Abstract
Pre-planning for a rational survey design is essential to improve the reliability and efficiency of the acoustic assessment of fishery resources in large water bodies. In this study, we compared the differences in acoustic estimates of fish resources between triangular and parallel transect designs in the Three Gorges Reservoir (TGR, China), aiming to provide a reference for fishery acoustic survey planning in such canyon-shaped reservoirs. We conducted hydroacoustic surveys using an echosounder (SIMRAD EY60, 120 kHz) in the Yangtze mainstream near the dam and an adjacent tributary with triangular and parallel designs. The independent samples t-test showed that the acoustic estimates of fish density were not significantly different between these two types of survey designs for both mainstream and tributary. The Fisher’s exact test indicated that there was no significant difference in fish size distributions, as measured by target strength (TS), between survey designs either. In view of reducing time spent in nearshore areas to improve efficiency and ensure safety, we recommend that the triangular design with reliable coverage be given priority for hydroacoustic sampling in the TGR and similar canyon-shaped reservoirs, especially when sampling at night.
1. Introduction
The use of acoustic techniques for studying fish populations is well developed, and it is an accepted sampling method, particularly in lake ecosystems [1]. The rapidity with which hydroacoustic methods can be deployed as well as their low operating costs give them undeniable advantages over other methods. Additionally, they are non-destructive and provide good precision and the repeatability of fish abundance estimates [2]. The reliability of acoustic assessment depends to a great degree on reasonable sampling effort and survey design because of the practical limitations on survey time, complicated environmental conditions, and spatial heterogeneity of fish distribution [3]. The hydroacoustic sampling effort in a given survey area is related to the degree of coverage that is determined by survey route length and transect spacing. Based on experimental and statistical analyses, Aglen [4,5] proposed a metric for the degree of coverage, i.e., the ratio between the total length of the survey route and the square root of the surface of the studied area, which has become a criterion for evaluating the reliability of survey results. According to him, if the required precision is 25%, the degree of coverage must be at least 4. Generally, the larger is degree of coverage, the smaller coefficient of variation, but it also depends on fish distribution. Godlewska et al. [6] has shown, that for the vendace stocks, the sampling error did not exceed 10% at a degree of coverage above 2. Another primary consideration is the survey design in advance of hydroacoustic sampling [3,6]. The survey design of the planning of the cruise track, i.e., the survey strategy and the shape of the survey grid, should be decided according to the geographical morphometry of the studied waters and the survey purpose, while ensuring the desirable degree of coverage. Proper survey design should improve sampling efficiency and compatibility with environmental conditions such as irregular shorelines. It should guarantee the reliability of fish abundance assessment and the safety of the survey vessel, e.g., by reducing the survey time near shoreline areas with potential reefs [3,7].
Two types of survey designs are most commonly used as options in hydroacoustic sampling: parallel transects (random or regularly spaced) and triangular (zigzag) transects, each with advantages under suitable conditions [3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11]. Parallel equally spaced transects are characterized by uniform sampling and in most cases provide the most precise estimate of fish densities, while triangular transects provide higher coverage, allow to save survey time, and avoid dangerous areas along the shoreline. Triangular transects can be used for waters with narrow strips of shoreline or circular islands, while parallel transects are suitable for most waters other than those with complex morphometry. So far, the technical requirements of hydroacoustic sampling, including survey design, have been studied mainly in Europe and North America, and relevant technical protocols have been available [7,9]. In Chinese inland waters, the application of hydroacoustics has developed rapidly in the last two decades, e.g., [12,13,14]; however, various aspects of hydroacoustic surveys still lack technical specifications suitable for the characteristics of Chinese waters and Chinese fish species. Most of Chinese freshwater fishes are Cypriniformes, while Perciformes and Salmoniformes played a more important role in European and American waters. Spatial distribution and migration patterns may differ in sensitivity to temperature, oxygen, and other environmental parameters, and so does the acoustic strategy. There is a strong need to develop reliable and reproducible standardized methods for routine use in acoustic surveys of inland fishery resources in China. Specifically for survey design, a pre-sampling technical aspect, targeted experimental studies and comparative studies are needed for major water types and environmental conditions to improve the assessment quality of hydroacoustic surveys, such as fish density estimation, and to provide a technical basis for long-term monitoring and comparability of data.
