Abstract
Poyang Lake is the largest freshwater lake in China and forms an essential component of the hydrological, nutrient, and carbon cycles, providing various ecosystem services to the local environment. Since changes in Poyang Lake’s water temperature can significantly affect the surrounding environment and social development, continuous monitoring of lake temperature changes is required. Traditional water monitoring methods are resource intensive and cannot simultaneously conduct extensive water monitoring. Remote sensing of temperature inversion has the advantages of all-weather, efficient, and large-scale real-time monitoring. Six Landsat 8 images from August to October in 2020 and 2021 were utilized to extract lake surface temperature (LST), and the variations in LST over the two years were analyzed to determine the impact of global climate anomalies on inland lakes. The results indicate that the LST in August and October 2021 was significantly higher than that in the same periods of the previous year, and the temperature difference in October reached 8 °C. In contrast to the overall normal distribution pattern of the water temperature in 2020, 2021 exhibited a relatively concentrated, unimodal distribution pattern. A trend analysis of the driving factors suggests that the LST of Poyang Lake is influenced by the global climate, and the artificial heat sources around the lake clearly alter the distribution characteristics of the LST simultaneously.
1. Introduction
Water temperature is a crucial factor influencing the ecological environment of rivers, lakes, oceans, and other water bodies. Affected by frequent extreme weather worldwide, water temperature anomalies occasionally occur [1,2,3]. Poyang Lake, a vital component of the Yangtze River Basin ecosystem, plays a significant role in ecological preservation, climate regulation, and water resource utilization [4]. Therefore, dynamic monitoring of the water temperature in Poyang Lake is of great significance. In recent years, the Poyang Lake area has experienced ecological problems caused by abnormal changes in water temperature, especially the extreme drought in the summer of 2022, resulting in the death of many aquatic organisms and serious destruction of the ecological environment [5]. Traditional in situ temperature measurements are real but sparse with low efficiency, which makes it difficult to analyze and predict the features of water temperature in high-resolution and wide areas. Compared to traditional measurement methods, remote sensing technology can rapidly and accurately extract large-scale water information, offering a long observation time and high accuracy. In recent decades, thermal infrared remote sensing technology has been gradually applied to temperature monitoring in large-scale waters, such as lakes and oceans [6]. However, the unsatisfactory performance of the sensor hardware and satellite orbit affects the temporal and spatial resolutions of remote sensing technologies.
As one of the most widely used remote sensing data sources for long-term water temperature inversion, studies based on Landsat thermal infrared data are relatively mature [7].
Multitemporal TM thermal infrared data have been used to determine the water temperature around the Daya Bay Nuclear Power Station [8]. A numerical forecasting model of the vertical profile of the Yellow Sea water temperature based on remote sensing data [9] has proven that remote sensing technology can effectively monitor temperature problems. Common algorithms for inverting the water surface temperature include the radiative transfer, single-window, and split-window algorithms [10]. The radiative transfer algorithm considers the influence of various atmospheres, correcting and eliminating atmospheric effects by calculating the atmospheric radiation and atmospheric transmittance. This algorithm has a high application accuracy for temperature anomaly monitoring and large-area water temperature inversion. The accuracy of inversion results can be improved significantly when combined with edge effect elimination [11,12,13,14]. However, complex calculations and the difficult acquisition of real-time atmospheric vertical contour data affect the accuracy of surface temperature inversion results. Unlike the complex radiative transfer algorithm, the single-window algorithm solely uses thermal infrared data to invert the surface temperature, which can exhibit a relatively high correlation with the in situ measured water temperature to a certain extent [15,16]. Compared to the single-window algorithm, introducing the split-window algorithm further reduces the required parameters for temperature inversion. Moreover, it can achieve high-precision inversion results without requiring precise atmospheric profile data and has gradually become the most widely used algorithm for water surface temperature inversion [17]. In recent years, continuous on-site and remote sensing research has been conducted on the water bodies of Poyang Lake. Comprehensive pollution index evaluation methods and principal component analysis allow for an accurate and objective assessment of the spatiotemporal evolution of water quality [18,19]. Using Landsat TM images through logical operations or water indices can effectively extract water bodies from Poyang Lake [20,21]. Additionally, GF-3 images combined with the KI algorithm to model SAR images and reconstruct the cost function, which can minimize the misclassification rate when the overall classification cost is the lowest, can provide good support for the dynamic monitoring of Poyang Lake [22].
While research on Poyang Lake has been ongoing for many years and various systematic research methods have been developed [23,24,25,26,27,28], most studies still rely on in situ measured temperature data, which are relatively time-consuming and labor-intensive, making it challenging to acquire water temperature information over a large area simultaneously. Applying remote sensing technology not only efficiently supplements in situ measured data with regional water temperature inversion data, but also saves human and material resources, generating reliable surface water temperature data for the Poyang Lake region. These data extract regional water temperature characteristics and support ecological conservation, environmental management, resource planning, and local production. The purpose of this study was to obtain the water temperature in the study area using data from the Landsat 8 remote sensing satellite, and to explore the effects of global climate anomalies and human factors on inland lakes and their internal relationships by combining climate and human activity data.
