Abstract
Atmospheric brown carbon (BrC) is a kind of organic aerosol that efficiently absorbs ultraviolet-visible light and has an impact on climate forcing. We conducted an in-depth field study on ambient aerosols at a monitoring point in Shanghai, China, aiming to investigate the potential emission sources, molecular structures, and the contributions to light absorptions of ambient BrC chromophores. The results indicated that nine molecules were identified as nitroaromatic compounds, five of which (4-nitrophenol, 4-nitrocatechol, 2-nitro-1-naphthol, 3-methyl-4-nitrocatechol, and 2-methyl-4-nitrophenol) usually came from biomass burning or were produced from the photo-oxidation of anthropogenic volatile organic compounds (e.g., toluene, benzene) under high-NOx conditions. 4-nitrophenol was the strongest BrC chromophore and accounted for 13% of the total aerosol light absorption at λ = 365 nm. The estimated light absorption of black carbon was approximately three times the value of methanol-soluble BrC at λ = 365 nm. The ratios of K+/OC and K+/EC, and the correlations with WSOC, OC, HULIS-C and K+, and MAE values of methanol extracts also indicated that the primary emissions from biomass burning contributed more aerosol light absorption compared to the secondary formation during the wintertime in Shanghai. Therefore, biomass burning control is still the most urgent strategy for reducing BrC in Shanghai.
1. Introduction
The light-absorbing carbonaceous aerosols in the atmosphere mainly come from the combustion of fossil fuels and biomass [1,2]. Such as black carbon (BC) which absorbs solar radiation with a wide incident light wavelength range, resulting in positive radiative forcing [3]. Yet, many studies have shown that atmospheric brown carbon (BrC) in carbonaceous aerosols not only effectively absorbs solar radiation in the ultraviolet–visible region (UV–vis), but also features a complex organic mixture [4]. BrC wrapped in cloud droplets can absorb light to promote water evaporation and the spread of clouds, thereby offsetting the indirect effect of cloud droplet cooling [5]. The light absorption of BrC in the UV–vis range may greatly reduce the photolysis rate of some compounds in the atmosphere, thereby affecting the concentration of oxidants [6].
Understanding BrC characteristics helps to improve the accuracy of assessing BrC radiative forcing in the global atmospheric model. BrC is generally emitted from primary sources of incomplete combustion [7] or secondary aerosols through nitrogen-related reactions [8,9]. For example, toxic soluble nitroaromatic hydrocarbons can be formed from polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons [10]. Secondary BrC can be formed by photo-oxidation of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) (including toluene and m-cresol) in the presence of NOx [11]. Degradation products of lignin are photo-oxidized in the presence of NOx to produce methyl-nitrocatechol, which is the main light-absorbing compound. Laboratory experiments and ambient aerosol sampling showed that nitrophenol and methyl-nitrocatechol are the main light-absorbing compounds in secondary BrC [11,12].
The water-soluble fraction of BrC accounts for about 70% of water-soluble organic carbon (WSOC), and about 90% of BrC can be extracted with organic solvents (such as methanol and acetonitrile) [13,14]. Kirchstetter et al. [15] separated organic components in biomass flue gas from insoluble soot-like carbon using solvents, and concluded when the absorption ångström exponent (AAE) was >2, the organic component of aerosol made a great contribution to light absorption at wavelengths of less than 600 nm. Southern California summer aviation network data also showed that the light absorption of BrC accounted for 40% of light absorption of BC at 440 nm, and only 10% of that at 635 nm [16]. Zhang et al. [14] compared the water-soluble components of BrC in aerosol samples collected by particle-into-liquid-sampler (PILS) with methanol-soluble BrC. The result of high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)/UV–vis/mass spectrometry (MS) showed that the content ratio of methanol-soluble nitroaromatic BrC was more than that of water-soluble BrC. Compared with water-soluble components, the mass absorption cross-section of BrC extracted by organic solvents is larger; that is, it has a stronger absorption capability [13,14,17,18].
The AAE of BrC from fossil fuel combustion is about 1, and the AAE from incomplete combustion of biomass ranges from 1 to 3 [19]. When fresh BrC changes into secondary BrC, the range of AAE values varies from 3 to 7, which indicates that the wavelength dependence of secondary BrC is higher, and the ability of secondary BrC to absorb radiation decreases with wavelength [20]. The AAE value of water-soluble BrC of Amazon biomass burning (BB) aerosol is 7.1 [21], while that of wood burning aerosols at different burning temperatures is 8–16 [17], and burning aerosols produced by straw, pine needles, and sesame stems are 7.4–8.3 [22]. In addition, the AAE values of WSOC for aerosol samples in urban and rural areas are in the range of 6–8 [7,14,18,23,24].
The mass absorption efficiency (MAE) of aerosol produced by fossil fuel combustion is significantly higher than that produced by incomplete biomass burning, indicating that the ability of fossil fuel combustion to absorb radiation is greater than that of incomplete biomass burning. This may be because the molecular composition of BrC produced by the combustion of fossil fuels differs under different combustion conditions [1]. It was found that BrC aerosol generated in the laboratory contained 41 compounds that absorbed light in the UV–vis region, including oxygen-containing compounds, conjugated compounds, nitro aromatic compounds, and S-containing compounds [25]. Strong chromophores are responsible for 50% of the total absorption of BrC between 300 and 500 nm. Among them, the light absorption of nitrophenol and its derivatives produced by biomass burning aerosols accounts for about 25%, and another 25% of total light absorption is attributed to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. The remaining 50% may be due to weak chromophores with a small molar absorption coefficient or low concentration in the environment and the complex conversion mechanism between larger molecules [26,27].
