Abstract
One of the principal sources of pollution, on a local scale for a water city, with a tourist and commercial port, is certainly the port. Monitoring what is happening here is essential in order to implement suitable measures to control and contain emissions with consideration for the increasingly delicate environmental problem. This paper details the methods and results of an experimental campaign of local-scale emission measurements conducted in the port of Naples for two weeks in 2021. The chosen instrumentation, its setup, post-processing of the data, and an analysis critique of the results will be presented in detail. The campaign is part of broader research attempting to superimpose the concentrations of pollutants measured ashore in the port area with what is emitted by moored ships.
1. Introduction
Emissions of atmospheric pollutants from harbors have adverse effects on the air quality in urban areas [1]. Ship exhaust emissions are analyzed for several reasons such as estimating the emission contribution of ships to local air quality [2,3,4,5], taking an emission inventory on a global scale, or assessing the impact of new legislation on air quality [6], and compliance monitoring in emission control areas to evaluate the impact on health and well-being [7]. One way to gain an insight into the emissions of ships is through fuel emission inventories obtained by calculating the amounts of sold or consumed fuel combined with emission factors [8,9,10,11,12,13] or from automatic identification system (AIS) data [13,14]. A further technique is to measure or calculate the concentration of emitted pollutants. This can be carried out by measuring at fixed or portable stations in harbors or on-shore [15] emission measurement systems (continuous or periodic monitoring campaigns) [16,17], sniffing methods (with drones, for example) [18], or dispersion models (based on a Gaussian puff model, for example) [19].
An alternative would be experimental measurements onboard, by equipping engines, shafts and propellers, and funnels [20]; this solution is nowadays difficult to undertake due to the necessity of shipowner authorization. One of the most-used approaches is the use of a bottom-up or a top-down approach to estimate emissions starting from fuel consumption and engine load (main and auxiliary) [21,22,23]. Finally, one approach is a monitoring system installed in the port area. The literature reviews offer several examples of the above-mentioned approaches. For example, several studies have carried out transport and dispersion simulations on a local, regional, or global scale [24,25,26,27,28]. Different approaches see the use of receptor-oriented approaches with high temporal resolution measurements correlated with wind conditions and maritime traffic [29,30]. The use of AIS has improved the estimation of ship emission inventories, or the data that can be used for their creation [31,32,33,34]. Figure 1 reports the first top ten environmental priorities of European ports for 2023: the top five issues maintain the same position as last year, namely climate change, air quality, energy efficiency, noise, and water quality. Climate change has moved up the priority list since 2017, when it first appeared. It became the industry’s top environmental concern in 2022 and retained this position in 2023. Climate change refers to the long-term alteration of Earth’s climate patterns and characteristics, primarily caused by human activities that release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. Climate change has emerged as a global challenge, attracting increasing political and social attention. European ports have long considered compliance with climate legislation, reducing carbon emissions, and the climate-resilient design of port infrastructure as top priorities. Increasingly collaborative efforts are being applied as industry and community actors seek to develop a low-carbon economy and become carbon neutral.

Figure 1.
ESPO (European Sea Port Organization) Top 10 of environmental priorities.
Aware of the importance of reducing their environmental impact, the ports of Naples and Salerno could implement several policies aimed at reducing emissions. A key strategy could include the adoption of an electric ship-charging infrastructure or the integration of shore power systems, allowing ships to turn off their engines during the docking period. In addition, incentivizing the use of alternative fuels, such as LNG (liquefied natural gas) or biofuels, could contribute significantly to lower atmospheric emissions. Promoting sustainable cargo-handling practices, such as optimizing routes and reducing dockside activities, could improve the overall energy efficiency of port operations. In addition, investments in innovative technologies, such as real-time emission-monitoring systems, would enable a more accurate assessment of the environmental impacts and facilitate the identification of areas for improvement. Actively working with shipping companies and neighboring port authorities to establish common environmental standards could facilitate a smooth transition to a more sustainable maritime industry. Finally, engaging the local community and raising awareness of the importance of sustainability could help create a collaborative and responsible environment, placing the Port of Naples as a pioneer in port environmental policies nationally and internationally. Adopting these solutions could help make ports more sustainable, by reducing emissions and mitigating the environmental impacts of port activities.
This paper presents the results of experimental measurements carried out in the port of Naples for two weeks of 2021 (measuring 24 h per day but for a limited period due to the availability of the equipment and location for only two weeks). The experimental campaign was born from a collaboration between the Department of Industrial Engineering and the Department of Chemical, Materials and Production Engineering of the University of Naples Federico II, with the Port Authority of the Central Tyrrhenian Sea, with the headquarters of the port of Naples. During the experimental campaign, the concentrations of numerous harmful compounds in the port air were recorded with a high temporal resolution. In addition, wind speed and direction, temperature, and humidity were collected for the same period. The novelties of this research activity are the position of the receiver (about 20 m on the ground level) which allows for the interception of emissions coming from the ship’s funnels, a high-time resolution approach, and the attempt to overlap the emissions with the maritime traffic. The experiments conducted in May 2021 were partially published [35]. In this initial paper, the focus was on measurements rather than on the correlation between ship presence and measured concentrations.
A further advancement was made in [36], where attempts were made to overlay measurements with emission estimates. The results of these analyses demonstrated how unfavorable winds at the measurement point prevented a detailed overlap. At this juncture, in this paper, we extracted useful days when the wind was favorable to us and delved deeper into CBPF techniques, combining them with a large-scale estimation of emissions using a new estimation method [37].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Port of Naples
The place chosen for carrying out the experimental campaign was the port of Naples (Figure 2), one of the largest Italian ports that welcomes millions of people and millions of tons of goods pass through every year [30]. In 2022, the port ranked ninth among the top 10 Italian ports for goods traffic, while it was in the top 3 in terms of passenger traffic. According to the data of 2022, the port of Naples handled about 19 million tons of goods, which is a significant amount, but less than that received at the ports of Trieste, Genoa, and Gioia Tauro. These three ports managed more than 40 million tons of goods each, with Trieste being the highest at 57.6 million tons. The port had 7.8 million passengers in the year, which is a considerable number, but lower than that received at the ports of Messina and Villa San Giovanni. The port of Messina had 10 million passengers while the port of Villa San Giovanni had 8.8 million passengers.
