Abstract
In newly reclaimed coastal soil, saline conditions and nutrient deficiency are the restraining factors for crop yield. Manure and plastic film mulch are proved to play a vital role in reducing soil salt, increasing soil water, and improving soil nutrients and plant growth. A field experiment was carried out with plastic film mulch, manure, and their combinations in the Tiaozini reclamation area; four treatments were set up as (1) control treatment (CK), (2) plastic film mulch (PM), (3) farmyard manure (FM), and (4) combined application of plastic film mulch and farmyard manure (PM+FM). The main results showed that, compared with CK treatment, the average soil water content under the FM+PM treatment was increased by 5.8% and 3.6%, and the average soil salt content was reduced by 20.2% and 10.0% at 0–20 cm and 20–40 cm soil layers, respectively. This was because of the decrease in soil bulk density and increase in saturated hydraulic conductivity and saturated water content. Meanwhile, soil organic matter, total nitrogen, available nitrogen, and available phosphorus were significantly increased under the PM+FM treatment, except that for AN, which was significantly decreased at the 0–10 cm soil layer owing to plant uptake. Based on the decrease in soil salt, there was an improvement in soil hydraulic properties and soil nutrients, which resulted in summer maize biomass and yield being increased by 106% and 137%, respectively, and barley biomass and yield were increased by 133% and 106%, respectively, under FM+PM treatment. Consequently, combined manure and plastic film mulch application was better at reducing soil salt; increasing soil water content; and improving soil nutrients, plant growth, and yield production in newly reclaimed salt-affected soils.
1. Introduction
The global area of saline-alkali soil is about 900 million ha [1]. In China, the area of saline-alkali soil is about 3.67 million ha and accounts for 4.88% of the total available land [2]. Saline-alkali soil is characterized by high salinity and sodicity and pH value [3], poor soil quality and structure [4], scarcity of organic matter [5], low hydraulic conductivity [6], and low resource utilization efficiency [7,8]. Reclamation of coastal saline soil in recent decades has greatly alleviated the shortage of cultivated land in coastal regions [9]. However, the newly reclaimed coastal saline soil has characteristics of high evaporation, seasonal precipitation, high groundwater table, and poor soil nutrients, which are not conducive to soil desalination and agricultural development. Thus, it is necessary to choose a suitable method to develop agriculture in salt-affected soil.
It has been reported that the use of organic fertilizer is beneficial in remediating salt-affected soil [10]. It can improve the physical properties of the soil [6], such as reducing soil bulk density, increasing soil porosity and saturated hydraulic conductivity, reducing soil salinity, improving soil quality and carbon sequestration [11], and increasing grain yield. Chen et al. (2021) reported that organic matter played a key role in soil quality, phosphorus availability, and plant growth [8]. Han et al. (2021) conducted a pot experiment with maize crop in newly cultivated land, indicating that soil fertility and microbial structure were rapidly improved with the organic fertilizer application [12]. Cao et al. (2021) suggested that straw return could be a promising management practice to reduce mineral phosphorus fertilization without a significant reduction in seed cotton yield on coastal saline lands [13].
Mulching is considered to be one of the positive ways to increase crop yield and is widely used around the world [14,15,16,17]. It can reduce evaporation from the soil because of the formation of mulch [15,18], inhibit soil salt ascending [19], reserve soil moisture [20], and improve water use efficiency and nitrogen use efficiency [21]. Based on plot and field experiments, Bu et al. (2013) showed that plastic film mulching can effectively increase maize yield and water use efficiency in Loess Plateau in China [14]. Li et al. (2018) reported that plastic film, gravel-sand, and straw surface mulch can decrease soil water evaporation during early crop growth stage and increase crop yield and water use efficiency, but the plastic film mulch works best [22]. Ding et al. (2019) indicated that the plastic film mulch significantly improve crop production and increase resource use efficiency in a winter wheat–summer maize rotation system [23]. Ramadhan (2021) reported that application of wheat straw mulch could be the most effective soil management practice for improving corn production in an arid subtropical climate region [16].
There are also reports about the combination of film mulch and organic fertilizer. Zhang et al. (2014) reported that farmyard manure and mulch increased water holding capacity, saturated water content, and saturated hydraulic conductivity and decreased soil bulk density [6]. Duan et al. (2022) indicated that ridge–furrow planting with mulching and organic amendment improved soil physical properties and increased soil organic and total nitrogen, which could be a sustainable and efficient cultivation practice for alleviating drought stress, improving soil properties, and increasing the economic benefit on the Tibetan Plateau [24]. However, the combined effects of mulch and manure on soil water and salt dynamics, soil properties, and crop yield of maize and barley in newly reclaimed coastal land remain unclear. Therefore, the objectives of this study were to (1) investigate the effects of manure and film mulch application on soil water and salt dynamics, soil properties, plant growth, and yield production; (2) clarify the effect of salt reduction and soil properties improvement on plant growth and yield production; and (3) determine an optimized practice for improving soil properties and crop yield in newly reclaimed salt-affected soil.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
Field experiments were conducted at Tiaozini reclamation area (32° 50′ N, 120° 56′ E, mean altitude 1.86 m), which is located in Dongtai, Jiangsu province of eastern China. The soils in this area are mainly halosols according to Chinese Soil classification system [25], which developed from the marine deposits [26]. The texture was silty loam and contained 6.3% of sand, 80.1% of silt, and 13.6% of clay. Initially, at the experiment site, the average soil properties of 0–20 cm soil layer were as follows: soil bulk density (BD) was 1.44 g/cm3; salt content, organic matter (OM), and total nitrogen (TN) were 1.8, 6.06, and 0.54 g/kg, respectively; pH was 9.20; and available nitrogen (AN) and available phosphorus (AP) were 63.11 and 17.2 mg/kg, respectively.