There is still a lack of research on the source, temporal variation of concentration, molecular structure, and absorption spectrum of BrC, and the internal correlation mechanism between these factors, which are important to global and regional climate and air quality models [28,29]. Therefore, we conducted an in-depth field study of monitoring ambient BC aerosols at a monitoring point in Shanghai, China, by aerosol optical property monitoring and samplings. This study aims to investigate the physical and chemical characteristics of atmospheric BrC and the factors based on sampling. The molecular structure and chromophores of the light-absorbing BrC component were explored using HPLC-DAD-TOF-MS.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Particle Samples
The sampling site was set on the rooftop of a seven-story building on the campus of Fudan University in Shanghai (31.3° N, 121.5° E). Ambient aerosols were sampled on quartz fiber filters (8 × 9 in, Whatman QM-A, Little Chalfont, Buckinghamshire, United Kingdom) using a high volume sampler with a flow rate of 1.05 m3/min for 24 h from 26 December 2018 to 29 January 2019. In this case, we selected this flow rate value to satisfy both high flow sampling and all filter membrane sampling analyses. The filters were prebaked at 600 °C for 6 h prior to sampling to remove the residual carbon. Before and after sampling, the filters were conditioned under constant temperature (20 °C) and relative humidity (40%) for 24 h and weighed by microbalance. The filter samples were wrapped, sealed separately in aluminum foil envelopes, and stored in a freezer at −10 °C until analysis to minimize the evaporation of volatile components. In this experiment, PM2.5 was not calculated as total sample equal to PM2.5, but was obtained in the following way:
where M0 and M are the mass of the filtration membrane before and after sampling, mg, V is the sampling volume, m3.
2.2. Analysis of Collected Samples
Water-soluble inorganic species concentrations
The major inorganic ions (SO42−, NH4+, NO3−, Cl−, Mg2+, Ca2+, and K+) of the extracts were determined by an ion chromatograph equipped with a Dionex CS12A column used for cation analysis (20 mM methane sulfonic acid as eluent) and a Dionex AS23 column for anion analysis (4.5 mM NaHCO3 and 0.8 mM Na2CO3 as eluent). KBB+ and the acidity of PM2.5 were obtained by ions concentrations. Punches with a diameter of 47 mm were cut from each filter sample and used for chemical analysis and light absorption measurements. A quarter of each filter was cut into pieces with scissors, then extracted with 30 mL Milli-Q water (18 MΩcm) under ultrasonication for 30 min. The extracted solution was filtered through a syringe with 0.2 μm pore size. The following equations were adopted from the literature to determine the :
where nss-K+ and KDust+ refer to non-sea-salt-potassium and dust-derived K+. Kaerosol+, Naaerosol+ and Caaerosol2+ represent the concentrations of K+, Na+ and Ca2+ in the aerosol samples, measured by ion chromatography. The parameters (0.6, 13.6, 0.037, 0.038) used were adopted from the literature [30,31].
The acidity of PM2.5 is commonly evaluated by anion equivalence (AE) and cation equivalence (CE) using the following equations:
Organic carbon (OC) and elemental carbon (EC)
Organic carbon (OC) and elemental carbon (EC) were measured using a thermal/optical carbon analyzer (Atmoslytic Inc., DRI 2000, Calabasas, CA, USA). A punch of each filter was measured stepwise at temperatures of 140 °C (OC1), 280 °C (OC2), 480 °C (OC3), and 580 °C (OC4) in a helium atmosphere, and 580 °C (EC1), 780 °C (EC2), and 840 °C (EC3) in a 2% oxygen/98% helium gas atmosphere. OC was calculated as OC1 + OC2 + OC3 + OC4 + OP and EC as EC1 + EC2 + EC3 − OP, where OP is the optical pyrolyzed OC. The instrument has a minimum detection limit of 0.82 μg/cm2 for OC and 0.82 μg/cm2 for EC. The carbon analyzer was checked using known quantities of CH4 each day and calibrated with sucrose. The concentrations of primary organic carbon (POC) and secondary organic carbon (SOC) were calculated according to the data of OC and EC using the following equation:
where TOC is total OC and (OC/EC)min is the minimum OC/EC ratio observed during sampling in Shanghai.
Primary organic carbon (POC) and secondary organic carbon (SOC)
A quarter of each filter was cut into pieces with scissors, then extracted in 30 mL Milli-Q water (18.2 MΩ cm) under ultrasonication for 45 min. The extracted solution was filtered through a syringe with 0.2 μm pore size. The extracts were analyzed with a TOC analyzer (Multi N/C2100, Analytik Jena AG, Jena, Germany). The detection limit of TOC is 0.1 mg/L to 40 mg/L.
Humic-like substances (HULIS)
The humic-like substances (HULIS) fraction was isolated from PM2.5 samples using a solid-phase extraction (SPE) technique. In brief, a punch of the filter was extracted in 30 mL Milli-Q water with ultrasonication for 30 min and then filtered through a syringe with 0.2 μm pore size to obtain the water extract. The extracted solution was adjusted to pH ≈ 2 using HCl and passed through preconditioned Oasis® hydrophilic–lipophilic balance (HLB) extraction cartridges (60 mg/cartridge, Waters, Milford, MA, USA). Thus, hydrophilic HULIS were retained by the HLB cartridge. The Oasis® HLB extraction cartridge was preconditioned with 2 mL methanol and 2 mL water (pH = 1). Then 2 mL Milli-Q water was injected into the HLB cartridge to remove residues of inorganic constituents, and a 2 mL mixture of methanol and ammonia was introduced into the HLB cartridge to elute retained organics (HULIS). Finally, the eluted HULIS were dried under nitrogen gas flow until fully dry; subsequently, they were diluted with 30 mL Milli-Q water and then measured with the TOC analyzer (Multi N/C2100, Germany, Analytik Jena AG).
A punch of each filter was cut into pieces using scissors and extracted in 15 mL methanol under ultrasonication for 30 min. The extracted solution was filtered through a syringe with 0.2 μm pore size. UV–vis absorption spectra were measured using a UV–vis spectrophotometer (S3100, Scinco, Seoul, Korea) over the wavelength range of 190–700 nm, and field blank filters were collected to correct for background concentration. The absorption coefficient of the methanol extracts (Absλ, Mm−1) was calculated using the following equation:
where Aλ and A700 are the light absorption of the water extracts at the given wavelength λ and 700 nm, respectively. Vl and Va are the solution volume (mL) and the sampling air volume through the filter punch (m3), respectively, and l is the absorbing path length (l = 0.01 m in this study). A700 was applied to correct the baseline drift during the absorption measurement. This study also presents the light absorption coefficient (babs) of uncoated BC at 365 nm which is calculated as [18]:
where ECm is the EC mass concentration, which is used as the BC mass, and MAE365,BC and MAE550,BC are the mass absorption efficiency of uncoated BC at 365 and 500 nm, respectively. MAE550,BC is assumed to be 7.5 m2/g according to the literature [32] and AAEBC is set to 1.
