Abstract
Polychaetes (such as Sternaspis sculata) can biotransform polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the environment, and the cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzyme is the key substance in this process. Here, a novel CYP gene was identified from S. sculata, a marine polychaete that is abundantly distributed along marine coasts worldwide. The full-length cDNA of the new CYP is a 1829 bp, encoding a protein of 509 amino acids. The deduced amino acid sequence of the CYP gene contains the conserved motifs of the P450 family (FxxGxxxCxG) and the characteristic sequences of the CYP4 family (EVDTFMFEGHDTT), showing high similarity to CYP4V from marine polychaetes. Therefore, the cDNA sequence might belong to the subfamily of CYP4V, tentatively named SsCYP4V. The expression levels of SsCYP4V in the field were detected in S. sculata sampled from six sites along the coasts of the Liaodong Peninsula. The results showed that the relative expression levels of SsCYP4V in S. sculata were significantly different among the sampling sites; however, no positive relationship was found between SsCYP4V expression levels and PAHs concentrations in the sediments. These findings suggested a complexity of CYP gene expression in the field, and SsCYP4V cannot be used as a biomarker for the field monitoring of PAH pollution.
1. Introduction
Polychaete worms are the most abundant taxa in the benthic community, and they play an important role in the energy flow and nutrient cycle of marine ecosystems [1,2]. Some polychaetes were also considered to be the biotransformation vector of exogenous compounds (e.g., polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and other xenobiotics) [3]. The mechanism of biotransformation of PAHs is to increase their water solubility, beginning with cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYPs) [4]. Therefore, the identification and functional analysis of polychaete CYP genes are essential for understanding the mechanism of CYPs-mediated PAH biotransformation [5].
In polychaetes, numerous CYP genes have been identified, and their functions were analyzed by mRNA expression research, with most of them being CYP4, and a few being CYP3 [6,7]. For example, two CYPs (CYP4AT1 and CYP331A1) were identified from Capitella sp. I, and studies showed that the transcriptional level of CYP4AT1 was increased only in response to 3-methylcholanthrene (3-MC), but the expression level of CYP331A1 was induced by benzo[a]pyrene (B[a]P) and fluoranthene exposure [8]. Won, Rhee, Shin, Jung, Shim, Lee, and Lee [7] identified three CYP genes (CYP432A1, CYP431A1, and CYP4DU1) in Perinereis nuntia, and their mRNA expression was significantly increased by B(a)P. Furthermore, three other CYP genes in P. nuntia (CYP4BB2, CYP423A1, and CYP424A1) were also significantly induced under B(a)P exposure [9]. Moreover, two novel CYP genes (CYP4BB4 and CYP4V82) from P. aibuhitensis were identified, and their transcriptional responses to the PAHs of different benzene rings and various doses were analyzed [6,10].
The polychaete Sternaspis sculata (Annelida, Polychaeta) is widely distributed in the sediment bottom of shallow waters all over the world [2]. In China, it is the dominant species of benthic polychaetes in Liaodong Bay, Bohai Bay, and Jiaozhou Bay [11]. This species lives in sediment, exhibiting low mobility and the characteristics of strong adaptability and pollution resistance [2,12]. These characteristics have resulted in the increased use of this species as a bioindicator in environmental monitoring and ecotoxicological research [13].
At present, the relevant research is mainly concentrated in the laboratory, while field research is lacking. This work aimed to identify a novel CYP gene (SsCYP4V) from S. sculata and to determine the relative transcriptional levels of the CYP gene in the field. Moreover, the correlation between the CYP gene transcription expression and the PAHs content in the sediments was analyzed to explore whether the CYP4 gene transcription expression level in the species can be used as a biomarker for the field monitoring of PAH pollution in the sediments.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Sampling and Sample Preparation
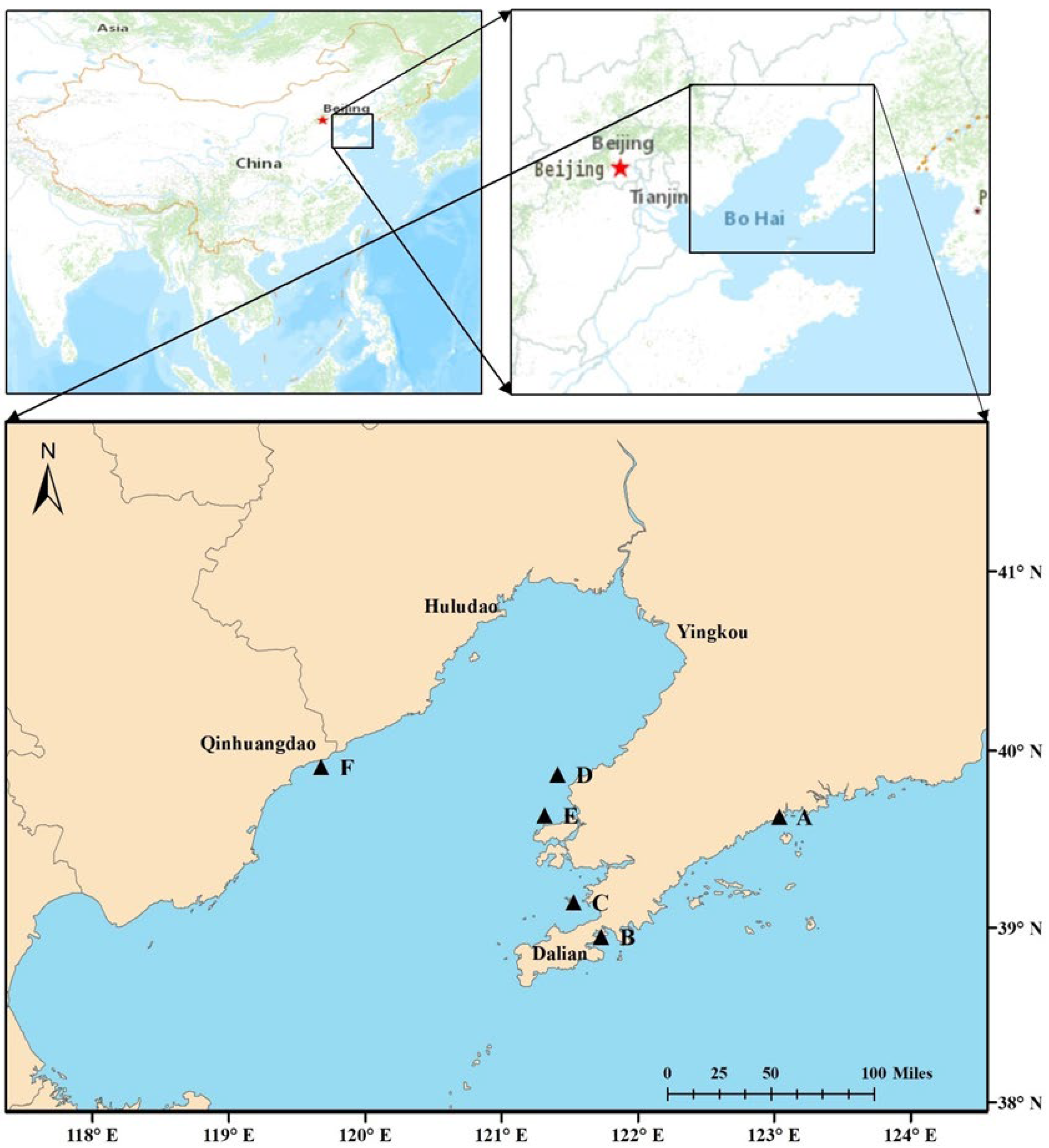
The worm Sternaspis scutate and sediments were gently collected from six sites around Liaodong Peninsula in the north of China, namely, Zhuanghe (A), Dalian Bay (B), Jinzhou Bay (C), Hongyanhe (D), Changxingdao (E), and Qinhuangdao (F) (Figure 1) using a stainless-steel grab sampler. For each site, 100 g of undisturbed surface sediment (uppermost 5 cm) was dispensed into sealing bags. Then, S. scutate was sieved from the remaining sediment. Triplicate sediment samples were collected from each sampling site, and at least three worms were obtained from each site. After collection, S. scutate were immediately cut into small pieces and placed in an EP tube (1.5 mL) containing 1 mL of RNAstore protection solution (Tiangen Biotech, Beijing, Co., Ltd. Beijing, China). The worms and sediments were initially stored in a freezer until delivery to the laboratory and kept at −80 °C (worms) and −20 °C (sediments) until analysis.