2. Research Area and Data Source
2.1. Research Area
During the wet season, Poyang Lake is the largest freshwater lake and becomes the second largest lake in China surpassed only by Qinghai Lake, which is the largest saltwater lake in the country. Poyang Lake is located in the northern part of Jiangxi Province and is a major tributary of the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, serving as a crucial lake with throughflow, discharge, and seasonal importance in the Yangtze River Basin (Figure 1). Poyang Lake is primarily fed by the Gan, Xiu, Xin, Rao, and Fu rivers. From south to north, it converges with the Yangtze River near Shizhong Mountain in Hukou County, Jiujiang City. At normal water levels (14–15 m), the lake’s surface area is 3150 km2. During high water levels (20 m), it exceeds 4125 km2, while at low water levels (12 m), it is reduced to only 500 km2. Poyang Lake plays a crucial role in regulating the water level of the Yangtze River, conserving water resources, improving the local climate, and maintaining the ecological balance in surrounding areas.
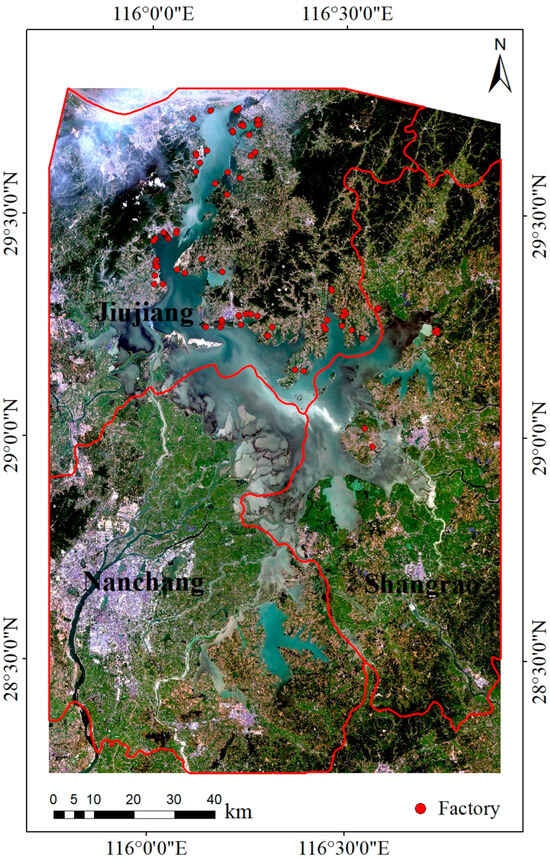
Figure 1.
Location of the research area.
2.2. Data Source
The in situ temperature was obtained from water temperature data measured within the jurisdictions of Jiujiang City, Nanchang City, and Shangrao City in the waters of Poyang Lake (https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/en/data/38ea426e-f99c-40c6-87a0-2354419eb2df) (accessed on 13 September 2023). The satellite remote sensing data were obtained from the Geospatial Data Cloud (https://www.gscloud.cn/) (accessed on 13 September 2023), the United States Geological Survey (https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov) (accessed on 13 September 2023), and the Level-1 and Atmosphere Archive & Distribution System Distributed Active Archive Center (https://ladsweb.modaps.eosdis.nasa.gov) (accessed on 13 September 2023). The temperature, irradiance, wind speed, and precipitation data used for subsequent regional analyses were sourced from the National Centers for Environmental Information (NCEI), a division of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) in the United States (https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/data/global-summary-of-the-day/archive/) (accessed on 13 September 2023).
3. Methods
3.1. Radiative Transfer Equation
In this study, based on the Landsat 8 satellite data, the OLI_TIRS data were preprocessed through radiometric calibration and atmospheric correction. Subsequently, the radiative transfer algorithm was employed to calculate the surface emissivity, leading to the temperature retrieval in the research area (Figure 2).
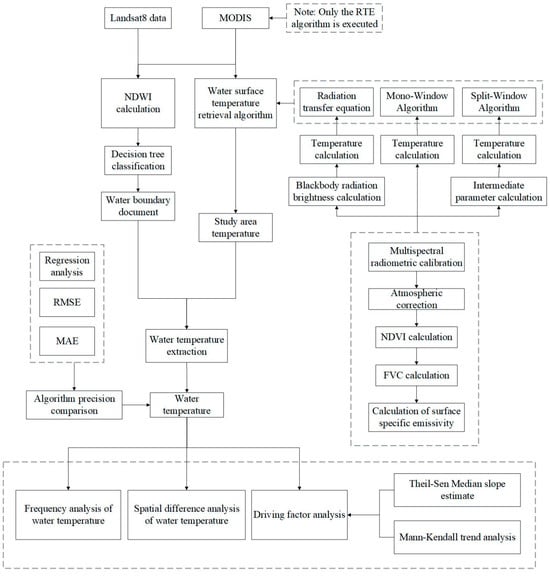
Figure 2.
Technical method diagram.
The principle was first to estimate the influence of the atmosphere on the surface thermal radiation, and then remove the atmospheric influence from the total thermal radiation obtained by the sensor, and acquire the surface thermal radiation intensity that could be converted into the surface temperature.
The radiative transfer algorithm first performed radiometric calibration [29] and atmospheric correction [30,31,32] on the raw data. The vegetation cover was calculated using the normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) [33] with the following formula:
FVC = (NDVI − NDVIs)/(NDVIv − NDVIs)
In Equation (1), FVC represents the vegetation coverage, NDVI represents the normalized difference vegetation index, NDVIs is the NDVI value without vegetation cover, and NDVIv is the NDVI value with full vegetation cover [34].
