Abstract
The western region of Jilin Province is located at the northeastern part of China. A large number of lakes are distributed in this region, where is one of five large lake regions within China, supporting both drinking water and agricultural water. The frequent human activities and scarce rainfall in this region have resulted in weaker lake connectivity and enrichment of the pollutants within the lakes. The lake ecosystems in the region have been degraded to varying degrees, and thus it is necessary to assess its ecological health. Macrobenthos multi-metric index (MMI) is a mature ecological health assessment method that has been widely used in the lake ecosystem assessment all over the world. However, it has not been well developed for assessing the lake water ecosystem in China. In this study, 11 lakes affected by human activities to different degrees were selected as the research objects. They were categorized into three types on the basis of trophic level. Through the comparison and screening of different biological indicators among different lake types, we selected appropriate indicators to construct the MMI. Four core indicators were selected from 58 candidate indicators to construct the MMI: the total number of taxa, Simpson index, percentage of Diptera + Mesogastropod, and percentage of pollution-intolerant species. MMI could distinguish lakes that are seriously and slightly disturbed by humans. The results of regression analysis also showed that the degree of lake eutrophication caused by human activities had a significant correlation with MMI, effectively explaining its changes. MMI can characterize the disturbance and influence of eutrophication on macrobenthos. The results of MMI can also be affected by the land use type and the coverage of aquatic vegetation around the lake, which are important factors affecting the ecological health of the lake. Research on the application of MMI method to assessment of the ecological health of lakes is very rare in Northeast China. This research can provide supplementary information beyond the traditional water environment assessment for the formulation of management strategies.
1. Introduction
The lake is an important inland water ecosystem that not only plays an important role in maintaining regional ecological balance and ecological health but also is vital to the sustainable development of the economy and society [1,2]. Since the 1950s, the ecosystem function of many lakes has gradually degraded, and the health of the ecosystem has been seriously threatened due to the greenhouse effect and irrational over-development by humans [3]. Therefore, the health assessment of lake water ecosystems is particularly important for achieving lake health management and protection [4]. Previous studies have shown that biological indicators could be used for long-term aquatic ecosystem health assessment. For example, phytoplankton, macrobenthos, fish, and aquatic plants could be used for the characterization of ecosystem health [5,6,7,8]. As one of the most effective tools to characterize human disturbance, the multi-metric index has been widely used all over the world as a more reliable tool as compared to a single index assessment [9,10,11,12,13,14].
Karr first proposed the application of a multi-metric index method to assess the ecological health of water bodies in 1981, which was applied to fish [15]. It was then applied to other aquatic organisms, such as diatom and macrobenthos [16,17]. In recent years, the macrobenthos multi-metric index (MMI), which is also known as the index of biological integrity (IBI) [18], has been applied in many aquatic ecosystems worldwide. MMI has become a recognized and effective ecological tool for monitoring and evaluating the freshwater ecosystem [13].
MMI is a combination of indicators that reflects the different environmental conditions and various aspects of the biological community (such as group richness, diversity indicator, the proportion of sensitive and tolerant species, and feeding structure). By comparing the reference and the impaired points, studies can select suitable indicators to construct MMI to achieve the objective that every single index in the combination could reasonably predict the impact of environmental changes [19]. One advantage of using multi-metric index is that the various biological attributes of macrobenthic communities can be integrated, showing the biological integrity of the study area [20]. At the same time, biological integrity has the function of characterizing the ecosystem degradation [4,21], in order to achieve the objective of evaluating the ecosystem’s health.
In China, the research on MMI assessment of lake ecosystem health is mostly concentrated in the eastern and southern regions, while it is relatively rare in the high latitude areas. At the same time, in the health assessment of lake ecosystem in China, the MMI method mainly takes a single lake as the research object [7,22,23,24]. The study by Huang et al. (2016) on the four major freshwater lakes in the lower reaches of the Yangtze River showed that MMI could characterize the impairment to each component of the lake’s ecological integrity. If combined with historical data, it could reflect the historical changes in the ecosystem’s integrity, thus providing the scientific support for protection and restoration of the lake ecosystem [7]. The studies done by Ma et al. (2008) and Cai et al. (2014) on Taihu Lake showed that from a scientific point of view, it is more appropriate to assess the lake ecological health by MMI, and it is better than a single biological index [22,23,24]. Zhang et al. (2019) conducted a large-scale study of multiple lakes in the Yangtze River Basin. They also assessed the ecological status of shallow lakes from the perspective of eutrophication, and for the first time proved a good response to eutrophication [25]. Therefore, taking specific types of lakes on a regional scale as the research object will be a breakthrough in assessing the health of lake ecosystems in those areas that have been severely affected by various human activities [25].
Jilin Province is located at northeast China in the hinterland of the Songnen Plain. There are many bogs in the western region, and large number of natural lakes are distributed to provide water, supporting lives, agriculture, and industry of millions of residents. The region is densely populated and has developed agriculture, a tourism industry, and animal husbandry. Although the history of resource development in the region is not long, the lakes show varying degrees of eutrophication due to the long-term overgrazing, cultivation, and irrational land use [26]. At the same time, reservoir construction in the upper reaches of the Huolin River has led to slow replacement and metabolism of nutrient elements in some of the small lakes with poor river connectivity. This continuous enrichment of various elements has resulted in serious eutrophication. Although the ecological state of the larger lakes (Chagan Lake, Yueliang Lake, etc.) has been gradually improved over time due to the government paying more attention to environmental protection and strengthening measures in the past 20 years, eutrophication still exists [27,28]. In this study region, the use of MMI to assess the lake ecosystem health has not been carried out. Only in places similar to this study region that are located in the northeast of China are there a few studies of rivers and wetlands that started in 2019. For example, Wang et al. (2019) used a biological integrity method to assess the ecological environment of the Songhua River Basin. Lu et al. (2019) adopted the same method for studying the impact of the barrier of the dam in the upper Wusuli River on the wetland ecosystem.
Regarding the widespread eutrophication phenomenon of lakes in this region, the lake types were defined along the trophic level, and the most distinguishable biological indicator between the most disturbed lakes and the least disturbed lakes was determined to establish the MMI. Then, the value of MMI is used to represent the health state of the lake ecology in the study region. We expect to show that the MMI can effectively represent the difference between the different lake ecosystems by human disturbance, as well as verify whether the assessment of lake ecosystem health through MMI is different from traditional physical and chemical index assessment methods. At the same time, we analyzed various environmental factors affecting the ecology according to the land use types and vegetation growth around the lake, which is considered vital for the protection and management of the lake ecosystem and can provide theoretical support for its protection and restoration as well [29].
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Sites
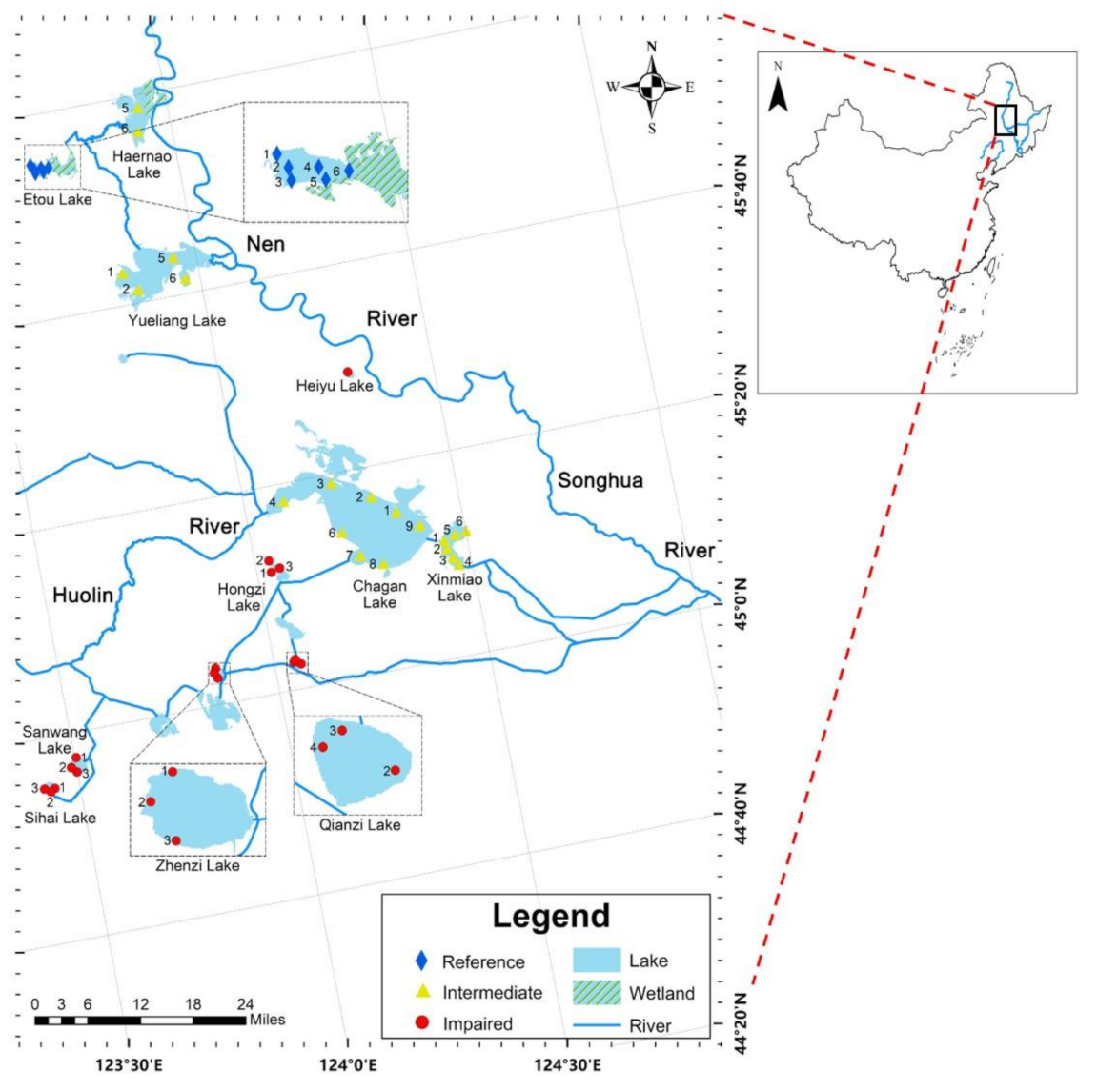
The research objects of this study are 11 lakes located in Chagan Lake area and Momoge National Nature Reserve (Figure 1). The study lakes in the Chagan Lake area include Chagan Lake and Xinmiao Lake, as well as 8 lakes in a group of lakes connected by Huolin River and connecting ditches. Momoge National Nature Reserve covers an area of 1440 km2, and has 3 study lakes: Etou Lake in the reserve experimental area, Haernao Lake, and the Yueliang Lake in the core area of reserve [30]. The study region is located between 44°40’–46°N and 123°-124°15’E. It has a mid-temperate, semi-humid continental monsoon climate with 4 distinct seasons. The multi-year average temperature is 4.5 °C, and the multi-year average rainfall is 400–500 mm [28,30,31,32]. According to previous studies in this region, the water environment in the Momoge National Nature Reserve was found to be better than that of the lakes in the Chagan Lake area [33,34]. However, the lakes in the Momoge National Nature Reserve are still in a state of light eutrophy.