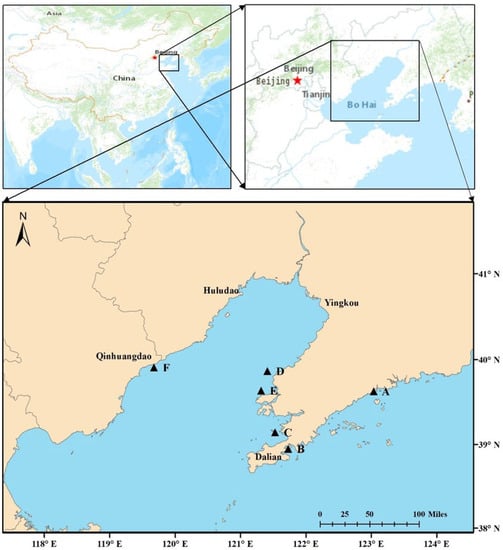
Figure 1.
Locations of sampling sites for S. scutata and sediments (A: Zhuanghe; B: Dalian Bay; C: Jinzhou Bay; D: Hongyanhe; E: Changxingdao; F: Qinhuangdao).
2.2. Cloning of Full-Length cDNA of CYP4
Total RNA (Supplementary Materials Figure S1) was extracted from the S. sculata using total RNA extractor (Tiangen Biotech, Beijing, China). The quality and quantity of total RNA were determined by electrophoresis in 1.0% (w/v) agarose gel and an ultramicro spectrophotometer, respectively.
Degenerate primers were designed according to the conserved region of the known CYP4 family. The forward primers were designed according to the hydrophobic helix I region, and the reverse primers were designed according to the heme binding region (Table 1). The amplification of the partial target gene was performed by PCR, as follows: pre denaturation at 94 °C for 3 min, denaturation at 94 °C for 30 s, annealing at 55 °C for 30 s, and extension at 72 °C for 2 min. A total of 30 cycles were carried out.

Table 1.
The primers used in this study.
The full-length cDNA of the target gene was obtained by the cDNA end rapid amplification (race) method using Takara La Taq ® with a GC buffer Kit (TaKaRa, Dalian, China). The 5′ and 3′ RACE-PCRs were performed by nested PCR with the specific primer (Table 1). The 3′ RACE PCR reaction conditions were: pre denaturation at 94 °C for 1 min, denaturation at 98 °C for 10 s, annealing at 55 °C for 15 s, and extension at 68 °C for 1 min. A total of 30 cycles were carried out. The 5 ′RACE PCR reaction conditions were: pre denaturation at 94 °C for 3 min; denaturation at 94 °C for 30 s, annealing at 55 °C for 30 s, and extension at 72 °C for 2 min. A total of 30 cycles were carried out. The obtained PCR products were analyzed by electrophoresis in 1% agarose gel, and the amplified cDNA fragments were purified by Gel Extraction Kit (Takara, Dalian, China) and sequenced by Takara Biotechnology (Dalian, China) Co., Ltd.
2.3. Sequence Analysis
The sequencing was completed by TaKaRa (Dalian, China). The obtained sequences were spliced into complete cDNA sequences using DNAStar software. The spliced sequences were analyzed for sequence homology and translated into amino acid sequences. The isoelectric point and relative molecular weight were predicted by the Expasy-compute pI/Mw tool (https://web.expasy.org/compute_pi/) (accessed on 10 March 2022). The protease cleavage sites were analyzed by Expasy-peptidecutter. Blast (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov) (accessed on 10 March 2022) was used for homology comparison. The signal peptide was predicted by signalP-4.1, and the transmembrane region of the protein was analyzed by TMHMM (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM) (accessed on 10 March 2022). Then, the hydrophobicity of the protein was analyzed by Expasy-Protscale (https://web.expasy.org/protscale/) (accessed on 10 March 2022), the tertiary structure of the protein was predicted by SWISS-MODEL, and the homology evolutionary tree was constructed by Mega 5.0 software. A bootstrap test was calculated from 1000 replicates.
2.4. Transcriptional Expression of CYP4 Gene in S. sculata
Using the actin gene (housekeeping gene) as the reference gene, primers were designed to obtain the actin partial sequence (1000 bp) of S. sculata, and real-time PCR primers of actin were designed according to the obtained sequence (Table 1). The primer of the CYP4 gene (NCBI No:KM104864) of S. sculata was designed with Primer 5 software. The total RNA was extracted from S. sculata and diluted to 500 ng/μL. The PrimeScript RT reagent Kit with a gDNA Eraser was used for purification and reverse transcription to synthesize cDNA.
The quantitative real-time PCR was performed on the ABI 7500 Sequence Detection System (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). The optimized real-time PCR reaction system is as follows: 10 μL SYBR® Premix Ex Taq™ II, 0.8 μL Primer F and Primer, 0.4 μL Rox reference dye II, and 7 μL RNase-Free dH2O (TAKARA, Beijing, China). The total reaction system equaled 20 μL. The two-step PCR procedure was used, and the real-time PCR reaction conditions were as follows: 95 °C for 30 s; 95 °C for 5 s, and 60 °C for 34 s, for a total of 40 cycles.
Reverse transcription and PCR were performed on the total RNA of all samples, according to the circulation conditions, annealing temperature, and other conditions in the established real-time quantitative detection method. Three parallel repeats were performed for each sample. To quantify the standard curve of the housekeeping gene and the target gene, take the mean value, and use the double standard curve method to analyze the relative expression: normalized value of sample = target gene concentration/reference gene concentration; F = (target gene concentration to be tested/housekeeping gene concentration to be tested)/(target gene concentration of the reference sample/housekeeping gene concentration of the reference sample). Then, calculate the expression difference multiple of the target gene between the test group and the control group [14].
2.5. Determination of PAHs in Sediments
About 20 g of sediment was used for freeze-drying (temperature −52 °C, pressure < 20 Pa, Biocool FD-1C-50 freeze dryer), and then the sediment was passed through an 80 mesh sieve. The 6890N/5975B gas chromatograph–mass spectrometer was used to analyze 16 PAH components under priority control of US EPA. For specific methods, see Yuan et al. [15].