The AAE of methanol extracts is determined by the linear regression relationship of ln (absλ) versus ln(λ) over the wavelength range 330–545 nm. The MAE of methanol extracts at 365 nm was calculated as:
where and MSOC are the absorption coefficient of the methanol extract at 365 nm and the mass concentration of MSOC, respectively. As the MSOC could not be measured by the TOC, we replaced it with OC to calculate AAE, assuming that methanol can extract all organic carbon.
HPLC-DAD-Q-TOF-MS
Two punches of each filter were cut into pieces using scissors and extracted in 30 mL methanol under ultrasonication for 30 min. The extracted solution was filtered (polytetrafluoroethylene membrane) through a syringe with 0.2 μm pore size. After concentration, the final volume was roughly 1 mL prior to HPLC-DAD-Q-TOF-MS analysis.
An Agilent 1200 series HPLC with a C18 column (SB-C18, 3.0 × 100 mm, 1.8 μm) was used for chromatographic separation with an injection volume of 2 μL. The flow rate was set to 0.4 mL/min and the gradient separation was conducted with 0.1% formic in water (A) and methanol (B). The concentration of B was 5% for the first 0.5 min, increased to 95% from 0.5 to 27 min, and then decreased back to 5% from 27 to 27.1 min. The identification of BrC was determined with an Agilent 6520 Q-TOF-MS and an Agilent G1315D diode array detector (DAD). UV–vis absorption was measured using the DAD detector over the wavelength range of 190–600 nm. The TOF-MS was equipped with electrospray ionization (ESI), operated in both positive and negative ion modes. The drying gas flow rate was 7 L/min, and the temperature and flow rate of sheath gas were 350 °C and 11 L/min, respectively. Before the experiment, the instrument was tuned and calibrated with a standard low-concentration tuning solution, ensuring the accuracy of the mass measured. The ion masses included in the tuning mixture were 112.98558, 301.9981, 601.9789, 1033.9881, 1333.9689, and 1633.9497 Da. External mass calibration was not used during data analysis.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Concentrations of Carbonaceous and Ionic Species
Table 1 provides a summary of the concentration of a variety of carbonaceous species and ionic species. The concentration range of PM2.5 for 24 h is from 14.67 μg/m3 to 119.80 μg/m3, with a mean value of 50.07 ± 30.49 μg/m3. PM2.5 in this study was lower than other historical average values, such as 104.61 μg/m3 in Shanghai during the winter of 2013–2014, 85.1 μg/m3 in Guangzhou from February 2010 to January 2011 [33], and 62.0 μg/m3 during November to December 2015 in Shanghai [34].

Table 1.
Chemical composition of carbonaceous and ionic species of PM2.5 in Shanghai during the monitoring period.
Figure 1 shows the daily average concentrations of OC, EC, WSOC, and HULIS-C, in which OC, WSOC, and HULIS-C displayed similar temporal patterns. HULIS-C accounted for 33.6–60.3% of WSOC in this study, which was comparable to that observed in Guangzhou (37–61%) [33], indicating that HULIS are a major component of WSOC. The higher WSOC/OC ratios (0.277–0.961) suggested that secondary organic aerosol (SOA) formation was enhanced during the sampling period. The average ratio of OC/EC in this study was 2.86, which was relatively low for winter in an urban area in Shanghai [35]. It was reported that the daily average values were within the range of 1.8–5.6 [36,37,38]. SOC exists under the circumstance of the OC/EC ratio being greater than 2 [39]. Therefore, it was speculated that secondary organic aerosol formed, which was related to vehicle exhausts and coal and biomass burning. This can be further verified based on the SOC concentrations calculated by OC and EC, as given in Table 1.
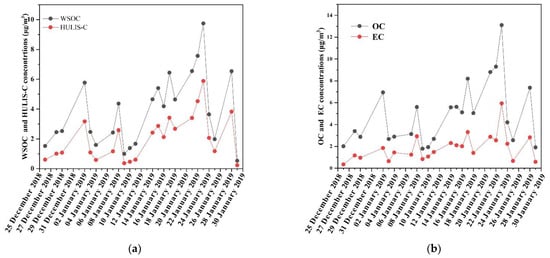
Figure 1.
Temporal profiles of carbonaceous species concentrations of (a) WSOC and HULIS-C (b) OC and EC.
Figure 2 shows that the ion concentration of exhibited the highest bulk concentrations among all the ionic species. The average concentrations of the secondary ionic species , and were 15.62 ± 13.24 μg/m3, 6.36 ± 3.94 μg/m3, 7.09 ± 4.66 μg/m3. The corresponding variation ranges were 1.55–49.19 μg/m3, 1.67–16.98 μg/m3, and 1.85–17.20 μg/m3, respectively. The ratios of were greater than 1, indicating that vehicle emissions could be a main factor for air pollution [40]. Water-soluble concentration ranged from 0.20 to1.44 μg/m3, with an average value of 0.55 μg/m3; concentration ranged from 0.07 to1.35 μg/m3, with an average value of 0.44 μg/m3. Previous studies concluded that both BB and traffic emissions contribute significantly to OC and EC concentrations, but BB emissions also contribute significantly to water-soluble [30]. A previous study [41] indicated that BB-influenced ambient aerosols had a ratio within the range of 0.08–0.11 and a ratio within the range of 0.42–0.54. Therefore, BB was the major contributor to ambient aerosols during the monitoring period in this study. The conclusion was consistent with the calculated concentrations of in Table 1.
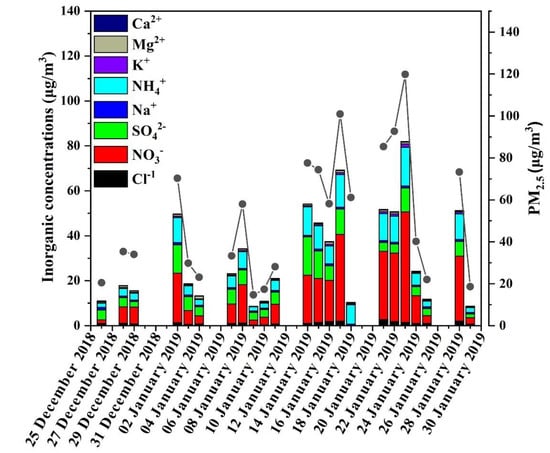
Figure 2.
