Abstract
Waterborne diseases have become one of the major public health concerns worldwide. This study is aimed to investigate and develop spatial distribution mapping of the potable water quality parameters in the city of Peshawar, Pakistan. A total of 108 water samples collected across the entire study area were subjected to physio-chemical and biological analyses. Tested parameters included pH, turbidity, temperature, fluoride concentration levels, and bacterial counts (faecal coliforms). Inverse distance weighting (IDW) interpolation in geographic information systems (GIS) was used for spatial analysis. Test results revealed that 48% of water samples had faecal coliforms count (per 100 mL) greater than World Health Organization (WHO) minimum limits, while 31% of samples had fluoride concentrations in excess of the WHO maximum guide values. Spatial distribution mapping was developed for faecal coliforms count and fluoride ion concentration using ArcGIS to highlight the high-risk settlements in the study area. Results showed that around 20% area under faecal coliforms and approximately 33% area based on fluoride concentrations fall under the need for treatment category. The pH and turbidity were found in compliance with WHO desirable limits. The sanitary inspection score significantly depicted that ineffective multi-barrier approaches consequently deteriorated the water quality at the consumer’s end. Findings from the present study shall be useful to policymakers for adopting necessary remedial measures before it severely affects public health.
1. Introduction
Water consumed by humans must be free from pathogenic micro-organisms and chemicals that might be harmful to health. Access to potable water is a prerequisite for health, an integral part of fundamental human rights, and effective health protection policies [1]. The potable water quality concerning physical, biological, and chemical properties are considered to be major health controlling factors [2]. Many previous studies have shown that land use/cover is a key factor affecting water quality pollution [3,4,5,6,7]. Globally, about 780 million people do not have access to safe drinking water, and 2.5 billion people do not have access to improved sanitation [8]. Access to safe drinking water ensures better community health and ultimately supports the economic growth in a community. Water used for drinking purposes is mainly derived from surface sources or aquifers near the ground surface near to vast water body reserves. However, accessibility to potable water reserves has become a global challenge [9]. Significant socio-economic consequences suffer from the use of contaminated water in the form of various diseases, including dysentery, hepatitis A, polio, vibriosis, typhoid fever, and Escherichia coli infections leading to increased medical cost [10,11]. Previous studies suggest that the implementation of suitable low-cost household water treatment systems could dramatically reduce several waterborne diseases [12,13,14]. Although waterborne outbreaks have been declining significantly since early 1900, the global burden of waterborne infectious diseases is still considerable [15].
Waterborne diseases are primarily caused by contaminated water, causing various types of diarrheal diseases, such as cholera and dysentery. Diarrhea is the principal cause of death in children, accounting for about 8% of the total deaths of children under the age of 5 years resulting in over 1300 child fatalities every day worldwide [16,17]. It is estimated that nearly 60% of deaths that occur globally from diarrhea are due to the utilization of deteriorated drinking water and lack of hygiene (personal, domestic, and environmental) and sanitation [18]. Studies suggest that waterborne diseases account for over 2.2 million annual deaths worldwide and also cause a substantial economic loss worth nearly 12 billion USD globally [15,19]. In Pakistan, about 40% of diseases prevalent in the country are waterborne, and 20–40% hospitalizations are due to waterborne diseases [20]. The same study also reported that poor drinking water quality is responsible for over 50% of all the diseases and almost 40% of the total deaths Lack of potable water supplies is a significant concern in urban as well as rural areas in Pakistan [21]. Further, it is also reported that about one-hundred million cases of diarrheal cases (related to poor water quality) are registered in the country every year [22], which is an alarming situation. The key drivers for deteriorating drinking water quality in the country include exponential growth in population, rapid industrialization, increased municipal sewage, lack of water quality monitoring at treatment plants, and lack of appropriate water disinfection [20,23].
In developing countries, rapid growth in population has deteriorated the drinking water quality, leaving the majority of the population with low access to safe drinking water [24]. In Pakistan, potable water is mostly supplied via a pipe network [25]. It is estimated that by 2025 the national population will increase from 141 million to 221 million and the water consumption will decrease from 5600 cubic meters to 1000 cubic meters per annum [26].