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Data related to the content of PAHs and the relative expression of the CYP4 gene of S. scutate in the sediments of different sampling sites were analyzed using a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). Tukey’s post hoc test was performed to identify significant differences among groups. The effect of PAHs on the expression of SsCYP4V was analyzed by Pearson’s correlation analysis, and a simple linear regression was performed. All data were reported as mean ± S.D. All statistical calculations were conducted using SPSS 26.0 software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA), and α-values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Complete Sequence and Analysis of CYP4 cDNA of S. scutate
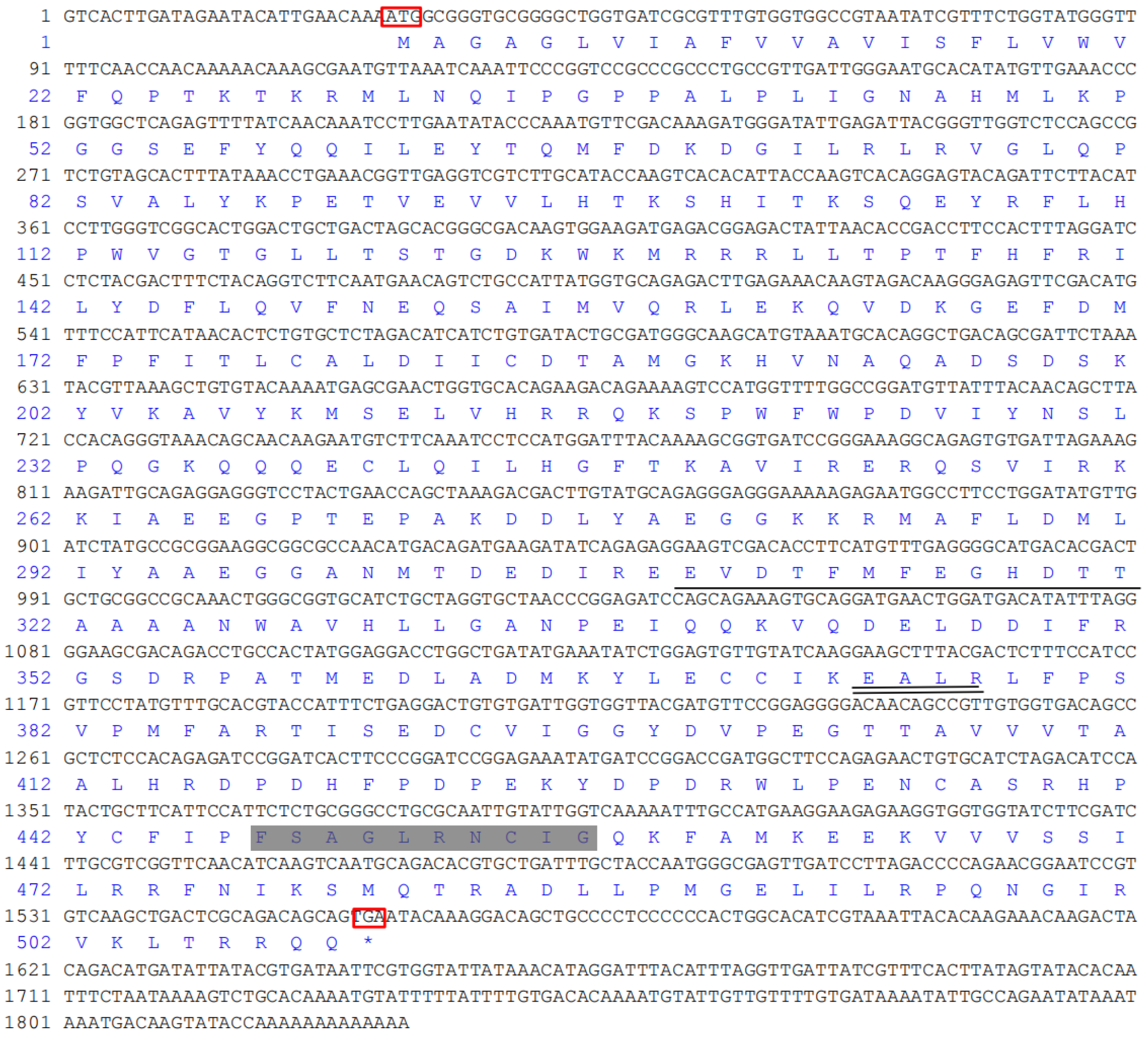
The full-length cDNA of S. scutate CYP (GenBank accession no. KM104864) was 1829 bp, consisting of a 27 bp 5′ untranslated region, a 272 bp 3′ untranslated region, and a 1529 bp open reading frame encoding 509 amino acids (Figure 2). The theoretical isoelectric point and the predicted molecular mass of this deduced protein were 4.96 and 149,744 Da, respectively. SignalP-4.1 analysis showed that it had no obvious signal peptide sites, which might make it a non-secretory protein. The 2nd to 24th amino acids of the CYP protein formed an obvious transmembrane region, suggesting that it might act as a membrane receptor. The maximum hydrophobicity of amino acids was 3.61, and the minimum was −3.99, with the mean of −0.265. It was further inferred that the protein was hydrophilic.
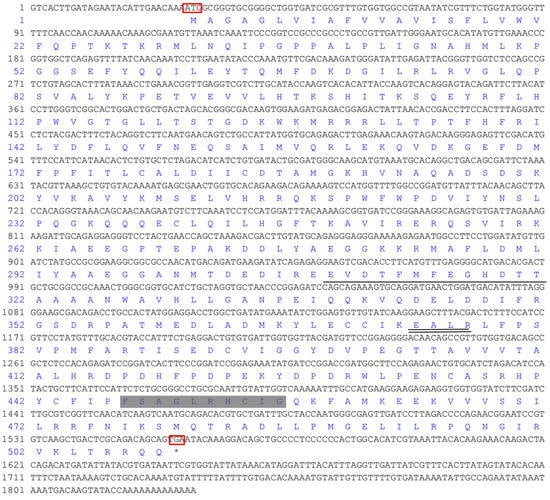
Figure 2.
Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequence of S. scutata CYP4. Note: 5′ untranslated regions are shown as 1–27, 3′ untranslated regions are shown as 1556–1829, the open reading frame is shown as 28–1555, and the deduced amino acid sequence is shown under the nucleotide. The initial codon and stop codon were underlined with red box. The terminator is shown as *. I-helix motifs are indicated with solid lines. K-helix motifs are shown with double-solid line. Heme-binding motifs are shown in a gray-filled box.
