Abstract
Mining activities have led to severe air pollution problems while they make great contributions to economic construction. Therefore, as a typical steel-industry city in southwest China, Panzhihua, its air pollution has received extensive attention. The characteristics of PM1 in different functional areas of Panzhihua from 2018 to 2019, and the changes of its microstructure and potentially toxic elements (PTEs) and the sources of PM1 were analyzed. The results showed that the mass concentrations of PM1 in the heavy pollution area of Nongnongping (NNP) and the complex industrial pollution area of Hemenkou (HMK) were 12.12–145.30 μg/m3 and 14.38–67.02 μg/m3, respectively. Seasonal PM1 mass concentrations in the two functional areas could be arranged in the following order: winter > autumn > spring > summer. The main particle types in PM1 were fly ash, soot, sulphate particles, aluminosilicate particles and metal particles. Potential sources of PM1 in Panzhihua included coal burning, biomass combustion, automobile exhaust and mining activities. At the same time, the average concentrations of PTEs at NNP were also higher than those at HMK because of smelting activities. Enrichment factor analysis showed that most of the PTEs came from human sources. The results could provide theoretical guidance for environmental management.
1. Introduction
Over the past 40 years of reform and opening-up, mining activities have contributed greatly to Chinese economic growth. But at the same time, the emissions of air pollutants have increased significantly, resulting in severe air pollution problems [1,2,3,4,5]. Air pollution problems have become a major environmental issue of national focus, especially the haze pollution caused by particulate matter. In the haze period, there are not only traffic problems due to reduced visibility [6,7,8], but also a series of related diseases that seriously threaten human health [9]. In addition, different particle size causes different health harms to humans. Generally, the smaller the particle size, the greater the harm to human health [10]. According to the particle size, particulate matter can be classified as PM10, PM2.5 and PM1.
PM1 refers to particles with an aerodynamic equivalent diameter less than or equal to 1 µm in ambient air. In recent years, it has recently garnered increasing attention. Several studies have shown that PM1 made a great contribution to PM2.5 [11,12,13]. PM1 mass concentration was higher in urban areas than in remote areas, as noted from 30 observation stations around the world [14]. PM1 mass concentration was higher in winter than in summer in Brno and Šlapanice, Czech Republic, due to the changes in emissions and wind speed [15]. In addition, the average mass concentration of PM1 in 73 cities in China was 41.9 μg/m3 (4.8–84.0 μg/m3) in 2013–2014 [16]. On the other hand, in recent years, the morphology and PTEs of particulate matter have received extensive attention due to the influence of particle shape and PTEs on their chemical properties, health effects and the application of these characteristics in source identification [17,18,19]. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) offers the possibility to visually relate the morphology, size, and texture of atmospheric particles with the corresponding chemical composition [20,21,22]. In this sense, total suspended particles (TSP) and PM2.5 were found through SEM to be mainly composed of quartz and clay minerals in the Canary Islands of Spain [23]. SEM analysis showed that the PM10 in an industrial Mediterranean city can be divided into three different groups: mineral phases, the compounds from combustion processes and the particles emitted from high-temperature processes [24]. The microscopic morphology of atmospheric particulate matter mainly included soot, fly ash, mineral particles, organic particles, sulphate particles, biomass particles [25,26,27]. The microscopic morphology of PM10 and PM2.5 in Panzhihua city mainly included aluminosilicate particles, sulphate particles, fly ash, biomass burning particles, metal particles and unrecognizable fine particles [19,28]. PTEs are important components of PM1. PTEs, such as lead (Pb), chromium (Cr), cadmium (Cd), nickel (Ni), and arsenic (As), which are genotoxic and nondegradable, can accumulate in organs and damage human organs and glandular metabolism [29]. PTEs such as lead (Pb), cadmium (Cd) and selenium (Se) were abundantly enriched in PM1 in Wuhan, China [30]. The most abundant elements in PM1 and PM2.5 in Bologna, Italy, were iron (Fe), aluminum (Al) and zinc (Zn), which accounted for about 80% of the total [31]. The main enriched PTEs in PM1 in Shanghai, China, were zinc (Zn), lead (Pb), manganese (Mn), copper (Cu) and vanadium (V) [32].
Panzhihua is a typical mining city in southwest China, which is famous for its rich mineral resources. Having the second largest V-Ti magnetite ore deposit in Asia, it is one of the most important metallogenic and processing areas for iron. Panzhihua has made great contributions to Chinese economic construction. However, environmental problems are becoming more and more serious. Therefore, it is necessary to study the characteristics of PM1 in different functional areas of mining cities, as well as its microstructure and PTEs.
Thus, the purpose of this study is to find out the characteristics of PM1 in different functional areas of Panzhihua and the changes of its microstructure and PTEs and the sources of PM1.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Sites and Sample Collection
According to the pollution characteristics and regional functions, two sampling sites were set up in Panzhihua (Figure 1). Among them, the sampling point Nongnongping (NNP, 26°34′2.62″ N, 101°39′55.67″ E), which represents the heavily polluted area of Panzhihua, is located on the roof of a hotel in the eastern smelting plant. In addition, the sampling point Hemenkou (HMK, 26°36′38.79″ N, 101°35′47.19″ E) representing the Panzhihua complex industrial pollution area is located on the roof of a residential building in the western district. It is surrounded by sources of pollution such as limestone mining plants, the Baguanhe slag yard and coal washing plants [33].
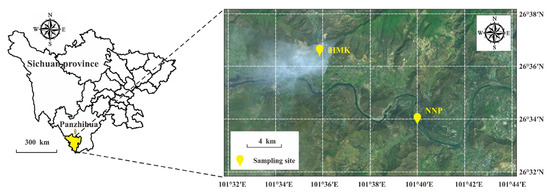
Figure 1.
Location of sampling sites in Panzhihua.
From October 2018 to September 2019, 10 samples were continuously collected every month, and the sampling period of each sample was 24 h. In the end, a total of 240 PM1 samples were collected. To make the samples representative, the cutter was cleaned for every 5 samples collected and the collected samples were dispensed using a special membrane box. The sampling instruments were TH-150C medium flow atmospheric sampler and the matching PM1 combined multi-function cutter (Wuhan Tianhong, Wuhan, China), with a calibrated flow rate of 100 L/min. Filter membranes made of quartz (Whatman, Φ90 mm, QMA) were chosen. Before sampling, the filter membranes were combusted in a muffle furnace (SX-8-13, Beijing, China) at 500 °C for 5 h to remove background contaminants. They were placed in a chamber for 48 h under conditions of 50% ± 5% relative humidity and 25 ± 5 °C both before and after sampling [34,35]. Thereafter, the filters were kept refrigerated at −20 °C until subsequent analysis.