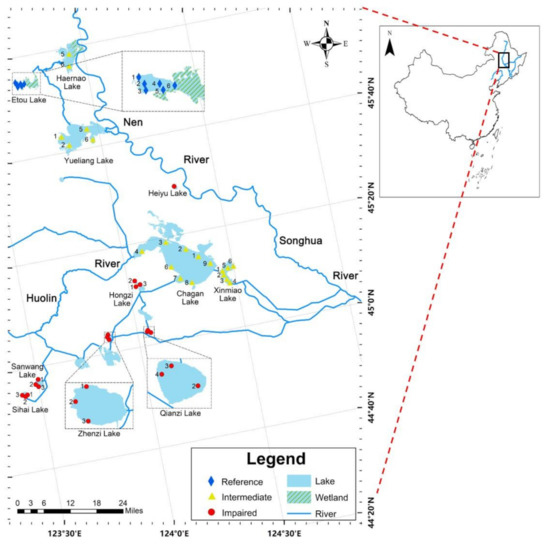
Figure 1.
The study region location and sampling sites: the rhombus represents the reference lake sampling sites; the triangles represent the intermediately impaired lake sampling sites; the points represent the impaired lake sampling sites. The number beside the sampling sites represents the serial number of that point in the lake.
In 2018, our researchers collected macrobenthos and measured water environmental indicators in 11 study lakes. This study used the lake as the basic unit of overall classification. Every sampling site in the lake was used as the basic unit to construct MMI. Therefore, a different number of sampling sites were set in each lake according to the acreage of the lake—the larger the acreage of the lake, the more sampling sites. A total of 42 sampling sites were set in 11 study lakes. The detection of water environment indicators and the collection of macrobenthos were carried out. Three samplings were conducted in May, July, and September of 2018. There were 8, 6, 4, 6, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, and 1 sampling sites in Chagan Lake, Xinmiao Lake, Yueliang Lake, Etou Lake, Haernao Lake, Sihai Lake, Sanwang Lake, Qianzi Lake, Hongzi Lake, Zhenzi Lake, and Heiyu Lake, respectively (Figure 1). Within 100 m of the sampling sites, a Peterson sediment sampler (1/16 m2) was used to collect sediment samples, and a 425 μm sieve was used to filter the macrobenthos. The collected macrobenthos were fixed with 75% alcohol, observed identified, and counted through a microscope. The identification of the macrobenthos was performed to the species or genus level [35,36]. At the time of sampling, the aquatic vegetation conditions of the research lakes and sampling sites were recorded.
While collecting macrobenthos, we used the HANNA HI98194 (Hanna Instruments, Woonsocket, RI, United States) portable multi-parameter water quality analyzer to measure water temperature, water pH, dissolved oxygen, electrical conductivity, total dissolved solids, and salinity. At the same time, the water samples were collected, stored at low temperature, and transported back to the laboratory. The total phosphorous (TP), total nitrogen (TN), and ammonia nitrogen contents were measured in the laboratory, referring to the determination method in the Water and Wastewater Monitoring and Analysis Method (Fourth Edition) [37].
2.2. Site Classification
In order to construct the MMI, it was necessary to compare and screen biological indicators of macrobenthic communities in the lakes severely impaired by human disturbance with that of the reference lakes without human disturbance under similar habitat types [38]. However, due to the frequent occurrence of freshwater pollution in western Jilin Province, eutrophication is widespread, and there are no lakes that are truly not disturbed by humans. Therefore, in this study, the determination of reference lakes and impaired lakes is relative [16,24].
This study used the comprehensive trophic level index (TLI) as a tool to distinguish between impaired lakes and reference lakes, and divided the studied lakes into 3 groups according to their nutritional status [39]:
- Impaired lakes: lakes with hyper-eutrophic conditions (TLI > 70).
- Reference lakes: since lakes in this region are generally disturbed by human activities, it is difficult to find truly undisturbed lakes. Therefore, the lake with the lowest TLI index and the same number of research sites as impaired lakes was selected as the reference lake. It represents the lake with the least human disturbance in this region.
- Intermediately impaired lakes: between the above two terms, these lakes are moderately affected by human disturbance.
The research sites in the reference lakes are the reference sites, and the research sites in the impaired lakes are the impaired sites (Figure 1).
2.3. Candidate Indicators
The first task of MMI construction was to determine the candidate macrobenthos biological indicators because they reflect the specific response of macrobenthic communities to human disturbance [19]. On the basis of domestic and foreign research and combined with the actual situation of the study region, we selected and calculated 58 candidate biological indicators [23,25,40,41,42]. These indicators were divided into 5 types:
Taxonomic richness: the number of various biological taxa [23], including the total number of taxa, the number of taxa of pollution tolerant, and pollution intolerant species.
Community structure composition: representing the relative abundance of various taxa of macrobenthos, such as percentage of Chironomidae representing the percentage of the number of Chironomidae to the total macrobenthos at each site, or percentage of dominant species representing the percentage of the number of dominant species (the species with the largest number at each site) to total macrobenthos at each site [19].
Biodiversity index: four kinds of diversity indexes were calculated, including Shannon–Wiener index, Margalef index, Pielou index, and Simpson index [43].
Pollution tolerance indicators: including the number of pollution-tolerant species and the percentage of pollution-intolerant species to the total (percentage of pollution-intolerant species). The species with pollution tolerance (“Monitoring map of benthic fauna in Liaohe River Basin”) value greater than 7 were considered to be pollution-tolerant macrobenthos, and rest were considered to be macrobenthos who were intolerant to pollution [25]. It also includes indicators related to the species sensitivity to pollution: biological monitoring working party (BMWP), which had been revised by Chinese researchers [27], and average score per taxon (ASPT) [44,45], as well as pollution tolerance indicators: family biotic index (FBI) and biotic index (BI) [46].
Feeding function group: macrobenthos were divided into five categories according to their different feeding habits, i.e., scrapers (SC), shredders (SH), collectors (GC), filter feeders (FC), and predators (PR). The proportion of each category to the total number of macrobenthos at each site was an indicator of the feeding function group, such as percentage of SC [19,47,48,49].
2.4. Screening of Candidate Indicators
It is important for the core indicators that make up the MMI to have the ability to distinguish between the impaired lakes and the reference lakes. Therefore, in order to filter the core indicators from the candidate indicators, we selected the following steps on the basis of previous studies [11,50]: (1) First, a normality test was performed for each indicator for the impaired lakes and the reference lakes, followed by a parametric test for the indicators that confirmed the normal distribution. Then, a non-parametric test was conducted for the indicators that did not confirm to the normal distribution. After the parametric/nonparametric test, the indicators with significant differences between reference lakes and impaired lakes were retained and screened in the next step. (2) Sensitivity analysis was carried out for the indicators with significant difference via box plot method. Interquartile range (IQ) overlap of the box plot was used to assess the sensitivity. The higher the IQ value between the impaired lakes and the reference lakes, the more sensitive the indicator, and the higher the ability to recognize human disturbance. This case was achieved:
- If there was no overlap in the interquartile range, IQ = 3.
- When there was a partial overlap but the median was outside others’ interquartile range, IQ = 2.
- When there was only one median within others’ quartile range, IQ = 1.
- When all medians were within the others’ quartile range, IQ = 0.
