Abstract
The concept of the Water–Energy–Food nexus (WEF), as documented by the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), suggests that the three resources are thoroughly interrelated, shaping a complicated web of interlinkages. Perceiving the three commodities as an interdependent variable system, rather than isolated subsystems is a step towards a more holistic approach, and thus a prerequisite to introducing a sustainable scheme for better managing resources. In this work, the well-documented WEF nexus is broadened to a five-dimensional nexus, also involving land use and climate. A methodology for drawing the interrelations among the five dimensions and unreeling the complicated system of direct and indirect interlinkages is given. The intensity of interlinkages among nexus components is initially assessed through a three-point typology with interlinkage scoring corresponding to resource use in Greece. The typology is used and is further expanded to quantify successfully all interlinkages among nexus components with a proposed heuristic algorithm. Results are used to create the cross-interlinkage matrix that identifies food as the most influencing resource and water as the resource mostly influenced by other nexus elements. Results show that indirect interlinkages of multiple resources can be very significant and should not be ignored when planning nexus-coherent policy initiatives and investments in different sectors, in order to promote resource efficiency.
1. Introduction
Even though the idea of holistic management of natural resources is old, the complex interrelations among different resources are not yet well characterized. As a result of this, developing and implementing such an integrated approach is hindered [1]. Subsequently, a challenge related to the management of one of the resources, such as energy, is often linked to other resources, such as water. Inclusive and holistic management of different resources in respect to the nexus concept should be introduced to boost resource efficiency and diminish environmental threats and ecological deterioration [2]. Although few decades have passed since the nexus idea was introduced in the sustainable management glossary, it has mainly gained the attention of scientists and policy makers mostly in the last couple of decades [3], particularly regarding the interconnections in the Water–Energy nexus and Water–Energy–Food (WEF) Nexus [4], which become crucial as the stresses of overpopulation and climate change are intensified. Recently, the nexus has been broadened to also involve other dimensions [5], resources and/or disciplines, such as soil, land use, climate, waste, ecosystems, health, and others, forming an even more multi-dimensional and multidisciplinary concept. Innovative means, such as serious games, participatory processes, and bottom up approaches are introduced to make the nexus more tangible and usable by policy makers and citizens [6]. Sustainable growth, circular economy, and efficient resource management issues are at the core of a nexus approach. As resources are thoroughly interlinked, and the exploitation of one often sets the prerequisite of the abundance of another (e.g., energy production needs water and food production needs energy and water), resource management involves multiple interdependencies and conflicts within the nexus web. This research introduces a simulation approach for these interlinkages and aspires to establish a clear methodology for ranking these interdependencies as an introductory phase to assessing the nexus. Depending on how many nexus dimensions are involved, such an analysis can grow complex and even chaotic at times; therefore, a methodology that assesses the complexity of interlinkages within the nexus is required. In this article, we highlight the complex interdependencies that are created within the resource nexus. Furthermore, we show that one sector’s priorities depend on how targets of other sectors are achieved. It is postulated that considering systemic effects provides an insightful understanding of the internal dynamics and better defines what the hierarchy of targets in investments or policies should be to enhance resource efficiency. To this effect, we propose a heuristic algorithm that quantifies the intensity of interlinkages among all nexus components, taking into account both direct and indirect interrelationships, while at the same time, highlighting the complexity of these interlinkages. This algorithm ranks nexus components and should help policy makers prioritize policy initiatives in different sectors. The algorithm is implemented for the case of Greece providing interlinkage scores for all resources comprising the nexus.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Nexus Interlinkages
