (Avaatech and ITRAX) is an automated, non-destructive and high-resolution technique, which acquires continuous, semi-quantitative, multi-element geochemical data (major and minor elements) with a measurement resolution of 100 µm [19]. When compared to spectrometric methods, which involve discrete sampling, XRF-CS offers lower analytical costs and faster, high-resolution data acquisition [19,20,21,22,23]. Therefore, XRF-CS has been widely used in paleoclimate and paleoenvironmental research as well as in pollution studies and environmental remediation [24,25]. This type of analysis is especially useful when working with continuous, long sedimentary records characterized by low accumulation rates, as it provides fast and low-cost semi-quantitative measurements enabling the estimation of relative elemental change [19,26]. However, one disadvantage of analyzing fresh sediment cores, compared to digestion-based procedures, are the matrix effects. These include grain-size heterogeneity, cracks and irregular core surfaces, variations in porosity and moisture, carbonate and organic contents, which can result in signal fluctuations and may impact the quality of results [25,27,28,29,30]. Furthermore, instrument settings, such as the data acquisition time, can be another potential variable that may influence the results [31]. Another potential disadvantage is that XRF core scanning only penetrates the near-surface of the sediment; thus, the chemical composition of the bulk of the sediment column may not be fully assessed [23]. To evaluate the potential influence of these factors on XRF-CS results, a comparison to quantitative analysis is usually required [26,32,33].
The field portable X-ray fluorescence (FPXRF) analyzer was initially designated as a portable instrument to determine the concentration of metals and metalloid of soils in a variety of contexts. In laboratory conditions, FPXRF is also used to screen lake sediments, but is also applied to pressed pellets. The main disadvantage of this technique is its lower detection limit and data resolution compared to XRF-CS and ICP-OES [34].
ICP-OES is a conventional, well-established technique, whereby discrete samples are analyzed after acid digestion. This approach allows for the acquisition of absolute element values at very low detection limits [35]. The main advantage of these methods is that they provide absolute chemical concentrations with high precision [18]. However, there are some limitations: as the nature of data recovery depends upon the digestion protocol, the dissolution procedure and, therefore, the analysis are relatively expensive. Element recovery based on this method can be restricted; Si, a major constituent of sediments and an important paleoerosion [24] and paleoproductivity proxy [36], is lost when samples are dissolved in hydrofluoric acid. As such, ICP-OES analyses are best applied to specific samples for which absolute chemical concentrations are required, but caution should be taken regarding the influence of the digestion protocol employed.
The aforementioned XRF-based techniques are now part of a routine analytical geochemistry toolbox and, since the introduction of XRF-CS, numerous studies have discussed the advantages and pitfalls of these techniques in comparison to spectrometry methods applied to a range of natural archives, e.g., marine [37] and lacustrine sediments [38], speleothems [39] and peat records [25,26,40]. In addition, there have been several attempts to calibrate the most recent XRF scanning methods against more conventional analytical techniques (i.e., ICP) and to convert semi-quantitative data (XRF-based) into quantitative data. The results have highlighted complications related to sediment type and protocol steps, and the need for study/sample-specific data preparation to ensure reproducibility between techniques [25,38]. However, there are still gaps in the knowledge and more detailed information is needed to test the performance and suitability of these techniques on karstic lake sediments and the implications for the use of such data in paleoenvironmental reconstructions.
This paper compares the results of geochemical measurements applied to sediment samples from karst Lake Ighiel, in the Romanian Carpathians (SE Europe), which enable a comparison of the three geochemical methods applied—XRF-CS (ITRAX), FPXRF and ICP-OES. Although comparisons between different methods, e.g., bulk and high-resolution point analyses, e.g., [25,26,38,40], were carried out previously, none of them specifically explored the relationship between XRF-CS, FPXRF and ICP-OES data obtained from a karstic sediment record. To ensure high data reproducibility, the analysis focused on assessing the patterns in a set of lithogenic indicators, Ti, K, Ca, Fe. These elements are commonly used as paleoenvironmental proxies and have the potential to disentangle the past and recent hydroclimate variability from the land-use changes that controlled the input of sediment into Lake Ighiel [5,41]. This paper assessed the strengths and weaknesses of more recent and conventional techniques applied to a single lake sediment record and evaluated the suitability of a selected set of elements in respect to a given method and their potential use as paleoclimatic and paleoenvironmental proxies.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Lake Sediment Record
Lake Ighiel is a karst lake located in the Apuseni Mountains (Romania) at 924 m above sea level (Figure 1). It has a small catchment area that comprises Jurassic limestones, but the southern inflow to the lake drains an area of Mesozoic molasse and volcanic rocks (diabase). Over time, changes in vegetation cover and the development of erosional features have occurred within the catchment; a detailed description is provided in References [5,41].
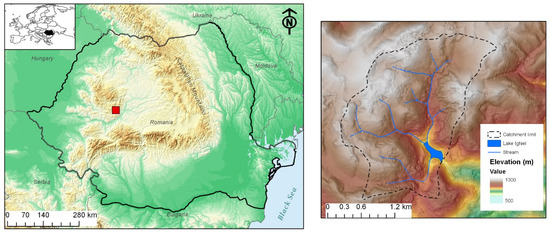
Figure 1.
The location of karstic Lake Ighiel in Romania and Europe (left panel), and a digital elevation model of the catchment and surroundings (right panel).
Sediment cores from Lake Ighiel were retrieved using a modified piston corer in 2013. A 553-cm-long composite profile was established based on the correlation (stratigraphy and magnetic susceptibility) of short-gravity and long-piston cores [41]. The sedimentary profile consists of four lithological units (I–IV): Unit I is composed of grey–brown clays and clayey silts, whereas Units II, III and IV consist of brown–grey laminated clays, brown–red layered and light-brown clays, respectively [41]. Millimeter-thick layers of coarse organic detritus are frequent in Unit III. An age–depth model based on 22 radiocarbon ages was established using the Bayesian age modelling software Bacon [42] and OxCal [43]. This indicates that the composite profile covers the last 6000 years of sedimentation; see details in Reference [41].