When IQ ≥ 2, the indicator was believed to have a higher ability to distinguish human disturbance with higher sensitivity [50]. Here, we should note that although the IQ value of some indicators meets the screening requirements, it may be because the data of the impaired lakes or the data of the reference lakes has too many 0 values. This means that although it meets the requirements from the perspective of indicators screening, it will lose the ability to distinguish between lakes and lakes or sites and sites in the subsequent calculations due to too many 0 values. Therefore, it is necessary to exclude indicators whose value of 0 accounts for more than one-third of all sites’ data (including impaired lakes, reference lakes, and intermediately impaired lakes) [51]. (3) The last step is to perform a correlation analysis between the remaining indicators to filter out redundant indicators. Spearman correlation analysis (2 indicators are not normally distributed) and Pearson correlation analysis (both indicators are normally distributed) is performed for each of the remaining indicators, using data from all points. If the correlation between the 2 indicators satisfies R > 0.8 and p < 0.05, it means that the 2 indicators are redundant, the stated function is repetitive, and thus the appropriate indicator is kept [52]. If 2 indicators are redundant, we should choose the remaining indicator according to the following criteria [19,51]: First, keep at least 1 indicator for each type to ensure that the biological index could reflect multiple ecosystem dimensions. Secondly, try to choose a set of indicators with lower correlation among the 2 sets of indicators. Finally, choose the indicator with a higher correlation with environmental factors (TLI). If an indicator is not significantly related to environmental factors, it can be directly excluded.
2.5. MMI Calculation
The final core indicator may contain multiple value ranges, which should be unified before calculation [19]. Due to the small study region and sample size, this study set the upper and lower anchor points as 25% and 75% of the value of reference point and the impaired point, respectively [53]. For the i-th index, we used its original value (Si), lower anchor (Li), and upper anchor (Ui) to calculate the score Mi for each site [40].
For indicators that decrease with increasing human disturbance, the 25th percentile value of the impaired point was taken for Li, and the 75th percentile value of the reference point was taken for Ui. The equation is as follows:
For indicators with smaller human disturbance and lower value, the 75th percentile value of the impaired point was taken for Li, and the 25th percentile value of the reference point for Ui was taken. The equation is as follows:
If the calculation result was lower than 0, the value was set to 0; if the calculation result was greater than 1, then the value was set to 1. The final MMI is the average of the calculation results of each core indicator at the site. The average of the scores of each indicator was taken at every site after reset to obtain the MMI value of site (MMIS). The average value of the MMI was calculated for all sites in each lake to obtain the MMI value of lake (MMIL).
2.6. Testing and Analysis of MMI
We chose a lake from the research lakes as the test lake. The process of constructing MMI does not include the test lake; after screening out the core indicators of MMI, the MMI value of the test lake and the other research lakes would be calculated. Through this way, the accuracy of the MMI can be tested.
After the MMI was calculated, the correlation analysis and linear regression analysis were carried out with the water environmental indicators to test whether there was any significant relation to the environmental indicators and whether the method was able to characterize human disturbance.
At the same time, we used geographic information software (ArcMap 10.5) to analyze land use types around research lakes, and we also preliminarily analyzed the relationship between land use type, aquatic vegetation coverage, water environment, and biological integrity.
3. Results
3.1. Selection of Metric and Calculation of MMI Results
A total of 1259 individual macrobenthos were collected in this study, all of which were identified at the species level, which included 3 phyla, 3 classes, 6 orders, 10 families, and 43 species [36,54]. The water quality test results showed that all lakes in the study region were eutrophic, as expected in the experiment (Appendix B). Among them, the trophic level of Sanwang Lake, Zhenzi Lake, Qianzi Lake, Heiyu Lake, and Hongzi Lake were hyper-eutrophic, and were categorized under impaired lakes. The remaining lakes were all light eutrophic, but the trophic level of Xinmiao Lake and Etou Lake were the lowest relative to this region (close to the mesotrophic state). According to the method, these two lakes should be reference lakes, but Xinmiao Lake receives the farmland recession flow in Qianguo Irrigation District all year round. Past studies have shown that the water quality of Xinmiao Lake is relatively poor, and the surrounding human activities are more frequent; thus, it cannot be selected as the reference lake [28,55]. Therefore, only Etou Lake was selected as the final reference lake. We chose Sanwang Lake among the impaired lakes as the test lake, which was randomly selected among the lakes with a relatively small number of sampling points but not the least. Therefore, Sanwang Lake was not considered in the subsequent screening process.