In our comparative study of survey designs in hydroacoustic sampling, we chose the Three Gorges Reservoir (TGR, China), a typical large canyon-shaped reservoir, as the study area, including the mainstream and its adjacent tributary, which is much smaller but generally has higher fish density [13,14]. It is notable that there are more than 98,000 reservoirs in China, a large proportion of which are canyon-shaped due to the geological topography [15]. Canyon-shaped reservoirs are mainly characterized by longitudinal elongation, narrow channels, and deep water [16,17]. Their littoral zones are usually narrow, with steep bottom profiles and complicated substrates, while being significantly influenced by water level fluctuations. Such morphometric features of canyon-shaped reservoirs and their potential effects on fish distribution and the safety of survey vessels should be fully considered in the survey design prior to hydroacoustic sampling. In this regard, we compared the degree of coverage of parallel and triangular transects, and the fish density estimates in two different habitats: within the mainstream and in the tributary of the TGR. We also compared the differences in fish size distribution, as measured by target strength (TS), between the two survey designs.
The aim of this study was to check whether, in Chinese waters, similar to the European experience [6,10], the parallel design that offers the most precise estimate of fish density can be replaced by triangular survey design, providing better time efficiency and safety of hydroacoustic sampling. We assumed that fish density and fish size estimates not differing statistically significantly between the two designs would justify using either of them; whichever is more convenient in a given situation. It was expected that our results will contribute to technical references for the hydroacoustic survey of fish resources in the TGR and other similar canyon-shaped reservoirs and will enhance the comparability of long-term surveys.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Survey Design
The study site was located near the Three Gorges Dam, comprising a segment of the Yangtze River mainstream and a segment of an adjacent tributary Baisui Creek (Figure 1) to account for different morphometric and trophic conditions. The average width of the selected mainstream segment is 1.6 km and the average depth is 85.3 m, while the average width of the tributary segment is 0.28 km and the average depth is 40.7 m. Apart from morphometry, the mainstream and tributary fish habitats differ greatly since the flow velocity is faster in the mainstream than in the tributary. The banks of the mainstream are steeper than those of the tributary; there is almost no vegetation in the riparian areas in the mainstream, compared with more vegetation along the banks of the tributary.
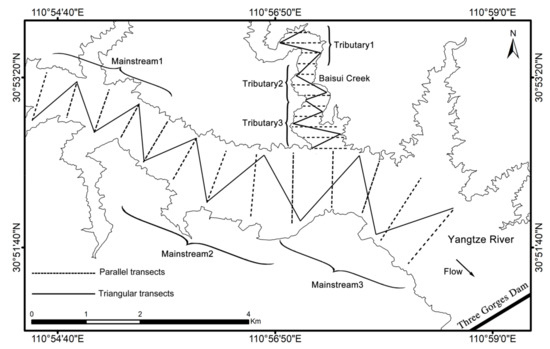
Figure 1.
Study area in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China, showing the two types of hydroacoustic survey transects designed in the Yangtze River mainstream and the adjacent tributary.
We applied the two types of survey designs through the following steps. First, we divided the study area of the mainstream and the tributary into three survey units respectively to obtain three random independent samples. Second, we set the equidistant spacing for parallel transects and the angle for triangular transect based on the width and shoreline of the units (Figure 1). Finally, we conducted the hydroacoustic cruise survey according to the above designs and compared the performance of these two types of survey designs.
We calculated the coverage of parallel transects and triangular transects for the survey units in the mainstream and the tributary using the following equation [4]:
where Λ is the coverage, D is the total transect length, and A is the survey area. It should be noted that the length of cruise along the shore between the parallel transects cannot be used for fish resource assessment and therefore does not contribute to the coverage.