Next, the surface emissivity was calculated using the NDVI threshold method [35] with the following formula:
εsurface = 0.004FVC + 0.0986
In Equation (2), εsurface represents the surface emissivity, and FVC represents the vegetation coverage.
Following this, the blackbody radiance in the thermal infrared band was computed based on the surface emissivity:
B(Ts) = [Lλ − L↑ − τ(1 − ε) L↓]/τε
In Equation (3), B(Ts) represents the blackbody radiance; ε is the surface emissivity; Ts is the actual surface temperature; τ is the atmospheric transmittance in the thermal infrared band, τ = 0.94; L↑ is the atmospheric upwelling radiance, L↑ = 0.37; L↓ is the atmospheric downwelling radiance, L↓ = 0.66; and Lλ is the thermal infrared radiance received by the satellite sensor [36,37].
Finally, the surface temperature was inverted using the Planck function with the following formula:
Ts = K2/ln[K1/B(Ts) + 1]
In Equation (4), Ts is the actual surface temperature; B(Ts) represents the blackbody radiance; and the values of K1 and K2 are determined based on the corresponding sensor, K1 = 774.89, K2 = 1321.08.
3.2. Mono-Window Algorithm
The mono-window algorithm is a retrieval method suitable for data with only one thermal infrared band. In this study, the 10th band in Landsat 8 was selected to use the mono-window algorithm [38] with the following formula:
TS = (a(1 − M − N) + [b(1 − M − N) + M + N]T10 − DTa)/M
In Equation (5), TS represents the surface temperature of the lake, a = −62.73566, b = 0.43404, T10 is the radiation brightness temperature of band 10, Ta is the average atmospheric temperature (K), and M and N are the intermediate variables.
There is a linear relationship between the atmospheric average temperature Ta and the near-surface temperature T0.
Ta = 0.92621T0 + 16.0110
In Equation (6), Ta is the average atmospheric temperature (K), and T0 is the near-surface temperature.
The two parameters M and N can be calculated using the following method:
M = ετ
N= (1 − τ)[1 + (1 − ε)τ]
In Equations (7) and (8), ε is the surface emissivity and τ is the atmospheric transmittance in the thermal infrared band, where τ = 0.94.
3.3. Split-Window Algorithm
The surface temperature inversion equation of the split-window algorithm [39] applicable to Landsat 8 remote sensing image data is shown as follows:
TR = T10A0 − T11A1 + A2
In Equation (9), TR represents the surface temperature of the lake, T10 and T11 are the radiation brightness temperature of band 10 and band 11, and A0, A1 and A2 are the parameters.
The formula for A0, A1, and A2 is as follows:
A0 = 1 + ([N10 + b10N11(1 − M10 − N10)]/(M10N11 − M11N10))
A1 = [N10 + b11N10(1 − M11 − N11)]/(M10N11 − M11N10)
A2 = [a10N11(1 − M10 − N10) − a11N10(1 − M11 − N11)]/(M10N11 − M11N10)
In Equations (10)–(12), a10, b10, a11, and b11 are constants, since the temperature during the study period was between 10 and 40 °C. The constants were a10 = −64.6081, b10 = 0.4399, a11 = −69.0215, and b11 = 0.4756, here used to calculate bands 10 and 11, corresponding to M and N.
Mi = εi τi
Ni = [1 − τi] [1 + (1 − εi) τi]
In Equations (13) and (14), i represents two bands, τi is the atmospheric transmittance in the thermal infrared band, τ10 = 0.94, τ11 = 0.92, and εi is the surface emissivity formula, as follows:
εi = PV RV εiv + (1 − PV) RS εis + dε
In Equation (15), i represents two bands, εi is the surface emissivity, εiv and εis are the surface emissivity of vegetation or bare land in the i band, ε10v = 0.98672, ε10s = 0.96767, ε11v = 0.98990, ε11s = 0.97790, PV is the vegetation cover, RV and RS represent the proportion of temperature of vegetation and bare land, and dε is a thermal radiation correction term, resulting from the interaction of thermal radiation between vegetation and bare ground, the formula for which is as follows:
RV = 0.0585PV + 0.9332
RS = 0.1068PV + 0.9902
dε = 0.003796 min (PV,1 − PV)
In Equations (16)–(18), RV and RS represent the proportion of temperature of vegetation and bare land, PV is the vegetation cover, and dε is a thermal radiation correction term, resulting from the interaction of thermal radiation between vegetation and bare ground.
3.4. Normalized Water Index Method
The normalized water index method involves classifying water bodies and conducting a comprehensive assessment by aggregating the evaluation indicators of various water bodies into an overall index. It primarily uses specific bands in remote sensing imagery for normalized difference processing to highlight water body information in the image.
NDWI = (Green − NIR)/(Green + NIR)
In Equation (19), green represents the green band corresponding to the second band in the TM images and the third band in the OLI images, whereas NIR represents the near-infrared band corresponding to the fourth band in the TM images and the fifth band in the OLI images [40].