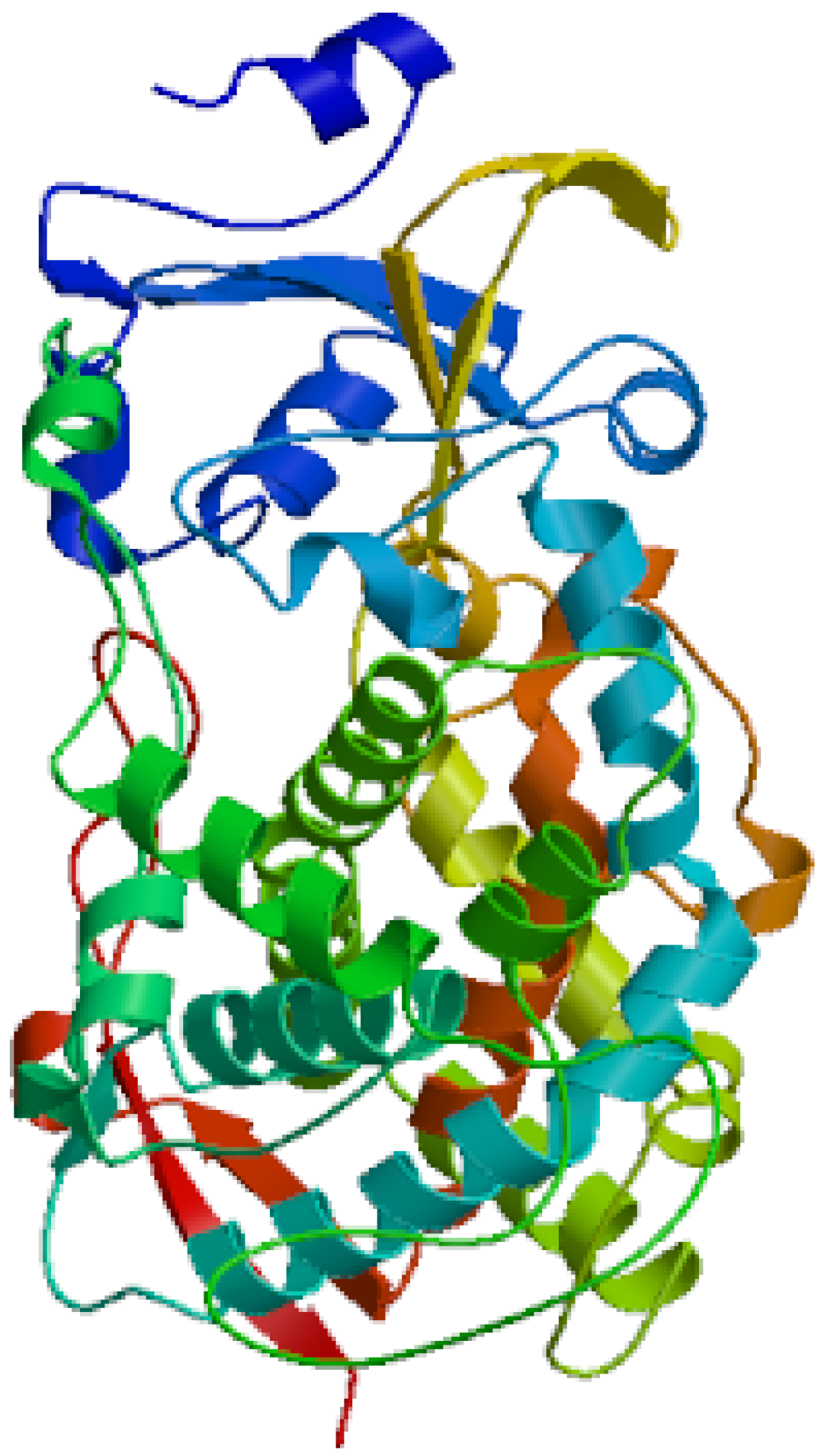
The secondary structure of the protein was composed of 43.42% α-helix, 9.04% extended strand, and 47.54% random coil. In the deduced amino acid sequence of CYP4 cDNA, the 309–321 amino acid sequence exhibited a hydrophobic helix I region, the 374–377 amino acid sequences contained the ExxR region of the K-helix characteristic motif, and the 447–456 amino acid sequences conformed to the conserved common sequence heme binding region of P450. The heme binding region (FxxGxxxxCxG), hydrophobic helix I region (EVDTFMFEGHDTT), and K helix region (ExxR) are ubiquitous characteristic sequences in the P450 family. The variation of some non-functional amino acid residues in the conserved region is normal and does not affect the identification of the conserved region. The tertiary structure of CYP4 protein is shown in Figure 3.
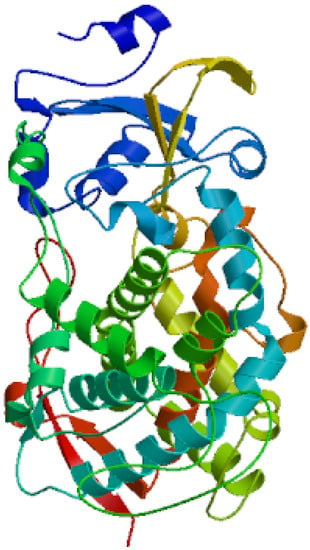
Figure 3.
Predicted three-dimensional structures of the CYP4 domain in S. scutate.
3.2. Similarity Comparison Constructs Evolutionary Tree
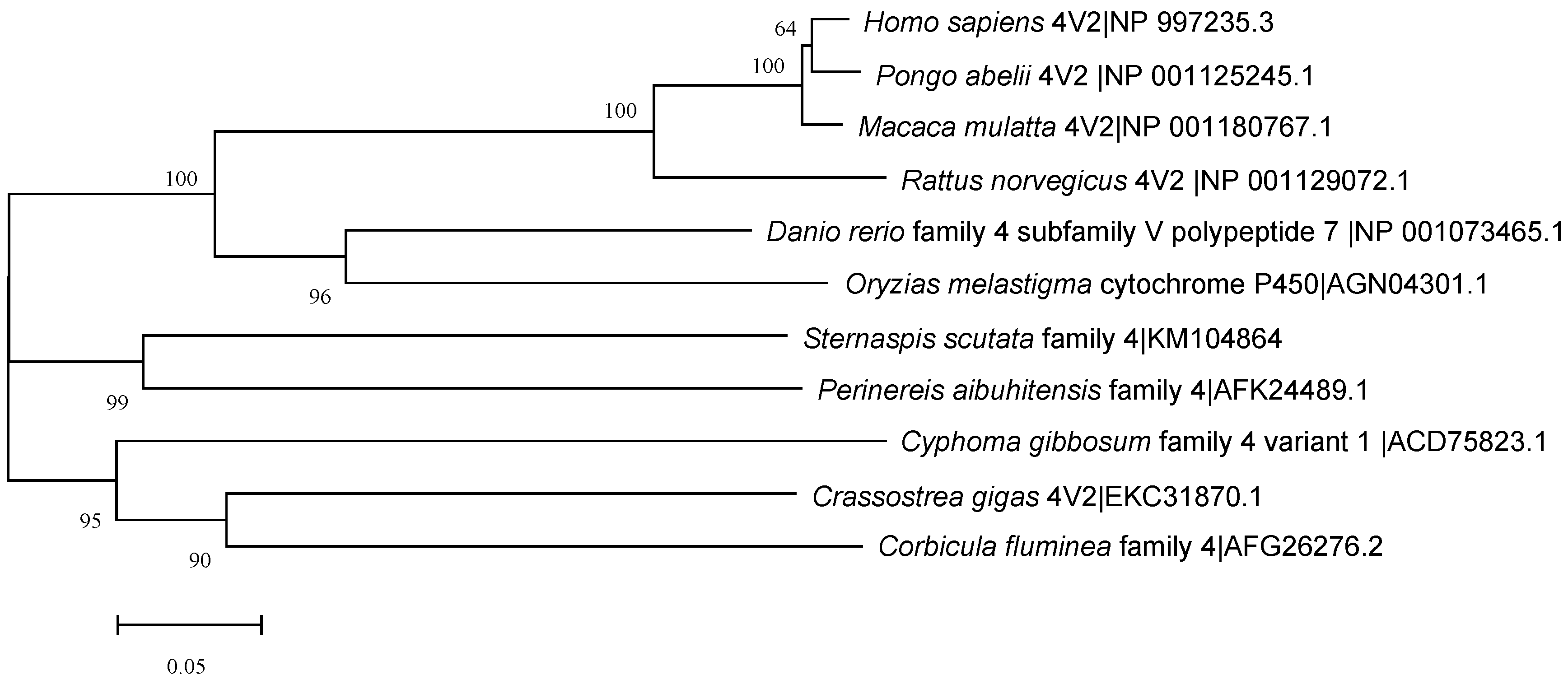
The CYP4 sequence was submitted to NCBI (No:KM104864), and the similarity was compared using online Blast. The results showed that the amino acid sequence of the CYP4 gene had 58% similarity with Nereis aibuhitensis CYP4V subfamily gene (JQ867402), 29% and 31% similarity with Alitta virens CYP4BB1 and CYP342A1, and 35% similarity with Capitella capitata CYP4AT1. The amino acid sequence showed similarity with mollusks Crassostrea gigas CYP4V2, Cyphoma gibbosum CYP4V1, Corbicula fluminea CYP4, Danio rerio CYP4V7, and Oryzias melastigma CYP4 and mammals Homo sapiens CYP4V2, Pongo abelii CYP4V2, Macaca mulatta CYP4V2, and Rattus norvegicus CYP4V2 was 51–57%. The amino acid sequence of CYP4 was compared with the GenBank database, and the similarity was analyzed by Clustal W (Figure 4). The NJ method was used to construct a homology tree with a bootstrapping value of 1000 (Figure 5). In summary, we speculated that the CYP4 gene was a new member of CYP4V subfamily, which was tentatively named SsCYP4V.