Λ = D/(A)0.5
2.2. Hydroacoustic Survey
The hydroacoustic survey was carried out on 12 November 2012, starting one hour after the sunset when fish were already scattered in the water [14]. We used SIMRAD EY60 (Kongsberg, Norway) split beam echosounder with 120 kHz circular transducer having beam angle 7 × 7 degrees at −3 dB level. The transducer was fixed to the right side of the survey vessel, 0.5 m below the water surface and directed vertically downward by a stainless steel bracket. The echosounder was connected to a laptop computer, which was used to control the echosounder, providing a real-time display and data storage. A global positioning system (Garmin 60CSx) was used to record the geographic coordinates. The power setting was 100 W, the pulse duration 0.128 ms, and the ping rate five pings per second. The echosounder was calibrated before the survey with a 23 mm diameter copper sphere, following the standard method [18]. The speed of the cruise vessel during the survey was about 2 ms−1.
2.3. Data Processing
The hydroacoustic data were processed with Echoview software (version 10.1). A surface line was fixed at a depth of 2 m to avoid surface noise. The bottom line was defined with the best bottom candidate algorithm built in the Echoview software and was corrected manually if necessary. In addition, some obvious noises, such as those caused by propellers or sonar from other vessels, were selected and defined as “bad data”, so that they were excluded from further analysis. The cleaned echogram was analyzed using the echointegration method with an integration interval of 800 pings, i.e., about 350 m, depending on the actual speed, which varied slightly. To detect fish and to use single target detection (SED) as the basis of average target strength (TS, dB) for calculating fish density, a single target detection echogram was established. The single target detection split beam method 2 was applied for the SED analysis with the parameters set as follows: TS threshold = −64 dB, volume backscattering strength (Sv) threshold = −70 dB; pulse length determination level = 6 dB; minimum normalized pulse length = 0.4; maximum normalized pulse length = 1.5; maximum 2-ways beam compensation = 6 dB; maximum standard deviation of minor-axis angles = 0.6; maximum standard deviation of major-axis angles = 0.6.
The mean TS characterizes the echo from a single fish of the average size, and the Sv represents the summation of the backscattering from all targeted fish within a sampling volume. Fish density can be calculated with the following equations, which relate linear and decibel scales:
where ρ is fish density, σbs is backscattering cross-section, TS (Target Strength) is a logarithmic measure of σbs, sv is volume backscattering coefficient (linear measure), and Sv is volume backscattering strength (log measure, in dB re 1 m−1).
TS = 10log<σbs>
Sv = 10logsv
ρ = sv/<σbs>
For the proper estimation of fish size acoustically, the TS was measured only for the echoes that fulfilled the SED criteria, i.e., those belonging to reflections from the single fishes. By definition, the acoustic size of a fish is described by the TS value, which is the logarithm of the backscattering cross-section of the fish [3]. Thus, a large value of TS implies a big fish and vice versa. Note that since there is a negative sign “-” in front of the TS value, a smaller negative number means a higher TS and a larger fish.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
We applied the independent samples t-test to compare the differences in fish density estimates between the two types of survey designs for each survey unit. The Shapiro–Wilk test was used to examine the normality of the fish density data, and if the data were not normally distributed, they were first log transformed. We calculated the percentage of individual fish corresponding to each class of TS in both types of transects from the same survey unit, and then applied the Fisher’s exact test to compare the differences in TS distribution between the parallel and triangular transect designs. The Fisher’s exact test is a non-parametric method for comparing the proportion of categories in two different independent groups and can be applied on small sample sizes [19]. All the statistical analysis and plotting were performed with SPSS 16.0 and Sigmaplot 12.0, and p = 0.05 was used to define statistical significance.
3. Results
3.1. Reservoir Morphometry and Survey Coverage
The depth and width of the survey units in the mainstream differed greatly from those in the tributary (Table 1). The maximum depths of the mainstream measured by the echosounder were around 140 m with the average depths exceeding 75 m. The maximum depths of the tributary were below 80 m with the average depths less than 40 m. The average width of the mainstream was about 1 km, and the average width of the tributary was less than 0.5 km.

Table 1.
Morphometric and transect information of the survey units in the mainstream and the tributary.
According to preliminary calculations, the total lengths of parallel and triangular transects in corresponding survey units of the mainstem and the tributary were similar as far as possible (Table 1). This assured that the degree of coverage also did not differ considerably between the two survey designs (Table 1). In the mainstream units, the maximum difference in coverage was 0.1 and in the tributary units it was 0.3.