3.5. Decision Tree
A simple binary decision tree was constructed using a decision tree to classify the normalized water body index images. Appropriate thresholds were initially set, and the image data were imported for classification to obtain the water body boundaries [41,42].
3.6. Theil–Sen Median Slope Estimation and Mann–Kendall Trend Analysis
The Theil–Sen Median method is a robust non-parametric statistical trend calculation method, which is suitable for the trend analysis of long time series data. Its calculation formula is as follows:
In Equation (20), Median is the formula for taking the mid-value, and i and j are the numbers of data. If β > 0, it is an increasing trend, and if β < 0, it is a decreasing trend.
The Mann–Kendall test is a non-parametric time series trend test method, which does not require the measured values to follow the positive distribution, is not affected by missing values and outliers, and is suitable for the trend significance testing of long time series data, the formula for which is as follows:
In Equations (21) and (22), sgn is a symbolic function, S is the test statistic, and i and j are the numbers of data.
Z is the test statistic, for which the formula is as follows:
In Equations (23) and (24), n is the number of data in the sequence, S is the test statistic, and Var is the intermediate variable.
4. Results
4.1. Comparison of Methods
The radiative transfer equation, mono-window, and split-window algorithms were used to retrieve the lake surface temperature of the study area in January and June 2021 based on the Landsat 8 data, and the radiative transfer equation algorithm was used to invert the lake surface temperature of January and June 2021 in the study area based on the MODIS data. Then, the four results were compared.
The surface temperature of Poyang Lake obtained by the inversion of the three algorithms and the surface temperature based on the MODIS data were analyzed by means of linear regression. The results of the regression analysis are shown in Figure 3. The negative correlation coefficients between the inversion values and the actual values of the four results were RTE (0.983), MW (0.982), SW (0.978), and MODIS (0.971). In Table 1, the RMSE (1.75 K) and MAE (2.16 K) of the RTE algorithm inversion results were the smallest, while the RMSE (4.25 K) and MAE (4.57 K) of the SW algorithm inversion results are the largest.
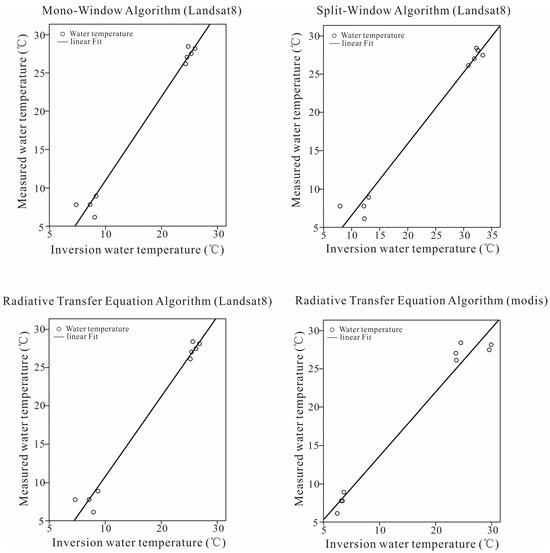
Figure 3.
Water temperature fitting results.

Table 1.
Method precision comparison.
According to the comprehensive statistical parameters, the inversion result of the RTE algorithm was the closest to the measured value and had the highest inversion accuracy, while the inversion result of the SW algorithm deviated farthest from the measured value and had the lowest inversion accuracy.
A significant correlation between the inverted lake surface temperature (LST) and the measured water temperatures was observed (Figure 3). The temperature inversion results in this study effectively represent the surface temperature variations in the water body. The LST inversion results for Poyang Lake show that the LST in 2021 was generally higher than that in the same period in 2020, with only a slight decrease in temperature observed in September (Figure 4).
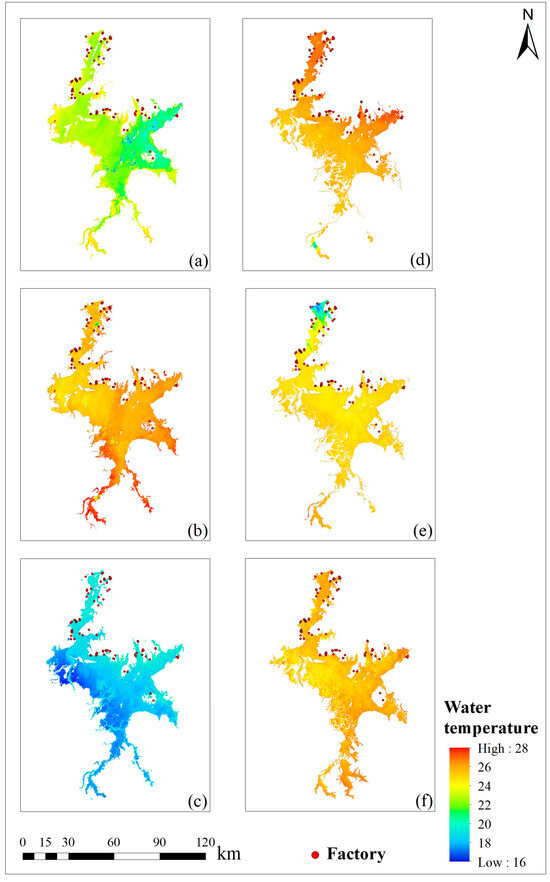
Figure 4.