The climate at the experiment site is monsoon with a mean annual temperature of 14.6 °C and a mean annual precipitation of 1100 mm [27]. Approximately 70% of the rainfall occurs from June to September. The groundwater table at this site was around 1.2 m, with a salt concentration of about 12 g/L.
2.2. Experimental Design and Field Management
The experiments were conducted from June 2016 to October 2017. The experiment was set up to include four treatments: (1) control treatment (CK), (2) plastic film mulch (PM), (3) farmyard manure (FM), and (4) combinations of plastic film mulch and farmyard manure (PM+FM). PM was the transparent plastic film (0.01 mm thickness), which was removed after harvesting and was mulched immediately at planting. FM was the chicken manure (TN 16.53 g/kg, OM 309.4 g/kg, and salt content 1.32 g/kg) applied at a rate of 1.5 t/ha, which was spread manually and mixed into 15 cm depth by means of rotary harrowing. The treatments were arranged as a randomized complete group design with three replications. Each plot was 3 m wide and 4 m long, isolated by drainage ditch with a width of 20 cm and depth of about 30 cm.
The amount of fertilizer applied is based on the local traditional application rate. The nitrogen fertilizer dosage of maize and barley in the whole growth period is 225 kg/ha N, and the phosphorus fertilizer dosage is 90 kg/ha P. The specific application is shown in Table 1. In 2016, maize was sown on 22 June and harvested on 5 October. In 2017, maize was sown on 22 June and harvested on 15 October. Barley was planted on 15 November and harvested on 21 May of the following year. Maize is sown directly after barley is harvested, but barley is sown after rotary tillage when maize is harvested. The daily precipitation and temperature during the three growing seasons are shown in Figure 1.Total precipitation during the maize growth stage in 2016 and 2017 was 723 mm and 663 mm, respectively. While the total precipitation during the barley growth stage was 334 mm. The 2016 maize growing season was a little wetter than the 2017 maize growing season, and more rainfall occurred in the later stages of maize growth compared with 2017.

Table 1.
Specific fertilization information (kg/ha).
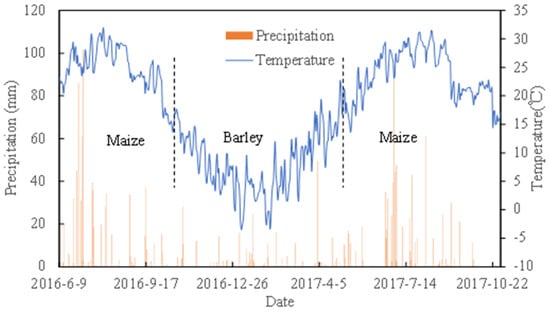
Figure 1.
Daily precipitation and temperature during the experimental period.
In the 2016 maize growing season, the mean air temperature ranged from 15 °C to 31.9 °C, averaging 25.2 °C. In the 2017 maize growing season, it was 18–31.5 °C, averaging 25.3 °C, and in the barley growing season, it was −3.5–24.9 °C, averaging 9.30 °C. The average and highest temperature of two maize growing seasons were largely the same, but the lowest temperature of the first growing season was 3 °C lower than that of the second maize growing season.
2.3. Sampling and Measurement Methods
During the crop growing season, the soil water content was measured gravimetrically at the depth of 0–20 cm and 20–40 cm with about a 30-day intervals (except for the barley overwintering stage). Soil sampling points were chosen between two rows of crops and as close to the center of the plot as possible. Samples were air-dried and ground to pass through a mesh of 2 mm size and were used for soil salt measurement. Soil salinity was measured by an extraction ration of 1:5 (EC1:5) using an electrical conductivity meter (LE438, Mettler Toledo, Shanghai, China). Then, the EC1:5 values were converted to the salt content in percent (total salt, TS) based on the formula of TS = 2.47EC1:5 + 0.26 (R2 = 0.96, p < 0.001). This formula is based on our measured data in the coastal area.
In addition, physical indexes such as soil bulk density (BD), saturated water conductivity (Ks), and saturated water content (SWC), as well as nutrient indexes such as soil organic matter (OM), total nitrogen (TN), available nitrogen (AN), and available phosphorus (AP), were measured in 0–10 cm and 10–20 cm soil depth. BD was determined by the cutting ring method [28] and Ks was measured by the constant head test [29]. OM was determined by oxidization by the potassium dichromate-external heating method, TN was measured by Kjeldahl distillation, AN was determined by alkaline hydrolysis diffusion method, and AP was analyzed by sodium bicarbonate extractionmolybdenum antimony anti colorimetry [28].