Water, energy, food, land use and climate, the five nexus components as defined in [7] are linked to one another, through numerous direct or indirect interrelations (Figure 1a). A direct interconnection between two variables (e.g., land use and water) is defined as the effect in a variable’s status (e.g., water), generated by a change in the other variable’s status (e.g., land use), assuming that all other components (e.g., food, energy, or climate) remained unchangeable and did not affect the state of the two variables. Indicatively, for the aforementioned example, a change in land use (ΔL), such as a shift into agricultural land, will cause a shift in water (ΔW), by increasing agricultural water demand. This is one of multiple direct paths through which a shift in land use would cause a shift in water. The sum of the direct pathways of ΔL to ΔW is referred to as the land–water direct interlinkage and is denoted as L→W, or simpler as LW; it comprises all the ways that a change in land use is expected to affect water (including water quantity, quality, location, etc.). It should be noted that, for the basis of this research, each direct pathway is unique and the opposite direction interlinkage is a different one; thus, LW is not the same to WL. The second refers to the effect that a shift in water can cause in land use, for example desertification caused by water scarcity, which is totally different. Respective to these definitions, the unique direct interlinkages of the nexus components are twenty in total. Those twenty interconnections are illustrated in Figure 1b and listed below:
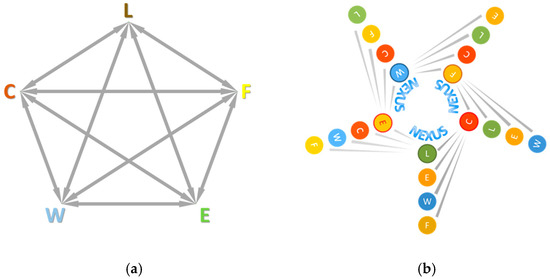
Figure 1.
(a) Nexus component interlinkages, showing all interrelations between different nexus components; (b) Schematic of nexus component interlinkages, showing how each one of the five nexus components relate to the other four.
- Water: WF, WC, WL, WE
- Energy: EW, EC, EF, EL
- Land Use: LE, LC, LW, LF
- Climate: CL, CE, CW, CF
- Food: FC, FL, FE, FW
The direct interconnections defined in the previous paragraph are perceived as first-order interlinkages. Apart from these twenty direct interconnections, one nexus variable may also affect another through indirect pathways. This implies that a shift in one component can cause an effect to a second variable, which in turn can cause a shift in a third one. To denote higher-order interconnections, three-, four- and five-letter notations were used, regarding to how many variables were interacting. For example, to present the effects caused to energy by an initial change in land use, through water, the LWE notation is used. This is a second-order interlinkage. Similarly, Energy → Climate → Food → Water (ECFW) is a third-order interlinkage and Food → Climate → Energy → Land Use → Water (FCELW) is a fourth-order pathway. An indicative case of a fourth-order indirect pathway is that of FLWEC: A rise in food production will typically lead to an increase in agricultural land. Such a shift in land use would require more agricultural water. In turn, this may cause an increase in energy demand for transferring, pumping, or treating water. Then, this effect will be more intense if irrigation is supplied by groundwater and pumping depths increase. Energy consumption increase results in an increase in greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, which implies a change in climate, especially if energy is dependent on fossil fuels. It is noteworthy that in indirect interlinkages, such as the interlinkage of F to C in FLWEC, the intermediate one-to-one interlinkages that are taken into account to construct the indirect pathway (such as FL in FLWEC, LW in FLWEC, WE in FLWEC, and EC in FLWEC) are all direct. For a more in-depth analysis of this, the reader is referred to [7].