2.2. Interpretation of Major Elements Found in Lake Ighiel Sediments
Ti and K are conservative, geochemically stable elements that are mainly found in weathering-resistant silicates and can be used as proxies for detrital load or physical erosion [44,45,46,47,48]. For Lake Ighiel, Ti and K were used as indicators of catchment dynamics, with their variability in the sediment column mainly controlled by runoff and changes in soil erosion. Their patterns appear to align with the forcing effects of past climate variability and, in the most recent 150 years, to reflect human-induced landscape changes enhancing soil erosion [5,41].
Fe, as a trace metal, is redox-sensitive and has received much attention in environmental research [49]. Although Fe can be mobilized by shifts in the redox state, it can also be a tracer for terrigenous input to the lake, delivery from sewage treatment and even tephra [24,49,50,51]. Considering that present paper is not focused on reconstructing palaeoredox changes, the Fe curve is only shown here to illustrate the variability of Fe over time and discuss the differences between the methods used to determine it.
In lake sediments, Ca can have a detrital origin, as it is a major bedrock component, but can also reflect a biogenic output through the precipitation of authigenic carbonate minerals driven by lake internal biogeochemical activity [45]. In Lake Ighiel, the Ca curve was interpreted in accordance with other proxies (i.e., organic matter content) and thin-section analysis for insights on the sediment composition; see details in Reference [41]. In the lower part of the profile, in Unit I, II and IV, covering the time interval from 6030 to 2500 cal yr BP, and 1250 cal yr BP to the present, the Ca curve depicts changes in catchment erosion and carbonates supplied from the limestone bedrock. In the laminated Unit III spanning from 2500 to 1500 cal yr BP, the Ca curve mainly seems to reflect lake-internal biogeochemical variability [41].
2.3. Geochemical Analyses
Three different methods, XRF-CS (ITRAX), FPXRF, and ICP-OES, were applied concurrently to better understand Lake Ighiel’s 6000-year long paleoenvironmental and geochemical record. XRF-CS was performed on the fresh sediment of intact core sections, whereas the other two approaches (FPXRF and ICP-OES) were carried out on dried and homogenized discrete samples (Table 1).

Table 1.
Characteristics of the analytical techniques used (FPXRF, ICP-OES, XRF-CS), including the pre-analytical steps, resolution of analysis, the time required to prepare and analyze samples, type of results and advantages versus disadvantages. LOD stands for limits of detection.
2.3.1. XRF Core Scanning (XRF-CS)
The surface of split (along the long axis), fresh sediment cores was cleaned and covered with 2-µm film to avoid contaminating the sensor and to reduce sediment desiccation during measurement. To ensure reliable readings, the film was carefully positioned to avoid air bubbles and wrinkles. The cores were scanned (Figure 2) using the XRF element core scanning method (XRF-CS) at the laboratory of the GFZ in Potsdam, Germany. Cr and Mo tubes were used to acquire data on light elements [44]. Analyses were made with a 15 s exposure time, 40 kV tube voltage, 40 mA tube current and a step size of 1 mm. Replicate measurements were performed to statistically evaluate the results and estimate the confidence limit for the intensities of the elements measured [23]. However, given the very high-resolution of XRF-CS, the non-averaged data are also presented here to assess the long-term high-resolution patterns. The raw data are expressed as peak area.
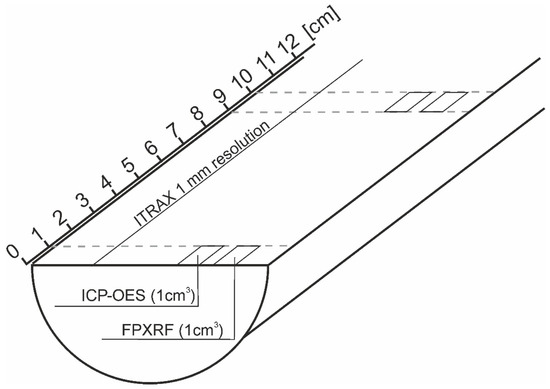
Figure 2.
The sampling scheme for the methodological technique used in this study.
2.3.2. Field Portable XRF Measurements (FPXRF)
The Lake Ighiel sediment record was subsampled at 10-cm resolution (Figure 2) (55 samples in total) for further sample-based geochemical analysis using a Niton XL3t GOLDD X-Ray Fluorescence analyzer (FPXRF) mounted in a shield and performed at the University of Salford, UK. After measuring the wet weight, each 1 cm3 sample was oven-dried at ~40 °C, ground to fine powder to homogenize the sample and carefully pressed into plastic cups above a 6-µm-thick polyester film, forming a measurement window. Each plastic cup was placed in the FPXRF laboratory stand and analyzed under main and low filters, each for 240 s [30]. The certified reference material (CRM) used was NCS DC73308 (Chinese stream sediment) as it has comparable elemental concentrations and a similar matrix to our lake sediment core. Results were acquired including the two-sigma error for each reading, which represents two standard deviations from the mean. For elements included in the study, the relative percent difference (RPD) between the concentration of the reference material and the concentration measured by FPXRF was less than 10%. The FPXRF data are expressed as Element/µg−1.
2.3.3. ICP-OES Analyses
Samples (1 cm3), each comprising one linear cm depth interval, were collected at 10-cm spacing along the sediment profile, dried and homogenized (Figure 2). Sample dissolution was performed using a mixed-acid (HNO3-HCl-HF), microwave-assisted approach. Digests were spiked with 1 ppm of internal standard (Sc) before analysis on a Perkin Elmer Optima 8000 ICP-OES system at the Northumbria University, UK. Two CRMs were digested and analyzed alongside the samples; Montana 2711 soil and IAEA-SL-1 Lake Sediment, with all analyses falling within 10% of expected recoveries. Method and instrument blanks were also run to assess for contamination and were found to contain negligible amounts of each element of interest. The data are expressed as ppm.