2.4. Plant Growth Measurements
At maturity, nine plants were randomly chosen in each plot to measure plant height. At harvest, all aboveground crop parts were harvested manually from each plot and grain yields were obtained. Six samples were collected from each plot and separated manually to straw and grain, and then oven drying was carried out to obtain the dry matter yield. The ratio between the straw and grain was determined. The straw biomass in each plot was calculated by multiplying the oven-dried yield and the ratio between the straw and the grain.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Excel 2016 software was used for basic data processing, including calculation of the mean value of each processing, standard deviation, and so on. SPSS program was used for one-way analysis of variance. Mean comparisons were performed using the Fisher’s LSD (the last significant difference) test at p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Soil Water Content
Soil water content dynamics within 0–20 cm and 20–40 cm are shown in Figure 2. In the top 0–20 cm soil layer, the initial soil water content among treatments was basically consistent. With the development of maize growth, the difference in soil water content among treatments first increased and then decreased. The soil water content on 15 August 2016 was 1.6%, 2.0%, and 5.6% higher under the FM+PM than that of PM, FM, and CK, respectively. During the barley growing season, the soil water contents under FM+PM and PM were higher than those of FM and CK. The largest difference occurred on 28 March 2017, when the soil water content under FM+PM was about 2.7% and 4.1% higher than that under FM and CK, respectively. In the 2017 maize season, the variation in soil water content in all treatments was similar to that of 2016, but there were significant differences among treatments, especially between the mulched and uncovered treatments. On 2 August 2017, the soil water contents under FM+PM were 14.8% and 20.0%, significantly higher than those under FM and CK.
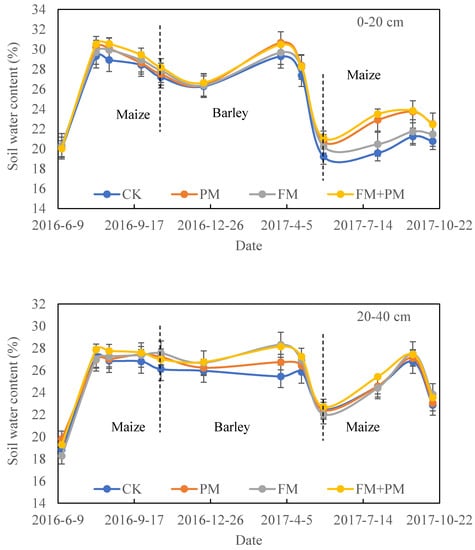
Figure 2.
Soil water content in the 0–20 cm and 20–40 cm soil layers under CK, PM, FM, and PM+FM treatments during the experimental period. CK: control treatment, PM: plastic film mulch, FM: farmyard manure, PM+FM: plastic film mulch combined with farmyard manure. The vertical bars represent the standard deviations of the data.
Different from 0–20 cm, the patterns of soil water content among treatments under 20–40 cm were more complicated, especially for the 2016 maize growing season. At the beginning of planting, the soil water content under PM treatment was higher than that under FM+PM, CK, and FM treatments, with the values of 2.8%, 5.2%, and 8.4%, respectively. Then, the soil water content under FM+PM began to be higher than that of other treatments until 26 September 2017. At harvest time, the soil water content of FM treatment was 1.3%, 2.0%, and 5.5% higher than that of FM+PM, PM, and CK, respectively. For the barley growing season, the soil water content under FM+PM and FM treatments was basically the same, and it was significantly higher than that under PM and CK treatments until 24 April 2017. The biggest difference occurred on 28 March in 2017, and the soil water content of FM treatment was 5.9% and 11.2% higher than that of PM and CK treatment, respectively. In the maize growing season of 2017, it was found that there was little difference among all treatments, especially for CK, PM, and FM treatments.
3.2. Salt Content
Changes in salt content at 0–20 cm and 20–40 cm depth among treatments during the three growing seasons are shown in Figure 3. At the 0–20 cm soil layer, the salt contents under PM and FM+PM were significantly lower than that under FM and CK during the whole experimental period. In the 2016 maize growing season, before 26 September, the soil salinity in all treatments fluctuated very little, and then the soil salinity began to increase rapidly, especially in the uncovered treatment. The average salt content under PM was 16.5%, 28.3%, and 25.5% lower than under FM+PM, FM, and CK, respectively. During the barley growing season, salt content in all treatments was on a downward trend until 28 March 2017, when soil salt content began to increase. Similarly, the average salt content under PM was 21.0%, 34.4%, and 31.1% lower than under FM+PM, FM, and CK, respectively. In the maize growing season of 2017, salt content under mulched treatment increased first and then decreased during the whole growth period, while salt content under non-mulched treatment showed an increasing trend and remained stable. The difference between mulched and non-mulched treatments was significant. The average salt content under PM was 20.2%, 55.4%, and 51.6% lower than under FM+PM, FM, and CK, respectively.
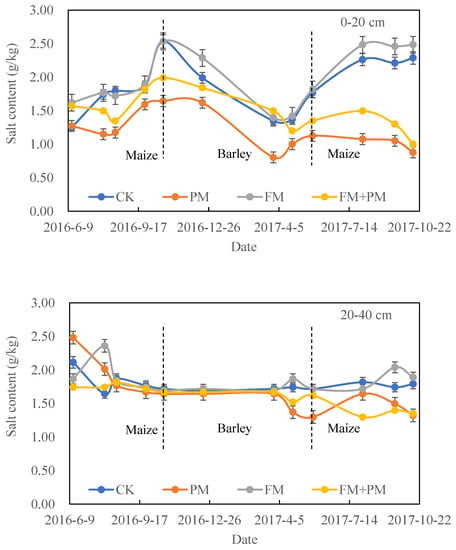
Figure 3.