For drawing and counting the multiple different interlinked pathways of all orders, the nexus tree was designed for one nexus dimension at the time (the water nexus tree is showcased as an example in Figure 2, showing all possible direct and indirect interlinkages of water). The nexus tree is a graphic representation of all alternative paths that lead to various changes generated by a single shift in one of the nexus elements. An initial virtual shift in the central nexus component (water in this example) caused corresponding shifts in the rest of the components through the nexus tree branches. In particular, for the water nexus tree depicted in Figure 2, firstly the four first-order interlinkages (WC, WE, WF and WL) were drawn as branches, showing how a single shift in water affected all the other dimensions. Drawing the second-order interlinkages, three branches were generated out of each one of the four nexus variables (C, E, F, and L), since the interconnection with water was already drawn (first-order connection). Therefore, from climate we get CE, CF, and CL; from energy we get EC, EF, and EL; from food we get FC FE, and FL and from land use we get LC, LE, and LF. Moving out to the third level, we get two branches out of each nexus variable, and finally at the fourth level, a single branch formed out of each nexus variable. This way, it was ensured that each path, when followed from the route to the end as it branched out, was not repeating a nexus component but had a unique sequence of the five nexus variables. Twenty-four unique sequences in total are depicted in the nexus tree of Figure 2, which shows water at the center; these are the following: WCLFE, WCELF, WCFLE, WCFEL, WCLEF, WELFC, WCEFL, WECLF, WEFLC, WEFCL, WELCF, WFLEC, WECFL, WFCLE, WFELC, WFECL, WFLCE, WLFEC, WFCEL, WLCFE, WLEFC, WLECF, WLFCE, WLCEF. Equivalent trees can be designed for the rest of the nexus components at their centers, giving a total number of 24 × 5 = 120 unique fourth-order sequences for the whole nexus web.
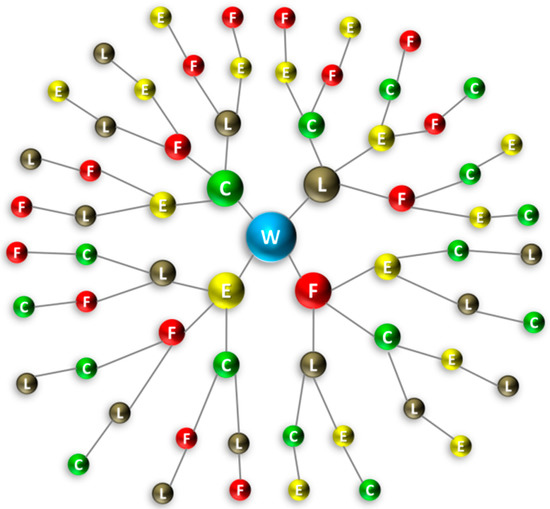
Figure 2.
A nexus tree for Water showing the formation of all 24 unique fourth-order interlinkages. Similar trees can be created for all five nexus dimensions (W = Water, E = Energy, F = Food, L = Land Use, C = Climate), creating a total of 120 unique fourth-order interlinkages for the five-dimensional nexus. Color representation for nexus tree nodes are as follows: Water = blue; Energy = yellow; Food = red; Land = brown; Climate = green.
Following this framework, one can define all pathways that can lead to a change in one nexus component because of a change in another. In this article, we present, with the following example, how a shift in water can affect land use, using the nexus tree: We firstly create all first-, second-, third-, and fourth-order links with water as a starting nexus component and land use as the final. This is depicted in Figure 3, in which the nexus tree depicted in Figure 2 is repeated, having erased all branches or branch parts that terminate in land use. This results to a sum of 16 paths: WL, WEL, WFL, WCL, WEFL, WECL, WFEL, WFCL, WCEL, WCFL, WEFCL, WECFL, WFECL, WFCEL, WCEFL, and WCFEL and includes all direct and indirect pathways though which a shift in water can cause a shift in land use. Following the schematic simulation approach presented above, all paths can actually be assessed. Therefore, the total influence that a shift in water will have on land use will be the conceptual sum of all direct and indirect interlinkages, as depicted below. Naturally, most high-order interlinkages may turn out to not be significant and may eventually drop out, allowing for the most important ones to shape up the total influence that water has on land use. A Table that lists all pathways for all nexus variables following the nexus tree approach is included in the Appendix in [7].
