Abstract
Moisture transport from its sources to surrounding continents is one of the most relevant topics in hydrology, and its role in extreme events is crucial for understanding several processes such as intense precipitation and flooding. In this study, we considered the Mediterranean Sea as the main water source and estimated its contribution to the monthly climatological and extreme precipitation events over the surrounding continental areas. To assess the effect of the Mediterranean Sea on precipitation, we used the Multi-Source Weighted-Ensemble Precipitation (MSWEP) database to characterize precipitation. The Lagrangian dispersion model known as FLEXPART was used to estimate the moisture contribution of this source. This contribution was estimated by tracking particles that leave the Mediterranean basin monthly and then calculating water loss (E − P < 0) over the continental region, which was modelled by FLEXPART. The analysis was conducted using data from 1980 to 2015 with a spatial resolution of 0.25°. The results showed that, in general, the spatial pattern of the Mediterranean source’s contribution to precipitation, unlike climatology, is similar during extreme precipitation years in the regions under study. However, while the Mediterranean Sea is usually not an important source of climatological precipitation for some European regions, it is a significant source during extreme precipitation years.
1. Introduction
Moisture transport from oceans to continents, precipitation, and evaporation are important elements in the hydrological cycle [1]. The connection between evaporation and precipitation on the planet is of great interest to present day meteorologists and hydrologists because of the importance of water resources on the quality of human life [2].
The reasons for precipitation in certain areas versus others may be explained through the presence of one (or more) of these factors: (i) the moisture already present in the atmosphere over the concerned areas, (ii) the transport of moisture by winds from another region, or (iii) moisture recycling. When we study each area over a longer period of time, we find that the contribution of the first source is low. We can, therefore, say that the two major sources of moisture that are responsible for precipitation in a region are advection and local evaporation [3].
Changes in global precipitation and in other categories of precipitation are significant for evaluating global climate change and its impacts. According to some studies, high precipitation events at present show an increasing trend in intensity and/or frequency [4,5]. Extreme events (such as droughts, floods, and landslides) and their changes in frequency and intensity as well as changes in the water cycle lead to major economic losses and human fatalities including in the Mediterranean area, which we study in this paper [6]. In addition, analysis of extreme precipitation trends and changes in water transport from the Mediterranean basin to different areas of the neighbouring continents is relevant for evaluating and predicting high precipitation events.
The Mediterranean region is very important for many sectors and has a huge impact on human life, natural processes, and the availability of water for different purposes [3] especially in Africa, Asia, and Europe [7]. Knowledge of the Mediterranean hydrological cycle and its variability may have a positive effect on the quality of human life in the Mediterranean area and increase socioeconomic benefits to this area.
1.1. Area in Study: The Mediterranean Region
The area of the Mediterranean basin or the Mediterranean area can be determined by considering the countries surrounding the Mediterranean Sea as well as the sea itself. The Mediterranean basin spans 3800 km east to west from the tip of Portugal to the shores of Lebanon and 1000 km north to south from Italy to Morocco and Libya, which have an area of 2.5 million km2 and an average depth of 1500 m. The climate of the Mediterranean varies by geographic location, but, in general, it is characterized by hot, dry summers and wet, cool winters, which follows a traditional climate classification [8]. The mountainous terrain (the highest peak in the Alps are 4800 m high) around the Mediterranean basin (see Figure 1) has a significant impact on the climate and meteorology in the region. Moreover, the complex land-sea distribution with many islands, peninsulas, and inner seas around the basin [9] makes the region an interesting area in terms of meteorology since it determines important consequences in the atmospheric circulation and is the reason for many sub-regional and mesoscale characteristics.
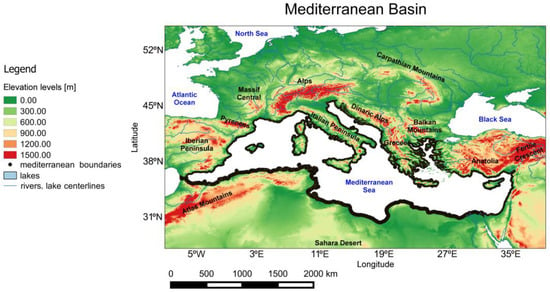
Figure 1.
The black line contour indicates the area of the Mediterranean basin. The green-red colored portions represent elevation levels in meters (m). Data is taken from the HydroSHEDS project (Hydrological data and maps based on shuttle elevation derivatives at multiple scales (available online at https://hydrosheds.cr.usgs.gov).
The most significant characteristic of the Mediterranean region is its position between the subtropics and the mid-latitudes, which means it is affected by the regimes of both zones [10]. Some typical mid-latitude variability defines the precipitation pattern in this region. The climate there is mostly affected by the westward movement of storms, which originate from the Atlantic Ocean and affect the western European coasts in the winter [11]. The general precipitation in this region is mostly affected by the North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO) in the western Mediterranean region [12], the East Atlantic Oscillation (EAO) in the northern and eastern areas, and the Scandinavian Patterns or the eastern Atlantic/Western Russia pattern [9,10,13]. However, the subtropical southern part of the Mediterranean basin is affected by systems such as the Hadley Cell throughout its descending branch for many months of the year and by the Asian and African monsoons during the summer [14]. The influences of El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO), hurricanes, and the dust intrusions from the Sahara (see Reference [14] for a review or Reference [15]) should not be neglected. In the summer period, a dominant high-pressure system presents a strong positive geopotential anomaly in many parts of Europe including the area of the Mediterranean basin, which leads to a prevalence of dry conditions over the southern Mediterranean region [11]. These highlighted anomalies are associated with blocking conditions, subsidence, stability, a warm lower troposphere, and small pressure gradients at sea level as well as above-normal Mediterranean Sea surface temperatures [16].
1.1.1. Precipitation Patterns and Synoptic Climatological Configuration
The complex morphology of the region and the different interactions between several patterns of climate variability contribute to significant seasonal and annual differences in total precipitation, daily distribution, and geographical distribution [9]. The highest quantities of precipitation occur over the Adriatic coast and the Alpine region mainly during the summer and over the coast of Turkey and the Atlantic Iberian Peninsula border in the winter. During this time, there is more than 1200 mm of precipitation. The lowest quantities occur in the southeast region of the basin and over the northern coast of Africa with less than 400 m of precipitation and over the southern Iberian Peninsula in the summer [17,18,19,20].
Large-scale precipitation events in the western, central, and eastern Mediterranean are related to local anomalies of high moisture over the Mediterranean Sea [21] and those are influenced by remote positive source anomalies [22]. Many studies have pointed out the important role of remote sources for the occurrence of extreme precipitation events in the Mediterranean Basin [22,23,24,25], which is one of the aims of the present study.
If the Mediterranean basin is characterized by something peculiar, it is the highest number of heavy precipitation events (the aim of this work) with approximately 60% of those events occurring during the extended winter season [26]. During the period between September and May, which is characterized as the most precipitative period of the year, the accumulated rainfall contributes more than 80% of the total annual precipitation [12,27]. This is the case, for instance, in the Alpine region [28]. During the summer (the dry season), some locations in the Balkans and the Caucasus have also recorded significant amounts of precipitation [20]. This type of rainfall over the Mediterranean basin is due to several factors such as mesoscale convective systems, cyclones, upper synoptic-scale-level troughs, and large-scale circulation teleconnection patterns [16,29,30,31,32]. At the local scale, the intensity of precipitation depends on the temperature profile, the atmospheric moisture, and the convergence at lower levels. However, moisture content along with intense convection are essential components for generating intense precipitation [33]. Around 90% of heavy precipitation events are associated with cyclones [27]. In general, a higher frequency of extreme precipitation and its impact has been recorded in the north-western part of the basin [34].