Although the vast majority of health-related water quality problems are the result of bacteriological contamination, chemical contamination of water sources can also cause serious health problems. For example, the presence of nitrate and nitrite in water may result from the excessive application of fertilizers or from seepage of wastewater into surface water and groundwater. Fluorosis is a common problem caused by exposure to high levels of naturally occurring fluoride in the water, which can lead to mottling of children’s teeth skeletal fluorosis and crippling. Tahir et al. [27] conducted a comprehensive study to explore the fluoride toxicity in surface and groundwater sources in 16 major cities, across all the four provinces in Pakistan. It was found that Baluchistan (22%) had the highest fluoride contamination, followed by Punjab (19%). It was also reported that a high concentration of fluoride in water supplies was prevalent in areas having frequent rocks weathering, excessive runoff and filtrations, as well as areas having relatively more volcanic particles deposition from the atmosphere. Khan et al. [28] examined the presence of fluoride in water in Lahore city and noted excessive fluoride concentrations/levels in the city’s water. National authorities in developing countries consider that a safe supply of water at a consumer end is one of their primary focuses. Opinya et al. [29] reported that both high and low fluoride ions concentration in water is the leading cause of dental fluorosis.
Recently, geostatistical technologies have smartly reduced the efforts and complexities involved in assessing the condition of natural resources and their environmental impacts [30,31]. A geographic information system (GIS) could provide smart solutions for various problems related to water availability and its quality assessment. Nelly and Muta used the Kriging interpolation method in ArcMap to obtain the groundwater quality index in Kenya [32]. The study revealed that there is a significant correlation between groundwater quality and land use. The contamination of groundwater is mainly attributed to anthropogenic or natural causes [33]. Castro et al. conducted a detailed study to explore the spatio-temporal variation of water quality governing processes for water samples collected from karst aquifer in the city of Yucatan, Mexico [34]. Results of hierarchical cluster analysis showed that spatio-temporal variability of groundwater collected in the study is mainly caused by factors, such as the high proportion of sulfates in groundwater, seawater intrusion, rocks–water interactions, and various anthropogenic activities. Pande and Moharir developed spatial distributing maps based on the interpolation tool in ArcGIS for examining the groundwater quality in the districts of Akola and Buldhana Maharashtra, India [35]. Water samples were randomly selected from 35 wells and tested for different parameters, such as total dissolved solids (TDS), Cl, Mg, pH, and electrical resistance. The study demonstrated the applicability of proposed methods and reports that approximately 80% of groundwater surveyed was suitable for drinking purposes.
The assertion of potable water quality deterioration, owing to the faecal contamination and high concentration of fluoride concentration in other parts of the country, had earlier been noted by several researchers who revealed that the potable water quality is highly impaired [22,36,37,38,39,40,41]. However, none of these researchers developed water quality maps of faecal coliform and fluoride concentration. It is also evident from existing literature that geospatial analysis could provide reliable insights on water quality monitoring and qualitative classification for any particular locality. The importance of the reference water quality data in this study was considered to be due to the spreading diarrhea outbreak and the increasing trend of children’s teeth skeletal fluorosis in District Peshawar. Therefore, the objective of this study was to analyze the potable water quality and to identify areas of waterborne diarrheal and fluorosis risks. This will have important implications for future safe drinking water supply project development and will be useful to policymakers by taking the necessary remedial measures before it affects the people’s health.
2. Study Area and Data Collection
2.1. Study Area
Peshawar is the capital city of the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan, located in a broad valley near the eastern end of historic Khyber Pass, close to the border with Afghanistan. The area is situated between 44°15′ and 34°15′ north latitude; 71°22′ and 71°42′ east longitude. The city has a total area of 1257 km2 and a population of approximately two million [42]. The city’s main source of drinking water is derived from groundwater supplies. It has a semi-arid climate. Rainfall mostly occurs in monsoon seasons (July and August). The city area is divided to four tentative zones/towns. Figure 1 presents the study area in its entirety.
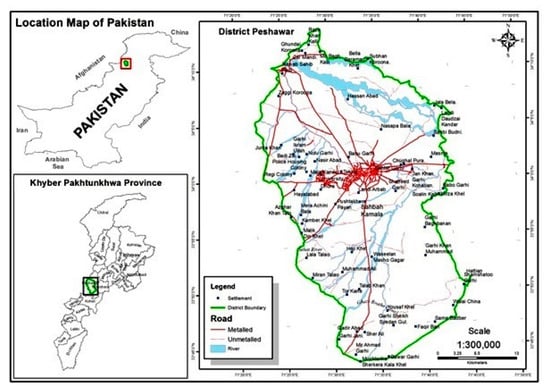
Figure 1.
Location map of study area, Peshawar.
2.2. Sampling and Data Collection
A total of 108 water samples were collected in sterilized sample bags of 120 mL capacity from tube wells, boreholes, and household pipe networks across the study area from May to June 2018. This study was initiated in response to an unusual outbreak of diarrheal cases and an alarming number of child’s tooth skeletal fluorosis cases at the start of summer during the same year. It was intended to simulate water quality across different regions in the study area to identify high-risk zones based on water quality for the subsequent short-term urgent action plan. Samples were randomly selected throughout the study area. Standard stated methods and procedures were adopted during sample collection and subsequent analysis was performed for different water quality parameters tests [43].
