Variability of Rainfall Erosivity and Erosivity Density in the Ganjiang River Catchment, China: Characteristics and Influences of Climate Change
Abstract
1. Introduction
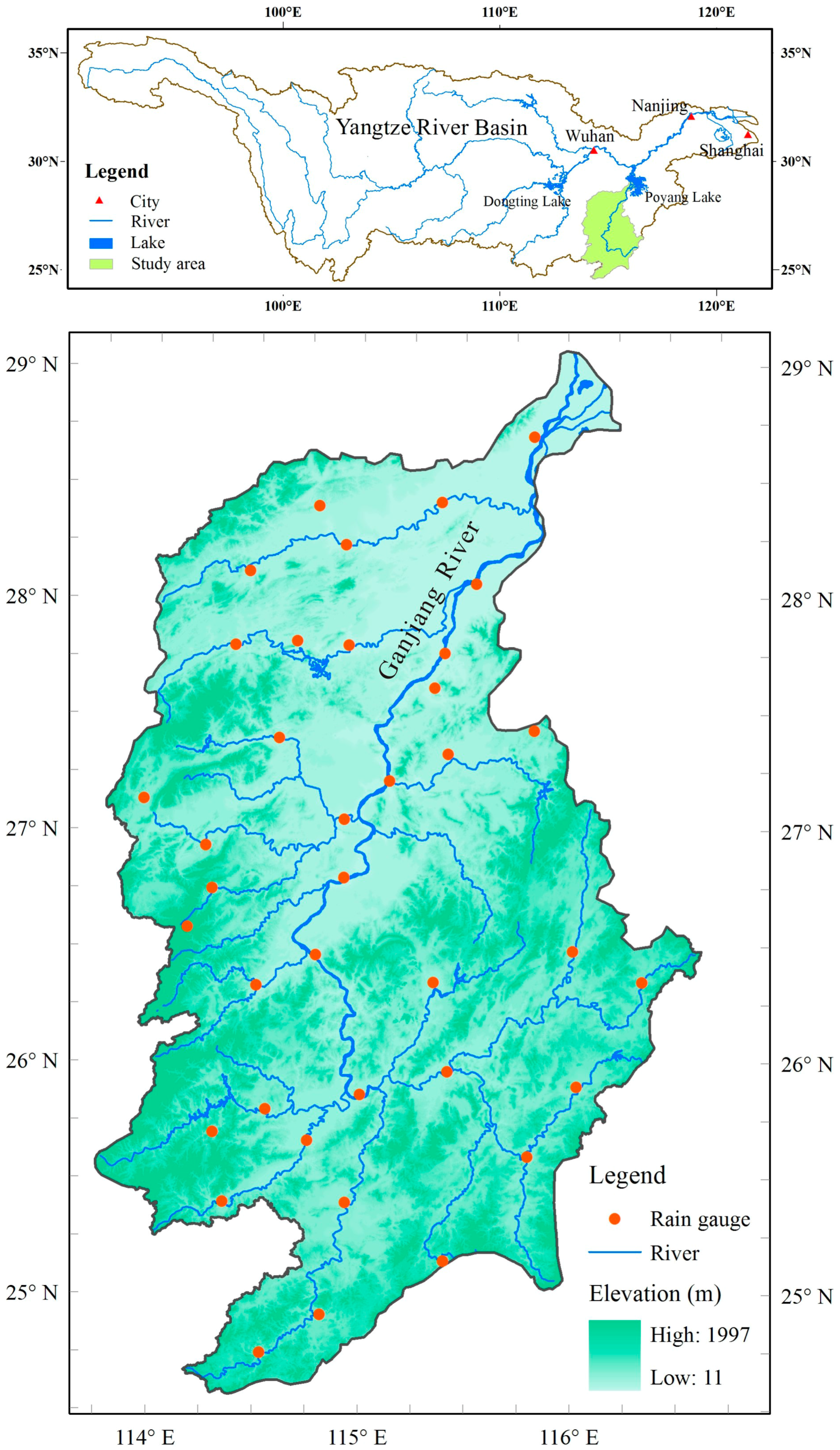
2. Study Area and Data
3. Methods
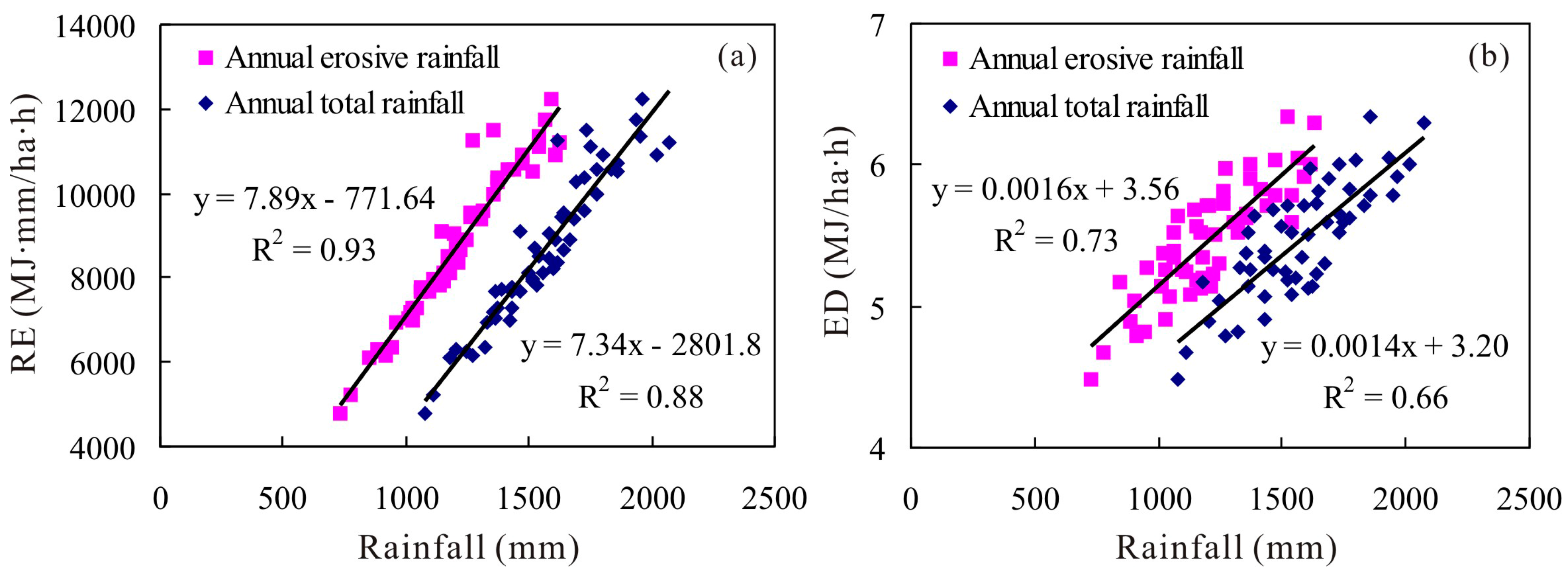
3.1. Rainfall Erosivity
3.2. Erosivity Density
3.3. Spatial Interpolation and Temporal Changes
4. Results
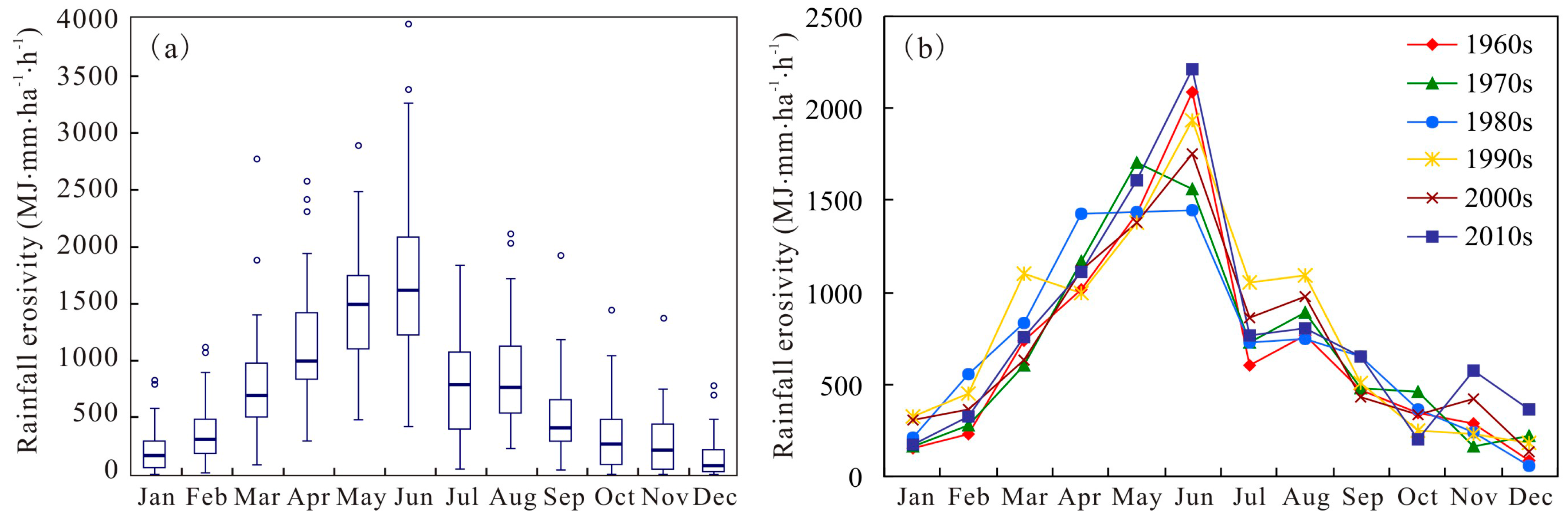
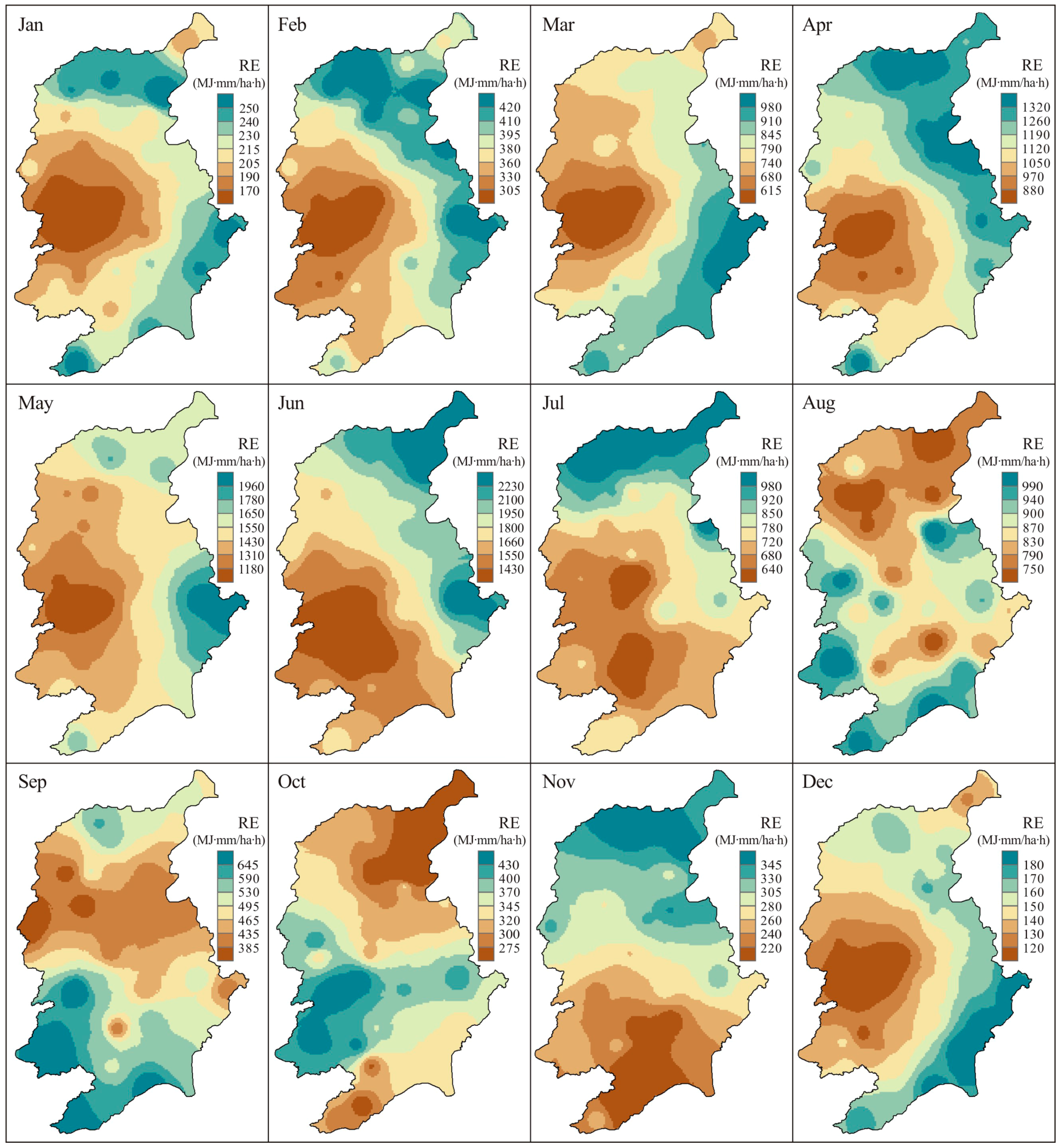
4.1. Intra-Annual Distribution of RE and ED
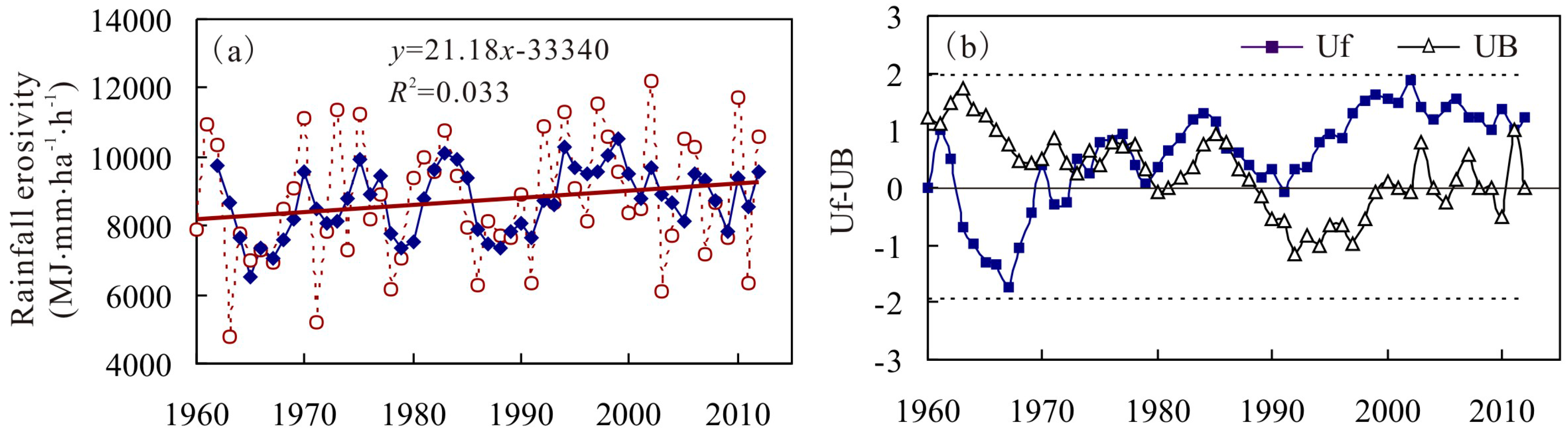
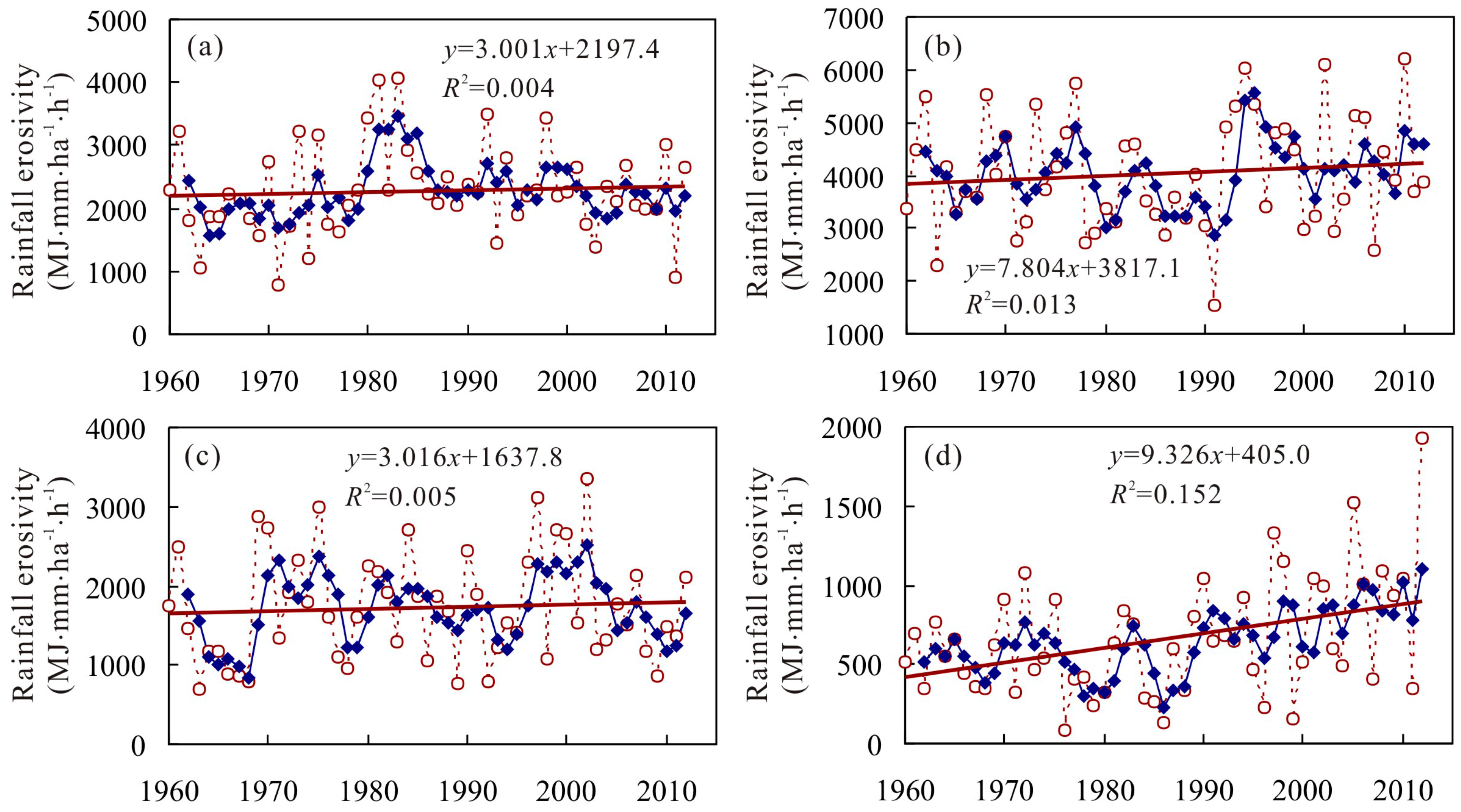