Many studies have analyzed trends in the occurrence of extreme precipitation, which points out that their frequency, intensity, and impacts do not show homogenous behavior across the entire area [34,35]. For instance, a significant increasing trend in torrential or heavy rainfall events was reported in the Iberian and Italian Peninsulas while, for both regions, decreasing trends in light and moderate precipitation levels were observed [36]. Other studies on climate extremes have demonstrated that, over the Italian Peninsula, there are positive trends in the number of days with precipitation amounts greater than 10 mm while a negative trend has been demonstrated in the eastern part of the Mediterranean [37]. Another example of this lack of homogeneity is that opposite trends for extreme precipitation have been found over other regions such as Greece [38]. Knowledge of the behavior and the impact of extreme precipitation in the past and present is crucial to understanding future climate change effects, which could be more evident through extreme events [39] under study.
1.1.2. Moisture Transport and Effects
As discussed, precipitation is highly sensitive to the location of the cyclones over the region and variations in climate. However, the role of moisture is also equally important [1]. The Mediterranean Sea was identified in previous works as one of the main sources of moisture for continental precipitation on global [1] and regional scales [2,3,40,41]. In this sense, regional studies show that the Mediterranean basin acts as a moisture source, which contributes to the entire Northern Hemisphere with the greatest amount of precipitation occurring over the Mediterranean Sea itself during the summer [2,3,42] with a higher influence near it. The Mediterranean basin supports significant moisture, for instance among others, over the Danube River Basin [43], the Iberian Peninsula [44], Southern France [45,46], and Southern Switzerland [47]. However, it is important to highlight the different influences by the inner sub-basins. In this sense, the eastern Mediterranean basin mainly affects the Middle East and Northern-east Africa. While the Western Mediterranean basin influences the European continent [42] (mainly over the Iberian, Italian, and Balkan Peninsulas and France) and Northern-Western Africa [3,23] and the Central Mediterranean Sea contributes more to the Italian Peninsula and Northern-Central Africa [3,42], which exhibits a huge influence on extreme precipitation in the Alpine region [48] due to the intensification of the moisture uptake from the Mediterranean basin during the autumn and winter [22]. However, the Mediterranean influence on even more distant regions is also known and the moisture that reaches regions such as the Sahel [49,50], Central Asia, and the Arabian Peninsula [51] is not negligible. In addition, it has been demonstrated that changes in the moisture evaporation from the Mediterranean Sea affect the wetness or dryness of conditions over areas where it sinks [23,52,53].
In the context of a changing climate, measurements over the Mediterranean Sea for the last few decades (from 1958), reveal a positive trend in the balance of surface freshwater fluxes (evaporation minus precipitation) reaching about 182 millimeters per year. However, the tendency is due to a combination of two factors including the decrease in precipitation during the 1980s and the increase in evaporation during more recent decades [54]. These changes also affect the transport of moisture to the continent, which affects trends in extreme precipitation and intensifies the influence of oceanic moisture on continental precipitation [55].
One of the objectives in this study is to analyze the percentage of precipitation over the Mediterranean continental areas during the last four decades (1980 to 2016), which is due to moisture from the Mediterranean Sea. The analysis has been done grid by grid with a high resolution of 0.25° degrees in latitude and longitude, which extends the time-period and the resolution of all the previous analyses. Since the significant characteristic of the region is the presence of high rainfall, we have also computed the changes in the moisture contribution for extreme monthly precipitation to highlight the importance of this source of moisture during the maxima peaks of rainfall. Although the work has been done for all months, in this paper, we discuss the results for January and July, the central months for winter (December, January, and February), and the summer season (June, July, and August) in the Mediterranean region.
To understand and describe features of extreme precipitation for the Mediterranean region, it is important to remark on the processes related to the seasonal variation of precipitation. Therefore, for Europe and North Africa, a typical configuration is the presence of two permanent centers of geopotential action—the Icelandic Low and the Azores High—located around 30° N during January and moving northward toward the British Isles in July [56]. The climate type of the Mediterranean region is in concordance with this latitudinal belt positioned north of the Sahara, which is characterized by rainy winters (above 30° N) and dry summers (below 45° N) [56]. This is why, in this paper, the results are focused in January and July.
So, and in view of the importance of extreme rainfall over the region, the main objectives of this study are: (i) to quantify the monthly contribution of the Mediterranean source of moisture to the precipitation over the surrounding continental areas, and (ii) to analyze the percentage contribution of this source to the extreme precipitation, grid by grid, with the best current resolution.
To estimate the monthly moisture that comes from the Mediterranean Sea and contributes to the precipitation over the continent, we used the Lagrangian tool FLEXPART (FLEXible PARTicle) dispersion model in version 9.0, which was developed initially by Stohl and James [57,58] and fed with ERA-Interim reanalysis data. The high resolution Multi-Source Weighted-Ensemble Precipitation (MSWEP) dataset [59] was used to compute the monthly mean and extreme (by the mean composite of the five monthly higher values between 1980 to 2016) precipitation climatology grid by grid (0.25°) for the first time over the Mediterranean region.
2. Data and Method
2.1. MSWEP Precipitation Dataset
In this study, we used the monthly precipitation dataset, MSWEP [59,60], from January 1980 to December 2015. However, only results for January and July are shown and described in the text. MSWEP is a new precipitation dataset that has been accessible since the beginning of 2017. The MSWEP was developed to merge the highest quality available precipitation data as a function of timescale and location. To determine the regions with the monthly highest precipitation values, taken over a large time period, the resolution and precision of the database used is very important.
The MSWEP database is specially designed for hydrological modeling due its 0.25° × 0.25° spatial resolution in latitude and longitude with accumulated data based on three-hour time periods. The database combines the advantages of a wide range of precipitation information including gauges, satellites, and atmospheric reanalysis models to obtain precipitation information with the highest possible accuracy on a global scale, which makes it unique in comparison with other databases. The database used to characterize the highest precipitation values in the Mediterranean region on a monthly scale cover a temporal period from January 1980 to December 2015, which coincides with the available FLEXPART outputs.
The MSWEP precipitation dataset has been validated on a global scale using observations from approximately 60,000 gauges around the world and hydrological modeling of approximately 9000 catchments [60]. The results showed that MSWEP performs better compared to other precipitation databases such as CHIRPS, CMORPH-CRT, GPCP-1DD, GSMaP, PERSIANN-CCS, PERSIANN-CDR, WFDEI-CRU, and TMPA 3B42.
We have used the MSWEP monthly precipitation dataset to compute the monthly climatological precipitation values over the Mediterranean region between 30° W–65° E and 5° N–70° N. Checking grid by grid for each individual month, we ranked the maximum precipitation. Considering only five years with the most intense precipitation values for each grid point, we composed a study of climatology for the extreme years.