Soil salt content in the 0–20 cm and 20–40 cm soil layers under CK, PM, FM, and PM+FM treatments during the experimental period. CK: control treatment, PM: plastic film mulch, FM: farmyard manure, PM+FM: plastic film mulch combined with farmyard manure. The vertical bars represent the standard deviations of the data.
At the 20–40 cm soil depth, less variation was observed, especially for the barley growing season. As for the maize growing season in 2016, there was no obvious pattern of changes in the salt content of all treatments until August 15, but they all showed a downward trend with the growth period, except for FM treatment. In the barley growing season, the salt content of all treatments was basically the same until March 28. Then, the soil salt content of FM treatment showed a trend of first increasing and then decreasing, while that of PM treatment showed a trend of decreasing, and that of FM+PM treatment showed a trend of first decreasing and then increasing. In the subsequent growing season of maize, the salt content under FM+PM and PM treatments maintained a consistent downward trend, while the salt content under CK treatment basically remained stable, and salt content under FM treatment first increased and then decreased. The average salt content under PM was 11.0%, 29.9%, and 27.1% lower than under FM+PM, FM, and CK, respectively.
3.3. Soil Physical Properties
Soil bulk density was reduced by applying plastic film mulch and organic fertilizer, and the effect of both was better than that of single treatment (Table 2). In the 0–10 cm soil layer, the BD under PM, FM, and FM+PM treatments decreased by 2.1%, 4.2%, and 5.6%, respectively, compared with that in CK, while that in the 10–20 cm soil layer under PM, FM, and FM+PM decreased by 2.1%, 4.9%, and 5.6%, respectively. The effects of mulching and organic fertilizer application on Ks and SWC were opposite to that of BD; especially, organic fertilizer application significantly improved soil water conductivity and water content. In the 0–10 cm soil layer, Ks under PM, FM, and FM+PM treatments increased by 9.4%, 18.0%, and 24.4%, respectively, compared with that under control treatments, and SWC increased by 1.3%, 2.5%, and 3.4%, respectively. In the 10–20 cm soil layer, the increase in Ks and SWC was less than that in the 0–10 cm soil layer. The Ks and SWC under PM, FM, and FM+PM treatments increased by 6.9% and 0.9%, 17.4% and 1.9%, and 19.6% and 2.5%, respectively, compared with that of CK.

Table 2.
Soil physical properties under different treatments.
3.4. Soil Nutrients
Film mulching and application of organic fertilizer significantly increased soil organic matter content (Table 3). The content of OM in the 0–10 cm and 10–20 cm soil layers under PM, FM, and PM+FM treatments increased by 19.3%, 57.5%, and 51.5%, respectively, and 22.6%, 58.9%, and 33.8%, respectively, compared with that under CK treatment. Similarly, film mulching and organic fertilizer application also increased TN and AP, especially for the organic fertilizer application treatment. In terms of TN in the 0–10 cm and 10–20 cm soil layers, PM, FM, and PM+FM treatments increased by 8.6%, 37.1%, and 40.0%, respectively, and 42.9%, 42.7%, and 39.3%, respectively, compared with that under CK treatment. Accordingly, AP under PM, FM, and PM+FM treatments increased by 45.9%, 190%, and 277%, respectively, and 6.0%, 105%, and 84.1%, respectively, in the 0–10 cm and 10–20 cm soil layers, respectively. However, the variation trend of AN among treatments was contrary to other indexes (OM, TN, and AP) in the 0–10 cm soil layer. The AN in mulched and organic fertilizer treatment was lower than that in the control treatment, which may be related to crop growth. Compared with that of CK treatment, AN under PM, FM, and PM+FM treatments decreased by 34.5%, 36.5%, and 38.9%, respectively, while for the soil layer of 10–20 cm, PM, FM, and PM+FM treatments increased by 52.7%, 87.6%, and 107% compared with CK treatment, respectively.

Table 3.
Soil nutrients under different treatments.
3.5. Plant Height
The maize height in two growing seasons is presented in Figure 4. For each season, plants were much taller under the FM+PM, PM, and FM treatments than that under CK treatment. There was no significance between the FM+PM and FM treatments, but they were significantly taller than that under PM and CK treatments. The plant height in the growing season of 2016 was higher than that in the growing season of 2017 under the corresponding treatment, This may be related to the higher rainfall in 2016 than in 2017 (Figure 1).