2.4. Data Processing
To assess the behavior of each element in relation to the method applied, the dataset was statistically treated. To evaluate the performance of each method and to investigate the correlation and similarities–dissimilarities between datasets, Pearson correlation coefficient (r) was applied. The strength of the correlation was assessed as: low for r < 0.3, moderate for 0.3 ≤ r < 0.6 and strong for r ≥ 0.6.
Descriptive statistics were used to evaluate data distribution (a normal distribution is defined when skewness equals/is close to 0 and kurtosis is close to 3), assess the overall changes with similarities and differences of the dataset. Box plots were used to interrogate the differences and similarities between geochemical outputs and evaluate, how element recovery depends on and/or behaves in terms of the method used, with a close look at the overall data variability and values (median, extreme values, outliers). To avoid the comparison of depth-based variables in absolute values and possible issues that might arise when comparing different units, the Z-score standardization was used to bring the data to the same unit.
3. Results
Intervals with higher values (TiXRF-CS > 10,000 peak area; TiFPXRF > 2000 µg g−1; TiICP-OES > 1000 ppm) are depicted by all methods in the lower part of the profile, below 400 cm depth (within Unit I) and in the uppermost 150 cm depth (Unit IV), which is characterized by a more dynamic pattern in sediment geochemical composition (Figure 3). However, distinct short-term peaks in Ti are clearly visible in the non-averaged TiXRF-CS curve, which are not captured by the coarser resolution of TiFP-XRF and TiICP-OES.
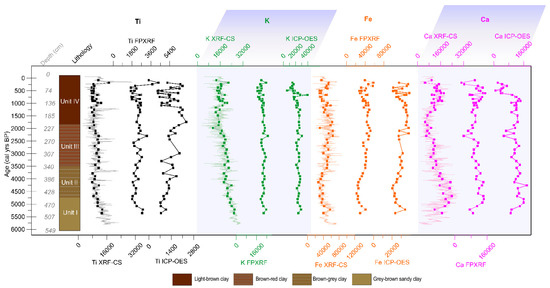
Figure 3.
Lithology of the Lake Ighiel record covering the last 6000 years and geochemical results from each analytical technique. The non-averaged data for XRF-CS are plotted with lighter colors under the point–line curves that show averaged values.
A rather stable pattern in K, mirrored in the results from all the methods, is visible between 500 cm and 140 cm depth (Unit I, II, III). Values are more dynamic for the last 140 cm (Unit IV) with marked peaks and dips (Figure 3). The highest concentration values for K (39,746 ppm) were registered by ICP-OES, which depicts relatively constant values with a peak at around 100 cm depth (Figure 3).
The Fe pattern depicted by all three methods is similar; low values (FeXRF-CS < 40,000 peak area, FeFPXRF < 30,000 µg g−1, FeICP-OES < 25,000 ppm) characterise the interval below 400 cm depth (Unit I). An increasing trend is visible between 400 cm and 150 cm (Unit III-II), followed by rapid changes between 150 cm and 0 cm depth (Unit IV) (Figure 3). FeXRF-CS also varies, and subtle shifts are evident in the non-averaged, high-resolution results (Figure 3).
The results from all methods show a similar pattern for Ca, with increasing values until 400 cm (Unit I), followed by a decreasing trend until 150 cm (Unit II and III), then sharp dips and peaks between 150 cm and 0 cm (Unit IV) (Figure 3).
The Pearson correlation coefficient (r) for the raw dataset shows strong correlations between XRF-CS and FPXRF for Ti (r = 0.60, p < 0.0001), Fe (r = 0.68, p < 0.0001) and Ca (r = 0.68, p < 0.0001) (Table 2; Figure 4) and a moderate correlation for K (r = 0.45, p < 0.0001). For most of the elements, XRF-CS displays moderate to low correlations with ICP-OES. FPXRF shows strong correlation with ICP-OES for K (r = 0.60, p < 0.0001), moderate correlations for Fe (r = 0.40, p < 0.003) and Ca (r = 0.30, p < 0.028) and a low correlation for Ti (r = 0.18, p < 0.185) (Table 2; Figure 4).

Table 2.
Pearson correlation coefficients r for the raw dataset. Strong and statistically significant correlations (p < 0.001) are marked in bold and with a star (*), whereas moderate correlations are marked in italics and with two stars (**).
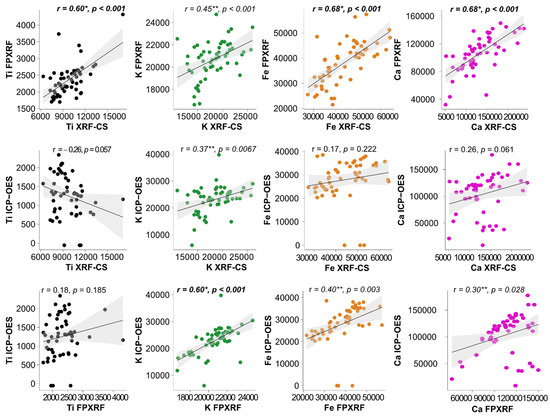
Figure 4.
Correlations between different methods with the regression line shown with a grey line and the 95% confidence interval represented by the grey shadow. Statistically significant correlations (p < 0.001) are marked in bold and with a star (*), whereas the moderate correlations are marked in italics and with two stars (**).
To minimize the noise and reduce the closed-sum effect, data normalisation is recommended, especially for highly organic sediments, although, in the case of Lake Ighiel, the sediments are very clastic [41]. It must be stated that the closed-sum effect is related to the impact that the high organic carbon content has on the overall counts. High organic content leads to a dilution of the overall signal (as O and C cannot be measured on XRF), which means, for core scanning, where the results are not calibrated, a drop in a certain element can be the result of high organic content, rather than an actual decrease. For FPXRF and ICP-OES, the results are calibrated to external standards, and the variable impacts of overall intensity can be ignored. Following general recommendations from the literature, a log-transformation was performed [23] (Table 3). A slight improvement in Pearson’s r values was only observed for Ca, most likely because this element showed a log-normal distribution.

Table 3.
Pearson correlations for log-transformed XRF-CS and raw FP-XRF and ICP-OES. Strong and statistically significant correlations (p < 0.001) are marked in bold and with a star (*), whereas the moderate correlations are marked in italics and with two stars (**).
