Multitask Learning Based on Improved Uncertainty Weighted Loss for Multi-Parameter Meteorological Data Prediction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Model
2.1. Data Description and Data Preprocessing
2.1.1. Data Standardization
2.1.2. Correlation Analysis
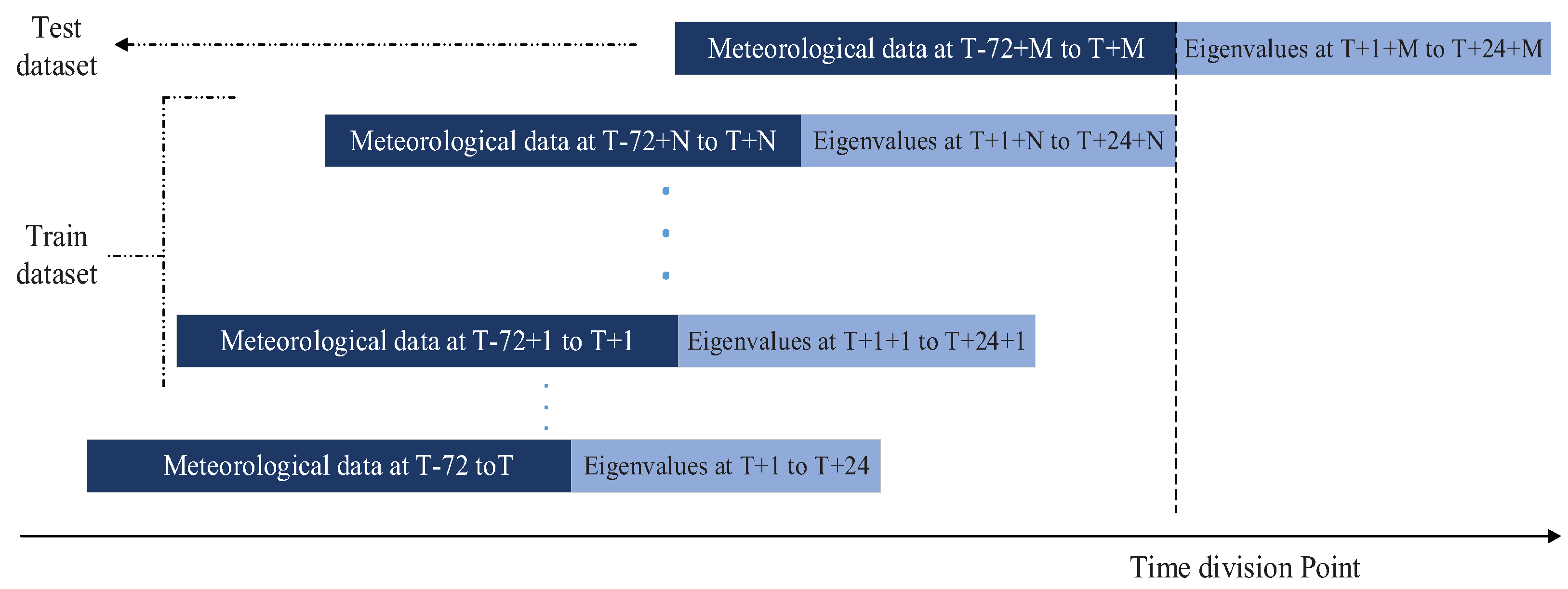
2.1.3. Time Sliding Window Processing
2.2. Multitask Loss Processing Method Based on Homoscedasticity Uncertainty Weighting
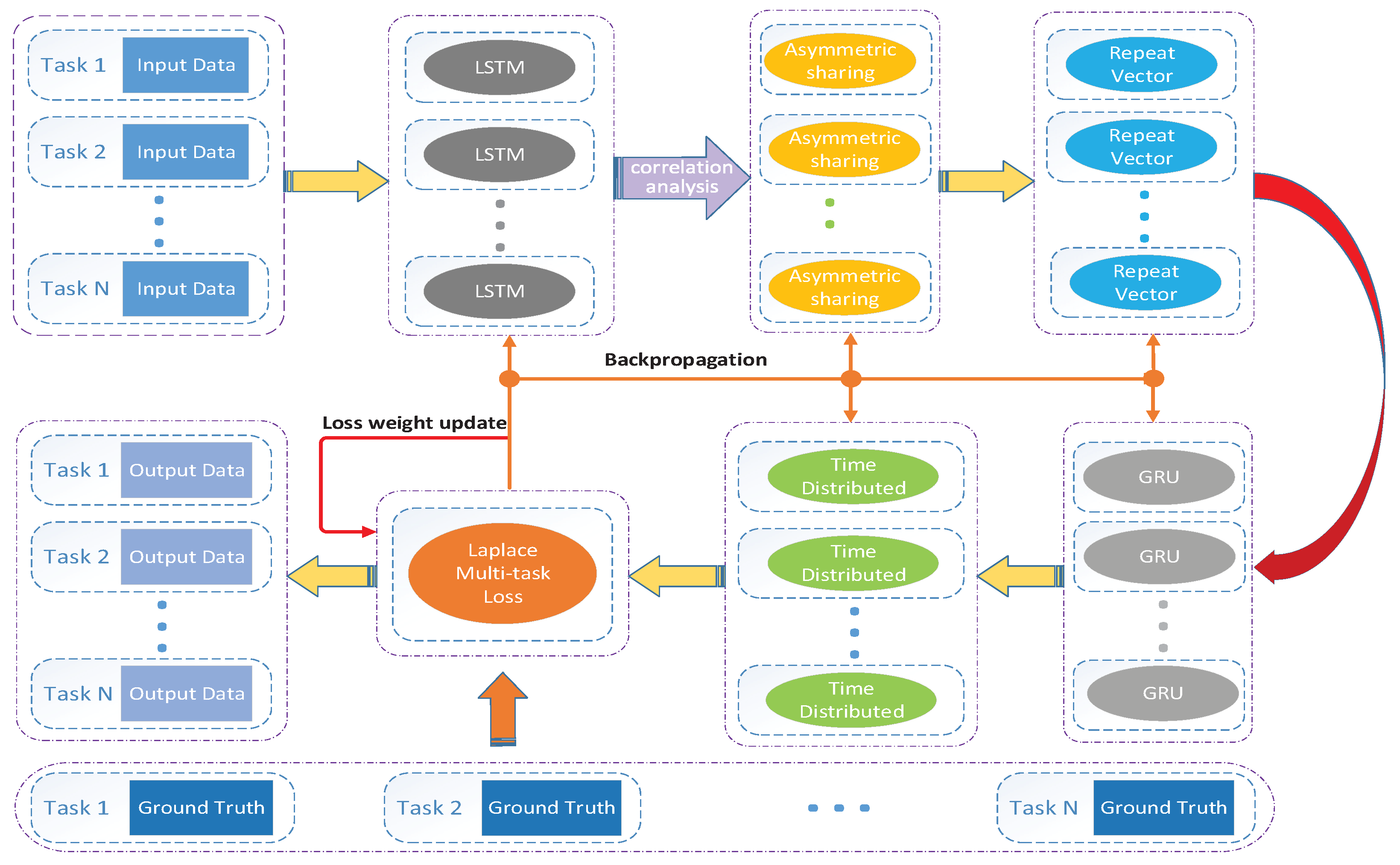
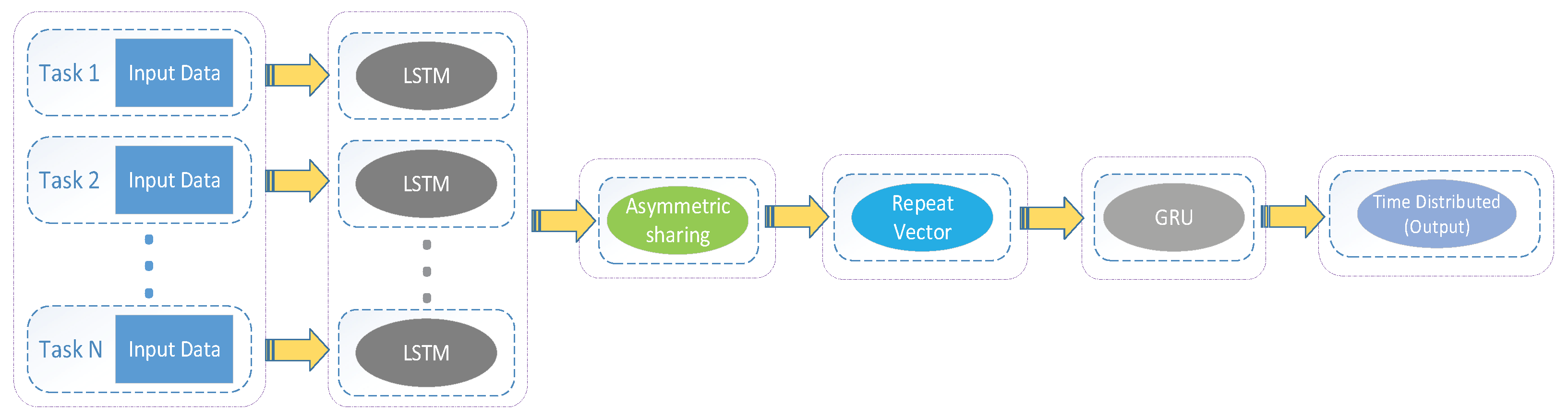
2.3. Multi-Parameter Meteorological Data Synchronization Prediction Model
2.3.1. RNN Layer
2.3.2. Laplace Multiple Loss Processing Layer
2.3.3. Model Based on the Laplace Multitask Loss
2.4. Baseline Model
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Evaluation Indicators
3.2. Analysis and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, S. Short-Term Weather Element Prediction Method Based on EMD with Phase Space Reconstruction Limit Learning Machine and Its Application Research; Nanchang University: Nanchang, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, C.; Li, W.T.; Ye, X.T.; Shi, X.W. Hybrid Genetic Algorithm and Modified Iterative Fourier Transform Algorithm for Large Thinned Array Synthesis. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2017, 16, 2150–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, G.; Mandal, D.; Kar, R.; Ghoshal, S.P. Optimal design of non-uniform circular antenna arrays using PSO with wavelet mutation. Int. J. Bio-Inspired Comput. 2014, 6, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saryazdi, N.P. GSA: A Gravitational Search Algorithm. Inf. Sci. 2009, 179, 2232–2248. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, L. Gravitational Search Algorithms and Their Applications; Shanghai People’s Publishing House: Shanghai, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Yang, Z.; Ma, T. Optimization of weather structured data query based on HBase. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2017, 53, 80–84. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X. Research and Application of Multivariate Meteorological Data Methods; Xi’an University of Electronic Science and Technology: Xi’an, China, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X. Research on Regional Air Temperature and Humidity Prediction Method Based on Deep Learning; Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University: Xianyang, China, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X. From physical models to intelligent analysis—A new exploration of reducing weather forecast uncertainty. Meteorology 2018, 44, 341–350. [Google Scholar]
- Das, M.; Ghosh, S.K. Data-driven Approaches for Meteorological Time Series Prediction: A Comparative Study of the State-of-the-Art Computational Intelligence Techniques. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2017, 105, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.B.; da Cunha, F.F.; Fernandes Filho, E.I. Exploring machine learning and multitask learning to estimate meteorological data and reference evapotranspiration across Brazil. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 259, 107281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seng, D.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Chen, G.; Chen, X. Spatiotemporal prediction of air quality based on LSTM neural network-ScienceDirect. Alex. Eng. J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaytar, M.A.; Amrani, C.E. Sequence to Sequence Weather Forecasting with Long Short-Term Memory Recurrent Neural Networks. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2016, 143, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Thrun, S. Is learning the n-th thing any easier than learning the first? In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 8; The MIT Press: Cambridge, CA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Caruana, R.A. Multitask Learning; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Hague, Holland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, L.B.; Cunha, F. Multi-step ahead forecasting of daily reference evapotranspiration using deep learning. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 178, 105728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Li, V.O.; Lam, J.C.; Pollitt, M. How BLUE is the Sky? Estimating air qualities in Beijing during the Blue Sky Day period (2008–2012) by Bayesian Multitask LSTM-ScienceDirect. Environ. Sci. Policy 2021, 116, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wu, S.; Wang, X.; Sun, B.; Liu, H. A PM2.5 concentration prediction model based on multitask deep learning for intensive air quality monitoring stations. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 275, 122722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, A.; Gal, Y.; Cipolla, R. Multitask Learning Using Uncertainty to Weigh Losses for Scene Geometry and Semantics. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sener, O.; Koltun, V. Multitask Learning as Multi-objective Optimization. In Proceedings of the 32nd Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 3–8 December 2018; pp. 527–538. [Google Scholar]
- Kendall, A.; Gal, Y. What Uncertainties do We Need in Bayesian Deep Learning for Computer Vision? In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 5580–5590. [Google Scholar]
- Franzese, M.; Iuliano, A. Correlation Analysis. 2019. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128096338203580?via%3Dihub (accessed on 1 June 2022).