Trend of ion concentrations during winter sampling in Shanghai.
Figure 3 shows the correlations of and with WSOC, OC, and HULIS-C. The BB emission marker () was significantly correlated with WSOC, OC, and HULIS-C, with respective values of 0.920, 0.959, and 0.908, suggesting that the WSOC, OC, HULIS-C and observed during the sampling period were associated with similar sources, and BB emission was dominating. The correlations between OC and EC were relatively high (), suggesting that the sources of OC could be the primary sources of EC. The high values indicated that there was a similar source between WSOC and (0.97) and (0.95).
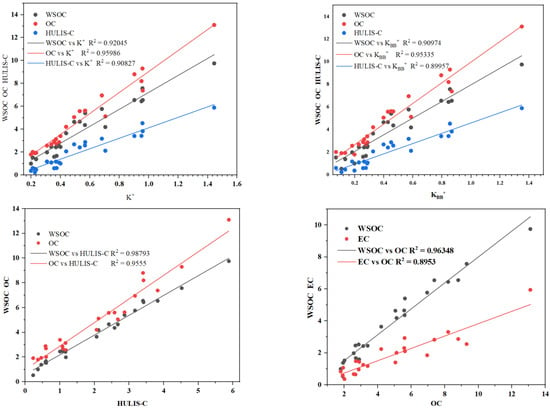
Figure 3.
Relationships between OC and EC and WSOC concentrations during winter.
3.2. Metallic Element Concentration Levels and Enrichment Factors (EFs)
The concentration and EF of 18 elements in the PM2.5 samples were analyzed using ICP-MS, as shown in Table S1: Se > Cd > Sb > Zn > Ag > Pb > Cu > Ni > Mn > V. The source of Sb is the worn brake pads of automobiles. V is regarded as a marker of heavy oil fuel [42], and it was reported that the cargo emission caused by heavy oil fuel accounted for 85% of anthropogenic V [43]. The elements of Se, Zn, Cu, and Pb are ubiquitous in the coal matrix, and Pb, in particular, has been identified as a prominent element of coal combustion that is released into the air in the effluent of most combustion processes [44]. The elements with EF values of 1–10 were Na, Mg, K, Fe, Co, Sr, and Ba, indicating that pollution came from both anthropogenic and natural sources [45] (Supplement S3.2).
3.3. Light Absorption by the Methanol Extracts
Figure 4a shows the average absorption spectra of methanol-soluble organic carbon (MSOC) within the incident wavelengths of 200–600 nm during the sampling time period, which is characteristic of the spectra of BrC. We chose babs at λ = 365 nm as the absorption of BrC [46], which varied slightly between 2.67 and 11.93 Mm−1 with an average of 6.28 Mm−1 in this study. The babs (365, methanol) from other studies include 26.2 ± 18.81 Mm−1 for Beijing [18], 8.80 ± 2.88 Mm−1 for Shanghai [47], and 7.1 ± 3.4 Mm−1 for Gwangju, Korea [48]. Figure 4b shows positive correlation between babs (365, methanol) and OC (R2 = 0.79), POC (R2 = 0.69) and SOC (R2 = 0.44), indicating that the primary emissions contributed more light absorption compared with the secondary formation in this study. This result was consistent with the study conducted in Yulin, China [46]. We also calculated the babs of uncoated BC at λ = 365 nm for comparison; the estimated babs (365, BC) was about three times the value of babs (365, methanol).
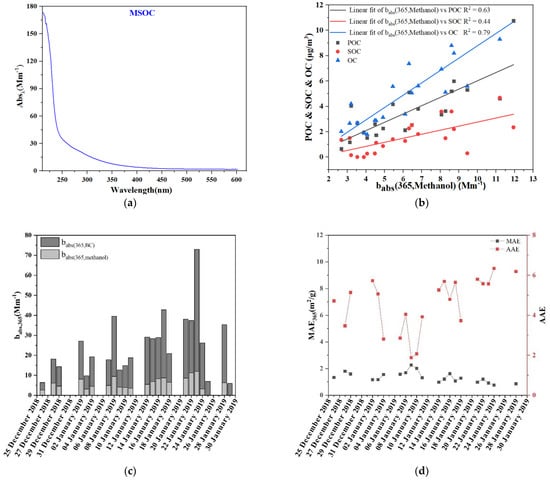
Figure 4.
(a) Average absorption spectra (200–600 nm) measured for methanol extracts from samples; (b) relationship between the light absorption coefficient at 365 nm for methanol extracts and POC, SOC, OC; (c) daily variation of babs (365, methanol) for the methanol extracts and babs (365, BC) estimated for uncoated BC; and (d) daily variations of the AAE and MAE365 values for methanol extracts.
The AAE of MSOC varied between 1.88 and 6.34 with a mean value of 4.58. This is consistent with the findings of previous studies for Beijing, Yulin in Northern China, the Ligurian Apennines in Italy, and Gwangju in Korea [18,46,48,49,50]. Furthermore, due to the difficulties in detecting MSOC, we replaced MSOC with OC, resulting in an underestimation of the MAE of methanol extracts. The mean MAE at λ = 365 nm in winter was 1.35 ± 0.39 m2/g, similar to those of previous studies in Yulin (1.4 ± 0.4 m2/g47) and Gwangju, Korea (1.3 ± 0.4 m2/g49). The MAE values in winter were within the range of the MAE for BB sources [22,51], which further supported the conclusion that BB was the major source during the sampling time period in Shanghai. If the MSOC/OC ratio is assumed to be 0.85 [18], the corrected MAE should be about 1.58 m2/g. The value is a bit lower than the corrected MAE values in the Los Angeles Basin (about 1.9 m2/g) [14] and Xi’an (about 1.72 m2/g) [52] and is strongly related to BB or coal combustion.
3.4. Analysis of Brown Carbon Chromophores
The methanol-extracted PM2.5 samples collected on different days were measured using an HPLC-DAD-Q-TOF-MS system, as given in Figure 5. The absorption spectrum of a single compound showed the optimal absorption wavelength of the substance. This study mainly analyzed the compounds with the absorption signal at λ = 365 nm due to the typical characterization wavelength of BrC. Only the main absorption peak was discussed. Figure 5 shows the specific BrC chromophores based on the peaks of the absorption chromatogram corresponding to the peak on the mass spectrum chromatogram. Most peaks corresponded to a major compound on the mass peak. Since ESI is not sensitive to unfunctionalized aromatic hydrocarbons, it is difficult to distinguish the absorption substance of some strong absorption peaks due to the unrecognized mass peak.