A total of 58 initial candidate indicators were selected (Appendix A). There were 22 sampling sites in the reference lakes and the impaired lakes. Because the number of sampling sites was less than 50, the Shapiro–Wilk test was selected for normality test. Then, an independent samples t-test was selected for parametric testing for the nine indicators that conform to the normal distribution, and the Mann–Whitney U test was selected for nonparametric testing for the 49 indicators that did not conform to the normal distribution. A total of 26 indicators with significant differences between the reference lakes and the impaired lakes were retained. The discrimination ability of these 26 indicators was analyzed, and 4 indicators with IQ < 2 were eliminated. Among the remaining 22 indicators, due to the number of Diptera taxa, percentage of Chironomidae, percentage of Diptera, and the other seven indicators having too many values of 0 (more than one-third of the data was 0), we eliminated them, as they had lost sufficient discrimination ability [51]. Then, through Spearman and Pearson correlation analysis, the two indicators with a correlation R > 0.8 (p < 0.05) were considered redundant [19], and only one of them was retained. Seven biological indicators, such as the number of pollution-intolerant species taxa, the number of Basommatophora taxa, Shannon–Wiener index, and BMWP index, were highly correlated with the total number of taxa. These indicators were excluded because the total number of taxa could display the most biological information and it was retained [23]. Since one indicator needed to be retained for each species, we excluded the percentage of dominant species that was highly correlated with the Simpson index. As the same type of index, percentage of pollution-intolerant species was highly correlated with the BI. Percentage of pollution-tolerant species was selected as the core indicator because it had a strong correlation with water environment indicators and could better represent the changes in water environment pollution. Under the same principle, two indicators of the number of Planorbidae taxa and ASPT index were eliminated because there was no significant correlation with the environmental factors. Therefore, the final MMI core indicators were as follows: the total number of taxa, Simpson index, percentage of Diptera + Mesogastropod, and percentage of pollution-tolerant species.
Finally, after resetting the index value and the calculated average value, we calculated the test lake in the same way. The calculation results of MMIS value ranged from 0 to 0.935, and the value of MMIL ranged from 0.121 to 0.866 (Appendix B). The final calculated MMI was divided into five quality levels as Table 1 [19]:

Table 1.
Lake ecological status level.
3.2. Correlation Between MMI and Environmental Indicators
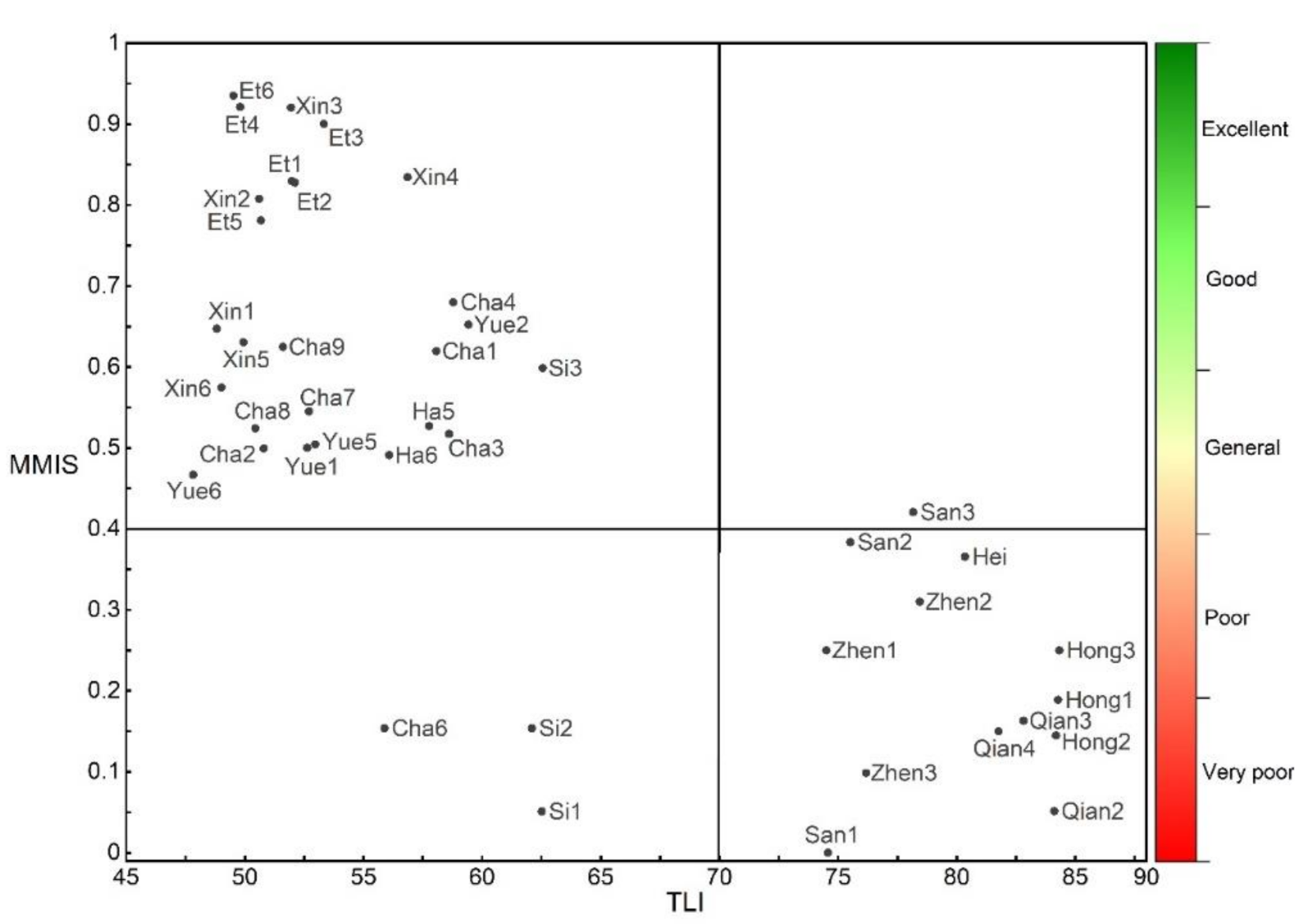
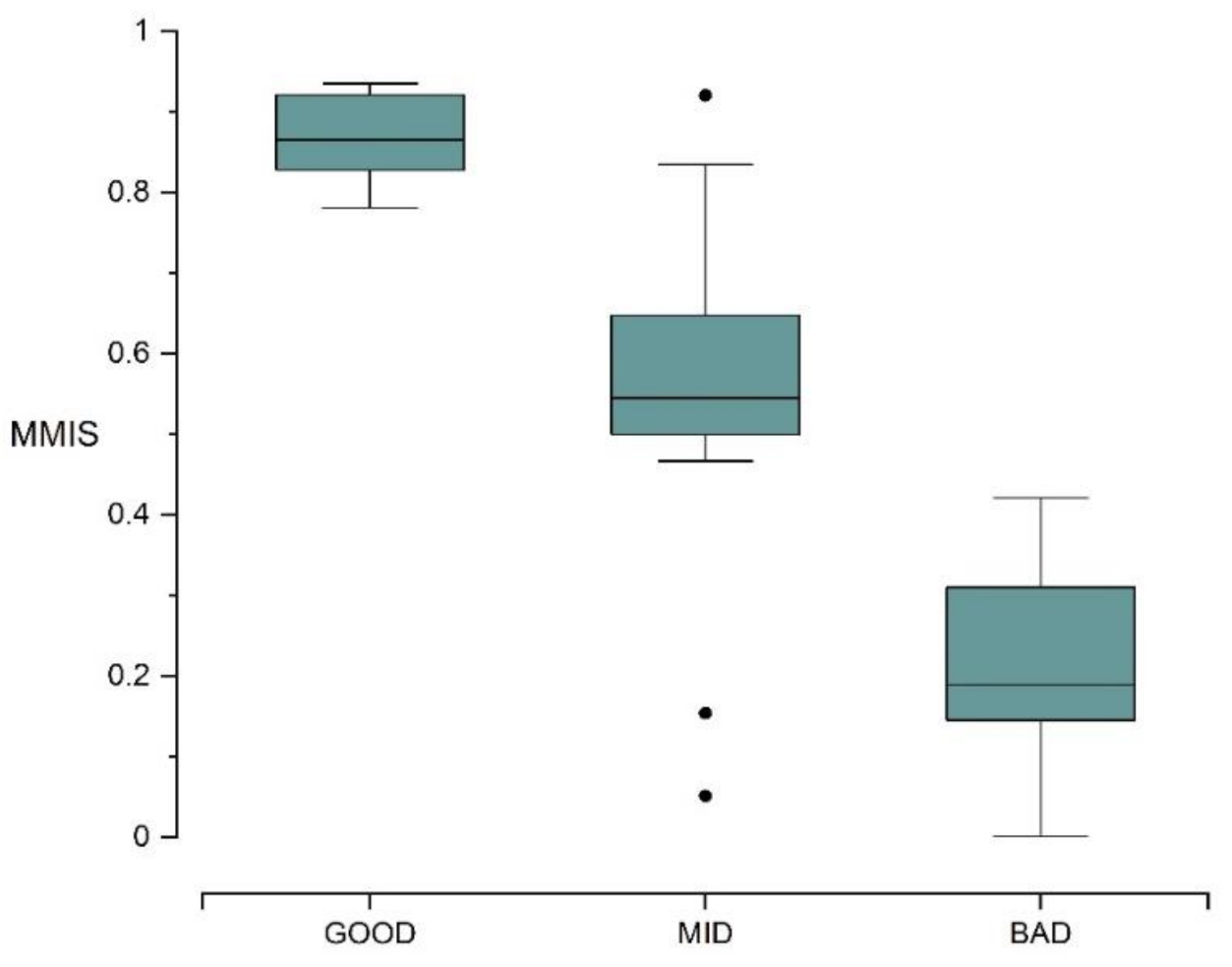
Among all the sampling sites in this study, 10 sites (23.8%) were in a very poor state, 5 sites (11.9%) were in a poor state, and 12 sites (28.57%) were in a general state, 7 sites (16.67%) were in a good state, and 8 sites (19.05%) were in an excellent state (Figure 2). By calculating the average value of each site, we obtained the overall MMI of the 11 lakes investigated. There were two lakes with very poor ecological level, these being Hongzi Lake (0.19) and Qianzi Lake (0.11); four lakes with poor ecological level, these being Zhenzi Lake (0.22), Sihai Lake (0.26), and Heiyu Lake (0.36), with the calculation results showing that the test lake (Sanwang Lake: 0.26) was also at a poor ecological level; three lakes with general ecological level, these being Chagan Lake (0.52), Yuliang Lake (0.53), and Haernao Lake (0.50); only one lake with a good ecological level, this being Xinmiao Lake (0.73); and only one lake with excellent ecological level, this being Etou Lake (0.86). The box plot of the MMI calculation results (Figure 3) show that the MMI value discrimination ability of reference lakes, impaired lakes, and intermediately impaired lakes was obvious. It indicated that MMI could effectively represent the water environment condition of lakes and assess the ecosystem health of lakes.
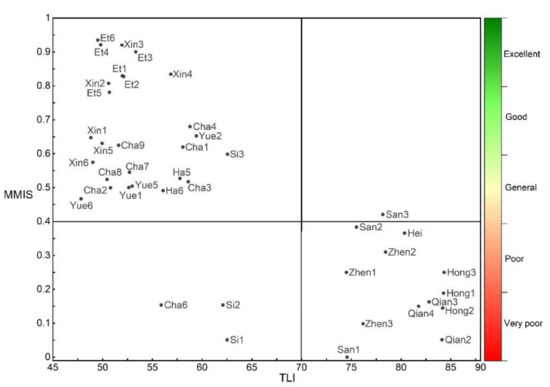
Figure 2.
Quadrant diagram of the trophic level index (TLI) and multi-metric index (MMI) of the research site: the horizontal axis represents the TLI value, and the vertical axis represents the MMI value of site (MMIS). The name of black points shown is the abbreviation of the lake + site number. The abbreviation of the lakes’ name is shown in Appendix B.
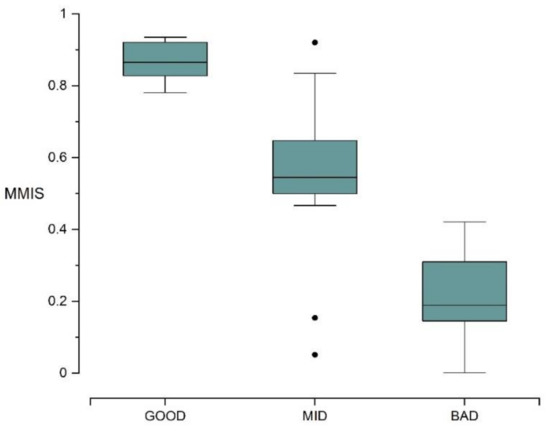
Figure 3.
Box plot of multi-metric index (MMI) discrimination ability among different lake types: the abscissa GOOD represents the reference lakes, MID represents the intermediately impaired lakes, and BAD represents the impaired lakes. The ordinate represents the MMIS value.