2.2. Analysis Methods
Before and after sampling, a one-hundred thousandth balance (Sartorius, Göttingen, Germany, CPA225D) was used to weigh each filter 3 times to ensure that the difference between any two weighing values did not exceed 0.00004 g. The mass concentrations of PM1 were the difference between the mass of the filters before and after sampling, which was then divided by the volume of the sampling gas under standard conditions (0 °C, 101.3 kPa).
A square of 0.16–0.25 cm2 filter was cut by ceramic knife from representative PM1 samples. Then, the filters were coated with gold to achieve conductivity and vacuum durability. Pre-treatment filters were attached to a stainless steel SEM stub to perceive the morphology and composition of PM1. A computer-controlled scanning electron microscope (SEM, FEI Inspect F50, Hillsboro, OR, USA) and an energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometry (EDX, INCAx-max 20, Oxford, UK) were used at 5 kV accelerating voltage to capture the microstructure image of PM1. At the same time, the blank filter membrane was also analyzed in order to eliminate the influence of Si and O elements on the results of the sample analysis (Figure 2).
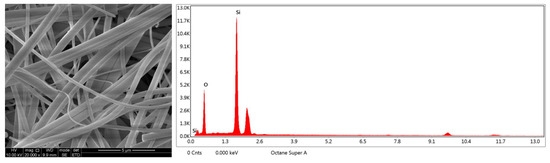
Figure 2.
SEM micrograph and EDX spectrum of the blank filter membrane.
The concentrations of PTEs in the samples were then analyzed. Before the experiment, all Teflon vials were thoroughly cleaned with 20% nitric acid solution and deionized water to avoid contamination. Then 1/4 of the filter was dissolved with 1 mL of nitric acid (HNO3) and 1 mL hydrofluoric acid (HF) in a closed-cap Teflon vial for 48 h at 180 °C. After that, the mixed solution was steamed to near dry, and then re-dissolved twice with 1 mL HNO3 (120 °C). After the last re-dissolution, HNO3 (1 mL), Rh solution (1 mL of 1000 ng/mL), and 5 mL deionized water were added and kept in Teflon vials for 6 h (100 °C) [36]. At this point, the sample pre-treatment was completed. The concentrations of the PTEs were analyzed by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS, Perkin Elmer Corp., Norwalk, CT, USA). The reference material GSS-4 was used to ensure analytical accuracy with recovery between 94.1% and 104.5%. In addition, for 10% of the samples analysis was repeated, and reagent blanks were also used to check the quality of the analysis (Table S4). A total of nine PTEs were measured, including vanadium (V), chromium (Cr), manganese (Mn), nickel (Ni), copper (Cu), zinc (Zn), arsenic (As), lead (Pb), and cadmium (Cd).
2.3. Data Analysis
The enrichment degrees of elements in atmospheric particulate matter vary according to the mechanism of formation and the source of the elements. Enrichment factors (EF) are used to study the enrichment degrees of elements in atmospheric particulate matter, so as to analyze the content level and source of the elements [37,38]. Generally, EF values are defined as the ratio of the elements content in a sample to the elements content of the background. In this study, EF values for the PTEs in PM1 were calculated using Equation (1):
where Cs means measured PTE concentration in PM1, Cref means Mn concentration in PM1, Bs means the measured PTE content in the reference, Bref means Mn content in the background reference [35,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46]. The contents of heavy elements in soil in Panzhihua were taken as the background values [47,48,49,50,51,52,53]. Elements are classified as hyper enrichment, anomalous enrichment, moderate enrichment, mild enrichment, and not enrichment, with corresponding values of EF > 1000, 100 < EF ≤ 1000, 10 < EF ≤ 100, 1 < EF ≤ 10, and EF ≤ 1, respectively [54].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Seasonal Variation of PM1 Mass Concentrations
During the sampling period, the annual average mass concentration of NNP in Panzhihua was 33.43 ± 15.11 μg/m3. Specifically, the PM1 mass concentrations of NNP in spring, summer, autumn, and winter were 17.95–55.84 (mean: 30.09 ± 9.41), 16.36–39.05 (mean: 26.86 ± 6.52), 12.12–44.73 (mean: 30.48 ± 7.13), and 22.10–145.30 (mean: 43.84 ± 22.44) μg/m3, respectively. The annual average mass concentration of HMK in Panzhihua was 29.87 ± 8.46 μg/m3. As a result, the PM1 mass concentrations of HMK in spring, summer, autumn, and winter were 14.38–51.49 (mean: 27.33 ± 8.89), 16.45–32.85 (mean: 25.94 ± 4.52), 17.08–37.06 (mean: 29.33 ± 5.88), and 20.77–67.02 (mean: 35.25 ± 9.36) μg/m3, respectively (Table S1). The PM1 mass concentrations of NNP and HMK showed the same seasonal distribution characteristics (Figure 3), i.e., the PM1 mass concentrations were lowest in summer, followed by spring, autumn; the highest PM1 mass concentrations were observed in winter. Meteorological conditions are the most important reason for this phenomenon. In winter, low temperature, weak solar radiation, low boundary layer and high frequency of calm wind lead to limited dispersion of pollutants. In addition, the reduced rainfall in winter is also favors the accumulation of pollution. Conversely, in summer, solar radiation is strong, the boundary layer tends to break down and atmospheric convection is enhanced [35,55], leading to a reduction in the mass concentration of PM1. Overall, the PM1 mass concentrations are negatively correlated with temperature, relative humidity and wind speed, and positively correlated with atmospheric pressure (Figures S1 and S2). In addition, the two sampling sites also showed the characteristics of geographical distribution, i.e., the PM1 mass concentration in the heavily polluted areas of NNP were higher than in the complex industrial polluted areas of HMK.
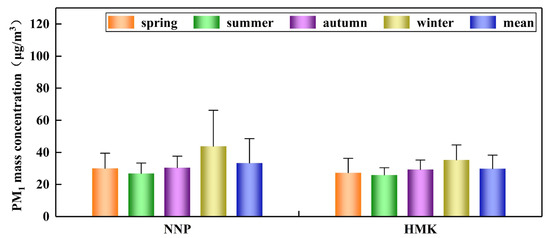
Figure 3.
Seasonal distribution characteristics of the PM1 mass concentrations in Panzhihua (NNP, HMK).