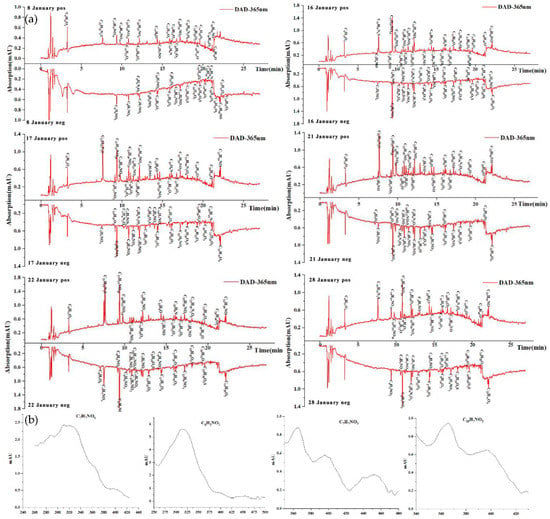
Figure 5.
(a) HPLC-DAD chromatograms of atmospheric particle samples. The molecular formula on the peak denotes BrC chromophores with well distinguished UV–vis spectra; (b) Selected examples of the UV–vis spectra from the above chromophores and their corresponding elemental composition as inferred from high-resolution mass spectrometry.
The formulae corresponding to the absorption peaks of λ = 365 nm in the positive and negative modes are shown in Table S3. These compounds all contributed to the bulk light absorption detected by spectrophotometry in the previous section. However, due to the dilution and separation of the extraction by HPLC, the absorption measured by DAD cannot be directly compared with bulk light absorption.
Nearly all days presented similar patterns. The BrC chromophores flowing out during the RT of 0–23 min showed a strong signal on the UV-absorption spectrum and the mass spectrum signal chromatogram. Most of these compounds were mainly detected in negative mode and contained a nitrogen atom and at least three oxygen atoms. These species have high saturation and aromaticity, indicating that BrC chromophores are mainly nitroaromatic compounds (such as nitrophenol and nitroaromatic acid). The UV–vis absorption spectrum of these substances can help to determine their possible structure. C6H5NO3, eluted at RT = 9.356 min, was characterized by a maximum absorption at λ = 318 nm, which matched with the UV–vis spectrum of 4-nitrophenol. Therefore, the high level of 4-nitrophenol in BrC was due to gas–particle partitioning, consistent with the lower vapor pressure and the higher Henry’s law constant of 4-nitrophenol [53]. Similarly, C6H5NO4 eluted at 9.692 min exhibits a maximum wavelength at 345 nm, resembling the literature-reported spectrum of 4-nitrocatechol, which is produced by aromatic SOA under high-NOx conditions. C6H5NO5 eluted at 9.146 min could be a nitro-benzenetriol produced through further oxidation of 4-nitrocatechol or directly emitted from wood burning [4,54]. C10H7NO3 eluted at 14.453 min could be a 2-nitro-1-naphthol according to its spectrum and the research of Xie et al. [55]. There is a characteristic RT in the chromatograms when the m/z of these compounds is extracted, suggesting there are no other isomers. Some species were found as multiple structural isomers for the same elemental formula. Two isomers of C7H7NO3 occurred at 11.381 and 12.149 min, resembling the spectra of 3-methyl-4-nitrocatechol and 2-methyl-4-nitrophenol. C7H7NO4 eluted at 7.494 min was similar to the spectrum of C6H5NO4. Perkampus [56] pointed out that the substitution of a methyl group did not change the absorption spectrum of aromatic compounds. The other C7H7NO4 eluted at 10.591 min may represent 4-nitroguaiacol. C8H9NO3 eluted at 14.029 min may be a benzene compound [57]. Phenolic compounds in some studies have been reported produced from biomass burning. The pyrolysis of lignin during biomass burning usually produces a variety of substituted phenols; subsequently, nitrophenol is generated through phenolic compounds with NOx. Overall, there were nine element formulae identified as nitroaromatic compounds, eight of which were also detected in Xie et al. Five of the nitroaromatic compounds (including 4-nitrophenol, 4-nitrocatechol, 2-nitro-1-naphthol, 3-methyl-4-nitrocatechol and 2-methyl-4-nitrophenol) usually come from biomass burning or are produced from the photo-oxidation of anthropogenic VOCs (e.g., toluene, benzene) under high-NOx in heavy traffic urban environments [58,59]. Moreover, C10H17NO7S (RT = 11.186 min) may be a nitroxy organic sulfate derived from monoterpenes, and C8H18O4S (RT = 13.446 min) detected in the sample may be an aliphatic organic sulfate [60]. Thus, we conclude that the pollution sources of BrC during the sampling period were mainly biomass burning, heavy oil combustion, and anthropogenic VOCs. The compound with an absorption peak detected at 365 nm in the positive mode had a larger molecular weight, which brought a great challenge in analyzing the species and structure. The compound eluted at 19.277 min matched the formula of C19H10O in the Shanghai winter samples and was also found in the research of Lin et al. [61].
3.5. Absorption Contribution of Brown Carbon Chromophores
As most of the chromophores in the BrC mixture are unknown, it is impractical to quantify the concentration of individual chromophores and evaluate their optical properties. Therefore, in this study, ESI-HR-MS was used as a qualitative probe at the molecular level, combined with UV–vis spectroscopy (DAD detector) to quantitatively measure the light absorption of atmospheric BrC chromophores with HPLC separation. This method can not only determine the molecular structure of different organic compounds but can also evaluate their contribution to light absorption, deepening the understanding of aerosol radiative forcing and climate effects.