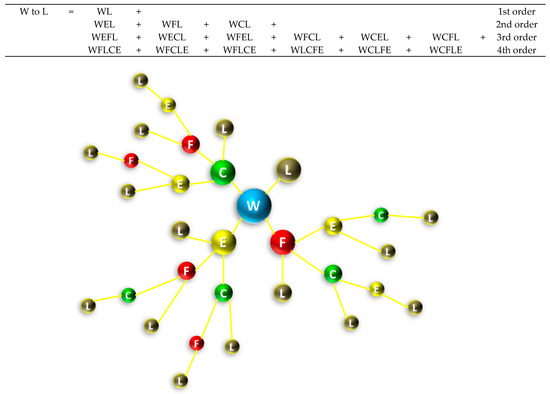
Figure 3.
Nexus tree for water to land use, showing the formation of all 16 direct and indirect pathways by which a change in water can bring about a change in land use. Color representation for nexus tree nodes are as follows: Water = blue; Energy = yellow; Food = red; Land = brown; Climate = green.
2.2. Scoring System
To proceed with quantitative modeling of nexus interrelations, an interlinkage scoring system was developed and was used for the implementation of a heuristic algorithm. To determine the interaction score, a conceptualization of interactions was used, concentrating on keeping it simple, without having to make many assumptions and introducing uncertainty. A three-point typology was used to rank the intensity of interlinkages within the resource nexus: All direct first-order interlinkages were characterized as “strong”, “weak”, or “negligible”. This initial assessment of the interlinkages was a result of information obtained from the literature, supplemented by consultations with experts and stakeholders and was created as a specific assessment of the national case study of Greece, explored in SIM4NEXUS project [8]. Other than the literature search, expert consultation was done as follows: In the framework of SIM4NEXUS, a series of experts (project partners) with specialized expertise on all nexus elements (water, energy, food, land use and climate) contributed towards the preparation of a document [9], that lists and describes all twenty first-order interlinkages. At least 3 different experts were consulted for each interlinkage, making this document a comprehensive list of ways that resources interact with each other and a powerful source of information for characterizing the interlinkages appropriately. In addition, stakeholder consultation was done through the stakeholder workshops organized in the framework of SIM4NEXUS for the case study of Greece. The process started with creating lists of relevant stakeholders and then contacting them for one-to-one interviews in order to record which interlinkages they identified as important and why. Stakeholder workshops were also organized bringing everyone together for nexus-relevant discussions and presentations on the progress made within the project, in order to address their needs and concerns. Stakeholders include Ministers and other policy-makers, farmer associations, regional and local authorities, representatives from the industry, water utilities, the banking sector, legal representatives, NGOs, and citizen organizations.
In many cases, the data mapped in different sectors for Greece were used to justify the score. In Table 1, all unique direct interlinkages are listed with a corresponding “strong”, “weak”, and “negligible” influence and an explanation on why this score was assigned to the specific interlinkage. Similar qualitative assessments of influences that resulted in scoring systems are presented elsewhere [10]. The resulting direct interlinkages of all five nexus components are shown in a schematic form in Figure 4.

Table 1.
Scoring table with interlinkage scores and corresponding explanations for Greece.
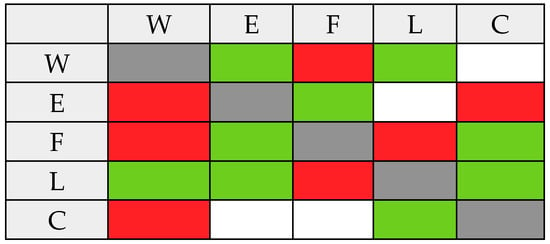
Figure 4.
Schematic representation of interlinkages among all five nexus components. Green represents a “weak” interlinkage, red represents a “strong” interlinkage and white stands for “negligible” interlinkages. Influencing nexus components are shown in the columns and influenced nexus components are shown in the rows. W = Water; E = Energy; F = Food; L = Land Use; C = Climate.