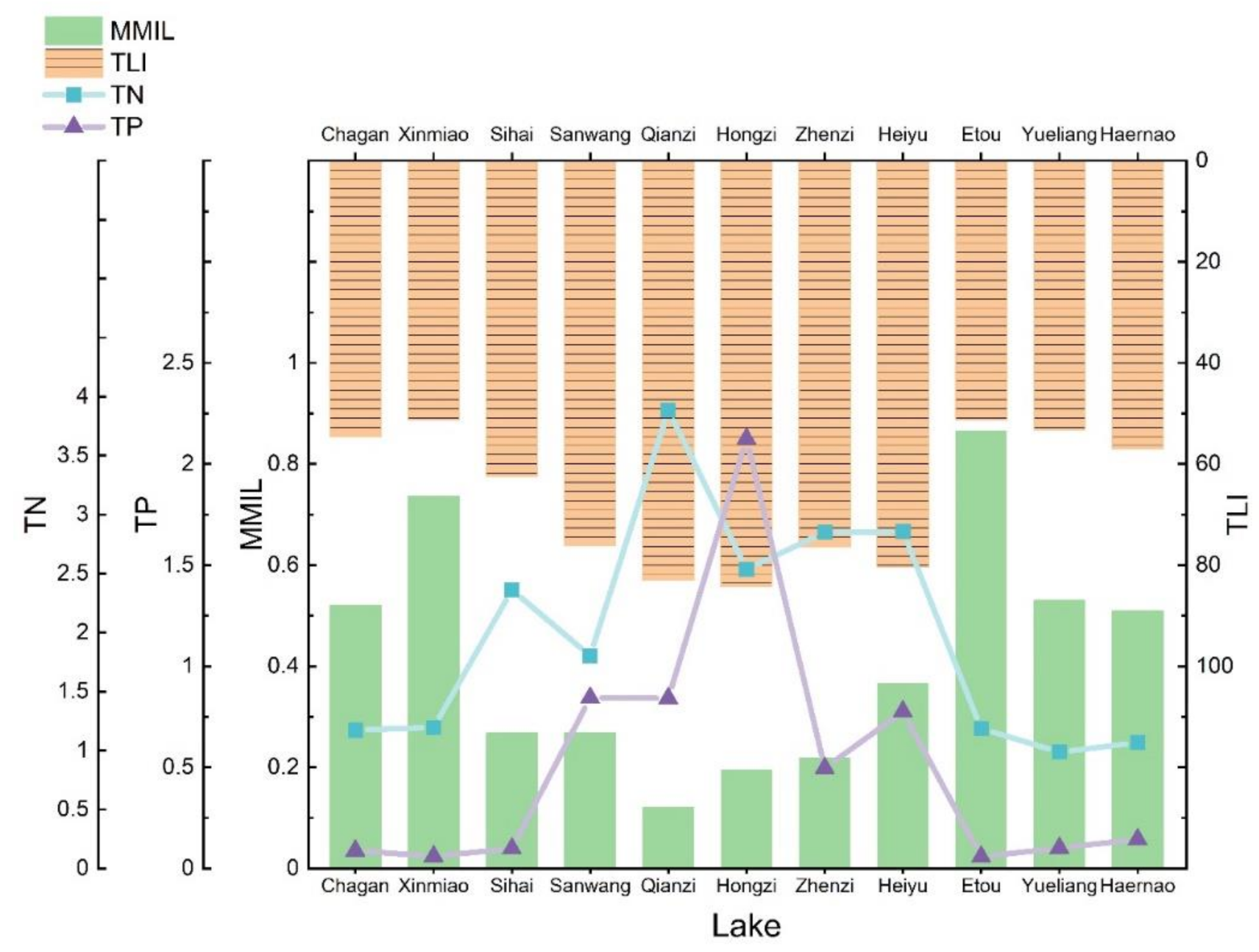
The MMIL and the environmental indicators of the lake were analyzed comprehensively (Figure 4). As a reference lake, Etou Lake showed the best biological integrity in the western Jilin Province, followed by Xinmiao Lake, and the trophic level indicator (TLI) value, which was the lowest. The trophic level of Chagan Lake, Yueliang Lake, Xinmiao Lake, and Etou Lake were similar, but Chagan Lake, Yueliang Lake’s MMI value were significantly lower than Etou Lake and Xinmiao Lake. The MMI value of lakes such as Sihai Lake, Sanwang Lake, Zhenzi Lake, Heiyu Lake, Qianzi Lake, and Hongzi Lake were significantly lower than those of other lakes. At the same time, their TLI values were significantly higher than that of the other lakes. Qianzi Lake and Hongzi Lake both had much higher TN and TP contents than all other lakes, and their MMI values were also the lowest. Although Sihai Lake was considered an impaired lake, its TLI value was lower when compared to similar lakes, while the TN content was close to that of the impaired lakes.

Figure 4.
Comprehensive analysis of MMI value of lake (MMIL) and lake water quality indicators. The horizontal axis represents different research lakes; the y1 axis (starting from the lower x-axis) represents MMIL; the y2 axis (starting from the upper x-axis) represents trophic level index (TLI); the relative value of total nitrogen (TN) and total phosphorus (TP) were used to plot points and lines.
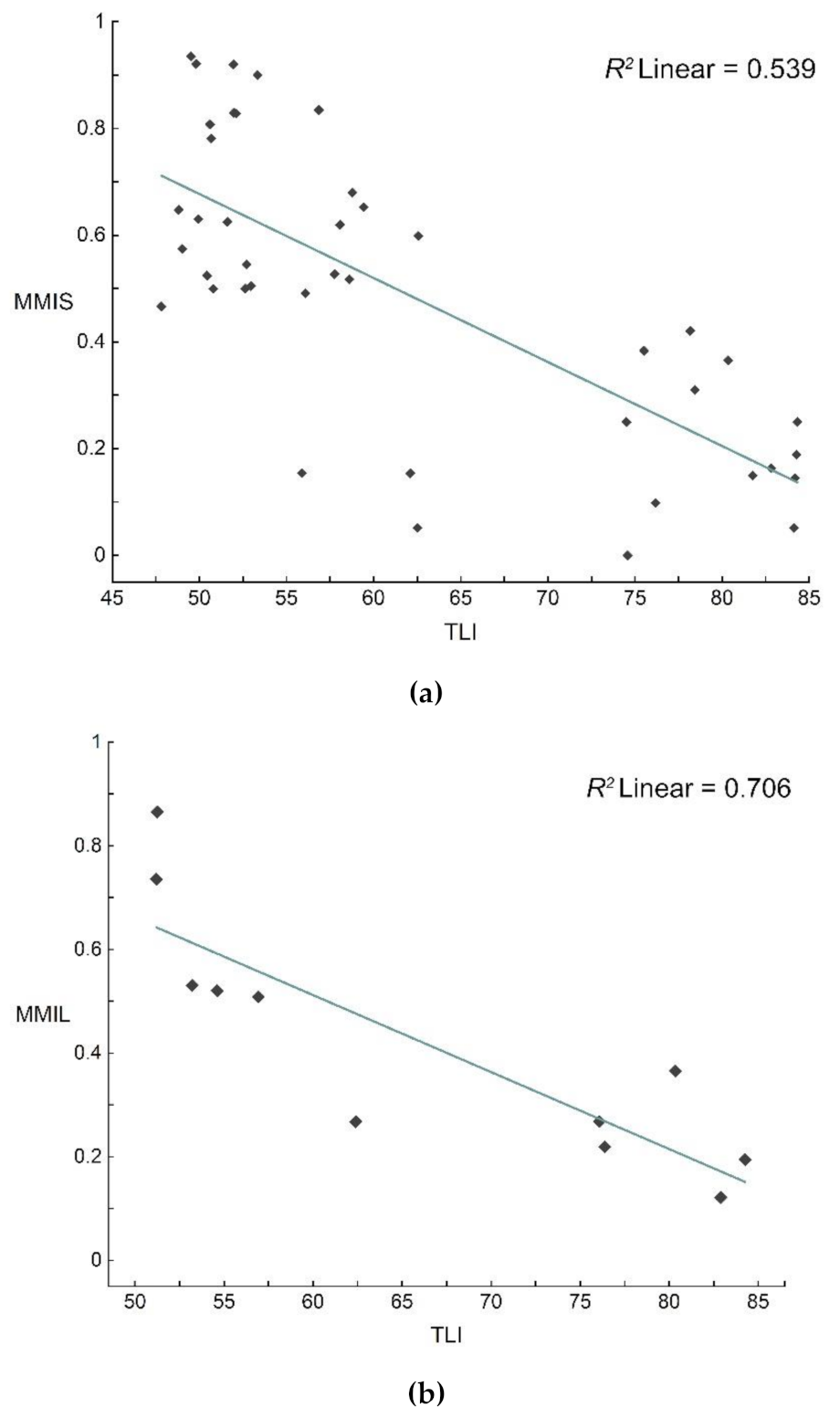
The Spearman correlation analysis result of MMIS and TLI shows that it had a significant correlation (R = −0.69) with a high significance level (p < 0.05), and MMIS and TLI showed a negative significant correlation. MMIL and TLI also showed a significant correlation (R = −0.92), with high significance level (p < 0.05), and MMIL and TLI showed a negative significant correlation. The results of linear regression analysis showed that TLI changes could effectively and significantly explain the changes in MMIS (linear R2 = 0.539, p = 0.00) and MMIL (linear R2 = 0.706, p = 0.001) (Figure 5), which indicated that lake eutrophication has a significant impact on the macrobenthos biological integrity in lakes, and could explain the changes in MMI, whether at different site levels or at the lake level. Such results also showed that MMI could characterize the disturbance and influence of eutrophication on macrobenthos.
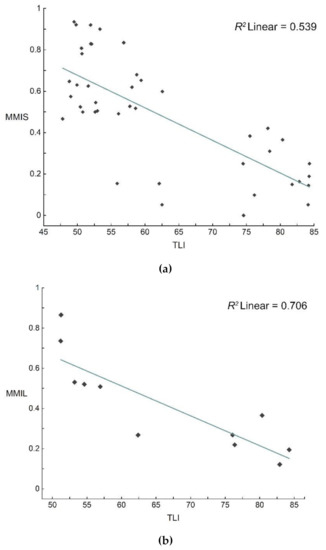
Figure 5.
Scatter plot of fitted line: R2 represents the fitting degree between the point and the line (a) MMI value of site (MMIS) and TLI value, (b) MMI value of lake (MMIL) and TLI value.
4. Discussion
4.1. Inspection of MMI
In this study, Sanwang Lake was selected as the test lake, which represented an experimental group. Although Sanwang Lake is an impaired lake according to the trophic level (TLI), it did not participate in the process of constructing MMI as an impaired lake. However, when calculating the final MMI value, Sanwang Lake was calculated in the same way, and the subsequent data analysis was performed as impaired lake.
Results of the analysis and calculations show that Sanwang lake was hyper-eutrophic, which was the same as other impaired lakes. In addition, the MMIS of the three sampling sites of Sanwang Lake were in poor or very poor ecological states. At the same time, its MMIL and the MMILs of Zhenzi Lake, Heiyu Lake, and Sihai Lake, which had similar TLI values, were in poor ecological state. From this aspect, it is verified that the MMI we constructed can characterize the ecological health of the lake.