- Yang, X. Research on Weather Prediction Based on Deep Learning; Harbin Institute of Technology: Harbin, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gal, Y.; Ghahramani, Z. Dropout as a Bayesian Approximation: Representing Model Uncertainty in Deep Learning. In International Conference on Machine Learning; PMLR: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kendall, A.; Badrinarayanan, V.; Cipolla, R. Bayesian SegNet: Model Uncertainty in Deep Convolutional Encoder-Decoder Architectures for Scene Understanding. Comput. Sci. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravanelli, M.; Brakel, P.; Omologo, M.; Bengio, Y. Light gated recurrent units for speech recognition. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. Intell. 2018, 2, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mumcuoğlu, E.; Öztürk, C.E.; Ozaktas, H.M.; Koç, A. Natural language processing in law: Prediction of outcomes in the higher courts of Turkey. Inf. Process. Manag. 2021, 58, 102684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.; Gulcehre, C.; Cho, K.; Bengio, Y. Empirical evaluation of gated recurrent neural networks on sequence modeling. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.3555. [Google Scholar]
- Salman, A.G.; Heryadi, Y.; Abdurahman, E.; Suparta, W. Weather forecasting using merged long short-term memory model. Bull. Electr. Eng. Inform. 2018, 7, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Gao, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Q.; Lin, L. Atmospheric Environment Data Generation Method Based on Stacked LSTM-GRU. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 15th International Conference on Electronic Measurement & Instruments (ICEMI), Nanjing, China, 29–31 October 2021; pp. 17–26. [Google Scholar]
- Sutskever, I.; Vinyals, O.; Le, Q.V. Sequence to sequence learning with neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 27, 3104–3112. [Google Scholar]
- Alexey, N.; Alois, K. Gradient boosting machines, a tutorial. Front. Neurorobot. 2013, 7, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, E.; Kohavi, R. An Empirical Comparison of Voting Classification Algorithms: Bagging, Boosting, and Variants. Mach. Learn. 1999, 36, 105–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