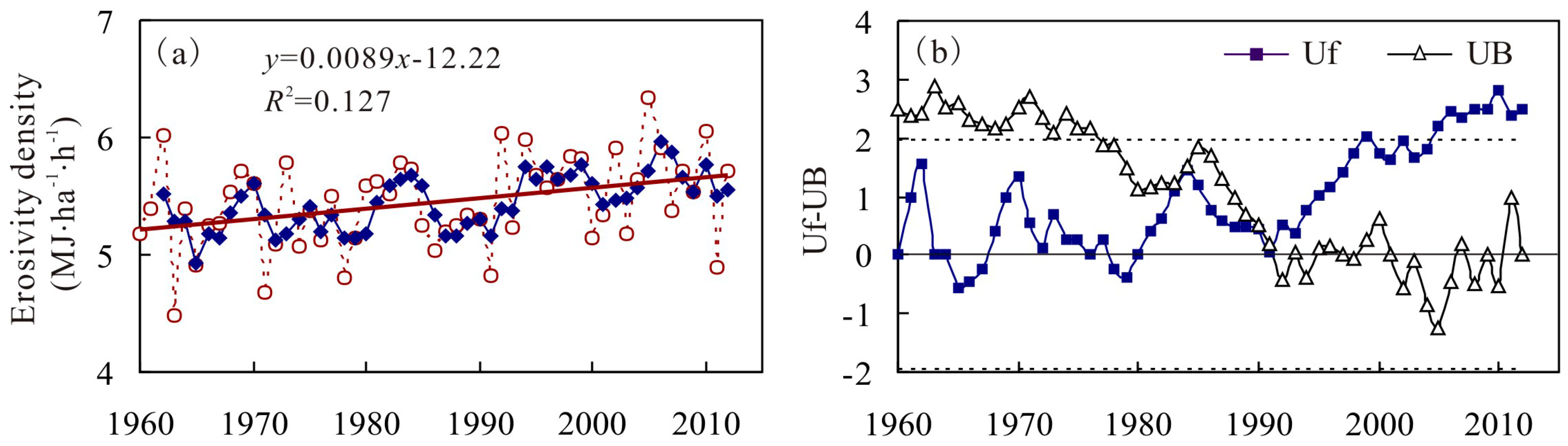
4.2. Inter-Annual Variation of RE and ED
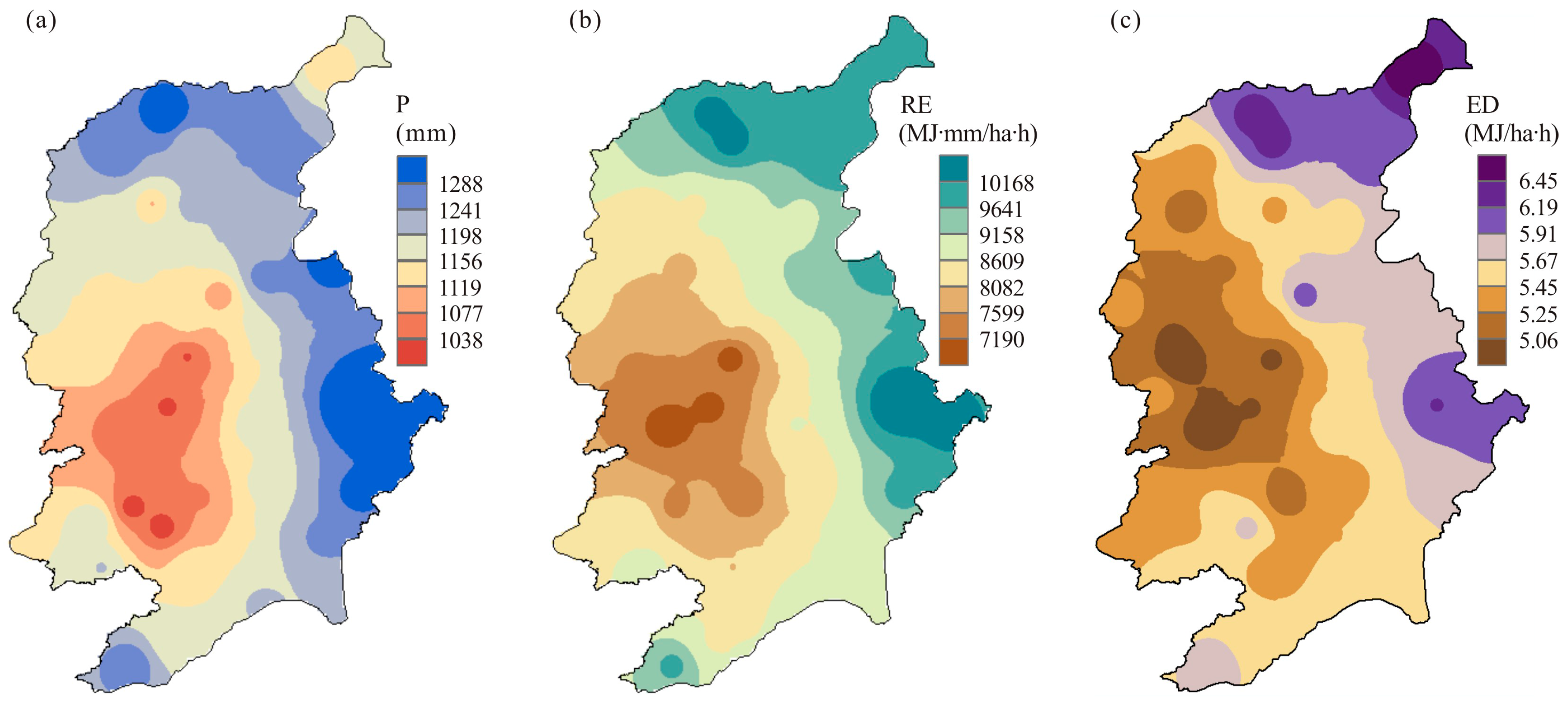
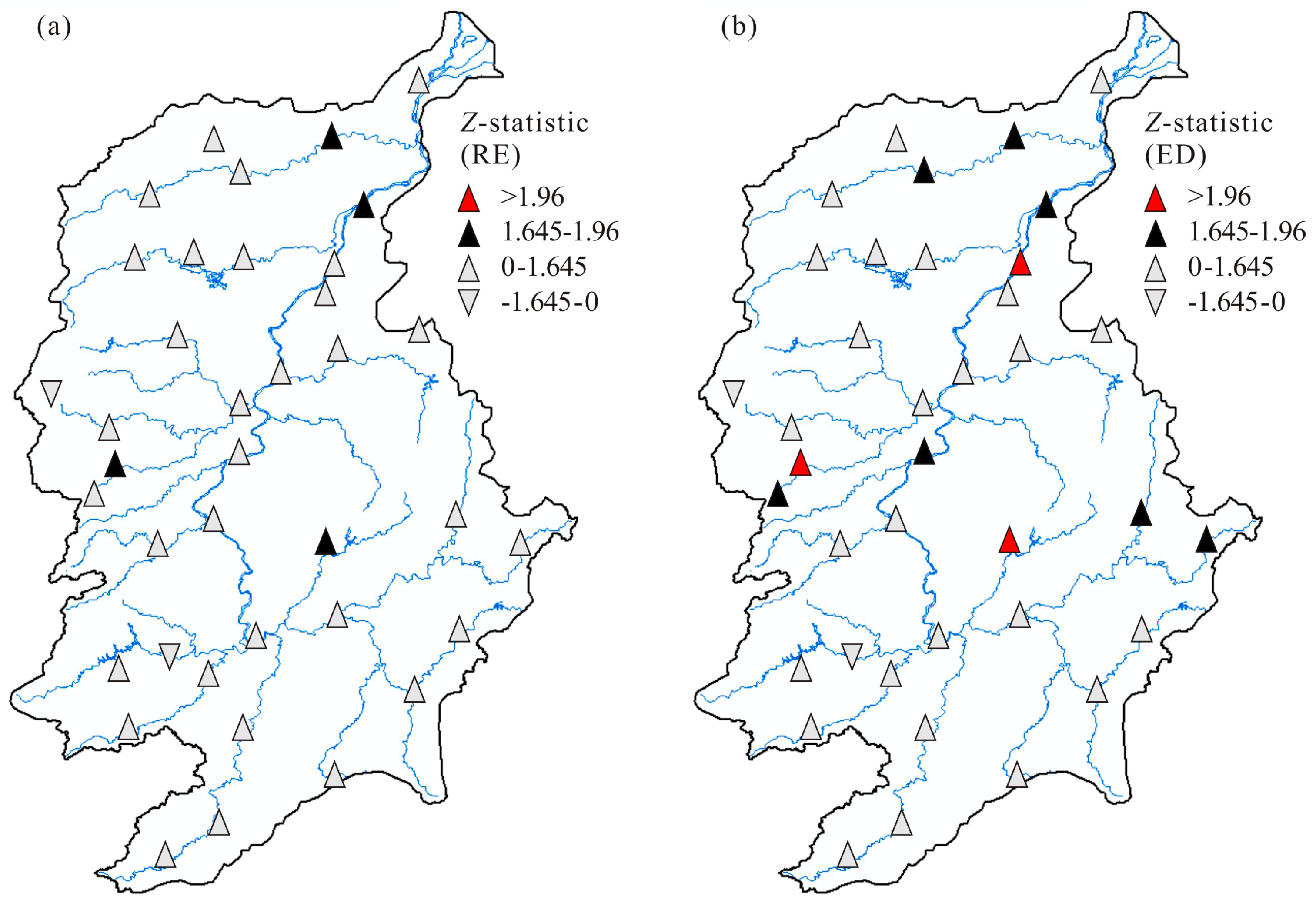
4.3. Spatial Distribution of RE and ED
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bahadur, K.C.K. Mapping soil erosion susceptibility using remote sensing and GIS: A case of the Upper Nam Wa Watershed, Nan Province, Thailand. Environ. Geol. 2009, 57, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplot, V. Impact of terrain attributes, parent material and soil types on gully erosion. Geomorphology 2013, 186, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Oost, K.; Quine, T.A.; Govers, G.; De Gryze, S.; Six, J.; Harden, J.W.; Ritchie, J.C.; McCarty, G.W.; Heckrath, G.; Kosmas, C.; et al. The impact of agricultural soil erosion on the global carbon cycle. Science 2007, 318, 626–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinton, J.N.; Govers, G.; Van Oost, K.; Bardgett, R.D. The impact of agricultural soil erosion on biogeochemical cycling. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, D. Soil erosion: A food and environmental threat. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2006, 8, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, A.; Khare, D.; Kundu, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Mondal, S. Uncertainty of soil erosion modelling using open source high resolution and aggregated DEMs. Geosci. Front. 2017, 8, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, P.T.S.; Wendland, E.; Nearing, M.A. Rainfall erosivity in Brazil: A review. Catena 2013, 100, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.Y.; Bi, X.G.; Fu, S.H. Beijing Soil Loss Equation; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2010. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, E.X.; Huang, W.; Zhou, J.Q.; Ju, J.H. Characteristic analysis of precipitation and temperature trend in Yunnan Province in recent 46 years. J. Catastrophol. 2010b, 25, 39–44. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Z.J.; Duan, X.W.; Liu, B.; Hu, J.M.; He, J.N. The spatial distribution and temporal variation of rainfall erosivity in the Yunnan Plateau, Southwest China: 1960–2012. Catena 2016, 145, 291–300. [Google Scholar]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses: A Guide to Conservation Planning; Agriculture Handbook No. 537; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1978.