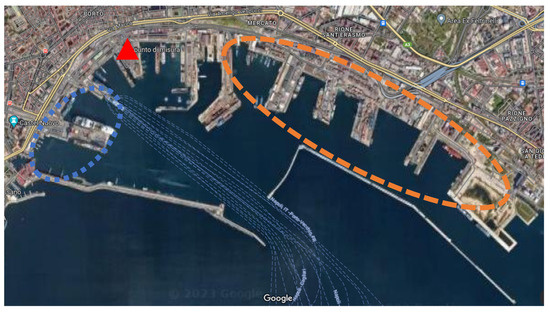
Figure 2.
The port of Naples (red triangle for the point of measure, blue zone for passenger moorings and orange zone for commercial vessels moorings).
The harbor has several mooring zones for large cruise vessels and for high-speed ferry craft (blue zone in Figure 2) on the west side, and, on the east side, numerous piers for container, cargo, and other commercial vessels (orange zone in Figure 2). The total number of berths is 75 distributed over 11 km [31]. According to the latest statistics, compared to the previous year, for 2022, the port registered +14.1% for the arriving fleet, +73.3% in the number of passengers, and 6.3% for cargo ships. About 11% of the ships moored were cruise ships, 45% were pax (>20 nm), 19% were container, and the rest were cargo ships. The registered number of passengers was 7,674,723 grouped as follows: about 6 mln for local passengers (<20 nm), about 1 mln for cruise, and about 1 mln for the rest of the connections (>20 nm, for and from Sardegna and Sicily, for example) [34].
A comparison of the traffic of the ports of Naples and Salerno (2022 compared to 2021) saw a movement of goods of +12.5% for the goods transported by liquid bulk ships, and 5% for dry bulk; container traffic decreased by approximately 13% at the port of Salerno and grew by almost 5% at the port of Naples. Passenger traffic was recovering with over 73.3% more for the port of Naples; finally, cruise traffic was growing significantly compared to 2021 (over 300%), although still 17% below the pre-pandemic period (2019).
2.2. Experimental Campaign
A fixed laboratory was located inside the harbor on the roof of the building of the Port Authority at about 20 m from ground level (see Figure 3).
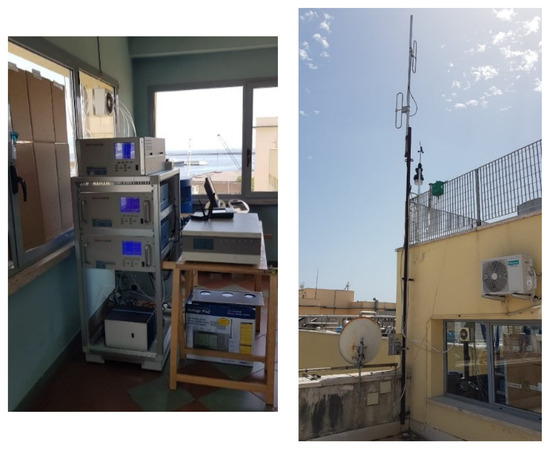

Figure 3.
Experimental campaign.
When the wind blows from the south-southwest and southwest sectors, this location is affected by cruise ships and ferries berthed in the port and by commercial ships when the wind comes from the east-southeast sectors. Along the SSW/SW direction, this site is at 200 m from the ferry boat, 700 m from the cruise ship, and 1 km from hydrofoil terminals. The measurements were conducted from 26 May to 13 June 2021.
The choice for the period and duration of the experimental campaign were influenced by the Port authority availability and the vessel traffic, of course; for the location, however, previous experimental campaigns carried out in the same port demonstrated how, if placed within the port, the instrumentation should be located at an appropriate height from sea level in order to record correctly the exhaust coming from the funnels [38,39]. In addition, all the instrumentation (except the receivers) for the data log and saving must be protected from meteorological conditions and need electricity.
The fixed station was capable of monitoring air pollution concentrations and meteorological parameters with a 1 Hz frequency. Air pollutants monitored were NO, NO2, NOx, SO2, PM10 and PM2.5, CO, and O3.
The Thermo Scientific 42i model was used to measure nitrogen monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, and nitrogen oxides (NO, NO2, NOX respectively). This chemiluminescence analyzer employs a single reaction chamber and photomultiplier to measure NO and NO2 cyclically. In addition, it has separate outputs for each gas and can be calibrated individually using zero and span mixtures generated by a chemical filter system and a NO cylinder.
As is well known, the fluorescent radiation emitted by SO2 molecules returning to their first state is directly proportional to the concentration. Based on this assumption, sulfur dioxide (SO2) concentrations were measured using the Thermo Electron 43i analyzer, which uses pulsed UV radiation at a wavelength of 214 nm. The analyzer has an internal calibration system using zero and span mixtures generated by a chemical filter system and a permeation tube with SO2. Carbon monoxide (CO) concentrations were measured using the Thermo Scientific 48i analyzer, which uses infrared radiation absorption at a wavelength of 4.6 μm. This analyzer is calibrated using zero and span mixtures generated internally and by a CO cylinder, respectively. The analyzer features an internal automatic calibration system using a UV lamp and an internal zero scrubber system for zero calibration. Ozone (O3) concentrations were measured using the Thermo Scientific 49i analyzer, which employs a dual reaction chamber. It measures UV radiation absorption at 254 nm by ozone molecules. Particulate matter with diameters of 10 μm and 2.5 μm (PM10 and PM2.5 respectively) was checked using DUST-IT-2 optical sensors. These sensors find the current fine dust levels and predict health hazards based on scattered light measurements. The sensors incorporate an electrostatic precipitator, pre-separator, and periodic zero point and reference point checks for accuracy. During the experimental campaign, a single tube, in contact with the external ambient, was installed in which the air was aspirated and it was split and sent to the different analyzers.
