Abstract
This paper investigates the sediment retention behaviour of laboratory-based permeable pavements using mono-sized sediments that were representative of the sizes typically found in urban stormwater. The sediments were applied in two cycles, namely in order of increasing and decreasing size. The results indicated that most of the sediment accumulation could be attributed to the depth of the pavement and the material used in the joint and bedding aggregates. Most of the sediment was retained in the bedding and surface layers, and little difference to the retention was made by the incorporation of a basecourse layer. When the mono-sized sediments were added in decreasing size order with the coarsest sediments applied first, the overall rate of retention increased.
1. Introduction
Urbanisation alters the natural hydrology of a catchment, increasing the risk of flooding and the need for stormwater drainage. Permeable pavements are a structural water sensitive urban design (WSUD) technology that is used to infiltrate stormwater runoff at the source without compromising the amenity of the area. In comparison to many other WSUD systems, the permeable interlocking concrete pavers (PICP) are one of few that offer structural stability for road or foot traffic [1]. The harvesting and reuse of stormwater is also becoming recognised as a viable component of sustainable urban water management with the household collection and storage of rainwater being the most common example of stormwater quantity management and reuse [2]. A typical permeable pavement system has a surface pavement layer (porous concrete or permeable interlocking concrete pavers), a thin bedding layer of fine aggregate, an underlying coarse aggregate layer (base course), and sometimes, a filter layer or fabric installed at the bottom [3]. Permeable pavement systems have the potential to harvest and store urban stormwater runoff [4] by enclosing the structurally supportive base course aggregates in an impermeable membrane [2].
A more recent use for permeable pavements is for stormwater storage following a high-intensity rainfall event. In the structural design of permeable pavements with water storage capacity, the system is lined with either a permeable or impermeable liner. The former allows for the slow infiltration into the sub-grade and groundwater, while the latter provides the harvesting and reuse of the stormwater collected (Figure 1).
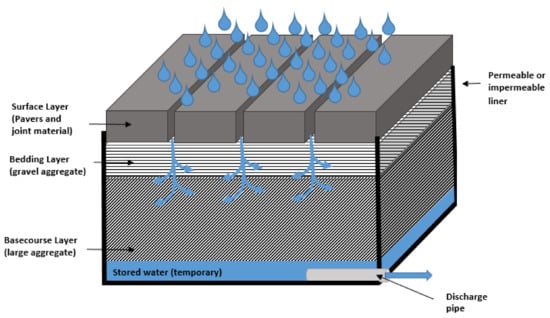
Figure 1.
A conceptual diagram of a permeable pavement which detains water prior to the discharge into the conventional urban drainage network or for withdrawal for reuse.
Several researchers have investigated the potential improvements to stormwater quality by use of permeable pavements [5,6]. Many of these studies focus on the stormwater pollutants commonly found in urban stormwater such as sediments, heavy metals, oils, and bacteria [5,6,7]. An investigation of the changes in the water quality with the use of two basecourse aggregate materials concluded that the presence of zinc, copper, and lead was reduced by 94–99% after 144 h of storage in the basecourse aggregate reservoir [6]. Several studies have examined the influence of sediment types on stormwater quality and these investigations have often involved the examination of turbidity and electrical conductivity [6,8]. In one of these studies, it was noted that the electrical conductivity increased in all tests. This was suggested to be a result of the dissolution of ions and mineral fractions on the surface of the aggregate particles in the reservoirs [8].
The application of permeable pavements in our urban environments has produced various maintenance issues that need to be addressed. The clogging of permeable pavements and the mechanisms of sediment transport within permeable pavement systems have been the subject of limited research. Sediment in the permeable pavement structure has been linked to an increased loss of infiltration capacity over time [9]. Field investigations have identified significant sediment accumulation between the pavement and bedding layers [10,11,12]. Other reasons for reduced infiltration capacities include poor construction and poor site conditions, whereby loose soils or excessive organic litter may be present near the pavement location [13,14,15]. Sediment mass is among one of the key factors known to affect permeable pavement clogging in laboratory-based research [16]. Other factors include sediment size and type [9,16,17,18], and the intermittent drying times between simulated rainfall events [13].
The physical process that dominates particle transport in permeable pavements is mechanical filtration, while the solute transport is affected by both physical and chemical processes such as advection, diffusion, dispersion, and sorption. A recent investigation into the influence of particle size on permeable pavement clogging involved the flushing of three different sediment particle sizes into experimental permeable pavement systems [16]. The sediment used consisted of natural and silica sediments from 300 µm up to 1.18 mm in diameter. Despite the common perception that sediment sizes <300 µm may have the greatest effect on clogging, the findings indicated that a larger fraction of ~1.18 mm sediment was retained in the permeable pavement system much more quickly than the finer fractions and that when subjected to a full range of particle sizes, the PICPs experienced a more rapid rate of clogging. It was suggested that the cause of this may be the large sediment particles getting trapped initially, followed by the finer sediments [16].