The annual average mass concentration of PM1 in Panzhihua obtained in this study was compared with other cities (Figure 4). The annual average mass concentration of PM1 in Panzhihua is lower than in Shanghai (49.8 μg/m3), Guangzhou (52.5 μg/m3), Beijing (61.5 μg/m3), Wuhan (82 μg/m3), Nanjing (72.5 μg/m3) and Xi’an (127.3 μg/m3). However, compared to some cities in other countries, the annual average mass concentration of PM1 in Panzhihua is high: 2.7 times higher than in Elche (Spain), 2.5 times higher than in Birmingham, 2.0 times higher than in Austria and 1.7 times higher than in Krakow, Poland. Obviously, there are differences in mass concentrations between different geographical areas, which are mainly influenced by the functional positioning of cities, urban atmospheric dispersion conditions and urban pollutant emissions. Although the PM1 mass concentration pollution in Panzhihua is not very significant compared to other cities, PM1 plays a much larger role than PM2.5 and PM10 in terms of air quality, deteriorating visibility, climate change and adverse effects on human health [13]. Therefore, action is still needed to control PM1 emissions.
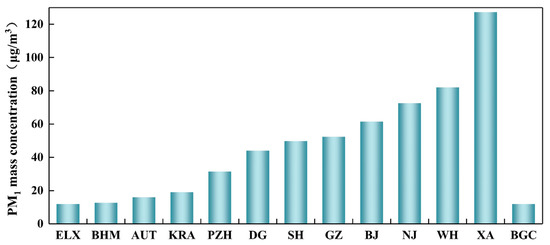
Figure 4.
Annual average mass concentration of PM1 in different cities. ELX: Elche, Spain [29]; BHM: Birmingham, UK [56]; AUT: Austria [57]; KRA: Krakow, Poland [58]; PZH: Panzhihua, China (This study); DG: Dongguan, China [59]; SH: Shanghai, China [11]; GZ: Guangzhou, China [60]; BJ: Beijing, China [61]; WH: Wuhan, China [59]; NJ: Nanjing, China [62]; XA: Xi’an, China [63]; BGC: Chinese background site [64].
3.2. Morphology Properties
In order to better investigate the sources of PM1 and its health effects, its particle morphology should be well understood. The observation and analysis of particle morphology of NNP and HMK in Panzhihua by SEM-EDX revealed no significant differences in the microscopic morphology of the particles in the two functional regions. Therefore, we will discuss them as a whole.
During the SEM-EDX analysis of PM1, the morphology and elemental composition was determined. Five morphological types were identified, including fly ash, soot, sulphate particles, aluminosilicate particles and metal particles (Figure 5).
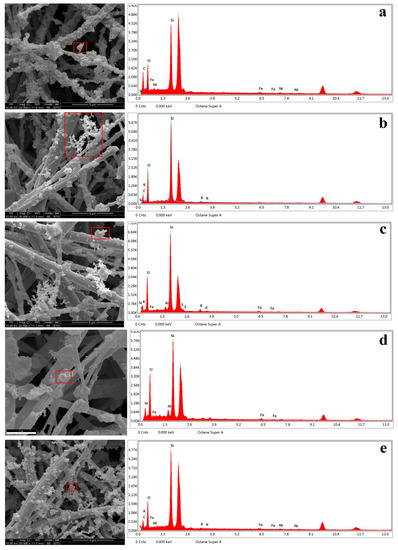
Figure 5.
SEM micrograph and EDX spectrum of PM1. (a): fly ash, (b): soot, (c): sulphate particles, (d): aluminosilicate particles, (e): metal particles.
Fly ash is mainly spherical, with a smooth surface and generally contains Si, O, C and variable amounts of Fe and Ni (Figure 5a). Typically fly ash is mainly derived from coal combustion and biomass burning [65,66,67,68].
The soot particles are predominantly in chain-like aggregates with C, O, Si and a small amount of K (Figure 5b). The soot particles are thought to consist of aggregates of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) [69], which appear microscopically as monolayers or stacked together in a more or less disordered manner [70]. Soot particle assemblages have a distinctive microscopic morphology and are usually composed of ultrafine particles [71]. The soot particles can be irregularly chained, fluffy, dense and clustered due to the type of fuel, combustion conditions and the physicochemical reaction in the atmosphere. The main sources of the soot particles are the combustion of fossil fuels, gas, diesel, and biomass [72,73,74,75].
The sulphate particles are mainly massive, with S, O and Si as the main components and Ca, Fe and Na as minor components (Figure 5c). Most sulphate particles are formed by the oxidation of SO2 from fossil fuel combustion and biomass burning [76,77]. Sulphate particles are often mixed with other aerosols and their optical properties and hygroscopic behavior can influence the climate [78]. Acid rain is formed when large quantities of acid are released into the atmosphere and can have a negative impact on terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, including soil and lake acidification, inhibition of plant growth, and loss of biodiversity [79,80].
Studies have shown that aluminosilicate particles are mainly from natural and anthropogenic sources, with the former being coarse and irregular in shape, while the latter are probably from combustion processes and are mainly round, spherical and flaky in shape [81,82,83,84]. The aluminosilicate particles in this study are small and predominantly spherical, with Si and O as the main constituents and Al and Fe as the minor constituents (Figure 5d), probably derived from products of high temperature combustion.
As a famous mining city, Panzhihua often generates particulate matter from its steel smelting activities with specific elements, such as Fe, Ni, etc. In this study, the Fe, Ni containing metal particles are nearly oval, with a smooth surface (Figure 5e), mainly from iron and steel smelting activities.
In summary, the main types of particulate matter in PM1 in Panzhihua are: fly ash, soot, sulphate particles, aluminosilicate particles and metal particles. The potential sources of PM1 in Panzhihua include coal burning, biomass combustion, automobile exhaust and mining activities.
3.3. Characteristics of PTEs
The seasonal distribution characteristics of PTEs in PM1 in Panzhihua are shown in Figure 6. The seasonal changes of Cd, Mn and Pb in PM1 of NNP were consistent with the seasonal change of the mass concentration of PM1, i.e., largest in winter and smallest in summer. The concentrations of Cr and Cu were the highest in summer and lowest in autumn. The concentrations of Zn and As were the highest in autumn and lowest in spring. The concentration of V was the highest in summer and the lowest in spring (Table S2). This phenomenon is mainly due to the complex sources around the NNP, which is surrounded by the steel smelting area and the different PTEs released by the complex smelting process. The study of element components in PM10 and PM2.5 at NNP also showed that there were differences between seasonal variations of individual elements and mass concentrations [33]. The seasonal change of Ni in PM1 of HMK was consistent with the seasonal change of the mass concentration of PM1, i.e., largest in winter and smallest in summer. However, the concentrations of Mn, Cd, Cu, Zn, As and Pb were the highest in autumn and lowest in spring (Table S3). The variation trend of V concentration of HMK was consistent with that of NNP.