2.2. Sinks for the Mediterranean Sea Moisture Source
In this study, we used a Lagrangian approach to evaluate the role of the moisture transport from the Mediterranean basin. The moisture sink regions are computed using the outputs of a global simulation of the Lagrangian FLEXPART V9.0 model [43,61] with ERA-Interim reanalysis data input from the ECMWF (European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecast) [62]. The ERA-Interim dataset has 1° spatial resolutions on 60 vertical levels from 1000 to 0.1 hPa, which is available at each 6-h time interval. The FLEXPART experiment is based on dividing the global atmosphere into approximately 2.0 million particles (air masses or atmospheric particles) of constant mass (m), which are moved along their trajectories using a three-dimensional (3D) wind field while retaining their meteorological characteristics (given by the ERA-Interim data) as well as their individual position (latitude, longitude, and elevation). Therefore, computing changes in specific humidity (q) along the trajectories allows us to identify moisture sources and/or sink regions [57,58] if we follow the particles backward or forward in time, respectively. As commented on previously, the changes in specific humidity (q) allow us to identify those moments when and where the particles obtain moisture through evaporation (e) or lose moisture through precipitation (p). Those changes are outlined in the equation below.
where m represents the mass of the particle. By adding, day by day, during the 10 days of analysis, the (e−p) for all the particles in the atmosphere over the area of interest, we can obtain instantaneous values of the surface freshwater flux (E − P) where (E) denotes the rate of evaporation and (P) denotes the rate of precipitation per unit area.
e − p = m (dq/dt)
To identify the moisture sink regions in the Mediterranean area due to the moisture that comes from the Mediterranean basin, we conducted a forward experiment in time from January 1980 to December 2016. The surface freshwater flux (E − P) takes into account only those particles leaving the Mediterranean basin. Using the forward mode to follow the particles from our area of study, we track the trajectories of the particles for 10 days (the typically mean water vapor lifetime in the atmosphere at mid-latitudes [63]), with the aim to identify the regions where the particles lost humidity. This includes the sink regions where E − P < 0.
The Lagrangian approach has been widely used during the last several years in moisture transport analysis for the identification of moisture sources and sinks all around the globe [1,64]. The model includes many physical and dynamical parametrizations (see [65] for a technical description and the continuously update FLEXPART webpage https://www.flexpart.eu/wiki). In comparison to the other approaches applied to moisture transport analysis (for example, box models and isotopes), the Lagrangian approach is one of the most suitable tools for computing moisture source-sink relationships, which was pointed out by Gimeno et al. [64]. However, this model has some limitations. For instance, the quality of input data is crucial for reliable results. To minimize these type of errors, the choice of ERA-Interim may be justified in terms of its performance in reproducing the hydrological cycle and water balance closure better than other available reanalysis products [66,67]. Another main disadvantage is that the model cannot make calculations of E and P separately and E and P should always be taken into consideration as part of a balance between them [57,58,64]. Therefore, this P calculated from E − P < 0 is not exactly equal to real precipitation [57]. It represents the moisture transported for precipitation. Other sources of error are the limited resolution, uncertainties, and the interpolation of input data. Additionally, the trajectory errors could be higher especially in areas with low meteorological data coverage [68,69]. The developers of the model [57] state that such errors may cancel each other out given the large number of trajectories considered in the experiment and given the number of particles found in the typical grid used. For a complete description of the advantages and disadvantages, we recommend the review by Gimeno et al. [64].
With regard to the precipitation analysis, January and July results for the sinks of moisture from the Mediterranean Sea are shown in the main text while all the months are included in the supplementary material.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Climatological and Extreme MSWEP Monthly Precipitation
To calculate the climatological value of monthly precipitation (namely MSWEP-Cli), we used the global precipitation database from MSWEP. The analysis covers the temporal period from 1980 to 2015. In this work, we put the focus on January and July (see Figure 2) (see the results in the Supplementary Materials for all months, Figure S1).
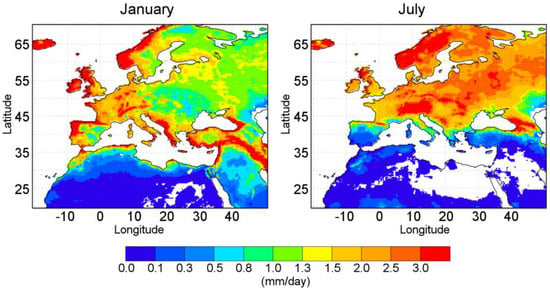
Figure 2.
Monthly climatological values from MSWEP (0.25°) global precipitation database (MSWEP-Cli) for January (right panel) and July (left panel) over the area of Mediterranean basin for 1980–2015. Units in mm/day. White color over continents indicates where the MSWEP database does not report values.
Results show that the highest climatological precipitation values (greater than 2 mm/day) in January are recorded along the Atlantic coast from the Iberian Peninsula to the Scandinavian lands and over Central Europe, the Italian Peninsula, the Balkans, the Middle East, the Anatolian Peninsula coasts, and the Fertile Crescent arch. Most of the precipitation over the Atlantic coast and northern Europe is typically due to fronts associated with the transit of mid-latitude cyclones. In addition, if they flow over the continent, they can continue eastward up to the Middle East [70]. Higher precipitation in the Northern Mediterranean basin and northern Africa is also due to convective events [22] and those over the Fertile Crescent are associated with cyclone systems that reach the region from the Mediterranean Sea combined with a dominant moisture southern flux [71,72]. Yet, very low values of precipitation (lower than 0.3 mm/day) occur in the semi-arid and arid regions of Africa and Asia. During July, the highest climatological values of precipitation are recorded northward of 42° latitude including practically the entire Eurasian continent with the exception of the Iberian Peninsula (where very low values of less than 0.3 mm/day are recorded), Northern Africa, and Western Asia.
Since the Mediterranean region is characterized by intense precipitation, after identifying the climatological values, we have computed, grid by grid, the precipitation values of the five years that exhibit the greatest values during both January and July (see Figure S2 in Supplementary Materials for the remaining months). The maps concerning the mean values of these five years (hereafter MSWEP-extreme) are shown in Figure 3.
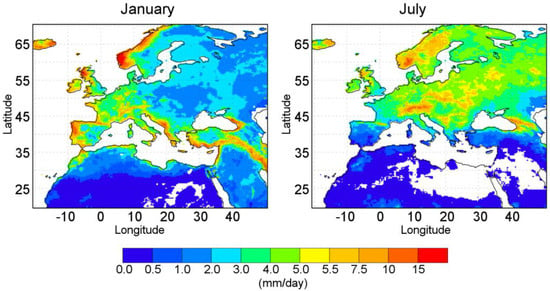
Figure 3.
Mean precipitation for each grid point for the identified five years with the highest value of precipitation (MSWEP-extreme) for January (right panel) and July (left panel). Results are obtained from the MSWEP precipitation dataset, which considers a 36-year temporal period (1980–2015). Units in mm/day. White color over continents indicates where the MSWEP database does not report values during any of the five months computed.
This pattern during both months exhibits a similar configuration compared to climatological conditions (see Figure 2). The highest values (greater than 5.5 mm/day, orange colors) in January are observed over the western Iberian and Scandinavian Peninsulas, the eastern coast of the Adriatic Sea, the eastern Mediterranean coast and Fertile Crescent, and over some areas of the Italian Peninsula. In Eastern Europe and northern Asia, the MSWEP-extreme values are lower and range between 0.5 and 2 mm/day. During July, the highest values of MSWEP-extreme (>5.5 mm/day) are mainly exhibited in the central part of the Euro-Asiatic continent, which highlights elevated terrains as the Alpine region, the Scandinavian Peninsula, and regions over the Carpathian Mountains. The plot also shows higher values over Central Africa below 15° N. However, this area is outside the Mediterranean region.