A comparison of analytical techniques showed that the element mean, and maximum values recovered by the three methods were very close, with exception of TiXRF-CS, which was higher compared with the other two methods (Table 4).

Table 4.
The results of descriptive statistics for each analytical technique and element used in this study. They include mean, maximum, median, kurtosis, skewness and number of samples (N). The analysis was performed on the raw dataset.
Overall, the boxplots (Figure 5) show that, for specific elements and methods, the data share the same stratigraphic pattern, varying across the same range of minimum and maximum values. However, some differences were observed for some methods for which median, extreme values and outliers are different. Across the methods, Ti shows median values, which are only slightly different, with TiXRF-CS and TiICP-OES sharing a similar median value. However, TiICP-OES display the greatest range of values. TiXRF-CS and TiFPXRF have negative and positive outliers with a wider distribution and scattered data. K analysed with XRF-CS shows a similar median value to K analysed with FPXRF, but KXRF-CS displays a greater range. KICP-OES is less dispersed, but outliers are present. FeXRF-CS shows widely scattered data, whereas FeXRF-CS and FeICP-OES share the same median values and only FeICP-OES shows outliers (Figure 5). CaXRF-CS displays widely scattered data, whereas CaXRF-CS and CaICP-OES have a similar median, but both show negative and positive outliers. More attention should be paid to elements and methods, e.g., TiICP-OES, FeICP-OES, CaICP-OES, for which the data show important outliers and a higher variability (larger boxes and longer whiskers), denoting scattered data. It is interesting that these elements are also the ones that do not mimic the trend of the raw data (Figure 3).
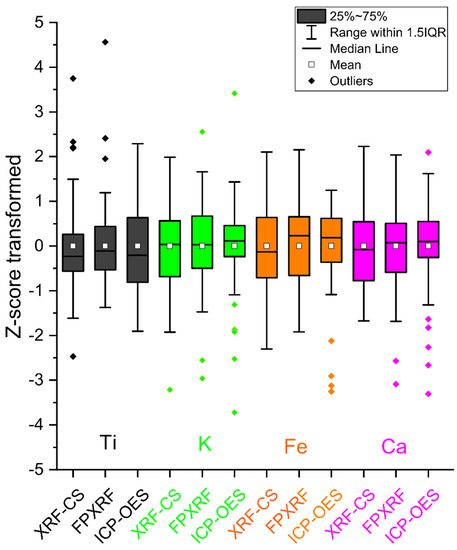
Figure 5.
Box plots of Z-score transformed values for Ti, K, Fe, Ca elements measured with XRF-CS, FPXRF, ICP-OES. The interquartile range (IQR) is delineated by the coloured box where the top represents the top of the upper, third quartile (75%) and the bottom represents the bottom of the lower, first quartile (25%). The black lines within the boxes correspond to mean values, the middle white squares represent the median values, the whiskers connect the maximum and minimum values (extend to 1.5 times the IQR), whereas the dots outside the whiskers represent outliers.
4. Discussion
4.1. Implications of Analytical Method Choice and Impediments to Proxy Interpretation
The present comparison between different analytical techniques shows that, overall, the investigated elements follow a similar pattern downcore, especially over specific intervals, with most of them showing strong to moderate correlations (Table 2). This section discusses how the preparation steps, technical settings of each technique employed, the sediment composition and/or type of sediment sample might influence the geochemical results and inferred environmental reconstruction from a karstic lake.
4.2. Preparation Steps
XRF-CS provides a detailed view of the chemical composition of the scanned sediment, but this is hampered by background noise and is highly sensitive to organic matter content, which can mask the lithogenic fraction [31,52]. Additionally, XRF-CS scans fresh sediments, whereas FPXRF, in this case, was employed on dried, ground and homogenized samples; thus, matrix effects in the latter analysis are limited. It is well documented that high-amplitude changes in porosity, granulometry and moisture can influence the x-ray-based results of the analyzed core [53,54,55], and care must be taken in the overall data interpretation. However, our results show strong and significant correlations between XRF-CS and FPXRF, suggesting that matrix effects might impact the method-specific element recovery in a similar manner.
In the case of ICP-OES analysis, although it provides absolute values, the quality of the recovered data can be influenced by the digestion method, matrix effects and spectral interferences [56]. As such, the sequence and combination of chemical treatments such as HNO3-HCl-HF/HClO4 and the digestion time play a major role in the recovery of specific elements and can lead to incomplete recovery. For Lake Ighiel, some elements analyzed by ICP-OES show a relatively higher variability (Ti), extreme values and outliers (K, Fe, Ca) (Figure 3). The recovery of these elements could be influenced by the protocol used to extract them. For example, the recovery of some elements, which have an affinity with aluminosilicates, is highly dependent on the digestion of this matrix. The complete digestion of Ti or K, a major component of the aluminosilicate matrix, is difficult to assure and, thus, the full recovery of elements that are trapped in such a matrix, is uncertain.
4.3. Method Efficiency and Optimal Use
In the case study discussed here, the comparison of several analytical techniques that are concomitantly applied to karstic Lake Ighiel’s clayey sediments reveals that the method choice will impact the usefulness of the data and, therefore, proxy applicability and inference potential. Given the significant time and costs of laboratory analyses, our assessment highlights some important considerations in planning sediment geochemical analyses (Figure 6). Therefore, the use of XRF-CS is recommended in laminated sediments, as this instrument is capable of providing further insight into the nature of the laminations, while homogenous sediments could be analysed with lower-resolution instruments (FPXRF, ICP-OES).
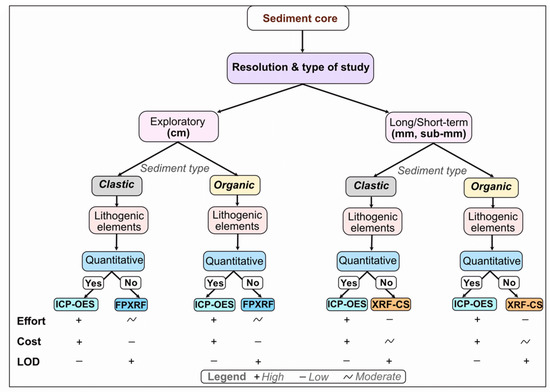
Figure 6.