3.2. Comparison of Fish Density Estimates
The results of descriptive values and statistical comparisons of acoustic fish density estimates are presented in Table 2. In the survey units of the Yangtze mainstream, fish density estimates varied between 0.32 ind./1000 m3 and 2.83 ind./1000 m3 under the parallel transect design and between 0.29 ind./1000 m3 and 3.55 ind./1000 m3 under the triangular transect design. In the survey units of the tributary, fish density estimates varied between 0.47 ind./1000 m3 and 42.85 ind./1000 m3 under the parallel design and between 0.32 ind./1000 m3 and 44.83 ind./1000 m3 under the triangular design. The Shapiro–Wilk test confirmed normal distribution of fish densities for all the studied units. For both mainstream and tributary, the t-tests showed no significant differences between the fish density estimates obtained from the two types of survey designs.

Table 2.
Descriptive values of fish density estimate in the survey units of the mainstream and the tributary, with the statistics of the Shapiro–Wilk test and the t-test.
Fish density estimates were similar for the three survey units of the mainstream, while there was a clear trend of increasing fish density with increasing distance from the mainstream in the tributary survey units (Table 2). For the mainstream, the standard deviations of density estimates under the triangular survey design were relatively higher than those under the parallel survey design, which was related to the outlier values under the triangular survey design (Figure 2a). For the tributary, in the survey unit close to the mainstream (i.e., Tributary3), the standard deviation of density estimates for the parallel design was considerably higher than for the triangular design (Figure 2b). The survey unit located at the furthest end of the tributary (i.e., Tributary1) had considerably higher density estimates with a large variation (Table 2, Figure 2b).
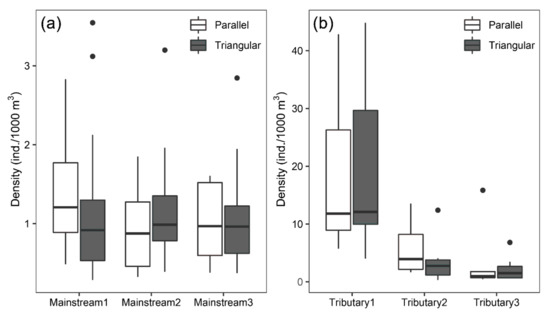
Figure 2.
Box–Whisker plots of fish densities estimated under the two type of survey designs in (a) the mainstream survey units and (b) the tributary survey units. The central box covers 50% of data values, the vertical line represents the range, and the horizontal line indicates the median. The points above the whiskers represent outliers.
3.3. Comparison of Size Distribution
The fish size distribution obtained from the hydroacoustic surveys was represented by the frequency distribution of TS values. Overall, the percentage of fish numbers decreased rapidly with increasing TS for all the survey units in both mainstream and tributary under the two types of survey designs (Figure 3), indicating a high proportion of small individuals (i.e., the left side of the TS frequency distribution) and a low proportion of large individuals (i.e., the right side of the TS frequency distribution).
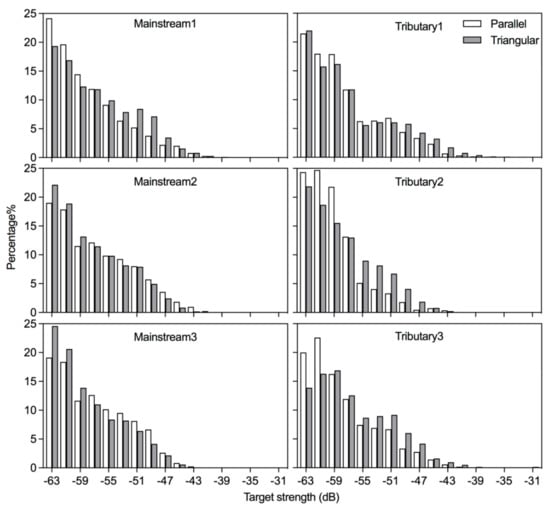
Figure 3.
Frequency distribution of fish target strength (TS) estimated acoustically under the two types of survey designs in the mainstream and the tributary. The horizontal axis represents the intervals of TS (2 dB wide), and the vertical axis represents the percentage of individual fish corresponding to each interval of TS.