3. Results
3.1. Meteorological Conditions
As is well known, the meteorological conditions, above all in terms of wind speed and direction, play a fundamental role as regards the transport, dispersion, and deposition of pollutants released by local sources. For this reason, during the same period and at the same location, the weather conditions were recorded. Meteorological data were recorded using the Davis Vantage Pro 2 meteorological station, which includes various sensors for measuring precipitation, temperature, humidity, wind direction, wind velocity, and atmospheric pressure. The recorded data show an average wind velocity of 1.4 m/s, a maximum of 7.5 m/s, and a SSE prevailing wind direction (Figure 4).
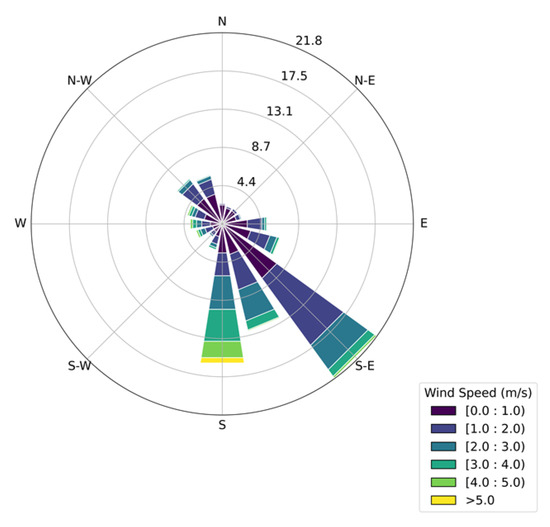
Figure 4.
Wind rose during the experimental campaign.
The daily wind roses (Figure 5) show a similar trend of the wind distribution on the different days. The winds blow mainly from the SSE direction. This may due to the sea breeze regime in Naples, characterized by a clockwise rotation of the wind direction during the day, from south-southwest to west-northwest, and a counter-clockwise rotation during the night, from NNE to ESE [40]. On the days 1 June and 8 June, the wind roses showed a high frequency of occurrence also along the NW/NNW directions. Only on the day of 31 May 2021 did the winds blow predominantly from the WNW sectors.
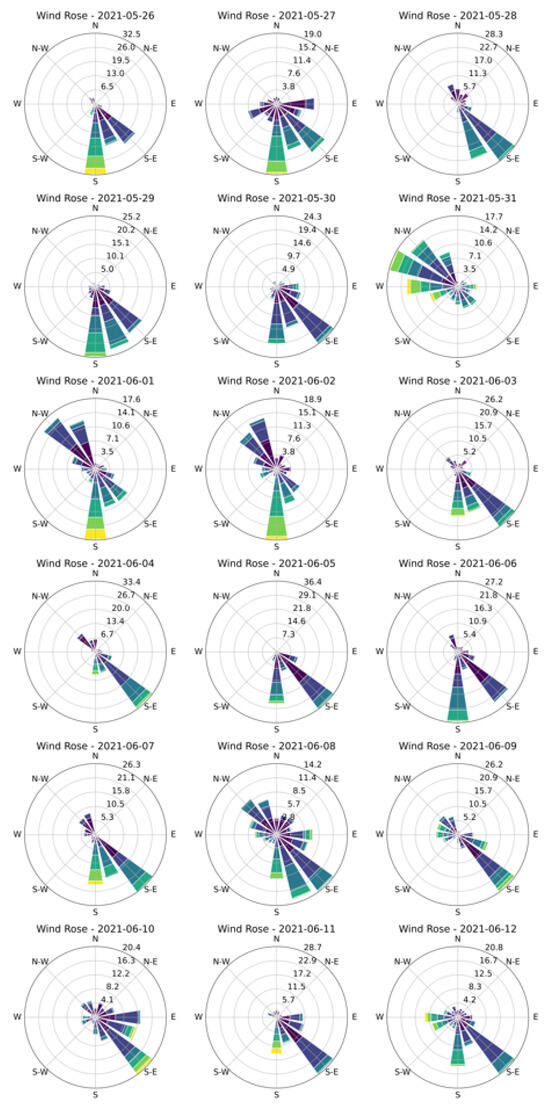
Figure 5.
Wind rose plot for each day.
3.2. Ship Traffic
Vessel traffic was studied for the same measurement days and the rates of emissions were calculated using a bottom-up activity-based method, using the AIS data. As is well known, AIS messages provide static information (MMSI number, type, and length) and dynamic information (the ship’s position, i.e., latitude and longitude, course over ground (COG), speed over ground (SOG), and datetime. The AIS transmits signals every 3 s to a few minutes, depending on the ship’s operation [23]. The AIS data used include more than 750,000 records, found by their MMSI (Maritime Mobile Service Identity) and grouped in categories. Among them, those belonging to some categories were eliminated because they corresponded to stationary objects or ships lacking adequate information and not relevant to the analysis. Consequently, sailing vessels, port tender and pleasure craft, military and law enforcers, and the null category of ships without data were excluded from the analysis.
In Figure 6, an overview of the data collection method based on AIS data is reported. The static data (name, IMO number, MMSI, GT, etc.) is used for the creation of a database of the fleet arriving in the port while dynamic information is useful for the creation of a calendar of approaching and mooring ships (time, speed, geo-localization, angle, etc.). The left branch of the flowchart allows you to start the database while the right branch allows you to create the arrivals and departures calendar.
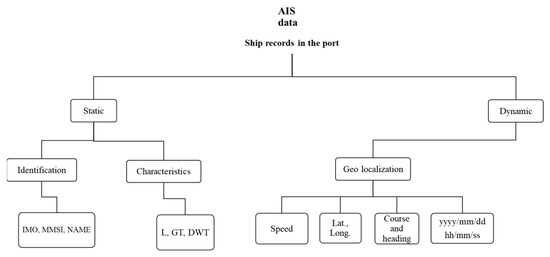
Figure 6.
AIS data usage scheme.
The AIS data acquired indicated a total of 318 ships in transit and 2599 calls during the monitoring campaign. From the static information, the ship category could be easily extracted. Figure 7 shows a pie diagram of the distribution of the arriving fleet; as is evident, passenger and cargo cover more than 65% of the total, followed by tanker and high-speed craft.