A scheme for choosing the most suitable analytical technique for paleoclimatic and/or paleoenvironmental studies based on lake sediment cores with respect to the type of study and resolution, type of sediments and efforts (preparation) costs and limits of detection (LOD).
XRF-CS appeared to be most suitable method for acquiring the fine-resolution data needed to characterize climatic and environmental changes over the past 6000 years, as recorded by the Lake Ighiel sediment archive (Figure 3). If the XRF-CS data were averaged or performed at a lower resolution, the paleoclimatic and paleoenvironmental reconstruction based on lithogenic elements would lose short-term (decadal to centennial) phases with important variability [41]. XRF-CS is much faster than spectrometric analysis [37]. Its advantages include time-efficiency, high-resolution data acquisition and the non-destructive nature of these measurements. However, this method has relatively high analytical costs. Nevertheless, with the increased availability of core scanners, it might be expected that, in the near future, such analyses will be commonly available.
The FPXRF results show that this analytical technique is more suitable for relatively rapid data acquisition, especially when qualitative, coarse-resolution data are sufficient. The technique provides a rapid overview of the sediment geochemical composition at Lake Ighiel and captured the main changes along the profile. FPXRF is a relatively inexpensive technique that can be used as a precursor step to more costly analyses and the prioritization of analysis for the intervals of greatest interest; for example, where elemental data show prominent geochemical changes. One of the downsides of the FPXRF used in the lab is that it runs on bulk samples, which require (semi)destructive preparation steps such as sub sampling, drying and grinding.
For Lake Ighiel, XRF-CS provides high-resolution data acquisition, whereas FPXRF provides a rapid assessment of geochemical composition while ICP-OES provides quantitative estimates. The digestion-based technique ICP-OES returned more variable results compared to XRF-CS and FPXRF (Figure 3). The main pitfalls of these techniques in terms of cost efficiency are represented by the time needed for multiple preparation-steps, the destruction of the sample and the greater logistic and human resource requirements. One of the greatest advantages of using these analytical techniques is the absolute precision of the obtained results, which seem to be more applicable to studies demanding quantitative results, e.g., targeting pollution reconstruction [57,58].
4.4. A Case Study of the Lake Ighiel Paleorecord Based on Multiple Geochemical Datasets
The information gathered by the geochemical methods and supported by other analyses, including thin-sections and rock magnetics on the 6-m-long sediment record, yielded the identification of the main processes that have controlled karstic lake hydrology and sedimentation over time. The first sedimentological phase (Unit I; Figure 3), which spanned between 6030 and 4200 cal yr BP, is characterized by higher values of terrigenous elements such as Ti and K, the deposition of sand layers and slightly lower carbonate content. These elements indicate a high detrital input and low lacustrine productivity, reflecting the enhanced surface runoff and sediment transport processes into Lake Ighiel. This was likely caused by enhanced rainfall, as was observed in other records from Central Eastern (CE) Europe and the NE Mediterranean, showing a strong connectivity between catchment-lake dynamics and changes in atmospheric circulation at that time. The stratigraphic variability of elements in Unit I is rather low, and they show a similar pattern across the tested methods. Therefore, it seems that, regardless of the approach used in this case, the interpretation of the environmental changes would remain the same. Between 4200 and 2500 cal yr BP (Unit II; Figure 3), the terrigenous input progressively declined (KXRF-CS and Ca of all methods; Figure 3), accompanied by a slight increase in the fine sediment fractions (TiXRF-CS), suggesting a more stable catchment and a decline in erosional activity. During this interval, a series of multi-century detrital events were identified, which are in agreement with records from central Europe that show increased flood activity, but contrast with the NE Mediterranean, where drier conditions are inferred. The contrasting conditions from different parts of Europe suggest a strong NW-SE hydro-climatic gradient. The identification of these events would not have been possible if a geochemical screening method other than XRF-CS had been applied.
Unit III, spanning 2500 and 1250 cal yr BP, covers the interval from the Iron Age to the Migration Period. During this time, intensive agriculture developed in the vicinity of the study area related mainly to the Dacian–Roman Period. One would expect an increase in terrigenous elements in the sediments, as intensified grazing, pasturing, and cultivation usually leads to increased erosion [9,58,59]. Indeed, after an initial decrease in Ti and K, a sudden increase is observed at around 2000 cal yr BP. Although this pattern was captured by every method, ICP-OES shows the highest amplitude changes. The most recent period (Unit IV), covering the time from 1250 cal yr BP to the present, shows a more variable and complex pattern in Lake Ighiel’s sedimentation, with a general decrease in terrigenous input. There was, however, a distinct event of increased Ti and K values related to the 6-cm-thick turbidite deposited around 150 cal yr BP. This layer was evident during a visual examination of the core, but it would be missed if interpretation relied solely on IPC-OES, which showed no such changes at that time. The hydrology of the lake was further influenced by increasing human pressure reported from the lakes worldwide [10] and regionally reported climatic events, dry spells [60]. Increasing Ca readings obtained from XRF-CS and FPXRF could be related to the increased calcite precipitation caused by lake trophic status changes, affected by combined human activity in the catchment and global temperature increase. In Lake Ighiel, variations in sediment’s Ca content could be also related to an increased delivery of dissolved bicarbonates from the catchment limestones, but as erosion decreased, both factors should be considered. Neither of these processes, however, is reflected by the ICP-OES results.
Our case study of Lake Ighiel illustrates that the reliability of the method used depends on understanding the factors that can affect the geochemical composition of the sediments. In most cases, paleoclimatic and sedimentological assessments based on XRF-CS measurements would lead to reasonable interpretations, but the response to some events could have been obscured due to the limitations of the method. It has also been confirmed that FPXRF can lead to similar conclusions as XRF-CS, but the high-resolution approach required for a detailed study would be time-consuming and limited by sampling resolution. ICP-OES showed distinct peaks, whereas other methods did not show any relevant changes. However, the high cost of the analysis and time needed for running samples would not allow for dense sampling in most studies. Building on these results, this paper proposes a schematic overview that could be helpful for choosing the most suitable analytic technique for paleostudies (Figure 6).