The ratio between these precipitation measurements (MSWEP-Cli divided by MSWEP-extreme) are plotted in Figure 4. This ratio highlights the areas where there is a greater difference between the climatology and the extreme precipitation (indicating that extreme precipitation occurs in a few isolated events but is important in quantity). However, ratio values around one (ratio ≈ 1) show the areas where precipitation quantities do not exhibit considerable change over the studied time period. For both months (see Figure S3 in Supplementary Materials for the remaining months), the results generally show that the ratio is higher in the arid and semiarid regions of Northern Africa, the Middle East, and the southern Iberian Peninsula where MSWEP-Cli values are very low (especially during July). In these areas, precipitation for extreme years can be as high as five times the climatological values. During January, values for MSWEP-extreme are twice the climatological values over central Europe, which shows that extreme precipitation modulates the mean climatological value. It is particularly interesting that the MSWEP-extreme over the Mediterranean coast of the Balkan, Greek, and Anatolian Peninsulas is twice the value of MSWEP-Cli. The South-western Iberian Peninsula also shows a particular behaviour. This region is characterized by higher values in both measurements and the ratio is also elevated with values over three. Therefore, in January, this region was affected by systems that bring extreme precipitation, which mostly determine its climatological value. In July, the highest ratio values, in addition to the already discussed dry areas, are located along the northern Mediterranean coast including the coast of France, Italy, Greece, and Turkey. In the Alpine regions such as the Scandinavian and Carpathian mountains where climatological precipitation values reached a maximum in both cases, the ratio is among the lowest, which indicates that these areas commonly experience extreme precipitation during the summer.
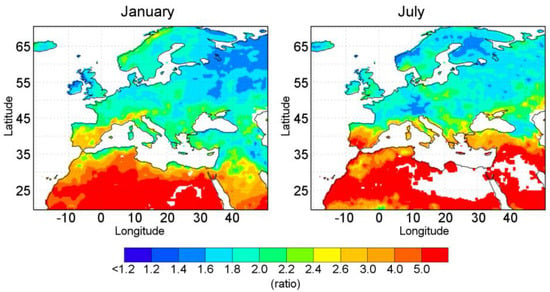
Figure 4.
Ratio between MSWEP-extreme and MSWEP-Cli during January (right panel) and July (left panel). White areas over the continent indicate where the MSWEP database does not report values.
3.2. Climatological and Extreme FLEXPART Monthly Precipitation with Origin in the Mediterranean Sea
To identify the major climatological monthly moisture sinks for the Mediterranean region, we tracked the air masses (the particles) residing in the atmosphere over the Mediterranean Sea forward in time for ten days from 1980 to 2016 every six hours. We computed month by month the balance of E − P for each grid point (as described in the methodology using the outputs of the FLEXPART model) and we maintained only monthly negative values ((E − P) < 0) to identify those areas where precipitation (P) exceeds evaporation (E) in the net moisture budget. Monthly positive values are removed. The final mean accumulated (E − P) < 0 over land (hereafter, PFLEX-Cli in this paper) shows the moisture sink regions for the moisture that comes from the Mediterranean Sea and produces precipitation over the neighborhood continental areas. January and July PFLEX-Cli values are shown in Figure 5 (see the results in the Supplementary Materials for all months, Figure S4). Colored areas are the sink for the Mediterranean moisture including those regions with precipitation.
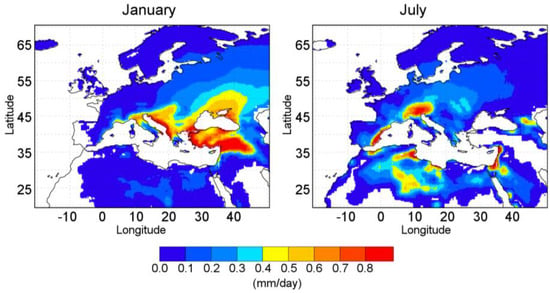
Figure 5.
Monthly-averaged value of E − P < 0 integrated over ten days (PFLEX-Cli) between 1980 to 2015 obtained from the forward Lagrangian experiment for Mediterranean Sea during January (right panel) and July (left panel). Units in mm/day. White areas over continent are regions not influenced by the Mediterranean moisture.
During January, the pattern of PFLEX-Cli has an eastern shift, which follows the mean winter general circulation in this latitude. The main moisture Mediterranean influence for precipitation occurs over the eastern areas. The highest values are found over the regions close to the Mediterranean Sea (reddish colours, >0.5 mm/day) over the Balkan Peninsula, pre-Alpine region, the Middle East, Turkey, the Fertile Crescent, and the northern Black Sea. By contrast, during July, the highest values do not exhibit this displacement and the PFLEX-Cli is based on the local source of moisture. The main affected areas are recorded over the eastern Iberian Peninsula, the Alps, the western Middle East, and Northern Africa (Saharan regions to the north of Ahaggar and Tibesti massifs that include Algeria, Tunisia, and Libya).
We have also conducted a grid-by-grid computation of the precipitation generated by moisture coming from the Mediterranean Sea and calculated by the Lagrangian experiment for the same five years of maximum precipitation used to compute MSWEP-extreme. These extreme E − P < 0 monthly values, hereafter PFLEX-extreme, for January and July are shown in Figure 6 (see Figure S5 in Supplementary Materials for the remaining months). Both patterns exhibit a similar geographical distribution to those recorded by PFLEX-Cli.
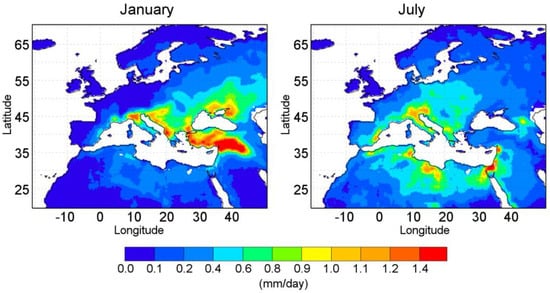
Figure 6.
Mean precipitation for each grid point was calculated by the Lagrangian experiment for moisture originating from the Mediterranean Sea (PFLEX-extreme) for the same five years, which was identified as MSWEP-extreme in January (right panel) and July (left panel) for a 36-year temporal period (1980–2016). Units in mm/day. White color over continents indicates where the PFLEX does not report values during any of the five months computed.
Compared to MSWEP maps (see Figure 2 and Figure 3), both PFLEX values are, as expected, lower because they exhibit only the portion of the precipitation that originates in the Mediterranean Sea.
As for MSWEP data, we show in Figure 7 the ratio between PFLEX-Cli and PFLEX-extreme.
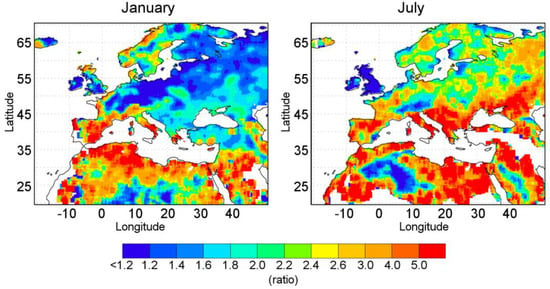
Figure 7.
Ratio between the mean values of the observed five years with highest values of E − P < 0, calculated using FLEXPART (PFLEX-extreme), and the mean climatological values of E − P < 0 (PFLEX-Cli) during January (right panel) and July (left panel), which is calculated for each grid point. Period: 1980–2016. White areas over the continent indicate where the PFLEX-Cli does not report values.