The descriptive statistics of TS values differed between the two types of survey designs (Table 3), but there was no constant pattern in such differences. In the mainstream survey unit 1, the maximum, mean, and standard deviation of TS were higher for the triangular design than for the parallel design, whereas in the mainstream survey unit 2 and unit 3, they were lower for the triangular design than for the parallel design. In the tributary survey units, the maximum value, mean, and standard deviation of TS were higher for the triangular design than for the parallel design. For the size distribution of fish community, the Fisher’s exact tests indicated that in each survey unit, there was no significant difference in the TS frequency distribution between parallel and triangular survey designs (p > 0.05, Table 3).

Table 3.
Descriptive values of fish target strength (TS) estimated acoustically under the two types of survey designs in the mainstream and tributary survey units with the statistics of Fisher’s exact test.
4. Discussion
In the present study, for the area of each survey unit, the coverage of acoustic survey transects ranged between 3.5 and 5.0, which meets the criteria for reliable assessment of fish resources [3,5]. Our results indicated that the acoustic estimates of fish density in both mainstream and tributary did not differ significantly between the triangular and parallel designs. These findings are in agreement with those of Godlewska et al. [6] for the vendace lakes of different shapes and sizes, and Guillard et al. [10] for small oligotrophic lake populated with perch and cyprynids in epilimnion and salmonids in hypolimnion. As a general rule, the efficiency of applying two types of survey designs depends mainly on the ratio of the transect length to the transect spacing, and only slightly on the range of the spatial correlation [8]. For transect lengths less than twice the transect spacing, the triangular design is the most efficient. For correlation ranges greater than 0.1 times the transect spacing, the parallel design is better when the transect length is more than twice the spacing [8]. The TGR is a typical canyon-shaped reservoir with meandering mainstream and tributary and transect lengths are in most cases less than twice the transect spacing. Alongshore cruises are needed when survey vessel crosses the spacing between the parallel transects, but such travel intervals cannot be used for fish resource evaluation and do not contribute to the coverage. Thus, the parallel design takes more time and labor than the triangular design for the same degree of coverage. Given the practical constraints of time and labor intensity during the hydroacoustic survey, the triangular design is more efficient than the parallel design. It is also important to note that cruising in triangular transects is safer due to greater avoidance of complex shallow waters along the shoreline, especially at night when the visibility is poor. Therefore, under the premise of satisfying coverage and uncorrelated adjacent routes, triangular transects are desirable when designing fishery acoustic surveys in canyon-shaped reservoirs like the TGR.
As with other sampling methods, the errors in the assessment of fish resources are closely related to the representativeness of the samples. Increasing sampling effort is often used to reduce random error in hydroacoustic surveys [3,6]; however, even at high sampling intensities, the acoustic beam insonifies only a small proportion of the total water volume, rarely exceeding 1% [3]. In practice, the improvement of the accuracy of acoustic estimation depends not only on the sampling intensity but also on the adequate consideration of fish distribution characteristics in the survey design [3,20]. At the local scale, fish distribution pattern is influenced by water depth and shoreline morphology [14,21], and density variation is usually related to offshore distance, so the transects are generally designed to be perpendicular to the shoreline in fishery acoustic surveys [7,9]. Due to the meandering and narrow longitudinal axis of the mainstream and tributaries in the TGR, the transects designed perpendicular to the shoreline on both sides will result in survey route shapes that are not parallel but triangular in most cases. From this aspect, the triangular transect design is more consistent with the channel morphology of canyon-shaped reservoir and fish distribution characteristics.
It is noteworthy that fish density estimates were evidently higher in the tributary than in the mainstream. Especially, the highest fish densities were found in the survey unit Tributary1. The possible reason for this phenomenon lies in the environmental differences between the mainstream and tributaries of the TGR. Tributaries have lower flow velocities than the mainstream and therefore are more favorable for the survival of lacustrine fish and juvenile fish with weaker swimming activity [16]. Additionally, the nutrient level in tributaries is higher than that in the mainstream, so forage organisms, such as phytoplankton and zooplankton, are more abundant and can support higher densities of fish [16]. This also implies, to some extent, the importance of tributaries as fish habitats, since some juveniles hatched in the mainstream migrate to tributaries to avoid unfavorable environmental conditions and to feed and grow [17,22].