Figure 6 shows the relative cumulative absorption contribution of BrC chromophores in the wavelength of 250–450 nm for different sampling days. It should be noted that some BrC compounds may interact with the stationary phase of the column to permanently capture them, resulting in underestimation of the total absorption. Table S2 lists the integration parameters of the absorption peak at a typical wavelength of 365 nm, and the area ratio represents the absorption ratio of a single absorption peak to the total absorption. Although the molecular structure and composition of these BrC chromophores are complex, the core structure and functional groups of some chromophores were identified. Based on the HPLC-DAD chromatogram and the results of Figure 3, the light absorption in the wavelength of 250–450 nm is explained by the strong chromophores of BrC. The DAD results of these six methanol extracts indicate the absorption contribution caused by 4-nitrophenol in the entire wavelength was the largest for 16 and 22 January, and relatively large for 17 and 21 January, indicating that 4-nitrophenol is an important chromophore of BrC during the sampling time period in Shanghai. In addition, for the sample of 28 January, the absorption of the compound eluted at 20.823 min (C23H32O2) was significantly greater than other species in the wavelength range of 250–300 nm. For the sample of 22 January, the absorption of 4-nitrophenol accounted for 13% of the total light absorption at λ = 365 nm, which was a single chromophore with the largest absorption. The absorption ratios of 4-nitrophenol at λ = 365 nm for the other samples are shown in Table S4, and are basically consistent with the trend in Figure 3. Yury et al. [54] found that the absorption of 4-nitrophenol in cloud water accounted for 55% of total absorption at λ = 370 nm, and the 46 nitrides accounted for 92% of the total absorption (300–400 nm), indicating that reduced nitrogenous species made a more important contribution to the total light absorption of BrC. Lin et al. [62] found that the absorption caused by 30 chromophores accounted for more than 70% of the total absorption in the wavelength range of 300–500 nm.
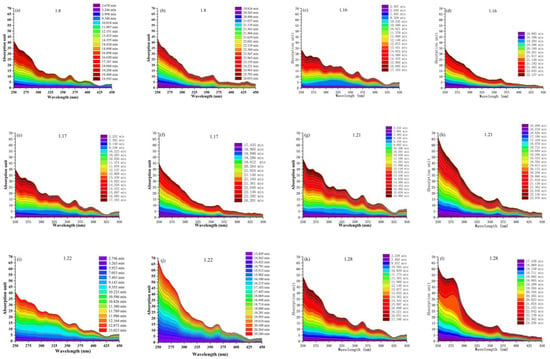
Figure 6.
Relative absorption contribution of diode array detector (DAD) peaks to the total light absorption in the DAD measurement. (a,b) are data for January 8th, (c,d) are data for January 16th, (e,f) are data for January 17th, (g,h) are data for January 21th, (i,j) are data for January 22th, (k,l) are data for January 28th.
The results identified five elements of nitroaromatic compounds including 4-nitrophenol, 4-nitrocatechol, 2-nitro-1-naphthol, 3-methyl-4-nitrocatechol, and 2-methyl-4-nitrophenol, which were possibly coming from biomass burning. Additionally, 4-nitrophenol was an important chromophore of BrC for Shanghai and accounted for 13% of the total light absorption at λ = 365 nm.
4. Conclusions
We found that primary emissions from biomass burning contributed more aerosol light absorption compared to the secondary formation during the winter time in Shanghai. The identified 4-nitrophenol, 4-nitrocatechol, 2-nitro-1-naphthol, 3-methyl-4-nitrocatechol, and 2-methyl-4-nitrophenol came from biomass burning or were produced from the photo-oxidation of anthropogenic VOCs under high-NOx conditions. 4-nitrophenol was the strongest BrC chromophore and accounted for 13% of the total aerosol light absorption at λ = 365 nm. In brief, the contribution of BrC to aerosol light absorption was about 25%, and biomass burning controlling is still the most urgent strategy for reducing BrC in Shanghai.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/atmos13060991/s1, Table S1: Concentration of metal elements (ng/m3) and enrichment factors (EFs) of elements in PM2.5 in Shanghai during winter, S3.2 Analysis Metallic Element Concentration, Table S2: Integration parameters of each absorption peak at 365 nm, Table S3: Elemental formulae assigned to the species responsible for major peaks in the UV–vis chromatogram, Table S4: The absorption ratios of 4-nitrophenol at 365 nm for the other samples as mentioned in [34,63,64,65] here in the text.
Author Contributions
L.Z. and J.H.S.: conducted the experiment, analyzed data, and wrote the draft paper. Z.B.: conducted the experiment. W.Z.: data analysis. L.L.: conducted the experiment. L.W.: supervised, wrote the draft paper. J.C.: revised the draft paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was financially sponsored by NSFC Project of 22076025, Talent Introduction Project of Fudan University (JIH1829013), and Key Projects of National Key Research and Development Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2018YFC0213800).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work, there is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service, and/or company that could be constructed as influencing the position presented in, or the review of, the manuscript entitled.