Water temperature data. (a) August 2020 (b) September 2020 (c) October 2020 (d) August 2021 (e) September 2021 (f) October 2021.
4.2. Frequency Distribution
The composition and characteristics of the LST during the different periods in Poyang Lake were analyzed by conducting a frequency analysis of the existing inverted temperature results (Figure 5). The LST in August 2020 and August 2021 were concentrated between 20 and 24 °C and 25 and 26 °C, respectively, with the temperatures in August 2021 being significantly higher than those during the same period in the previous year (Figure 5a,d). In September 2020, the LST was concentrated between 24 and 27 °C, while in September 2021, it was concentrated between 24 and 25 °C, with a small difference between the two years (Figure 5b,e). In October 2020, the LST was concentrated between 17 and 19 °C, whereas in October 2021, it was concentrated in the range of 24–25 °C, indicating a striking difference between the two years (Figure 5c,f). The LST in 2020 exhibited an overall normal distribution pattern, whereas the LST distribution in 2021 was relatively concentrated, showing a unimodal distribution. Unlike the gradual decrease in LST from August to October 2021, the LST in September 2020 was significantly higher than that in August 2020 and September 2021. The imagery acquisition time for September 2020 was at the beginning of the month, which was influenced by local temperature warming, and there was a slight increase in the LST of Poyang Lake (Figure 5).
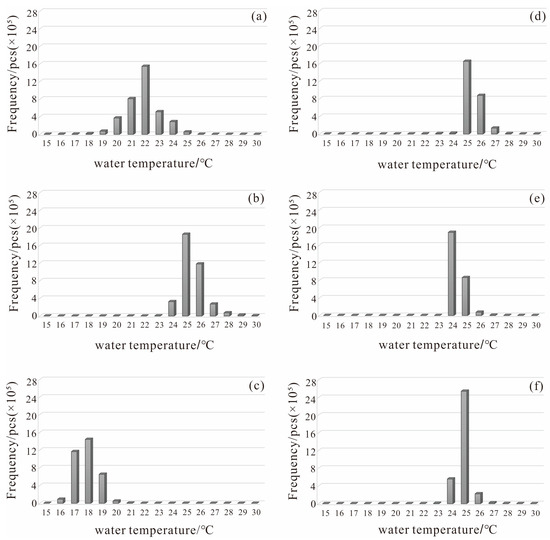
Figure 5.
Monthly water temperature frequency. (a) August 2020, (b) September 2020, (c) October 2020, (d) August 2021, (e) September 2021, (f) October 2021.
5. Discussion
5.1. Relationship between Water Temperature and Air Temperature
The average daily air temperatures for August and October 2020–2021 showed a decrease in air temperature from August to September 2020 (Figure 6), which is inconsistent with the inverting trend of the rising LST. This discrepancy is primarily attributed to the fact that the imagery for September 2020 was acquired on 6 September, with a daily average air temperature of 24.3 °C. The overall climate in the lake area was still warm in August, and the temperature had not decreased.
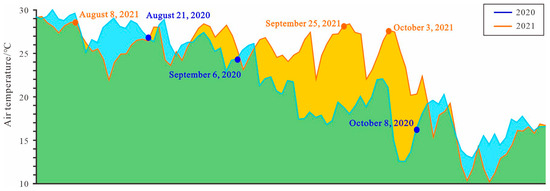
Figure 6.
Air temperature trend.
In August and September 2021, the monthly average temperature slightly decreased, with the monthly average temperature being 17.5 °C in October. Compared to the previous month, there was a significant temperature drop of up to 8.4 °C, contrasting with the inverted LST results. October’s inverted LST was slightly higher than that of the previous month and significantly higher than the local monthly average temperature, indicating a deviation from the overall temperature trend. An analysis revealed that the imagery for October 2021 was captured on 3 October, with a daily average air temperature of 27.7 °C. Because significant cooling had not yet occurred, there was a noticeable deviation between the inverted LST results and the monthly average temperature for that month. The inverted LST in August 2020 was lower than that of the same period in August 2021, deviating from the local temperature trend, which is also attributed to the influence of the imagery acquisition time.
By analyzing the daily average temperatures for 2020 and 2021 (Figure 6), along with the climate anomaly phenomena (Table 2), it was observed that although there were some fluctuations in the trend of temperature change, the overall declining trend corresponded to the occurrence of La Niña. This indicates that global climate anomalies can affect inland temperatures. The frequency analysis of the LST and daily average air temperature for 2020 and 2021 indicated a corresponding relationship between the LST and air temperature. The LST can, to some extent, reflect the local air temperature. However, owing to the large specific heat capacity of water, LST has a certain lag compared to air temperature.

Table 2.
Climate anomalies from 2020 to 2021.
Gifty Attiah et al. applied a retrieval algorithm to the thermal bands of the Landsat archives to generate an LST dataset (North Slave LST dataset) for 535 lakes in the North Slave Region (NSR) of the Northwest Territories (NWT), Canada, for the period of 1984 to 2021. According to the generated North Slave LST, the warm lakes are mainly located around Yellowknife and in the southwest of the NSR.
The authors mentioned that lakes have been treated as homogenous entities in some studies. However, there is spatial variability in the surface temperature of lakes, which depends on several factors, including morphological differences or biological, physical, and human activities occurring on the lake at a given time [43].