While there have been recent studies that have investigated the clogging process and maintenance of permeable pavements [19], no attempts have been made to pass mono-sized sediments through permeable pavement systems [16]. Mono-sized sediments are defined as being within a range of ±5% of a specified sediment diameter. One of the objectives of the research described in this paper is to investigate the effects of sediment size on permeable pavement clogging using mono-sized sediments applied in both increasing and decreasing size order. The aim of the research is to study the clogging mechanisms of sediment in the surface, bedding, and basecourse layers of a permeable pavement system. The outcomes of this research will inform researchers and designers on the possible causes of sediment accumulation within these systems, which should lead to improved design practices.
2. Materials and Methods
This study used three pavement designs, namely Design A, Design B, and Design C (Figure 2). Sediment accumulation was quantified by running two cycles of sediments through the PICPs. Firstly, sediments of increasing size (Cycle 1) were applied, followed by an experiment where sediments were applied in decreasing size (Cycle 2). The experimental design was a split plot based on a randomised design with sediment application as the main plot treatment factor and the pavement design as a subplot treatment factor. The experiment had four replications. The controls had no sediment applied throughout testing but received the same rainfall inflow conditions. This allowed for the assessment of the effects of pre-existing sediments that were washed off the aggregate material during testing, and also of pavement consolidation.
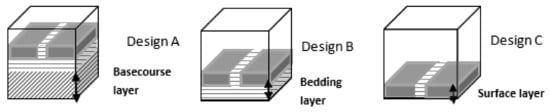
Figure 2.
A conceptual model of the pavement designs.
2.1. Experimental Configurations
Three permeable pavement configurations, each 250 mm × 250 mm × 500 mm, were constructed using impermeable sheet metal containers, with a clear Perspex frontage to allow for visual observations of the sediment and stormwater infiltration. These configurations were based on an earlier model that had been successfully tested [2,6].
The containers were fitted with an underlying steel mesh to allow the outflow to be collected from each of the permeable pavement systems. Design A was filled with a washed basecourse aggregate up to 300 mm in depth. Designs A and B had a washed bedding aggregate of 30 mm depth and Designs A, B, and C were topped with concrete pavers and joints filled with a washed aggregate (60 mm in depth). Pre-washing of the aggregates was undertaken to reduce the effect of additional sediment entering the system through wash-off effects. The final apparatus consisted of 12 permeable pavement sections, consisting of three replicates and one control for each design. A schematic diagram of the permeable pavement experiment is shown in Figure 3.
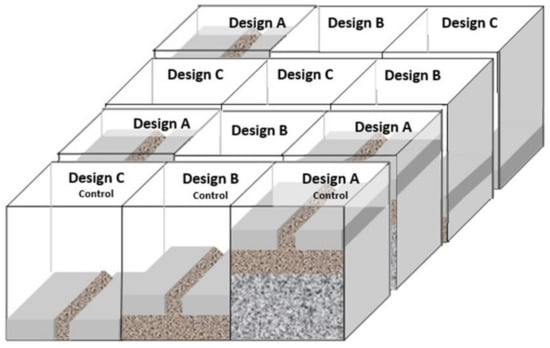
Figure 3.
Schematic diagram of the experimental design.
2.2. Aggregate Types
The laboratory scale PICP designs (Figure 2) used Boral ClassicpaveTM concrete pavers of 80 mm thickness with joint material filling a 5 mm gap between the pavers. The joint material was the same as that used for the bedding aggregate and was a 2–5 mm diameter quartzite gravel mixture, sourced from Boral Quarry at Blacktop, South Australia. The basecourse aggregate was made of 20 mm diameter dolomite and sourced from Montacute Quarry, Athlestone, South Australia. The aggregates used were representative of the dominant types and sizes which are available for paving construction in Australia and typical of permeable pavements constructed in South Australia. The pavement construction was in accordance with current permeable paving guidelines [20].
2.3. Sediment Application
Nine mono-sized sediment fractions were applied in this study. The mono-sized sediments consisted of natural sediments sourced from an impermeable area adjacent to a pre-existing permeable pavement system at the Mawson Lakes Campus, University of South Australia. The range of sizes used in the study was based on an established review of aggregate sizes in similar clay-based soils in Adelaide, South Australia [21].