Figure 4.
Alignment of deduced protein sequences of CYP4 with selected amino acid sequences was performed using Clustal W. Amino acid residues that are conserved in at least of 50% of the sequence are shaded in gray, and similar amino acids are shaded in black.
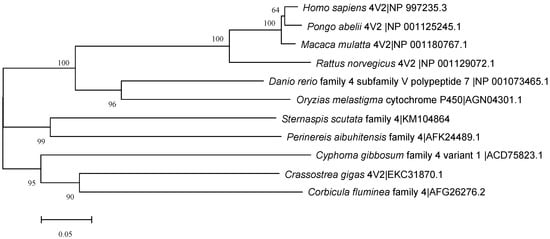
Figure 5.
Phylogenetic NJ tree of the 509 amino acid sequences of CYP4 with the corresponding regions of 10 representatives from other species.
3.3. Expression Level of SsCYP4V in the Field
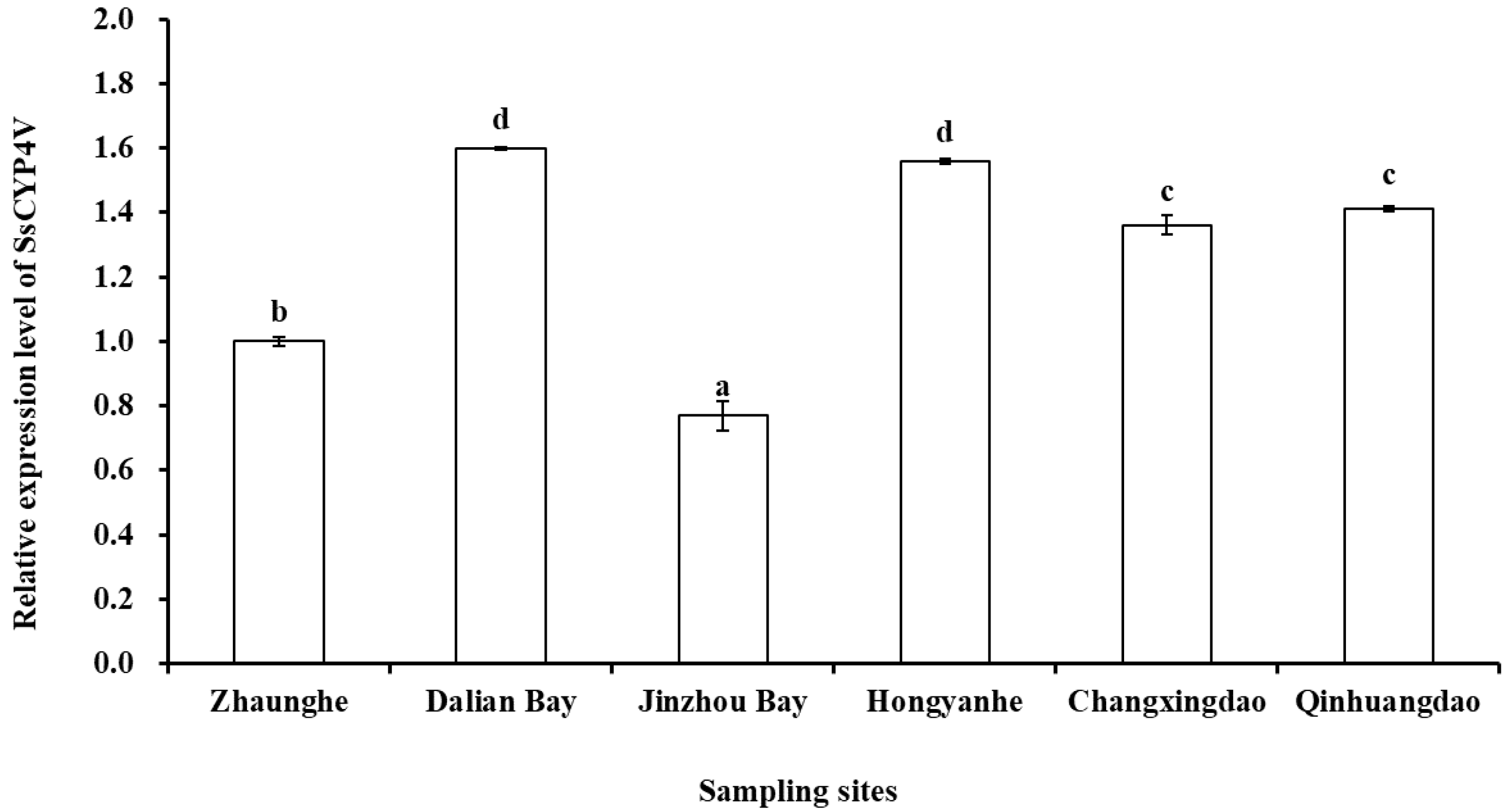
The relative expression of SsCYP4V gene of S. sculata was significantly different in the sampling sediments (F = 569.58, p < 0.001, Figure 6). The relative expression of the SsCYP4V gene of S. scutata in Jinzhou Bay was significantly lower than that in other sites (p < 0.05), and the relative expression of the SsCYP4V gene of S. scutata in Zhuanghe was significantly higher than that in Jinzhou Bay (p < 0.05). The relative expression of the SsCYP4V gene of S. scutata in Changxingdao and Qinhuangdao was significantly higher than that in Zhuanghe (p < 0.05), but there was no significant difference between the two sampling sites (p = 0.161). Meanwhile, the relative expression in Dalian Bay and Hongyanhe was significantly higher than that in other sites (p < 0.05), but there was no significant difference between the two sampling sites (p = 0.383).