4.2. Indicator Selection and MMI Application
The biological integrity of a site is inevitably affected by many factors, and the purpose of constructing MMI is also to reflect the impact of these factors as much as possible [56]. Therefore, it is necessary and recommended to retain each type of biological indicators to reflect the complexity of the macrobenthos community [19,51]. However, in the present research, due to the low discrimination of the feeding function group indicators, such indicators could not be used as the core indicators of MMI, and thus the final core indicators were only the other four categories. Although the feeding function group is a widely used indicator in the MMI assessment of rivers, it is much less used in the MMI construction of lakes [41]. The study by Miller et al. (2013) showed a significant correlation between feeding function indicators and lakeshore vegetation degradation [57]. Thus, in this study, the feeding function indicators were still considered because of their poor discrimination ability. Therefore, it was not involved in the construction of MMI. In other MMI studies, Ephemeroptera, Plecoptera, and Trichoptera have commonly used indicators of richness and community structure [50,58]. These macrobenthos are more sensitive. However, in this study, the researchers did not find these three orders. The possible reason is the different sampling method—the columnar sediment sampler was used in this study to collect and screen sediments, and few macrobenthos suspended in the water were collected. This is also the point that needs improvement in future studies.
With reference to similar research and analysis in other regions, the researchers of the present study did not find the core indicators for MMI construction to be exactly similar. Even in the Songhua River, which is very close to this study region [42], the final core indicators were not the same. This showed that not only the MMI of different regional characteristics remained different but also the MMI of lakes and rivers were different. The index of the total number of species taxa represents the most biological community information and is the most common indicator in all other studies [23,40,42,50,59], which was also adopted in this study. It can indeed be useful to distinguish impaired lakes from reference lakes, having integrity and good stability for the MMI construction. Percentage of Diptera + Mesogastropod is not a common indicator in other studies, which is the peculiarity of the current study region. The Diptera dominated by Chironomid species are pollution-tolerant species and the Mesogastropoda appearing in this study region were all pollution-tolerant species. The combined indicators of these two types of species can significantly distinguish local polluted lakes, thus indicating that eutrophication has various effects, not single or absolute effect, on macrobenthos [60].
In related studies conducted in Northeast China, although the MMI indicators were not the same, they all had similarities. As shown below. Lu et al. (2019) used four core indicators for MMI construction on the Wusuli River Wetland. The total number of taxa and percentage of Gastropoda were similar to the current indicators but Pielou index and Simpson index were connotatively different, which indicated the difference among the macrobenthic communities [40]. Wang et al. (2019) studied the total number of taxa in Songhua River and the percentage of pollution-intolerant species. These two indicators were similar to the current indicators used in the study. In addition to diversity indicators, BI was also used, which is the most commonly used water quality biological assessment index related to the pollution tolerance of macrobenthos. It not only considers the pollution tolerance of each species itself but also considers the number of species, which can more accurately determine the degree of water pollution [61]. The biggest difference between this study and the study by Wang et al. and Lu et al. is the method of sampling macrobenthos. Both studies used macrobenthos collected by D-shaped sweep net, and this is also an aspect that needs to be improved in our next research, that is, to compare and analyze the two sampling methods.
4.3. MMI Assessment Results
From the results reflected in Figure 5, we can see that the Etou Lake had the highest biological integrity (MMI) and the lowest eutrophication indicator (TLI) value, which is in line with the expectations. Etou Lake is a well-protected lake in the Momoge National Nature Reserve. The water ecosystem’s health is in an excellent state. Chagan Lake, Yueliang Lake, Xinmiao Lake, and Etou Lake were found to have almost the same level of eutrophication, which was verified in accordance with Frouin et al. (2000). Species richness of macrobenthos at oligotrophic status was not the best, but in terms of mesotrophic status it showed improvement, thus making the reference sample a reasonable choice for the current study [62]. The MMI value of Chagan Lake, Yueliang Lake, and Xinmiao Lake were significantly lower than those of the Etou Lake. This may have been due to the low vegetation coverage around Chagan Lake and Yueliang Lake in similar environments, which was also confirmed by scarce aquatic plants. Through field investigation in the study region, only Xinmiao Lake and Etou Lake had a large number of algae, while the algae were almost invisible in other lakes. This was consistent with the previous studies. In areas rich in aquatic plants, the biomass of macrobenthos is significantly higher than in areas where aquatic plants do not exist [63]. This indicates that MMI could characterize the disturbance of human activities to the ecosystem. The Momoge Wetland, where the Etou Lake is located, is a national nature reserve. Human cultivation and overgrazing caused serious impairment in this region. However, due to effective protection in recent years, its ecological environment has recovered well. Although from the perspective of trophic level, Etou Lake was not clearly distinguished from other lakes in the same area, the highest MMI value showed that its biological integrity was better than other lakes and the ecosystem was healthier. This may be related to the distribution of the surrounding wetlands. There are many aquatic plants, such as algae and reeds, which build an ecosystem with richer biodiversity and provide a better habitat for macrobenthos.
The MMI value of lakes such as Sihai Lake, Sanwang Lake, Zhenzi Lake, Heiyu Lake, Qianzi Lake, and Hongzi Lake were significantly lower than those of other lakes, and their TLIs were significantly higher compared to other lakes. The TLI of Sihai Lake was not much higher than that of the other lakes because the TP content of the lake was much lower than the other lakes, which were severely disturbed by human activities. However, its TN content was very high, which might be the reason behind its low biological integrity. Qianzi Lake and Hongzi Lake were the two lakes with extremely low biological integrity indexes. Although their TLIs were not significantly higher than those of other lakes severely disturbed by human activities, the TN concentration of Qianzi Lake was significantly higher than that of the other lakes. The TP concentration of Hongzi Lake was also the same—its content was several times high as compared to the lake with the second highest TP concentration. This abnormal water environment index was accompanied by extremely low MMI, which showed very high level of N and P pollution that also had a significant impact on lake macrobenthos, that is, the impact of human disturbance. At the same time, it also proved the research of Odountan et al. (2019) in that it is difficult for a single biological index and water quality physical and chemical index to effectively characterize the combination of multiple disturbances, and therefore the multi-scale method could better assess the ecosystem health [56].
In 2017, the Chinese government initiated the construction of the water supply project in western Jilin Province. The water from Songhuaj River, Nen River, Taoerhe River, and other rivers were introduced into the Chagan Lake ecological zone, Momoge ecological zone, Xianghai ecological zone, and Baluo Lake ecological zone where water resources are scarce and land salinization is serious. However, the project is currently not entirely completed. It can be seen from Figure 1 that the lakes in the study region are all connected by rivers or ditches, however, the impaired lakes’ ditches except that of Sihai Lake did not inject water when the ditches were completed. Therefore, it could be considered that good water circulation will alleviate the adverse effects of eutrophication caused by human activities.
4.4. The Relationship Between MMI Index and Land Use Types Around the Lakes
Among several lakes seriously affected by human disturbance, the MMI value of Sihai Lake, Sanwang Lake, Hongzi Lake, and Zhenzi Lake were similar, while that of Qianzi Lake was significantly lower. From the land use type around the lakes, we were able to see that the human activities around Sihai Lake, Sanwang Lake, Hongzi Lake, and Zhenzi Lake mainly consisted of cultivation and grazing, and there were no large-scale urban and industrial lands. Qianzi Lake is not only surrounded by agricultural land, but there are also four villages and one city. There are many types of urban land that may be the cause of this serious impairment to its ecosystem.
The MMIs and TLIs of Chagan Lake, Yueliang Lake, and Haernao Lake were all at the same level, which indicated that they were very similar in terms of either ecosystem health or water quality. However, Etou Lake and Xinmiao Lake, which had the same TLIs as Chagan Lake, Yueliang Lake, and Haernao Lake, had much higher MMI values and better biological integrity. For Etou Lake, this is because it is located in the core area of the Momoge Wetland, which is an experimental area in a national nature reserve with many wetlands and abundant aquatic plants. The surrounding land use types are wetlands and grasslands. Although the Etou Lake is slightly eutrophic, it still showed high biological integrity and a relatively healthy ecosystem. This indicates that the physical and chemical indicators alone are not sufficient to assess the health of the lake ecosystem. This is one aspect of the MMI that makes it better than other methods of assessment.
5. Conclusions
The research on MMI in the Northeast of China is still in its infancy. Therefore, such studies still need to be improved in terms of the method of collecting macrobenthic samples and improving the applicability of MMI. In the next step, we will explore more macrobenthos collection methods and tools, and try to find a more suitable method for our research region. Due to long-term human activities in the study region, it is difficult to find truly distributed lakes. Most lakes have a certain degree of nutrient enrichment. In the research of MMI around the world, the selected core indicators were different. The same core indicator system has not been found in different regions, and even the most commonly used total number of taxa and the number of EPT taxa were different. This study found that the biomass and diversity of macrobenthos in lake sediments dominated by fine sands and gravels were extremely low and the growth of aquatic vegetation had a positive impact on the biological integrity of macrobenthos. The above results show that a single chemical index or a single point of biological index cannot describe the health of the complex lake ecosystem, which is the superiority of MMI.
The research results showed that MMI could effectively characterize the impact of human disturbance on the macrobenthos community in lakes, thereby reflecting the health of the lake ecosystem, and the results of the test lake inspection MMI also confirmed this conclusion. The degradation of lake ecosystem is affected by many factors, including the surrounding land use type, growth of aquatic plants, and pollution caused by human activities. This study showed that the use of macrobenthos as an assessment tool could effectively assess the health of the lake ecology and identify the strength of human disturbance. However, it could not clearly show the degree of influence by a single factor. It is necessary to continue research in this direction in the future. We will also assess whether the MMI constructed in this study can be applied to lakes in nearby areas with similar geographic conditions, and further improve this model through the accumulation of more data.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.-f.D. and S.-j.S.; methodology, Y.-f.D. and Z.-y.L.; software, Y.-f.D. and Z.-y.L.; validation, Y.-f.D. and J.F.; formal analysis, Y.-f.D.; investigation, Y.-f.D., Z.-y.L., and D.Z.; resources, Y.-f.D., S.-j.S., and P.C.; data curation, Y.-f.D.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.-f.D.; writing—review and editing, S.-j.S., J.F., and Y.-f.D.; visualization, P.C. and D.Z.; supervision, J.F. and S.-j.S.; project administration, Z.-y.L. and P.C.; funding acquisition, S.-j.S. and P.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 31670469.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to the continued use in the next step of the research.