To create nine mono-sized sediments, a variety of wet and dry sieving techniques commonly used in clogging research [16] were applied to natural sediments collected from an impermeable surface at the University of South Australia, Mawson Lakes Campus. The fractions into which the sediment was sieved are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
The mono-sized sediment fractions based on the Adelaide clay soils (PSD = Particle Size Distribution).
After sieving, each of the nine mono-sized sediment fractions was analysed using a laser diffraction technique (Malvern Mastersizer, 2000). The results from the particle size detection are shown in Figure 4, which describes the distribution of each of the fractions shown in Table 1. From this analysis, the average sediment size was obtained and reported as the mono-sized sediment (Table 1). The 9 peaks evident in Figure 4 are, therefore, directly relate to each of the 9 mono-sized sediment fractions used in this research.
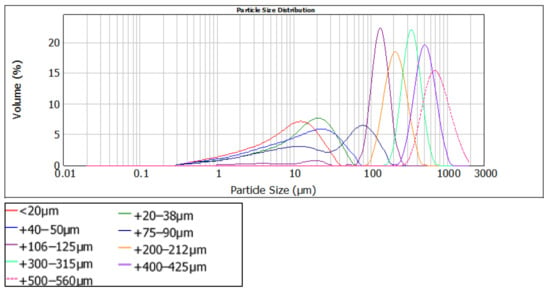
Figure 4.
The size distribution of the applied nine mono-sized sediments.
The mono-sized sediments were applied in size order. The application of sediments followed two cycles. Cycle 1 was the sequential application of sediments sized from small to large (sediment sizes 1–9 shown in Table 1) and Cycle 2 was the sequential application of sediments sized from large to small (sizes 9–1 shown in Table 1). The apparatus was cleaned and reassembled between the two cycles.
In the accelerated testing, which simulated 15 years of rainfall, a sediment concentration of 335 mg/L was applied to the permeable pavement. This was based on a review of stormwater quality studies and it corresponds well to similar studies [22]. Prior to the experimental procedure, the 12 pavement units were all tested for their Surface Infiltration Rate (SIR). Each of the pavements tested had a 0.25 m × 0.25 m square surface area. To determine the SIR of the pavements, each design unit was filled with water to a height of 30 mm. The SIR was estimated by measuring the time taken for 10 L of sediment-free water to pass through the pavement while the water level remained constant. The SIR was determined in litres per second (L/s). In this research, a flow rate of 1.62 L/s was applied, which was reflective of the Adelaide climate. The method used to calculate this was adapted from a previous Australian study [23]. At a flow rate of 1.62 L/s, for each cycle of testing, a total of 10.5 h of continuous wetting was required to deliver the average annual rainfall of Adelaide (571 mm). To ensure the correct sediment dosage of 335 mg/L, a mass of sediment of 5.6 g was added to 17 L of water which was then applied over a duration of 10.5 h producing an application of 0.56 g/h. To ensure effective mixing, continuous stirring was applied prior to the application of the water and sediment.
2.4. Sediment Analysis
Samples were collected from the outflow after each simulated year of rainfall for the complete 15 years of accelerated testing (Figure 5). Following the collection of the outflow samples at the end of the 15 years’ accelerated testing, the pavements were left to dry and the SIR was again measured and recorded. Flow rates were monitored continuously throughout the experiment [24]. The samples were dried and weighed to quantify the mass of sediment in the outflow samples before the particle size distribution was measured using a Laser Diffraction Particle Size Analyser (Malvern Mastersizer 2000).
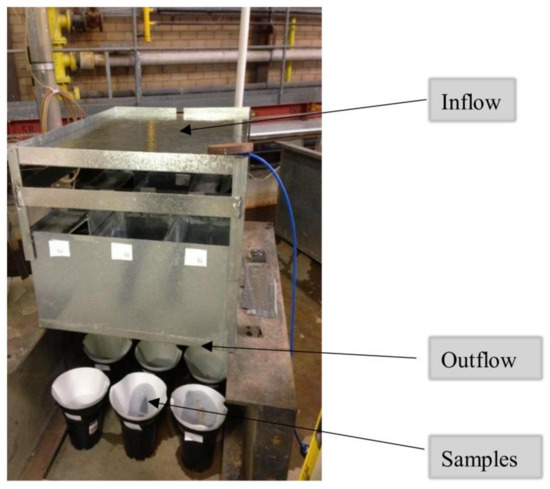
Figure 5.
The inflow, outflow, and sampling locations.
3. Results
Figure 6 and Figure 7 show the measured SIRs of the pavements in Cycles 1 and 2, respectively; both before (Year 0) and after (Year 15) the application of the equivalent of 15 years of rainfall and sediment. Each pavement configuration (Designs A, B, and C) are shown, together with their respective controls (Ca, Cb, and Cc). The SIR values presented in Figure 6 and Figure 7 are averages, although there was little variation across the replicates [24].