Among other things, the authors also raised issues that affect the accuracy of the data, primarily including potential mixed pixels that may not be captured by the algorithm, the presence of “no data” pixels on the lake, and an inconsistent temporal resolution for each lake dataset [44].
5.2. Driving Factor Trend Analysis
Data on the temperature, precipitation, wind speed, and global irradiance were collected from the three cities where Poyang Lake spans to further determine the relationship between lake water temperature and various natural elements. Theil–Sen Median slope estimation and Mann–Kendall trend analysis [45,46,47] were carried out to calculate the trends in the elements for each month and year. The temperature, precipitation, and wind speed trends were almost consistent across the different cities during the same period, indicating a basic similarity in climatic conditions.
In 2021, the overall irradiance increased (Table 3), whereas the temperature gradually decreased. This phenomenon can be attributed to the transitional study period between summer and autumn. The decreasing precipitation trend was due to the global occurrence of warm and dry climatic conditions, which resulted in less precipitation. The increased irradiance and decreased temperature from 2020 to 2021 are speculated to be related to the La Niña climate anomaly, characterized by cold and dry conditions, which is consistent with the trend analysis results for temperature and precipitation.

Table 3.
Trend table of driving factors.
Landsat 8 OLI satellite data with a resolution of 30 m were used in this study. Limited image resolution may result in the omission of some small water bodies, leading to errors in water body extraction and influencing the research results. It is advisable to use high-resolution imagery more frequently in future studies to enhance the accuracy of water body identification.
5.3. Spatial Differences in Water Temperature
The existing inverted LST results were reclassified to visually display the spatial differences in the water temperature of Poyang Lake for better analysis of the regional temperature characteristics (Figure 7). The LST exhibited zonal spatial characteristics unrelated to regional climate variations from August to October 2020 and September 2021 (Table 3). An investigation of local human activities revealed that factories in the Poyang Lake Basin are mainly concentrated along the northeast coast at a high density. In contrast, the southwest coast, because it is submerged in lake water during the flood season, has more muddy areas and relatively inconvenient transportation, with almost no distribution of factories. These results suggest that the continuous input of heat from the factories along the northern coast was the reason for the regional temperature difference on both sides, causing generally higher water temperatures northeast of Poyang Lake than southwest. There was no apparent boundary in water temperature for September and October 2021 due to the strict epidemic control measures in 2021. Coastal factories mostly halted production, and the climatic conditions primarily influenced the water temperature. Therefore, the LST across various locations in Poyang Lake tended to be more uniform.
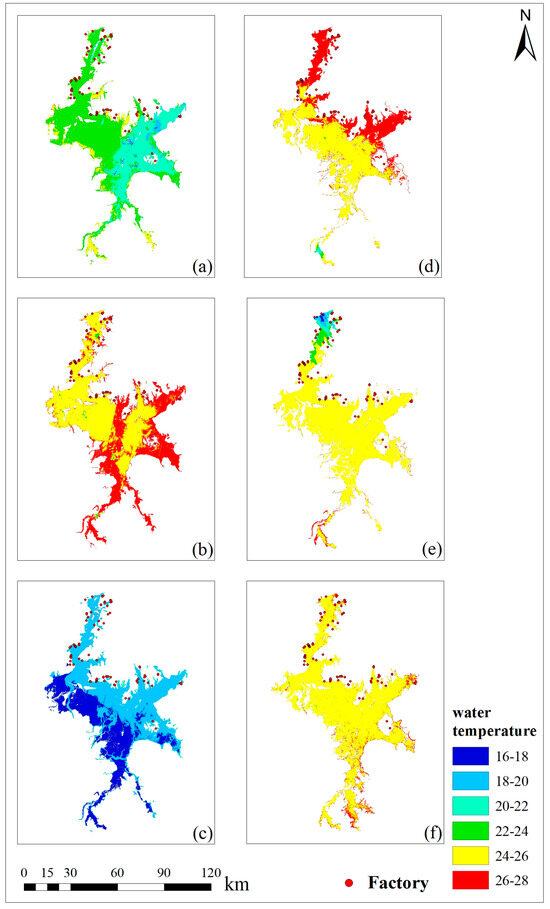
Figure 7.
Water temperature reclassification results. (a) August 2020 (b) September 2020 (c) October 2020 (d) August 2021 (e) September 2021 (f) October 2021.
6. Conclusions
The radiative transfer equation, mono-window, and split-window algorithms were used to retrieve the lake surface temperature of the study area based on the Landsat 8 data, and the radiative transfer equation algorithm was used to invert the lake surface temperature of the study area based on the MODIS data. Then, the four results were compared. The radiative transfer equation algorithm based on Landsat 8 has the highest accuracy and reliable results.
This study utilized a radiative transfer equation algorithm to invert the lake surface temperature from Landsat 8 OLI images from six periods, obtaining the LST of Poyang Lake at a large spatial scale for the same periods. By conducting a frequency analysis of the inverted LST, reclassification analysis, temperature correlation analysis, and Mann–Kendall trend analysis on various meteorological data, including irradiance, temperature, precipitation, and wind speed across different cities in the Poyang Lake region, the following conclusions were drawn:
(1) In August 2021, the LST was significantly higher than in the same period in the previous year. The difference in LST was relatively small between September 2020 and September 2021, while the LST in October 2021 was markedly higher than that in the same period in the previous year, with a temperature difference of 8 °C. Unlike the gradual decrease in LST from August to October 2021, the LST in September 2020 was significantly higher than that in August and the same period in September 2021. Compared with the overall normal distribution pattern of the LST in 2020, the distribution in 2021 showed a relatively concentrated unimodal pattern.