2.3. The Heuristic Algorithm: The Nexus Tree Graph
This heuristic algorithm is only used to calculate the influence of higher-order (indirect) interlinkages. Direct interlinkages are assigned a value of 60 if “strong”, a value of 30 if “weak”, and 0 if “negligible”. Only strong and weak interlinkages are mapped on the graph, while negligible interlinkages are eliminated completely and are not shown at all. Initial nodes (n0) are assigned the value of 20 (c0 = 20). To proceed from the initial node to a higher-order node (n0 to n1, n1 to n2, or ni to ni+1, where i is the number of nodes in a path, ranging from 0 to 4), we follow the edge that links the two nodes and calculate the value of the higher-order node as follows:
where, β takes the value of , if the interlinkage is classified as “weak” and , if the interlinkage is classified as strong.
The graph is solved starting from the initial node and working through the different paths, until all paths have been scanned. The influence of each indirect interlinkage path is the value of its final node, as it is calculated when equation 1 was solved. For example, according to the graph shown in Figure 3, one would have to work through all second-, third- and fourth-order paths, a total of 15 paths. In each case, the contribution of each path to the total W to L influence would be the value of the last L node, and the total score of the total W to L interlinkage would be the sum of all final path node values plus the first-order interlinkage, which is scored separately. To ensure that there is no double counting, the algorithm only allows a change to the value of each node once, so once a node obtains a value, this is the value it keeps, even if it is involved in various “paths” in the tree.
The algorithm is a heuristic and it was set up in such a way so as to take into account both the order and strength of interlinkages. Therefore, a path with a strong first-order interlinkage and a weak second-order interlinkage gives a higher score than a path with a weak first-order interlinkage and a strong second-order interlinkage. Moreover, the further away we move from the initial node, the smaller the influence. Therefore, at no time do we have a fourth-order path giving a higher influence score than a third-order path, since fourth-order paths are longer and their influence on the initial node is weakened.
3. Results and Discussion
The nexus tree approach constitutes a method for depicting the chain of interlinkages and can be a useful tool for modelers as a step-by-step approach to take into account all interlinkages, direct and indirect, so that no indirect relationship is left out, when considering the whole convoluted tree of effects. Nexus trees are shown in Figure 5 for all 20 interlinkages that link all nexus elements with one another, for the case of Greece. These nexus trees start from the initial structure, which is analogous to the one shown in Figure 3 for WL, and take into account the scoring system shown in Table 1: When an interlinkage is “strong”, it is shown as a red line; when it is weak, it is shown as a black line and when it is “negligible”, the whole branch is eliminated. We see that some trees are simpler than others; e.g., CL is a simple tree with relatively few nodes and paths, while WC and FW are quite complex with multiple nodes, links and interactions. The heuristic is applied to all trees, considering first-, second-, third- and fourth-order interlinkages; trees are worked from the central node outwards and scores of indirect (higher-order) interlinkages are obtained, thus quantifying the intensity of their relationship. The interlinkage scores obtained from the application of the heuristic for all twenty interlinkages are shown underneath each tree and are included in a cross-interlinkage matrix in Figure 6. It should be noted that interlinkage scores should only be seen qualitatively and in comparative terms, i.e., in order to compare the relative influence among nexus components. Besides, the values have no physical meaning.