For both central months, January in the winter and July in the summer (see Figure S6 in Supplementary Materials for the remaining months), the results show that the ratio has higher values (reddish colors, greater than 3) in the semi-arid and arid regions of Northern Africa, Middle Eastern coast, and Iberian and Italian Peninsulas. These high ratio values denote that, in those areas, a greater amount of moisture comes from the Mediterranean Sea when compared to local sources during extreme events (PMWEP-extreme). It is important to emphasize the differences between January and July over the Alpine region, the Balkans, and the Greek areas as well as the eastern longitudes. Both exhibit contrary behavior in the sense that the contribution by the Mediterranean moisture is very important for the extreme precipitation over the Alpine region (ratio values up to 5) during the winter while the contribution to extreme precipitation is close to the PFLEX-Cli values (ratio values around 1, bluish colors) during the summer.
However, during July, PFLEX-extreme exhibits notable differences compared to PFLEX-Cli over the Balkan Peninsula, Ukraine, Georgia, and western Turkey (reddish colors), which indicates that in these areas, extreme precipitation events are mostly present during the summer period when the moisture comes from the Mediterranean Sea.
Very similar amounts of precipitation during PFLEX-Cli and PFLEX-extreme are recorded in Central and Western Europe in January. During July, the difference is more notable since PFLEX-extreme values are more than twice the PFLEX-Cli values (ratio up to 2).
3.3. Identification of Differences between FLEXPART and MSWEP Climatological Monthly Precipitation and Extreme Monthly Precipitation
To show the influence of the Mediterranean Sea moisture in the rainfall tracked during the winter (January) and the summer (July) (see the results in the Supplementary Materials for all months, Figure S7), we have calculated the percentage between the mean climatological value of precipitation obtained via the forward Lagrangian experiment (PFLEX-Cli) and the monthly climatological precipitation in the Mediterranean region (MSWEP-Cli) using the MSWEP precipitation dataset (see Figure 8).
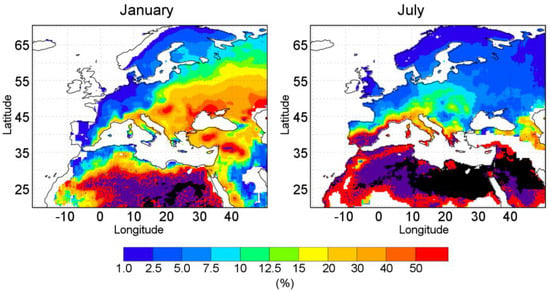
Figure 8.
Monthly climatological percentage of the Mediterranean moisture contribution (PFLEX-Cli) to precipitation (MSWEP-Cli) during January (right panel) and July (left panel). Violet represents percentage values of 100% and a black color indicates those regions where the MSWEP precipitation dataset does not show values. White areas are those regions where PFLEX-Cli does not report values.
The results show that, for both months, the Mediterranean moisture had the highest contribution to the total precipitation over semiarid and arid regions in Africa (values greater than 40%, reddish colors). These results are in concordance with other studies that suggest the Mediterranean Sea is an important moisture source of precipitation over Eastern-North Africa [52]. Focusing on the European continent, during January, higher values were recorded over Ukraine, Turkey, some parts of Russia, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, and the Middle East. The amount of precipitation from these areas is more than twice the moisture that comes from the Mediterranean Sea. However, more than 20% of the precipitation of Eastern Europe comes from the Mediterranean moisture. This pattern changes during the summer (July) when the Mediterranean Sea contributes more rain (up to 40%) to the mean climatological precipitation in areas around the southern Iberian Peninsula, Italian Peninsula, and Middle East coasts. These regions are typically sinks for moisture originating from the Mediterranean [42,46,52,73].
The same computation was done to check the percentage difference between monthly extreme precipitation values (PFLEX-extreme versus MSWEP-extreme) over five years with maximum grid-by-grid values during January and July (see Figure 9) (see Figure S8 in Supplementary Materials for the remaining months).
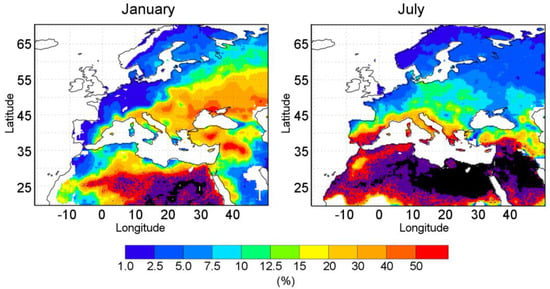
Figure 9.
Similar to Figure 8 but comparing the percentage between PFLEX-extreme and MSWEP-extreme during January (right panel) and July (left panel). White areas over the continent indicate where the PFLEX-Cli does not report values. Violet represents percentage values of 100% and the black color indicates those regions where the MSWEP precipitation dataset does not show values.
The patterns of these results are quite similar to that exhibited in Figure 8. This indicates that the moisture contribution from the Mediterranean Sea to extreme precipitation events are of the same proportion as the contribution to the mean climatology. However, they also explain that extreme precipitation in the area is caused by moisture from the Mediterranean source over North Africa, Eastern Europe, and the Anatolian Peninsula during January and the influence is most concentrated along the Mediterranean Sea borders during July.
To highlight the different Mediterranean precipitation contributions by percentage toward extreme events and climatology, Figure 10 shows the differences between the plots in Figure 8 and Figure 9 (see Figure S9 in Supplementary Materials for the remaining months).
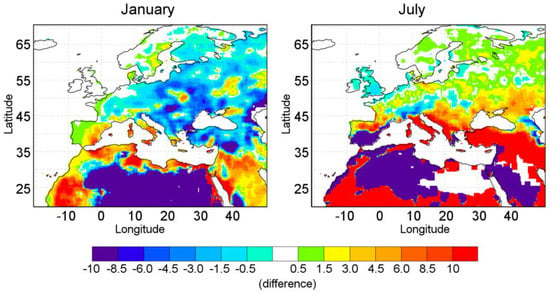
This last figure shows where the Mediterranean moisture supplied to extreme events was higher (or lower) than the climatological mean values. Generally, the Mediterranean supplies more moisture to extreme events (reddish colors) in the southern and western borders of the basin during January and over the northern side during July. The contribution to the mean values (bluish colors) was highest over central Europe in January and over the Alps and the Carpathian Mountains as well as the British Isles during June. The arid regions over Africa always received a smaller percentage of contribution during extreme events.
4. Summary and Conclusions
In this work, we estimated the contribution of the Mediterranean Sea as the main moisture source of the monthly precipitation over the surrounding continental areas. We analyzed both the mean climatological behavior and the extreme values. The analysis was done in three steps. First, we characterized the precipitation patterns for both the 1980–2015 climatology and the five extreme years, grid by grid, by using the MSWEP database. Next, we estimated the moisture contribution from the Mediterranean basin to the precipitation through the Lagrangian FLEXPART model for both monthly climatological values and five-year values, grid by grid, which was demonstrated in step one. Finally, we compared both patterns, precipitation and contribution, by calculating the differences between them.