Sanitary surveys are a comprehensive inspection of the entire water delivery system from the source to the mouth and are, therefore, the best means of identifying potential problems and changes in the quality of drinking water. They play a fundamental role in ensuring that consistent and safe drinking water supply is provided to the community by identifying and correcting any deficiencies in the system and helping to identify public health risks related to drinking water. A sanitary survey or inspection is a relatively simple technique that depends on gathering information, principally by observation, and also by making inquiries. The two critical elements that one should focus on are the water source (its physical components, protection, and condition of any associated structures) and the use of water at home. A sanitary inspection score survey was also carried out that qualitatively ranged from 0–10 during sample water samples to identify potential risk factors associated with water samples. The form of the questionnaire used in this study is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Sanitary inspection survey questionnaire example.
2.3. Parameters Tested
Water samples were examined for various physio-chemical and biological parameters, i.e., pH, turbidity, temperature, faecal coliforms count, and fluoride ion concentration levels using Wagtech field kit. Parameters such as pH, turbidity, and temperature were examined owing to the significance in the chlorination process of the potable water, while faecal coliforms indicate the presence and absence of pathogenic bacteria. The presence of faecal coliforms in the aquatic environment indicates that water is contaminated by animal and/or human feces. Table 2 illustrates the parameters tested, the methods used to measure these parameters, and their detection limits.

Table 2.
Water quality parameters and testing methods.
3. Methods
The inverse distance weighted (IDW) interpolation method was adopted for water quality assessment and mapping. The IDW method has been most commonly used by many researchers owing to its robustness [44]. Potable water quality characteristics values were measured by surrounding an unmeasured site that has been utilized for the forecast of potable water quality values in the study area. Predictions by this deterministic method are based on a linear combination of weights at known points for estimating the unknown point values [45]. The general mathematical expression of IDW is given by Equation (1):
where zx is the concentration at an unknown location x, zi are the concentrations at the measured locations i, di is the distance from x to i, and p is the power by which the distance is weighted.
IDW relies primarily on the inverse of the distance raised to mathematical power. The power parameter controls the importance of known points on the interpolated values based on their distance from the output point. It is a positive, real number, and its default value is 2. With a variable search radius, the number of points used in calculating the value of the interpolated cell is specified, which makes the radius distance vary for each interpolated cell, depending on how far it has to search around each interpolated cell to reach the specified number of input points. Thus, some neighborhoods will be small, and others will be large, depending on the density of the measured points near the interpolated cell. In this study, the search radius setting consists of 12 points and the default value of maximum distance is the length of the extent’s diagonal with output cell size is 142.893. IDW may exhibit a “bull’s-eye effect” phenomenon that is considered one of the criticisms of the method, which may lead to significantly misleading results, particularly in mountainous terrain. However, for current the study area has almost level terrain, and we have taken a good number of water samples spatially well distributed in an attempt to minimize the estimation errors caused by IDW bull’s-eye effect. More details about IDW methods in GIS may be found in [46,47].
The sampling positions were recorded as latitude and longitude data in degrees, minutes, and seconds (DMS) format. GPS was used to determine the exact coordinates of sample points/stations. Data were converted into decimal degrees for all sampling points and sorted in Microsoft Excel (2016) (Microsoft Corporation, Washington, US) and exported as text files. In the spatial analyst tool, IDW, a raster interpolation in GIS software was used for data analysis. IDW is an algorithm-based technique to interpolate data spatially between known measurements. IDW implies a deterministic method that yields and estimates the neighboring values by averaging the values of the sample surrounding data points. The method provides a continuous surface between the observed data points. The principle of IDW is that the closer a measured point is to the center of the cell being estimated, the more influence or weight it has in the averaging process. IDW provides more accurate predictions when the data points are adequately dense to indicate the local variations. In this study, faecal coliforms count and fluoride concentrations were interpolated, and raster maps of the study area were created using IDW-based analysis in ArcGIS (version 10.5). The software was acquired from its manufacturer and developers Environmental System Research Institute (ERSI) headquartered in Redlands, California, in the US.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Bacteriological Parameter-Faecal Coliforms
Faecal coliforms were used as indicator bacteria to evaluate bacteriological contamination of drinking water supplies. Results reveled that tubewell and borehole water were found safe as represented in Figure 2, while water samples collected from household pipe network showed that 35% of samples had microbial values within World Health Organization (WHO) desirable limits (see Figure 2). Similarly, for the household pipe network, approximately 57% of the samples matched the World Health Organization (WHO) fluoride guide values. Boreholes were the second deteriorated source as far as fluoride concentration is concerned, with 64% of samples within the guide value. Whereas all the samples tested for the microbial parameter from boreholes and tube wells were deemed microbially safe, as per the WHO guide values.