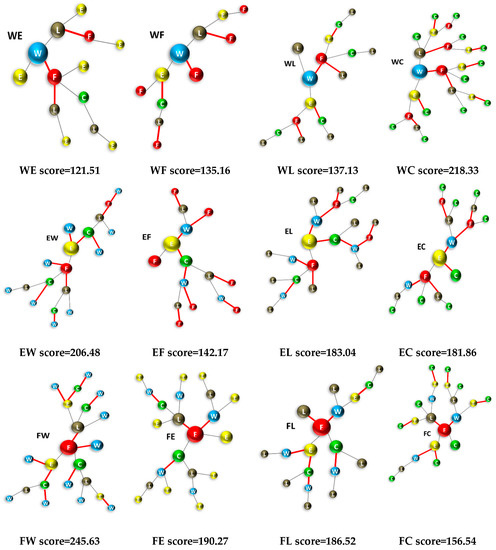
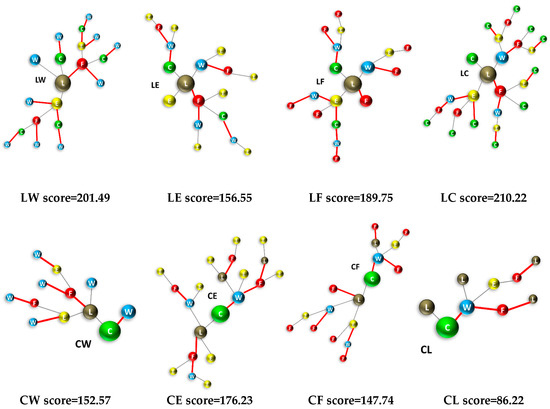
Figure 5.
Nexus trees for all interlinkages among all five nexus elements, showing the extent of interactions for the 20 nexus interlinkages. Red lines represent “strong” interlinkages, while black lines represent “weak” interlinkages. Total interlinkage scores are written under each tree. Color representation for nexus tree nodes are as follows: Water = blue; Energy = yellow; Food = red; Land = brown; Climate = green.
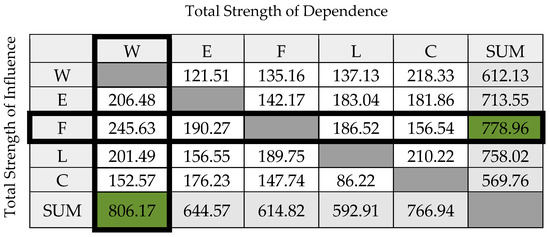
Figure 6.
Cross-interlinkage matrix of five nexus components and their interactions for Greece. The total strength of interlinkage from a nexus component on all other nexus components is shown by the row-sum and the column-sum shows how much a nexus component is influenced by all other nexus components in total. Highest row- and column-sums are marked in green. W = Water; E = Energy; F = Food; L = Land Use; C = Climate.
From the cross-interlinkage matrix (Figure 6), we see that out of all nexus elements, food is the one with the highest influence on all other nexus elements (highest of all row-sums). When it comes to prioritizing investments or interventions, policy-makers should give special attention to food strategies due to their systemic effect on other resources, since this analysis shows that food highly influences all other nexus dimensions. This can be seen as a synergistic effect on the other sectors, making the achievement of targets in other sectors easier, if focus is placed on improving food, through efficient production, for example. A high row-sum signifies a strong effect on the other interconnected nexus sectors, but not necessarily a positive one. Therefore, an inefficiently managed food sector will strongly influence other sectors in a negative way through their direct and indirect interlinkages. On the other hand, the most vulnerable of all nexus elements, or the one mostly influenced by other nexus components is water (highest column-sum). A high-column sum indicates that this resource is strongly influenced by others, so recording progress and achieving targets in this sector strongly depends on the other nexus components. These results are reasonable for Greece, a country that has serious water scarcity issues, with the largest percentage of water being used by agriculture for food production. It provides evidence for facts that most stakeholders agree upon—that water is a really vulnerable resource in the Mediterranean, and agriculture is the sector that needs to see the most improvements. However, it also highlights the fact that if a systemic view of all sectors is not taken, water will have difficulty in achieving its targets, since it is so strongly influenced by the other sectors and the cross-sectoral policies and strategies.