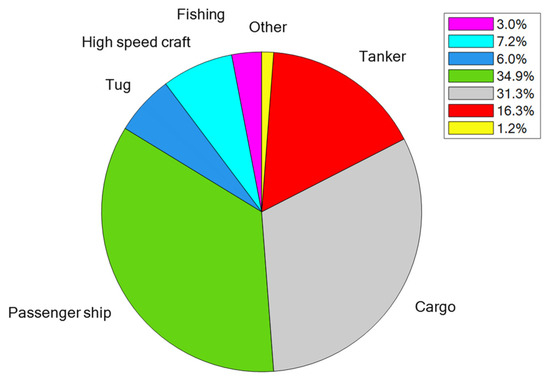
Figure 7.
Ships’ category distribution.
To better manipulate the AIS data, a MATLAB code was developed to create a calendar of the activity in port (arrival, departure, mooring, etc.).
The code is based on the observation of timestamp, speed, and geolocalization and can flag each record with the phase in the port.
Of course, the code, in a preprocessing phase, deletes errors, spikes, and bugs within the AIS database.
By analyzing the AIS data of the fleet, the density map of the ship traffic reported in Figure 8 was realized; the map shows how the density is homogeneous throughout the port, with higher values in the mooring points, mainly in the berths of passenger ships (located in the west part of the port) and in the entry and exit routes from the port. The hot colored areas show the areas of highest recorded traffic density. The focus is the inside of the breakwater; therefore, ship’s speeds > 0 kn are reported in Figure 9.
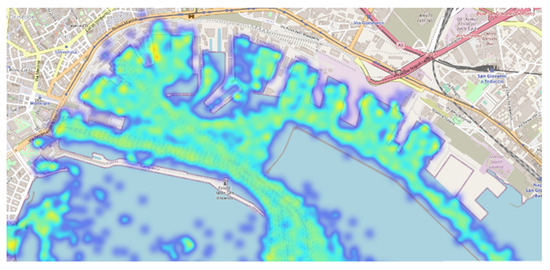
Figure 8.
AIS dynamic data.
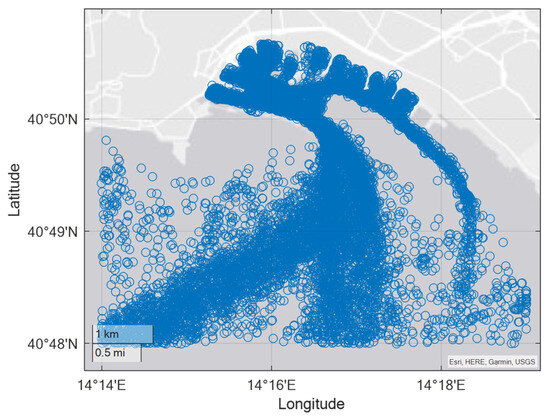
Figure 9.
AIS nonzero speed data.
For the calculation of the engine load, useful for figuring out consumption and emissions, the records of low speed and maneuvering in port were chosen. Figure 10 reports the histogram of the speed records (>0.1 kn). The graph shows the histogram of all arriving ships and therefore includes arrival, departure and maneuvers in port. Obviously, the data at higher speeds of >15 knots, more or less depending on the ship category, correspond to the entry or exit records to/from the port. The data lower than 15 knots are low speeds in the port (from the breakwater to the several mooring piers); clearly, most of the records are from 0 to 15 knots with peaks at 10, 11, 14, and 1 kn.
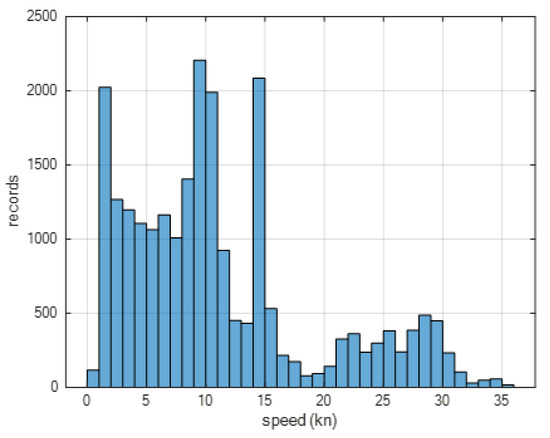
Figure 10.
Speed distribution of arriving ships.
According to Toscano et al. 2023, and Schwarzkopf et al. 2021 [33,37], based on the engine load profile and the declared max speed of the ship, it is possible to estimate the specific fuel consumption which is reported in Figure 11.
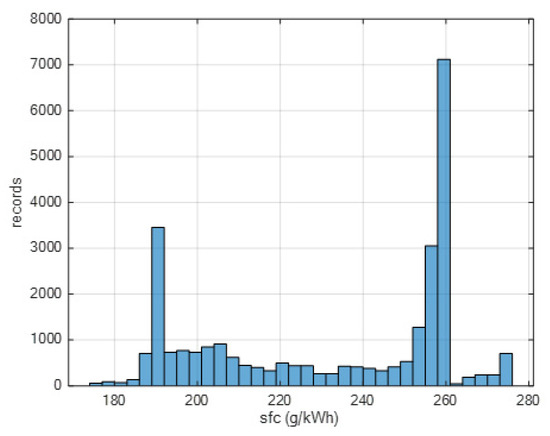
Figure 11.
Specific fuel consumption distribution.
Starting from the ratio between the actual speed and the max speed declared by the ship-owners and updated in the database of the fleet arriving at the port, it is possible to have an engine load factor ((v_actual/v_max)3). During navigation at low speed in port, this load factor was useful in obtaining a better approximation of the specific fuel consumption of the main and auxiliary engines of each ship.
In particular, the specific fuel consumption was estimated by regression analysis (second order polynomial) based on this engine load and three coefficients were customized for engine power <2000 kW, >10,000 kW, and in between.
As is clear, there are two peaks for 260 and 190 g/kWh, respectively, representing two typical engine configurations. According to the procedure proposed by [37] and applied also in [34] for the same engine power ranges and based on the same engine load profile, it is possible to obtain nitrogen oxide-, and sulfur oxide-specific emissions.