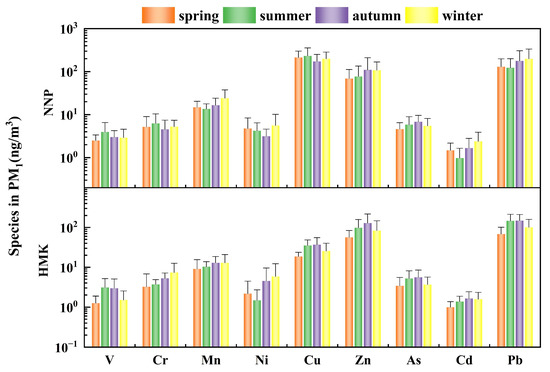
Figure 6.
Seasonal distribution characteristics of PTEs in PM1.
The annual average concentrations of PTEs in PM1 in Panzhihua are given in Figure 7. The average concentration of PTEs at NNP are as follows: Cu (203.09) > Pb (161.07) > Zn (93.34) > Mn (17.66) > As (5.77) > Cr (5.30) > Ni (4.43) > V (3.12) > Cd (1.67) (ng/m3). The average concentration of PTEs at HMK as follows: Pb (112.63) > Zn (90.64) > Cu (28.31) > Mn (11.49) > Cr (5.10) > As (4.35) > Ni (3.78) > V (2.09) > Cd (1.40) (ng/m3). From the perspective of spatial variation characteristics, affected by the smelting area, the average concentrations of PTEs at NNP were higher than those at HMK. Since some PTEs may cause toxicity and carcinogenic effects [85,86,87,88,89,90], the Ministry of Environmental Protection of China has issued some reference concentration limits for PTEs (GB 3095-2012) (Table S5). By calculation [29,91], the annual average concentrations of Cr(VI) in NNP and HMK were 0.88 ng/m3 and 0.85 ng/m3, respectively, which were 35.2 and 34.0 times of the standard limit, respectively. Although the annual average concentrations of As in NNP and HMK did not exceed the standard limit, their concentrations accounted for 96.2% and 72.5% of the standard limit, respectively. Similarly, the annual average concentrations of Cd in NNP and HMK were also lower than the standard limit.
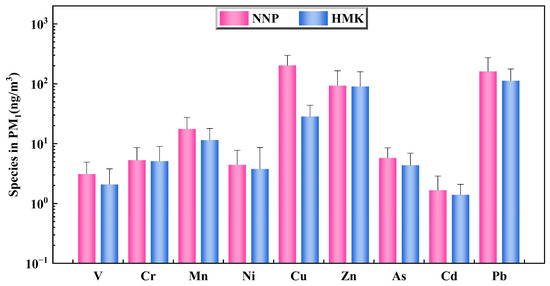
Figure 7.
Annual average concentrations of PTEs in PM1.
The average concentrations of PTEs in PM1 in Panzhihua obtained in this study were compared with other cities (Figure 8). The average concentrations of PTEs in PM1 in Panzhihua were generally lower than other cities in China, but some PTEs also showed higher concentrations. For example, the concentration of Cu in Panzhihua was higher than that in Changji, Xinjiang and Beijing, the concentration of Cd in Panzhihua was higher than that in Shijiazhuang and the concentration of Pb in Panzhihua was higher than that in Beijing. Compared with foreign cities (except Algiers, Algeria), the average concentrations of PTEs in PM1 in Panzhihua were generally higher. Therefore, there are apparent differences in the concentrations of PTEs in different countries and cities. These differences are often caused by complex factors, such as pollutant emissions, atmospheric diffusion conditions and geographic locations.
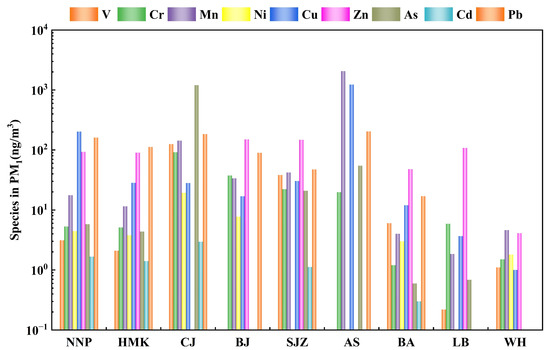
Figure 8.
Average concentrations of PTEs in PM1 in different cities. NNP, HMK: Panzhihua, China (This study); CJ: Changji, Xinjiang, China [92]; BJ: Beijing, China [13]; SJZ: Shijiazhuang, China [93]; AS: Algiers, Algeria [94]; BA: Barcelona, Spain [95]; LB: Istanbul, Turkey [96]; WH: Whyalla, Australia [97].
The EF values of PTEs in PM1 in Panzhihua are given in Figure 9. The EF values for the PTEs of V, Ni, Cr, Pb, As, Zn, Cd and Cu in PM1 at NNP were calculated as 1.14, 3.31, 1.34, 405.84, 28.25, 33.97, 49.99 and 272.55, respectively. The EF values of Pb and Cu exceeded 100, indicating anomalous enrichment of these PTEs, attributable primarily to anthropogenic activity. The EF values of As, Zn and Cd reflect moderate enrichment, indicating that anthropogenic activity was an important source of these PTEs. The EF values of V, Ni, and Cr were <10, indicating that these PTEs have only mild enrichment, attributable partly to the natural background (crust or soil) and partly to anthropogenic activity. The EF values for the PTEs of V, Ni, Cr, Pb, As, Zn, Cd and Cu in PM1 at HMK were calculated as 1.07, 4.76, 1.79, 436.83, 31.55, 49.18, 69.20 and 56.13, respectively. The enrichment degrees of PTEs in NNP and HMK were the same. The enrichment degrees of PTEs in NNP and HMK were consistent with the pollution characteristics of the respective sampling sites. Specifically, NNP is located on the roof of a hotel in the smelting plant, while HMK is located on the roof of a residential building, surrounded by sources of pollution such as limestone mining plants, the Baguanhe slag yard and coal washing plants. It can be seen that anthropogenic activity contributes significantly to the sources of PTEs and should be given sufficient attention.
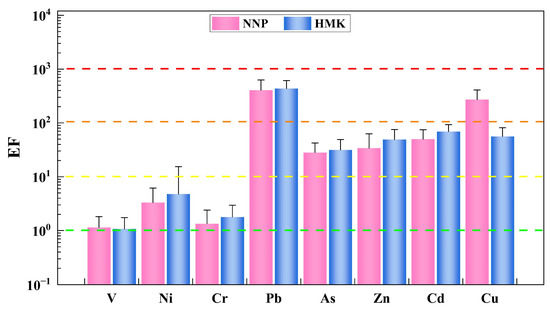
Figure 9.