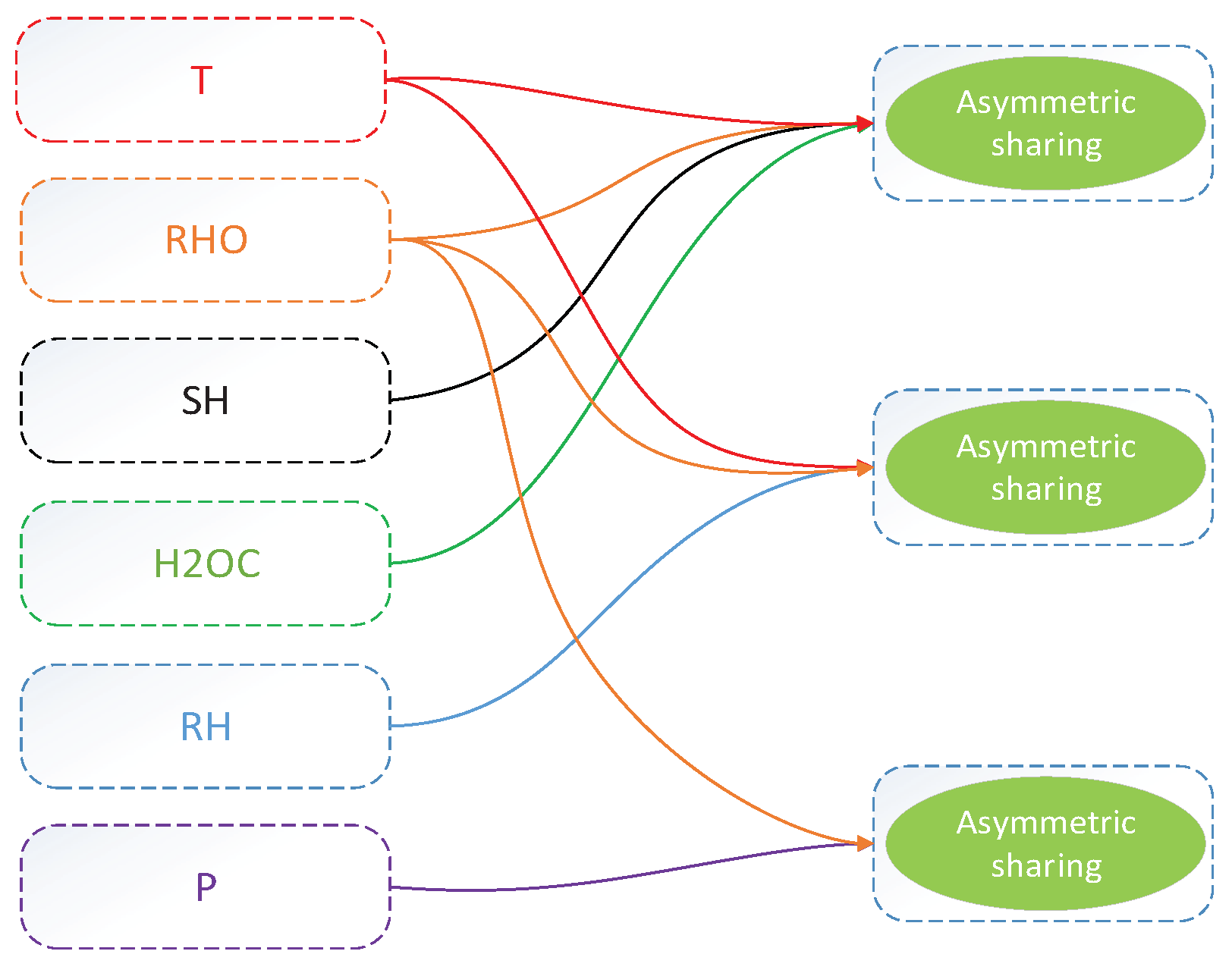

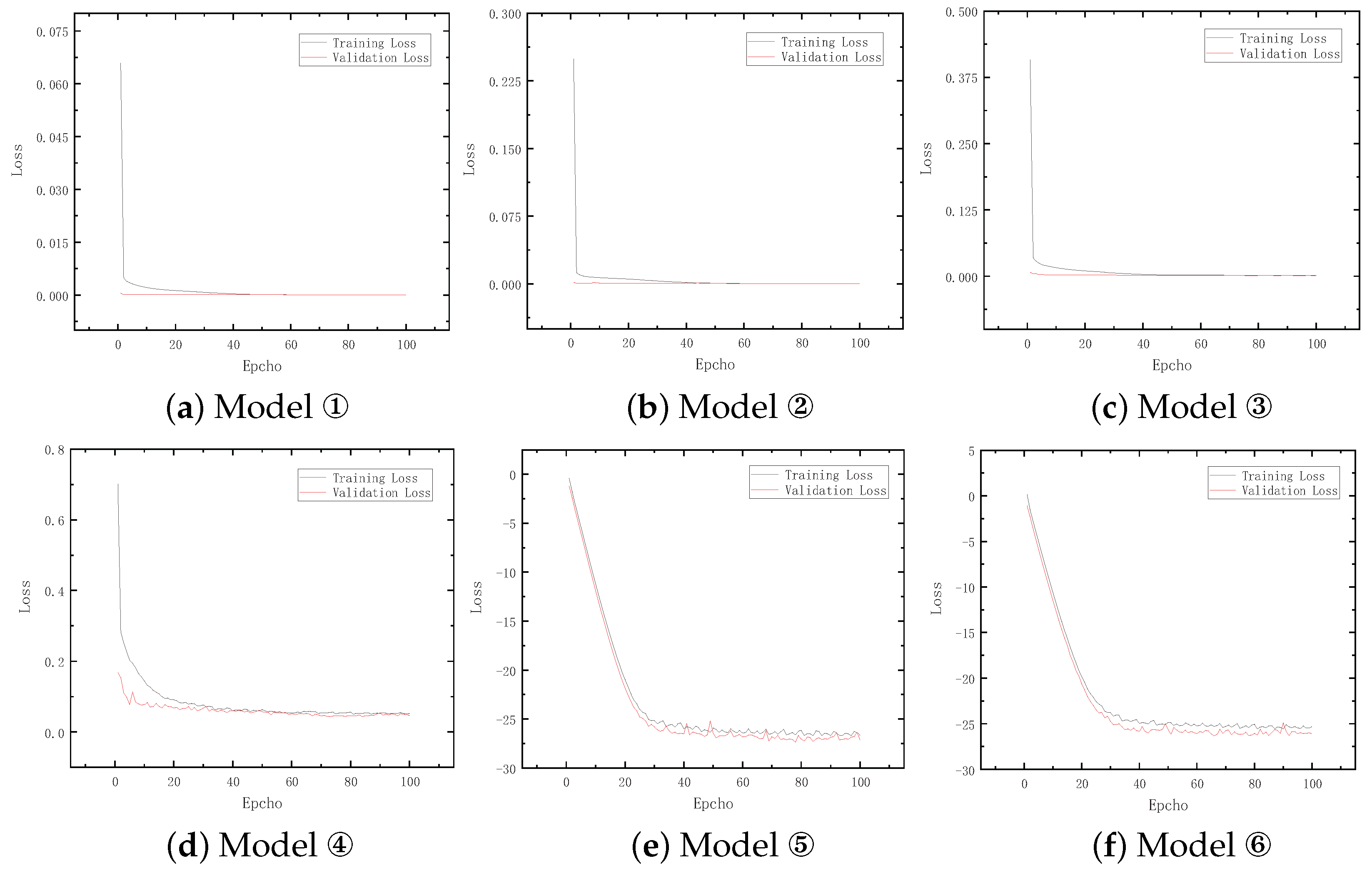
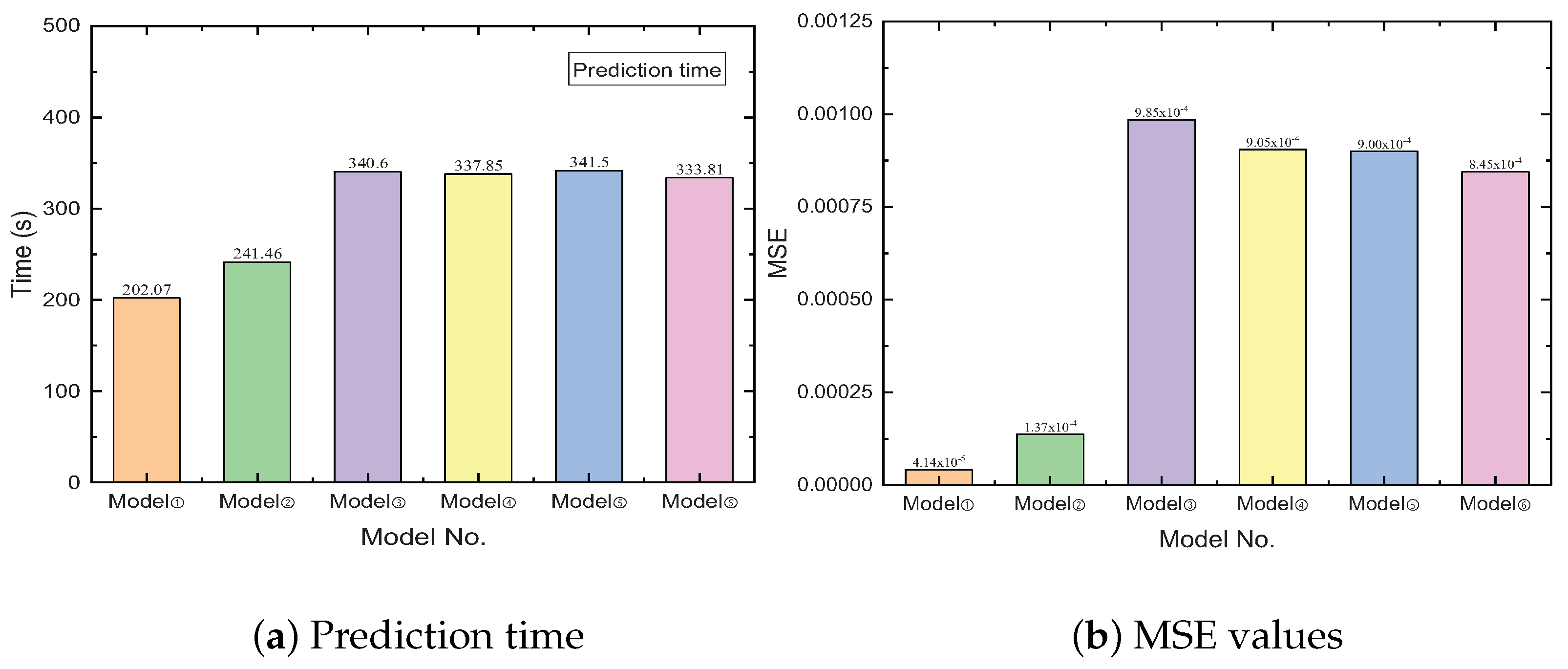
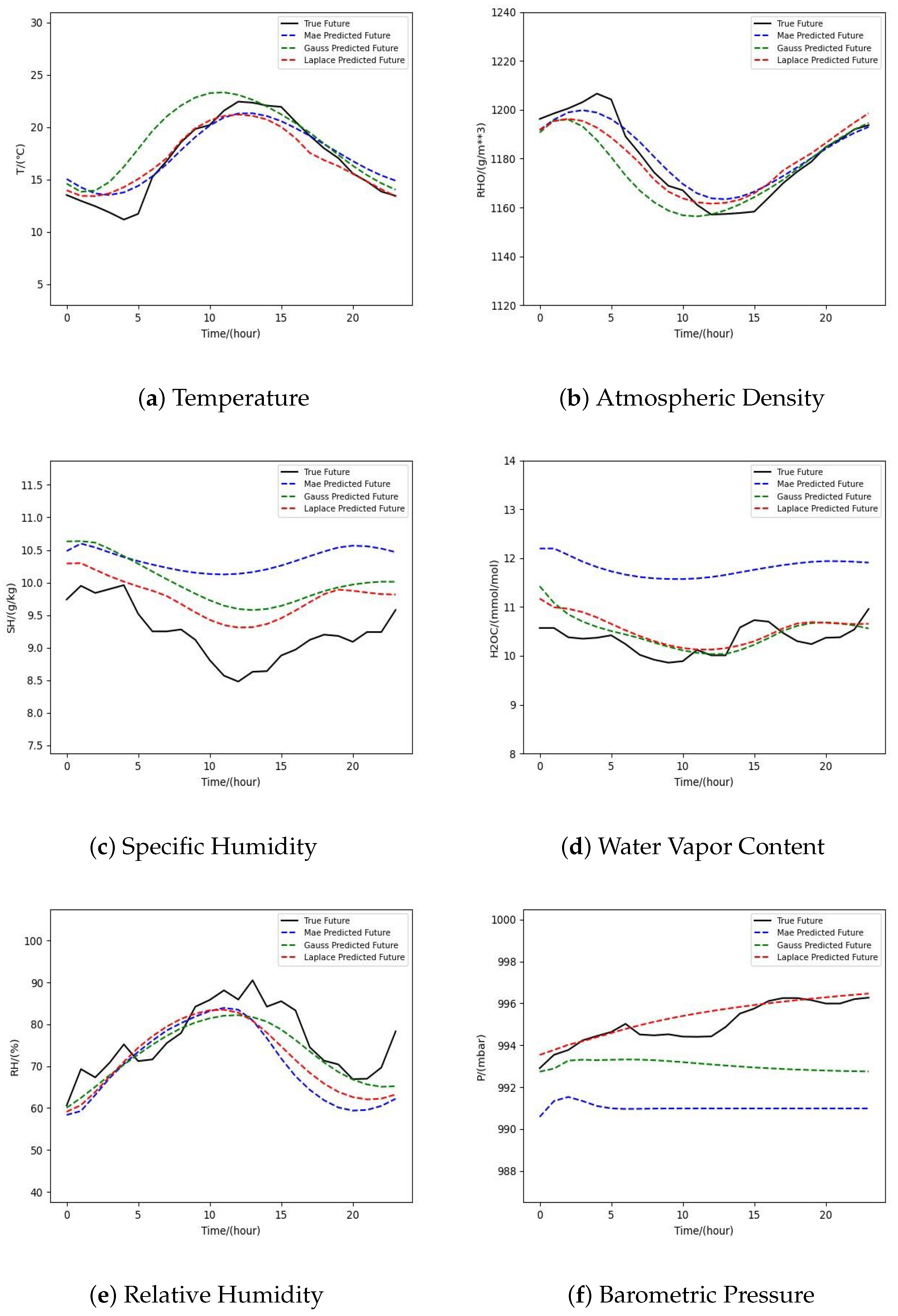
| Correlation Coefficient | T | P | RHO | RH | WV | SH | H2OC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | 1.0000 | −0.0453 | −0.9634 | −0.5724 | −0.0046 | 0.8668 | 0.8671 |
| P | −0.0453 | 1.0000 | 0.3076 | −0.0183 | −0.0057 | −0.0697 | −0.0698 |
| RHO | −0.9634 | 0.3076 | 1.0000 | 0.5142 | 0.0032 | −0.8533 | −0.8537 |
| RH | −0.5724 | −0.0183 | 0.5142 | 1.0000 | −0.0050 | −0.1508 | −0.1509 |
| WV | −0.0046 | −0.0057 | 0.0032 | −0.0050 | 1.0000 | −0.0094 | −0.0095 |
| SH | 0.8668 | −0.0697 | −0.8533 | −0.1508 | −0.0094 | 1.0000 | 0.9999 |
| H2OC | 0.8671 | −0.0698 | −0.8537 | −0.1509 | −0.0095 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 |
| Model No. | Classify | Parameters | Output Type | Loss Handling Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ① | I | H2OC/SH/WV/P | Single | MSE |