In order to handle and better understand the experimental approach, the arriving fleet was geolocalized according to the wind sector with the center on the measuring point highlighted in Figure 2. Figure 12 shows that passenger and high-speed craft are the ships that most frequently (30%) moor in the southwest sector, while the commercial ships, especially tanker and cargo ships, are moored in the east-southeast sector.
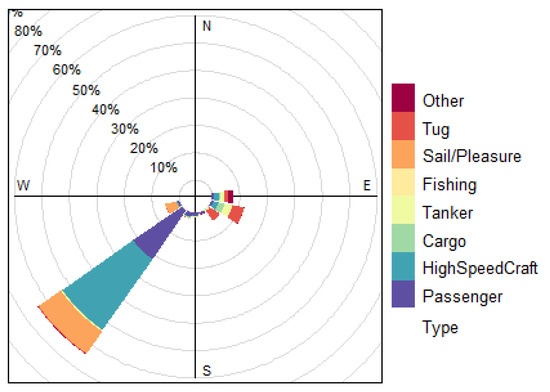
Figure 12.
Geolocation of arriving ships.
3.3. Time Pattern
In this work, we focus on the concentration of three main pollutants emitted by ships, NO2, SO2, PM10 and PM2.5. These three pollutants, NO2, SO2, PM10 and PM2.5, are among the key pollutants emitted by ships and are of significant importance in the context of port emissions [40,41,42]. We acknowledge the importance of meteorological conditions in influencing pollutant dispersion and concentrations. However, in our current paper, we have specifically focused on presenting the acquired concentrations’ data during the experimental campaign in the port of Naples.
Figure 13 reports the time pattern in 1 min intervals. A number of peaks, with extremely high values in some instances, of gaseous pollutants were measured at the receptor location, showing the impact of local sources of emissions.
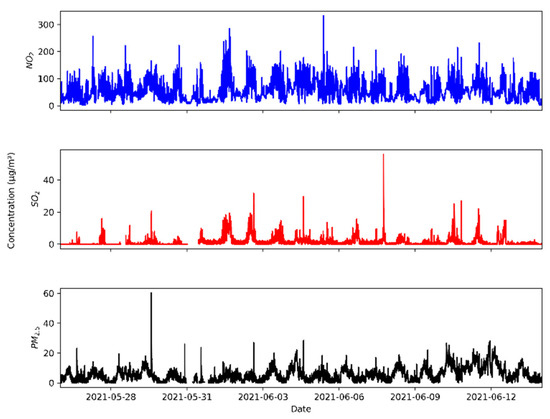
Figure 13.
Time pattern example for NO2, SO2, and PM.
To analyze the impact of ship emissions in the port of Naples, CBPF (conditional bivariate probability function) diagrams were reported for three days (Figure 14, Figure 15 and Figure 16). The first day, 29 May 2021, was a typical day with normal meteorological conditions, with the wind direction blowing from the SSE sector. The second day, 31 May 2021, saw the wind direction blowing from the WNW sectors. Finally, the third day, 2 June 2021, had wind directions blowing from both the SSE and WNW sectors. The graphs are reported for each day and the following pollutants: NO2, SO2, PM10, and PM2.5.
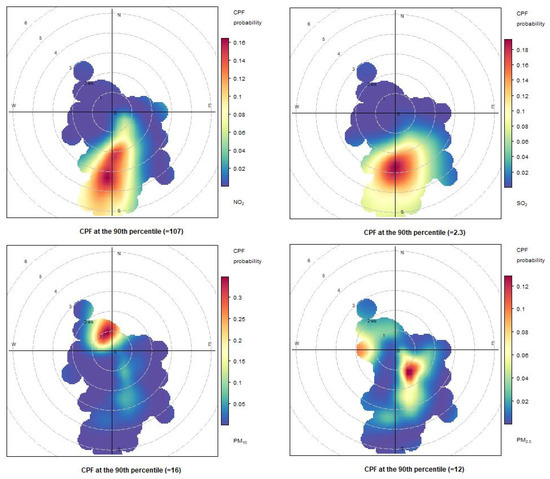
Figure 14.
Conditional bivariate probability function (CBPF) plots computed for atmospheric concentrations measured at Naples port 29 May 2021.
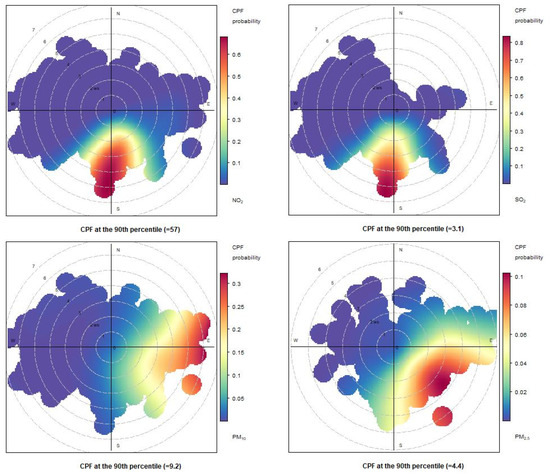
Figure 15.
Conditional bivariate probability function (CBPF) plots computed for atmospheric concentrations measured at Naples port 31 May 2021.
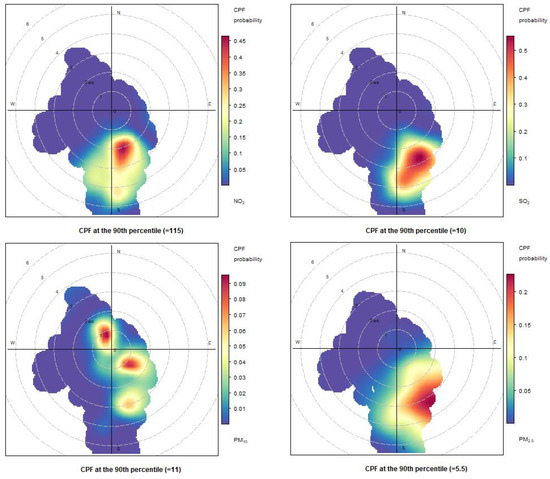
Figure 16.
Conditional bivariate probability function (CBPF) plots computed for atmospheric concentrations measured at Naples port during 2 June 2021.