Enrichment factors (EFs) of PTEs in PM1.
4. Conclusions
The present study analyzed the characteristics of PM1 in different functional areas of Panzhihua from 2018 to 2019, and the changes of its microstructure and PTEs and the sources of PM1 were analyzed. The mean mass concentration of PM1 at NNP was 30.09 ± 9.41 μg/m3 for spring, 26.86 ± 6.52 μg/m3 for summer, 30.48 ± 7.13 μg/m3 for autumn and 43.84 ± 22.44 μg/m3 for winter. Furthermore, the mean mass concentrations of PM1 at HMK in spring, summer, autumn and winter were 27.33 ± 8.89 μg/m3, 25.94 ± 4.52 μg/m3, 29.33 ± 5.88 μg/m3 and 35.25 ± 9.36 μg/m3, respectively. The mass concentrations of PM1 at both sampling sites showed the same seasonal variation. The PM1 mass concentration at NNP was higher than HMK. The main particle types in PM1 were fly ash, soot, sulphate particles, aluminosilicate particles and metal particles. Potential sources of PM1 in Panzhihua included coal burning, biomass combustion, automobile exhaust and mining activities. The seasonal changes of Cd, Mn and Pb in PM1 at NNP and Ni in PM1 at HMK were consistent with the seasonal changes of their mass concentrations, while the concentrations of all elements at NNP were higher than HMK due to the influence of the smelting area. The EFs of different PTEs varied dramatically. At NNP, both Pb and Cu were enriched anomalously, As, Zn and Cd were enriched moderately; V, Ni and Cr were mildly enriched. Most of the PTEs at HMK showed the same enrichment characteristics as NNP. However, Cu was moderately enriched at HMK, which was different from NNP. On the whole, human activities made a significant contribution to PTEs. Our findings provide indispensable information for the study of the physical and chemical characteristics and source analysis of PM1 in mining cities.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/atmos13081304/s1, Figure S1: Meteorological parameters of Panzhihua (2018–2019); Figure S2: Wind frequency rose chart of Panzhihua (2018–2019); Table S1: Seasonal distribution characteristics of the PM1 mass concentrations (μg/m3); Table S2: Seasonal distribution characteristics of PTEs in PM1 of NNP (ng/m3); Table S3: Seasonal distribution characteristics of PTEs in PM1 of HMK (ng/m3); Table S4: QA/QC parameters for ICP-MS analysis of PTEs; Table S5: The reference concentration limits for PTEs (GB 3095-2012).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.S. and Y.H.; methodology, H.S.; data curation, H.S. and J.W.; writing—original draft preparation, H.S.; writing—review and editing, Y.H.; project administration, X.C. and Z.L.; funding acquisition, Y.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 41977289, the Science and Technology Department of Sichuan Province, grant number 2021JDTD0013 and the State Key Laboratory of Geohazard Prevention and Geoenvironment Protection Independent Research Project, grant number SKLGP2021Z002.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Scientific Foundation of China (41977289), the Science and Technology Department of Sichuan Province (2021JDTD0013), and the State Key Laboratory of Geohazard Prevention and Geoenvironment Protection Independent Research Project (SKLGP2021Z002).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Zhang, X.P.; Cheng, X.M. Energy consumption, carbon emissions, and economic growth in China. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 68, 2706–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.F.; Mauzerall, D.L.; Zhu, T.; Liang, S.; Ezzati, M.; Remais, J.V. Environmental health in China: Progress towards clean air and safe water. Lancet 2010, 375, 1110–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.M.; Li, S.S.; Tian, Z.X.; Pan, X.C.; Zhang, J.L.; Williams, G. The burden of air pollution on years of life lost in Beijing, China, 2004–2008: Retrospective regression analysis of daily deaths. BMJ Br. Med. J. 2013, 347, f7139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.J.; Fang, C.L.; Guan, X.L.; Pang, B.; Ma, H.T. Urbanisation, energy consumption, and carbon dioxide emissions in China: A panel data analysis of China’s provinces. Appl. Energy 2014, 136, 738–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.B.; Knibbs, L.D.; Zhang, W.Y.; Li, S.S.; Cao, W.; Guo, J.P.; Ren, H.Y.; Wang, B.G.; Wang, H.; Williams, G.; et al. Estimating spatiotemporal distribution of PM1 concentrations in China with satellite remote sensing, meteorology, and land use information. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 233, 1086–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Dey, S. Influence of aerosol composition on visibility in megacity Delhi. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 62, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Zhang, M.G.; Tao, J.H.; Wang, L.L.; Gao, J.; Wang, S.L.; Chai, F.H. Modeling aerosol impacts on atmospheric visibility in Beijing with RAMS-CMAQ. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 72, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Wong, M.S.; Kim, K.; Park, S.S. Analytical approach to estimating aerosol extinction and visibility from satellite observations. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 91, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, J.N.; Ma, G.X.; Zhang, Y.S. China tackles the health effects of air pollution. Lancet 2013, 382, 1959–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.J. Environmental Behavior and Human Inhalation Exposure of Particles and Typical Organic Contaminants in Indoor and Outdoor Air. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 2018. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, T.; Zhao, M.F.; Xiu, G.L.; Yu, J.Z. Simultaneous monitoring and compositions analysis of PM1 and PM2.5 in Shanghai: Implications for characterization of haze pollution and source apportionment. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 557, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.H.; Duan, J.C.; Zhen, N.J.; He, K.B.; Hao, J.M. Chemical characteristics and source of size-fractionated atmospheric particle in haze episode in Beijing. Atmos. Res. 2016, 167, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Lang, J.L.; Cheng, S.Y.; Li, S.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, D.S.; Zhang, H.Y.; Wang, H.Y. Chemical composition and sources of PM1 and PM2.5 in Beijing in autumn. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 630, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Jimenez, J.L.; Canagaratna, M.R.; Allan, J.D.; Coe, H.; Ulbrich, I.; Alfarra, M.R.; Takami, A.; Middlebrook, A.M.; Sun, Y.L.; et al. Ubiquity and dominance of oxygenated species in organic aerosols in anthropogenically-influenced Northern Hemisphere midlatitudes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L13801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumal, K.; Mikuska, P.; Vecera, Z. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and hopanes in PM1 aerosols in urban areas. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 67, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.B.; Morawska, L.; Zhang, W.Y.; Li, S.S.; Cao, W.; Ren, H.Y.; Wang, B.G.; Wang, H.; Knibbs, L.D.; Williams, G.; et al. Spatiotemporal variation of PM1 pollution in China. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 178, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.Y.; Hu, W.; Zhang, D.Z.; Wu, Z.J.; Guo, S.; Pian, W.; Cheng, W.J.; Hu, M. Variations of fine particle physiochemical properties during a heavy haze episode in the winter of Beijing. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cao, J.J.; Huang, R.J.; Yang, F.M.; Wang, Q.Y.; Wang, Y.C. Characterization, mixing state, and evolution of urban single particles in Xi’an (China) during wintertime haze days. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Huang, Y.; Liu, C.; Ni, S.J.; Wang, R.; Long, Z.J. Assessment of Air Pollution around the Panzhihua V-Ti Magnetite Mine Region, Southwest China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 1204–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Reyes, A.; Orozco-Rivera, G.; Acuna-Askar, K.; Villarreal-Chiu, J.F.; Alfaro-Barbosa, J.M. Characterization of atmospheric black carbon in particulate matter over the Monterrey metropolitan area, Mexico, using scanning electron microscopy. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2016, 9, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, L.T.; Rodriguez, F.E.L.; Sanchez-Dominguez, M.; Leyva-Porras, C.; Silva-Vidaurri, L.G.; Acuna-Askar, K.; Kharisov, B.I.; Chiu, J.F.V.; Barbosa, J.M.A. Chemical and morphological characterization of TSP and PM2.5 by SEM-EDS, XPS and XRD collected in the metropolitan area of Monterrey, Mexico. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 143, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, L.T.; Rodriguez, F.E.L.; Sanchez-Dominguez, M.; Cavazos, A.; Leyva-Porras, C.; Silva-Vidaurri, L.G.; Askar, K.A.; Kharissov, B.I.; Chiu, J.F.V.; Barbosa, J.M.A. Determination of trace metals in TSP and PM2.5 materials collected in the Metropolitan Area of Monterrey, Mexico: A characterization study by XPS, ICP-AES and SEM-EDS. Atmos. Res. 2017, 196, 8–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alastuey, A.; Querol, X.; Castillo, S.; Escudero, M.; Avila, A.; Cuevas, E.; Torres, C.; Romero, P.M.; Exposito, F.; Garcia, O.; et al. Characterisation of TSP and PM2.5 at Izana and Sta. Cruz de Tenerife (Canary Islands, Spain) during a Saharan Dust Episode (July 2002). Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 4715–4728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolis, E.I.; Gkanas, E.I.; Pavlidou, E.; Skemperi, A.; Pey, J.; Perez, N.; Bartzis, J.G. Microstuctural analysis and determination of PM10 emission sources in an industrial Mediterranean city. Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 2014, 12, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.J.; Shao, L.Y. Observation of nitrate coatings on atmospheric mineral dust particles. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 1863–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.J.; Shao, L.Y. Chemical Modification of Dust Particles during Different Dust Storm Episodes. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2012, 12, 1095–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.J.; Shao, L.Y.; Shi, Z.B.; Chen, J.M.; Yang, L.X.; Yuan, Q.; Yan, C.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Sun, J.Y.; et al. Mixing state and hygroscopicity of dust and haze particles before leaving Asian continent. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 1044–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Huang, Y.; Long, Z.J.; Ni, S.J.; Shi, Z.M.; Zhang, C.J. Characteristics, Sources and Health Risk Assessment of Trace Metals in PM10 in Panzhihua, China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2017, 98, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, N.; Yubero, E.; Nicolas, J.F.; Varea, M.; Crespo, J. Characterization of metals in PM1 and PM10 and health risk evaluation at an urban site in the western Mediterranean. Chemosphere 2018, 201, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, X.P.; Wang, Z.W.; Cheng, H.R.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, G.; Wang, X.M.; Ling, Z.H.; Wang, N. Chemical characteristics of submicron particulates (PM1.0) in Wuhan, Central China. Atmos. Res. 2015, 161, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarti, E.; Pasti, L.; Rossi, M.; Ascanelli, M.; Pagnoni, A.; Trombini, M.; Remelli, M. The composition of PM1 and PM2.5 samples, metals and their water soluble fractions in the Bologna area (Italy). Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2015, 6, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.J.; Wu, Y.Z.; Wang, Y.L.; Li, Y.S.; Jin, C.Y. Physicochemical properties, in vitro cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of PM1.0 and PM2.5 from Shanghai, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 19508–19516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X. Study on Geochemical Characteristics of Atmospheric Inhalable Particulate Matter in Panzhihua City. Ph.D. Thesis, Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu, China, 2017. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, S.P.; Ni, S.J.; Long, Z.J. Characteristics, sources, and health risk assessment of trace elements in PM10 at an urban site in Chengdu, Southwest China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Huang, Y.; Li, T.; Shi, H.B.; He, M.; Cheng, X.; Ni, S.J.; Zhang, C.J. Annual Characteristics, Source Analysis of PM1-bound Potentially Harmful Elements in the Eastern District of Chengdu, China. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 79, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, L.; Cheng, X.; Wang, J.J.; Li, T.; He, M.; Shi, H.B.; Zhang, M.; Hughes, S.S.; Ni, S.J. Characteristics of Particulate Matter at Different Pollution Levels in Chengdu, Southwest of China. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajusz-Zubek, E.; Radko, T.; Mainka, A. Fractionation of trace elements and human health risk of submicron particulate matter (PM1) collected in the surroundings of coking plants. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovelli, S.; Cattaneo, A.; Nischkauer, W.; Borghi, F.; Spinazze, A.; Keller, M.; Campagnolo, D.; Limbeck, A.; Cavallo, D.M. Toxic trace metals in size-segregated fine particulate matter: Mass concentration, respiratory deposition, and risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongarra, G.; Manno, E.; Varrica, D.; Vultaggio, M. Mass levels, crustal component and trace elements in PM10 in Palermo, Italy. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 7977–7986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabretti, J.F.; Sauret, N.; Gal, J.F.; Maria, P.C.; Scharer, U. Elemental characterization and source identification of PM2.5 using Positive Matrix Factorization: The Malraux road tunnel, Nice, France. Atmos. Res. 2009, 94, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, E.C.; Meira, L.; de Santana, E.R.R.; Wiegand, F. Chemical Composition of PM10 and PM2.5 and Seasonal Variation in South Brazil. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2009, 199, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, N.; Eav, J.; Xie, M.J.; Hannigan, M.P.; Miller, S.L.; Navidi, W.; Peel, J.L.; Schauer, J.J.; Shafer, M.M.; Milford, J.B. Concentrations and source insights for trace elements in fine and coarse particulate matter. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 89, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enamorado-Baez, S.M.; Gomez-Guzman, J.M.; Chamizo, E.; Abril, J.M. Levels of 25 trace elements in high-volume air filter samples from Seville (2001-2002): Sources, enrichment factors and temporal variations. Atmos. Res. 2015, 155, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajusz-Zubek, E.; Kaczmarek, K.; Mainka, A. Trace Elements Speciation of Submicron Particulate Matter (PM1) Collected in the Surroundings of Power Plants. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 13085–13103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, J.J.; Palmiero, R.; Han, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.Q.; Zhang, T.Y.; Sun, M.Q.; Wang, H.; Yu, G.P.; Yi, X.L.; et al. Characterization of PM1-Bound Metallic Elements in the Ambient Air at a High Mountain Site in Northern China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 2967–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, W.Y.; Li, L.L.; Li, J.J.; Wei, L.L.; Chi, W.Q.; Hong, L.J.; Zhao, Q.L.; Jiang, J.Q. Seasonal concentration distribution of PM1.0 and PM2.5 and a risk assessment of bound trace metals in Harbin, China: Effect of the species distribution of heavy metals and heat supply. Sci Rep. 2020, 10, 8160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.D.; Lu, G.F.; Liu, Q.H. The natural background values of some elements in the soil of the city of Du Kou. J. Nanjing Univ. Nat. Sci. 1985, 21, 166–176. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Ding, Z.H.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.Y.; Wu, J.C.; Chen, Y.J.; Lian, H.Z. Size Distribution and Source Apportionment of Airborne Metallic Elements in Nanjing, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2013, 13, 1796–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.P.; Zhang, Z.S.; Liu, H.F.; Zhou, H.; Fan, Z.Y.; Lin, M.; Wu, D.L.; Xia, B.C. Characteristics, sources and health risk assessment of toxic heavy metals in PM2.5 at a megacity of southwest China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2016, 38, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Meng, D.; Han, M.M.; Jia, C.Q. Heavy metal characteristics and health risk assessment of PM2.5 in three residential homes during winter in Nanjing, China. Build. Environ. 2018, 143, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, J.; Han, M.M.; Jia, C.Q.; Zhou, Y.Y. Heavy metal characteristics and health risk assessment of PM2.5 in students’ dormitories in a university in Nanjing, China. Build. Environ. 2019, 160, 106206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.H.; Yu, J.; Bi, C.L.; Yue, J.J.; Li, Q.Q.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.P.; Xiao, Z.M.; Guo, L.Q.; Huang, B.J. Health risk assessment for highway toll station workers exposed to PM2.5-bound heavy metals. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 1024–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.C.; Luo, X.S.; Li, H.B.; Cang, L.; Yang, J.; Yang, J.L.; Zhao, Z.; Tang, M.W. Seasonal Levels, Sources, and Health Risks of Heavy Metals in Atmospheric PM2.5 from Four Functional Areas of Nanjing City, Eastern China. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.J.; Yang, D.R.; Ye, Z.X.; Zhang, H.D.; Ma, X.K.; Tang, Z.Y.; Mao, D.Y. Characteristics of elements and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in PM2.5 at the southwest suburb of Chengdu in spring. Environ. Sci. 2016, 37, 4490–4503. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, S.P.; Zhang, M.; Wang, J.J.; Cheng, X.; Li, T.; He, M.; Ni, S.J. Source apportionment and health risk assessment of air pollution particles in eastern district of Chengdu. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 2251–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.X.; Harrison, R.M. Pragmatic mass closure study for PM1.0, PM2.5 and PM10 at roadside, urban background and rural sites. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 980–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomiscek, B.; Hauck, H.; Stopper, S.; Preining, O. Spatial and temporal variations of PM1, PM2.5, PM10 and particle number concentration during the AUPHEP-project. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 3917–3934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samek, L.; Furman, L.; Mikrut, M.; Regiel-Futyra, A.; Macyk, W.; Stochel, G.; van Eldik, R. Chemical composition of submicron and fine particulate matter collected in Krakow, Poland. Consequences for the APARIC project. Chemosphere 2017, 187, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L. Physicochemical Properties and Source Apportionment of Urban Ambient Particulate Matter in Dongguan and Wuhan. Ph.D. Thesis, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, 2016. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Tao, J.; Shen, Z.X.; Zhu, C.S.; Yue, J.H.; Cao, J.J.; Liu, S.X.; Zhu, L.H.; Zhang, R.J. Seasonal variations and chemical characteristics of sub-micrometer particles (PM1) in Guangzhou, China. Atmos. Res. 2012, 118, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.C.; Lang, J.L.; Cheng, S.Y.; Wang, X.Q.; Lu, Z. Seasonal variation and source analysis for PM2. 5, PM1 and their carbonaceous components in Beijing. Environ. Sci. 2018, 39, 4430–4438. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, W.J. Characteristics of Carbonaceous Components and Stable Isotope Tracing in PM1.1 and Biomass in Nanjing. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing, China, 2016. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Z.X.; Arimoto, R.; Cao, J.J.; Zhang, R.J.; Li, X.X.; Du, N.; Okuda, T.; Nakao, S.; Tanaka, S. Seasonal Variations and Evidence for the Effectiveness of Pollution Controls on Water-Soluble Inorganic Species in Total Suspended Particulates and Fine Particulate Matter from Xi’an, China. J. Air Waste Manage. Assoc. 2008, 58, 1560–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W. Chemical Characterization of Submicron Aerosols and Particle Growth Events at a National Background Site (3295 m a.s.l.) in the Tibetan Plateau. Master’s Thesis, Chengdu University of Information Technology, Chengdu, China, 2015. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z.B.; Shao, L.Y.; Jones, T.P.; Whittaker, A.G.; Lu, S.L.; Berube, K.A.; He, T.; Richards, R.J. Characterization of airborne individual particles collected in an urban area, a satellite city and a clean air area in Beijing, 2001. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 4097–4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posfai, M.; Gelencser, A.; Simonics, R.; Arato, K.; Li, J.; Hobbs, P.V.; Buseck, P.R. Atmospheric tar balls: Particles from biomass and biofuel burning. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109, D06213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.; Jones, T.; BeruBe, K. The internal microstructure and fibrous mineralogy of fly ash from coal-burning power stations. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 3324–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zyrkowski, M.; Neto, R.C.; Santos, L.F.; Witkowski, K. Characterization of fly-ash cenospheres from coal-fired power plant unit. Fuel 2016, 174, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, L.B.; Scanlon, J.C.; Clausen, C.A. Combustion tube soot from a diesel fuel/air mixture: Issues in structure and reactivity. Energy Fuels 1988, 2, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apicella, B.; Pre, P.; Alfe, M.; Ciajolo, A.; Gargiulo, V.; Russo, C.; Tregrossi, A.; Deldique, D.; Rouzaud, J.N. Soot nanostructure evolution in premixed flames by High Resolution Electron Transmission Microscopy (HRTEM). Proc. Combust. Inst. 2015, 35, 1895–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.D.; Ming, C.B.