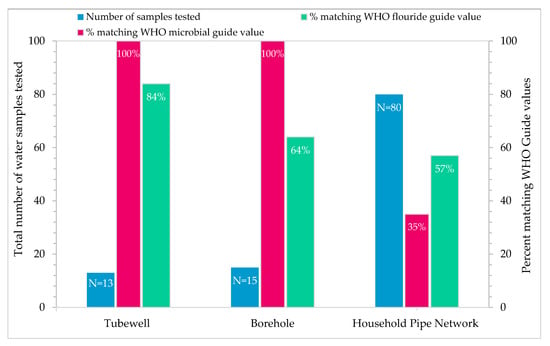
Figure 2.
Potable water quality sample test results.
The sanitary inspection score shown in Figure 3 that suggested that 56 water samples were at very low, 17 water samples were at medium, and 35 were at high health risk categories. Most settlements had water supply lines laid side by side or in close proximity with the main drain without considerable provisions for an adequate safe distance. The absence of water quality monitoring and surveillance programs in the study area, legal framework, and poor institutional arrangements for quality testing issues have eventually exacerbated the situation.
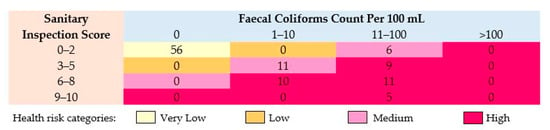
Figure 3.
Health risk categories for faecal coliforms for examining the potable water quality of the study area.
It was noted that the tube well and borehole water samples were found free from faecal contamination. All tube wells and boreholes had properly well sanitary completion structures. Table 3 shows that the count range of faecal coliforms was from 0 to 48 (mean: 7.5 ± 11.3) per 100 mL and the corresponding coefficient of variance (COV) was 1.5.

Table 3.
Descriptive statistics of potable water quality parameters.
The grading standard of water quality parameters presented in Table 4 is based on environmental engineering judgment, and expert experience in the field is illustrated. The presence of faecal contamination is an indication of potential health risk for individuals drinking this water. It indicates that 11% of the area is in guideline compliment, 69% of the area is the intolerable region, and 20% of the total area is cursory with respect to faecal coliform count. Results in Table 4 show the three grades of faecal coliform count that are guidelines compliment, tolerable region, and need for a treatment region.

Table 4.
Grading standard for potable water quality parameter.
The spatial distribution of faecal coliforms map of district Peshawar is shown in Figure 4, which is a ready reference guide for identification of the vulnerable community-based faecal coliform counts per 100 mL. It may be noted from Figure 4 that different settlements, including Sadder, Babu Garhi, Landi Arbab, Tehkal, Pushtakhera Payan, and Garhi Baghbanan were prone to high counts of faecal coliforms, indicating a high health risk compared to sanitary score. Samples collected in these settlements indicated a high vulnerability of community health and warranted immediate treatment and attention from the concerned authorities. A study previously conducted by Naeem et al. also augmented similar findings for samples collected from most of these areas, where water supply lines are laid closely with sewerage lines and had a high coliform count [48]. The Pakistan Council of Research in Water Resources (PCRWR) analysis report also highlighted that 62% of the samples in Peshawar were microbiologically contaminated [49]. Further, a study recently conducted by Mohapatra Laxmipriya also demonstrated the adequacy of IDW method for water quality mapping (for faecal coliform and other physio-chemical parameters) in the district of Odisha, India [44].
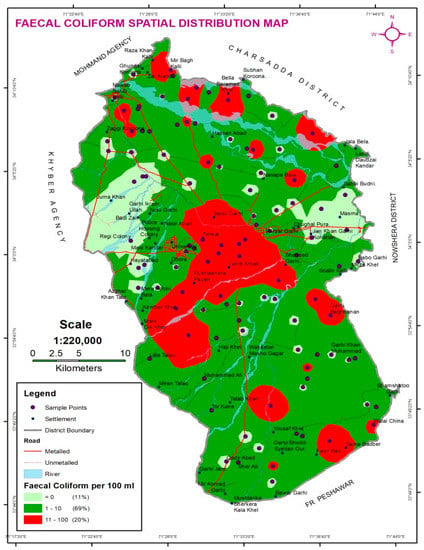
Figure 4.