Our results showed no significant differences in fish size distribution assessed by the two types of survey designs both in the mainstream and tributary. Only small and inconsistent differences were observed. In the mainstream, there were two survey units with a higher mean TS for the parallel design and one survey unit higher for the triangular design. In the tributary, the triangular design had a higher mean TS in all the three survey units. These differences may be related to environmental variations, fish composition, and spatio-temporal dynamics between mainstream and tributaries, and between open-water and littoral areas. A number of studies on the diurnal distribution behavior of fish have shown that small fish move from the shelters near the shoreline to open water after dusk to feed [23,24]. Therefore, the proportion of small fish will be increased in the pelagic zone at night. Since fish density is generally higher in the littoral zone than in the open-water and the triangular design sampled more volume near the bank (as well as more fish) than the parallel design, it is inferred that this may be one of the main reasons for the higher TS for the triangular design during the night. Moreover, the majority of the mainstream in the TGR is represented by the pelagic zone, and the proportion of coastal zone is much lower than that of tributary. In consequence, the sheltering effect of littoral zone on small fish is not as remarkable as that of tributary. However, more research is needed regarding spatial and temporal differences in fish composition and size distribution, e.g., through a combination of hydroacoustic methods and other conventional sampling techniques.
5. Conclusions
Hydroacoustic approach has become an important tool for the long-term monitoring of fish resources in the TGR but technical specifications for fisheries acoustic surveys are still lacking. This study focuses on the design of cruising routes prior to hydroacoustic surveys. Our field experiments in the mainstream and tributary of the TGR demonstrated that the differences in the estimates of fish density and size distribution between the triangular and parallel designs were not significant under the environmental conditions of the canyon-shaped reservoir. Since the parallel design will take more time and labor at the same degree of coverage, to improve efficiency and ensure safety, we recommend that the triangular transect design with reliable coverage be prioritized for hydroacoustic sampling in the TGR and similar canyon-shaped reservoirs, especially when sampling at night. More research is needed on the technical specifications of hydroacoustic sampling in the TGR and other reservoirs in China, including the choice of survey time and time allocation. Emphasis should be placed on the documentation of meta-data regarding survey design during the planning and sampling to allow for comparability of long-term data.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.L. and S.Y.; methodology, Y.L., S.Y. and M.G.; investigation, Y.L., S.Y., G.H. and J.W.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.L. and S.Y.; writing—review and editing, Y.L., S.Y. and M.G.; visualization, Y.L.; supervision, S.Y. and Z.L.; funding acquisition, S.Y., J.L. and Z.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (no. 2019YFD0900603) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 32072983; 51679230).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Kaiping Wang for his help in field sampling. We also thank the Fishery Administration Station of Zigui County for supporting our sampling safety.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The sponsors had no role in the design, execution, interpretation, or writing of the study.
References
- CEN. EN 15910; Water Quality—Guidance on Estimation of Fish Abundance with Mobile Hydroacoustic Methods. Comité Européen de Normalisation: Brussels, Belgium, 2014.