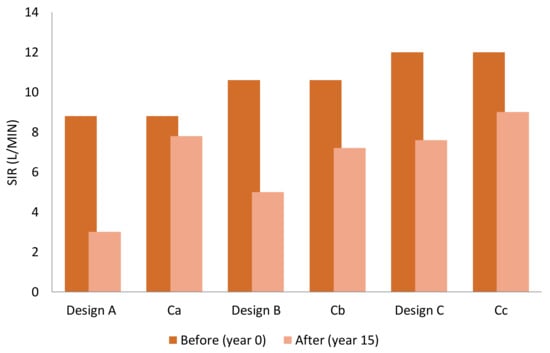
Figure 6.
The average surface infiltration rate (SIR) before and after 15 years’ stormwater and sediment application (Cycle 1).
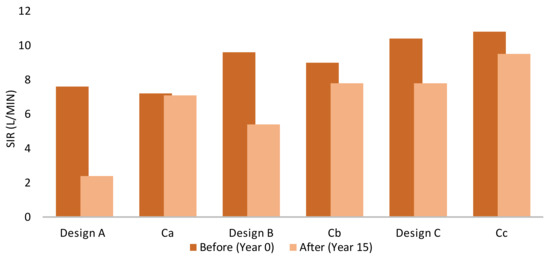
Figure 7.
The average SIR before and after 15 years’ stormwater and sediment application (Cycle 2).
From the analysis of the sediment mass collected from the outflows, the retention capacities of each pavement were also estimated. Figure 8A,B present the cumulative sediment mass data for Cycles 1 and 2, respectively. Considering that 84 g of sediment was applied in total, there was a cumulative retention of 48–81% in Cycle 1, and 74–94% in Cycle 2.
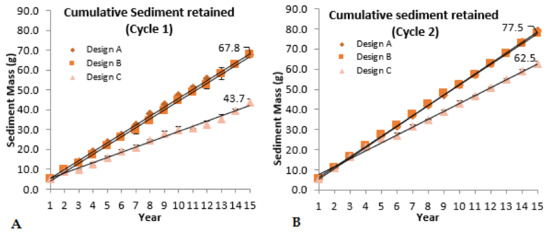
Figure 8.
The cumulative sediment retention of permeable interlocking concrete pavers (PICPs) in (A) Cycle 1 and (B) Cycle 2.
4. Discussion
As expected, the SIR generally decreased with an increasing number of infiltration layers from Design C (highest SIR) to Design A (lowest SIR). The only exception to this was observed in the control for Design A in both Cycles 1 and 2 (Figure 6 and Figure 7). In all tests, the clogging process was clearly evident, with all designs across both cycles showing substantial reductions in the infiltration rates over time. This clearly indicates a process of mechanical filtering of the sediment particles. However, differences were evident between the two sediment application cycles, indicating that the physical process changes depending on whether small or large particles pass through the system first. This may also be influenced by the aggregate sizes used in the bedding and basecourse layers. Designs A, B, and C all displayed a smaller reduction in SIR when sediments were applied in decreasing size order (Cycle 2) than when applied in increasing size order (Cycle 1).
From Figure 8A,B, it is clear that in both cycles there was a good sediment retention in the joint material (Design C) with very little difference between the sediment retentions in Designs A and B. This indicates that most of the sediment that migrates through the joint material is retained in the bedding layer and does not pass through to the basecourse layer. More sediment is retained in Cycle 2 (Figure 8B) than in Cycle 1 (Figure 8A). This might indicate that in Cycle 2, the coarser sediment sizes cause blockages that then prevent the (later applied) finer sediment sizes from passing through the joint and bedding material. In Cycle 1, the same finer sediment sizes pass through the joint and bedding material before the coarser sediment sizes are applied, resulting in lower overall sediment retention rates.
The significance of this study is that it is the first to investigate how mono-sized sediments are trapped inside three different permeable pavement configurations. It was found that coarse particles cause an earlier blockage, possibly due to the accumulation of finer sediments behind them.
5. Conclusions
Previous research suggests a link between applying a full range of sediment sizes and increased sediment retention, with a suggestion that coarse particles become trapped first, followed by finer particles. The research presented in this paper supports the idea of a range of particle sizes causing a greater clogging effect. By applying sediments in order of size, both from fine to coarse (Cycle 1) and coarse to fine (Cycle 2), it was found that coarse particles play an important role in the accumulation process, particularly when a full range of particle sizes are applied.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the funding received from the Australian Research Council under grant LP110100222. The collaboration and funding from the industry partners in this project (City of Salisbury Council, SA Water Corporation, Adelaide, SA, Australia and Zero Waste SA) is also greatly appreciated.