Faecal coliforms spatial distribution map of Peshawar.
4.2. Physico-Chemical Parameters
Results from physio-chemical parameters analysis are shown in Table 4. Determination of pH, temperature, and turbidity of all the water samples was evaluated owing to the effectiveness of the chlorination process. pH and turbidity values of all the collected water samples complied with the World Health Organization (WHO) guide values. Temperature and pH are the primarily significant parameters that have inverse relationships with the reduction of residual chlorine levels in water distribution networks [50]. WHO has proposed no health base guide values for the pH of potable water. There is no direct effect of potable water pH on human health, but there are few indirect health effects that cause further water quality characteristics to change, for instance, metal solubility and pathogen existence rate [51]. Higher values of pH, above 8.5 of the potable water, are not appropriate for an efficient chlorination process, while lesser values, i.e., less than 6.5, favor corrosion in the water supply network and household plumbing system.
In the study area, fluoride ion concentrations level ranged from 0.1 to 2.5 mg/L (mean: 1.03 ± 0.69 mg/L) with COV 0.67 (Table 3). Table 4 results show that the 33 water samples are less than 0.5 mg/L, 41 water samples are in 0.5–1.5 mg/L, and 34 water samples are high concentrations of fluoride greater than 1.5 mg/L covering 17%, 68%, and 16% area, respectively, in Peshawar. The results of fluoride concenrtrations from Figure 2 indicate that the tubewell (84%), borehole (64%), and household pipe network (57%) water samples were found in the range of WHO permissiable limit. Spatial distribution mapping of fluoride concentrations (shown in Figure 5) level highlighted the settlements having low, medium, and higher fluoride concentrations. Less concentration of fluoride ingestion is also a probable risk factor in considering fluoride loss in bones. A previous study has examined the applicability of different interpolation-based spatial distribution methods for capturing groundwater quality based on fluoride ion concentration and other important variables [52]. Generally, the most favorable fluoride concentration in potable water for dental health is ranged from 0.5–1.5 mg/L and depended on the consumption of potable water and other sources of intake and exposure. Sufficiently high and low fluoride concentrations could affect fluorosis prevalence. Mostly, fluoride found naturally in groundwater is produced by the decomposition of rocks and soil by weathering action. Fluoride may also come from surface runoff and infiltration of fertilizers in agricultural areas, sewage system discharges, and industrial wastewater. Pakistan is an agricultural country, and the annual agricultural sector consumes 96% of its total water resources. In the past 30 years, the country’s fertilizer consumption has increased by triple. The amount of nutrients utilized (in million of tons) were increased by over 200% between 1980/1981 and 2002/2003, which is one of the significant factors in the increase of fluoride contamination [53]. Fluoride in potable water accelerates the risk of hip joint fractures in women because the indication for fluoride might be related to certain gender-dependent mechanisms [54]. During sampling, it has been observed the possible signs and symptoms in a few individuals of communities, including bones and dental fluorosis, which are most likely due to excessive fluoride concentration in their drinking water.
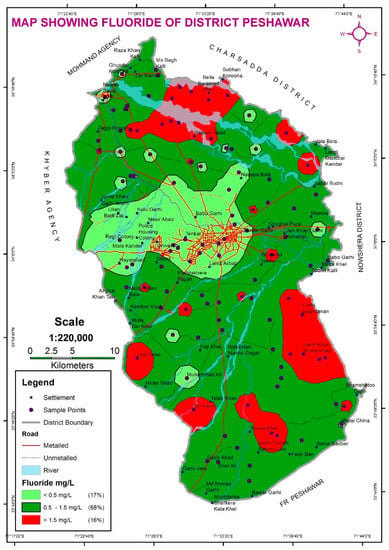
Figure 5.
Fluoride concentration levels spatial distribution map of Peshawar.