- Pollom, R.A.; Rose, G.A. A Global Review of the Spatial, Taxonomic, and Temporal Scope of Freshwater Fisheries Hydroacoustics Research. Environ. Rev. 2016, 24, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmonds, J.; MacLennan, D. Fisheries Acoustics: Theory and Practice, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Aglen, A. Random Errors of Acoustic Fish Abundance Estimates in Relation to the Survey Grid Density Applied; FAO Fisheries Report (FAO); FAO: Rome, Italy, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Aglen, A. Reliability of Acoustic Fish Abundance Estimates. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Bergen, Bergen, Norway, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Godlewska, M.; Długoszewski, B.; Doroszczyk, L.; Jóźwik, A. The Relationship between Sampling Intensity and Sampling Error—Empirical Results from Acoustic Surveys in Polish Vendace Lakes. Fish. Res. 2009, 96, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker-Stetter, S.L.; Rudstam, L.G.; Sullivan, P.J.; Warner, D.M. Standard Operating Procedures for Fisheries Acoustic Surveys in the Great Lakes; Great Lakes Fishery Commission: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Rivoirard, J.; Simmonds, E.J.; Foote, K.; Fernandes, P.G.; Bez, N. Geostatistics for Estimating Fish Abundance; Blackwell Science Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds, E.J.; Williamson, N.J.; Gerlotto, F.; Aglen, A. Acoustic Survey Design and Analysis Procedure: A Comprehensive Review of Current Practice; ICES Cooperative Research Report; ICES: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Guillard, J.; Verges, C. The repeatability of fish biomass and size distribution estimates obtained by hydroacoustic surveys using various sampling strategies and statistical analyses. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2007, 92, 605–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doroszczyk, L.; Długoszewski, B.; Godlewska, M. Comparison of Acoustical Estimates of Fish Abundance for Different Coverage and Survey Design. Hydroacoustics 2007, 10, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.J.; Yang, D.G.; Wei, Q.W.; Du, H.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.H. Hydroacoustic Survey on Fishes in the Reach from Gezhouba Dam to Gulaobei of the Yangtze River. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2007, 16, 86–91, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Tao, J.P.; Chen, Y.B.; Qiao, Y.; Tan, X.C.; Chang, J.B. Hydroacoustic Surveys on Spatial Distribution of Fishes in the Three Gorges Reservoir During the First Impoundment. J. Hydroecology 2008, 1, 25–33, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lian, Y.; Ye, S.; Godlewska, M.; Huang, G.; Wang, J.; Chen, S.; Zhao, X.; Du, X.; Liu, J.; Li, Z. Diurnal, Seasonal and Inter-Annual Variability of Fish Density and Distribution in the Three Gorges Reservoir (China) Assessed with Hydroacoustics. Limnologica 2017, 63, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Water Resources, China; National Bureau of Statistics, China. Bulletin of First National Census for Water; China Water & Power Press: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Thornton, K.W.; Kimmel, B.L.; Payne, F.E. Reservoir Limnology: Ecological Perspectives; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Prchalová, M.; Kubečka, J.; Vašek, M.; Peterka, J.; Sed’a, J.; Jůza, T.; Říha, M.; Jarolím, O.; Tušer, M.; Kratochvíl, M.; et al. Distribution Patterns of Fishes in a Canyon-Shaped Reservoir. J. Fish Biol. 2008, 73, 54–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foote, K.G.; Knudsen, H.P.; Vestnes, G.; Maclennan, D.N.; Simmonds, E.J.N. Calibration of Acoustic Instruments for Fish Density Estimation: A Practical Guide; Cooperative Research Report No.144; International Council for the Exploration of the Sea: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Zar, J.H. Biostatistical Analysis, 5th ed.; Pearson Education Limited: Edinburgh, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gimona, A.A. Conditional Simulation of Acoustic Survey Data: Advantages and Potential Pitfalls. Aquat. Living Resour. 2003, 16, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järvalt, A.; Krause, T.; Palm, A. Diel Migration and Spatial Distribution of Fish in a Small Stratified Lake. Hydrobiologia 2005, 547, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vašek, M.; Kubečka, J.; Peterka, J.; Čech, M.; Draštík, V.; Hladík, M.; Prchalová, M.; Frouzová, J. Longitudinal and Vertical Spatial Gradients in the Distribution of Fish within a Canyon-Shaped Reservoir. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2004, 89, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gliwicz, Z.M.; Slon, J.; Szynkarczyk, I. Trading Safety for Food: Evidence from Gut Contents in Roach and Bleak Captured at Different Distances Offshore from Their Daytime Littoral Refuge. Freshw. Biol. 2006, 51, 823–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Říha, M.; Kubečka, J.; Mrkvička, T.; Prchalová, M.; Čech, M.; Draštík, V.; Frouzová, J.; Hladík, M.; Hohausová, E.; Jarolím, O.; et al. Dependence of Beach Seine Net Efficiency on Net Length and Diel Period. Aquat. Living Resour. 2008, 21, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).