Acknowledgments
I would like to express my gratitude to my graduate tutor for his instruction and help, and to the School of Environment of Northeast Normal University for its support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Appendix A
List of candidate indicators and the process of screening core indicators.
| Metric Type | Candidate Metrics | Normal Distribution | Significant Difference | IQ | More than 1/3 Data were 0 |
| Taxonomic richness | The total number of taxa | Non-normal | YES | 3 | NO |
| The number of pollution-intolerant species taxa | Non-normal | YES | 3 | NO | |
| The number of pollution-tolerant species taxa | Non-normal | YES | 3 | NO | |
| The number of Arthropoda taxa | Non-normal | YES | 1 | - | |
| The number of Mollusca taxa | Normal | YES | 3 | NO | |
| The number of Annelida taxa | Non-normal | NO | - | - | |
| The number of Basommatophora taxa | Non-normal | YES | 3 | NO | |
| The number of Haplotaxida taxa | Non-normal | NO | - | - | |
| The number of Diptera taxa | Non-normal | YES | 2 | YES | |
| The number of Heterostropha taxa | Non-normal | NO | - | - | |
| The number of Mesogastropoda taxa | Non-normal | NO | - | - | |
| The number of Planorbidae taxa | Non-normal | YES | 3 | NO | |
| The number of Lymnaeidae taxa | Non-normal | YES | 3 | YES | |
| The number of Chironomidae taxa | Non-normal | YES | 3 | YES | |
| Community structure composition | % of Chironomidae | Non-normal | YES | 3 | YES |
| % of Lymnaeidae | Non-normal | YES | 3 | YES | |
| % of Planorbidae | Non-normal | NO | - | - | |
| % of Planorbidae + Tubificidae | Non-normal | NO | - | - | |
| % of Planorbidae + Lymnaeidae | Non-normal | NO | - | - | |
| % of Planorbidae + Chironomidae | Non-normal | NO | - | - | |
| % of Planorbidae + Valvatatiea | Non-normal | NO | - | - | |
| % of Haplotaxida | Non-normal | NO | - | - | |
| % of Basommatophora | Non-normal | NO | - | - | |
| % of Diptera | Non-normal | YES | 3 | YES | |
| % of Heterostropha | Non-normal | NO | - | - | |
| % of Mesogastropoda | Non-normal | NO | - | - | |
| % of Basommatophora + Haplotaxida | Non-normal | NO | - | - | |
| % of Basommatophora + Diptera | Non-normal | NO | - | - | |
| % of Basommatophora + Mesogastropoda | Non-normal | NO | - | - | |
| % of Basommatophora + Heterostropha | Non-normal | NO | - | - | |
| % of Diptera + Mesogastropoda | Non-normal | YES | 3 | NO | |
| % of Diptera + Heterostropha | Non-normal | NO | - | - | |
| % of Gastropoda | Non-normal | NO | - | - | |
| % of Oligochaeta | Non-normal | NO | - | - | |
| % of Insecta | Non-normal | NO | - | - | |
| % of Gastropoda + Oligochaeta | Non-normal | NO | - | - | |
| % of Gastropoda + Insecta | Non-normal | NO | - | - | |
| % of Oligochaeta + Insecta | Non-normal | NO | - | - | |
| % of dominant species | Normal | YES | 3 | NO | |
| Biodiversity index | Simpson index | Normal | YES | 3 | NO |
| Shannon–Wiener index | Normal | YES | 3 | NO | |
| Pielou index | Normal | YES | 1 | - | |
| Margalef index | Normal | YES | 3 | NO | |
| Pollution tolerance indicators | % of pollution-intolerant species | Non-normal | YES | 3 | NO |
| Biological monitoring working party (BMWP) | Normal | YES | 3 | NO | |
| Average score per taxon (ASPT) | Normal | YES | 3 | NO | |
| Family biotic index (FBI) | Non-normal | NO | - | - | |
| Biotic index (BI) | Normal | YES | 3 | NO | |
| Feeding function groups | % of SC | Non-normal | NO | - | - |
| % of GC | Non-normal | YES | 3 | YES | |
| % of FC | Non-normal | NO | - | - | |
| % of PR | Non-normal | NO | - | - | |
| % of SC + GC | Non-normal | YES | 1 | - | |
| % of SC + FC | Non-normal | NO | - | - | |
| % of SC + PR | Non-normal | NO | - | - | |
| % of GC + FC | Non-normal | NO | - | - | |
| % of GC + PR | Non-normal | NO | - | - | |
| % of FC + PR | Non-normal | YES | 1 | - |
Appendix B
Lake Information table.
| Lake | Abbreviated Name | Normal Acreage (km2) | Depth (m) | TLI | Aquatic Plant | MMI |
| Etou Lake | Et | 15 | 2.1 | 51.2 | Abundant | 0.86 |
| Haernao Lake | Ha | 33 | 3 | 56.9 | None | 0.50 |
| Yueliang Lake | Yue | 150 | 2.4 | 53.2 | None | 0.53 |
| Heiyu Lake | Hei | 1.5 | 1.8 | 80.4 | None | 0.36 |
| Chagan Lake | Cha | 307 | 4 | 54.6 | None | 0.52 |
| Xinmiao Lake | Xin | 31 | 2.2 | 51.2 | Abundant | 0.73 |
| Hongzi Lake | Hong | 18 | 2.7 | 84.3 | None | 0.19 |
| Qianzi Lake | Qian | 2.4 | 2 | 82.9 | None | 0.11 |
| Zhenzi Lake | Zhen | 3.7 | 2.1 | 76.4 | None | 0.22 |
| Sihai Lake | Si | 9.5 | 2 | 62.4 | None | 0.26 |
| Sanwang Lake | San | 4 | 2.3 | 76.1 | None | 0.26 |
References
- Xie, H.L.; Wang, P.; Huang, H.S. Ecological Risk Assessment of Land Use Change in the Poyang Lake Eco-economic Zone, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 328–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.L.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Zhan, W.; Zhao, S.S.; Dawson, R.W.; Tao, S. An ecosystem health index methodology (EHIM) for lake ecosystem health assessment. Ecol. Model. 2005, 188, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, F. Research on the Degrades Mechanism and the Repairing Theory and Technology for Lake Ecosystem. Ph.D. Thesis, Changan University, Xian, China, August 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, G.; Wan, R. Ecosystem Health Assessment Indictors for Lakes. Resour. Sci. 2014, 36, 1306–1315. [Google Scholar]
- Birk, S.; Bonne, W.; Borja, A.; Brucet, S.; Courrat, A.; Poikane, S.; Solimini, A.; van de Bund, W.V.; Zampoukas, N.; Hering, D. Three hundred ways to assess Europe’s surface waters: An almost complete overview of biological methods to implement the Water Framework Directive. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 18, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HaRa, J.; Mamun, M.; An, K.G. Ecological River Health Assessments Using Chemical Parameter Model and the Index of Biological Integrity Model. Water 2019, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, R.; Wang, Y.; Cai, Y. Aquatic ecological integrity assessment of four large lakes in the middle-to-lower reaches of the Yangtze River, China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 36, 118–126. [Google Scholar]
- Poikane, S.; Ritterbusch, D.; Argillier, C.; Bialokoz, W.; Blabolil, P.; Breine, J.; Jaarsma, N.G.; Krause, T.; Kubecka, J.; Lauridsen, T.L.; et al. Response of fish communities to multiple pressures: Development of a total anthropogenic pressure intensity index. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Hughes, R.M.; Xu, S.; Zhang, J.; Cai, D.; Wang, B. Evaluating performance of macroinvertebrate-based adjusted and unadjusted multi-metric indices (MMI) using multi-season and multi-year samples. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 36, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemm, D.J.; Blocksom, K.A.; Fulk, F.A.; Herlihy, A.T.; Hughes, R.M.; Kaufmann, P.R.; Peck, D.V.; Stoddard, J.L.; Thoeny, W.T.; Griffith, M.B.; et al. Development and evaluation of a Macroinvertebrate Biotic Integrity Index (MBII) for regionally assessing Mid-Atlantic Highlands streams. Environ. Manag. 2003, 31, 656–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakew, A.; Moog, O. A multimetric index based on benthic macroinvertebrates for assessing the ecological status of streams and rivers in central and southeast highlands of Ethiopia. Hydrobiologia 2015, 751, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondy, C.P.; Villeneuve, B.; Archaimbault, V.; Usseglio-Polatera, P. A new macroinvertebrate-based multimetric index (I2M2) to evaluate ecological quality of French wadeable streams fulfilling the WFD demands: A taxonomical and trait approach. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 18, 452–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.R.O.; Herlihy, A.T.; Hughes, R.M.; Callisto, M. An improved macroinvertebrate multimetric index for the assessment of wadeable streams in the neotropical savanna. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 81, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoolmaster, D.R.; Grace, J.B.; Schweiger, E.W. A general theory of multimetric indices and their properties. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2012, 3, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karr, J.R. Assessment of Biotic Integrity Using Fish Communities. Fisheries 1981, 6, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierro, P.; Arismendi, I.; Hughes, R.M.; Valdovinos, C.; Jara-Flores, A. A benthic macroinvertebrate multimetric index for Chilean Mediterranean streams. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 91, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larras, F.; Coulaud, R.; Gautreau, E.; Billoir, E.; Rosebery, J.; Usseglio-Polatera, P. Assessing anthropogenic pressures on streams: A random forest approach based on benthic diatom communities. Sci Total Environ. 2017, 586, 1101–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolding, M.T.; Kraft, A.J.; Robinson, D.T.; Rooney, R.C. Improvements in multi-metric index development using a whole-index approach. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hering, D.; Feld, C.K.; Moog, O.; Ofenböck, T. Cook book for the development of a Multimetric Index for biological condition of aquatic ecosystems: Experiences from the European AQEM and STAR projects and related initiatives. Hydrobiologia 2006, 566, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, R.M.; Kaufmann, P.R.; Herlihy, A.T.; Kincaid, T.M.; Reynolds, L.; Larsen, D.P. A process for developing and evaluating indices of fish assemblage integrity. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1998, 55, 1618–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karr, J.R.; Dudley, D.R. Ecological perspective on water quality goals. Environ. Manag. 1981, 5, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, K.