The information included in the cross-interlinkage matrix is also depicted in Figure 7 and Figure 8, where nexus elements are listed separately in ranking order, depending on whether they influence other nexus elements (Figure 7) or are influenced by nexus elements (Figure 8). Interlinkage scores obtained from the application of the heuristic for all 20 interlinkages are also shown in the chart of Figure 9, in which both direct (first-order) and indirect (higher-order) interlinkage scores are shown. We see that the strongest total interlinkage is the one of food to water (FW), while the highest indirect interlinkage score is that of Water to Climate (WC). In fact, the water to climate (WC) pair has the second highest total interlinkage score, signifying that the impact of water on climate is strong, even though the direct relationship is classified as “negligible” according to Table 1. This is supported by the fact that the WC nexus tree (Figure 5) is complex with many nodes and high-order paths, which results in the high indirect score. The results in Figure 8 provide evidence that the nexus tree heuristic algorithm is important and reveals the fact that indirect interlinkages may play a prominent role in the overall interlinkage strength and should not be either ignored or underestimated. A nexus analysis that does not acknowledge the significance of indirect interlinkages and only focuses on direct relationships will lead to erroneous results. Most nexus analyses, however, would only focus on direct interlinkages, completely by-passing the effect of a series of indirect relationships that can, after all, play an important role.
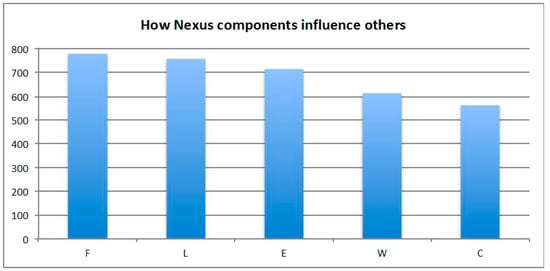
Figure 7.
Nexus components and influence scores showing how nexus components influence others.
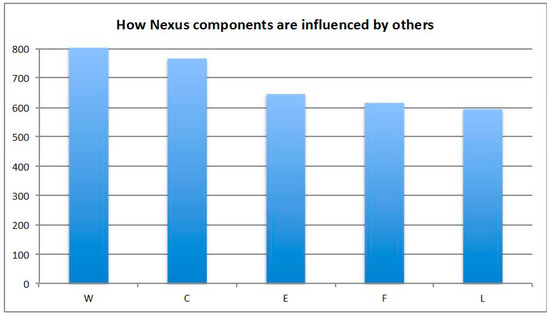
Figure 8.
Nexus components and influence scores showing how nexus components are influenced by others.
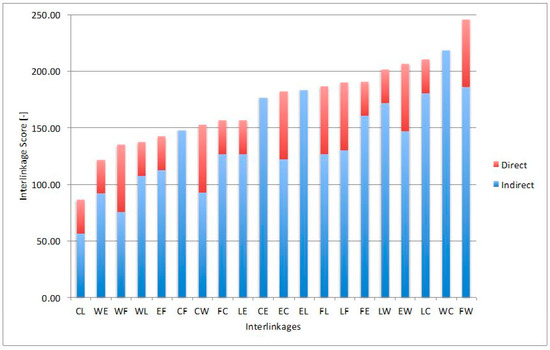
Figure 9.
Quantified interlinkages between all twenty nexus element pairs. Interlinkages are shown as the sum of direct (first-order) and indirect (higher-order). The following notation applies: W = Water; E = Energy; F = Food; L = Land; C = Climate.
4. Conclusions
In this article, a practical heuristic approach for gaining a systemic and contextual perspective on nexus component interlinkages is presented, by building on a simple three-point typology of interactions. The approach is simple and can be applied in any case study a nexus analysis is pursued, regardless of data availability. The approach is systemic since it enables a structured way to document and encode interconnectedness between resource nexus components. Furthermore, it provides a methodology for deriving system-wide effects from the initial understanding of interlinkages. Naturally, the potential weakness of this approach is that the quality of the analysis strongly depends on the scoring of interactions entered into the cross-interlinkage matrix, so the methodology is vulnerable to wrong or deficient scores. This methodology is only illustrative, since it is based on a scoring system obtained for Greece through a combination of expert and stakeholder consultations, the literature and available data for the country. The basic strength of the approach is that it provides a tool to support policy making and to encourage stakeholders to think about cross-sectoral implications of single-sector strategies. Furthermore, it gives them a tool to quantify the impacts of such strategies to other sectors and to prioritize investments and policy interventions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.S.L., D.K. and N.M.; Methodology, C.S.L., D.K. and N.M.; Validation, N.M. and C.S.L.; Formal Analysis, C.S.L., N.M. and D.K.; Writing-Original Draft Preparation, C.S.L.; Writing-Review & Editing, D.K.; Visualization, D.K. and N.M.; Supervision, C.S.L.; Project Administration, C.S.L.; Funding Acquisition, C.S.L.