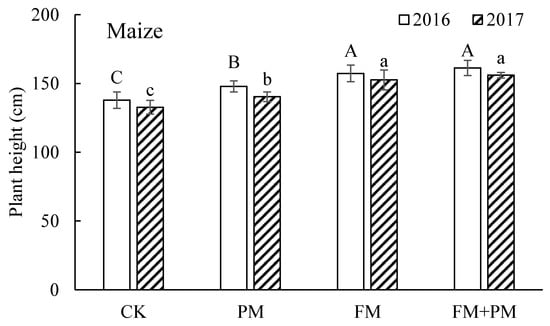
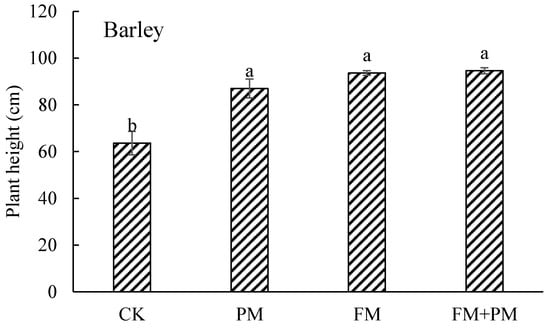
Figure 4.
Plant height under CK, PM, FM, and PM+FM treatments. CK: control treatment, PM: plastic film mulch, FM: farmyard manure, PM+FM: plastic film mulch combined with farmyard manure. The vertical bars represent the standard deviations of the data and the values followed by the same letter are not significantly different (LSD, p < 0.05).
The barley height was significantly higher under the FM+PM, PM, and FM treatments than that under CK treatment. It was found the height under the FM+PM treatment was the highest, but there was no significant difference among the FM+PM, FM, and PM treatments.
3.6. Biomass and Grain Yield
The biomass of maize varied significantly among the treatments (Table 4). The biomass under the FM+PM, FM, and PM treatments was always higher than that under CK treatment, but only that of the FM+PM and FM treatments was significantly higher than that of CK in both growing seasons. Averaging the results for the two years, the biomass under FM+PM treatment was 29.5%, 79.7%, and 106% higher than that of FM, PM, and CK treatment, respectively. For barley, the biomass under FM+PM treatment was 12.2%, 30.3%, and 133% higher than that under FM, PM, and CK treatments, respectively, and the difference was also significant.

Table 4.
Biomass (kg/ha) and yield (kg/ha) under different treatments during the 2016–2017 growing seasons.
The results of maize yields’ variation among different treatments were consistent over two years. The yields under FM+PM, FM, and PM treatments were always higher than that under CK treatment, but there was no significant difference between PM and CK treatments. Averaged for the two growing seasons, FM+PM treatment improved the yield by 43.1%, 102%, and 137% compared with FM, PM, and CK treatments, respectively. The barley yield under FM+PM, FM, and PM treatments was 106%, 66.3%, and 57.5% higher than that under CK treatment, respectively.
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil Water and Salt Content
Soil water content increased under mulch treatment, because mulch can reduce evaporation from soil surface and reserve soil water content. Many studies have reported that mulching can reserve soil water and reduce evaporation. Zhang et al. (2021) used the AquaCrop model assessed the mulching effects at the regional scale, which indicated that plastic film mulching improved soil water storage and significantly decreased nonproductive evaporation [30]. Li et al. (2018) presented that the average soil water storage during the jointing stage under the plastic film, gravel-sand, and straw mulching treatments was 34% higher than the control treatment [22]. The results also showed an increase in soil water content under the FM treatment compared with the CK treatment. This is because of loosening soil, decreasing its density and increasing its ability to conserve water. It was reported that the application of manure significantly increased capillary water holding capacity, SWC, and Ks, and decreased BD and cone index [6]. In our study, BD under the PM and FM treatment was decreased by 2.1% and 4.6%, respectively, while Ks and SWC under the PM and FM treatment were increased by 8.2% and 17.7% and 1.1% and 2.2%, respectively. The average soil water content under the FM+PM treatment was the highest owing to the double effect of mulch and manure, which was 5.8% and 3.6% higher than that in CK treatment at the 0–20 cm and 20–40 cm soil depth, respectively. Duan et al. (2022) reported that organic amendments and the ridge–furrow mulching system improved soil water storage in the 0–120 cm soil layer [24].
The change in surface soil salinity is closely related to meteorological conditions (Figure 1). From September to October in 2016, soil salinity increased and then began to decrease. This is because rainfall began to decrease after September, while evaporation was still relatively strong, causing salt to rise. After October, the temperature drops, soil evaporation and root water absorption also decrease, and soil salinity reaches its lowest level in April of the following year. Then, the temperature rises, evaporation becomes stronger, and soil salinity begins to rise gradually.
In the present study, it was found that the reduction in BD and the improvement in hydraulic parameters were conducive to salt leaching. The soil salt content was positively correlated with BD (R2 = 0.060) and negatively correlated with Ks (R2 = −0.064) and SWC (R2 = −0.100). The average salt content under the PM treatment was 35.8% and 6.3% lower than that in the CK treatment during the experiment at the 0–20 cm and 20–40 cm soil layers, respectively. This was because of the decrease in soil evaporation, where the mulching measures not only increased the soil water content (Figure 2), but also contributed to the leaching of soil salt and reduced soil salt content. Similarly, Mohammad et al. (2018) showed that the electrical conductivity of soil was significantly reduced by film mulching in south coastal saline soils of Bangladesh, regardless of film materials and color [31]. El-Mageed et al. (2016) showed that all mulch materials (without mulch, farmyard manure, rice straw, and white polyethylene) effectively reduced salt accumulation in the root zone [32]. In addition, the average soil salt content in the 0–20 cm and 20–40 cm soil layers under FM treatment increased by 6.5% and 3.8%, respectively, compared with the CK treatment, indicating that the soil salt content was increased by the application of manure alone, because the farmyard manure contained salt. Hao and Chang (2003) indicated that high rates of manure application are not sustainable as they cause soil salinization under non-irrigated conditions [33]. Yao et al. (2007) also assessed the possibility of secondary soil salinization by continuous application of chicken manure and pigeon manure on a garden soil, resulting in an increase in soil salinity from low to moderate levels and a slight decrease in soil pH [34]. However, the use of farmyard manure and film mulch together can not only avoid the increase of soil salt content caused by the application of organic fertilizer alone, but also reduce soil salt and increase soil fertility. In this study, the average soil salt content in the 0–20 cm and 20–40cm soil layers under FM+PM treatment was reduced by 20.2% and 10.0%, respectively.