References
- Bond, T.C. Spectral dependence of visible light absorption by carbonaceous particles emitted from coal combustion. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 4075–4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castro, L.M.; Pio, C.A.; Harrison, R.M.; Smith, D.J.T. Carbonaceous aerosol in urban and rural European atmospheres: Estimation of secondary organic carbon concentrations. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 2771–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, M.A.; Romshoo, S.A.; Beig, G. Aerosol black carbon at an urban site-Srinagar, Northwestern Himalaya, India: Seasonality, sources, meteorology and radiative forcing. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 165, 336–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Bluvshtein, N.; Rudich, Y.; Nizkorodov, S.A.; Laskin, J.; Laskin, A. Molecular Chemistry of Atmospheric Brown Carbon Inferred from a Nationwide Biomass Burning Event. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 11561–11570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hansen, J.; Sato, M.; Ruedy, R. Radiative forcing and climate response. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 6831–6864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Wiedinmyer, C.; Carlton, A.M. Aerosols from Fires: An Examination of the Effects on Ozone Photochemistry in the Western United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11878–11886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecobian, A.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, M.; Edgerton, E.S.; Weber, R.J. Water-Soluble Organic Aerosol material and the light-absorption characteristics of aqueous extracts measured over the Southeastern United States. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 5965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shapiro, E.L.; Szprengiel, J.; Sareen, N.; Jen, C.N.; Giordano, M.R.; McNeill, V.F. Light-absorbing secondary organic material formed by glyoxal in aqueous aerosol mimics. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 2289–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nizkorodov, S.A.; Bones, D.L.; Henricksen, D.K.; Mang, S.A.; Bateman, A.P.; Pan, X.; Nguyen, T.B.; Gonsior, M.; Cooper, W.; Laskin, J.; et al. Effect of Slow Aging Reactions on Optical Properties of Secondary Organic Aerosol Prepared by Oxidation of Selected Monoterpenes. In AGU Spring Meeting Abstracts; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2009; p. A23B-04. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, P.; Harger, W.P.; Arey, J. The contribution of nitro- and methylnitro-naphthalenes to the vapor-phase mutagenicity of ambient air samples. Atmos. Environ. 1996, 30, 3157–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Liu, J.; Shilling, J.E.; Kathmann, S.M.; Laskin, J.; Laskin, A. Molecular characterization of brown carbon (BrC) chromophores in secondary organic aerosol generated from photo-oxidation of toluene. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 23312–23325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iinuma, Y.; Boege, O.; Graefe, R.; Herrmann, H. Methyl-Nitrocatechols: Atmospheric Tracer Compounds for Biomass Burning Secondary Organic Aerosols. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 8453–8459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Bergin, M.; Guo, H.; King, L.; Kotra, N.; Edgerton, E.; Weber, R.J. Size-resolved measurements of brown carbon in water and methanol extracts and estimates of their contribution to ambient fine-particle light absorption. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 12389–12404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Lin, Y.-H.; Surratt, J.D.; Weber, R.J. Sources, Composition and Absorption Angstrom Exponent of Light-absorbing Organic Components in Aerosol Extracts from the Los Angeles Basin. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 3685–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchstetter, T.W.; Novakov, T.; Hobbs, P.V. Evidence that the spectral dependence of light absorption by aerosols is affected by organic carbon. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2004, 109, D21208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bahadur, R.; Praveen, P.S.; Xu, Y.; Ramanathan, V. Solar absorption by elemental and brown carbon determined from spectral observations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2012, 109, 17366–17371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Bond, T.C. Light absorption by organic carbon from wood combustion. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 1773–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Y.; He, K.-B.; Du, Z.-Y.; Engling, G.; Liu, J.-M.; Ma, Y.-L.; Zheng, M.; Weber, R.J. The characteristics of brown carbon aerosol during winter in Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 127, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinsson, J.; Eriksson, A.C.; Nielsen, I.E.; Malmborg, V.B.; Ahlberg, E.; Andersen, C.; Lindgren, R.; Nystrom, R.; Nordin, E.Z.; Brune, W.H.; et al. Impacts of Combustion Conditions and Photochemical Processing on the Light Absorption of Biomass Combustion Aerosol. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 14663–14671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Cao, J.; Zhang, L.; Lei, Y.; Huang, Y.; Huang, R.J.; Gao, J.; Zhao, Z.; Zhu, C.; et al. Optical properties and possible sources of brown carbon in PM2.5 over Xi’an, China. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 150, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffer, A.; Gelencser, A.; Guyon, P.; Kiss, G.; Schmid, O.; Frank, G.P.; Artaxo, P.; Andreae, M.O. Optical properties of humic-like substances (HULIS) in biomass-burning aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 3563–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.S.; Yu, J. Chemical and light absorption properties of humic-like substances from biomass burning emissions under controlled combustion experiments. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 136, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; He, K.; Cheng, Y.; Duan, F.; Ma, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, M.; Weber, R. A yearlong study of water-soluble organic carbon in Beijing II: Light absorption properties. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 89, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirillova, E.N.; Andersson, A.; Han, J.; Lee, M.; Gustafsson, O. Sources and light absorption of water-soluble organic carbon aerosols in the outflow from northern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 1413–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Budisulistiorini, S.H.; Riva, M.; Williams, M.; Chen, J.; Itoh, M.; Surratt, J.D.; Kuwata, M. Light-Absorbing Brown Carbon Aerosol Constituents from Combustion of Indonesian Peat and Biomass. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 4415–4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S.M.; Smith, G.D. Light Absorption by Charge Transfer Complexes in Brown Carbon Aerosols. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2014, 1, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phillips, S.M.; Smith, G.D. Further evidence for charge transfer complexes in brown carbon aerosols from excitation-emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. A 2015, 119, 4545–4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, D.S.; Park, R.J.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.-W.; Zhang, X. A global simulation of brown carbon: Implications for photochemistry and direct radiative effect. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 3413–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Heald, C.L.; Ridley, D.A.; Schwarz, J.P.; Spackman, J.R.; Perring, A.E.; Coe, H.; Liu, D.; Clarke, A.D. Exploiting simultaneous observational constraints on mass and absorption to estimate the global direct radiative forcing of black carbon and brown carbon. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 10989–11010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajput, P.; Sarin, M.M.; Sharma, D.; Singh, D. Organic aerosols and inorganic species from post-harvest agricultural-waste burning emissions over northern India: Impact on mass absorption efficiency of elemental carbon. Environ. Sci. Processes Impacts 2014, 16, 2371–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keene, W.C.; Pszenny, A.A.P.; Galloway, J.N.; Hawley, M.E. Sea-salt corrections and interpretation of constituent ratios in marine precipitation. J. Geophys. Res. 1986, 91, 6647–6658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, T.C.; Bergstrom, R.W. Light Absorption by Carbonaceous Particles: An Investigative Review. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 27–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Song, J.; Peng, P.A. Temporal variations of the abundance and optical properties of water soluble Humic-Like Substances (HULIS) in PM2.5 at Guangzhou, China. Atmos. Res. 2016, 172, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, X.; Cao, X. In vitro bioaccessibility and health risk assessment of heavy metals in atmospheric particulate matters from three different functional areas of Shanghai, China. Sci. Environ. 2018, 610, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zihe, L.; Yunhua, C.; Mengying, B.; Yanlin, Z.; Fang, C.; Geng, C.; Shengcheng, S.; Meiyi, F.; Shoudong, L. Pollution Characteristics and Source Analysis of PM2. 5 Carbonaceous Components in Shanghai Heavy Duty Period. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2019, 19, 328–338. [Google Scholar]