5. Conclusions
This study aimed to investigate spatial variability of potable water quality parameters using GIS-based spatial interpolation analysis in the city of Peshawar, Pakistan. Different physio-chemical and bacteriological assessement were conducted for examining water quality parameters like pH, turbidity, faecal coliform, and fluoride ion concentration. Water quality test results obtained during the study were compared to the World Health Organization (WHO) guide values to identify risk parameters and the potential for improvement. Spatial distribution maps were also developed for faecal coliform and fluoride ion concentration to highlight areas prone to a different level of risk category. The present study found that both physio-chemical parameters, pH, and turbidity of all water samples collected were below the WHO permissible limits, while deteriorated bacteriological water quality was primarily observed at the household pipe network. The sanitary inspection score survey concluded that the risk to health category was medium to high, which was mainly due to a lack of drainage systems, old rusted water supply pipes, and placement water supply pipes nearby the main drain. The lack of drinking water quality monitoring programs in the study area, the absence of a legal framework, and the poor institutional arrangements for potable water quality issues have exacerbated the situation. Water samples collected from tube wells and boreholes were found well within the WHO guide values. Deteriorated potable water quality was observed in the household piped network. All tube wells and boreholes in the study area were provided with proper sanitary completion structures. Faecal coliforms bacteria were the main contributor to water contamination. However, individual settlements had an unbalanced concentration of fluorides. The spatial distributions of faecal coliforms count, and fluoride concentrations guided in the identification of the potentially vulnerable community with respect to the deteriorated water quality characteristics. The developed spatial distribution maps provided useful insights for water quality in the study area. The findings of this study could provide useful guidance to policymakers and others concerned to adopt suitable preventative measures to restore water quality before it becomes disastrous to the public’s health in the city. It would also support the national authorities in strengthening its monitoring and surveillance efforts of safe access to the drinking water.
In future studies, it is recommended to consider more water quality parameters, such as chlorides, suspended and dissolved solids, and heavy metals. Similarly, it would be interesting to see the effect of agriculture contaminations, such as nitrates, etc. The applicability of other methods, such as geographically and temporally weighted regression (WTGR), could be sought in future studies. Studies could also focus on the characterization of industrial effluents and their reclamation. Finally, the current study could be extended to other provincial cities.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.A., X.-W.T., and M.A.A.-S.; methodology, M.A., A.J., and H.M.A.-A.; software, M.A. and F.A.; validation, A.J., H.M.A., and M.A.A.-S.; formal analysis, M.A., A.J. and H.M.A.-A.; investigation, M.A., A.J., and F.A.; resources, H.M.A.-A., X.-W.T., and M.A.A.-S.; data curation, M.A. and A.J.; writing—original draft preparation, M.A. and A.J.; writing—review and editing, M.A., A.J., and H.M.A.; visualization, M.A.A.-S. and F.A.; supervision, X.-W.T., M.A.A.-S., and H.M.A.-A.; project administration, X.-W.T. and H.M.A.-A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The work presented in this paper was part of the research sponsored by the National Key Research and Development Plan of China under Grant No. 2016YFE0200100 and the Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 51639002.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge and appreciate the support provided by King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals (KFUPM).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- World Health Organization. W.H.O Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: First Addendum to the Fourth Edition; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kazi, T.G.; Arain, M.B.; Jamali, M.K.; Jalbani, N.; Afridi, H.I.; Sarfraz, R.A.; Baig, J.A.; Shah, A.Q. Assessment of water quality of polluted lake using multivariate statistical techniques: A case study. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2009, 72, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, F. Effects of land use/cover on surface water pollution based on remote sensing and 3D-EEM fluorescence data in the Jinghe Oasis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Li, P.; Lu, K.; Tantai, Z.; Zhang, J.; Ren, Z.; Wang, X.; Yu, K.; Shi, P.; Cheng, Y. Seasonal changes in water quality and its main influencing factors in the Dan River basin. Catena 2019, 173, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgoglione, A.; Gregorio, J.; Ríos, A.; Alonso, J.; Chreties, C.; Fossati, M. Influence of Land Use/Land Cover on Surface-Water Quality of Santa Lucía River, Uruguay. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakather, O.Y.; Fard, A.K.; Ihsanullah; Khraisheh, M.; Nasser, M.S.; Atieh, M.A. Enhanced Adsorption of Selenium Ions from Aqueous Solution Using Iron Oxide Impregnated Carbon Nanotubes. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2017, 2017, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmaly, H.A.; Abussaud, B.; Saleh, T.A.; Bukhari, A.A.; Laoui, T.; Shemsi, A.M.; Gupta, V.K.; Atieh, M.A. Evaluation of micro- and nano-carbon-based adsorbents for the removal of phenol from aqueous solutions. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2015, 97, 1164–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Global Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene WASH. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/healthywater/global/ (assessed on 11 May 2019).