4.2. Soil Properties
Soil bulk density, saturated hydraulic conductivity, and saturated water content play important roles in soil water–salt movement. Organic fertilizer application can significantly reduce BD, enhance soil porosity, and improve saturated hydraulic characteristics [35,36]. In the present study, manure application (FM and FM+PM treatments) significantly decreased BD and improved Ks and SWC at 0–20 cm soil depth compared with the control treatment (CK), except for BD at 10–20 cm soil depth (Table 2). However, there were no significant effects of film mulch (PM) on BD, Ks, and SWC at 0–20 cm soil depth compared with CK. Khaliq and Kaleen Abbasi (2015) indicated that soil amendments significantly decreased surface BD and increased Ks [37]. Bilong et al. (2022) showed that the application of poultry manure decreased BD by 21.5–26.2% and increased the water holding capacity by 13.3–30.3% [38]. Duan et al. (2022) reported that organic amendment significantly decreased BD and increased Ks at 0–60 cm soil depth [24]. Zhang et al. (2022) reported that straw returning combined with nitrogen application under plastic film mulch significantly improved soil hydrothermal conditions and maize yield [39], consistent with our results.
Soil organic matter, total nitrogen, available nitrogen, and available phosphorus are basic indicators of soil nutrients that affect soil fertility and crop production. Organic fertilizer application can directly improve the soil nutrient content [24,40], while film mulching can indirectly affect the soil nutrient content by improving crop growth and development [21], thus the root biomass and plant residues were increased; ultimately, the soil organic matter and total nitrogen content were improved. In this study, the influence of manure on soil nutrients is greater than that of film mulching, because organic fertilizer can not only directly increase soil nutrient content, but also improve crop growth and ultimately improve root residue inputs [41]. Similarly, Wu et al. (2022) also reported that the application of 100% cow manure significantly increased nitrogen and carbon from full fruiting to the end-fruiting period [35].
4.3. Plant Growth and Yield
These beneficial effects on soil water content and soil salinity probably explain some of the positive effects on plant growth and yield. Film mulching and manure application promoted the growth and biomass of crops. Although the effect of manure application alone is better than that of film mulch alone, the effect of mulch combined with manure was better than that of film mulch or manure alone. Meanwhile, film mulch and manure treatment also leads to a significantly higher crop yield and biomass than other treatments. For maize, the biomass and yield under PM treatment were improved, but there was no significant difference compared with CK treatment.
In terms of plant height and yield of each treatment, the effect of FM treatment was better than that of PM treatment, indicating that the application of manure was more conducive to promoting crop growth and yield improvement. However, both manure and film mulch work better together than either alone. All of this was possibly attributed to improved hydraulic parameters and increased soil nutrients while applying manure and mulching during the time of the experiment (Table 2 and Table 3). OM, nitrogen, and phosphorus are the direct suppliers of nutrients for crop growth, so plant height, biomass, and yield are positively correlated with OM, TN, and AP (Table 5). However, there was a negative correlation between plant height, biomass, and yield and AN, which may also be related to crop growth. The better the crop growth and the higher the crop yield, the higher the content of AN absorbed by crop, resulting in less residual AN in the soil.

Table 5.
Pearson correlation coefficient between the yield, biomass, plant height, and soil properties.
Plastic film mulch is likely to create favorable soil moisture conditions and a low salinity root zone for the crop growth. Ramadhan (2021) reported similar results, finding that straw mulch increased grain yield significantly compared with the control treatment [16]. Wang et al. (2020) reported that the annual yield of the winter wheat–summer maize system can be maintained or even increased by replacing mineral nitrogen with manure [42].
5. Conclusions
Three seasons of field study confirmed that the combined use of plastic film mulch and manure fertilizer significantly improved crop growth and production. It was found plastic film mulch or manure fertilizer application decreased the soil bulk density (BD) and increased the saturated water conductivity (Ks) and saturated water content (SWC), and the effect was strengthened when plastic film mulch and manure fertilizer were combined. In addition, organic matter (OM), total nitrogen (TN), and available phosphorus (AP) were increased with plastic film mulch and manure fertilizer application, while available nitrogen (AN) was decreased as a result of plant uptake. The improved soil properties (BD, Ks, SWC, OM, TN, AN, and AP) in turn improved plant growth and crop production. Therefore, combined plastic film mulch and manure fertilizer application could be a better agronomy practice for improving saline-alkali land and increasing crop yield in saline-alkali land.