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, G.A.; McCool, D.K.; Yoder, D.C. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE); Agriculture Handbook, No. 703; U.S. Departement of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1997.
- Wang, Y.S.; Tan, S.; Liu, B.Y.; Yang, Y. Estimating rainfall erosivity by incorporating seasonal variations in parameters into the Richardson model. J. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 275–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Liu, X.; Ma, X.Y. Spatiotemporal distribution of rainfall erosivity in the Yanhe River watershed of hilly and gully region, Chinese Loess Plateau. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Ballabio, C.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K. Spatio-temporal analysis of rainfall erosivity and erosivity density in Greece. Catena 2016, 137, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyos, N.; Waylen, P.R.; Jaramillo, A. Seasonal and spatial patterns of erosivity in a tropical watershed of the Colombian Andes. J. Hydrol. 2005, 314, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshesha, D.T.; Tsunekawa, A.; Tsubo, M.; Haregeweyn, N.; Adgo, E. Evaluating spatial and temporal variations of rainfall erosivity, case of central rift valley of Ethiopia. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 119, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, B.J.; Shi, Z.H.; Fang, N.F. Evaluation of rainfall erosivity and its temporal variation in the Yanhe River catchment of the Chinese Loess Plateau. Nat. Hazards 2014, 74, 585–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diodato, N.; Borrelli, P.; Fiener, P.; Bellocchi, G.; Romano, N. Discovering historical rainfall erosivity with a parsimonious approach: A case study in Western Germany. J. Hydrol. 2017, 544, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meusburger, K.; Steel, A.; Panagos, P.; Montanarella, L.; Alewell, C. Spatial and temporal variability of rainfall erosivity factor for Switzerland. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, A.M. Rainfall erosivity map for Brazil. Catena 2004, 57, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Heo, J.H. Evaluation of estimation methods for rainfall erosivity based on annual precipitation in Korea. J. Hydrol. 2011, 409, 30–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loureiro, N.D.; Coutinho, M.D. A new procedure to estimate the RUSLE EI30 index, based on monthly rainfall data and applied to the Algarve Region, Portugal. J. Hydrol. 2001, 250, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.B.; Xie, Y.; Liu, B.Y. Rainfall erosivity estimation using daily rainfall amounts. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2002, 22, 705–711. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Diodato, N. Estimating RUSLE’s rainfall factor in the part of Italy with a Mediterranean rainfall regime. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2004, 8, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diodato, N.; Bellocchi, G. Estimating monthly (R)USLE climate input in a Mediterranean region using limited data. J. Hydrol. 2007, 345, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Xie, Y.; Nearing, M.A.; Wang, C. Estimation of rainfall erosivity using 5-to 60-minute fixed-interval rainfall data from China. Catena 2007, 70, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.H.; Wen, Y. Estimation of soil erosion using RUSLE in Caijiamiao watershed, China. Nat. Hazards 2014, 71, 2187–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M.J.; Shepherd, K.D.; Walsh, M.G. Empirical reformulation of the universal soil loss equation for erosion risk assessment in a tropical watershed. Geoderma 2005, 124, 235–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luis, M.; Brunetti, M.; Gonzalez-Hidalgo, J.C.; Longares, L.A.; Martin-Vide, J. Changes in seasonal precipitation in the Iberian peninsula during 1946–2005. Glob. Planet Chang. 2010, 74, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.W.; Kanae, S.; Oki, T.; Koike, T.; Musiake, K. Global potential soil erosion with reference to land use and climate changes. Hydrol. Process. 2003, 17, 2913–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beskow, S.; Mello, C.R.; Norton, L.D.; Curi, N.; Viola, M.R.; Avanzi, J.C. Soil erosion prediction in the Grande River Basin, Brazil using distributed modeling. Catena 2009, 79, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernando, D.; Romana, M.G. Estimating the rainfall erosivity factor from monthly precipitation data in the Madrid Region (Spain). J. Hydrol. Hydromech. 2015, 63, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meddi, M.; Toumi, S.; Assani, A.A. Spatial and temporal variability of the rainfall erosivity factor in Northern Algeria. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, S.H.; Tavangar, S. Development of stational models for estimation of rainfall erosivity factor in different timescales. Nat. Hazards 2015, 77, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.R.; Chen, Y.; Yan, D.; Guo, F.F. Characteristics of rainfall erosivity based on tropical rainfall measuring mission data in Tibet, China. J. Mt. Sci-Engl. 2013, 10, 1008–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.B.; Fu, J.S. Rainfall Erosivity Estimation under Different Rainfall Amount. Resour. Sci. 2003, 25, 35–41. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Angulo-Martinez, M.; Begueria, S. Estimating rainfall erosivity from daily precipitation records: A comparison among methods using data from the Ebro Basin (NE Spain). J. Hydrol. 2009, 379, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.B.; Xie, Y.; Liu, B.Y. Spatial distribution of rainfall erosivity in China. J. Mt. Sci. 2003, 21, 33–40. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ballabio, C.; Borrelli, P.; Spinoni, J.; Meusburger, K.; Michaelides, S.; Begueria, S.; Klik, A.; Petan, S.; Janecek, M.; Olsen, P.; et al. Mapping monthly rainfall erosivity in Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 1298–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, W.; Guo, Q.K.; Zuo, C.Q.; Shan, Z.J.; Ma, L.; Sun, G. Spatial distribution and temporal trends of rainfall erosivity in mainland China for 1951–2010. Catena 2016, 147, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamlaoui-Moulai, L.; Mesbah, M.; Souag-Gamane, D.; Medjerab, A. Detecting hydro-climatic change using spatiotemporal analysis of rainfall time series in Western Algeria. Nat. Hazards 2013, 65, 1293–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Ballabio, C.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K.; Klik, A.; Rousseva, S.; Tadic, M.P.; Michaelides, S.; Hrabalikova, M.; Olsen, P.; et al. Rainfall erosivity in Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 511, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klik, A.; Haas, K.; Dvorackova, A.; Fuller, I.C. Spatial and temporal distribution of rainfall erosivity in New Zealand. Soil Res. 2015, 53, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilla, C.A.; Vidal, K.L. Rainfall erosivity in central Chile. J. Hydrol. 2011, 410, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.C.; Durán, B. Assessment of rainfall erosivity and its spatial and temporal variabilities: Case study of the Penedes Area (NE Spain). Catena 2014, 123, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Yin, S.Q.; Liu, B.Y.; Nearing, M.A.; Zhao, Y. Models for estimating daily rainfall erosivity in China. J. Hydrol. 2016, 535, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Xie, Y.; Liu, B.; Nearing, M.A. Rainfall erosivity estimation based on rainfall data collected over a range of temporal resolutions. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 4113–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.B.; Lu, C.H. Spatiotemporal variation and trends in rainfall erosivity in China’s dryland region during 1961–2012. Catena 2015, 133, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.F.; Yu, M.X.; Lu, G.B.; Cai, T.; Bai, X.; Xia, Z.Q. Impacts of the Gezhouba and Three Gorges reservoirs on the sediment regime in the Yangtze River, China. J. Hydrol. 2011, 403, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.H.; Zheng, F.L.; Zhang, X.C.; Wang, B. Trends and variability of daily precipitation and extremes during 1960–2012 in the Yangtze River Basin, China. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 1282–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.P.; Sun, J.Q.; Chen, X.L.; Zhou, W. CGCM projections of heavy rainfall events in China. Int. J. Climatol. 2012, 32, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.J. Coauthors, Extreme Climate in China: Facts, Simulation and Projection. Meteorol. Z. 2012, 21, 279–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.J.; Chen, D.L. Trends in extreme precipitation indices across China detected using quantile regression. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2016, 17, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplot, V. Impact of spatial input data resolution on hydrological and erosion modeling: Recommendations from a global assessment. Phys. Chem. Earth 2014, 67–69, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi, M.; Govindaraju, R.S.; Hantush, M.M.; Engel, B.A. Role of watershed subdivision on modeling the effectiveness of best management practices with SWAT. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2006, 42, 513–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Jiang, G.H.; Zuo, C.Q.; Qiu, G.Y.; Huo, H.G. Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of rainfall erosivity changes in Jiangxi Province over more than 50 years. Trans. CSAE 2009, 25, 61–68. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Sun, S.L.; Zhang, J.C. Detection of trends in precipitation during 1960–2008 in Jiangxi Province, Southeast China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2013, 114, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.C.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Li, X.H.; Xu, C.Y. Distinguishing the relative impacts of climate change and human activities on variation of streamflow in the Poyang Lake catchment, China. J. Hydrol. 2013, 494, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.L.; Yang, X.H.; Chen, S.X.; Cai, H.Y. An assessment of erosivity distribution and its influence on the effectiveness of land use conversion for reducing soil erosion in Jiangxi, China. Catena 2015, 125, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankman, D.; Keim, B.D.; Song, J. Flood frequency in China’s poyang lake region: Trends and teleconnections. Int. J. Climatol. 2006, 26, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.F.; Yang, D.W.; Wang, Y.T.; Yang, H.B. Accuracy and spatio-temporal variation of high resolution satellite rainfall estimate over the Ganjiang River Basin. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2013, 56, 853–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; You, Q.L.; Lin, H.B.; Chen, C.C. Analysis of dry/wet conditions in the Gan River Basin, China, and their association with large-scale atmospheric circulation. Glob. Planet Chang. 2015, 133, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.Y. Suitability of the TRMM satellite rainfalls in driving a distributed hydrological model for water balance computations in Xinjiang catchment, Poyang Lake Basin. J. Hydrol. 2012, 426–427, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Yao, J.; Li, Y.L.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.Y. A modeling study of the influences of Yangtze River and local catchment on the development of floods in Poyang Lake, China. Hydrol. Res. 2016, 47, 102–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Ye, X.C. Investigation of the drought-flood abrupt alternation of streamflow in Poyang Lake catchment during the last 50 years. Hydrol. Res. 2017, 48, 1402–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnell, P.I.A. Event soil loss, runoff and the universal soil loss equation family of models: A review. J. Hydrol. 2010, 385, 384–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabney, S.M.; Yoder, D.C.; Vieira, D.A.N.; Bingner, R.L. Enhancing RUSLE to include runoff-driven phenomena. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 1373–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.H.; Li, J.; Li, X.L.; Xu, X.G. Analysis on quasi-periodic characteristics of precipitation in recent 50 years and trend in next 20 years in China. Arid Zone Res. 2012, 29, 1–10. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, R.O. Statistical Methods for Environmental Pollution Monitoring; Van Nostrand Reinhold Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Salmi, T.; Maata, A.; Antilla, P.; Ruoho-Airola, T.; Amnell, T. Detecting Trends of Annual Values of Atmospheric Pollutants by the Mann–Kendall Test and Sen's Slope Estimates—The Excel Template Application Makesens; Finnish Meteorological Institute: Helsinki, Finland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, S.; Alewell, C.; Panagos, P.; Meusburger, K. Regionalization of monthly rainfall erosivity patterns in Switzerland. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 4359–4373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, X.L.; Lim, K.J.; Cai, X.B.; Sagong, M. Assessment of soil erosion and sediment yield in Liao watershed, Jiangxi Province, China, using USLE, GIS, and RS. J. Earth Sci.-China 2010, 21, 941–953. [Google Scholar]
- Routschek, A.; Schmidt, J.; Enke, W.; Deutschlaen, T. Future soil erosion risk—Results of GIS-based model simulations for a catchment in Saxony/Germany. Geomorphology 2014, 206, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukundan, R.; Pradhanang, S.M.; Schneiderman, E.M.; Pierson, D.C.; Anandhi, A.; Zion, M.S.; Matonse, A.H.; Lounsbury, D.G.; Steenhuis, T.S. Suspended sediment source areas and future climate impact on soil erosion and sediment yield in a New York City water supply watershed, USA. Geomorphology 2013, 183, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Xie, L. Spatiotemporal changes in precipitation extremes over Yangtze River basin, China, considering the rainfall shift in the late 1970s. Glob. Planet Chang. 2016, 147, 106–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Zhou, L. Observed trends in extreme precipitation events in china during 1961–2001 and the associated changes in large-scale circulation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, l09707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.Y.; Zhang, Z.X.; Chen, Y.Q.D.; Liu, C.L.; Lin, H. Spatial and temporal variability of precipitation maxima during 1960–2005 in the Yangtze River Basin and possible association with large-scale circulation. J. Hydrol. 2008, 353, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Q.L.; Kang, S.C.; Aguilar, E.; Pepin, N.; Flugel, W.A.; Yan, Y.P.; Xu, Y.W.; Zhang, Y.J.; Huang, J. Changes in daily climate extremes in china and their connection to the large scale atmospheric circulation during 1961–2003. Clim. Dyn. 2011, 36, 2399–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.C.; Li, X.H.; Liu, J.; Xu, C.Y.; Zhang, Q. Variation of reference evapotranspiration and its contributing climatic factors in the Poyang Lake Catchment, China. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 6151–6162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Hong, H.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Nie, R. Effects of climatic variation on pan-evaporation in the Poyang Lake Basin, China. Clim. Res. 2014, 61, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prein, A.F.; Rasmussen, R.M.; Ikeda, K.; Liu, C.H.; Clark, M.P.; Holland, G.J. The future intensification of hourly precipitation extremes. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2017, 7, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xiao, M.Z.; Singh, V.P.; Wang, Y.Q. Spatiotemporal variations of temperature and precipitation extremes in the Poyang Lake Basin, China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2016, 124, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, C.W.; Foster, G.R.; Wright, D.A. Estimation of erosion index from daily rainfall amount. Trans. ASAE 1983, 26, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Decades | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | Annual RE | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RE (MJ·mm/ha·h) | P (%) | RE (MJ·mm/ha·h) | P (%) | RE (MJ·mm/ha·h) | P (%) | RE (MJ·mm/ha·h) | P (%) | RE (MJ·mm/ha·h) | P (%) | |
| 1960s | 1988 | 24.2 | 4119 | 50.1 | 1578 | 19.2 | 529 | 6.4 | 8214 | 100 |
| 1970s | 2057 | 24.4 | 4004 | 47.5 | 1834 | 21.8 | 536 | 6.4 | 8431 | 100 |
| 1980s | 2814 | 32.4 | 3611 | 41.6 | 1759 | 20.3 | 498 | 5.7 | 8682 | 100 |
| 1990s | 2545 | 26.8 | 4370 | 46.0 | 1855 | 19.5 | 727 | 7.7 | 9497 | 100 |
| 2000s | 2114 | 24.2 | 3996 | 45.8 | 1751 | 20.1 | 859 | 9.8 | 8720 | 100 |
| 2010s | 2198 | 23.0 | 4584 | 48.1 | 1651 | 17.3 | 1107 | 11.6 | 9540 | 100 |
| Average | 2298 | 26.2 | 4052 | 46.3 | 1749 | 20.0 | 657 | 7.5 | 8756 | 100 |
| Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | Annual RE | Annual ED | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M-K statistic | 0.64 | 0.68 | 0.35 | 2.13 * | 1.21 | 2.50 * |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Ye, X. Variability of Rainfall Erosivity and Erosivity Density in the Ganjiang River Catchment, China: Characteristics and Influences of Climate Change. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9020048
Li X, Ye X. Variability of Rainfall Erosivity and Erosivity Density in the Ganjiang River Catchment, China: Characteristics and Influences of Climate Change. Atmosphere. 2018; 9(2):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9020048
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xianghu, and Xuchun Ye. 2018. "Variability of Rainfall Erosivity and Erosivity Density in the Ganjiang River Catchment, China: Characteristics and Influences of Climate Change" Atmosphere 9, no. 2: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9020048
APA StyleLi, X., & Ye, X. (2018). Variability of Rainfall Erosivity and Erosivity Density in the Ganjiang River Catchment, China: Characteristics and Influences of Climate Change. Atmosphere, 9(2), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9020048