- Bartram, J.; Brocklehurst, C.; Fisher, M.B.; Luyendijk, R.; Hossain, R.; Wardlaw, T.; Gordon, B. Global monitoring of water supply and sanitation: History, methods and future challenges. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 8137–8165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, E.M.; Gerhard, M.I.; Zanella, M.S.; Bogo, M.; Scapin, D.; Oro, D. Assessment of microbiological quality of water wells in rural properties of the city of West of Santa Catarina, Brazil. Resour. Environ. 2012, 2, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsin, M.; Safdar, S.; Asghar, F.; Jamal, F. Assessment of drinking water quality and its impact on residents health in Bahawalpur city. Int. J. Humanit. Soc. Sci. 2013, 3, 114–128. [Google Scholar]
- Moropeng, R.C.; Budeli, P.; Mpenyana-Monyatsi, L.; Momba, M.N.B. Dramatic reduction in diarrhoeal diseases through implementation of cost-effective household drinking water treatment systems in Makwane Village, Limpopo Province, South Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzenbach, R.P.; Egli, T.; Hofstetter, T.B.; Von Gunten, U.; Wehrli, B. Global water pollution and human health. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2010, 35, 109–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartram, J.; Cairncross, S. Hygiene, sanitation, and water: Forgotten foundations of health. PLoS Med. 2010, 7, e1000367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Castillo, F.Y.; Loera-Muro, A.; Jacques, M.; Garneau, P.; Avelar-González, F.J.; Harel, J.; Guerrero-Barrera, A.L. Waterborne pathogens: Detection methods and challenges. Pathogens 2015, 4, 307–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochoa, T.J.; Salazar-Lindo, E.; Cleary, T.G. Management of Children with Infection-Associated Persistent Diarrhea. In Proceedings of the Seminars in Pediatric Infectious Diseases; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; Volume 15, pp. 229–236. [Google Scholar]
- Aliabadi, N.; Pham, H.; Curns, A.T.; Rha, B.; Tate, J.E.; Parashar, U.D. Diarrhea-Associated Mortality in Children Less Than 5 Years of Age in the United States, 2005–2016. Pediatric Infect. Dis. J. 2019, 38, e153–e154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diarrhoea Remains a Leading Killer of Young Children, Despite the Availability of a Simple Treatment Solution The United Nations Children’s Fund, UNICEF. Available online: https://data.unicef.org/topic/child-health/diarrhoeal-disease/ (assessed on 17 May 2019).
- Alhamlan, F.S.; Al-Qahtani, A.A.; Al-Ahdal, M.N. Recommended advanced techniques for waterborne pathogen detection in developing countries. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2015, 9, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daud, M.K.; Nafees, M.; Ali, S.; Rizwan, M.; Bajwa, R.A.; Shakoor, M.B.; Arshad, M.U.; Chatha, S.A.S.; Deeba, F.; Murad, W.; et al. Drinking Water Quality Status and Contamination in Pakistan. BioMed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 7908183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeba, F.; Abbas, N.; Butt, M.; Irfan, M. Ground water quality of selected areas of Punjab and Sind Provinces, Pakistan: Chemical and microbiological aspects. Ground water quality of selected areas of Punjab and Sind Provinces, Pakistan: Chemical and microbiological aspects. Chem. Int. 2019, 5, 241–246. [Google Scholar]
- Shahid, S.U.; Iqbal, J.; Khan, S.J. A comprehensive assessment of spatial interpolation methods for the groundwater quality evaluation of Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan. NUST J. Eng. Sci. 2017, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, U.; Batool, A.; Ghufran, M.A. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in the drinking water of muzaffarabad, Azad Jammu and Kashmir, Pakistan. Int. J. Hydro. 2019, 3, 331–337. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.H.; Xia, J. Barriers to sustainable water-quality management. J. Environ. Manag. 2001, 61, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Planning, Development and Reform Pakistan Millennium Development Goals Report; Planning Commission: Islamabad, Pakistan, 2013; pp. 1–195.