Funding
The work described in this paper has been conducted within the project SIM4NEXUS. This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under Grant Agreement No. 689150 SIM4NEXUS. This paper and the content included in it do not represent the opinion of the European Union, and the European Union is not responsible for any use that might be made of its content.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Brouwer, F.; Giampietro, M.; Anzaldi, G.; Blanko, M.; Bukkens, S.; Castro, B.; Domingo, X.; Fournier, M.; Funtowicz, S.; Kovacic, Z.; et al. The nexus: Efficient approaches. Pan Eur. Netw. Sci. Technol. 2017, 25, 274–277. [Google Scholar]
- Brouwer, F.; Avgerinopoulos, G.; Fazekas, D.; Laspidou, C.; Mercure, J.F.; Pollitt, H.; Pereira Ramos, E.; Howells, M. Energy modelling and the nexus concept. Energy Strategy Rev. 2018, 19, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoff, H. Understanding the Nexus. In The Water, Energy and Food Security Nexus, Proceedings of the Bonn2011 Conference, Bonn, Germany, 16–18 November 2011; Stockholm Environment Institute (SEI): Stockholm, Sweden, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). The Water-Energy-Food Nexus: A New Approach in Support of Food Security and Sustainable Agriculture; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2014; Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/a-bl496e.pdf (accessed on 26 March 2018).
- Avellan, T.; Roidt, M.; Emmer, A.; von Koerber, J.; Schneider, P.; Raber, W. Making the Water-Soil-Waste Nexus Work: Framing the Boundaries of Resource Flows. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susnik, J.; Chew, C.; Domingo, X.; Mereu, S.; Trabucco, A.; Evans, B.; Vamvakeridou-Lyroudia, L.; Savic, D.A.; Laspidou, C.; Brouwer, F. Multi-Stakeholder Development of a Serious Game to Explore the Water-Energy-Food-Land-Climate Nexus: The SIM4NEXUS Approach. Water 2018, 10, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laspidou, C.S.; Kofinas, D.T.; Mellios, N.K.; Witmer, M. Modelling the Water – Energy – Food – Land Use – Climate Nexus: The Nexus Tree Approach. Proceedings 2018, 2, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SIM4NEXUS. Available online: https://sim4nexus.eu/ (accessed on 30 March 2018).
- Laspidou, C.; Mellios, N.; Kofinas, D.; Papadopoulou, M.; Papadimitriou, T.; Ganoulis, P.; Janse, J.; Pokorny, J.; Teutschbein, C.; Conradt, T.; et al. Deliverable 1.1: Scientific Inventory of the Nexus, 2017, SIM4NEXUS Project. Available online: https://www.sim4nexus.eu/userfiles/Deliverables/D1.1%20Final%20submitted%20v03.pdf (accessed on 27 November 2018).
- Weitz, N.; Carlsen, H.; Nilsson, M.; Skanberg, K. Towards systemic and contextual priority setting for implementing the 2030 Agenda. Sustain. Sci. 2018, 13, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrens, P.; van Vilet, M.T.H.; Nanninga, T.; Walsh, B.; Rodrigues, J.F.D. Climate change and the vulnerability of electricity generation to water stress in the European Union. Nat. Energy 2017, 2, 17114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUROSTAT Statistics Explained: Water Statistics. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php/Water_statistics (accessed on 27 November 2018).
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).