(2) The correlation between LST and air temperature indicates that the surface temperature of inland water bodies is influenced to some extent by regional air temperature. Although there were slight differences in the temperature trends between 2020 and 2021, the overall decreasing trend corresponds to the occurrence of La Niña, suggesting that global climate anomalies impact lake surface temperatures.
(3) The spatial distribution of the LST from August to October 2020 and August 2021 exhibited higher temperatures in the northeast compared to the southwest. The temperatures were higher closer to the shore, and the continuous heat input from the factories along the northern coast is believed to have caused the regional differences in the water temperature between the two shores. Owing to the strict epidemic control measures in September and October 2021, coastal factories were mostly shut down, resulting in the water temperatures being primarily influenced by the regional climate and exhibiting regional temperature homogeneity.
Author Contributions
Methodology, X.K.; Software, L.W.; Resources, H.L.; Data curation, L.W. and H.L., Writing—Original draft, X.K., Writing—Review & editing, Y.L.; Supervision, Y.L.; Project administration, Y.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the “National Natural Science Foundation of China” [grant number 41902156], and China Geological Survey [project code: DD20191006].
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in this article.
Conflicts of Interest
Lingli Wang and Huijie Liu were employed by the company Beijing SatImage Information Technology Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Sun, J. Temporal and Spatial Variation of Lake Water Temperature in the Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River and Its Response to Climate Warming. Master’s Thesis, Tianjin University, Tianjin, China, 2021. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q. Variation characteristics of surface water temperature in Qinghai Lake and its response to climate change. Yellow River 2018, 40, 25–29. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Shi, K.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, B. Response of lake surface water temperature to climate change: Past, present and future. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2023, 68, 3002–3004. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; He, X.; He, M. Flood Monitoring Using Sentinel-1 SAR for Agricultural Disaster Assessment in Poyang Lake Region. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xue, C.; Xia, J. The impact, causes, and countermeasures of extreme drought in Poyang Lake. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2023, 38, 1894–1902. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CHerrick, C.; Steele, B.G.; Brentrup, J.A.; Cottingham, K.L.; Ducey, M.J.; Lutz, D.A.; Palace, M.W.; Thompson, M.C.; Trout-Haney, J.V.; Weathers, K.C. lakeCoSTR: A tool to facilitate use of Landsat Collection 2 to estimate lake surface water temperatures. Ecosphere 2023, 14, e4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Wu, L.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, C.; Wang, L. Review of research on inversion of water surface temperature. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2015, 17, 969–978. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Wang, Q.; Wang, W.; Wang, C. Monitoring and Evaluating Therm-water Pollution of Dayawan by TM Images. Environ. Monit. China 2006, 22, 80–84. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, S.; Pang, A.; Shen, H.; Zhang, Q. Remote Sensing Inversion and Numerical Prediction Model for the Temperature Vertical Profile in the Yellow Sea. Adv. Mar. Sci. 2009, 27, 444–451. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Xia, J.; Sun, J. Comparison of methods to derive river water temperature using thermal infrared imagery: A case study of the upper Yangtze River catchment. J. Lake Sci. 2022, 34, 307–319. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gong, S.; Sun, H.; Wang, S.; Guo, W.; Li, Y. Study on atmospheric transmittance of thermal infrared remote sensing(II): Application of atmospheric transmittance model. Infrared Laser Eng. 2015, 44, 2013–2020. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Sun, J.; Shi, L. Derivation of river surface temperature from Landsat thermal infrared data. J. Hydroelectr. Eng. 2021, 40, 121–130. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, L. A comparative study of IRS and TM Image Monitoring of Thermal Pollution in Daya Bay. Master’s Thesis, CUGB, Beijing, China, 2013. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Qi, J.; Li, X. Research on Retrieval of Surface Temperature Based on Landsat8 Data Atmospheric Correction Method. Acad. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 4, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Mao, Z.; Xing, X.; Sun, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Huang, W. A Model for Water Surface Temperature Retrieval from HJ-1B/IRS Data and Its Application. Remote Sens. Land Resour. 2011, 6, 81–86. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Liang, D. Comparison of two algorithms for water temperature of Taihu Lake based on HJ/IRS data. J. Shaanxi Meteorol. 2012, 5, 25–28. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lv, C. Temperature Drainage Monitoring of Hongyanhe Nuclear Power Plant Based on Landsat8 Data Split Window Algorithm. Master’s Thesis, Liaoning Technical University, Fuxin, China, 2016. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Chu, Y.; Tan, Q.; Chen, J.; Yang, L.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, Z.; He, F. Distributional characteristics and evaluation of nitrogen, phosphorus and organic matter in the surface sediments of rural ponds around the western part of Lake Poyang in summer. J. Lake Sci. 2023, 35, 192–202. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xie, H.; Hu, M.; Ji, X.; Cao, B.; Jia, S.; Xu, J.; Jin, X. Water Quality Evolution Characteristics and Pollution Factor Analysis in Poyang Lake from 2011 to 2019. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 5585–5597. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Chen, Z.; Feng, C.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Z. Monitoring of Poyang Lake area and its relationship with water level based on Landsat images. Remote Sens. Nat. Resour. 2023, 9, 1–9. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Yan, L.I. The Calculation of Area and Storage of Poyang Lake Based on Remote Sensing Technology. Remote Sens. Inf. 2012, 2, 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Cui, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Chen, D.; Zha, C.; Wang, X. Dynamic Monitoring and Impact Assessment of Poyang Lake Flood in 2020 Based on GF-3. Hydrology 2022, 42, 43–47. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Hu, C.; Chen, X.; Tian, L.; Chen, L. Human induced turbidity changes in Poyang Lake between 2000 and 2010: Observations from MODIS. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Chen, X.; Feng, L. Four decades of winter wetland changes in Poyang Lake based on Landsat observations between 1973 and 2013. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michishita, R.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, B. Monitoring two decades of urbanization in the Poyang Lake area, China through spectral unmixing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 117, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.C.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, J. Impacts of Climate Change and Human Activities on Runoff of Poyang Lake Catchment. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2009, 31, 835–842. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhou, B.; Tian, L.; Yuan, X.; Feng, L. Assessment of total suspended sediment concentrations in Poyang Lake using HJ-1A/1B CCD imagery. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2012, 30, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Hu, C.; Chen, X.; Li, R.; Tian, L.; Murch, B. MODIS observations of the bottom topography and its inter-annual variability of Poyang Lake. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2729–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, A.K.M.A.; Blanton, R.; Mathias, C.A. Quantitative remote sensing of surface water quality in southeast tennessee using planet dove imagery. In Proceedings of the Joint 69th Annual Southeastern/55th Annual Northeastern GSA Section Meeting-2020, Reston, VA, USA, 20–22 March 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H. Study on Applicability Evaluation of Atmospheric Correction Method in Poyang Lake. Master’s Thesis, Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, Ganzhou, China, 2022. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Zhao, S.; Pei, L.; Liu, S.; Wang, X. Precision Evaluation on Atmospheric Correction Reflectance of GF-5 Satellite Hyperspectral Data. Remote Sens. Inf. 2021, 36, 93–98. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bernardo, N.; Watanabe, F.; Rodrigues, T.; Alcântara, E. Atmospheric correction issues for retrieving total suspended matter concentrations in inland waters using OLI/Landsat-8 image. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 59, 2335–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, T.N.; Ripley, D.A. On the relation between NDVI, fractional vegetation cover, and leaf area index. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 62, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.; Jing, L.; Qinhuo, L.; Baodong, X.; Xihan, M.; Yadong, D. Generation of a 16 m/10-day fractional vegetation cover product over China based on Chinese GaoFen-1 observations: Method and validation. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2023, 16, 4229–4246. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.; Wu, Z.; Wang, R. Research on heat island effect in Nanguan District of Changchun City based on remote sensing. Jilin Norm. Univ. J. 2021, 42, 134–140. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, J.; Li, Z. Characteristics and Influence Factors of Summer Surface Urban Heat Island under Arid and Semi-arid Climate. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2017, 17, 160–165. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Z.H.; Li, W.J.; Xu, B. The estimation of land surface emissivity for landsat TM6. Remote Sens. Land Resour. 2004, 3, 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Y.; Zhang, D. Comparative study of land surface temperature inversion methods based on Landsat 8 remote sensing images. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2019, 35, 142–147. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Xu, C.; Guo, J. Comparative analysis of land surface temperature inversion methods based on Landsat 8 data. Arid Environ. Monit. 2023, 37, 137–144. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Jackson, T.J.; Li, F.; Cosh, M.H.; Walthall, C. Estimation of vegetation water content for corn and soybeans with a normalized difference water index (NDWI) using Landsat Thematic Mapper data. In Proceedings of the Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003. IGARSS’03 Proceedings. [Google Scholar]
- Feyisa, G.L.; Meilby, H.; Fensholt, R.; Proud, S.R. Automated Water Extraction Index: A new technique for surface water mapping using Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuangtong, L.; Mingxiao, W.; Shuwen, Y.; Mingze, Y.; Lihua, Y.; Geomatics, F.O.; University, L.J. Research on Water Body Extraction Method Based on GF-2 High Resolution Remote Sensing Image. GNSS World China 2018, 43, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Crosman, E.T.; Horel, J.D. MODIS-derived surface temperature of the Great Salt Lake. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 113, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gifty, A.; Homa, K.P.; Andrea, S.K. Lake surface temperature retrieved from Landsat satellite series (1984 to 2021) for the North Slave Region. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2023, 15, 1329–1355. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Z. Characteristics and Driving Factors of Surface Water Temperature Variation in Major Large Lakes in China. Master’s Thesis, Yunnan Normal University, Kunming, China, 2022. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Mesias, J.M.; Bisagni, J.J.; Brunner, A.-M.E.G. A high-resolution satellite-derived sea surface temperature climatology for the western North Atlantic Ocean. Cont. Shelf Res. 2006, 27, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.; Byrne, D.; Weatherbee, R. Coastal sea surface temperature variability from Landsat infrared data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 81, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).