As shown in Figure 15, Figure 16 and Figure 17 for NO2 and SO2 pollutants, the highest probability for measuring high concentration levels is in the S/SSW sector. On 29 May 2021, this was reasonable because there were low probabilities of wind blowing from other sectors in the CBPF diagrams due to the rare occurrence of the wind blowing from these directions.
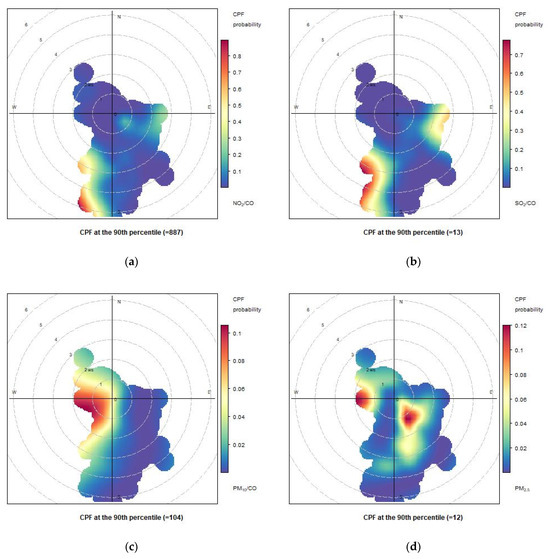
Figure 17.
Conditional bivariate probability function (CBPF) plots computed for atmospheric concentrations measured at Naples port on 29 May 2021, considering the ratios of NO2/CO (a), SO2/CO (b), PM10/CO (c) and PM2.5/CO (d).
In contrast, on 31 May 2021, the prevailing wind directions (Figure 5) were from the WNW sectors, highlighting the significant impact of the ships in the port.
For the PM10 and PM2.5 pollutants, the CBPF diagrams show quite different trends over the three days. The CBPF for PM10 on 29 May 2021, showed a higher probability of exceeding the 90th percentile when the wind blew from the north and northwest, thus indicating sources coming from the urban area. On the same day, the CBPF diagram for PM2.5 shows a probability of exceeding the 90th percentile with winds coming from the west and the southeast, especially in this case with low wind speeds, thus highlighting a certain impact coming from the moored ships.
The CBPF diagrams for PM2.5 on the days 31 May 2021 and 2 June 2021 show a similar trend. The highest probabilities of reaching concentrations higher than the 90th percentile occur when the wind blows from the SE. This result indicates that there is a certain relevance to the impact of commercial ships on PM2.5.
Also, for PM10 on 31 May 2021, there is a high probability that the concentrations would exceed the 90th percentile when the wind blows from the east, seeming to indicate a significant contribution from both commercial ships and other sources external to the port.
The results in the CBPF diagram for 2 June 2021 are particularly non-homogeneous, showing different wind directions in which there is a higher probability of exceeding the 90th percentile.
We extended our analysis by considering the conditional bivariate function (CBPF) for the ratios NO2/CO, SO2/CO), PM10/CO (c) and PM2.5/CO (d) (Figure 17, Figure 18 and Figure 19), which provide insights into the potential sources and spatial distribution of nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and sulfur dioxide (SO2), PM10 and PM2.5 emissions relative to carbon monoxide (CO) levels. From the comparison between the various days, the weight of the various areas of the port on the various pollutants is better highlighted. The CBPF diagrams for these ratios on the same days (29 May 2021, 31 May 2021, and 2 June 2021) revealed interesting patterns. For all three days, the CBPF diagrams consistently showed a higher probability of elevated ratios (indicating higher concentrations of NO2 and SO2 relative to CO) when the wind originated from the south to southwest directions. This suggests a potential influence from ship emissions, as well as other anthropogenic sources, from south/southwest. As regards PM10 (and PM2.5), the results showed higher concentrations when the wind originated from westerly (south-southeasterly for PM2.5) directions.
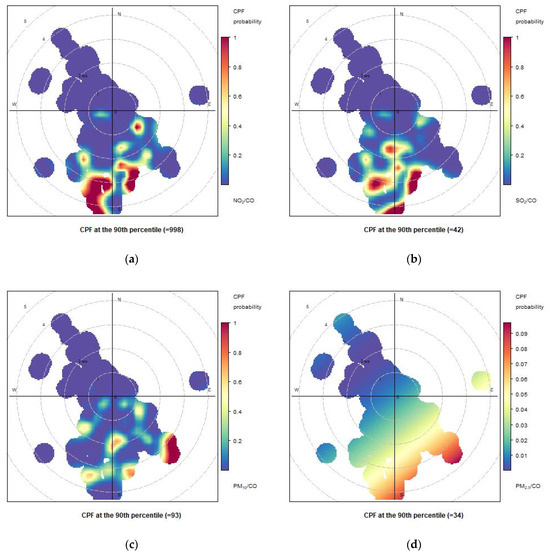
Figure 18.
Conditional bivariate probability function (CBPF) plots computed for atmospheric concentrations measured at Naples port on 31 May 2021, considering the ratios of NO2/CO (a), SO2/CO (b), PM10/CO (c) and PM2.5/CO (d).
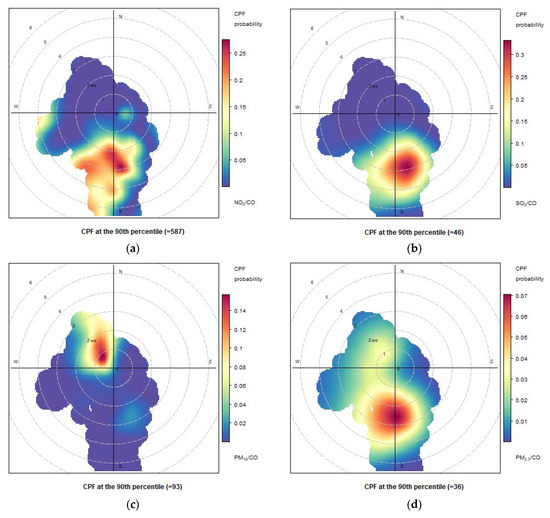
Figure 19.