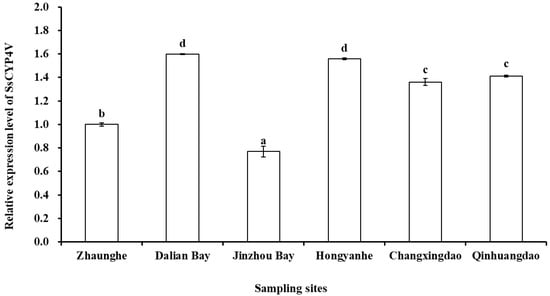
Figure 6.
SsCYP4V mRNA expression levels in S. scutata from the sampling stations (values expressed in mean + SD, n = 3; different letters in columns indicate a significant difference).
3.4. PAHs in Sediments and the Correlation with Expression of SsCYP4V
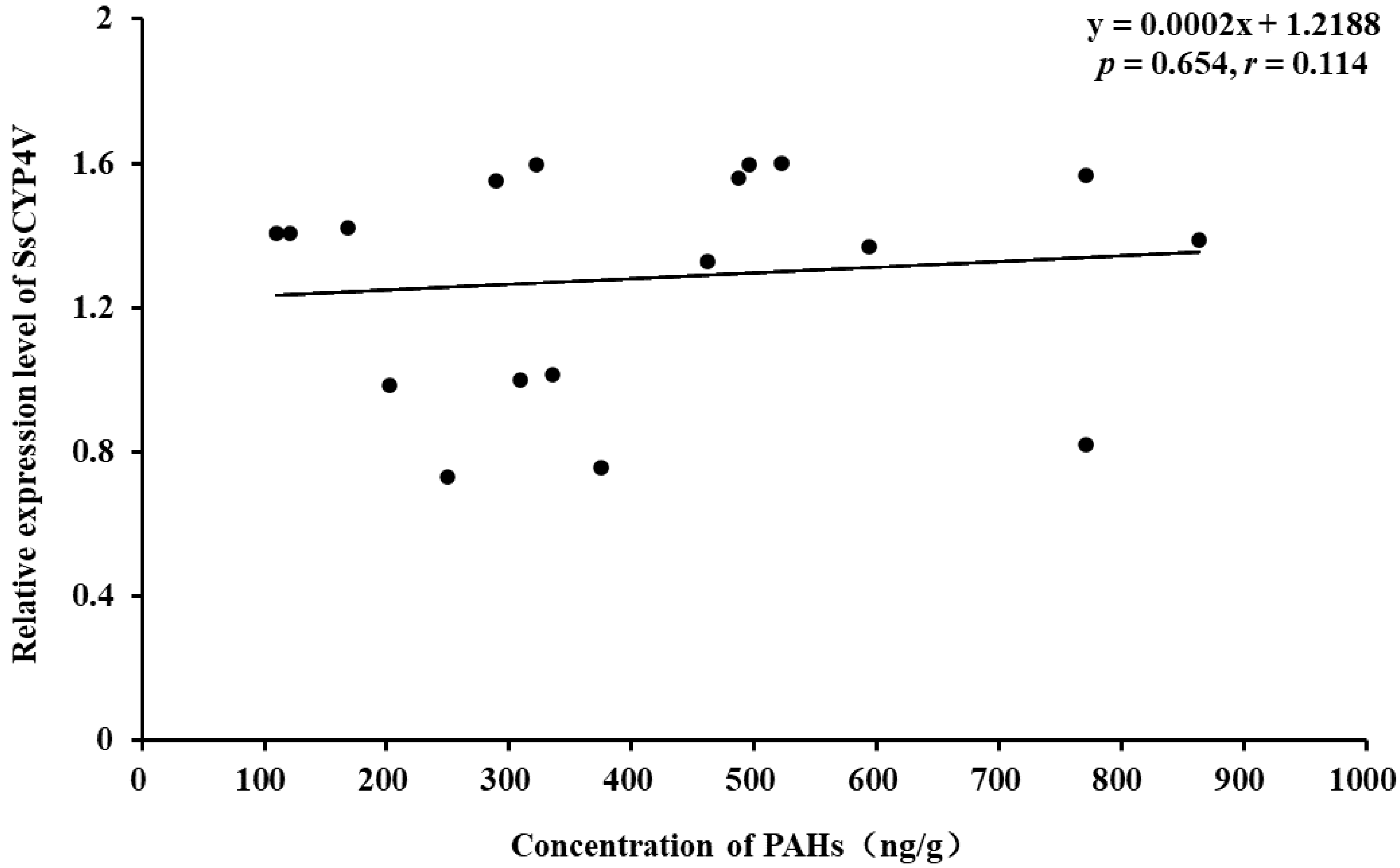
The component and total amount of 16 PAHs in sediment are shown in Table 2. The PAH content in sediments from different sampling sites, listed from low to high, is as follows: Qinhuangdao (133 ng/g) < Zhuanghe (282 ng/g) < Dalian Bay (447 ng/g) < Jinzhou Bay (465 ng/g) < Hongyanhe (516 ng/g) < Changxingdao (640 ng/g), successively. Correlation analysis showed that there was no significant correlation between the relative expression of the SsCYP4V gene in S. scutata and the content of PAHs in sediments (p = 0.654, r = 0.114, Figure 7).

Table 2.
Concentrations of PAHs in sediments from the sampling sites. Note: different letters indicated a significant difference. The weight of PAHs was shown per dry weight of sediment.
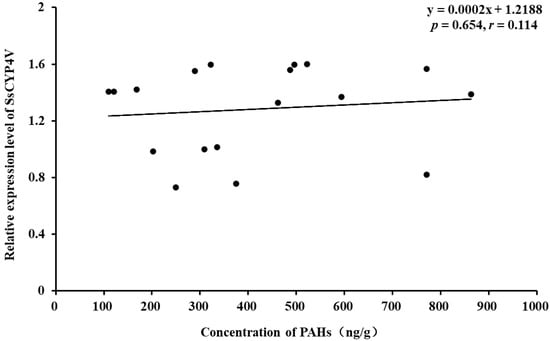
Figure 7.
Relationship of the SsCYP4V mRNA relative expression level in S. scutata and concentration of sediment-borne PAHs.4.