- Schauer, J.J.; Kleeman, M.J.; Cass, G.R.; Simoneit, B.R.T. Measurement of emissions from air pollution sources. 2. C-1 through C-30 organic compounds from medium duty diesel trucks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 1578–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yingjun, C.; Guoying, S.; Xinhui, B.; Yanli, F.; Bixian, M.; Jiamo, F. Emission factors for carbonaceous particles and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from residential coal combustion in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 1861–1867. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.-X.; Shao, M.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Zeng, L.-M.; He, L.-Y.; Zhu, B.; Wei, Y.-J.; Zhu, X.-L. Source profiles of particulate organic matters emitted from cereal straw burnings. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.-Y.; Liu, M.; Yang, J.; Du, W.-N.; Sun, X.; Huang, Y.-P.; Zhang, X.; Khalil, S.K.; Luo, D.-M.; Zhou, Y.-D. Characterization of PM2.5-bound PAHs and carbonaceous aerosols during three-month severe haze episode in Shanghai, China: Chemical composition, source apportionment and long-range transportation. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 203, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arimoto, R.; Duce, R.A.; Savoie, D.L.; Prospero, J.M.; Talbot, R.; Cullen, J.D.; Tomza, U.; Lewis, N.F.; Ray, B.J. Relationships among aerosol constituents from Asia and the North Pacific during PEM-West A. J. Geophys. Res. 1996, 101, 2011–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Engling, G.; Yu, J.Z. Humic-like substances in fresh emissions of rice straw burning and in ambient aerosols in the Pearl River Delta Region, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 6487–6500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, L.; Fairley, D.; Kleeman, M.J.; Harley, R.A. Effects of switching to lower sulfur marine fuel oil on air quality in the San Francisco Bay area. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 10171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, J.; Tan, J. Atmospheric heavy metals and Arsenic in China: Situation, sources and control policies. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 74, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcazzan, G.; Valli, G.; Vecchi, R. Factors influencing mass concentration and chemical composition of fine aerosols during a PM high pollution episode. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 298, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jianmin, C.; Mingguang, T.; Yulan, L.; Jian, Z.; Yuanmao, Z.; Zuci, S.; Guilin, Z.; Yan, L. Characteristics of trace elements and lead isotope ratios in PM(2.5) from four sites in Shanghai. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 156, 36–43. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Y.L.; Shen, Z.X.; Wang, Q.Y.; Zhang, T.; Cao, J.J.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, L.Q.; Xu, H.M.; Tian, J.; et al. Optical characteristics and source apportionment of brown carbon in winter PM2.5 over Yulin in Northern China. Atmos. Res. 2018, 213, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunzhu, S. The Characterization Methods and Pollution Characteristics of the Brown Carbon in Atmospheric Particulate Matter in Shanghai. Master’s Thesis, East China University of Science and Technology, Shanghai, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Yu, G.-H.; Lee, S. Optical absorption characteristics of brown carbon aerosols during the KORUS-AQ campaign at an urban site. Atmos. Res. 2018, 203, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Zheng, M.; Sullivan, A.P.; Bosch, C.; Desyaterik, Y.; Andersson, A.; Li, X.; Guo, X.; Zhou, T.; Gustafsson, O. Chemical characteristics and light-absorbing property of water-soluble organic carbon in Beijing: Biomass burning contributions. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 121, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Massabo, D.; Caponi, L.; Bove, M.C.; Prati, P. Brown carbon and thermal–optical analysis: A correction based on optical multi-wavelength apportionment of atmospheric aerosols. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 125, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Chen, Y.J.; Bond, T.C. Light absorption of organic aerosol from pyrolysis of corn stalk. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 144, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, Z.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Tao, J.; Zhu, C.-S.; Cao, J.; Xu, H.; Liu, S. Methanol Extracted Brown Carbon in PM2.5 Over Xi’an, China: Seasonal Variation of Optical Properties and Sources Identification. Aerosol Sci. Eng. 2017, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service. Toxicological profile for Dinitrophenols; Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR): Atlanta, GA, USA, 1995.
- Desyaterik, Y.; Sun, Y.; Shen, X.; Lee, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Collett, J.L., Jr. Speciation of “brown” carbon in cloud water impacted by agricultural biomass burning in eastern China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 7389–7399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Chen, X.; Hays, M.D.; Lewandowski, M.; Offenberg, J.; Kleindienst, T.E.; Holder, A.L. Light Absorption of Secondary Organic Aerosol: Composition and Contribution of Nitroaromatic Compounds. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 11607–11616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, C. UV-VIS atlas: UV-VIS Atlas of Organic Compounds, by H.-H. Perkampus, VCH, Weinheim, 1992, DM 750.00 (Part 1: II+ 336; Part 2: II+ 1189 pages), ISBN: 1-56081-268-0. Adv. Mater. 1993, 10, 770. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, L.; Zhen, Y.J.; Guenter, E.; Markus, K. Organosulfates in humic-like substance fraction isolated from aerosols at seven locations in East Asia: A study by ultra-high-resolution mass spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 13118–13127. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, M.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Shang, D.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Tang, R.; Zhu, W. The formation of nitro-aromatic compounds under high NOx and anthropogenic VOC conditions in urban Beijing, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 7649–7665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, Y.; Ning, Z.; Zhang, T.; Lei, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, G.; Sun, J. Investigation of primary and secondary particulate brown carbon in two Chinese cities of Xi’an and Hong Kong in wintertime. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 3803–3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, S.L.; MacMillan, A.C.; Drozd, G.T.; Goldstein, A.H.; Chu, R.K.; Paša-Tolić, L.; Shaw, J.B.; Tolić, N.; Lin, P.; Laskin, J.; et al. Molecular Characterization of Organosulfur Compounds in Biodiesel and Diesel Fuel Secondary Organic Aerosol. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 5683–5695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Fleming, L.T.; Nizkorodov, S.A.; Laskin, J.; Laskin, A. Comprehensive Molecular Characterization of Atmospheric Brown Carbon by High Resolution Mass Spectrometry with Electrospray and Atmospheric Pressure Photoionization. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 12493–12502. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, P.; Laskin, J.; Nizkodorov, S.A.; Laskin, A. Revealing Brown Carbon Chromophores Produced in Reactions of Methylglyoxal with Ammonium Sulfate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 14257–14266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, H.; Yihua, Z.; Qianbiao, Z. Characteristics and sources of inorganic elements in PM2.5 during wintertime in Shanghai. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2015, 35, 1993–1999. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Lei, Y.; Ren, H.; Gao, J.; Xu, H.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, C.; Liu, H.; Zhang, R. In Seasonal Variation and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in PM2.5 during Winter and Summer over Xi’an, China. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, J.; Yuan, C.; Xie, J.; Shen, Y.; He, K.; Zhang, K. Speciation and bioaccessibility of heavy metals in PM2.5 in Baoding city, China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).