The monthly mean climatological precipitation (MSWEP-Cli) shows a clear dichotomy between the winter and summer. During January, the highest rainfall values were recorded along the European Atlantic coast and parts of Central Europe due to the typical frontal precipitation associated with cyclones over the northern and eastern limits of the basin and the Fertile Crescent due to convective systems. However, during July, the pattern shows its maximum values for covering practically the entire Eurasian continent with the exception of the Iberian and Anatolian Peninsulas and northern Africa. The analysis of the monthly mean extreme values of precipitation (MSWEP-extreme) shows that the pattern is similar to the climatological one. The highest values in January occur over areas in the Western Iberian Peninsula, Northern British Isles, Scandinavia, the eastern coast of the Adriatic Sea, Southern Anatolian Peninsula, and the Fertile Crescent reaching north of the Persian Gulf. During July, higher values of MSWEP-extreme are also expressed in the central part of the Euro-Asiatic continent, which highlights the peaks over the Alps and the Carpathian and Scandinavian Mountains. When the ratio of the climatology and extreme events is analyzed, it becomes evident that extreme precipitation is modulated over some parts of the continental Mediterranean region compared to the mean climatological values. This behavior is clear over arid and semi-arid regions including southern Iberian Peninsula during both seasons when the extreme events yield values greater than three times the mean precipitation. Over the Anatolian and southern Greek Peninsulas, this event occurs in July. However, it is also remarkable that, in the same areas, this ratio reaches lower values, which indicates that, throughout the analyzed period (36 years), precipitation is quite regular. This occurs over elevated terrains such as the Alps and the Carpathian and Scandinavian Mountains, which commonly experience extreme precipitation.
The analysis of the contribution of the Mediterranean basin to the precipitation over land showed that climatologically (PFLEX-Cli) during January, the main moisture sink areas for the moisture coming from the Mediterranean basin are found over the North-eastern Mediterranean region with a clear eastern shift caused by westerly winds. During July, when the values are smaller, the areas affected are more local (with a high impact over the Alpine region, the eastern Iberian Peninsula, Middle East, and northern Africa).
The contribution of the Mediterranean moisture to the extreme precipitation (PFLEX-extreme) shows similar geographical distribution patterns in both months as those recorded by PFLEX-Cli. The arid regions could be positively biased by the overestimation of PFLEX-Cli and PFLEX-extreme if we compare the precipitation simulated by the model and the MSWEP data. PFLEX represents the moisture available for precipitation since it is pointed in the methodology.
When MSWEP-extreme and PFLEX-extreme precipitation values are compared, PFLEX-extreme values are, as expected, lower because PFLEX only computes those amounts of continental precipitation with origin in the Mediterranean Sea. The ratio between PFLEX-Cli and PFLEX-extreme shows that the contribution of the Mediterranean Sea to extreme events during both boreal months is most pronounced over the Iberian and Italian Peninsula, Middle East coast, and in the desert regions of Northern Africa where the ratio can be up to three times the climatological precipitation values. An interesting case appears over the Alpine regions and over the Balkan and the Greek Peninsulas where the ratio exhibits opposite behavior during the winter and summer. During the winter, the Mediterranean Sea is the most important provider of moisture (ratio approximately 5) for extreme precipitation while, during the summer, the contribution is quite similar to PFLEX-Cli (ratio approximately 1). In Central and Western Europe, a similar pattern is recorded in January when the ratio is around 1. These values show that PFLEX-Cli and PFLEX-extreme exhibit quite similar amounts of precipitation.
The Mediterranean contribution and the precipitation was compared with respect to the difference between MSWEP and PFLEX climatological monthly and extreme monthly recorded precipitation. The difference was analyzed for two fields of the precipitation, which includes the percentage difference between PFLEX-Cli and MSWEP-Cli and the percentage difference between PFLEX-extreme and MSWEP-extreme. The results show that, for the first case, the Mediterranean Sea contributes significantly to total precipitation (around 40%) in both months in semi-arid and arid regions of Africa while the European continent results differ depending on the season. Therefore, during January, the Mediterranean Sea contributes more than twice the precipitation recorded in areas over Ukraine, Turkey, and the European part of Russia. In July, the Italian and Iberian Peninsulas are the most affected areas where the moisture originating from the Mediterranean Sea can be greater than 40%, which was confirmed by numerous studies conducted in these regions. The Mediterranean Sea has been detected as the main moisture source [42,52]. For the second case, the percentage between PFLEX-extreme and MSWEP-extreme exhibits quite similar behavior to the percentage between monthly climatological precipitation values. From the climatological point of view, during the winter season, the rainfall contribution from the Mediterranean Sea is highest over Central Europe (the Alps and the Carpathian Mountains), but, in the summer, the precipitation values originating from the Mediterranean are highest around the British Isles. During extreme events, the Mediterranean Sea is declared as the main moisture provider in the southern and western parts of the basin during January while, during July, this contribution is exhibited more over the northern side. The semi-arid and arid regions in Africa are areas where the Mediterranean contributes the least to extreme precipitation.
To summarize, the results showed that the spatial pattern of rainfall contribution from the Mediterranean source is similar for extreme precipitation years when compared to climatology. However, significant differences could occur locally particularly in any European region where the Mediterranean is not an important regular source for climatological precipitation but is a significant source in extreme precipitation years.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at http://www.mdpi.com/2073-4441/10/4/519/s1, Figure S1: As Figure 2 but for all months, Figure S2: As Figure 3 but for all months, Figure S3: As Figure 4 but for all months, Figure S4: As Figure 5 but for all months, Figure S5: As Figure 6 but for all months, Figure S6: As Figure 7 but for all months, Figure S7: As Figure 8 but for all months, Figure S8: As Figure 9 but for all months, and Figure S9: As Figure 10 but for all months.
Funding
Danica Ciric is supported by the European Commission under the Erasmus Mundus Project Green-Tech-WB: Smart and Green Technologies for Innovative and Sustainable Societies in the Western Balkans (551984-EM-1-2014-1-ES-ERA Mundus-EMA2). This research was partially supported by Xunta de Galicia under project ED413C 2017/64 “Programa de Consolidacion e Estructuracion de Unidades de Investigacion Competitivas (Grupos de Referencia Competitiva)” co-funded by the European Regional Development Fund (FEDER).
Author Contributions
Danica Ciric, Raquel Nieto, and Luis Gimeno conceived and designed the experiments. Danica Ciric and Lucia Losada performed the experiments. Danica Ciric, Raquel Nieto, Anita Drumond, and Luis Gimeno analyzed the data. Danica Ciric and Raquel Nieto wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ECMWF | European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecast |
| ERA | European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasting Re-Analysis |
| FLEXPART | FLEXible PARTicle dispersion model |
| HydroSHEDS | Hydrological data and maps based on Shuttle elevation derivatives at multiple scales |
| MSWEP | Multi-Source Weighted-Ensemble Precipitation |
| MSWEP-Cli | Monthly climatological value from MSWEP global precipitation database |
| MSWEP-extreme | Mean precipitation for the identified 5 years with the highest value of precipitation from MSWEP global precipitation database |
| PFLEX-Cli | Monthly averaged value of E - P < 0 integrated over 10 days obtained from the forward Lagrangian experiment |
| PFLEX-extreme | Mean precipitation for the identified 5 years with the highest value of precipitation from FLEXPART monthly precipitation data |
References
- Gimeno, L.; Drumond, A.; Nieto, R.; Trigo, R.M.; Stohl, A. On the origin of continental precipitation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 3, L13804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Hernandez, M.; Drumond, A.; Gimeno, L.; Garcia-Herrera, R. Variability of moisture sources in the Mediterranean region during the period 1980–2000. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 6781–6794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, R.; Gimeno, L.; Drumond, A.; Hernandez, E. A Lagrangian identification of the main moisture sources and sinks affecting the Mediterranean area. WSEAS Ttrans. Environ. Dev. 2010, 6, 1790–5079. [Google Scholar]
- Westra, S.; Alexander, L.V.; Zwiers, F.W. Global Increasing Trends in Annual Maximum Daily Precipitation. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 3904–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, L.V.; Zhang, X.; Peterson, T.C.; Caesar, J.; Gleason, B.; Klein Tank, A.M.G.; Haylock, M.; Collins, D.; Trewin, B.; Rahimzadeh, F.; et al. Global observed changes in daily climate extremes of temperature and precipitation. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, D05109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EASAC. Trends in Extreme Weather Events in Europe: Implications for National and European Union Adaptation Strategies; EASAC Policy Report 22; European Academies Science Advisory Council: Halle, Germany, 2013; Available online: www.easac.eu (accessed on 30 October 2017).