- Ali, A.; Intikhab, A.Q.; Shawar, D. Low-Cost filter for flood affected areas of Pakistan. Electron. J. Environ. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 10, 2945–2950. [Google Scholar]
- Tahir, M.A.; Rasheed, H. Fluoride in the drinking water of Pakistan and the possible risk of crippling fluorosis. Drink. Water Eng. Sci. Discuss. 2012, 5, 495–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyaz, A.K.; Whelton, H.; O’Mullane, D. A map of natural fluoride in drinking water in Pakistan. Int. Dent. J. 2002, 52, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opinya, G.N.; Pameijer, C.H.; Gron, P. Analysis of Kenyan drinking water. East Afr. Med. J. 1987, 64, 194–201. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H. Spatial analysis of water quality trends in the Han River basin, South Korea. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3285–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Kazama, F. Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: A case study of the Fuji river basin, Japan. Environ. Model. Softw. 2007, 22, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheronomelly, K.; Mutua, F. Groundwater quality assessment using GIS and remote sensing: A case study of Juja location, Kenya. Am. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2016, 5, 12–23. [Google Scholar]
- Programme, U.N.D. Human Development Report 2006: Beyond Scarcity: Power, Poverty and the Global Water Crisis; Palgrave Macmillan: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Pacheco Castro, R.; Pacheco Ávila, J.; Ye, M.; Cabrera Sansores, A. Groundwater quality: Analysis of its temporal and spatial variability in a karst aquifer. Groundwater 2018, 56, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pande, C.B.; Moharir, K. Spatial analysis of groundwater quality mapping in hard rock area in the Akola and Buldhana districts of Maharashtra, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, M.S.; Nasir, A.; Rashid, H.; Shah, S.H.H. Spatial variability and long-term analysis of groundwater quality of Faisalabad industrial zone. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 3197–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleem, M.; Shun, C.J.; Li, C.; Aslam, A.M.; Yang, W.; Nawaz, M.I.; Ahmed, W.S.; Buttar, N.A. Evaluation of groundwater quality in the vicinity of Khurrianwala industrial zone, Pakistan. Water 2018, 10, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, S.; Ali, A.; Ullah, S. Spatial assessment of water quality parameters in Jhelum city (Pakistan). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, Y.; Dilawar, A.; Ullah, S.F.; Akhter, G.; Martinez-Carvajal, H.; Hussain, M.B.; Aslam, A.Q. Modelling the spatial distribution of arsenic in water and its correlation with public health, central Indus Basin, Pakistan. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2016, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ahmad, M.; Ahmad, N.; Rahman, Z.U.; Ali, S. Bacteriological Assessment of the Potable Water Quality in the Urban Informal Settlement Centers of District Bannu, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. In Proceedings of the First International Conference on “Emerging Trends in Engineering, Management and Scineces” (ICETEMS-2014), Peshawar, Pakistan, 28–30 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, M.; Ahmad, N. Potable water quality characteristics of the rural areas of District Hangu, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa-Pakistan. Int. J. Multidiscip. Sci. Eng. 2012, 3, 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, J. Peshawar: Oldest living City in South Asia. Dawn 2018. Available online: https://www.dawn.com/news/880603/peshawar-oldest-living-city-in-south-asia (accessed on 10 May 2020).
- Clesceri, L.S. Standard Methods: For the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Pollution Control Federation, American Public Health Ass: Washington, WA, USA, 1998; ISBN 978-0-87553-235-6. [Google Scholar]
- Mohapatra, L. Spatio-Temporal Analysis and Modelling of Water Quality in Mahanadi River Basin. Ph.D. Thesis, The National Institute of Technology, Rourkela, Odisha, India, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- ESRI, ArcGIS 10.5. Using ArcGIS Spatial Analyst; Software User Guide ESRI: Redlands, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zahid, M.; Chen, Y.; Khan, S.; Jamal, A.; Ijaz, M.; Ahmed, T. Predicting Risky and Aggressive Driving Behavior among Taxi Drivers: Do Spatio-Temporal Attributes Matter. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, M.; Chen, Y.; Jamal, A.; Al-Ahmadi, H.M.; Al-Ofi, A.K. Adopting Machine Learning and Spatial Analysis Techniques for Driver Risk Assessment: Insights from a Case Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, M.; Danish, Z.; Sufian, M.; Saleem, W. Bacteriological analysis of drinking water in urban areas of district Peshawar, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 25, 107–109. [Google Scholar]
- Kahlown, M.A.; Tahir, M.A.; Rasheed, H. Water Quality Status of Pakistan; Pakistan Council of Research in Water Resources (PCRWR): Islamabad, Pakistan, 2007.
- Liu, B.; Reckhow, D.A.; Li, Y. A two-site chlorine decay model for the combined effects of pH, water distribution temperature and in-home heating profiles using differential evolution. Water Res. 2014, 53, 47–57. [Google Scholar]
- Zabed, H.; Suely, A.; Faruq, G.; Sahu, J.N. Water quality assessment of an unusual ritual well in Bangladesh and impact of mass bathing on this quality. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fertilizer Use by Crop in Pakistan, Land and Plant Nutrition Management Service, Land and Water Development Division; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2004.
- Arif, M.; Hussain, I.; Hussain, J.; Sharma, M.K.; Kumar, S.; Bhati, G. GIS-Based inverse distance weighting spatial interpolation technique for fluoride distribution in south west part of Nagaur district, Rajasthan. Cogent Environ. Sci. 2015, 1, 1038944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurttio, P.; Gustavsson, N.; Vartiainen, T.; Pekkanen, J. Exposure to natural fluoride in well water and hip fracture: A cohort analysis in Finland. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1999, 150, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).