4. Discussion
4.1. Sequence and Evolutionary Tree Analysis of SsCYP4V Gene
Identification and functional analysis of the CYP family genes play an important role in understanding the mechanism of CYP enzyme-mediated PAH transformation stage I [3,16]. So far, work related to sequencing and phylogenetic analysis of some CYP family genes of polychaetes has been carried out. For example, CYP342A1 and CYP4BB1 were obtained from the intestine of Nereis virens by Rewitz, et al. [17]. Further studies showed that less than 40% of the amino acid sequence of CYP342A1 was the same as that of the CYP enzymes found in other species, which was attributed to a new gene family CYP4F, and CYP4BB1 belonged to a subfamily of CYP4F [18]. Li, Bisgaard, and Forbes [8] cloned CYP4AT1 and CYP331A1 from Capitella sp. I, belonging to CYP4F and CYP45 subfamilies, respectively. Chen, Zhou, Yang, Zhao, Wang, and Yuan [10] cloned a CYP4 gene from P. aibuhitensis and deduced it to be from the CYP4B subfamily. Zheng, Chen, Qiu, Lin, and Yu [9] cloned three CYP4 genes from P. nuntia, namely, CYP4BB2, CYP423A1, and CYP424A1. CYP4BB2 and CYP424A1 are listed as members of the CYP4 clan, while CYP423A1 belongs to the CYP2 family. Zhao, Wang, Lei, Wang, Yang, Zhou, and Yuan [6] identified a new CYP gene (CYP4V82) from the polychaete worm P. aibuhitensis, which has high similarity to CYP4V.
In this study, a CYP4 gene (SsCYP4V) was cloned for the first time from S. scutata. According to the similarity comparison analysis, the amino acid similarity with the Nereis aibuhitensis CYP4V subfamily gene (JQ867402) was the highest at 58%. The similarity to the Alitta virens CYP4BB1 and CYP342A1 was 29% and 31%, respectively. The similarity to the Capitella capitata CYP4AT1 was 35%, and the amino acid similarity to mollusks, fish, and mammals was 51–57%. CYPs, with 40% primary amino acid sequence identity, belong to the same family, while CYPs, with 55% sequence identity, are classified into the same subfamily [19]. Therefore, it can be concluded that the CYP4 gene (SsCYP4V) of S. scutata belongs to CYP4V subfamily. At the same time, this study also suggests that there are different subfamilies of CYP4 genes in polychaetes.
4.2. PAHs at Different Sampling Sites
From the total content of PAHs preferentially controlled by US EPA in different sea areas, each sampling station was determined to be polluted by PAHs, to varying degrees, reflecting that PAH pollution in sea areas was greatly affected by land sources [15,20]. The average concentration range of PAHs in different sampling sites in this study is 133–640 ng/g, which is consistent with the concentration range (56–3700 ng/g) in the Bohai Sea [21]. Dalian Bay is one of the busiest ports in north China; there was an oil spill accident in 2010, and a large amount of crude oil leaked out [22]. Jinzhou Bay, Changxingdao, and Hongyanhe are located on the west coast of the Liaodong Peninsula, adjacent to the Changxingdao industrial zone, the most important petrochemical base in northern China. Under this background, the total content of PAHs in the sediments of Dalian Bay, Jinzhou Bay, Hongyanhe, and Changxingdao exceeded 400 ng/g, with the highest content of 640 ng/g. The level of PAHs in the Zhuanghe coast is lower than those of the above sampling sites, but it is affected by the oil spill accident in Dalian Bay, to some extent. Qinhuangdao, as a control point of this study, has the lowest level of PAHs in its sedimentary environment, which is lower than that in sediments from the Qinhuangdao coastal wetland (341.61–4703.80 ng/g) [23].
4.3. Correlation between PAHs and SsCYP4V Expression in Field Sediments
The CYP4 gene can be induced by PAHs in the laboratory and has been shown to degrade PAHs in polychaetes, showing an obvious dose–effect relationship [24]. For example, Zhao, Wang, Lei, Wang, Yang, Zhou, and Yuan [6] exposed P. aibuhitensis to different concentrations of PAHs in the laboratory and found that PAHs were associated with the induction of CYP4V82 and CYP4BB4 (CYP4 genes) expression. In addition, Rewitz, Kjellerup, Jørgensen, Petersen, and Andersen [17] exposed N. virens to crude oil and B(a)P. The transcription of the CYP4(2) gene was upregulated, by about 2.6 times that of the expression in control group. Li, Bisgaard and Forbes [8] exposed capitella sp. I to different concentrations of 3-Mc (463.8 ng/g in sediment), and the expression of CYP4AT1 was upregulated by 20–90% compared with the control group, while the expression of CYP331A1 induced by different concentrations of B(a)P and fluoranthene was 2–3 times that of the control group. Chen, Zhou, Yang, Zhao, Wang, and Yuan [10] showed that under the induction of petroleum hydrocarbon, the expression of CYP4B in P. aibuhitensis showed an upward trend with the exposure time, and this trend was proportional to the induction concentration, which was 2.97–35.94 times than that of the control group.
SsCYP4V of S. scutata also belongs to CYP4 gene. Since it is difficult to breed S. scutata in the laboratory, we only studied the correlation between the transcription and expression of SsCYP4V gene of S. scutata and the content of PAHs in the habitat sediments in the field. The results showed that the conclusion based on the dose–effect relationship in the laboratory (the correlation between the transcription and expression of polychaete CYP gene and the content of PAHs in sediments) was not verified in the field, at least in our survey area. Zheng, Chen, Qiu, Lin, and Yu [9] found a similar phenomenon that CYP424A1, CYP4BB2, and CYP423A1 responded differently to a mixture of heterologous compounds in wastewater, suggesting that the mechanisms governing the transcriptional regulation of these CYPs may differ, depending on the presence of PAHs. Meanwhile, Zhao, Wang, Lei, Wang, Yang, Zhou, and Yuan [6] found that CYP4V82 and CYP4BB4 exhibited different expression patterns for the same PAHs, which may be caused by the metabolic specificity of the CYP4 subfamily.
The non-positive correlation between the relative expression of the SsCYP4V gene and the content of PAHs in the sediments indicated that the response of the CYP4 gene transcription to PAHs in wild environment was complex, and the reasons may be due to the following three points. First, the PAHs content in S. scutata should theoretically be positively correlated with the expression of the SsCYP4V gene, but the PAH content in S. scutata does not necessarily have a positive correlation with the PAH content in the sedimentary environment. Therefore, there is no correlation between the PAH content in the environment and the relative expression of the SsCYP4V gene. PAHs in polychaetes were not detected in this study due to the low abundance of S. scutata. Second, most of the pollution in the real environment is compound pollution [25], so the transcription and expression of the SsCYP4V gene of S. scutata is the result of the comprehensive action of various external compounds. Third, different CYP genes from different organisms show different susceptibility to specific PAHs [26], and each CYP is part of a specific biological pathway acting on a specific substrate [9]. The expression of SsCYP4V may be related to some specific substances in the PAH mixture, rather than to the overall PAH mixture.
The current study was mainly conducted in the laboratory, demonstrating the ability of polychaetes to degrade PAHs [6,7], while related studies in the field are lacking. Field pollutants are often complex mixtures of different toxic chemicals, sometimes making it difficult to predict the toxicity of a single biomarker [9]. Our research shows that in the field environment, the response of SsCYP4V gene transcription and expression to PAHs in S. scutata is complex, and the level of SsCYP4V gene transcription and expression may not be suitable as a biomarker for monitoring PAH pollution in sediments in the field. Therefore, the impact of multiple PAH interactions on CYP gene expression needs to be investigated, so as to fill the gap between the testing of single pollutants in the laboratory and mixed pollutants in the field.