- Gualdi, S.; Somot, S.; Li, L.; Artale, V.; Adani, M.; Bellucci, A.; Braun, A.; Calmanti, S.; Carillo, A.; Dell’Aquila, A.; et al. The CIRCE Simulations Regional Climate Change Projections with Realistic Representation of the Mediterranean Sea. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köppen, W. Versuch einer Klassifikation der Klimate, vorzugsweise nach ihren Beziehungen zur Pflanzenwelt. Geographische Zeitschrift 1990, 6, 593–611. [Google Scholar]
- Lionello, P.; Malanotte-Rizzoli, P.; Boscolo, R.; Alpert, P.; Artale, V.; Li, L.; Luterbacher, J.; May, W.; Trigo, R.; Tsimplis, M.; et al. The Mediterranean climate: An overview of the main characteristics and issues, Mediterranean Climate Variability. Dev. Earth Environ. Sci. 2006, 4, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigo, R.; Xoplaki, E.; Zorita, E.; Luterbacher, J.; Krichak, S.O.; Alpert, P.; Jacobeit, J.; Saenz, J.; Fernandez, J.; González-Rouco, F.; et al. Relations between variability in the Mediterranean region and mid-latitude variability. Dev. Earth Environ. Sci. 2006, 4, 179–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, F.; Lionello, P. Climate Change Projections for the Mediterranean Region. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2008, 63, 90–104. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/223492610_Climate_change_projections_for_the_Mediterranean_region#pff (accessed on 28 September 2017). [CrossRef]
- Hurrell, J.W. Decadal trends in the North Atlantic Oscillation: Regional temperature and precipitation. Science 1995, 269, 676–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trigo, R.M.; Valente, M.A.; Trigo, I.F.; Miranda, P.; Ramos, A.M.; Paredes, D.; Garcıa-Herrera, R. North Atlantic wind and cyclone trends and their impact in the European precipitation and Atlantic significant wave height. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1146, 212–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alpert, P.; Baldi, M.; Ilany, R.; Krichak, S.; Price, C.; Rodo, X.; Saaroni, H.; Ziv, B.; Kishcha, P.; Barkan, J.; et al. Relations between climate variability in the Mediterranean region and the tropics: ENSO, South Asian and African monsoons, hurricanes and Saharan dust. Dev. Earth Environ. Sci. 2006, 4, 149–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krichak, S.; Breitgand, J.S.; Gualdi, S.; Feldstein, S.B. Teleconnection–extreme precipitation relationships over the Mediterranean region. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2014, 117, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xoplaki, E.; González-Rouco, J.F.; Luterbacher, J.; Wanner, H. Wet season Mediterranean precipitation variability: Influence of large-scale dynamics and trends. Clim. Dyn. 2004, 23, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönwiese, C.D.; Rapp, J. Climate Trend Atlas of Europe Based on Observations 1891–1990; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, Netherlands; Boston, MA, USA; London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Kadoglu, M.; Tulunay, Y.; Borhan, Y. Variability of Turkish precipitation compared to E1 Niño Events. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1991, 26, 1597–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigo, R.M.; Palutikof, J.P. Precipitation Scenarios over Iberia: A Comparison between Direct GCM Output and Different Downscaling Techniques. J. Clim. 2001, 14, 4422–4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelieveld, J.; Hadjinicolaou, P.; Kostopoulou, E.; Chenoweth, J.; El Maayar, M.; Giannakopoulos, C.; Hannides, C.; Lange, M.A.; Tanarhte, M.; Tyrlis, E.; et al. Climate change and impacts in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Middle East. Clim. Chang. 2012, 114, 667–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raveh-Rubin, S.; Wernli, H. Large-scale wind and precipitation extremes in the Mediterranean: A climatological analysis for 1979–2012. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 141, 2404–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winschall, A.; Sodemann, H.; Pfahl, S.; Wernli, H. How important is intensified evaporation for Mediterranean precipitation extremes? J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 5240–5256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciric, D.; Nieto, R.; Ramos, A.M.; Drumond, A.; Gimeno, L. Wet Spells and Associated Moisture Sources Anomalies across Danube River Basin. Water 2017, 9, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knippertz, P.; Martin, J.E. Tropical plumes and extreme precipitation in subtropical and tropical West Africa. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2005, 131, 2337–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, J.G.; Ulbrich, S.; Parodi, A.; Rudari, R.; Boni, G.; Ulbrich, U. Identification and ranking of extraordinary rainfall events over Northwest Italy: The role of Atlantic moisture. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 2085–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toreti, A.; Xoplaki, E.; Maraun, D.; Kuglitsch, F.G.; Wanner, H.; Luterbacher, J. Characterisation of extreme winter precipitation in the Mediterranean and associated anomalous atmospheric circulation patterns. Nat. Hazard Earth Syst. 2010, 10, 1037–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaetani, M.; Baldi, M.; Dalu, G.A.; Maracchi, G. Jetstream and rainfall distribution in the Mediterranean region. Nat. Hazard Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 11, 2469–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinié, G.; Ceresetti, D.; Anquetin, S.; Dominique Creutin, J.; Boudevillain, B. Rainfall Regime of a Mountainous Mediterranean Region: Statistical Analysis at Short Time Steps. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2012, 51, 429–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayan, U.; Nissen, K.; Ulbrich, U. Review Article: Atmospheric conditions inducing extreme precipitation over the eastern and western Mediterranean. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 15, 2525–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayan, U.; Ziv, B.; Margalit, A.; Morin, E.; Sharon, D. A severe autumn storm over the Middle-East: Synoptic and Mesoscale convection. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2001, 69, 103–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homar, V.; Stensrud, D.J. Sensitivities of an intense Mediterranean cyclone: Analysis and validation. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2004, 130, 2519–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotroni, V.; Lagouvardos, K.; Defer, E.; Dietrich, S.; Porcu, F.; Medaglia, C.M.; Demirtas, M. The Antalya 5 December 2002 storm: Observations and model analysis. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2006, 45, 576–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massacand, A.C.; Wernli, H.; Davies, H.C. Heavy precipitation on the alpine southside: An upper-level precursor. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 1435–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llasat, M.C.; Llasat-Botija, M.; Prat, M.A.; Porcu, F.; Price, C.; Mugnai, A.; Lagouvardos, K.; Kotroni, V.; Katsanos, D. High-impact floods and flash floods in Mediterranean countries: The FLASH preliminary database. Adv. Geosci. 2010, 23, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo, F.S.; Trigo, R.M. Trends in daily rainfall in the Iberian Peninsula from 1951 to 2002. Int. J. Climatol. 2007, 27, 513–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpert, P.; Ben-Gai, T.; Baharad, A.; Benjamini, Y.; Yekutieli, D.; Colacino, M.; Diodato, L.; Ramis, C.; Homar, V.; Romero, R.; et al. The paradoxical increase of Mediterranean extreme daily rainfall in spite of decrease in total values. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostopoulou, E.; Jones, P.D. Assessment of climate extremes in the Eastern Mediterranean. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2005, 89, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norrant, C.; Douguedroit, A. Monthly and daily precipitation trends in the Mediterranean (1950–2000). Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2006, 83, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation. A Special Report of Working Groups I and II of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Field, C.B.V., Barros, T.F., Stocker, D., Qin, D.J., Dokken, K.L., Ebi, M.D., Mastrandrea, K.J., Mach, G.-K., Plattner, S.K., Allen, M., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012; p. 582. [Google Scholar]