| ② | II | H2OC/SH/WV/P | Multi | MSE |
| ③ | II | T/RHO/SH/H2OC/RH/P | Multi | MSE |
| ④ | II | T/RHO/SH/H2OC/RH/P | Multi | MAE |
| ⑤ | III | T/RHO/SH/H2OC/RH/P | Multi | GAUSS |
| ⑥ | III | T/RHO/SH/H2OC/RH/P | Multi | LAPLACE |
| Platform | Windows 10 | GPU | TensorFlow | Cuda | Cudnn | Keras |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 1909 | Nvidia Titan XP | 2.3.0 | 10.1 | 7.6 | 2.3.1 |
| Label | Model ③ | Model ④ | Model ⑤ | Model ⑥ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | ||||
| RHO | ||||
| SH | ||||
| H2OC | ||||
| RH | ||||
| P | ||||
| SUM |
| Label | Laplace/Gauss | Laplace/Mse | Laplace/Mae | Gauss/Mse | Gauss/Mae | Mae/Mse |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | 11.85 | 14.29 | 5.92 | 2.77 | −6.72 | 8.89 |
| RHO | 8.40 | 1.91 | 5.14 | −7.09 | −3.56 | −3.41 |
| SH | 2.07 | 34.46 | 9.55 | 33.08 | 7.64 | 27.54 |
| H2OC | −2.69 | 32.82 | 5.75 | 34.58 | 8.22 | 28.71 |
| RH | −1.96 | 24.07 | 5.61 | 25.53 | 7.42 | 19.55 |
| P | 16.35 | 55.10 | 27.83 | 46.33 | 13.72 | 37.79 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Lin, L.; Teng, Z.; Zhang, Y. Multitask Learning Based on Improved Uncertainty Weighted Loss for Multi-Parameter Meteorological Data Prediction. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 989. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13060989
Wang J, Lin L, Teng Z, Zhang Y. Multitask Learning Based on Improved Uncertainty Weighted Loss for Multi-Parameter Meteorological Data Prediction. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(6):989. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13060989
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Junkai, Lianlei Lin, Zaiming Teng, and Yu Zhang. 2022. "Multitask Learning Based on Improved Uncertainty Weighted Loss for Multi-Parameter Meteorological Data Prediction" Atmosphere 13, no. 6: 989. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13060989
APA StyleWang, J., Lin, L., Teng, Z., & Zhang, Y. (2022). Multitask Learning Based on Improved Uncertainty Weighted Loss for Multi-Parameter Meteorological Data Prediction. Atmosphere, 13(6), 989. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13060989