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Z.a.; Wu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B. Application of a benthic index of biotic integrity for the ecosystem health assessment of Lake Taihu. J. Lake Sci. 2014, 26, 74–82. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Q.; Gao, J.; Cai, Y.; Yin, H.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, L.; Huang, J. Development and application of benthic macroinvertebrate-based multimetric indices for the assessment of streams and rivers in the Taihu Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taowu, M.; Qinghui, H.; Hai, W.; Zijian, W.; Chunxia, W.; Shengbiao, H. Selection of benthic macroinvertebrate-based multimetrics and preliminary establishment of biocriteria for the bioassessment of the water quality of Taihu Lake, China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2008, 28, 1192–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cheng, L.; Kong, M.; Li, W.; Gong, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Cai, Y.; Li, K. Utility of a macroinvertebrate-based multimetric index in subtropical shallow lakes. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jingting, G. Dynamic Changes and Driving Forces of Lake Resources in Jilin Province in Recent 20 Years. Master’s Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Leng, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, M.; Li, T.; Liu, X.; Qu, X. Application of The Biological Monitoring Working Party (BMWP) Score System of Macroinvertebrates for River Health In Taizi River Basin. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2016, 25, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Zhang, G.; Wei, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Sun, S. The Evolutional Characteristics ofWater Environment of Chagan LakeWetland. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2014, 34, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano Balderas, E.C.; Grac, C.; Berti-Equille, L.; Armienta Hernandez, M.A. Potential application of macroinvertebrates indices in bioassessment of Mexican streams. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 61, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honglei, L. Water Resource Management and Protection in Momogee Wetland. Master’s Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Long, Z.; Sun, S.; Ou, Y.; Cui, P.; Ran, X. Characteristics of Quality ofWater Enviroment and Macrobenthos Community in the 10 Shallow Lakes inWestern Jilin Province. Wetland Sci. 2018, 16, 642–650. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, D.; Sun, S.; Feng, J.; Long, Z.; Ou, Y.; Cui, P. Distribution Characteristics of Macrobenthos in Chagan Lake and Their Influencing Factors. J. Jilin Agric. Univ. 2019, 41, 365–372. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.W.; Zhang, G.X.; Xu, Y.J.; Chen, S.B.; Wu, Y.F.; Gao, Z.T.; Yu, H.Y. Human Activities and Climate Variability Affecting Inland Water Surface Area in a High Latitude River Basin. Water 2020, 12, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, M.; Cui, L.; Sheng, L.; He, C.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, S. Ecosystem Health Assessment of Momoge Wetland in Jilin. Wetland Sci. Manag. 2016, 12, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Demin, L. Freshwater Biology, 1st ed.; Soochow University Press: Suzhou, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Weiguang, Q. Monitoring Map of Benthic Fauna in Liaohe River Basin, 1st ed.; China Environment Publishing Group: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- China, E.P.A. Methods for Monitoring and Analysis of Water and Wastewater, 4th ed.; China Environment Publishing Group: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, R.M.; Larsen, D.P.; Omernik, J.M.J.E.M. Regional reference sites: A method for assessing stream potentials. Environ. Manag. 1986, 10, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M. Evaluate method and classification standard on lake eutrophication. Environ. Monit. China 2002, 18, 47–49. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, K.L.; Wu, H.T.; Xue, Z.S.; Lu, X.G.; Batzer, D.P. Development of a multi-metric index based on aquatic invertebrates to assess floodplain wetland condition. Hydrobiologia 2019, 827, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hering, D.; Moog, O.; Sandin, L.; Verdonschot, P.F.M. Overview and application of the AQEM assessment system. Hydrobiologia 2004, 516, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Lin, K.; Zhu, Y.; Xia, Y.; Liu, L. Development and Applicability Analysis of Benthic-Macroinvertebrate Index of Biotic Integrity in the Songhua River Basin. Environ. Monit. China 2019, 35, 20–30. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, F.; Yu, R.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, M. Application of excel in calculation of biodiversity indices. Marine Sci. 2012, 36, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Cai, K.; Yu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, S.; Xie, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jin, X.; Wang, B. Establishment of Chinese Macroinvertebrate Score Index and Water Quality Boundary. Environ. Monit. China 2018, 34, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeybek, M.; Kalyoncu, H.; Karakas, B.; Ozgul, S. The use of BMWP and ASPT indices for evaluation of water quality according to macroinvertebrates in Degirmendere Stream (Isparta, Turkey). Turk. J. Zool. 2014, 38, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, S.-W.; Qu, X.-D.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, K.-D. Comparison and application of biological indices of macroinvertebrates in river health assessment. Huan jing ke xue Huanjing kexue 2012, 33, 2281–2287. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Ding, S.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, X.; Wang, S.; Lin, J. Effects of Land Use on Macroinvertebrate Functional Feeding Groups in Taizi River Basin. Res. Environ. Sci. 2018, 31, 1527–1536. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Wu, D.; Zhang, J.; Yin, X.; Zhao, C.; Dou, T. Diversity and temporal-spatial dynamics of macroinvertebrate functional feeding groups in the rivers of the Jinan Region. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 7128–7139. [Google Scholar]
- Barbour, M.T.; Gerritsen, J.; Snyder, B.D.; Stribling, J.B. Rapid Bioassessment Protocols Foruse in Streams and Wadable Rivers: Periphyton, Benthic Invertebrates and Fish; US Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water: Washington, DC, USA, 1999.
- Mereta, S.T.; Boets, P.; De Meester, L.; Goethals, P.L.M. Development of a multimetric index based on benthic macroinvertebrates for the assessment of natural wetlands in Southwest Ethiopia. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 29, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoddard, J.L.; Herlihy, A.T.; Peck, D.V.; Hughes, R.M.; Whittier, T.R.; Tarquinio, E. A process for creating multimetric indices for large-scale aquatic surveys. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2008, 27, 878–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, Y.C.; Won, D.H.; Lee, S.H.; Kong, D.S.; Hwang, S.J. A multimetric benthic macroinvertebrate index for the assessment of stream biotic integrity in Korea. Int J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 3599–3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.B.S.; Baptista, D.F.; Mugnai, R.; Castro, C.M.; Hughes, R.M. Towards rapid bioassessment of wadeable streams in Brazil: Development of the Guapiacu-Macau Multimetric Index (GMMI) based on benthic. Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 1584–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fengxia, Z.; Jianhong, C. Freshwater Microbiome and Benthic Fauna Map, 2nd ed.; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Tianyi, Z.; Xindong, W.; Jianwei, D. Analysis on Water Quality Changes in Chagan Lake. China Resour. Compr. Utiliz. 2015, 33, 56–61. [Google Scholar]
- Odountan, O.H.; de Bisthoven, L.J.; Abou, Y.; Eggermont, H. Biomonitoring of lakes using macroinvertebrates: Recommended indices and metrics for use in West Africa and developing countries. Hydrobiologia 2019, 826, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miler, O.; Porst, G.; McGoff, E.; Pilotto, F.; Donohue, L.; Jurca, T.; Solimini, A.; Sandin, L.; Irvine, K.; Aroviita, J.; et al. Morphological alterations of lake shores in Europe: A multimetric ecological assessment approach using benthic macroinvertebrates. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 34, 398–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellucci, C.J.; Becker, M.E.; Beauchene, M.; Dunbar, L.J.E.M. Classifying the Health of Connecticut Streams Using Benthic Macroinvertebrates with Implications for Water Management. Environ. Manag. 2013, 51, 1274–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangle, L.U.; Haitao, W.U.; Xianguo, L.U.; Qiang, G.; Zhanyan, C.J.W.E. Health Assessment of Marsh Wetlands in the Sanjiang Plain Using Index of Biotic Integrity of Aquatic Invertebrates. Wetl. Sci. 2017, 15, 670–679. [Google Scholar]
- Shull, D.R.; Smith, Z.M.; Selckmann, G.M. Development of a benthic macroinvertebrate multimetric index for large semiwadeable rivers in the Mid-Atlantic region of the USA. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, H.; Li, L.; Huang, D.; Tian, Q.; Chen, X.; Gong, Z.; Li, H. Macrozoobenthic community structure and bioassessment of water quality in Lake Dongting, China. J. Lake Sci. 2016, 28, 395–404. [Google Scholar]
- Frouin, P. Effects of anthropogenic disturbances of tropical soft-bottom benthic communities. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 194, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Gallego, L.; Meerhoff, E.; Clemente, J.M.; Conde, D. Can ephemeral proliferations of submerged macrophytes influence zoobenthos and water quality in coastal lagoons? Hydrobiologia 2010, 646, 253–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).