- Mariotti, A.; Struglia, M.V.; Zeng, N.; Lau, K.-M. The hydrological cycle in the Mediterranean region and implications for the water budget of the Mediterranean Sea. J. Clim. 2002, 15, 1674–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, J.; Saenz, J.; Zorita, E. Analysis of the wintertime atmosphere moisture transport and its variability over the Mediterranean Basin. Clim. Res. 2003, 23, 195–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schicker, I.; Radanovics, S. and Seibert, P. Origin and transport of Mediterranean moisture and air. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 5089–5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanovic, M.; Drumond, A.; Nieto, R.; Gimeno, L. Moisture Transport Anomalies over the Danube River Basin during Two Drought Events: A Lagrangian Analysis. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigo, R.M.; Añel, J.A.; Barriopedro, D.; Garcia-Herrera, R.; Gimeno, L.; Nieto, R.; Castillo, R.; Allen, M.R.; Massey, N. The record winter drought of 2011–2012 in the Iberian Peninsula. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, S41–S45. [Google Scholar]
- Nuissier, O.; Ducroq, V.; Ricard, D.; Lebeaupin, C.; Anquetin, S. A numerical study of three catastrophic precipitating evens over southern France. I: N numerical framework and synoptic ingredients. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2008, 134, 111–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricard, D.; Ducroq, V.; Auger, L. A climatology of the mesoscale environment associated with heavily precipitating events over a northwestern Mediterranean area. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2012, 51, 468–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodemann, H.; Zubler, E. Seasonal and inter-annual variability of the moisture sources for Alpine precipitation during 1995–2002. Int. J. Climatol. 2010, 30, 947–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martius, O.; Schwierz, C.; Davies, H.C. Far-upstream precursors of heavy precipitation events on the alpine south-side. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2008, 134, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, A.A.M.; Zhang, Q.; Pausata, F.S.R.; Tjernström, M. Sources of Sahelian-Sudan moisture: Insights from a moisture-tracing atmospheric model. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 7819–7832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, R.; Vázquez, M.; Algarra, I.; Gimeno, L. An Analysis of the Water Cycle in the Sahel through a Lagrangian Perspective. In Proceedings of the 1st International Electronic Conference on Atmospheric Sciences, 16–31 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nieto, R.; Castillo, R.; Drumond, A.; Gimeno, L. A catalog of moisture sources for continental climatic regions. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 5322–5328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drumond, A.; Nieto, R.; Hernández, E.; Gimeno, L. A Lagrangian analysis of the variation in moisture sources related to drier and wetter conditions in regions around the Mediterranean basin. Nat. Hazards Earth Sys. Sci. 2011, 11, 2307–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druyan, L.M.; Koster, R.D. Sources of Sahel Precipitation for Simulated Drought and Rainy Seasons. J. Clim. 1989, 2, 1438–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionello, P. The Climate of the Mediterranean Region, from the Past to the Future, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; p. 502. ISBN 9780124160422. [Google Scholar]
- Gimeno, L.; Nieto, R.; Drumond, A.; Castillo, R.; Trigo, R. Influence of the intensification of the major oceanic moisture sources on continental precipitation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 1443–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rego, F.C.; Rocha, M.S. Climatic Patterns in the Mediterranean Region. Ecol. Mediterr. 2014, 40, 50. Available online: http://www.isa.utl.pt/ceabn/uploads/docs/publicacoes/FR_e_MR_Ecologia_Mediterranea_2014.pdf (accessed on 21 November 2017).
- Stohl, A.; James, P. A Lagrangian analysis of the atmospheric branch of the global water cycle. Part I: Method description, validation, and demonstration for the August 2002 flooding in central Europe. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 656–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohl, A.; James, P. A Lagrangian analysis of the atmospheric branch of the global water cycle: Part II: Moisture transports between Earth’s ocean basins and river catchments. J. Hydrometeorol. 2005, 6, 961–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.E.; van Dijk, A.I.J.M.; Levizzani, V.; Schellekens, J.; Miralles, D.G.; Martens, B.; de Roo, A. MSWEP: 3-hourly 0.25° global gridded precipitation (1979–2015) by merging gauge, satellite, and reanalysis data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 589–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.E.; Vergopolan, N.; Pan, M.; Levizzani, V.; van Dijk, A.I.J.M.; Weedon, G.P.; Brocca, L.; Pappenberger, F.; Huffman, G.J.; Wood, E.F. Global-scale evaluation of 23 precipitation datasets using gauge observations and hydrological modeling. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2017, 21, 6201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciric, D.; Stojanovic, M.; Drumond, A.; Nieto, R.; Gimeno, L. Tracking the Origin of Moisture over the Danube River Basin Using a Lagrangian Approach. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, P.; et al. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numaguti, A. Origin and recycling processes of precipitating water over the Eurasian continent: Experiments using an atmospheric general circulation model. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 1957–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno, L.; Stohl, A.; Trigo, R.M.; Domínguez, F.; Yoshimura, K.; Yu, L.; Drumond, A.; Durán-Quesada, A.M.; Nieto, R. Oceanic and Terrestrial Sources of Continental Precipitation. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50, RG4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohl, A.; Forster, C.; Frank, A.; Seibert, P.; Wotawa, G. Technical note: The Lagrangian particle dispersion model FLEXPART version 6.2. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 2461–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Fasullo, J.T.; Mackaro, J. Atmospheric Moisture Transports from Ocean to Land and Global Energy Flows in Reanalyses. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 4907–4924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, C.; Kunstmann, H. The Hydrological Cycle in Three State-of-the-Art Reanalyses: Intercomparison and Performance Analysis. J. Hydrometeorol. 2012, 13, 1397–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlosser, E.; Oerter, H.; Masson-Delmotte, V.; Reijmer, C. Atmospheric influence on the deuterium excess signal in polar firn: Implications for ice-core interpretation. J. Glaciol. 2008, 54, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Scarchilli, C.; Frezzotti, M.; Ruti, P.M. Snow precipitation at four ice core sites in East Antarctica: Provenance, seasonality and blocking factors. Clim. Dyn. 2011, 37, 2107–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, A.V.; Yang, S. Precipitation climatology over Mediterranean Basin from ten years of TRMM measurements. Adv. Geosci. 2008, 17, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.P.; Smith, R.B.; Oglesby, R.J. Middle East climate simulation and dominant precipitation processes. Int. J. Climatol. 2004, 24, 1671–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, Z.; Nieto, R.; Drumond, A.; Gimeno, L.; Vicente-Serrano, S.M. A Lagrangian analysis of the moisture budget over the Fertile Crescent during two intense drought episodes. J. Hydrol. 2018, 560, 382–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, J.P.; De Almeida, M.; Rosen, R.D.; Salstein, D.A. Atmospheric moisture transport and the water balance of the Mediterranean Sea. Water Resour. Res. 1982, 18, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).