Conditional bivariate probability function (CBPF) plots computed for atmospheric concentrations measured at Naples port during 2 June 2021, considering the ratios of NO2/CO (a), SO2/CO (b), PM10/CO (c) and PM2.5/CO (d).
As regards, the ships arriving in the port please refer to the Table 1 reported below.

Table 1.
Distribution of the fleet over three days.
Below are the bubble graphs of SOX and NOX (left and right) for each of the chosen days (rows 1, 2, and 3 of Figure 20)
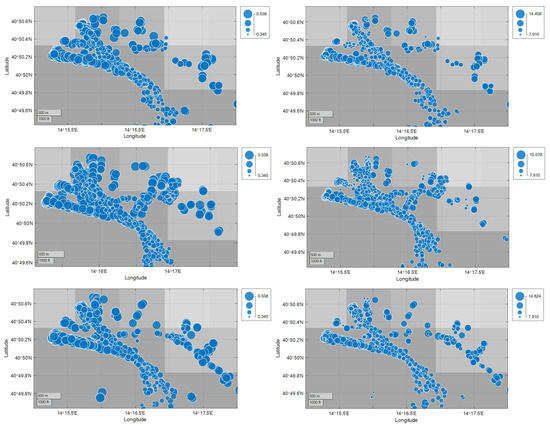
Figure 20.
Geobubble of SOX and NOX emissions in g/kWh (left and right, respectively) for each day (first row 29 May, second row 31 May and third row 2 June).
From the comparison of the CBPF with the bubble maps of the SOX and the estimated NOX, it is highlighted that the docking areas of the passenger ships and the central areas of the port where the maneuvers take place are responsible for the measured emissions (see Figure 20).
4. Conclusions
The port is undoubtedly one of the main local sources of pollution for a water city that has both a business and a tourism port. Given the increasingly serious environmental issues, it is imperative to track what is going on to implement measures to regulate and contain emissions. This paper reveals the outcomes of a two-week experimental campaign conducted in the Port of Naples, specifically aimed at monitoring emissions from ships within the port. Simultaneously, AIS data were acquired and utilized to overlap maritime traffic and emission measurements. The preliminary graphs provided offer a concise glimpse into the results obtained during this experimental monitoring initiative. The study analyzed the ship emissions’ impact in the port of Naples using CBPF diagrams for three days, focusing on NO2, SO2, PM10, and PM2.5 pollutants. Regardless of the specific dates, high concentrations of NO2 and SO2 were consistently associated with the wind blowing from the S/SSW sector. On days with prevailing winds from the WNW sectors, such as on 31 May 2021, ship emissions had a notable impact on air quality. For PM10 and PM2.5, varied trends were observed, with indications of urban sources on 29 May 2021 and ship contributions on subsequent days. Notably, on 2 June 2021, diverse wind directions led to a heterogeneous distribution of pollutant concentrations, suggesting multiple sources of pollution. The data collected from this campaign will be crucial in establishing a correlation between the port’s air quality and its maritime traffic. Future developments include a comprehensive analysis using CFD analysis to further dissect dispersion patterns. Additionally, the data will be employed to validate and refine pollutant dispersion models, which will incorporate detailed engine simulation models. This integrated approach aims to enhance our understanding of the environmental impact of maritime activities in ports and contribute to more effective mitigation strategies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.M., F.M., F.Q. and D.T.; methodology, L.M., F.M., F.Q. and D.T.; software, L.M. and D.T.; validation, L.M. and D.T.; formal analysis, L.M. and D.T.; investigation, L.M., F.M., F.Q. and D.T.; resources, L.M., F.M., F.Q. and D.T.; data curation, L.M. and D.T.; writing—original draft preparation, L.M. and D.T.; writing—review and editing, L.M. and D.T; visualization, L.M. and D.T; supervision, L.M., F.M., F.Q. and D.T.; project administration, L.M., F.M., F.Q. and D.T.; funding acquisition, L.M., F.M., F.Q. and D.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data available on request due to restrictions eg privacy or ethical.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Port Authority of the Central Tyrrhenian Sea and all the personnel of the Port Authority of Naples, for the support provided during the experimental campaign in port.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Toscano, D. The Impact of Shipping on Air Quality in the Port Cities of the Mediterranean Area: A Review. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lu, X.; Feng, J.; Fan, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X. Influence of ship emissions on urban air quality: A comprehensive study using highly time-resolved online measurements and numerical simulation in Shanghai. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, D.; Uibel, S.; Takemura, M.; Klingelhoefer, D.; Groneberg, D.A. Ships, ports and particulate air pollution—An analysis of recent studies. J. Occup. Med. Toxicol. 2011, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shen, Y.; Lin, Y.; Pan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Louie, P.K.K.; Li, M.; Fu, Q. Atmospheric pollution from ships and its impact on local air quality at a port site in Shanghai. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 6315–6330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Brown, R.; Yang, L.; Morawska, L.; Ristovski, Z.; Fu, Q.; Huang, C. Shipping emissions and their impacts on air quality in China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 581–582, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, L.; Fairley, D.; Kleeman, M.J.; Harley, R.A. Effects of switching to lower sulfur marine fuel oil on air quality in the San Francisco Bay area. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 10171–10178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbett, J.J.; Winebrake, J.J.; Green, E.H.; Kasibhatla, P.; Eyring, V.; Lauer, A. Mortality from ship emissions: A global assessment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 8512–8518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbett, J.J.; Koehler, H.W. Updated emissions from ocean shipping. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meyer, P.; Maes, F.; Volckaert, A. Emissions from international shipping in the Belgian part of the North Sea and the Belgian seaports. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyring, V.; Köhler, H.W.; Van Aardenne, J.; Lauer, A. Emissions from international shipping: 1. The last 50 years. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IMO. Third IMO Greenhouse Gas Study 2014: Executive Summary and Final Report; International Maritime Organization: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Schrooten, L.; De Vlieger, I.; Panis, L.I.; Styns, K.; Torfs, R. Inventory and forecasting of maritime emissions in the Belgian sea territory, an activity-based emission model. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, H.; Welch, W.A.; Henningsen, S.; Miller, J.W.; Cocker III, D.R. Emissions from main propulsion engine on container ship at sea. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zhao, Y.; Nelson, P.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Lang, J.; Guo, X. Estimating ship emissions based on AIS data for port of Tianjin, China. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 145, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passig, J.; Schade, J.; Irsig, R.; Li, L.; Li, X.; Zhou, Z.; Adam, T.; Zimmermann, R. Detection of ship plumes from residual fuel operation in emission control areas using single-particle mass spectrometry. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2021, 14, 4171–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schalm, O.; Carro, G.; Lazarov, B.; Jacobs, W.; Stranger, M. Reliability of lower-cost sensors in the analysis of indoor air quality on board ships. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillot, D.; Guiot, B.; Le Cottier, P.; Perret, P.; Tassel, P. Exhaust emissions from in-service inland waterways vessels. In TAP 2016, 21st International Transport and Air Pollution Conference; Scienpress Ltd.: Christchurch, New Zealand, 2016; Volume 6, p. 205. [Google Scholar]