The example of Lake Ighiel’s paleorecord shows the potential of high-resolution XRF-CS method for acquiring a detailed paleoenvironmental reconstruction from karstic sediments. However, the reliability of this tool is case-specific and depends on a deep understanding of the possible factors that might affect the sediment geochemical composition and its connection to climatic and environmental processes. With the increasing use of these high-resolution methods [61,62], more work is needed to test its performance on different sedimentary records and narrow the apparent knowledge gaps in data treatment and paleoenvironmental interpretation.
5. Conclusions
Lake Ighiel archives 6000 years of sedimentation, and hence records a range of paleolimnological and/or environmental/climatic conditions that have influenced the previous deposition of sediments and its geochemical characteristics. In this study, we tested three geochemical measurement approaches (XRF-CS, FPXRF, ICP-OES) applied to a set of lithogenic elements (Ti, K, Ca, Fe) to assess method-specific element recovery for achieving similar or complementary environmental reconstructions. Our results show a similar down-core pattern, independent of the method applied; however, using the lower-resolution data resulting from FPXRF and ICP-OES could affect the paleoenvironmental interpretation as a result of their slightly different geochemical profiles, which may obscure the core’s reconstruction potential. Strong to moderate correlations were found between the data from multiple methods, especially between the XRF-CS and FPXRF results, and also between the FPXRF and ICP-OES datasets. This comparison highlights that the method choice should reflect the initial research questions. Based on this assessment, the advantages and disadvantages of each method and recommendations for their optimal use are summarized here: (i) the XRF-CS method should be used when high-resolution data are required. The method is rapid and non-destructive, but analytical costs are substantial; (ii) the FPXRF method provides fast data acquisition and allows for the rapid assessment of variability in sediment composition under laboratory conditions. The method is relatively cheap, but one disadvantage is the preparation time and higher lower detection limits; (iii) the ICP-OES method provides comparable results to FPXRF, providing quantitative estimates with a limited influence of physical sediment features. However, the method is expensive and time-consuming.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and methodology, A.H., A.B., J.L., S.M.H., M.Z., D.V.; software, A.H., A.B. and J.L.; data analysis and data collection, A.H., A.B., J.L., S.M.H., D.V.; writing—review and editing, A.H., A.B., J.L., S.M.H., M.Z., D.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by a grant of the Romanian Ministry of Education and Research, CNCS–UEFISCDI, project number PN-III-P4-ID-PCE-2020-0914, within PNCDI III, and by a grant of the Ministry of Research and Innovation, project number PN-III-P4-ID-PCCF-2016-0016 (DARKFOOD). AH was partially sponsored by the Romanian Young Academy, which is funded by Stiftung Mercator and the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation for the period 2020–2022.
Acknowledgments
Achim Brauer and Rik Tjallingii are thanked for supporting part of the analytical investigations and coring. Alexandru Frantiuc is acknowledged for advice on spatial data processing.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dearing, J.A. Climate-human-environment interactions: Resolving our past. Clim. Past 2006, 2, 187–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francus, P.; Lamb, H.; Nakagawa, T.; Marshall, M.; Brown, E.; Suigetsu 2006 Project Members. The potential of high-resolution X-ray fluorescence core scanning: Applications in paleolimnology. PAGES News 2009, 17, 93–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolitschka, B.; Francus, P.; Ojala, A.E.K.; Schimmelmann, A. Varves in lake sediments—A review. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2015, 117, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, J.; Anderson, N.J.; Knudsen, M.F. Variability of the North Atlantic Oscillation over the past 5200 years. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 808–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haliuc, A.; Buczkó, K.; Hutchinson, S.M.; Ács, É.; Magyari, E.K.; Korponai, J.; Begy, R.C.; Vasilache, D.; Zak, M.; Veres, D. Climate and Land-Use as the Main Drivers of Recent Environmental Change in a Mid-Altitude Mountain Lake, Romanian Carpathians. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renberg, I.; Korsman, T.; Birks, H.J.B. Prehistoric increases in the pH of acid-sensitive Swedish lakes caused by land-use changes. Nature 1993, 362, 824–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaud, F.; Révillon, S.; Debret, M.; Revel, M.; Chapron, E.; Jacob, J.; Giguet-Covex, C.; Poulenard, J.; Magny, M. Lake Bourget regional erosion patterns reconstruction reveals Holocene NW European Alps soil evolution and paleohydrology. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2012, 51, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaud, F.; Giguet-Covex, C.; Wilhelm, B.; Fouinat, L.; Doyen, E.; Chapron, E.; Vanniere, B. Erosion under climate and human pressures: An alpine lake sediment perspective. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2016, 152, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonk, A.; Kinder, M.; Enters, D.; Grosjean, M.; Meyer-Jacob, C.; Tylmann, W. Sedimentological and geochemical responses of Lake Żabińskie (north-eastern Poland) to erosion changes during the last millennium. J. Paleolimnol. 2016, 56, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenny, J.P.; Koirala, S.; Gregory-Eaves, I.; Francus, P.; Niemann, C.; Ahrens, B.; Brovkin, V.; Baud, A.; Ojala, A.E.K.; Normandeau, A.; et al. Human and climate global-scale imprint on sediment transfer during the Holocene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 22972–22976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longman, J.; Veres, D.; Ersek, V.; Haliuc, A.; Wennrich, V. Runoff events and related rainfall variability in the Southern Carpathians during the last 2000 years. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatier, P.; Wilhelm, B.; Ficetola, F.; Moiroux, F.; Poulenard, J.; Develle, A.-L.; Bichet, A.; Chen, W.; Pignol, C.; Reyss, J.-L.; et al. 6-Kyr Record of Flood Frequency and Intensity in the Western Mediterranean Alps e Interplay of Solar and Temperature Forcing. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2016, 170, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czymzik, M.; Brauer, A.; Dulski, P.; Plessen, B.; Naumann, R.; Von Grafenstein, U.; Scheffler, R. Orbital and solar forcing of shifts in Mid- to Late Holocene flood intensity from varved sediments of pre-alpine Lake Ammersee (southern Germany). Quat. Sci. Rev. 2013, 61, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battarbee, R.W.; Anderson, N.J.; Bennion, H.; Simpson, G.L. Combining limnological and palaeolimnological data to disentangle the effects of nutrient pollution and climate change on lake ecosystems: Problems and potential. Freshw. Biol. 2012, 57, 2091–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearing, J.A.; Battarbee, R.W.; Dikau, R.; Larocque, I.; Oldfield, F. Human–environment interactions: Learning from the past. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2006, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, N.; Saulnier-Talbot, É.; Mills, K.; Gell, P.; Battarbee, R.; Bennion, H.; Chawchai, S.; Dong, X.; Francus, P.; Flower, R.; et al. First human impacts and responses of aquatic systems: A review of palaeolimnological records from around the world. Anthr. Rev. 2017, 5, 28–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poraj-Górska, A.I.; Bonk, A.; Żarczyński, M.; Kinder, M.; Tylmann, W. Varved lake sediments as indicators of recent cultural eutrophication and hypolimnetic hypoxia in lakes. Anthropocene 2021, 36, 100311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krachler, M.; Mohl, C.; Emons, H.; Shotyk, W. Influence of digestion procedures on the determination of rare earth elements in peat and plant samples by USN-ICP-MS. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2002, 17, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croudace, I.W.; Löwemark, L.; Tjallingii, R.; Zolitschka, B. High resolution XRF core scanners: A key tool for the environmental and palaeoclimate sciences. Quater. Int. 2019, 514, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, J.H.F.; Van Der Gaast, S.J.; Koster, B.; Vaars, A.J. CORTEX, a shipboard XRF-scanner for element analyses in split sediment cores. Mar. Geol. 1998, 151, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, T.O.; Van Der Gaast, S.; Koster, B.; Vaars, A.; Gieles, R.; De Stigter, H.C.; De Haas, H.; Van Weering, T.C.E. The Avaatech XRF Core Scanner: Technical description and applications to NE Atlantic sediments. In New Techniques in Sediment Core Analysis; Rothwell, R.G., Ed.; Special Publications; Geological Society: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothwell, R.G.; Croudace, I.W. Micro-XRF Studies of Sediment Cores: Applications of a Non-Destructive Tool for the Environmental Sciences; Croudace, I.W., Rothwell, R.G., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weltje, G.J.; Tjallingii, R. Calibration of XRF core scanners for quantitative geochemical logging of sediment cores: Theory and application. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2008, 274, 423–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kylander, M.E.; Ampel, L.; Wohlfarth, B.; Veres, D. High-resolution X-ray fluorescence core scanning analysis of Les Echets (France) sedimentary sequence: New insights from chemical proxies. J. Quat. Sci. 2011, 26, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longman, J.; Veres, D.; Wennrich, V. Utilisation of XRF core scanning on peat and other highly organic sediments. Quatern. Int. 2019, 514, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poto, L.; Gabrieli, J.; Crowhurst, S.; Agostinelli, C.; Spolaor, A.; Cairns, W.R.L.; Cozzi, G.; Barbante, C. Cross calibration between XRF and ICP-MS for high spatial resolution analysis of ombrotrophic peat cores for palaeoclimatic studies. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyraki, A.; Ramsey, M.H.; Potts, P.J. Evaluation of portable X-ray fluorescence instrumentation for in situ measurements of lead on contaminated land. Analyst 1997, 122, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, J.F.; Chiverell, C.; Schillereff, D. Approaches to water content correction and calibration for µXRF core scanning: Comparing X-ray scattering with simper regression of element concentrations. In Micro-XRF Studies of Sediment Cores Applications of a Non-Destructive Tool for the Environmental Sciences; Croudace, I.W., Rothwell, R.G., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 373–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennekam, R.; De Lange, G. X-ray fluorescence core scanning of wet marine sediments: Methods to improve quality and reproducibility of high-resolution paleoenvironmental records. Limnol. Oceanogr. Meth. 2012, 10, 991–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilbride, C.; Poole, J.; Hutchings, T.R. A comparison of Cu, Pb, As, Cd, Zn, Fe, Ni and Mn determined by acid extraction/ICP-OES and ex situ field portable X-ray fluorescence analyses. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 143, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löwemark, L.; Chen, H.-F.; Yang, T.-N.; Kylander, M.; Yu, E.-F.; Hsu, Y.-W.; Lee, T.-Q.; Song, S.-R.; Jarvis, S. Normalizing XRF-scanner data: A cautionary note on the interpretation of high-resolution records from organic-rich lakes. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2011, 40, 1250–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longman, J.; Veres, D.; Ersek, V.; Salzmann, U.; Hubay, K.; Bormann, M.; Wennrich, V.; Schäbitz, F. Periodic input of dust over the Eastern Carpathians during the Holocene linked with Saharan desertification and human impact. Clim. Past 2017, 13, 897–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löwemark, L.; Bloemsma, M.; Croudace, I.; Daly, J.S.; Edwards, R.J.; Francus, P.; Galloway, J.M.; Gregory, B.R.; Huang, J.J.S.; Jones, A.F.; et al. Practical guidelines and recent advances in the Itrax XRF core-scanning procedure. Quatern. Int. 2019, 514, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potts, P.J. X-ray fluorescence analysis: Principles and practice of wavelength dispersive spectrometry. In A Handbook of Silicate Rock Analysis; Potts, P.J., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1987; pp. 226–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, M.; Walsh, N. Handbook of Inductively Coupled Plasma Spectrometry; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.C.; Brown, E.T.; Shi, J. Biogenic silica deposition in Lake Malawi, East Africa over the past 150,000 years. Palaeogeogr. Palaeocl. 2011, 303, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelms-Dick, D.; Westerhold, T.; Röhl, U.; Wilhelms, F.; Vogt, C.; Hanebuth, T.J.; Römmermann, H.; Kriews, M.; Kasten, S. A comparison of mm scale resolution techniques for element analysis in sediment cores. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2012, 27, 1574–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, B.R.B.; Patterson, R.T.; Reinhardt, E.G.; Galloway, J.M.; Roe, H.M. An evaluation of methodologies for calibrating Itrax X-ray fluorescence counts with ICP-MS concentration data for discrete sediment samples. Chem. Geol. 2019, 521, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finné, M.; Kylander, M.; Boyd, M.; Sundqvist, H.; Löwemark, L. Can XRF scanning of speleothems be used as a non-destructive method to identify paleoflood events in caves? Int. J. Speleol. 2015, 44, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kern, O.A.; Koutsodendris, A.; Mächtle, B.; Christanis, K.; Schukraft, G.; Scholz, C.; Kotthoff, U.; Pross, J. XRF core scanning yields reliable semiquantitative data on the elemental composition of highly organic-rich sediments: Evidence from the Füramoos peat bog (Southern Germany). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 134110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haliuc, A.; Veres, D.; Brauer, A.; Hubay, K.; Hutchinson, S.M.; Begy, R. Palaeohydrological changes over mid and late Holocene in the Carpathian area, central-eastern Europe. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2017, 152, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaauw, M.; Christen, J.A. Bacon Manual—v2.2. 2013. Available online: https://chrono.qub.ac.uk/blaauw/manualBacon_2.3.pdf (accessed on 26 February 2022).