Author Contributions
Simon Beecham conceived and designed the experiments; Kelly Diane Hill performed the experiments and analysed the data; Simon Beecham and Kelly Diane Hill wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sansalone, J.; Kuang, X.; Ying, G.; Ranieri, V. Filtration and clogging of permeable pavement loaded by urban drainage. Water Res. 2012, 46, 6763–6774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, B.R.; Beecham, S.; Van Leeuwen, J.; Keegan, A. Depletion of E. coli in permeable pavement mineral aggregate storage and reuse systems. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 60, 3091–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chowdhury, R.K.; Sharvelle, S.E.; Beecham, S. Greywater quality changes in a permeable pavement reservoir. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Water Manag. 2016, 169, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beecham, S.; Myers, B. Structural and design aspects of porous and permeable block pavements. J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. 2007, 43, 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Brattebo, B.O.; Booth, D.B. Long-term stormwater quantity and quality performance of permeable pavement systems. Water Res. 2003, 37, 4369–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, B.; Beecham, S.; van Leeuwen, J. Water quality with storage in permeable pavement basecourse. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Water Manag. 2011, 164, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryal, R.; Beecham, S.; Lee, B. Evaluation of particle transport in permeable pavements under oil loadings. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2015, 19, 2000–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, F.; Hill, K. Effect of permeable pavement basecourse aggregates on stormwater quality for irrigation reuse. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 77, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucke, T.; Beecham, S. Field investigation of clogging in a permeable pavement system. J. Build. Res. Inf. 2011, 39, 603–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boogaard, F.; Lucke, T.; van de Giesen, N.; van de Ven, F. Evaluating the infiltration performance of eight Dutch permeable pavements using a new full-scale infiltration testing method. Water 2014, 6, 2070–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boogaard, F.; Lucke, T.; Beecham, S. Effect of age of permeable pavements on their infiltration function. Clean Soil Air Water 2013, 42, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzaniti, D.; Beecham, S.; Kandasamy, J. Influence of clogging on the effective life of permeable pavements. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Water Manag. 2009, 162, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassman, E.; Blackbourn, S. Urban runoff mitigation by a permeable pavement system over impermeable soils. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2010, 15, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bean, E.Z.; Hunt, W.F.; Bidelspach, D.A. Evaluation of four permeable pavement sites in eastern North Carolina for runoff reduction and water quality impacts. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2007, 133, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, P.W.B.; Lucke, T.; Dierkes, C. Comparing two methods of determining infiltration rates of permeable interlocking concrete pavers. Water 2014, 6, 2353–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, P.W.B.; White, R.; Lucke, T. Do sediment type and test durations affect results of laboratory-based, accelerated testing studies of permeable pavement clogging? Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 511, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, K.; Kozak, J.; Hundal, L.; Cox, A.; Zhang, H.; Granato, T. In-situ infiltration performance of different permeable pavements in an employee used parking lot—A four-year study. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 167, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Støvring, J.; Dam, T.; Jensen, M.B. Surface sedimentation at permeable pavement systems: Implications for planning and design. Urban Water J. 2018, 15, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, H.; Rockaway, T.D.; Rivard, J.; Abdollahian, S. Assessment of surface infiltration performance and maintenance of two permeable pavement systems in Louisville, Kentucky. J. Sustain. Water Built Environ. 2017, 3, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concrete Masonry Association of Australia (CMAA). Permeable Paving Design Guidelines. Available online: https://cmaa.blob.core.windows.net/media/1044/pe01-permeable-interlocking-concrete-pavements-design-and-construction-guide.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2017).
- Oades, J.M.; Waters, A.G. Aggregate hierarchy in soils. Aust. J. Soil Res. 1991, 29, 815–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Duin, B.; Brown, C.; Chu, A.; Marsalek, J.; Valeo, C. Characterization of long-term solids removal and clogging processes in two types of permeable pavement under cold climate conditions. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Urban Drainage, Edinburgh, UK, 31 August–5 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Yong, C.F.; Deletic, A.; Fletcher, T.D.; Grace, M.R. Hydraulic and treatment performance of pervious pavements under variable drying and wetting regimes. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 64, 1692–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadiar, K. An Examination into the Mechanisms and Behaviours Associated with Sediment Accumulation in Permeable Pavements. Ph.D. Thesis, University of South Australia, Adelaide, Australia, 2017; p. 225. [Google Scholar]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).