Author Contributions
X.W. and J.Y. designed the research. X.W. performed the experiments and wrote the manuscript. R.Y. provided the technical assistance. W.X. and X.Z. reviewed and edited the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was jointly supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2019YFD1002702; 2019YFD0900702) and the Natural Science Foundation of China (42077084; U1906221; U1806215).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments that greatly improved this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rath, K.M.; Fierer, N.; Murphy, D.V.; Rousk, J. Linking bacterial community composition to soil salinity along environmental gradients. ISME J. 2019, 13, 836–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.G.; Pu, L.J.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, P.; Dai, X.Q.; Xu, Y.; Liu, L.L. Evolution of soil properties following reclamation in coastal areas: A review. Geoderma 2014, 226, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.X.; Miao, C.Y.; Borthwick, A.G.L.; Duan, Q.Y.; Liu, H.; Sun, Q.H.; Ye, A.Z.; Di, Z.H.; Gong, W. Evolution of the Yellow River Delta and its relationship with runoff and sediment load from 1983 to 2011. J. Hydrol. 2015, 520, 157–167. [Google Scholar]
- Lakhdar, A.; Rabhi, M.; Ghnaya, T.; Montemurro, F.; Jedidi, N.; Abdelly, C. Effectiveness of compost use in salt-affected soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stagg, C.L.; Baustian, M.M.; Perry, C.L.; Carruthers, T.J.B.; Hall, C.T. Direct and indirect controls on organic matter decomposition in four coastal wetland communities along a landscape salinity gradient. J. Ecol. 2018, 106, 655–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.B.; Yang, J.S.; Yao, R.J.; Yu, S.P.; Li, F.R.; Hou, X.J. The effects of farmyard manure and mulch on soil physical properties in a reclaimed coastal tidal flat salt-affected soil. J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 13, 1782–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Yuan, G.D.; Feng, L.R.; Bi, D.X.; Wei, J. Soil properties and the growth of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and maize (Zea mays L.) in response to reed (phragmites communis) biochar use in a salt-affected soil in the Yellow River Delta. Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 303, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.M.; Zhang, S.R.; Liu, L.; Wu, L.P.; Ding, X.D. Combined organic amendments and mineral fertilizer application increase rice yield by improving soil structure, P availability and root growth in saline-alkaline soil. Soil. Tillage Res. 2021, 212, 105060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.L.; Kang, Y.H. Changes in soil properties under the influences of cropping and drip irrigation during the reclamation of severe salt-affected soils. Agric. Sci. China 2009, 8, 1228–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.F.; Lashari, M.S.; Liu, X.Y.; Ji, H.; Li, L.Q.; Zheng, J.F.; Kibue, G.W.; Joseph, S.; Pan, G.X. Changes in soil microbial community structure and enzyme activity with amendment of biochar-manure compost and pyroligneous solution in a saline soil from Central China. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2015, 70, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.P.; Zhang, S.R.; Ma, R.H.; Chen, M.M.; Wei, W.L.; Ding, X.D. Carbon sequestration under different organic amendments in saline-alkaline soils. Catena 2021, 196, 104882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.Q.; Dong, Y.Y.; Zhang, M. Chemical fertilizer reduction with organic fertilizer effectively improve soil fertility and microbial community from newly cultivated land in the Loess Plateau of China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 165, 103966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, N.; Wang, J.; Pang, J.; Hu, W.; Bai, H.; Zhou, Z.; Meng, Y.; Wang, Y. Straw retention coupled with mineral phosphorus fertilizer for reducing phosphorus fertilizer input and improving cotton yield in coastal saline soils. Field Crop Res. 2021, 274, 108309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, L.D.; Liu, J.L.; Zhu, L.; Luo, S.S.; Chen, X.P.; Li, S.Q.; Hill, R.L.; Zhao, Y. The effects of mulching on maize growth, yield and water use in a semi-arid region. Agri. Water Manag. 2013, 123, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.G.; Pang, H.C.; Wang, J.; Hou, L.; Li, Y.Y. Effects of straw mulch and buried straw on soil moisture and salinity in relation to sunflower growth and yield. Field Crop. Res. 2014, 161, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadhan, M.N. Yield and yield components of maize and soil physical properties as affected by tillage practices and organic mulching. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021, 28, 7152–7159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Xie, Z.K.; Malhi, S.S.; Vera, C.L.; Zhang, Y.B.; Guo, Z.H. Effects of gravel–sand mulch, plastic mulch and ridge and furrow rainfall harvesting system combinations on water use efficiency, soil temperature and watermelon yield in a semi-arid Loess plateau, china. Agri. Water Manag. 2011, 96, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.X.; Wang, Z.H.; Li, S.Q.; Gao, Y.J.; Tian, X.H. Effect of plastic sheet mulch, wheat straw mulch, and maize growth on water loss by evaporation in dryland areas of China. Agri. Water Manag. 2013, 116, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, H.C.; Li, Y.Y.; Yang, J.S.; Liang, Y.S. Effect of brackish water irrigation and straw mulching on soil salinity and crop yields under monsoonal climatic conditions. Agri. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 1971–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamir, S.I.; Asif, M.; Ihtisham-ul-haq, U.A.; Hussain, S. Maize phenology, yield and its quality is affected by organic mulches and various irrigation regimes. Int. J. Mod. Agric. 