- Ramsey, Ã.C.B. Deposition models for chronological records. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2008, 27, 42–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croudace, I.W.; Rindby, A.; Rothwell, R.G. ITRAX: Description and Evaluation of a New Multi-Function X-ray Core Scanner; Special Publications; Geological Society: London, UK, 2006; Volume 267, pp. 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.S. Paleolimnology: The History and Evolution of Lake Systems, 1st ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Koinig, K.; Shotyk, W.; Lotter, A.; Ohlendorf, C. 9000 Years of Geochemical Evolution of Lithogenic Major and Trace Elements in the Sediment of an alpine lake. J. Paleolimnol. 2003, 4, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kylander, M.E.; Klaminder, J.; Wohlfarth, B.; Löwemark, L. Geochemical responses to paleoclimatic changes in southern Sweden since the late glacial: The Hässeldala Port lake sediment record. J. Paleolimnol. 2013, 50, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Puertas, C.; Tjallingii, R.; Bloemsma, M.; Brauer, A. Varved sediment responses to early Holocene climate and environmental changes in Lake Meerfelder Maar (Germany) obtained from multivariate analyses of micro X-ray fluorescence core scanning data. J. Quat. Sci. 2017, 32, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeher, S.; Gilli, A.; North, R.P.; Hamann, Y.; Schubert, C.J. Tracing bottom water oxygenation with sedimentary Mn/Fe ratios in Lake Zurich, Switzerland. Chem. Geol. 2013, 352, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuven, S.; Francus, P.; Lamoureux, S.F. Estimation of grain size variability with micro X-ray fluorescence in laminated lacustrine sediments, Cape Bounty, Canadian High Arctic. J. Paleolimnol. 2010, 44, 803–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietze, E.; Słowiński, M.; Zawiska, I.; Veh, G.; Brauer, A. Multiple drivers of Holocene lake level changes at a lowland lake in northeastern Germany. Boreas 2016, 45, 828–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothwell, R.G.; Croudace, I.W. Micro-XRF Studies of Sediment Cores: A perspective on Capability and Application in the Environmental Sciences. In Micro-XRF Studies of Sediment Cores: Applications of a Non-Destructive Tool for the Environmental Sciences; Croudace, I.W., Rothwell, R.G., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Lai, W.; Lin, Y. Influence of and correction for moisture in rocks, soils and sediments on in situ XRF analysis. X-ray Spectrom. 2005, 34, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, S.; Croudace, I.W.; Rothwell, G. Parameter optimisation for the ITRAX Core Scanner. In Micro-XRF Studies of Sediment Cores: Applications of a Non-Destructive Tool for the Environmental Sciences; Croudace, I.W., Rothwell, R.G., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 535–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjallingii, R.; Röhl, U.; Kölling, M.; Bickert, T. Influence of the water content on X-ray fluorescence corescanning measurements in soft marine sediments. Geochem. Geophy. Geosy. 2007, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falciani, R.; Novaro, E.; Marchesini, M.; Gucciardi, M. Multi-element analysis of soil and sediment by ICP-MS after a microwave assisted digestion method. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2000, 15, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longman, J.; Veres, D.; Finsinger, W.; Ersek, V. Exceptionally high levels of lead pollution in the Balkans from the Early Bronze Age to the Industrial Revolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 5661–5668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augustsson, A.; Gaillard, M.-J.; Peltola, P.; Mazier, F.; Bergbäck, B.; Saarinen, T. Effects of land use and climate change on erosion intensity and sediment geochemistry at Lake Lehmilampi, Finland. Holocene 2013, 23, 1247–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bork, H.R.; Lang, A.A. Quantification of past soil erosion and land use/land cover changes in Germany. In Long Term Hillslope and Fluvial System Modelling: Concepts and Case Studies from the Rhine River Catchment—Lecture Notes in Earth Sciences; Lang, A., Heinrich, K., Dikau, R., Eds.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 232–239. [Google Scholar]
- Ionita, M.; Scholz, P.; Chelcea, S. Assessment of droughts in Romania using the Standardized Precipitation Index. Nat. Hazards 2016, 81, 1483–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doufexi, M.; Gamvroula, D.E.; Alexakis, D.E. Elements’ Content in Stream Sediment and Wildfire Ash of Suburban Areas in West Attica (Greece). Water 2022, 14, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arienzo, M.; Ferrara, L.; Trifuoggi, M.; Toscanesi, M. Advances in the Fate of Rare Earth Elements, REE, in Transitional Environments: Coasts and Estuaries. Water 2022, 14, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).