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zheng, M. Microscopic morphology and size distribution of PM2.5 in Guangzhou urban area in fall 2011. China Environ. Sci. 2015, 35, 1013–1018. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yue, W.S.; Lia, X.L.; Liu, J.F.; Li, Y.; Yu, X.H.; Deng, B.; Wan, T.M.; Zhang, G.L.; Huang, Y.Y.; He, W.; et al. Characterization of PM2.5 in the ambient air of Shanghai city by analyzing individual particles. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 368, 916–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.S. Physicochemical Characteristics of Indoor PM10 and PM2.5 in Xuanwei Lung Cancer Area. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Mining and Technology-Beijing, Beijing, China, 2013. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y. Domestic Coal Combustion Emissions and the Lung Cancer Epidemic in Xuanwei, China. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Mining and Technology-Beijing, Beijing, China, 2016. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Hou, C. Characteristics and Aging Process pf Individual Particles in the Traffic-Derived PM2.5 in Highway Tunnels and Urban Roads. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Mining and Technology-Beijing, Beijing, China, 2017. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.J.; Shao, L.Y. Transmission electron microscopy study of aerosol particles from the brown hazes in northern China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, D09302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satsangi, P.G.; Yadav, S. Characterization of PM2.5 by X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy–energy dispersive spectrometer: Its relation with different pollution sources. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 11, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, I.; Gali, S.; Marcos, C. Atmospheric inorganic aerosol of a non-industrial city in the centre of an industrial region of the North of Spain, and its possible influence on the climate on a regional scale. Environ. Geol. 2009, 56, 1551–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.H.; Xie, X.F.; Qi, J.Y.; Lippold, H.; Luo, D.G.; Wang, C.L.; Su, L.X.; He, L.C.; et al. Thallium transformation and partitioning during Pb-Zn smelting and environmental implications. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 212, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.L.; Liang, J.H.; Fu, H.B.; Zhang, L.W. The contributions of socioeconomic and natural factors to the acid deposition over China. Chemosphere 2020, 253, 126491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, R.K.; Seip, H.M.; Leinum, J.R.; Winje, T.; Xiao, J.S. Chemical characterization of individual particles (PM10) from ambient air in Guiyang City, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 343, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pipal, A.S.; Kulshrestha, A.; Taneja, A. Characterization and morphological analysis of airborne PM2.5 and PM10 in Agra located in north central India. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 3621–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.L.; Zhang, R.; Yao, Z.K.; Yi, F.; Ren, J.J.; Wu, M.H.; Feng, M.; Wang, Q.Y. Size distribution of chemical elements and their source apportionment in ambient coarse, fine, and ultrafine particles in Shanghai urban summer atmosphere. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 882–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Ji, H.B. Microscopic morphology and seasonal variation of health effect arising from heavy metals in PM2.5 and PM10: One-year measurement in a densely populated area of urban Beijing. Atmos. Res. 2018, 212, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamyrbaev, A.A.; Dzharkenov, T.A.; Imangazina, Z.A.; Satybaldieva, U.A. Mutagenic and carcinogenic actions of chromium and its compounds. Environ. Health Prev. 2015, 20, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Su, H.; Gu, Y.L.; Song, X.; Zhao, J.S. Carcinogenicity of chromium and chemoprevention: A brief update. Onco Targets Ther. 2017, 10, 4065–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodhi, K.K.; Kumar, M.; Agrawal, P.K.; Singh, D.K. Perspectives on arsenic toxicity, carcinogenicity and its systemic remediation strategies. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2019, 16, 100462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, A.; Sathyapalan, T.; Moallem, S.A.; Sahebkar, A. Counteracting arsenic toxicity: Curcumin to the rescue? J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 123160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaabane, M.; Bejaoui, S.; Trabelsi, W.; Telahigue, K.; Chetoui, I.; Chalghaf, M.; Zeghal, N.; El Cafsi, M.; Soudani, N. The potential toxic effects of hexavalent chromium on oxidative stress biomarkers and fatty acids profile in soft tissues of Venus verrucose. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 196, 110562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Signes-Pastor, A.J.; Gutierrez-Gonzalez, E.; Garcia-Villarino, M.; Rodriiguez-Cabrera, F.D.; Lopez-Moreno, J.J.; Varea-Jimenez, E.; Pastor-Barriuso, R.; Pollan, M.; Navas-Acien, A.; Perez-Gomez, B.; et al. Toenails as a biomarker of exposure to arsenic: A review. Environ. Res. 2020, 195, 110286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, R.J.C.; van Aswegen, S.; Webb, W.R.; Goddard, S.L. UK concentrations of chromium and chromium (VI), measured as water soluble chromium, in PM10. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 99, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Shen, Y.X.; Liu, C.; Liu, H.F. Enrichment and assessment of the health risks posed by heavy metals in PM1 in Changji, Xinjiang, China. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A Toxic/Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2017, 52, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.N.; Zuo, H.; Zhang, J.Q.; Li, Z.N.; Li, S.R. Comparative study on the distribution characteristics and sources of heavy metal elements in PM1, PM2.5, and PM10 in Shijiazhuang City. Earth Sci. Front. 2019, 26, 263–270. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Talbi, A.; Kerchich, Y.; Kerbachi, R.; Boughedaoui, M. Assessment of annual air pollution levels with PM1, PM2.5, PM10 and associated heavy metals in Algiers, Algeria. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 232, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, N.; Pey, J.; Querol, X.; Alastuey, A.; Lopez, J.M.; Viana, M. Partitioning of major and trace components in PM10–PM2.5–PM1 at an urban site in Southern Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 1677–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onat, B.; Sahin, U.A.; Akyuz, T. Elemental characterization of PM2.5 and PM1 in dense traffic area in Istanbul, Turkey. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2013, 4, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohiuddin, K.; Strezov, V.; Nelson, P.F.; Stelcer, E. Characterisation of trace metals in atmospheric particles in the vicinity of iron and steelmaking industries in Australia. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 83, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).