5. Conclusions
In this study, a 1829 bp complete CYP4 cDNA sequence was obtained and submitted to GenBank with accession number KM104864. The cDNA sequence included 27 bp of 5′ non-translated region and 272 bp of 3′ non-translated region. The open reading frame was 1529 bp, encoding 509 amino acids. After Blast homology comparison with the amino acid sequences of the known species in GenBank, it was concluded that CYP4 gene of S. scutata. belonged to CYP4V subfamily, tentatively named SsCYP4V. The relative expression level of the SsCYP4V gene was significantly different in the sea area around the Liaodong Peninsula in northern China, but the correlation between the SsCYP4V gene and PAHs in the sediments was not obvious. This indicated that the transcription and expression of the SsCYP4V gene in S. scutata in the field environment was complex in response to PAHs, and the transcription and expression level of the SsCYP4V gene might not be suitable as a biomarker for the field monitoring of PAH pollution in sediments.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w14213489/s1, PCR reaction condition; Figure S1: Result of total RNA of S. scutata.
Author Contributions
Methodology, A.Q. and D.L.; investigation, A.Q., X.Y. and A.Z.; data curation, Z.Y. and A.Q.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.Y., A.Q. and E.S.; writing—review and editing, L.W.; visualization, Z.Y.; funding acquisition, L.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41106115), the National Marine Public Welfare Research Project (201305043), and the Young Marine Science Foundation of SOA (2012118).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We thank the sources of funds and data, as well as all those involved in the work. We also thank the editors and reviewers who helped improve this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wu, B.L.; Sun, R.P.; Yang, D.J. Studies on Nereidae in the Coastal Waters of China; China Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.J.; Sun, R.P. Polychaete Annelids in the Coastal Waters of China; Agricultural Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen, A.; Giessing, A.M.; Rasmussen, L.J.; Andersen, O. Biotransformation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in marine polychaetes. Mar. Environ. Res. 2008, 65, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoddard, E.G.; Nag, S.; Martin, J.; Tyrrell, K.J.; Gibbins, T.; Anderson, K.A.; Shukla, A.K.; Corley, R.; Wright, A.T.; Smith, J.N. Exposure to an Environmental Mixture of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Induces Hepatic Cytochrome P450 Enzymes in Mice. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2021, 34, 2145–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifian, S.; Homaei, A.; Kamrani, E.; Etzerodt, T.; Patel, S. New insights on the marine cytochrome P450 enzymes and their biotechnological importance. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 142, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, L.; Lei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, D.; Zhou, Y.; Yuan, X. Identification of a novel CYP4V gene in the polychaete Perinereis aibuhitensis: Transcriptional comparison with a CYP4B gene exposed to PAHs. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 47527–47538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, E.-J.; Rhee, J.-S.; Shin, K.-H.; Jung, J.-H.; Shim, W.J.; Lee, Y.-M.; Lee, J.-S. Expression of three novel cytochrome P450 (CYP) and antioxidative genes from the polychaete, Perinereis nuntia exposed to water accommodated fraction (WAF) of Iranian crude oil and Benzo[α]pyrene. Mar. Environ. Res. 2013, 90, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Bisgaard, H.C.; Forbes, V.E. Identification and expression of two novel cytochrome P450 genes, belonging to CYP4 and a new CYP331 family, in the polychaete Capitella capitata sp.I. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 325, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.; Chen, B.; Qiu, X.; Lin, K.; Yu, X. Three novel cytochrome P450 genes identified in the marine polychaete Perinereis nuntia and their transcriptional response to xenobiotics. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 134–135, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, D.; Zhao, H.; Wang, L.; Yuan, X. CYP4 mRNA expression in marine polychaete Perinereis aibuhitensis in response to petroleum hydrocarbon and deltamethrin. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 1782–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.Q.; Meng, W.; Liu, L.S.; Zhu, Y.Z.; Zhou, J. Long-term trends of the dominant macrozoobenthos in Bohai Bay. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2013, 33, 2332–2340. [Google Scholar]
- Reish, D.J.; Gerlinger, T.V. A review of the toxicological studies with polychaetous annelids. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1997, 60, 584–607. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, X.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, D.; Zhang, A.; Yang, X.; Ma, X.; Yang, D.; Zhou, Y. Expression profile of a novel glutathione S-transferase gene in the marine polychaete Perinereis aibuhitensis in short-term responses to phenanthrene, fluoranthene, and benzo[α]pyrene. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 169, 112552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, W.N.; Wu, R.; Diao, X.L. Development and primary application of double-standard curves method of a real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR assay for detection of PRNP. Chin. Vet. Sci. 2013, 43, 1240–1245. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, A.; Ma, X.; Gao, H.; Na, G.; Zong, H.; Liu, G.; Sun, Y. Distribution, potential sources and ecological risks of two persistent organic pollutants in the intertidal sediment at the Shuangtaizi Estuary, Bohai Sea of China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 114, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, W. Origin of metabolites diversity and selectivity of P450 catalyzed benzo[a]pyrene metabolic activation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 435, 129008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rewitz, K.; Kjellerup, C.; Jørgensen, A.; Petersen, C.; Andersen, O. Identification of two Nereis virens (Annelida: Polychaeta) cytochromes P450 and induction by xenobiotics. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharm. 2004, 138, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penry, D.L.; Weston, D.P. Digestive determinants of benz[a]pyrene and phenanthrene bioaccumulation by a deposit-feeding polychaete. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1998, 17, 2254–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.; Koymans, L.; Kamataki, T.; Stegeman, J.J.; Feyereisen, R.; Waxman, D.; Waterman, M.R.; Gotoh, O.; Coon, M.J.; Estabrook, R.W.; et al. P450 superfamily: Update on new sequences, gene mapping, accession numbers and nomenclature. Pharmacogenetics 1996, 6, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Han, Y.; Duan, Y.; Lai, X.; Fu, R.; Liu, S.; Leong, K.H.; Tu, Y.; Zhou, L. Review on the contamination and remediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in coastal soil and sediments. Environ. Res. 2021, 205, 112423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhang, H.; Lang, Y.; Li, Z. Pollution status of PAHs in surface sediments from different marginal seas along China Mainland: A quantitative evaluation on a national scale. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.-J.; Jia, H.; Li, Y.-F.; Sun, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, L. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and alkylated PAHs in the coastal seawater, surface sediment and oyster from Dalian, Northeast China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 128, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Han, B.; Ding, Y.; Li, Q.; Gao, W.; Zheng, L. Distribution characteristics, sources, and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments from the Qinhuangdao coastal wetland, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 127, 788–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jørgensen, A.; Rasmussen, L.J.; Andersen, O. Characterisation of two novel CYP4 genes from the marine polychaete Nereis virens and their involvement in pyrene hydroxylase activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 336, 890–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.Y.; Yuan, X.T.; Zhang, S.L.; Yang, D.Z.; Guo, H.; Zhou, Y.B. Single and joint toxic effects of benzo(a)pyrene and cadmium on development of three-setiger juvenile of polychaete Perinereis aibuhitensis Grube. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2011, 30, 333–336. [Google Scholar]
- Koenig, S.; Fernández, P.; Solé, M. Differences in cytochrome P450 enzyme activities between fish and crustacea: Relationship with the bioaccumulation patterns of polychlorobiphenyls (PCBs). Aquat. Toxicol. 2012, 108, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).