2014, 3, 56–59. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, X.L.; Huang, T.T.; Lu, C.; Dang, P.F. Benefits and limitations of straw mulching and incorporation on maize yield, water use efficiency, and nitrogen use efficiency. Agri. Water Manag. 2021, 256, 107128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Y.; Li, Y.; Lin, H.X.; Feng, H.; Dyck, M. Effects of different mulching technologies on evapotranspiration and summer maize growth. Agri. Water Manag. 2018, 201, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Feng, H.; Zhao, Y.; Hill, R.L.; Yan, H.; Chen, H.; Hou, H.J.; Chu, J.C.; Liu, J.C.; Wang, N.J.; et al. Effects of continuous plastic mulching on crop growth in a winter wheat-summer maize rotation system on the loess plateau of china. Agr. Forest Meteorol. 2019, 271, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.X.; Chen, J.F.; Li, J.B.; Feng, H.; Wu, S.F.; Meng, Q.T.; Siddique, K.H.M. Effects of organic amendments and ridge–furrow mulching system on soil properties and economic benefits of wolfberry orchards on the Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 827, 154317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Z.T.; Zhang, G.L.; Chen, Z.C. Development of soil classification in China. In Soil Classification: A GlobalDesk Reference; Eswaran, H.R.T., Ahrens, R., Stewart, B.A., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; pp. 110–125. [Google Scholar]
- Chuang, C.H.; Zhou, R.Z.; Xu, G.W. Creation of spartina plantations for reclaiming Dongtai, China, tidal flats and offshore sands. Ecol. Eng. 2004, 23, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.P.; Gao, S.; Jia, J.J.; Thompson, C.E.L.; Gao, J.H.; Yang, Y. Sediment transport over an accretional intertidal flat with influences of reclamation, Jiangsu coast, China. Mar. Geol. 2012, 291–294, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.K. Analytical Methods for Soil and Agricultural Chemistry; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 1999; pp. 107–108, 147–148, 150–152, 180–181, 269–271. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shao, M.A.; Wang, Q.J.; Huang, M.B. Soil Physics; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2006; pp. 37–38, 84. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Tian, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zheng, C.M. How does plastic film mulching affect crop water productivity in an arid river basin? Agri. Water Manag. 2021, 258, 107218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, A.H.; Mohammad, J.; Derek, C. Effect of plastic mulch on crop yield and land degradation in south coastal saline soils of Bangladesh. Int. Soil Water Conse. 2018, 6, 317–324. [Google Scholar]
- El-Mageed, T.; Semida, W.M.; El-Wahed, M. Effect of mulching on plant water status, soil salinity and yield of squash under summer-fall deficit irrigation in salt affected soil. Agri. Water Manag. 2016, 173, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.Y.; Chang, C. Does long-term heavy cattle manure application increase salinity of a clay loam soil in semi-arid southern Alberta? Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 2003, 94, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.X.; Li, G.L.; Tu, S.H.; Gavin, S.; He, Z.H. Salinity of animal manure and potential risk of secondary soil salinization through successive manure application. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 383, 106–114. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.J.; Lin, Z.; Zhu, X.P.; Li, G.Y.; Zhang, W.J.; Chen, Y.J.; Ren, L.; Luo, S.W.; Lin, H.H.; Zhou, H.K.; et al. Improved tomato yield and quality by altering soil physicochemical properties and nitrification processes in the combined use of organic-inorganic fertilizers. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2022, 109, 103384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.B.; Hu, Y.J.; Hill, R.L.; Wu, S.F.; Song, X.L. Combined effects of biomaterial amendments and rainwater harvesting on soil moisture, structure and apple roots in rainfed apple orahard on the Loess Plateau, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 248, 106776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaliq, A.; Kaleem Abbasi, M. Improvements in the physical and chemical characteristics of degraded soils supplemented with organic–inorganic amendments in the Himalayan region of Kashmir, Pakistan. Catena 2015, 126, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilong, E.G.; Abossolo-Angue, M.; Ajebesone, F.N.; Anaba, B.D.; Madong, B.A.; Nomo, L.B.; Bilong, P. Improving soil physical properties and cassava productivity through organic manures management in the southern Cameroon. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.M.; Song, D.P.; Pu, X.; Dang, P.F.; Qin, X.L.; Siddique, K.H.M. Effect of different straw returning measures on resource use efficiency and spring maize yield under a plastic film mulch system. Europ. J. Agron. 2022, 134, 126461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Ren, Y.Y.; Zhang, S.Q.; Chen, Y.L.; Wang, N. Applications of organic manure increased maize (Zea mays L.) yield and water productivity in a semi-arid region. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 187, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Chen, X.L.; Wei, T.; Yang, Z.; Jia, Z.K.; Yang, B.P.; Han, Q.F.; Ren, X.L. Effects of straw incorporation on the soil nutrient contents, enzyme activities, and crop yield in a semiarid region of China. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 160, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Q.; Yang, Y.D.; Zhao, J.; Nie, J.W.; Zang, H.D.; Zeng, Z.H.; Olesen, J.E. Yield benefits from replacing chemical fertilizers with manure under water deficient conditions of the winter wheat—Summer maize system in the North China Plain. Europ. J. Agron. 2020, 119, 126118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).