- Van Roy, W.; Scheldeman, K.; Van Roozendael, B.; Van Nieuwenhove, A.; Schallier, R.; Vigin, L.; Maes, F. Airborne monitoring of compliance to NOx emission regulations from ocean-going vessels in the Belgian North Sea. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2022, 13, 101518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekmekçioğlu, A.; Kuzu, S.L.; Ünlügençoğlu, K.; Çelebi, U.B. Assessment of shipping emission factors through monitoring and modelling studies. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 743, 140742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murat, D.; Kalender, S.S.; Ergin, S. Experimental study on the effects of ultra-low sulfur diesel fuel to the exhaust emissions of a ferry. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2017, 26, 5833–5840. [Google Scholar]
- Aulinger, A.; Matthias, V.; Zeretzke, M.; Bieser, J.; Quante, M.; Backes, A. The impact of shipping emissions on air pollution in the greater North Sea region—Part 1: Current emissions and concentrations. Part 1: Current emissions and concentrations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 739–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsworthy, L.; Goldsworthy, B. Modelling of ship engine exhaust emissions in ports and extensive coastal waters based on terrestrial AIS data—An Australian case study. Environ. Model. Softw. 2015, 63, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonsen, M.; Walnum, H.J.; Gössling, S. Model for Estimation of Fuel Consumption of Cruise Ships. Energies 2018, 11, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Mao, J.; Patton, A.P.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, W.; Liu, C.; Kan, H.; Huang, C.; et al. The influence of spatiality on shipping emissions, air quality and potential human exposure in the Yangtze River Delta/Shanghai, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 6167–6183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merico, E.; Dinoi, A.; Contini, D. Development of an integrated modelling-measurement system for near-real-time estimates of harbour activity impact to atmospheric pollution in coastal cities. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2019, 73, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, A.; Russo, M.; Gama, C.; Borrego, C. How important are maritime emissions for the air quality: At European and national scale. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murena, F.; Mocerino, L.; Quaranta, F.; Toscano, D. Impact on air quality of cruise ship emissions in Naples, Italy. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 187, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramacher, M.O.P.; Matthias, V.; Aulinger, A.; Quante, M.; Bieser, J.; Karl, M. Contributions of traffic and shipping emissions to city-scale NOx and PM2.5 exposure in Hamburg. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 237, 117674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contini, D.; Gambaro, A.; Belosi, F.; De Pieri, S.; Cairns, W.; Donateo, A.; Zanotto, E.; Citron, M. The direct influence of ship traffic on atmospheric PM2.5, PM10 and PAH in Venice. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 2119–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocerino, L.; Rizzuto, E. Preliminary approach to the application of the environmental ship index. In Sustainable Development and Innovations in Marine Technologies: Proceedings of the 18th International Congress of the Maritme Association of the Mediterranean (IMAM 2019), Varna, Bulgaria, 9–11 September 2019; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; p. 285. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://adsptirrenocentrale.it/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/12_Bollettino-statistico-12-mesi-2022.pdf (accessed on 31 January 2024).
- Ledoux, F.; Roche, C.; Cazier, F.; Beaugard, C.; Courcot, D. Influence of ship emissions on NOx, SO2, O3 and PM concentrations in a North-Sea harbor in France. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 71, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toscano, D.; Murena, F.; Quaranta, F.; Mocerino, L. Assessment of the impact of ship emissions on air quality based on a complete annual emission inventory using AIS data for the port of Naples. Ocean Eng. 2021, 232, 109166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toscano, D.; Murena, F.; Quaranta, F.; Mocerino, L. Impact of ship emissions at a high receptor point in the port of Naples. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 286, 119253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocerino, L.; Murena, F.; Quaranta, F.; Toscano, D. Validation of the estimated ships’ emissions through an exper-imental campaign in port. Ocean Eng. 2023, 288, 115957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzkopf, D.A.; Petrik, R.; Matthias, V.; Quante, M.; Majamäki, E.; Jalkanen, J.-P. A ship emission modeling system with scenario capabilities. Atmos. Environ. X 2021, 12, 100132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocerino, L.; Murena, F.; Quaranta, F.; Toscano, D. A methodology for the design of an effective air quality moni-toring network in port areas. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carratelli, E.P.; Budillon, G.; Dentale, F.; Napoli, F.; Reale, F.; Spulsi, G. An experience in monitoring and integrating wind and wave data in the Campania Region. Boll. Geofis. Teor. Appl. 2007, 48, 215–226. [Google Scholar]
- Eyring, V.; Stevenson, D.S.; Lauer, A.; Dentener, F.J.; Butler, T.; Collins, W.J.; Ellingsen, K.; Gauss, M.; Hauglustaine, D.A.; Isaksen, I.S.A.; et al. Multi-model simulations of the impact of international shipping on Atmospheric Chemistry and Climate in 2000 and 2030. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 757–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, L.; Jalkanen, J.-P.; Kukkonen, J. Global assessment of shipping emissions in 2015 on a high spatial and temporal resolution. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 167, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridell, E.; Steen, E.; Peterson, K. Primary particles in ship emissions. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 1160–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridell, E. Emissions and fuel use in the shipping sector. In Green Ports; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 19–33. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).